| Revision as of 21:03, 16 September 2016 editThere, I have entered a username (talk | contribs)224 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:55, 27 October 2024 edit undoMonkbot (talk | contribs)Bots3,695,952 editsm Task 20: replace {lang-??} templates with {langx|??} ‹See Tfd› (Replaced 1; ignored 2: Lang-zh, Lang-mnc);Tag: AWB | ||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 20 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Infobox river | |||
| {{Geobox | |||
| | name = Zeya | |||
| | River | |||
| | native_name ={{native name|ru|Зея}} | |||
| <!-- *** Name section *** --> | |||
| | |
| name_other = | ||
| | name_etymology = | |||
| |native_name = Зея | |||
| <!---------------------- IMAGE & MAP --> | |||
| |other_name = | |||
| | |
| image = Zeya River and Island.jpg | ||
| | image_size = 250px | |||
| <!-- *** Image *** ---> | |||
| | |
| image_caption = Island on the Zeya. | ||
| | |
| map = Zeyarivermap.png | ||
| | |
| map_size = 250px | ||
| | map_caption = Map of the Amur drainage basin with the Zeya highlighted | |||
| <!-- *** Country etc. *** --> | |||
| | |
| pushpin_map = | ||
| | pushpin_map_size = 250px | |||
| |country1 = | |||
| | pushpin_map_caption= | |||
| |state = | |||
| <!---------------------- LOCATION --> | |||
| |state1 = | |||
| | subdivision_type1 = Country | |||
| |region = | |||
| | subdivision_name1 = ] | |||
| |region1 = | |||
| | subdivision_type2 = Federal subject | |||
| |district = | |||
| | subdivision_name2 = ] | |||
| |district1 = | |||
| | subdivision_type3 = | |||
| |city = | |||
| | subdivision_name3 = | |||
| |city1 = | |||
| | subdivision_type4 = | |||
| |city2 = | |||
| | subdivision_name4 = | |||
| |city3 = | |||
| | subdivision_type5 = | |||
| |city4 = | |||
| | subdivision_name5 = | |||
| |city5 = | |||
| <!---------------------- PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS --> | |||
| |city6 = | |||
| | length = {{convert|1,242|km|mi|abbr=on}}<ref name="Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader">{{cite web|url=https://wwfeu.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/ahrbr.pdf|title=Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader|isbn=9789881722713}}</ref> | |||
| <!-- *** Geography *** --> | |||
| | |
| width_min = | ||
| | |
| width_avg = | ||
| | |
| width_max = | ||
| | depth_min = | |||
| |discharge_location = ] <ref>Sokolov, // Hydrography of USSR. {{ru icon}}</ref> | |||
| | |
| depth_avg = | ||
| | |
| depth_max = | ||
| | discharge1_location= ]<ref>Sokolov, // Hydrography of USSR. {{in lang|ru}}</ref><ref name="Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader">{{cite web|url=https://wwfeu.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/ahrbr.pdf|title=Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader|isbn=9789881722713}}</ref> | |||
| |discharge1_location = | |||
| | discharge1_min = {{convert|1.5|m3/s|cuft/s|abbr=on}} | |||
| |discharge1 = | |||
| | discharge1_avg = {{convert|1,810|m3/s|cuft/s|abbr=on}} | |||
| <!-- *** Source *** --> | |||
| | discharge1_max = {{convert|14,200|m3/s|cuft/s|abbr=on}} | |||
| |source_name = | |||
| <!---------------------- BASIN FEATURES --> | |||
| |source_location = ] | |||
| | |
| source1 = ] | ||
| | source1_location = | |||
| |source_region = ] | |||
| | source1_coordinates= | |||
| |source_state = | |||
| | source1_elevation = | |||
| |source_country = | |||
| | |
| mouth = ] | ||
| | mouth_location = | |||
| |source_lat_m = | |||
| | mouth_coordinates = {{coord|50.2419|N|127.598|E|source:kolossus-ruwiki|display=it}} | |||
| |source_lat_s = | |||
| | mouth_elevation = | |||
| |source_lat_NS = | |||
| | |
| progression = {{RAmur}} | ||
| | |
| river_system = | ||
| | basin_size = {{convert|233,000|km2|mi2|abbr=on}}<ref name="Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader">{{cite web|url=https://wwfeu.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/ahrbr.pdf|title=Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader|isbn=9789881722713}}</ref> | |||
| |source_long_s = | |||
| | tributaries_left = | |||
| |source_long_EW = | |||
| | tributaries_right = | |||
| |source_elevation = | |||
| | |
| custom_label = | ||
| | custom_data = | |||
| <!-- *** Mouth *** --> | |||
| | |
| extra = | ||
| |mouth_location = ] | |||
| |mouth_district = | |||
| |mouth_region = | |||
| |mouth_state = | |||
| |mouth_country = | |||
| |mouth_lat_d = | |||
| |mouth_lat_m = | |||
| |mouth_lat_s = | |||
| |mouth_lat_NS = | |||
| |mouth_long_d = | |||
| |mouth_long_m = | |||
| |mouth_long_s = | |||
| |mouth_long_EW = | |||
| |mouth_elevation = | |||
| <!-- *** Tributaries *** --> | |||
| |tributary_left = | |||
| |tributary_left1 = | |||
| |tributary_right = | |||
| |tributary_right1 = | |||
| <!-- *** Free fields *** --> | |||
| |free_name = | |||
| |free_value = | |||
| <!-- *** Map section *** --> | |||
| |map = Zeyarivermap.png | |||
| |map_size = 250px | |||
| |map_caption = Map of the Amur river drainage basin with the Zeya river highlighted | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Zeya |
The '''Zeya''' ({{langx|ru|Зе́я}}; from indigenous ] word "djee" (blade); {{lang-zh|结雅}}; {{lang-mnc|m={{ManchuSibeUnicode|ᠵᡳᠩᡴᡳᡵᡳ<br> ᠪᡳᡵᠠ}}}}, ] jingkiri bira) is a northern, left ] of the ] in ], ]. It is {{convert|1,242|km|sp=us|abbr=on}} long, and has a ] of {{convert|233,000|km2|sp=us|abbr=on}}.<ref name=gvr>{{GVR|289255|Река ЗЕЯ}}</ref> The average flow of the river is {{convert|1,810|m3/s|cuft/s|abbr=on}}.<ref name="Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader">{{cite web|url=https://wwfeu.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/ahrbr.pdf|title=Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader|isbn=9789881722713}}</ref> | ||
| ==History== | |||
| Zeya flows through the ] and joins the ] near ], in Russia's ]. Regulation of river discharge by ] mitigates extrimities of river flow down to 5000 m³/s. | |||
| The first Russian documented to enter the area was ]. | |||
| ==Course== | |||
| The main tributaries of the Zeya River are ], ], ], ], and ] on the right, and ], ], ], ], and ] on the left. | |||
| It rises in the ] mountain ridge, a part of the ]. | |||
| The Zeya flows through the ], at the junction of the ] and ], and joins the ] near ], at the border with China. Regulation of river discharge by ] mitigates extremities of river flow down to 5000 m³/s. The Zeya contributes around 16% of both the average and maximum flow of de Amur because of the flow regulations. In the past, the Zeya could have contributed up to almost 50% of the Amur's maximum flow of approximately 30,000 m³/s. | |||
| The river freezes from November to May. It is navigable with the most important river ports being ], ], and ]. | |||
| {{Commons category|Zeya River}} | |||
| The main tributaries of the Zeya are ], ], ], ], and ] on the right, and ], ], ], ], and ] on the left.<ref name=bse>, ]</ref> | |||
| The river freezes from November to May. When it is unfrozen, the river is navigable with the most important river ports being ], ], and ]. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{coord|50.2419|N|127.598|E|source:kolossus-ruwiki|display=title}} | |||
| *{{Commons category-inline|Zeya River}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| {{Russia-river-stub}} | {{FarEast-Russia-river-stub}} | ||
| {{AmurOblast-geo-stub}} | |||
Latest revision as of 12:55, 27 October 2024
River in Amur Oblast, Russia| Zeya | |
|---|---|
 Island on the Zeya. Island on the Zeya. | |
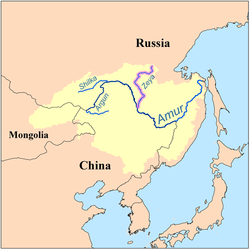 Map of the Amur drainage basin with the Zeya highlighted Map of the Amur drainage basin with the Zeya highlighted | |
| Native name | Зея (Russian) |
| Location | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal subject | Amur Oblast |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Toko-Stanovik |
| Mouth | Amur |
| • coordinates | 50°14′31″N 127°35′53″E / 50.2419°N 127.598°E / 50.2419; 127.598 |
| Length | 1,242 km (772 mi) |
| Basin size | 233,000 km (90,000 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Blagoveshchensk |
| • average | 1,810 m/s (64,000 cu ft/s) |
| • minimum | 1.5 m/s (53 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 14,200 m/s (500,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Amur→ Sea of Okhotsk |
The Zeya (Russian: Зе́я; from indigenous Evenki word "djee" (blade); Chinese: 结雅; Manchu: ᠵᡳᠩᡴᡳᡵᡳ
ᠪᡳᡵᠠ, Mölendroff: jingkiri bira) is a northern, left tributary of the Amur in Amur Oblast, Russia. It is 1,242 km (772 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 233,000 km (90,000 sq mi). The average flow of the river is 1,810 m/s (64,000 cu ft/s).
History
The first Russian documented to enter the area was Vassili Poyarkov.
Course
It rises in the Toko-Stanovik mountain ridge, a part of the Stanovoy Range.
The Zeya flows through the Zeya Reservoir, at the junction of the Tukuringra Range and Dzhagdy Range, and joins the Amur near Blagoveshchensk, at the border with China. Regulation of river discharge by Zeya Dam mitigates extremities of river flow down to 5000 m³/s. The Zeya contributes around 16% of both the average and maximum flow of de Amur because of the flow regulations. In the past, the Zeya could have contributed up to almost 50% of the Amur's maximum flow of approximately 30,000 m³/s.
The main tributaries of the Zeya are Tok, Mulmuga, Bryanta, Gilyuy, and Urkan on the right, and Kupuri, Argi, Dep, Selemdzha, and Tom on the left.
The river freezes from November to May. When it is unfrozen, the river is navigable with the most important river ports being Zeya, Svobodny, and Blagoveshchensk.
See also
References
- ^ "Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader" (PDF). ISBN 9789881722713.
- Sokolov, Far East // Hydrography of USSR. (in Russian)
- "Река ЗЕЯ in the State Water Register of Russia". textual.ru (in Russian).
- Зея (река в Амурской обл.), Great Soviet Encyclopedia
External links
- [REDACTED] Media related to Zeya River at Wikimedia Commons
This article related to a river in the Russian Far East is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This Amur Oblast location article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |