| Revision as of 13:56, 15 January 2011 editAnolian (talk | contribs)4 edits changed tcourtier to courtier← Previous edit | Revision as of 05:06, 26 December 2024 edit undoSmasongarrison (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers732,621 edits General + punct fixesTag: AWBNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Castilian warlord and Prince of Valencia from 1094 to 1099}} | |||
| {{Other uses}} | {{Other uses}} | ||
| {{Infobox royalty | |||
| {{No footnotes|date=June 2009}} | |||
| |title= ] of ] | |||
| ] | |||
| | full name = Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar | |||
| '''Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar''' (c. 1043 – July 10, 1099), known as '''El Cid Campeador''', was a ] nobleman, a military leader and diplomat who, after being exiled, conquered and governed the city of ]. Rodrigo Díaz was educated in the royal court of ] and became the '']'', or chief general, of ], and his most valuable asset in the fight against the ]. | |||
| | image = Estatua del Cid (Burgos).jpg | |||
| | caption = Statue of El Cid in ], Spain | |||
| | succession = ] | |||
| | reign= 1094{{snd}}1099 | |||
| | coronation= 1094 | |||
| | predecessor = ] | |||
| | successor = ] | |||
| | spouse = ] | |||
| | house = | |||
| | father = Diego Laínez | |||
| | mother = | |||
| | issue = ]<br/>]<br/>] | |||
| | birth_name = Rodrigo Díaz | |||
| | birth_date = {{circa|1043}} | |||
| | birth_place = ], ] | |||
| | death_date = {{death date|1099|7|10|df=y}} (aged around 56) | |||
| | death_place = ] | |||
| | place of burial = ] | |||
| | signature = Signature of El Cid.svg | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar''' ({{circa|1043}} – 10 July 1099) was a Castilian ] and ruler in ]. Fighting both with ] and ] armies during his lifetime, he earned the Arabic honorific {{transl|ar|as-Sayyid}} ("the Lord" or "the Master"), which would evolve into '''El Çid''' ({{IPA|es|el ˈθið|lang}}, {{IPA-all|el ˈts̻id|Old Spanish:}}), and the Spanish honorific '''El Campeador''' ("the Champion"). He was born in ], a village near the city of ]. | |||
| As the head of his loyal knights, he came to dominate the ] of the ] at the end of the 11th century. He reclaimed the ] from Moorish control for a brief period during the '']'', ruling the ] from 17 June 1094 until his death in 1099. His wife, ], inherited the city and maintained it until 1102 when it was reconquered by the Moors. | |||
| Díaz de Vivar became well known for his service in the armies of both Christian and Muslim rulers. After his death, El Cid became Spain's most celebrated national hero and the protagonist of the most significant medieval Spanish epic poem, {{lang|osp|]}},<ref>{{Cite book|last=Barton|first=Simon & Richard Fletcher|title=The world of El Cid: chronicles of the Spanish reconquest|date=2000|publisher=Manchester University Press|isbn=0-7190-5225-4|location=Manchester|oclc=45486279}}</ref> which presents him as the ideal medieval knight: strong, valiant, loyal, just, and pious. | |||
| There are various theories on his family history, which remains uncertain; however, he was the grandfather of ] de Pamplona, King of Navarre, the first son of his daughter ]. To this day, El Cid remains a popular Spanish folk hero and national icon, with his life and deeds remembered in popular culture.<ref>Ventura Fuentes (1908). "]". In ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. '''3.''' New York: Robert Appleton Company.</ref><ref>Henry Edward Watts (1911). "]". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. '''6.''' (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 361–362.</ref> | |||
| == Etymology: ''Cid'' and ''Campeador'' == | |||
| ] | |||
| Rodrigo Díaz was recognized with the honorary title ''Campeador'' during his lifetime, as is evidenced by a document that he signed in 1098, which he signed in the Latinized expression, {{lang|la|ego Rudericus Campidoctor}}. The title ''Campeador'' comes from the Latin {{lang|la|Campidoctor}}, literally meaning "Teacher of the Field", but translatable as "Master of the Battlefield". Arabic sources from the late 11th century and early 12th century call him {{lang|ar|الكنبيطور}} ({{transl|ar|al-Kanbīṭūr}}), {{lang|ar|القنبيطور}} ({{transl|ar|al-Qanbīṭūr}}), also preceded by {{transl|ar|Rudrīq}} or {{transl|ar|Ludrīq}}, which are Arabized forms of his title and name, respectively.<ref>{{Cite web |last=gigatos |date=2022-03-12 |title=El Cid |url= https://www.trenfo.com/en/history/biographies/el-cid |access-date=2023-02-23 |website=Trenfo.com |language=en-GB |archive-date=2023-02-23 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20230223071517/https://www.trenfo.com/en/history/biographies/el-cid |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| The epithet ''El Cid'' meant "the Lord", probably from the original Arabic ({{langx|ar|السَّيِّد|as-]|label=none}}), and was a title given to other Christian leaders. It has been conjectured that Rodrigo Díaz received the honorific title and respectful treatment of contemporaries in ] because of his victories in the service of the King of the Taifa of Zaragoza between 1081 and 1086; however, he more likely received the epithet after his conquest of Valencia in 1094. This title appears for the first time, as {{lang|osp|Meo Çidi}}, in the {{lang|es|Poema de Almería}}, composed between 1147 and 1149.<ref>{{Cite book |title=El Cid : del hombre a la leyenda: Claustro bajo de la Catedral de Burgos, septiembre–noviembre 2007 |date=2007 |publisher=Junta de Castilla y León |author=Juan Carlos Elorza Guinea |author2=María Pilar Alonso Abad |author3=Castilla y León Junta |isbn=978-84-935781-4-5 |location= Valladolid |page=46 |oclc=433366647}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Ignacio Ruiz Rodríguez |first=Félix Martínez Llorente |title=Recuerdos literarios en honor a un gran historiador de Castilla: Gonzalo Martínez Díez (1924–2015) |date=2016 |isbn=978-84-9085-787-8 |location=Madrid |pages=315 |oclc=964290692}}</ref> | |||
| The combination of ''Cid Campeador'' is documented from 1195 in {{lang|es|Linaje de Rodrigo Díaz}} ("The Lineage of Rodrigo Díaz") in Navarro-Aragonese which form part of the {{lang|la|Liber regum}} written as {{lang|osp|mio Cit el Campiador}}; and in {{lang|osp|El Cantar de mio Cid}}.<ref>{{Citation |last=Deyermond |first=Alan |title=El Cantar de mio Cid y la épica anglosajona |date=2013 |work=Sonando van sus nuevas allent parte del mar |pages=217–226 |publisher=Presses universitaires du Midi |doi=10.4000/books.pumi.38431 |isbn=978-2912025852 |doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| == Summary == | |||
| Born a member of the minor nobility, El Cid was brought up at the court of ] and served Ferdinand's son, ]. He rose to become the commander and royal standard-bearer (''armiger regis'') of ] upon Sancho's ascension in 1065. El Cid went on to lead the Castilian military campaigns against Sancho's brothers, ] and ], as well as in the Muslim kingdoms in ]. He became renowned for his military prowess in these campaigns, which helped expand the territory of the Crown of Castile at the expense of the Muslims and Sancho's brothers' kingdoms. | |||
| When conspirators murdered Sancho in 1072, El Cid found himself in a difficult situation. Since Sancho was childless, the throne passed to his brother Alfonso, whom El Cid had helped remove from power. Although El Cid continued to serve the sovereign, he lost his ranking in the new court, which treated him suspiciously and kept him at arm's length. Finally, in 1081, he was exiled.<ref name="Mythology">{{cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Hkx472N8Bk8C&q=Rodrigo+%22El+Cid%22+suspicious+alfonso&pg=PA161 | title=Mythology in the Middle Ages: Heroic Tales of Monsters, Magic, and Might | publisher=ABC-CLIO | author=Fee, Christopher R. | year=2011 | pages=161 | isbn=978-0275984069}}</ref> | |||
| El Cid found work fighting for the ] rulers of ], whom he defended from its traditional enemy, ]. While in exile, he regained his reputation as a strategist and formidable military leader. He was repeatedly victorious in battle against the Muslim rulers of ] and their Christian allies, as well as against a large Christian army under King ] of Aragon. In 1086, an expeditionary army of ]n ] inflicted a severe defeat to Castile, compelling Alfonso to overcome the resentment he harboured against El Cid. The terms for El Cid's return to Christian service must have been attractive enough since El Cid soon found himself fighting for his former lord. Over the next several years, however, El Cid set his sights on the kingdom-city of ], operating more or less independently of Alfonso, while politically supporting the ] and other Muslim dynasties opposed to the Almoravids. He gradually increased his control over Valencia; the Islamic ruler, ], became his tributary in 1092. When the Almoravids instigated an uprising that resulted in the death of al-Qadir, El Cid responded by laying siege to the city. Valencia finally fell in 1094, and El Cid established an independent principality on the Mediterranean coast of Iberia. He ruled over a ] society with the popular support of Christians and Muslims alike.<ref name="Quest">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=W-MIChVmZwQC|title=The Quest for El Cid|author=Fletcher, Richard A.|publisher=Oxford University Press|year=1989|isbn=978-0195069556|location=Oxford, UK|pages=166–168, 198}}</ref> | |||
| El Cid's final years were spent fighting the Almoravid ]. He inflicted upon them their first major defeat in 1094, on the plains of Caurte, outside Valencia, and continued opposing them until his death. Although El Cid remained undefeated in Valencia, Diego Rodríguez, his only son and heir, died fighting against the Almoravids in the service of Alfonso in 1097. After El Cid's death in 1099, his wife, ], succeeded him as ruler of Valencia, but she was eventually forced to surrender the principality to the Almoravids in 1102.{{sfn|Mikaberidze|2011|p=91}} | |||
| ==Title== | ==Title== | ||
| ]'', the earliest literary treatment of El Cid's life, written to celebrate El Cid's defeat of some counts and champions]] | |||
| The name "El Cid" comes from the Spanish article ''el'' (meaning "the"), and the dialectal Arabic word سيد '']'' or ], which means "Lord" or "The Master". The title ''Campeador'' is the ] version of the ] ''campi doctor'' or ''campi doctus''; the term can be found in writings of late Latinity (4th – 5th century) and can be found in some inscriptions of that era. After that period it became rare, although still sometimes found in the writings of the less educated writers of the Middle Ages. The literal significance of the expression ''campi doctor'' is "master of the military arts", and its use in the period of the late Roman Empire appears to have signified only one who instructed new military recruits. But it was in current usage when El Cid was still alive, and was applied to Rodrigo by a member of his circle in an official document promulgated in his name in 1098. Overall, then, ''El Cid Campeador'' translates as "The lord, master of military arts", or more directly, "The Champion." | |||
| The name ''El Cid'' ({{IPA|es|el ˈθið|lang}}) is a modern Spanish denomination composed of the article ''el'' meaning "the" and ''Cid'', which derives from the Old Castilian loan word ''Çid'' borrowed from the dialectal Arabic word سيد '']'' or ], which means "lord" or "master". The ] or the Arabs that served in his ranks may have addressed him in this way, which the Christians may have transliterated and adopted. Historians, however, have not yet found contemporary records referring to Rodrigo as ''Cid.'' Arab sources use instead ''Rudriq'', ''Ludriq al-Kanbiyatur'' or ''al-Qanbiyatur'' (''Rodrigo el Campeador'').<ref>María Jesús Viguera Molins, «El Cid en las fuentes árabes», in César Hernández Alonso (coord.), ''Actas del Congreso Internacional el Cid, Poema e Historia (12–16 de julio de 1999)'', Ayuntamiento de Burgos, 2000, pp. 55–92. {{ISBN|84-87876-41-2}}</ref> | |||
