| Revision as of 08:13, 19 October 2021 edit4throck (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users18,187 editsNo edit summaryTag: 2017 wikitext editor← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 03:59, 4 October 2024 edit undoRolf acker (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users856 editsm syntax error | ||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 18 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{ |
{{Short description|None}} | ||
| {{expand list|date=July 2020}} | {{expand list|date=July 2020}} | ||
| This is a list of designs for crewed ]s, |
This is a list of designs for crewed ]s, spacecraft intended to land on the Moon. A key aspect is achieving a ], and for an ascent stage to successfully escape the ]'s gravity.<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|url=https://spacenews.com/nasa-studying-three-stage-approach-to-human-class-lunar-landers/|title=NASA studying three-stage approach to human-class lunar landers|date=2018-11-20|website=SpaceNews.com|language=en-US|access-date=2019-11-08}}</ref> Another aspect is how many stages the design has to undergo to achieve its objective, and the number of passengers and amount of payload it can carry.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| ! Name !! Manufacturer !! Operator (program and operational timeline) !! Stages !! Crew !! Payload Mass !! Status !! Image | ! Name !! Manufacturer !! Operator (program and operational timeline) !! Stages !! Crew !! Payload Mass !! Status !! Image | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] || ] || ] (], |
| ] || ] || ] (], 2005–2009) || Descent, Ascent || 4 || 14,500 kg (32,000 lb) || {{No|Canceled}} || ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] || ] || ] (], 1969–1972) || Descent, Ascent || 2 || || {{Included|Retired}} || ] | | ] || ] || ] (], 1969–1972) || Descent, Ascent || 2 || || {{Included|Retired}} || ] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| | ] || ] || Dynetics, ] (Artemis, 2017–present) || Single-stage with drop tanks || 2-4 || || {{No|Rejected}} || | | ] || ] || Dynetics, ] (Artemis, 2017–present) || Single-stage with drop tanks || 2-4 || || {{No|Rejected}} || | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] || ], ], ], ] || Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Draper Laboratory, ] || Transfer, |
| ] || ], ], ], ] || Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Draper Laboratory, ] || Transfer, Lander/Ascent || 4 || || {{Planned}} || | ||
| |- | |||
| | ] || ] || ] (]) || Descent propulsion stage, Lander/Ascent || 2 || || {{Planned}} || ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] || ]/] || ] (], 1969-1974) || Descent, Ascent || 1 || || {{No|Canceled}} || ] | | ] || ]/] || ] (], 1969-1974) || Descent, Ascent || 1 || || {{No|Canceled}} || ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] || ] || Lockheed Martin, ] (Artemis, 2017–present) || Single-stage || 4 || 1,000 |
| ] || ] || Lockheed Martin, ] (Artemis, 2017–present) || Single-stage || 4 || 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) || {{No|Rejected}}<br /><small>(elements incorporated into Blue Moon Mk 2)</small> || | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] || ] || SpaceX || Single-stage || || || {{Planned}} || ] | | ] || ] || SpaceX || Single-stage || || || {{Planned}} || ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ]|| ] || ] (Artemis, 2017–present), SpaceX || Single-stage || 4 || 100–200 t (220,000–440,000 |
| ]|| ] || ] (Artemis, 2017–present), SpaceX || Single-stage || 4 || 100–200 t (220,000–440,000 lb) || {{Planned}} || | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.astronautix.com/b/bislunarlander.html|title=BIS Lunar Lander|website=www.astronautix.com}}</ref> || || ] || Single-stage || 3 || || Studies (1939, 1947) || | | ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.astronautix.com/b/bislunarlander.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160820165259/http://www.astronautix.com/b/bislunarlander.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=August 20, 2016|title=BIS Lunar Lander|website=www.astronautix.com}}</ref> || || ] || Single-stage || 3 || || Studies (1939, 1947) || | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.astronautix.com/v/vonbraunlunarlander.html|title=Von Braun Lunar Lander|website=www.astronautix.com}}</ref>|| || US (1977) || Single-stage with drop tanks || 20 || 259 metric tons (with a crew of 10) || Study (1952) || | | ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.astronautix.com/v/vonbraunlunarlander.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160820150934/http://www.astronautix.com/v/vonbraunlunarlander.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=August 20, 2016|title=Von Braun Lunar Lander|website=www.astronautix.com}}</ref>|| || US (1977) || Single-stage with drop tanks || 20 || 259 metric tons (with a crew of 10) || Study (1952) || | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.astronautix.com/h/horizonlerv.html|title=Horizon LERV|website=www.astronautix.com}}</ref>|| || ] (], 1966) || Descent, Ascent || 10 - 16 || 2,700 - 22,000 |
| ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.astronautix.com/h/horizonlerv.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161228020518/http://astronautix.com/h/horizonlerv.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=December 28, 2016|title=Horizon LERV|website=www.astronautix.com}}</ref>|| || ] (], 1966) || Descent, Ascent || 10 - 16 || 2,700 - 22,000 kg || Study (1959) || ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.astronautix.com/l/lunexlunarlander.html|title=Lunex Lunar Lander|website=www.astronautix.com}}</ref>|| || ] (], 1967) || Descent, Ascent || 3 || 20,500 |
| ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.astronautix.com/l/lunexlunarlander.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161228024113/http://astronautix.com/l/lunexlunarlander.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=December 28, 2016|title=Lunex Lunar Lander|website=www.astronautix.com}}</ref>|| || ] (], 1967) || Descent, Ascent || 3 || 20,500 kg || Study (1958–1961) || ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] || || NASA Langley Research Center, (], 1963) || Single || 1 || || {{No|Canceled}} || ] | | ] || || NASA Langley Research Center, (], 1963) || Single || 1 || || {{No|Canceled}} || ] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | LEK<ref>https://web.archive.org/web/20060316185549/http://www.astronautix.com/craft/lek.htm</ref>|| || Soviet Union, (Zvezda |
| ]<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.astronautix.com/craft/lek.htm |title=LEK |website=www.astronautix.com |access-date=12 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060316185549/http://www.astronautix.com/craft/lek.htm |archive-date=16 March 2006 |url-status=dead}}</ref>|| || Soviet Union, (], 1974) || Descent, Ascent, Reentry || 3 || || {{No|Canceled}} || | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] || || NASA (], |
| ] || || NASA (], 1992–93) || Descent, Ascent || 4 || 5,000 kg|| {{No|Canceled}} || ] | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| * |
*] | ||
| *{{annotated link|Lunar module}} | *{{annotated link|Lunar module}} | ||
| Line 54: | Line 56: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 03:59, 4 October 2024
| This list is incomplete; you can help by adding missing items. (July 2020) |
This is a list of designs for crewed lunar landers, spacecraft intended to land on the Moon. A key aspect is achieving a soft landing, and for an ascent stage to successfully escape the Moon's gravity. Another aspect is how many stages the design has to undergo to achieve its objective, and the number of passengers and amount of payload it can carry.
| Name | Manufacturer | Operator (program and operational timeline) | Stages | Crew | Payload Mass | Status | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altair | Northrop Grumman | NASA (Constellation, 2005–2009) | Descent, Ascent | 4 | 14,500 kg (32,000 lb) | Canceled | 
|
| Apollo Lunar Module | Grumman | NASA (Apollo, 1969–1972) | Descent, Ascent | 2 | Retired | 
| |
| Boeing Lunar Lander | Boeing | Boeing, NASA (Artemis, 2017–present) | Descent, Ascent | Rejected | |||
| Dynetics HLS | Dynetics | Dynetics, NASA (Artemis, 2017–present) | Single-stage with drop tanks | 2-4 | Rejected | ||
| Blue Moon Mark 2 | Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Draper Laboratory | Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Draper Laboratory, NASA | Transfer, Lander/Ascent | 4 | Planned | ||
| Lanyue Lunar Lander | CAST | CMSA (CLEP) | Descent propulsion stage, Lander/Ascent | 2 | Planned | 
| |
| LK | RSC Energia/Yuzhnoye Design Office | Soviet Union (N1-L3, 1969-1974) | Descent, Ascent | 1 | Canceled | 
| |
| Lockheed Martin Lunar Lander | Lockheed Martin | Lockheed Martin, NASA (Artemis, 2017–present) | Single-stage | 4 | 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) | Rejected (elements incorporated into Blue Moon Mk 2) |
|
| Starship | SpaceX | SpaceX | Single-stage | Planned | 
| ||
| Starship HLS | SpaceX | NASA (Artemis, 2017–present), SpaceX | Single-stage | 4 | 100–200 t (220,000–440,000 lb) | Planned | |
| BIS Lunar Lander | British Interplanetary Society | Single-stage | 3 | Studies (1939, 1947) | |||
| Von Braun Lunar Lander | US (1977) | Single-stage with drop tanks | 20 | 259 metric tons (with a crew of 10) | Study (1952) | ||
| Horizon LERV | US Army (Project Horizon, 1966) | Descent, Ascent | 10 - 16 | 2,700 - 22,000 kg | Study (1959) | 
| |
| Lunex Lunar Lander | US Air Force (Lunex Project, 1967) | Descent, Ascent | 3 | 20,500 kg | Study (1958–1961) | 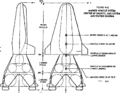
| |
| Gemini lunar lander | NASA Langley Research Center, (Project Gemini, 1963) | Single | 1 | Canceled | 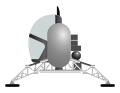
| ||
| LEK | Soviet Union, (Zvezda Moon base, 1974) | Descent, Ascent, Reentry | 3 | Canceled | |||
| FLO Eagle lander | NASA (Space Exploration Initiative, 1992–93) | Descent, Ascent | 4 | 5,000 kg | Canceled | 
|
See also
- Human spaceflight
- Lunar module – Lunar lander designed for human spaceflight
References
- ^ "NASA studying three-stage approach to human-class lunar landers". SpaceNews.com. 2018-11-20. Retrieved 2019-11-08.
- "BIS Lunar Lander". www.astronautix.com. Archived from the original on August 20, 2016.
- "Von Braun Lunar Lander". www.astronautix.com. Archived from the original on August 20, 2016.
- "Horizon LERV". www.astronautix.com. Archived from the original on December 28, 2016.
- "Lunex Lunar Lander". www.astronautix.com. Archived from the original on December 28, 2016.
- "LEK". www.astronautix.com. Archived from the original on 16 March 2006. Retrieved 12 January 2022.