| Revision as of 23:48, 12 February 2007 view sourceKing of Hearts (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Autopatrolled, Administrators68,838 editsm Reverted edits by 208.104.229.173 (talk) to last version by King of Hearts← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 16:25, 20 January 2025 view source Golikom (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,346 edits Undid revision 1270651783 by AimanAbir18plus (talk)RV. Take it to talkTag: Undo | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Military commander and king of Macedon (356–323 BC)}} | |||
| {{For|the film of the same name|Alexander the Great (1956 film)}}<!-- This is used as an example on the Misplaced Pages:Disambiguation guideline page PLEASE DO NOT CHANGE IT without first posting a message on Misplaced Pages talk:Disambiguation. Thank you, CarolGray, 21/12/2006. --> | |||
| {{About|the ancient king of Macedon}} | |||
| {|align=right | |||
| {{pp-semi-indef}} | |||
| |{{Infobox Emperor | |||
| {{pp-move}} | |||
| | name =Alexander III, the Great | |||
| {{Good article}} | |||
| | title =King of Macedon, Shah of Persia, Pharaoh of Egypt | |||
| {{Use Oxford spelling|date=September 2020}} | |||
| | image =] | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=January 2025}} | |||
| | caption =Alexander fighting Persian king ]. From ], from ], ], Museo Archeologico Nazionale. | |||
| {{Infobox royalty | |||
| | reign =336 BC-323 BC | |||
| | |
| name = Alexander the Great | ||
| | title = ] | |||
| | predecessor =] | |||
| | |
| image = Alexander the Great mosaic (cropped).jpg | ||
| | |
| caption = Alexander in the '']'' | ||
| | |
| succession = ] | ||
| | |
| reign = October 336 – June 323 BC | ||
| | predecessor = ] | |||
| | royal house = | |||
| | successor = {{plainlist| | |||
| | royal anthem = | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ]}} | |||
| | mother =] | |||
| | succession2 = ] of the ] | |||
| | date of birth =], ] | |||
| | reign2 = 336–323 BC | |||
| | place of birth =], ] | |||
| | predecessor2 = Philip II | |||
| | date of death =], ] | |||
| | successor2 = ] | |||
| | place of death =] (Most probable) | |||
| | succession3 = ] | |||
| | place of buril= | |||
| | reign3 = 332–323 BC | |||
| |}} | |||
| | predecessor3 = ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | successor3 = {{plainlist| | |||
| |{{Campaignbox Wars of Alexander the Great}} | |||
| * Alexander IV | |||
| |} | |||
| * Philip III}} | |||
| | reg-type3 = '' '' | |||
| | regent3 = {{Ancient Egyptian royal titulary case |nomen={{ubl|{{transliteration|egy|ꜣrwksjndrs}}|{{transliteration|egy|Aluksindres}}|Alexandros}} |nomen_hiero=<hiero>A-rw:k:z-i-n:d:r:z</hiero> |horus={{ubl|{{transliteration|egy|mk-kmt}}|{{transliteration|egy|Mekemet}}|Protector of Egypt}} {{Infobox pharaoh/Serekh |Horus=<hiero>S-HqA-q:n:nw-D40</hiero>}}{{pb}}Second Horus name:{{ubl|{{transliteration|egy|ḥḳꜣ-ḳnj tkn-ḫꜣswt}}|{{transliteration|egy|Heqaqeni tekenkhasut}}|The brave ruler who has attacked foreign lands}} {{Infobox pharaoh/Serekh |Horus=<hiero>HqA-q:n:nw:D40-t:k:n:D54-N25:N25:N25</hiero>}}{{pb}}Third Horus name:{{ubl|{{transliteration|egy|ḥḳꜣ ḥḳꜣw nw tꜣ (r) ḏr-f}}|{{transliteration|egy|Heqa heqau nu ta (er) djeref}}|The ruler of the rulers of the entire land}} {{Infobox pharaoh/Serekh |Horus=<hiero>HqA-q-HqA-HqA-q-N33-nw-N33-N17:N34-r:f</hiero>}}Fourth Horus name:{{ubl|{{transliteration|egy|ṯmꜣ-ꜥ}}|{{transliteration|egy|Tjema'a}}|The sturdy-armed one}} {{Infobox pharaoh/Serekh |Horus=<hiero>T:mA-a</hiero>}} |nebty={{ubl|{{transliteration|egy|mꜣj wr-pḥty jṯ ḏww tꜣw ḫꜣswt}}|{{transliteration|egy|Mai werpehty itj dju tau khasut}}|The lion, great of might, who takes possession of mountains, lands, and deserts}} |nebty_hiero=<hiero>E23-wr:r-F9:F9-V15-N25:N25:N33-N17:N17:N33-N25:N25:N33</hiero> |golden={{ubl|{{transliteration|egy|kꜣ (nḫt) ḫwj bꜣḳ(t) ḥḳꜣ wꜣḏ(-wr) šnw n jtn}}|{{transliteration|egy|Ka (nakht) khui baq(et) heqa wadj(wer) shenu en Aten}}|The (strong) bull who protects Egypt, the ruler of the sea and of what the sun encircles}} |golden_hiero=<hiero>E1:n-i-w*x-D40-q:t-b-</hiero>{{pb}}<hiero>D10-HqA-M14-N35A-V9:Z1-i-t:n:HASH</hiero> |prenomen={{ubl|{{transliteration|egy|stp.n-rꜥ mrj-jmn}}|{{transliteration|egy|Setepenre meryamun}}|Chosen by Ra, beloved by Amun{{pb}}{{Infobox pharaoh/Prenomen |Prenomen=<hiero>C2\-C12-stp:n:N36</hiero>}}{{pb}}{{Infobox pharaoh/Prenomen |Prenomen=<hiero>mr\-C12\-C2-stp:n</hiero>}}}}}} | |||
| | succession4 = ] | |||
| | reign4 = 330–323 BC | |||
| | predecessor4 = Darius III | |||
| | successor4 = {{plainlist| | |||
| * Alexander IV | |||
| * Philip III}} | |||
| | full name = | |||
| | spouse = {{hlist|]|]|] | |||
| }} | |||
| | issue = 3, including {{plainlist| | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ]{{Cref2|a}} | |||
| }} | |||
| | native_lang1 = ] | |||