| The cognomen ''Campeador'' derives from Latin ''campi doctor,'' which means "battlefield master". He probably gained it during the campaigns of ] against his brothers, kings ] and ]. While his contemporaries left no historical sources that would have addressed him as ''Cid'', they left plenty of Christian and Arab records, some even signed documents with his autograph, addressing him as ''Campeador'', which prove that he used the Christian cognomen himself.<ref name=egoruderico>See Ramón Menéndez Pidal, , ''Revista de Filología Española'', t. 5 (1918), Madrid, Sucesores de Hernando, 1918. Digital copy Valladolid, Junta de Castilla y León. Consejería de Cultura y Turismo. Dirección General de Promociones e Instituciones Culturales, 2009–2010. Original in Archivo de la Catedral de Salamanca, caja 43, legajo 2, n.º 72.</ref><ref>Alberto Montaner Frutos y Ángel Escobar, «El ''Carmen Campidoctoris'' y la materia cidiana», in ''Carmen Campidoctoris o Poema latino del Campeador'', Madrid, Sociedad Estatal España Nuevo Milenio, 2001, p. 73 . {{ISBN|978-84-95486-20-2}}</ref><ref>Alberto Montaner Frutos, </ref><ref>Georges Martin , en el de la revista electrónica , n.º 10 (diciembre de 2010). Online since 22 January 2011. Last time visited November 28th 2011. Complete text (Edition of the Latin text) in José Luis Martín Martín ''& al.'', .</ref> The whole combination ''Cid Campeador'' is first documented c. 1195 in the ] ''{{ill|Linage de Rodric Díaz|es|Linaje de Rodrigo Díaz}}'' included in the '']'' under the formula ''mio Cid el Campeador''.{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | |||
| ==Life and career== | ==Life and career== | ||
| ] | |||
| ] Queen of ], ] and ] from 1109 until her death. ]] | |||
| ===Origins=== | ===Origins=== | ||
| El Cid was born |
El Cid was born Rodrigo Díaz circa 1043 in ],<ref name="ThackerayFindling2012">{{cite book|author=Tim Watts|editor=Frank W. Thackeray |editor2=John E. Findling|title=Events That Formed the Modern World|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BRl1sWYShpcC&pg=PA19|date= 2012|publisher=ABC-CLIO|isbn=978-1-59884-901-1|page=19}}</ref> also known as Castillona de Bivar, a small town about ten kilometers (or six miles) north of ], the capital of ]. His father, Diego Laínez, was a ], ], and ]man who had fought in several battles. Despite the fact that El Cid's mother's family was aristocratic, in later years, the peasants would consider him one of their own. However, his relatives were not major court officials; documents show that El Cid's paternal grandfather, Laín, confirmed{{vague|date=September 2022}} only five documents of ]'s; his maternal grandfather, Rodrigo Álvarez, certified only two of ]'s; and El Cid's father confirmed only one.{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | ||
| ===Service under Sancho II=== | ===Service under Sancho II=== | ||
| As a young |
As a young man in 1057, El Cid fought against the Moorish stronghold of ], making its ] ] a vassal of Sancho. In the spring of 1063, El Cid fought in the ], where Ferdinand's half-brother, ], was laying siege to the Moorish town of Graus, which was fought on Zaragozan lands in the valley of the ]. Al-Muqtadir, accompanied by Castilian troops including El Cid, fought against the Aragonese. The party slew Ramiro I, setting the Aragonese army on the run, and emerged victorious. One legend has said that during the conflict, El Cid killed an Aragonese knight in single combat, thereby receiving the honorific title "''Campeador''".<ref>{{Citation |last=Weiss |first=Julian |title='El Cid' (Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar) |date=2018-12-31 |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/product/identifier/9781108672832%23CN-bp-12/type/book_part |work=The Cambridge Companion to the Literature of the Crusades |pages=184–199 |editor-last=Bale |editor-first=Anthony |edition=1 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |doi=10.1017/9781108672832.013 |isbn=978-1-108-67283-2 |s2cid=165471019 |access-date=2022-11-12}}</ref> | ||
| When Ferdinand died, Sancho continued to enlarge his territory, conquering both |
When Ferdinand died, Sancho continued to enlarge his territory, conquering both Christian strongholds and the ] cities of ] and ]. When Sancho learned that Alfonso was planning on overthrowing him in order to gain his territory, Sancho sent Cid to bring Alfonso back so that Sancho could speak to him.{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | ||
| ===Service under Alfonso VI=== | ===Service under Alfonso VI=== | ||
| ] Oath". In the middle of the scene, ] (with red cape) is swearing with his right hand on the ] that he did not take part in the murder of his brother ], while El Cid stands as a witness in front of him.]] | |||
| Sancho was assassinated in 1072. This was the result of a pact between his brother Alfonso and his sister ]; In any case, since Sancho died unmarried and childless, all of his power passed to his brother Alfonso. | |||
| Sancho was assassinated in 1072, during a siege of his sister's town of Zamora.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Catlos |first1=Brian |title=Infidel kings and Unholy Warriors: Faith, power, and violence in the age of crusade and jihad |date=2015 |publisher=Farrar, Straus and Giroux |chapter=The Cid Rides Again |page=73}}</ref> Since Sancho died unmarried and childless, all of his power passed to his brother Alfonso who, almost immediately, returned from exile in ] and took his seat as king of Castile and León. He was, however, deeply suspected of having been involved in Sancho's murder. According to the 11th century epic poem '']'', the Castilian nobility led by El Cid and a dozen "oath-helpers" forced Alfonso to ] publicly on holy relics multiple times in front of ] (]) Church in ] that he did not participate in the plot to kill his brother. This is not mentioned in the more reliable 12th century chronicle '']'', however. El Cid's position as ''armiger regis'' was taken away and given to his enemy, Count ].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Russell |first=Peter Edward |date=2024-04-18 |title=El Cid |url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/El-Cid-Castilian-military-leader |access-date=2024-04-28 |website=Encyclopaedia Britannica}}</ref> | |||
| In 1079, El Cid was sent by Alfonso VI to ] to the court of ] to collect the '']'' owed by that '']'' to León–Castile.<ref name="Chaytor-3">{{Cite book|author=Chaytor, Henry John|year=1933|chapter=Chapter 3: The Reconquest|title=A History of Aragon and Catalonia|location=London|publisher=Methuan|pages=39–40|url=http://libro.uca.edu/chaytor/achistory.htm}}</ref> While he was there Granada, assisted by other Castilian knights, attacked Seville, and El Cid and his forces repulsed the Christian and Grenadine attackers at the ], in the (probably mistaken) belief that he was defending the king's tributary. During the aftermath of this battle the Muslim troops under El Cid's command would hail him as Sayyidi.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Catlos |first1=Brian |title=Infidel kings and Unholy Warriors: Faith, power, and violence in the age of crusade and jihad |date=2015 |publisher=Farrar, Straus and Giroux |chapter=The Cid Rides Again |page=74}}</ref> Count García Ordóñez and the other Castilian leaders<ref>The '']'' says that the other two Castilian leaders were Diego Pérez and Lope Sánchez. {{Cite book|author=de los Rios, José Amador|title=Historia Crítica de la Literatura Española, Tomo III, (II Parte, Subciclo I) (The History and Criticism of Spanish Literature, Volume III (Second Part, subpart I))|publisher=J. Rodriguez|year=1863|location=Madrid, Spain|page=|language=es|chapter=Capitulo 3: Primeros Monumentos Escritos de la Poesía Castellana (Chapter 3: First-Written Monuments of Castilian Poetry)}}</ref> were taken captive and held for three days before being released.<ref name="Chaytor-3"/> | |||
| ===Exile=== | ===Exile=== | ||
| In the ] (1079), El Cid rallied his troops and turned the battle into a rout of Emir |
In the ] (1079), El Cid rallied his troops and turned the battle into a rout of Emir Abdullah of ] and his ally García Ordóñez. This unauthorized expedition into Granada, however, greatly angered Alfonso and May 8, 1080, was the last time El Cid confirmed a document in King Alfonso's court. The most likely reason was El Cid's incursion into Toledo, which happened to be under the control of Alfonso's vassal, Yahya Al-Qadir.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Ángel Ferreiro |first1=Miguel |title="La Conquista De Toledo, Mayo De 1085," |url=https://elretohistorico.com/la-capitulacion-de-toledo-en-mayo-de-1085/. |website=El Reto Histórico |access-date=15 December 2022}}</ref> Alfonso's anger over El Cid's unsanctioned incursion into his vassal's territory would lead him to exile the knight.<ref>{{cite book |last1=García Fitz |first1=Francisco |title=Relaciones Políticas y Guerra: La Experiencia Castellano-Leonesa Frente Al Islam: Siglos XI–XIII |date=2015 |publisher=Sevilla: Universidad de Sevilla |pages=47–48 |isbn=978-8447207084 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3o0CJVLbZKIC&pg=PA47 |access-date=15 December 2022}}</ref> | ||
| This is the generally accepted reason for the exile of El Cid, although several others are plausible and indeed may have been contributing factors to the exile: jealous nobles turning Alfonso against El Cid through court intrigue, and Alfonso's own personal animosity towards El Cid. The song of El Cid and subsequent tales state that Alfonso's and his court's animosity toward Rodrigo was the primary reason the expulsion of the knights from León,<ref>{{cite book |last1=Inti Fernandez |first1=Yanes |title=The Cross and the Sword: Political Myth-Making, Hegemony, and Intericonicity in the Christianization of the Iberian Peninsula and Britain |date=May 1, 2018 |publisher=OAKTrust |page=138 |url=https://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/handle/1969.1/173380. |access-date=15 December 2022 }}{{Dead link|date=February 2024 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> as well as a possible misappropriation of some of the tribute from Seville by El Cid.{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | |||
| At first he went to Barcelona where ] (1076–1082) and ] |
At first he went to ], where ] refused his offer of service.{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | ||
| ==Moorish service== | |||
| According to Moorish accounts: ''] ]s found El Cid their foe ill, thirsty and exiled from the court of ], he was presented before the elderly ] and accepted command of the forces of the ] as their Master.'' | |||
| ], he had gained a prominent reputation and the title ''El Cid'' (the lord). He is also known to have developed links with the other ] in 1080.]] | |||
| ], in the ]]] | |||
| The exile was not the end of El Cid, either physically or as an important figure. After being rejected by ], El Cid journeyed to the ], where he received a warmer welcome. In 1081, El Cid went on to offer his services to the king of ], ], and served both him and his successor, ]. He was given the title ''El Cid'' (''The Master'') and served as a leading figure in a diverse Moorish force consisting of ]s, ]s, ]s, and ]ans within the respective Taifa.{{citation needed|date=June 2017}} | |||
| According to Moorish accounts: | |||
| O'Callaghan writes: | |||
| {{blockquote|] ]s found El Cid their foe ill, thirsty and exiled from the court of ], he was presented before the elderly ] and accepted command of the forces of the ] as their Master.}} | |||
| ]'', the earliest literary treatment of El Cid's life, written by a Catalan partisan to celebrate the Cid's defeat of Berenguer Ramon.]] | |||
| That kingdom was divided between ] (1081–1085) who ruled ] proper, and his brother al-Mundhir, who ruled ] and ]. El Cid entered al-Mutamin's service and successfully defended Zaragoza against the assaults of al-Mundhir, Sancho I of Aragón, and Ramón Berenguer II, whom he held captive briefly in 1082. In 1084, El Cid and the ] armies defeated Sancho of Aragon at the ] near ]. He was then troubled by the fierce conflicts between the ]s of ] and the Arabs of ]. | |||
| In his ''History of Medieval Spain'' (Cornell University Press, 1975), Joseph F. O'Callaghan writes: | |||
| In 1086, the ] invasion of the ] through and around ] began. The Almoravids, ] residents of present-day ], led by ], were asked to help defend the divided ] from ]. El Cid had probably commanded a large ] force during the great ], which took place in 1086, near the ]. The ] and ] ]s, including the armies of ], ], ], ] and ], defeated a combined army of ], ] and ]. | |||
| {{blockquote|That kingdom was divided between ] (1081–1085) who ruled ] proper, and his brother ], who ruled ] and ]. El Cid entered al-Mutamin's service and successfully defended Zaragoza against the assaults of al-Mundhir, ], and Ramon Berenguer II, whom he held captive briefly in 1082.}} | |||
| Terrified after his crushing defeat, Alfonso recalled the best Christian general from exile — El Cid. It has been shown that the Cid was at court on July 1087; however, what happened after that is unclear. | |||
