| Revision as of 18:44, 26 February 2007 editMeta-Physician (talk | contribs)79 editsmNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:43, 28 February 2007 edit undoAlison (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Autopatrolled, Checkusers, Administrators47,273 editsm +cat - LaxativesNext edit → | ||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| | bioavailability = Negligible | | bioavailability = Negligible | ||
| | protein_bound = 94% | | protein_bound = 94% | ||
| | smiles = CCCCC(C1(CCC2C(O1)CC(=O)C2CCCCCCC(=O)O)O)(F)F | |||
| | synonyms = Amitiza<br>RU-0211<BR>SPI-0211 | |||
| | metabolism = Extensive, ] not involved | | metabolism = Extensive, ] not involved | ||
| | elimination_half-life = Unknown (lubiprostone)<br>0.9–1.4 hours (main metabolite) | | elimination_half-life = Unknown (lubiprostone)<br>0.9–1.4 hours (main metabolite) | ||
| Line 18: | Line 20: | ||
| | pregnancy_US = C | | pregnancy_US = C | ||
| | legal_US = Rx-only | | legal_US = Rx-only | ||
| | routes_of_administration = Oral | | routes_of_administration = ] | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Lubiprostone''' (], marketed under the trade name '''Amitiza''') is a ] used in the management of ] ]. It was approved by the U.S. ] for this purpose on ], ]. | '''Lubiprostone''' (], marketed under the trade name '''Amitiza''') is a ] used in the management of ] ]. It was approved by the U.S. ] for this purpose on ], ]. | ||
| Line 45: | Line 47: | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{sourcesstart}} | |||
| 1. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Katzung B.G., ed. 10th edition. ] Companies. 2007. | |||
| #{{cite book | last = Katzung | first = B.G. | title = Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 10th edition | publisher = ] | date = 2007}} | |||
| #{{cite web | title = Clinical Pharmacology Online Database | url = http://www.clinicalpharmacology.com/default.asp | accessdate = 2007-02-28 }} | |||
| {{sourcesend}} | |||
| {{drug-stub}} | {{drug-stub}} | ||
| ] | ] ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 20:43, 28 February 2007
Pharmaceutical compound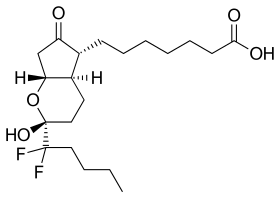 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Amitiza RU-0211 SPI-0211 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Negligible |
| Protein binding | 94% |
| Metabolism | Extensive, CYP not involved |
| Elimination half-life | Unknown (lubiprostone) 0.9–1.4 hours (main metabolite) |
| Excretion | Renal (60%) and fecal (30%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.107.168 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H32F2O5 |
| Molar mass | 390.462 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Lubiprostone (rINN, marketed under the trade name Amitiza) is a medication used in the management of chronic constipation. It was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for this purpose on January 31, 2006.
Indications
Lubiprostone is a gastrointestinal agent used for the treatment of idiopathic chronic constipation. It is well-tolerated in adults, including elderly patients. As of July 20, 2006, Lubiprostone had not been studied in pediatric patients.
There is current research underway to determine the efficacy of Lubiprostone in patients with constipation-predominant IBS, postoperative bowel dysfunction, and opioid-induced bowel dysfunction.
Mode of action
Lubiprostone is a bicyclic fatty acid (prostaglandin E1 derivative) which acts by specifically activating ClC-2 chloride channels on the apical aspect of gastrointestinal epithelial cells, producing a chloride-rich fluid secretion. These secretions soften the stool, increase motility, and promote spontaneous bowel movements (SBM).
Symptoms of constipation (pain, bloating) are usually observed within one week, and SBM may occur within one day.
Pharmacokinetics
Unlike many laxative products, Lubiprostone does not show signs of tolerance, dependency, or altered serum electrolyte concentration. There was no rebound effect following withdrawal of treatment, but a gradual return to pre-treatment bowel movement frequency should be expected.
Minimal distribution of the drug occurs beyond the immediate GI tissues. Lubiprostone is rapidly metabolized by reduction/oxidation, mediated by carbonyl reductase. There is no metabolic involvement of the hepatic cytochrome P450 system. The measurable metabolite, M3, exists in very low levels in plasma and makes up less than 10% of the total administered dose.
Data indicates that metabolism occurs locally in the stomach and jejunum.
Contraindications
There is no current data on use in patients with hepatic and/or renal complications. The effects on pregnancy have not been studied.
Lubipristone is contraindicated in patients exhibiting chronic diarrhea or GI obstruction.
References
- Katzung, B.G. (2007). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 10th edition. McGraw-Hill.
- "Clinical Pharmacology Online Database". Retrieved 2007-02-28.
This pharmacology-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
Categories: