| Revision as of 18:09, 1 September 2024 editMarcocapelle (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers557,894 edits →Further reading: Removed grandparent category of Category:Spanish SaharaTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 13:33, 28 October 2024 edit undoMonkbot (talk | contribs)Bots3,695,952 editsm Task 20: replace {lang-??} templates with {langx|??} ‹See Tfd› (Replaced 1);Tag: AWB | ||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Spanish West Africa''' ({{ |
'''Spanish West Africa''' ({{Langx|es|África Occidental Española}}, AOE) was a grouping of ] along the Atlantic coast of northwest Africa. It was formed in 1946 by joining the southern zone (the ]) of the ] with the colonies of ], ] and ] into a single administrative unit. Following the ] (1957–58), Spain ceded the Cape Juby Strip to ] by the ], and created separate provinces for Ifni and the ] in 1958.<ref>Shannon E. Fleming, "Decolonization and the Spanish Army, 1940–76", in Wayne H. Bowen and José E. Alvarez, eds., ''A Military History of Modern Spain: From the Napoleonic Era to the International War on Terror'' (Praeger Security, 2007), p. 129. {{ISBN|9780275993573}}</ref><ref>Susan Martin-Márquez, ''Disorientations: Spanish Colonialism in Africa and the Performance of Identity'' (Yale University Press, 2008), p. 378. {{ISBN|978-0-300-15252-4}}</ref> | ||
| Spanish West Africa was formed by a decree of 20 July 1946. The new governor sat at Ifni. He was '']'' the delegate of the ] in the southern zone of the protectorate, to facilitate its government along the same lines as the other Spanish possessions on the coast. On 12 July 1947, Ifni and the Sahara were raised into distinct entities, but still under the authority of the governor in Ifni. On 10 and 14 January 1958, respectively, the Sahara and Ifni were raised into regular Spanish ]s completely independent of one another.<ref>Robert Rézette, ''The Western Sahara and the Frontiers of Morocco'' (Nouvelles Éditions Latines, 1975), p. 101.</ref><ref name=Villanova>José Luis Villanova, "La organización política del territorio de Ifni duranta la dominación colonial española (1934–1969)", ''Anales: Revista de Estudios Ibéricos e Iberoamericanos'' (2007): 49–82, esp. 62–72.</ref> | Spanish West Africa was formed by a decree of 20 July 1946. The new governor sat at Ifni. He was '']'' the delegate of the ] in the southern zone of the protectorate, to facilitate its government along the same lines as the other Spanish possessions on the coast. On 12 July 1947, Ifni and the Sahara were raised into distinct entities, but still under the authority of the governor in Ifni. On 10 and 14 January 1958, respectively, the Sahara and Ifni were raised into regular Spanish ]s completely independent of one another.<ref>Robert Rézette, ''The Western Sahara and the Frontiers of Morocco'' (Nouvelles Éditions Latines, 1975), p. 101.</ref><ref name=Villanova>José Luis Villanova, "La organización política del territorio de Ifni duranta la dominación colonial española (1934–1969)", ''Anales: Revista de Estudios Ibéricos e Iberoamericanos'' (2007): 49–82, esp. 62–72.</ref> | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
| |Served at the start of the ]. | |Served at the start of the ]. | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| === Vice Governors === | |||
| * 1947-1955: Rufino Pérez Barruecos<ref name="VG">{{Cite web |title=BOE.es - Gazeta: formulario de búsqueda de disposiciones y noticias |url=https://www.boe.es/buscar/gazeta.php?campo%5B0%5D=ID_HIST&dato%5B0%5D=&campo%5B1%5D=TITULOS&dato%5B1%5D=Subgobernador&operador%5B1%5D=and&campo%5B2%5D=RNG.ID&dato%5B2%5D=&operador%5B2%5D=and&campo%5B3%5D=DEM.ID&dato%5B3%5D=&operador%5B3%5D=and&campo%5B4%5D=DOC&dato%5B4%5D=&operador%5B4%5D=and&campo%5B5%5D=TITULOS&dato%5B5%5D=&operador%5B5%5D=and&campo%5B6%5D=GAZ.ID&dato%5B6%5D=8&campo%5B7%5D=NBO&dato%5B7%5D=&operador%5B8%5D=and&campo%5B8%5D=FPU&dato%5B8%5D%5B0%5D=&dato%5B8%5D%5B1%5D=&operador%5B9%5D=and&campo%5B9%5D=FAP&dato%5B9%5D%5B0%5D=&dato%5B9%5D%5B1%5D=&page_hits=2000&sort_field%5B0%5D=FPU&sort_order%5B0%5D=desc&sort_field%5B1%5D=REF&sort_order%5B1%5D=asc&accion=Buscar |access-date=2024-10-07 |website=www.boe.es}}</ref> | |||
| * 1956-1958: Manuel Mulero Clemente<ref name="VG" /> | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 13:33, 28 October 2024
Spanish colony from 1946 to 1958Spanish West AfricaÁfrica Occidental Española (Spanish)
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1946–1958 | |||||||||||||||||||