| In 1082, the army of the ] under El Cid defeated the ] at the ]. In 1084, he defeated the ]ese at the ] near ], but in autumn the Castilians started a loose siege of ] and later the next year the Christians captured ], a stronghold of the ].{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | |||
| In 1086, the ] invasion of the ], through and around ], began. The Almoravids, a ] dynasty from ], led by ], were asked to help defend the divided Moors from Alfonso. The Almoravid army, joined by that of several Taifas, including ], ], ], ] and ], defeated a combined army of ], ], and ] at the ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Baer |first1=George |last2=Dupuy |first2=Trevor N. |last3=Johnson |first3=Curt |last4=Bongard |first4=David L. |date=July 1994 |title=The Harper Encyclopedia of Military Biography. |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/2944137 |journal=The Journal of Military History |volume=58 |issue=3 |pages=515 |doi=10.2307/2944137 |jstor=2944137 |issn=0899-3718}}</ref> | |||
| In 1087, ] and his Christian allies attempted to weaken the Taifa of Zaragoza's northernmost stronghold by initiating the ] and Alfonso captured ], blocking the route between the Taifas in the eastern and western Iberian Peninsula.{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | |||
| ==Recall from exile== | |||
| ] allies after his conquest of Valencia in 1094]] | |||
| ] (21 October 1094). El Cid's troops are in green, ] troops are in red.]] | |||
| Terrified after his crushing defeat, Alfonso recalled El Cid, rewarding him lavishly with lands and lordships, such as the fortress of Gormaz. In the year 1087 Alfonso sent him to negotiate with the emboldened Taifa kingdoms.<ref name="Catlos2015">{{cite book |last1=Catlos |first1=Brian A. |title=Infidel Kings and Unholy Warriors: Faith, Power, and Violence in the Age of Crusade and Jihad |date=2015 |publisher=Farrar, Straus and Giroux |page=127 |isbn=978-0809058372 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7Z4WBAAAQBAJ&pg=PT127 |access-date=9 December 2022}}</ref> | |||
| El Cid returned to Alfonso, but now he had his own plans. He only stayed a short while and then returned to Zaragoza. El Cid was content to let the Almoravid armies and the armies of Alfonso fight without his help, even when there was a chance that the Almoravids might defeat Alfonso and take over all of Alfonso's lands. El Cid chose not to fight because he was hoping that both armies would weaken themselves. {{Citation needed|date=February 2012}} | |||
| ===Conquest of Valencia=== | ===Conquest of Valencia=== | ||
| {{main|Siege of Valencia (1092–1094)}} | |||
| ] of the Cid ordering the execution of the instigator of the revolt and almoravid after his conquest of the city in 1094.]] | |||
| {{See also|Lordship of Valencia}} | |||
| Around this time, the Cid, with a combined Christian and Moorish army, began maneuvering in order to create his own fiefdom in the Moorish ] coastal city of ]. Several obstacles lay in his way. First was Berenguer Ramón II, who ruled nearby ]. In May 1090, the Cid defeated and captured Berenguer in the Battle of Tébar (nowadays Pinar de Tévar, near ], ]). Berenguer was later released and his nephew Ramón Berenguer III married the Cid's youngest daughter Maria to ward against future conflicts. | |||
| Around this time, El Cid, with a combined Christian and Moorish army, began maneuvering in order to create his own fief in the Moorish ] coastal city of ]. Several obstacles lay in his way. First was Berenguer Ramon II, who ruled nearby ]. In May 1090, El Cid defeated and captured Berenguer in the Battle of Tébar (nowadays Pinar de Tévar, near ], ]). Berenguer was later released and his nephew Ramon Berenguer III married El Cid's youngest daughter Maria to ward against future conflicts.{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | |||
| Along the way to Valencia, El Cid also conquered other towns, many of which were near Valencia, |
Along the way to Valencia, El Cid also conquered other towns, many of which were near Valencia, such as ] and ].{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | ||
| El Cid gradually came to have more influence |
El Cid gradually came to have more influence in Valencia, then ruled by ], of the ] Berber ]. In October 1092 an uprising occurred in Valencia, inspired by the city's chief judge Ibn Jahhaf and the Almoravids. El Cid began a siege of Valencia. A December 1093 attempt to break the siege failed. By the time the siege ended in May 1094, El Cid had carved out his own principality on the coast of the Mediterranean. Officially, El Cid ruled in the name of Alfonso; in practice, El Cid was fully independent. The city was both Christian and Muslim, and both Moors and Christians served in the army and as administrators. ] was made bishop.{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | ||
| ===Death=== | ===Death=== | ||
| ] of El Cid and his wife Doña Jimena at the ]]] | |||
| El Cid and Jimena, (his wife) lived peacefully in Valencia for 3 years until the Almoravids besieged the city. El Cid was fighting one of the men when he was shot in the heart with an arrow. Valencia's troops were losing spirit when Jimena thought if she set the corpse of El Cid atop his horse Babieca, the morale of Valencia's troops would soar. The inspired soldiers fought hard but the Almoravids overcame their efforts. Alfonso ordered the city burned to prevent it from falling into the hands of the ]. Valencia was captured by ] on May 5, 1102 and would not become a Christian city again for over 125 years. Jimena fled to Burgos with her husband's body. Originally buried in Castile in the monastery of San Pedro de Cardeña, his body now lies at the center of the ]. | |||
| El Cid and his wife ] lived peacefully in Valencia until the Almoravids besieged the city. | |||
| But he defeated them and died 5 years later, on July 10, 1099. | |||
| Afterward Valencia was captured by ] on May 5, 1102. Jimena fled to Burgos, Castile, in 1101. She rode into the town with her retinue and the body of El Cid. Originally buried in Castile in the monastery of ], his body now lies at the center of ].<ref>Henry Edward Watts (1911). "]" . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. '''6.''' (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 361–362.</ref> | |||
| ===Legend of posthumous victory=== | |||
| After his demise, but still during the siege of Valencia, legend holds that Jimena ordered that the corpse of El Cid be fitted with his armor and set on his horse, Babieca, to bolster the morale of his troops. In several variations of the story, the dead Rodrigo and his knights win a thundering charge against Valencia's besiegers, resulting in a war-is-lost-but-battle-is-won ] for generations of Christian Spaniards to follow. It is believed that the legend originated shortly after Jimena entered Burgos, and that it is derived from the manner in which Jimena's procession rode into the city, i.e. alongside her deceased husband.<ref name="Perea Rodríguez">{{cite web|last=Perea Rodríguez|first=Óscar|title=Díaz de Vivar, Rodrigo o El Cid (1043–1099)|url=http://www.mcnbiografias.com|access-date=23 April 2012|archive-date=14 April 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120414202417/http://www.mcnbiografias.com/}}</ref> | |||
| ==Warrior and general== | ==Warrior and general== | ||
| ===Battle tactics=== | |||
| During his campaigns, the Cid often ordered that books by classic ] and ] authors on military themes be read in loud voices to him and his troops, both for entertainment and inspiration before battle. El Cid's army had a novel approach to planning strategy as well, holding what might be called ] sessions before each battle to discuss tactics. They frequently used unexpected strategies, engaging in what modern generals would call ]—waiting for the enemy to be paralyzed with terror and then attacking them suddenly, distracting the enemy with a small group of soldiers, etc. (El Cid used this distraction in capturing the town of Castejón as depicted in '']'' (''The Song of my Cid'')). El Cid accepted or included suggestions from his troops. In ''The Song'' the man who served him as his closest adviser was his vassal and kinsman, ] "''Minaya''" (meaning ''"My brother"'', a compound word of Spanish possessive ''Mi'' (My) and ''Anaia'', basque word for ''brother''), although the historical Álvar Fáñez remained in Castile with Alfonso VI. | |||
| ===Battle tactics=== | |||
| Taken together, these practices imply an educated and intelligent commander who was able to attract and inspire good subordinates, and who would have attracted considerable loyalty from his followers including those who were not Christian. It is these qualities, coupled with El Cid's legendary martial abilities, which have fueled his reputation as an outstanding battlefield commander. | |||
| During his campaigns, El Cid often ordered that books by classic ] and ] authors on military themes be read aloud to him and his troops, for both entertainment and inspiration before battle. El Cid's army had a novel approach to planning strategy as well, holding what might be called "]" sessions before each battle to discuss tactics. They frequently used unexpected strategies, engaging in what modern generals would call ]—waiting for the enemy to be paralyzed with terror and then attacking them suddenly; distracting the enemy with a small group of soldiers, etc. (El Cid used this distraction in capturing the town of Castejón as depicted in '']'' (''The Song of my Cid'').) El Cid accepted or included suggestions from his troops. In ''The Song'' the man who served him as his closest adviser was his vassal and kinsman ] "''Minaya''" (meaning ''"My brother"'', a compound word of Spanish possessive ''Mi'' (My) and ''Anaia'', the basque word for ''brother''), although the historical Álvar Fáñez remained in Castile with Alfonso VI.{{Citation needed|date=April 2022}} | |||
| ===Babieca=== | ===Babieca=== | ||
| ] |
]]] | ||
| '''Babieca''' or '''Bavieca''' was El Cid's ]. Several stories exist about the Cid and Babieca. One well-known legend about the Cid describes how he acquired the ]. According to this story, Rodrigo's godfather, Pedro El Grande, was a monk at a ] ]. Pedro's coming-of-age gift to El Cid was his pick of a horse from an ] herd. El Cid picked a horse that his godfather thought was a weak, poor choice, causing the monk to exclaim "''Babieca''!" (stupid!) Hence, it became the name of El Cid's horse. Another legend states that in a competition of battle to become King Sancho's "Campeador", or champion, a knight on horseback wished to challenge the Cid. The King wished a fair fight and gave the Cid his finest horse, Babieca, or Bavieca. This version says Babieca was raised in the royal stables of Seville and was a highly trained and loyal war horse, not a foolish stallion. The name in this instance could suggest that the horse came from the Babia region in ]. In the poem ], Babieca appears as a gift from "a barbarian" to the Cid, so its name could also be derived from "Barbieca", or "horse of the barbarian". | |||
| '''Babieca''', or '''Bavieca''', was El Cid's ]. Several stories exist about El Cid and Babieca. One well-known legend about El Cid describes how he acquired the ]. According to this story, Rodrigo's godfather, Pedro El Grande, was a monk at a ] ]. Pedro's coming-of-age gift to El Cid was his pick of a horse from an ] herd. El Cid picked a horse that his godfather thought was a weak, poor choice, causing the monk to exclaim "''Babieca!''" (stupid!). Hence, it became the name of El Cid's horse. Another legend states that in a competition of battle to become King Sancho's "Campeador", or champion, a knight on horseback wished to challenge El Cid. The King wished a fair fight and gave El Cid his finest horse, Babieca, or Bavieca. This version says Babieca was raised in the royal stables of Seville and was a highly trained and loyal war horse, not a foolish stallion. The name in this instance could suggest that the horse came from the Babia region in ]. In the poem '']'', Babieca appears as a gift from "a barbarian" to El Cid, so its name could also be derived from "Barbieca", or "horse of the barbarian".<ref>{{Cite web |last=Bergen |first=Ard van |title=Rodrigo 'el Cid' "El Cid" Díaz de Vivar príncipe de Valencia (± 1043–1099) » maximum test » Genealogy Online |url=https://www.genealogieonline.nl/en/maximum-test/I5666856869970026974.php |access-date=2022-06-24 |website=Genealogy Online |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Regardless, Babieca became a great warhorse, famous to the ]s, feared by El Cid's enemies, and loved by the Cid, who allegedly requested that Babieca be buried with him in the monastery of ].{{Citation needed|date=December 2008}} His name is mentioned in several tales and historical documents about El Cid, including ''The Lay of the Cid''. | |||
| Regardless, Babieca became a great warhorse, famous to the Christians, feared by El Cid's enemies, and loved by El Cid, who allegedly requested that Babieca be buried with him in the monastery of ].<ref name="Quest"/> Babieca is mentioned in several tales and historical documents about El Cid, including ''The Lay of El Cid''.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Project Gutenberg's "The Lay of the Cid" |url=https://www.gutenberg.org/files/6088/6088-h/6088-h.htm |access-date=2022-06-26 |website=www.gutenberg.org}}</ref> | |||
| ===Swords=== | ===Swords=== | ||
| A weapon traditionally identified as El Cid's ], ], used to be displayed in the Army Museum (Museo del Ejército) in Toledo. In 1999, a small sample of the blade underwent metallurgical analysis which confirmed that the blade was made in Moorish ] in the eleventh century and contained amounts of ].<ref name="John Wiley & Sons, Ltd">{{cite journal |last1=Alonso |first1=J. I. Garcia |last2=Martinez |first2=J. A. |last3=Criado |first3=A. J. |year=1999 |title=Origin of El Cid's sword revealed by ICP-MS metal analysis |journal=Spectroscopy Europe |volume=11 |issue=4 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.}}</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| A weapon traditionally identified as El Cid's ], ], used to be displayed in the Army Museum (Museo del Ejército) in Toledo. In 1999, a small sample of the blade underwent metallurgical analysis which confirmed that the blade was made in Moorish ] in the eleventh century and contained amounts of ].{{Citation needed|date=December 2008}} | |||
| In 2007 the |
In 2007, the Autonomous Community of ] bought the sword for €1.6 million,<ref name="Hill2014">{{cite book|author=Tom Hill|title=Swords of El Cid: "Rodrigo! May God curse him!"|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RhG_BAAAQBAJ&pg=PT330|date= 2014|publisher=Andrews UK Limited|isbn=978-1-78333-651-7|page=330}}</ref> and it is currently on display at the Museum of ].<ref>{{cite book|title=Handbook of Medieval Culture|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LR5pCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA1739|date=31 August 2015|publisher=De Gruyter|isbn=978-3-11-037761-3|page=1739}}</ref> | ||
| El Cid also had a sword called ].<ref name="HamiltonMichael1984">{{cite book|author1=Rita Hamilton|author2=Ian Michael|title=Cantar de mio Cid|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dYPWN2RMcFoC&pg=PA187|year=1984|publisher=Penguin|isbn=978-0-14-044446-9|page=187}}</ref> | |||
| El Cid also had a sword called ]. | |||
| == |
==Wife and children== | ||
| ] | |||
| El Cid was married in July 1075 to Alfonso's kinswoman ]. The '']'' calls her daughter of a Count Diego of ], a person unknown to contemporary records, while later poetic sources name her father as an otherwise unknown Count Gomez de Gormaz. | |||
| El Cid married ], who was said to be part of an aristocratic family from Asturias, in the mid-1070s.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Barton |first1=Simon |last2=Fletcher |first2=Richard |title=The World of El Cid |year=2000 |publisher=Manchester University Press |isbn=978-1526112637 |page=90 |url=https://www.manchesterhive.com/view/9781526112637/9781526112637.00013.xml?rskey=bpxyLl&result=2 |access-date=23 April 2019}}</ref> The '']'' calls her a daughter of a Count ]. Tradition states that when El Cid first laid eyes on her, he was enamoured of her great beauty. El Cid and Jimena had two daughters, Cristina and María, and a son. The latter, ], was killed while fighting against the invading Muslim Almoravids from ] at the ] in 1097. El Cid's daughters ] and ] both married into noble families. Cristina married ], Lord of ] and grandson of ]. | |||
| Tradition states that when the Cid laid eyes on her he was enamored of her beauty. Together El Cid and Jimena had three children. Their daughters Cristina and María both married into the high nobility; Cristina to ], Lord of ], grandson of ] via an illegitimate son; María, first (it is said) to a prince of Aragon (presumably the son of ]) and second to ], count of ]. El Cid's son Diego Rodríguez was killed while fighting against the invading Muslim Almoravids from ] at the ] (1097). | |||
| Her own son, El Cid's grandson, would be elevated to the throne of ] as King ]. The other daughter, ] (also known as Sol), is said first to have married a prince of Aragon, presumably the son of ], and she later married ], count of ]. Both the poem and the chronicle may state a previous marriage to the {{ill|infantes de Carrión|es}}; however, these marriages are not a historical fact and are an important element in the construction of the poem.<ref>{{Cite book|last1=Girón Alconchel|first1=José Luis|title=Cantar de mio Cid|last2=Pérez Escribano|first2=María Virginia|publisher=Ed. Castalia|year=1995|isbn=84-7039-719-2|location=Madrid|pages=11–50}}</ref> | |||
| His own marriage and those of his daughters raised his status by connecting El Cid to the peninsular royalty; even today, most European monarchs and many commoners of European ancestry descend from El Cid, through Cristina's son, king ] and to a lesser extent via a granddaughter Jimena of Barcelona, who married into the Counts of Foix. | |||
| ==In literature, music, video games, and film== | |||
| The figure of El Cid has been the source for many literary works, beginning with the '']'', an ] from the 12th century which gives a partly-fictionalized account of his life, and was one of the early ]s. This poem, along with similar later works such as the '']'', contributed to portray El Cid as a chivalric hero of the Reconquista,<ref name="Woolf2011">{{cite book|author=Daniel Woolf|title=A Global History of History|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Q7r7SaTXGXEC&pg=PA110|date= 2011|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-0-521-87575-2|page=110}}</ref> making him a legendary figure in Spain. El Cid is one of the few examples of knight errantry formally recognized by the priest in ]'s '']'' (1605–1615).<ref>Cervantes. Don Quixote of La Mancha. 1605.</ref> | |||
| In the early 17th century, the Spanish writer ] wrote a play called ''Las Mocedades del Cid'', on which French playwright ] based one of his most famous tragicomedies, '']''.<ref name="Gale2016">{{cite book|author=Gale|title=A Study Guide for Pierre Corneille's 'Le Cid'|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Xtn2DAAAQBAJ&pg=PT3|year=2016|publisher=Gale, Cengage Learning|isbn=978-1-4103-5088-6|page=3}}</ref> He was also a popular source of inspiration for Spanish writers of the ], such as ], who wrote ''La Jura de Santa Gadea'', or ], who wrote a long poem called ''La Leyenda del Cid''. In 2019, ] published the novel entitled ''Sidi: Un relato de frontera''.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Pérez-Reverte |first1=Arturo |title='Sidi', un relato de frontera |url=https://elpais.com/elpais/2019/09/10/eps/1568111634_521646.html |access-date=6 October 2019 |work=El País |date=15 September 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last1=Pérez-Reverte |first1=Arturo |title=Adelanto del primer capítulo de la nueva novela de Pérez-Reverte, 'Sidi' |url=https://www.elmundo.es/cultura/laesferadepapel/2019/09/02/5d651af921efa0440b8b45b6.html |access-date=6 October 2019 |work=El Mundo |date=2 September 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] references El Cid when introducing the character of Samoa in Chapter 21 of '']'' (1849): "He alighted about six paces from where we stood, and balancing his weapon, eyed us bravely as the Cid".<ref>{{Cite book |last=Melville |first=Herman |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mUNVW_2p5U8C&dq=He+alighted+about+six+paces+from+where+we+stood%2C+and+balancing+his+weapon%2C+eyed+us+bravely+as+the+Cid&pg=PA76 |title=The Works of Herman Melville: no. 3. Mardi, and a voyage thither |date=1922 |publisher=Constable Limited |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| In 1929, Chilean writer ] published his poetic novel ''Mío Cid Campeador. Hazaña.'' This work, together with other novels (and plays) he published between 1929 and 1939, defied the traditional realistic style of the early 20th century Chilean novel. The English version was published in 1931.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Novelas de Vicente Huidobro (1929–1939) |url=https://www.memoriachilena.gob.cl/602/w3-article-545667.html |access-date=June 19, 2024 |website=Memoria Chilena. Biblioteca Nacional de Chile |language=es}}</ref> | |||
| ] worked on ''Don Rodrigue'' in 1873 that was set aside and never completed. ] wrote an opera, '']'', in 1885, based on Corneille's play of the same name. ] began work in 1890 on an opera, '']'', which he abandoned as unsuitable for his temperament; it was orchestrated for performance by ] circa 1993.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Devoto |first1=Mark |title=Review: Claude Debussy Rodrigue et Chimène. Édition de Richard Langham Smith |journal=Notes: Quarterly Journal of the Music Library Association |date=December 2004 |volume=61 |issue=2 |doi=10.1353/not.2004.0131 |s2cid=194081830}}</ref> | |||
| El Cid is portrayed by American actor ] in a 1961 ]<ref name="Fletcher1991">{{cite book|author=Richard A. Fletcher|title=The Quest for El Cid|url=https://archive.org/details/questforelcid00flet|url-access=registration|year=1991|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-506955-6|page=}}</ref> directed by ], where the character of Doña Ximena is portrayed by Italian actress ].<ref name="Smith2009">{{cite book|author=Gary Allen Smith|title=Epic Films: Casts, Credits and Commentary on More Than 350 Historical Spectacle Movies|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ihaBCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA76|edition=2nd|date= 2009|publisher=McFarland|isbn=978-1-4766-0418-3|page=76}}</ref><ref name="Gale 20168">{{cite book|author=Gale|title=A Study Guide for Anonymous's "Cantar de mio Cid (El Cid)"|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CxszDQAAQBAJ&pg=PT8|year=2016|publisher=Gale, Cengage Learning|isbn=978-1-4103-4239-3|page=8}}</ref> In 2020, ] premiered a ] with ] starring as ''El Cid''.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Silvestre |first1=Juan |title='El Cid' de Jaime Lorente para Amazon Prime Video completa su reparto |url=https://www.fotogramas.es/series-tv-noticias/a29318222/el-cid-amazon-prime-video-reparto/ |access-date=20 January 2020 |work=Fotogramas |date=1 October 2019}}</ref> | |||
| In 1979, ], one of the most prominent progressive rock bands from Spain, released their first and only album ''Si Todo Hiciera Crack'' including "Marchando una del Cid", a song based on the epic legend of El Cid.<ref name="DiGioiaA2020">{{cite book|author=Amanda DiGioia|title=Multilingual metal music: Sociocultural, linguistic, and literary perspectives on heavy metal music|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=XyYNEAAAQBAJ|date=2020|publisher=United Kingdom: Emerald Publishing Ltd.|isbn=978-1-8390-9950-2|pages=61–77|access-date=8 October 2022}}</ref> | |||
| In 1980, '']'' was an ] based on El Cid's childhood made by ].<ref>{{Citation |title=Ruy, el pequeño Cid |date=1980-10-05 |url=https://www.imdb.com/title/tt1304919/ |type=Animation, Adventure, Drama |publisher=BRB Internacional S.A., Nippon Animation Co., Televisión Española (TVE) |access-date=2023-01-22}}</ref> | |||
| El Cid was described to inspire Ferny about his Spanish heritage in "The Legend of Raloo", episode 16 of season 1 of '']'' in 2004.<ref>{{cite web |title=Age of Empires II: The Conquerors (Manual) |url=https://archive.org/details/manual_201704/page/n1/mode/2up |website=Archive.org |access-date=15 July 2022}}</ref> | |||
| In the second '']'' video game installment, '']'' expansion pack, there is a campaign starring El Cid Campeador.<ref>{{cite web |title=texts Age of Empires II: The Conquerors (Manual) |url=https://archive.org/details/manual_201704/mode/2up |website=Archive.org |access-date=15 July 2022 |ref=33 |pages=3}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=https://gamerant.com/age-of-empires-ranked-best-worst/|last=Hospodar|first=Mark|date=2021-11-09|publisher=GameRant|title=Every Age Of Empires Game, Ranked|quote=In 2000, The Conquerors expansion was released, which added new campaigns such as Attila the Hun and El Cid.}}</ref> | |||
| In both the first and second '']'' games, El Cid appears as a powerful independent general in the castle of Valencia.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Adams |first=Dan |date=2002-01-09 |title=Medieval: Total War |url=https://www.ign.com/articles/2002/01/09/medieval-total-war-6 |access-date=2023-01-18 |website=IGN |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| In 2003, the Spanish animated film '']'' was released.<ref name="Muñoz 2023 a617">{{cite web | last=Muñoz | first=Michel | title=Las Miradas Sobre Mío Cid | publisher=El Diadigital | date=2023-12-08 | url=https://eldiadigital.es/art/445618/las-miradas-sobre-mio-cid | language=es | access-date=2024-05-02}}</ref> | |||
| '']'', a Spanish science fiction television series, portrayed El Cid in season 2, episode 1.<ref>{{Cite web |title=El Ministerio del Tiempo – Capítulo 9 – T2 |url=https://www.rtve.es/television/ministerio-del-tiempo/capitulos-completos/temporada-2/capitulo-9/index.shtml |access-date=2023-01-22 |website=RTVE.es |language=es}}</ref> | |||
| El Cid is a playable character in the Mobile/PC Game ]. | |||
| El Cid is a playable character in '']'' and Crusader Kings III in start dates corresponding to his historical rule over Valencia. | |||
| ==Gallery== | |||
| {{gallery | |||
| |File:Monumento al Cid (Burgos) 01.jpg|General view of the 1954 Juan Cristóbal González Quesada's statue of El Cid in ] | |||
| |File:Burgos - Arco de Santa Maria - El Cid.JPG|Statue of El Cid included in the 14th- to 15th-century "Santa María" gateway, Burgos | |||
| |File:Cid.png|1344 medieval ] showing the decapitation of Count Lozano by El Cid | |||
| |File:Burgos gigantones 1.jpg|Burgalese traditional representation (called "''Gigantones''") of El Cid that is taken to the streets during the town major festivity. Doña Jimena's representation is behind. | |||
| |File:Burgos. El Solar del Cid.jpg|The terrain known as the "Solar del Cid", where his house was located. The monument was erected in 1784. Photo taken in Burgos, c. 1865–1892. | |||
| |File:Rodrigo Diaz de Vivar crop.jpg|El Cid depiction on the book ''Portraits of illustrious Spaniards'' (1791) | |||
| |File:Camino del Cid Mecerreyes.jpg|In 2008, this El Cid statue made by Ángel Gil Cuevas was placed in ], at the path of the "]". | |||
| |File:La Jura de Santa Gadea. Armando Menocal. 1889.JPG|Another version of the "Santa Gadea Oath", painted by Armando Menocal in 1889 | |||
| |File:El cofre del Cid.Catedral de Burgos (4952394218).jpg|El Cid's chest at Burgos Cathedral | |||
| |File:El Cid portrait · HHWX54.svg|El Cid portrait from '']'' | |||
| |File:El Cid-Med-Plaza Mayor (Salamanca).jpg|El Cid medallion (1733–34) at the ] | |||
| |File:Vicents Cots Primera hazaña del Cid.jpeg|1864 Juan Vicens Cots painting "''La Primera hazaña de El Cid''" depicts a young Rodrigo Díaz showing his father Diego Laínez the severed head of ] Lozano, the father of his future wife ]. Count Lozano had previously mocked and slapped elderly Diego Laínez. | |||
| |File:Balboa Park El Cid statue in Citizen Kane.jpg|El Cid statue at ], a filming location for ]' ].<ref>{{cite web |last=Williams |first=Gregory L. |title=Filming San Diego |url=http://www.sandiegohistory.org/journal/2002-2/filming.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110521030941/http://www.sandiegohistory.org/journal/2002-2/filming.htm |archive-date=May 21, 2011 |access-date=April 6, 2012 |publisher=San Diego History Center}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| {{Commons category|El Cid}} | |||
| ===Bibliography=== | |||
| == General and cited sources== | |||
| *Simon Barton and Richard Fletcher. ''The world of El Cid, Chronicles of the Spanish reconquest''. Manchester: University Press, 2000. ISBN 0-7190-5225-4 hardback, ISBN 0-7190-5226-2 paperback. | |||
| ===Primary=== | |||
| *Gonzalo Martínez Díez, "El Cid Histórico: Un Estudio Exhaustivo Sobre el Verdadero Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar", (Spain, June 1999). ISBN 84-08-03161-9 | |||
| *Kurtz, Barbara E. University of Illinois. | |||
| *Richard Fletcher. "The Quest for El Cid". ISBN 0-19-506955-2 | |||
| *I. Michael. ''The Poem of El Cid''. Manchester: 1975. | |||
| *Kurtz, Barbara E. University of Illinois. | |||
| * |
*''The Song of El Cid.'' Translated by Burton Raffel. Penguin Classics, 2009. | ||
| * (free PDF) | |||
| *C. Melville and A. Ubaydli (ed. and trans.), ''Christians and Moors in Spain, vol. III, Arabic sources (711-1501)''. (Warminster, 1992). | |||
| * in the ] (third item on page) | |||
| *R. Selden Rose and Leonard Bacon (trans.) ''The Lay of El Cid.'' Semicentennial Publications of the University of California: 1868–1918. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1997. | |||
| * (1828) | |||
| * (1533) | |||
| * | |||
| ===Secondary (not cited)=== | |||
| *Simon Barton and Richard Fletcher. ''The world of El Cid, Chronicles of the Spanish reconquest''. Manchester: University Press, 2000. {{ISBN|0-7190-5225-4}} hardback, {{ISBN|0-7190-5226-2}} paperback. | |||
| *Gonzalo Martínez Díez, "El Cid Histórico: Un Estudio Exhaustivo Sobre el Verdadero Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar", (Spain, 1999). {{ISBN|84-08-03161-9}} | |||
| *C. Melville and A. Ubaydli (ed. and trans.), ''Christians and Moors in Spain, vol. III, Arabic sources (711–1501)''. (Warminster, 1992). | |||
| *{{cite encyclopedia |encyclopedia=Conflict and Conquest in the Islamic World: A Historical Encyclopedia |title=Almoravids |volume=I |editor-first=Alexander |editor-last=Mikaberidze |publisher=ABC-CLIO |year=2011 }} | |||
| *Joseph F. O'Callaghan. ''A History of Medieval Spain.'' Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1975 | *Joseph F. O'Callaghan. ''A History of Medieval Spain.'' Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1975 | ||
| *Peter Pierson. ''The History of Spain.'' Ed. John E. Findling and Frank W. Thacheray. Wesport, |
*Peter Pierson. ''The History of Spain.'' Ed. John E. Findling and Frank W. Thacheray. Wesport, CN: Greenwood Press, 1999. 34–36. | ||
| * Princeton, |
* Princeton, NJ: University Press, 1988. | ||
| * | |||
| *''The Song of the Cid.'' Translated by Burton Raffel. Penguin Classics, 2009. | |||
| * Semicentennial Publications of the University of California: 1868-1918. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1997. | |||
| * | |||
| *M. J. Trow,''El Cid The Making of a Legend,'' Sutton Publishing Limited, 2007. | *M. J. Trow,''El Cid The Making of a Legend,'' Sutton Publishing Limited, 2007. | ||
| *Henry Edwards Watts. "The Story of |
*Henry Edwards Watts. "The Story of El Cid (1026–1099)" in ''The Christian Recovery of Spain: The Story of Spain from the Moorish Conquest to the Fall of Granada (711–1492 AD)''. New York: Putnam, 1894. 71–91. | ||
| * (free PDF) | |||
| * in the ] (third item on page) | |||
| *T.Y. Henderson. "Conquests Of Valencia" | *T.Y. Henderson. "Conquests Of Valencia" | ||
| *J. I. Garcia Alonso, J. A. Martinez, A. J. Criado, "Origin of El Cid's sword revealed by ICP-MS metal analysis", Spectroscopy Europe, 11/4 (1999). | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| ==Sources and external links== | |||
| * McNair, Alexander J. ''Essays in Medieval Studies'', Volume 26, 2010, pp. 45–68 | |||
| * | |||
| == |
==External links== | ||
| {{ |
{{wikiquote}} | ||
| {{commons category}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite EB1911|wstitle=Cid, The|volume=6|pages=361–362|short=1}} | |||
| {{s-start}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=]<br /><small>(as King of Valencia)</small>}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=1094–1099}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=]<br /><small>(as Lady of Valencia)</small>}} | |||
| {{s-end}} | |||
| {{Rodrigo Díaz}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Cid, El}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Cid, El}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link GA|zh-classical}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Revision as of 05:06, 26 December 2024
Castilian warlord and Prince of Valencia from 1094 to 1099 For other uses, see El Cid (disambiguation).| El Cid | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prince of Valencia | |||||
 Statue of El Cid in Burgos, Spain Statue of El Cid in Burgos, Spain | |||||
| Prince of Valencia | |||||
| Reign | 1094 – 1099 | ||||
| Coronation | 1094 | ||||
| Predecessor | Ibn Jahaf | ||||
| Successor | Jimena Díaz | ||||
| Born | Rodrigo Díaz c. 1043 Vivar, Burgos | ||||
| Died | (1099-07-10)10 July 1099 (aged around 56) Valencia | ||||
| Burial | Burgos Cathedral | ||||
| Spouse | Jimena Díaz | ||||
| Issue | Diego Rodríguez Cristina Rodríguez María Rodríguez | ||||
| |||||
| Father | Diego Laínez | ||||
| Signature | |||||
Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar (c. 1043 – 10 July 1099) was a Castilian knight and ruler in medieval Spain. Fighting both with Christian and Muslim armies during his lifetime, he earned the Arabic honorific as-Sayyid ("the Lord" or "the Master"), which would evolve into El Çid (Spanish: [el ˈθið], Old Spanish: [el ˈts̻id]), and the Spanish honorific El Campeador ("the Champion"). He was born in Vivar, a village near the city of Burgos.
As the head of his loyal knights, he came to dominate the Levante of the Iberian Peninsula at the end of the 11th century. He reclaimed the Taifa of Valencia from Moorish control for a brief period during the Reconquista, ruling the Principality of Valencia from 17 June 1094 until his death in 1099. His wife, Jimena Díaz, inherited the city and maintained it until 1102 when it was reconquered by the Moors.
Díaz de Vivar became well known for his service in the armies of both Christian and Muslim rulers. After his death, El Cid became Spain's most celebrated national hero and the protagonist of the most significant medieval Spanish epic poem, El Cantar de mio Cid, which presents him as the ideal medieval knight: strong, valiant, loyal, just, and pious.
There are various theories on his family history, which remains uncertain; however, he was the grandfather of García Ramírez de Pamplona, King of Navarre, the first son of his daughter Cristina Rodríguez. To this day, El Cid remains a popular Spanish folk hero and national icon, with his life and deeds remembered in popular culture.
Etymology: Cid and Campeador

Rodrigo Díaz was recognized with the honorary title Campeador during his lifetime, as is evidenced by a document that he signed in 1098, which he signed in the Latinized expression, ego Rudericus Campidoctor. The title Campeador comes from the Latin Campidoctor, literally meaning "Teacher of the Field", but translatable as "Master of the Battlefield". Arabic sources from the late 11th century and early 12th century call him الكنبيطور (al-Kanbīṭūr), القنبيطور (al-Qanbīṭūr), also preceded by Rudrīq or Ludrīq, which are Arabized forms of his title and name, respectively.
The epithet El Cid meant "the Lord", probably from the original Arabic (السَّيِّد, as-Sayyid), and was a title given to other Christian leaders. It has been conjectured that Rodrigo Díaz received the honorific title and respectful treatment of contemporaries in Zaragoza because of his victories in the service of the King of the Taifa of Zaragoza between 1081 and 1086; however, he more likely received the epithet after his conquest of Valencia in 1094. This title appears for the first time, as Meo Çidi, in the Poema de Almería, composed between 1147 and 1149.
The combination of Cid Campeador is documented from 1195 in Linaje de Rodrigo Díaz ("The Lineage of Rodrigo Díaz") in Navarro-Aragonese which form part of the Liber regum written as mio Cit el Campiador; and in El Cantar de mio Cid.
Summary
Born a member of the minor nobility, El Cid was brought up at the court of Ferdinand the Great and served Ferdinand's son, Sancho II of León and Castile. He rose to become the commander and royal standard-bearer (armiger regis) of Castile upon Sancho's ascension in 1065. El Cid went on to lead the Castilian military campaigns against Sancho's brothers, Alfonso VI of León and García II of Galicia, as well as in the Muslim kingdoms in al-Andalus. He became renowned for his military prowess in these campaigns, which helped expand the territory of the Crown of Castile at the expense of the Muslims and Sancho's brothers' kingdoms.