 Flag
Flag | |||||||||||||||||||
| Anthem: Marcha Real "Royal March" | |||||||||||||||||||
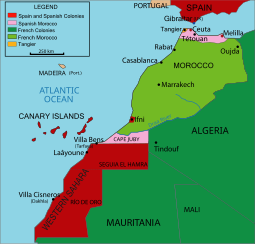 Spanish Northwestern African possessions in 1912. Spanish Northwestern African possessions in 1912. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Federation of Spanish colonial possessions | ||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Sidi Ifni | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Spanish Arabic | ||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism Islam | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Colonial administration | ||||||||||||||||||
| Head of State | |||||||||||||||||||
| • 1946–1958 | Francisco Franco | ||||||||||||||||||
| Governor | |||||||||||||||||||
| • 1946–1949 (first) | José Bermejo López | ||||||||||||||||||
| • 1957–1958 (last) | Mariano Gómez-Zamalloa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Established | 20 July 1946 | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Disestablished | 10 January 1958 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Spanish peseta | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Spanish West Africa (Spanish: África Occidental Española, AOE) was a grouping of Spanish colonies along the Atlantic coast of northwest Africa. It was formed in 1946 by joining the southern zone (the Cape Juby Strip) of the Spanish protectorate in Morocco with the colonies of Ifni, Saguia el-Hamra and Río de Oro into a single administrative unit. Following the Ifni War (1957–58), Spain ceded the Cape Juby Strip to Morocco by the Treaty of Angra de Cintra, and created separate provinces for Ifni and the Sahara in 1958.
Spanish West Africa was formed by a decree of 20 July 1946. The new governor sat at Ifni. He was ex officio the delegate of the Spanish high commissioner in Morocco in the southern zone of the protectorate, to facilitate its government along the same lines as the other Spanish possessions on the coast. On 12 July 1947, Ifni and the Sahara were raised into distinct entities, but still under the authority of the governor in Ifni. On 10 and 14 January 1958, respectively, the Sahara and Ifni were raised into regular Spanish overseas provinces completely independent of one another.
Governors
Main article: List of colonial governors of Spanish Sahara| Tenure | Incumbent | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 24 July 1946 to 17 August 1949 | José Bermejo López,
Governor |
|
| 17 August 1949 to 29 March 1952 | Francisco Rosaleny Burguet,
Governor |
|
| 29 March 1952 to 26 February 1954 | Venancio Tutor Gil,
Governor |
|
| 26 February 1954 to 23 May 1957 | Ramón Pardo de Santayana y Suárez,
Governor |
Apostolic Prefecture of Spanish Sahara and Ifni established on 5 July 1954, with Félix Erviti Barcelona OMI as the first apostolic prefect. |
| 23 May 1957 to 10 January 1958 | Mariano Gómez-Zamalloa y Quirce,
Governor |
Served at the start of the Ifni War. |
Vice Governors
- 1947-1955: Rufino Pérez Barruecos
- 1956-1958: Manuel Mulero Clemente
References
- Shannon E. Fleming, "Decolonization and the Spanish Army, 1940–76", in Wayne H. Bowen and José E. Alvarez, eds., A Military History of Modern Spain: From the Napoleonic Era to the International War on Terror (Praeger Security, 2007), p. 129. ISBN 9780275993573
- Susan Martin-Márquez, Disorientations: Spanish Colonialism in Africa and the Performance of Identity (Yale University Press, 2008), p. 378. ISBN 978-0-300-15252-4
- Robert Rézette, The Western Sahara and the Frontiers of Morocco (Nouvelles Éditions Latines, 1975), p. 101.
- José Luis Villanova, "La organización política del territorio de Ifni duranta la dominación colonial española (1934–1969)", Anales: Revista de Estudios Ibéricos e Iberoamericanos 3 (2007): 49–82, esp. 62–72.
- ^ "BOE.es - Gazeta: formulario de búsqueda de disposiciones y noticias". www.boe.es. Retrieved 2024-10-07.
Further reading
- José Antonio Rodriguez Esteban, "El Mapa del África Occidental Española de 1949 a escala 1:500.000: orgullo militar, camelladas y juegos poéticos saharauis", Cybergeo: European Journal of Geography. Online since 20 January 2011.
Categories:
- Spanish Africa
- Spanish Sahara
- History of West Africa
- Colonial history of Morocco
- 20th century in Morocco
- States and territories established in 1946
- States and territories disestablished in 1958
- 1946 establishments in Africa
- 1958 disestablishments in Africa
- Former countries in Africa
- Former colonies in Africa
- Former Spanish colonies