When conspirators murdered Sancho in 1072, El Cid found himself in a difficult situation. Since Sancho was childless, the throne passed to his brother Alfonso, whom El Cid had helped remove from power. Although El Cid continued to serve the sovereign, he lost his ranking in the new court, which treated him suspiciously and kept him at arm's length. Finally, in 1081, he was exiled.
El Cid found work fighting for the Muslim rulers of Zaragoza, whom he defended from its traditional enemy, Aragon. While in exile, he regained his reputation as a strategist and formidable military leader. He was repeatedly victorious in battle against the Muslim rulers of Lérida and their Christian allies, as well as against a large Christian army under King Sancho Ramírez of Aragon. In 1086, an expeditionary army of North African Almoravids inflicted a severe defeat to Castile, compelling Alfonso to overcome the resentment he harboured against El Cid. The terms for El Cid's return to Christian service must have been attractive enough since El Cid soon found himself fighting for his former lord. Over the next several years, however, El Cid set his sights on the kingdom-city of Valencia, operating more or less independently of Alfonso, while politically supporting the Banu Hud and other Muslim dynasties opposed to the Almoravids. He gradually increased his control over Valencia; the Islamic ruler, Yahya al-Qadir, became his tributary in 1092. When the Almoravids instigated an uprising that resulted in the death of al-Qadir, El Cid responded by laying siege to the city. Valencia finally fell in 1094, and El Cid established an independent principality on the Mediterranean coast of Iberia. He ruled over a pluralistic society with the popular support of Christians and Muslims alike.
El Cid's final years were spent fighting the Almoravid Berbers. He inflicted upon them their first major defeat in 1094, on the plains of Caurte, outside Valencia, and continued opposing them until his death. Although El Cid remained undefeated in Valencia, Diego Rodríguez, his only son and heir, died fighting against the Almoravids in the service of Alfonso in 1097. After El Cid's death in 1099, his wife, Jimena Díaz, succeeded him as ruler of Valencia, but she was eventually forced to surrender the principality to the Almoravids in 1102.
Title

The name El Cid (Spanish: [el ˈθið]) is a modern Spanish denomination composed of the article el meaning "the" and Cid, which derives from the Old Castilian loan word Çid borrowed from the dialectal Arabic word سيد sîdi or sayyid, which means "lord" or "master". The Mozarabs or the Arabs that served in his ranks may have addressed him in this way, which the Christians may have transliterated and adopted. Historians, however, have not yet found contemporary records referring to Rodrigo as Cid. Arab sources use instead Rudriq, Ludriq al-Kanbiyatur or al-Qanbiyatur (Rodrigo el Campeador).
The cognomen Campeador derives from Latin campi doctor, which means "battlefield master". He probably gained it during the campaigns of King Sancho II of Castile against his brothers, kings Alfonso VI of León and García II of Galicia. While his contemporaries left no historical sources that would have addressed him as Cid, they left plenty of Christian and Arab records, some even signed documents with his autograph, addressing him as Campeador, which prove that he used the Christian cognomen himself. The whole combination Cid Campeador is first documented c. 1195 in the Navarro-Aragonese Linage de Rodric Díaz [es] included in the Liber Regum under the formula mio Cid el Campeador.
Life and career
Origins
El Cid was born Rodrigo Díaz circa 1043 in Vivar, also known as Castillona de Bivar, a small town about ten kilometers (or six miles) north of Burgos, the capital of Castile. His father, Diego Laínez, was a courtier, bureaucrat, and cavalryman who had fought in several battles. Despite the fact that El Cid's mother's family was aristocratic, in later years, the peasants would consider him one of their own. However, his relatives were not major court officials; documents show that El Cid's paternal grandfather, Laín, confirmed only five documents of Ferdinand I's; his maternal grandfather, Rodrigo Álvarez, certified only two of Sancho II's; and El Cid's father confirmed only one.
Service under Sancho II
As a young man in 1057, El Cid fought against the Moorish stronghold of Zaragoza, making its emir al-Muqtadir a vassal of Sancho. In the spring of 1063, El Cid fought in the Battle of Graus, where Ferdinand's half-brother, Ramiro I of Aragon, was laying siege to the Moorish town of Graus, which was fought on Zaragozan lands in the valley of the river Cinca. Al-Muqtadir, accompanied by Castilian troops including El Cid, fought against the Aragonese. The party slew Ramiro I, setting the Aragonese army on the run, and emerged victorious. One legend has said that during the conflict, El Cid killed an Aragonese knight in single combat, thereby receiving the honorific title "Campeador".
When Ferdinand died, Sancho continued to enlarge his territory, conquering both Christian strongholds and the Moorish cities of Zamora and Badajoz. When Sancho learned that Alfonso was planning on overthrowing him in order to gain his territory, Sancho sent Cid to bring Alfonso back so that Sancho could speak to him.
Service under Alfonso VI

Sancho was assassinated in 1072, during a siege of his sister's town of Zamora. Since Sancho died unmarried and childless, all of his power passed to his brother Alfonso who, almost immediately, returned from exile in Toledo and took his seat as king of Castile and León. He was, however, deeply suspected of having been involved in Sancho's murder. According to the 11th century epic poem Cantar de mio Cid, the Castilian nobility led by El Cid and a dozen "oath-helpers" forced Alfonso to swear publicly on holy relics multiple times in front of Santa Gadea (Saint Agatha) Church in Burgos that he did not participate in the plot to kill his brother. This is not mentioned in the more reliable 12th century chronicle Historia Roderici, however. El Cid's position as armiger regis was taken away and given to his enemy, Count García Ordóñez.
In 1079, El Cid was sent by Alfonso VI to Seville to the court of al-Mutamid to collect the parias owed by that taifa to León–Castile. While he was there Granada, assisted by other Castilian knights, attacked Seville, and El Cid and his forces repulsed the Christian and Grenadine attackers at the Battle of Cabra, in the (probably mistaken) belief that he was defending the king's tributary. During the aftermath of this battle the Muslim troops under El Cid's command would hail him as Sayyidi. Count García Ordóñez and the other Castilian leaders were taken captive and held for three days before being released.
Exile
In the Battle of Cabra (1079), El Cid rallied his troops and turned the battle into a rout of Emir Abdullah of Granada and his ally García Ordóñez. This unauthorized expedition into Granada, however, greatly angered Alfonso and May 8, 1080, was the last time El Cid confirmed a document in King Alfonso's court. The most likely reason was El Cid's incursion into Toledo, which happened to be under the control of Alfonso's vassal, Yahya Al-Qadir. Alfonso's anger over El Cid's unsanctioned incursion into his vassal's territory would lead him to exile the knight. This is the generally accepted reason for the exile of El Cid, although several others are plausible and indeed may have been contributing factors to the exile: jealous nobles turning Alfonso against El Cid through court intrigue, and Alfonso's own personal animosity towards El Cid. The song of El Cid and subsequent tales state that Alfonso's and his court's animosity toward Rodrigo was the primary reason the expulsion of the knights from León, as well as a possible misappropriation of some of the tribute from Seville by El Cid.
At first he went to Barcelona, where Ramon Berenguer II refused his offer of service.
Moorish service


The exile was not the end of El Cid, either physically or as an important figure. After being rejected by Ramon Berenguer II, El Cid journeyed to the Taifa of Zaragoza, where he received a warmer welcome. In 1081, El Cid went on to offer his services to the king of Zaragoza, Yusuf al-Mu'taman ibn Hud, and served both him and his successor, al-Musta'in II. He was given the title El Cid (The Master) and served as a leading figure in a diverse Moorish force consisting of Muwallads, Berbers, Arabs, and Malians within the respective Taifa.
According to Moorish accounts:
Andalusi Knights found El Cid their foe ill, thirsty and exiled from the court of Alfonso, he was presented before the elderly Yusuf al-Mu'taman ibn Hud and accepted command of the forces of the Taifa of Zaragoza as their Master.
In his History of Medieval Spain (Cornell University Press, 1975), Joseph F. O'Callaghan writes:
That kingdom was divided between al-Mutamin (1081–1085) who ruled Zaragoza proper, and his brother al-Mundhir, who ruled Lérida and Tortosa. El Cid entered al-Mutamin's service and successfully defended Zaragoza against the assaults of al-Mundhir, Sancho I of Aragón, and Ramon Berenguer II, whom he held captive briefly in 1082.
In 1082, the army of the Taifa of Zaragoza under El Cid defeated the Taifa of Lleida at the Battle of Almenar. In 1084, he defeated the Aragonese at the Battle of Morella near Tortosa, but in autumn the Castilians started a loose siege of Toledo and later the next year the Christians captured Salamanca, a stronghold of the Taifa of Toledo.
In 1086, the Almoravid invasion of the Iberian Peninsula, through and around Gibraltar, began. The Almoravids, a Berber dynasty from North Africa, led by Yusuf ibn Tashfin, were asked to help defend the divided Moors from Alfonso. The Almoravid army, joined by that of several Taifas, including Badajoz, Málaga, Granada, Tortosa and Seville, defeated a combined army of León, Aragón, and Castile at the Battle of Sagrajas.
In 1087, Raymond of Burgundy and his Christian allies attempted to weaken the Taifa of Zaragoza's northernmost stronghold by initiating the Siege of Tudela and Alfonso captured Aledo, Murcia, blocking the route between the Taifas in the eastern and western Iberian Peninsula.
Recall from exile


Terrified after his crushing defeat, Alfonso recalled El Cid, rewarding him lavishly with lands and lordships, such as the fortress of Gormaz. In the year 1087 Alfonso sent him to negotiate with the emboldened Taifa kingdoms.
El Cid returned to Alfonso, but now he had his own plans. He only stayed a short while and then returned to Zaragoza. El Cid was content to let the Almoravid armies and the armies of Alfonso fight without his help, even when there was a chance that the Almoravids might defeat Alfonso and take over all of Alfonso's lands. El Cid chose not to fight because he was hoping that both armies would weaken themselves.
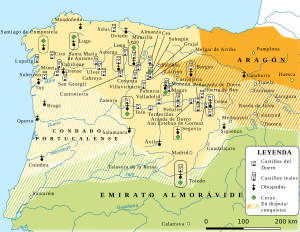
Conquest of Valencia
Main article: Siege of Valencia (1092–1094) See also: Lordship of ValenciaAround this time, El Cid, with a combined Christian and Moorish army, began maneuvering in order to create his own fief in the Moorish Mediterranean coastal city of Valencia. Several obstacles lay in his way. First was Berenguer Ramon II, who ruled nearby Barcelona. In May 1090, El Cid defeated and captured Berenguer in the Battle of Tébar (nowadays Pinar de Tévar, near Monroyo, Teruel). Berenguer was later released and his nephew Ramon Berenguer III married El Cid's youngest daughter Maria to ward against future conflicts.
Along the way to Valencia, El Cid also conquered other towns, many of which were near Valencia, such as El Puig and Quart de Poblet.
El Cid gradually came to have more influence in Valencia, then ruled by Yahya al-Qadir, of the Hawwara Berber Dhulnunid dynasty. In October 1092 an uprising occurred in Valencia, inspired by the city's chief judge Ibn Jahhaf and the Almoravids. El Cid began a siege of Valencia. A December 1093 attempt to break the siege failed. By the time the siege ended in May 1094, El Cid had carved out his own principality on the coast of the Mediterranean. Officially, El Cid ruled in the name of Alfonso; in practice, El Cid was fully independent. The city was both Christian and Muslim, and both Moors and Christians served in the army and as administrators. Jerome of Périgord was made bishop.
Death

El Cid and his wife Jimena Díaz lived peacefully in Valencia until the Almoravids besieged the city. But he defeated them and died 5 years later, on July 10, 1099.
Afterward Valencia was captured by Mazdali on May 5, 1102. Jimena fled to Burgos, Castile, in 1101. She rode into the town with her retinue and the body of El Cid. Originally buried in Castile in the monastery of San Pedro de Cardeña, his body now lies at the center of Burgos Cathedral.
Legend of posthumous victory
After his demise, but still during the siege of Valencia, legend holds that Jimena ordered that the corpse of El Cid be fitted with his armor and set on his horse, Babieca, to bolster the morale of his troops. In several variations of the story, the dead Rodrigo and his knights win a thundering charge against Valencia's besiegers, resulting in a war-is-lost-but-battle-is-won catharsis for generations of Christian Spaniards to follow. It is believed that the legend originated shortly after Jimena entered Burgos, and that it is derived from the manner in which Jimena's procession rode into the city, i.e. alongside her deceased husband.
Warrior and general
Battle tactics
During his campaigns, El Cid often ordered that books by classic Roman and Greek authors on military themes be read aloud to him and his troops, for both entertainment and inspiration before battle. El Cid's army had a novel approach to planning strategy as well, holding what might be called "brainstorming" sessions before each battle to discuss tactics. They frequently used unexpected strategies, engaging in what modern generals would call psychological warfare—waiting for the enemy to be paralyzed with terror and then attacking them suddenly; distracting the enemy with a small group of soldiers, etc. (El Cid used this distraction in capturing the town of Castejón as depicted in Cantar de mio Cid (The Song of my Cid).) El Cid accepted or included suggestions from his troops. In The Song the man who served him as his closest adviser was his vassal and kinsman Álvar Fáñez "Minaya" (meaning "My brother", a compound word of Spanish possessive Mi (My) and Anaia, the basque word for brother), although the historical Álvar Fáñez remained in Castile with Alfonso VI.
Babieca

Babieca, or Bavieca, was El Cid's warhorse. Several stories exist about El Cid and Babieca. One well-known legend about El Cid describes how he acquired the stallion. According to this story, Rodrigo's godfather, Pedro El Grande, was a monk at a Carthusian monastery. Pedro's coming-of-age gift to El Cid was his pick of a horse from an Andalusian herd. El Cid picked a horse that his godfather thought was a weak, poor choice, causing the monk to exclaim "Babieca!" (stupid!). Hence, it became the name of El Cid's horse. Another legend states that in a competition of battle to become King Sancho's "Campeador", or champion, a knight on horseback wished to challenge El Cid. The King wished a fair fight and gave El Cid his finest horse, Babieca, or Bavieca. This version says Babieca was raised in the royal stables of Seville and was a highly trained and loyal war horse, not a foolish stallion. The name in this instance could suggest that the horse came from the Babia region in León, Spain. In the poem Carmen Campidoctoris, Babieca appears as a gift from "a barbarian" to El Cid, so its name could also be derived from "Barbieca", or "horse of the barbarian".
Regardless, Babieca became a great warhorse, famous to the Christians, feared by El Cid's enemies, and loved by El Cid, who allegedly requested that Babieca be buried with him in the monastery of San Pedro de Cardeña. Babieca is mentioned in several tales and historical documents about El Cid, including The Lay of El Cid.
Swords
A weapon traditionally identified as El Cid's sword, Tizona, used to be displayed in the Army Museum (Museo del Ejército) in Toledo. In 1999, a small sample of the blade underwent metallurgical analysis which confirmed that the blade was made in Moorish Córdoba in the eleventh century and contained amounts of Damascus steel.
In 2007, the Autonomous Community of Castile and León bought the sword for €1.6 million, and it is currently on display at the Museum of Burgos.
El Cid also had a sword called Colada.
Wife and children

El Cid married Jimena Díaz, who was said to be part of an aristocratic family from Asturias, in the mid-1070s. The Historia Roderici calls her a daughter of a Count Diego Fernández de Oviedo. Tradition states that when El Cid first laid eyes on her, he was enamoured of her great beauty. El Cid and Jimena had two daughters, Cristina and María, and a son. The latter, Diego Rodríguez, was killed while fighting against the invading Muslim Almoravids from North Africa at the Battle of Consuegra in 1097. El Cid's daughters Cristina Rodríguez and María both married into noble families. Cristina married Ramiro, Lord of Monzón and grandson of García Sánchez III of Navarre.
Her own son, El Cid's grandson, would be elevated to the throne of Navarre as King García Ramírez. The other daughter, María (also known as Sol), is said first to have married a prince of Aragon, presumably the son of Peter I, and she later married Ramon Berenguer III, count of Barcelona. Both the poem and the chronicle may state a previous marriage to the infantes de Carrión [es]; however, these marriages are not a historical fact and are an important element in the construction of the poem.
In literature, music, video games, and film
The figure of El Cid has been the source for many literary works, beginning with the Cantar de mio Cid, an epic poem from the 12th century which gives a partly-fictionalized account of his life, and was one of the early chivalric romances. This poem, along with similar later works such as the Mocedades de Rodrigo, contributed to portray El Cid as a chivalric hero of the Reconquista, making him a legendary figure in Spain. El Cid is one of the few examples of knight errantry formally recognized by the priest in Miguel de Cervantes's Don Quixote (1605–1615).
In the early 17th century, the Spanish writer Guillén de Castro wrote a play called Las Mocedades del Cid, on which French playwright Pierre Corneille based one of his most famous tragicomedies, Le Cid. He was also a popular source of inspiration for Spanish writers of the Romantic period, such as Juan Eugenio Hartzenbusch, who wrote La Jura de Santa Gadea, or José Zorrilla, who wrote a long poem called La Leyenda del Cid. In 2019, Arturo Pérez-Reverte published the novel entitled Sidi: Un relato de frontera.
Herman Melville references El Cid when introducing the character of Samoa in Chapter 21 of Mardi (1849): "He alighted about six paces from where we stood, and balancing his weapon, eyed us bravely as the Cid".
In 1929, Chilean writer Vicente Huidobro published his poetic novel Mío Cid Campeador. Hazaña. This work, together with other novels (and plays) he published between 1929 and 1939, defied the traditional realistic style of the early 20th century Chilean novel. The English version was published in 1931.
Georges Bizet worked on Don Rodrigue in 1873 that was set aside and never completed. Jules Massenet wrote an opera, Le Cid, in 1885, based on Corneille's play of the same name. Claude Debussy began work in 1890 on an opera, Rodrigue et Chimène, which he abandoned as unsuitable for his temperament; it was orchestrated for performance by Edison Denisov circa 1993.
El Cid is portrayed by American actor Charlton Heston in a 1961 epic film of the same name directed by Anthony Mann, where the character of Doña Ximena is portrayed by Italian actress Sophia Loren. In 2020, Amazon Prime Video premiered a Spanish TV series with Jaime Lorente starring as El Cid.
In 1979, Crack, one of the most prominent progressive rock bands from Spain, released their first and only album Si Todo Hiciera Crack including "Marchando una del Cid", a song based on the epic legend of El Cid.
In 1980, Ruy, the Little Cid was an animated series based on El Cid's childhood made by Nippon Animation.
El Cid was described to inspire Ferny about his Spanish heritage in "The Legend of Raloo", episode 16 of season 1 of Jakers! The Adventures of Piggley Winks in 2004.
In the second Age of Empires video game installment, The Conquerors expansion pack, there is a campaign starring El Cid Campeador.
In both the first and second Medieval: Total War games, El Cid appears as a powerful independent general in the castle of Valencia.
In 2003, the Spanish animated film El Cid: The Legend was released.
The Ministry of Time, a Spanish science fiction television series, portrayed El Cid in season 2, episode 1.
El Cid is a playable character in the Mobile/PC Game Rise of Kingdoms.
El Cid is a playable character in Crusader Kings II and Crusader Kings III in start dates corresponding to his historical rule over Valencia.
Gallery
-
 General view of the 1954 Juan Cristóbal González Quesada's statue of El Cid in Burgos
General view of the 1954 Juan Cristóbal González Quesada's statue of El Cid in Burgos
-
Statue of El Cid included in the 14th- to 15th-century "Santa María" gateway, Burgos
-
 1344 medieval miniature showing the decapitation of Count Lozano by El Cid
1344 medieval miniature showing the decapitation of Count Lozano by El Cid
-
 Burgalese traditional representation (called "Gigantones") of El Cid that is taken to the streets during the town major festivity. Doña Jimena's representation is behind.
Burgalese traditional representation (called "Gigantones") of El Cid that is taken to the streets during the town major festivity. Doña Jimena's representation is behind.
-
 The terrain known as the "Solar del Cid", where his house was located. The monument was erected in 1784. Photo taken in Burgos, c. 1865–1892.
The terrain known as the "Solar del Cid", where his house was located. The monument was erected in 1784. Photo taken in Burgos, c. 1865–1892.
-
 El Cid depiction on the book Portraits of illustrious Spaniards (1791)
El Cid depiction on the book Portraits of illustrious Spaniards (1791)
-
 In 2008, this El Cid statue made by Ángel Gil Cuevas was placed in Mecerreyes, at the path of the "Camino del Cid".
In 2008, this El Cid statue made by Ángel Gil Cuevas was placed in Mecerreyes, at the path of the "Camino del Cid".
-
Another version of the "Santa Gadea Oath", painted by Armando Menocal in 1889
-
 El Cid's chest at Burgos Cathedral
El Cid's chest at Burgos Cathedral
-
 El Cid portrait from The Historians' History of the World
El Cid portrait from The Historians' History of the World
-
 El Cid medallion (1733–34) at the Plaza Mayor, Salamanca
El Cid medallion (1733–34) at the Plaza Mayor, Salamanca
-
 1864 Juan Vicens Cots painting "La Primera hazaña de El Cid" depicts a young Rodrigo Díaz showing his father Diego Laínez the severed head of Count Lozano, the father of his future wife Doña Jimena. Count Lozano had previously mocked and slapped elderly Diego Laínez.
1864 Juan Vicens Cots painting "La Primera hazaña de El Cid" depicts a young Rodrigo Díaz showing his father Diego Laínez the severed head of Count Lozano, the father of his future wife Doña Jimena. Count Lozano had previously mocked and slapped elderly Diego Laínez.
-
 El Cid statue at Balboa Park (San Diego), a filming location for Orson Welles' Citizen Kane.
El Cid statue at Balboa Park (San Diego), a filming location for Orson Welles' Citizen Kane.
See also
References
- Barton, Simon & Richard Fletcher (2000). The world of El Cid: chronicles of the Spanish reconquest. Manchester: Manchester University Press. ISBN 0-7190-5225-4. OCLC 45486279.
- Ventura Fuentes (1908). "El Cid". In Catholic Encyclopedia. 3. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- Henry Edward Watts (1911). "Cid, The". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. 6. (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 361–362.
- gigatos (2022-03-12). "El Cid". Trenfo.com. Archived from the original on 2023-02-23. Retrieved 2023-02-23.
- Juan Carlos Elorza Guinea; María Pilar Alonso Abad; Castilla y León Junta (2007). El Cid : del hombre a la leyenda: Claustro bajo de la Catedral de Burgos, septiembre–noviembre 2007. Valladolid: Junta de Castilla y León. p. 46. ISBN 978-84-935781-4-5. OCLC 433366647.
- Ignacio Ruiz Rodríguez, Félix Martínez Llorente (2016). Recuerdos literarios en honor a un gran historiador de Castilla: Gonzalo Martínez Díez (1924–2015). Madrid. p. 315. ISBN 978-84-9085-787-8. OCLC 964290692.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Deyermond, Alan (2013), "El Cantar de mio Cid y la épica anglosajona", Sonando van sus nuevas allent parte del mar, Presses universitaires du Midi, pp. 217–226, doi:10.4000/books.pumi.38431, ISBN 978-2912025852
- Fee, Christopher R. (2011). Mythology in the Middle Ages: Heroic Tales of Monsters, Magic, and Might. ABC-CLIO. p. 161. ISBN 978-0275984069.
- ^ Fletcher, Richard A. (1989). The Quest for El Cid. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. pp. 166–168, 198. ISBN 978-0195069556.
- Mikaberidze 2011, p. 91.
- María Jesús Viguera Molins, «El Cid en las fuentes árabes», in César Hernández Alonso (coord.), Actas del Congreso Internacional el Cid, Poema e Historia (12–16 de julio de 1999), Ayuntamiento de Burgos, 2000, pp. 55–92. ISBN 84-87876-41-2
- See Ramón Menéndez Pidal, «Autógrafos inéditos del Cid y de Jimena en dos diplomas de 1098 y 1101», Revista de Filología Española, t. 5 (1918), Madrid, Sucesores de Hernando, 1918. Digital copy Valladolid, Junta de Castilla y León. Consejería de Cultura y Turismo. Dirección General de Promociones e Instituciones Culturales, 2009–2010. Original in Archivo de la Catedral de Salamanca, caja 43, legajo 2, n.º 72.
- Alberto Montaner Frutos y Ángel Escobar, «El Carmen Campidoctoris y la materia cidiana», in Carmen Campidoctoris o Poema latino del Campeador, Madrid, Sociedad Estatal España Nuevo Milenio, 2001, p. 73 . ISBN 978-84-95486-20-2
- Alberto Montaner Frutos, «Rodrigo el Campeador como princeps en los siglos XI y XII»
- Georges Martin «El primer testimonio cristiano sobre la toma de Valencia (1098)», en el número monográfico «Rodericus Campidoctor» de la revista electrónica e-Spania, n.º 10 (diciembre de 2010). Online since 22 January 2011. Last time visited November 28th 2011. Complete text (Edition of the Latin text) in José Luis Martín Martín & al., Documentos de los Archivos Catedralicio y Diocesano de Salamanca (siglos XII–XIII), Salamanca, Universidad, 1977, doc. 1, pp. 79–81.
- Tim Watts (2012). Frank W. Thackeray; John E. Findling (eds.). Events That Formed the Modern World. ABC-CLIO. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-59884-901-1.
- Weiss, Julian (2018-12-31), Bale, Anthony (ed.), "'El Cid' (Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar)", The Cambridge Companion to the Literature of the Crusades (1 ed.), Cambridge University Press, pp. 184–199, doi:10.1017/9781108672832.013, ISBN 978-1-108-67283-2, S2CID 165471019, retrieved 2022-11-12
- Catlos, Brian (2015). "The Cid Rides Again". Infidel kings and Unholy Warriors: Faith, power, and violence in the age of crusade and jihad. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. p. 73.
- Russell, Peter Edward (2024-04-18). "El Cid". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 2024-04-28.
- ^ Chaytor, Henry John (1933). "Chapter 3: The Reconquest". A History of Aragon and Catalonia. London: Methuan. pp. 39–40.
- Catlos, Brian (2015). "The Cid Rides Again". Infidel kings and Unholy Warriors: Faith, power, and violence in the age of crusade and jihad. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. p. 74.
- The Historia Roderici says that the other two Castilian leaders were Diego Pérez and Lope Sánchez. de los Rios, José Amador (1863). "Capitulo 3: Primeros Monumentos Escritos de la Poesía Castellana (Chapter 3: First-Written Monuments of Castilian Poetry)". Historia Crítica de la Literatura Española, Tomo III, (II Parte, Subciclo I) (The History and Criticism of Spanish Literature, Volume III (Second Part, subpart I)) (in Spanish). Madrid, Spain: J. Rodriguez. p. 104.
- Ángel Ferreiro, Miguel. ""La Conquista De Toledo, Mayo De 1085,"". El Reto Histórico. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- García Fitz, Francisco (2015). Relaciones Políticas y Guerra: La Experiencia Castellano-Leonesa Frente Al Islam: Siglos XI–XIII. Sevilla: Universidad de Sevilla. pp. 47–48. ISBN 978-8447207084. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- Inti Fernandez, Yanes (May 1, 2018). The Cross and the Sword: Political Myth-Making, Hegemony, and Intericonicity in the Christianization of the Iberian Peninsula and Britain. OAKTrust. p. 138. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- Baer, George; Dupuy, Trevor N.; Johnson, Curt; Bongard, David L. (July 1994). "The Harper Encyclopedia of Military Biography". The Journal of Military History. 58 (3): 515. doi:10.2307/2944137. ISSN 0899-3718. JSTOR 2944137.
- Catlos, Brian A. (2015). Infidel Kings and Unholy Warriors: Faith, Power, and Violence in the Age of Crusade and Jihad. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. p. 127. ISBN 978-0809058372. Retrieved 9 December 2022.
- Henry Edward Watts (1911). "Cid, The" . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. 6. (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 361–362.
- Perea Rodríguez, Óscar. "Díaz de Vivar, Rodrigo o El Cid (1043–1099)". Archived from the original on 14 April 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2012.
- Bergen, Ard van. "Rodrigo 'el Cid' "El Cid" Díaz de Vivar príncipe de Valencia (± 1043–1099) » maximum test » Genealogy Online". Genealogy Online. Retrieved 2022-06-24.
- "Project Gutenberg's "The Lay of the Cid"". www.gutenberg.org. Retrieved 2022-06-26.
- Alonso, J. I. Garcia; Martinez, J. A.; Criado, A. J. (1999). "Origin of El Cid's sword revealed by ICP-MS metal analysis". Spectroscopy Europe. 11 (4). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
- Tom Hill (2014). Swords of El Cid: "Rodrigo! May God curse him!". Andrews UK Limited. p. 330. ISBN 978-1-78333-651-7.
- Handbook of Medieval Culture. De Gruyter. 31 August 2015. p. 1739. ISBN 978-3-11-037761-3.
- Rita Hamilton; Ian Michael (1984). Cantar de mio Cid. Penguin. p. 187. ISBN 978-0-14-044446-9.
- Barton, Simon; Fletcher, Richard (2000). The World of El Cid. Manchester University Press. p. 90. ISBN 978-1526112637. Retrieved 23 April 2019.
- Girón Alconchel, José Luis; Pérez Escribano, María Virginia (1995). Cantar de mio Cid. Madrid: Ed. Castalia. pp. 11–50. ISBN 84-7039-719-2.
- Daniel Woolf (2011). A Global History of History. Cambridge University Press. p. 110. ISBN 978-0-521-87575-2.
- Cervantes. Don Quixote of La Mancha. 1605.
- Gale (2016). A Study Guide for Pierre Corneille's 'Le Cid'. Gale, Cengage Learning. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-4103-5088-6.
- Pérez-Reverte, Arturo (15 September 2019). "'Sidi', un relato de frontera". El País. Retrieved 6 October 2019.
- Pérez-Reverte, Arturo (2 September 2019). "Adelanto del primer capítulo de la nueva novela de Pérez-Reverte, 'Sidi'". El Mundo. Retrieved 6 October 2019.
- Melville, Herman (1922). The Works of Herman Melville: no. 3. Mardi, and a voyage thither. Constable Limited.
- "Novelas de Vicente Huidobro (1929–1939)". Memoria Chilena. Biblioteca Nacional de Chile (in Spanish). Retrieved June 19, 2024.
- Devoto, Mark (December 2004). "Review: Claude Debussy Rodrigue et Chimène. Édition de Richard Langham Smith". Notes: Quarterly Journal of the Music Library Association. 61 (2). doi:10.1353/not.2004.0131. S2CID 194081830.
- Richard A. Fletcher (1991). The Quest for El Cid. Oxford University Press. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-19-506955-6.
- Gary Allen Smith (2009). Epic Films: Casts, Credits and Commentary on More Than 350 Historical Spectacle Movies (2nd ed.). McFarland. p. 76. ISBN 978-1-4766-0418-3.
- Gale (2016). A Study Guide for Anonymous's "Cantar de mio Cid (El Cid)". Gale, Cengage Learning. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-4103-4239-3.
- Silvestre, Juan (1 October 2019). "'El Cid' de Jaime Lorente para Amazon Prime Video completa su reparto". Fotogramas. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- Amanda DiGioia (2020). Multilingual metal music: Sociocultural, linguistic, and literary perspectives on heavy metal music. United Kingdom: Emerald Publishing Ltd. pp. 61–77. ISBN 978-1-8390-9950-2. Retrieved 8 October 2022.
- Ruy, el pequeño Cid (Animation, Adventure, Drama), BRB Internacional S.A., Nippon Animation Co., Televisión Española (TVE), 1980-10-05, retrieved 2023-01-22
- "Age of Empires II: The Conquerors (Manual)". Archive.org. Retrieved 15 July 2022.
- "texts Age of Empires II: The Conquerors (Manual)". Archive.org. p. 3. Retrieved 15 July 2022.
- Hospodar, Mark (2021-11-09). "Every Age Of Empires Game, Ranked". GameRant.
In 2000, The Conquerors expansion was released, which added new campaigns such as Attila the Hun and El Cid.
- Adams, Dan (2002-01-09). "Medieval: Total War". IGN. Retrieved 2023-01-18.
- Muñoz, Michel (2023-12-08). "Las Miradas Sobre Mío Cid" (in Spanish). El Diadigital. Retrieved 2024-05-02.
- "El Ministerio del Tiempo – Capítulo 9 – T2". RTVE.es (in Spanish). Retrieved 2023-01-22.
- Williams, Gregory L. "Filming San Diego". San Diego History Center. Archived from the original on May 21, 2011. Retrieved April 6, 2012.
General and cited sources
Primary
- Kurtz, Barbara E. El Cid. University of Illinois.
- I. Michael. The Poem of El Cid. Manchester: 1975.
- The Song of El Cid. Translated by Burton Raffel. Penguin Classics, 2009.
- Cantar de mío Cid – Spanish (free PDF)
- Poema de Mio Cid, Códice de Per Abbat in the European Library (third item on page)
- R. Selden Rose and Leonard Bacon (trans.) The Lay of El Cid. Semicentennial Publications of the University of California: 1868–1918. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1997.
- Romancero e historia del muy valeroso caballero El Cid Ruy Díaz de Vibar (1828)
- Cronica del muy esforçado cavallero el Cid ruy diaz campeador (1533)
- Carmen Campidoctoris, a Latin poem on El Cid
Secondary (not cited)
- Simon Barton and Richard Fletcher. The world of El Cid, Chronicles of the Spanish reconquest. Manchester: University Press, 2000. ISBN 0-7190-5225-4 hardback, ISBN 0-7190-5226-2 paperback.
- Gonzalo Martínez Díez, "El Cid Histórico: Un Estudio Exhaustivo Sobre el Verdadero Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar", Editorial Planeta (Spain, 1999). ISBN 84-08-03161-9
- C. Melville and A. Ubaydli (ed. and trans.), Christians and Moors in Spain, vol. III, Arabic sources (711–1501). (Warminster, 1992).
- Mikaberidze, Alexander, ed. (2011). "Almoravids". Conflict and Conquest in the Islamic World: A Historical Encyclopedia. Vol. I. ABC-CLIO.
- Joseph F. O'Callaghan. A History of Medieval Spain. Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1975
- Peter Pierson. The History of Spain. Ed. John E. Findling and Frank W. Thacheray. Wesport, CN: Greenwood Press, 1999. 34–36.
- Bernard F. Reilly. The Kingdom of León-Castilla under King Alfonso VI, 1065–1109 Princeton, NJ: University Press, 1988.
- Steven Thomas. 711–1492: Al-Andalus and the Reconquista.
- M. J. Trow,El Cid The Making of a Legend, Sutton Publishing Limited, 2007.
- Henry Edwards Watts. "The Story of El Cid (1026–1099)" in The Christian Recovery of Spain: The Story of Spain from the Moorish Conquest to the Fall of Granada (711–1492 AD). New York: Putnam, 1894. 71–91.
- T.Y. Henderson. "Conquests Of Valencia"
- J. I. Garcia Alonso, J. A. Martinez, A. J. Criado, "Origin of El Cid's sword revealed by ICP-MS metal analysis", Spectroscopy Europe, 11/4 (1999).
Further reading
- McNair, Alexander J. "El Cid, the Impaler?: Line 1254 of the Poem of the Cid." Essays in Medieval Studies, Volume 26, 2010, pp. 45–68
External links
- Information about The Route of El Cid – English
- "Cid, The" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 6 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 361–362.
| Preceded byIbn Jahaf (as King of Valencia) |
Prince of Valencia 1094–1099 |
Succeeded byXimena Díaz (as Lady of Valencia) |
- El Cid
- 1040s births
- 1099 deaths
- 11th-century Roman Catholics
- 11th-century people from the Kingdom of León
- Burials in the Province of Burgos
- Characters in epic poems
- Christians from al-Andalus
- Heroes in mythology and legend
- Medieval legends
- Military history of Spain
- People of the Reconquista
- Spanish knights
- Spanish Roman Catholics
- Taifa of Valencia
- 11th-century monarchs in Al-Andalus
- 11th-century military personnel
- 11th-century Spanish nobility