| | native_lang1_name1 = {{lang|grc|Ἀλέξανδρος}}{{Cref2|b}} | |||
| | house = ] | |||
| | house-type = Dynasty | |||
| | father = ] | |||
| | mother = ] | |||
| | birth_date = 20 or 21 July 356 BC | |||
| | birth_place = ], ] | |||
| | death_date = 10 or 11 June 323 BC (aged 32)<!-- 32 years, 10 months and 20 days (approx.) --> | |||
| | death_place = ], Macedon | |||
| | religion = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Alexander III of Macedon''' ({{langx|grc|]|Aléxandros}}; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as '''Alexander the Great''',{{Cref2|c}} was a king of the ] kingdom of ].{{Cref2|d}} He succeeded his father ] to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy ] throughout ], ], parts of ], and ]. By the age of 30, he had created one of the ] in history, stretching from ] to northwestern ].<ref>Bloom, Jonathan M.; Blair, Sheila S. (2009), ''The Grove Encyclopedia of Islamic Art and Architecture: Mosul to Zirid, Volume 3''. (Oxford University Press Incorporated, 2009), 385; "; As the easternmost outpost of the empire of Alexander the Great, the city was renamed Alexandria Eschate ("furthest Alexandria") in 329 BCE."{{pb}}Golden, Peter B. ''Central Asia in World History'' (Oxford University Press, 2011), 25;" his campaigns in Central Asia brought Khwarazm, Sogdia, and Bactria under Graeco-Macedonian rule. As elsewhere, Alexander founded or renamed a number of cities, such as Alexandria Eschate ("Outernmost Alexandria," near modern Khojent in Tajikistan)."</ref> He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders.{{Sfn |Yenne|2010 | page = 159}}<ref name=":8">{{Cite book |last=Grant |first=R.G. |url=https://archive.org/details/epdf.pub_commanders-rg-grant-dk/page/n19 |title=Commanders: History's Greatest Military Leaders |publisher=DK Publishing |year=2011 |isbn=978-1-4053-3696-3 |pages=18}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Beaton |first=Roderick |author-link=Roderick Beaton |title=The Greeks: A Global History |publisher=Basic Books |year=2021 |isbn=9781541618299 |edition=1st |location=New York |pages=163}}</ref> | |||
| Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by ]. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he ] and reasserted control over ] and parts of ] before marching on the city of ], which was ]. Alexander then led the ], and used his authority to launch the ] envisaged by his father, assuming leadership over all ] in their conquest of ].{{sfn|Heckel|Tritle|2009|p=99}}<ref>{{cite book |last1=Burger |first1=Michael |title=The Shaping of Western Civilization: From Antiquity to the Enlightenment |date=2008 |publisher=University of Toronto Press |isbn=978-1-55111-432-3 |page=76}}</ref> | |||
| In 334 BC, he invaded the ] and began ] that lasted for 10 years. Following his conquest of ], Alexander broke the power of Achaemenid Persia in a series of decisive battles, including those at ] and ]; he subsequently overthrew ] and conquered the Achaemenid Empire in its entirety.{{Cref2|e}} After the fall of Persia, the ] held a vast swath of territory between the ] and the ]. Alexander endeavored to reach the "ends of the world and the Great Outer Sea" and ] in 326 BC, achieving an important victory over ], an ancient Indian king of present-day ], at the ]. Due to the mutiny of his homesick troops, he eventually turned back at the ] and later died in 323 BC in ], the city of ] that he had planned to establish as his empire's capital. ] left unexecuted an additional series of planned military and mercantile campaigns that would have begun with a Greek invasion of ]. In the years following his death, ] broke out across the Macedonian Empire, eventually leading to its disintegration at the hands of the ]. | |||
| With his death marking the start of the ], Alexander's legacy includes the ] and ] that his conquests engendered, such as ] and ]. ], with the most prominent being the city of ] in Egypt. Alexander's settlement of ] and the resulting spread of ] led to the overwhelming dominance of ] and influence as far east as the ]. The Hellenistic period developed through the ] into modern ]; the ] became the '']'' of the region and was the predominant language of the ] until its collapse in the mid-15th century AD. | |||
| Alexander became legendary as a classical hero in the mould of ], featuring prominently in the historical and mythical traditions of both Greek and non-Greek cultures. His military achievements and unprecedented enduring successes in battle made him the measure against which many later military leaders would compare themselves,{{cref2|f}} and his tactics remain a significant subject of study in ] worldwide.{{Sfn|Yenne|2010|page=viii}} Legends of Alexander's exploits coalesced into the third-century '']'' which, in the premodern period, went through over one hundred recensions, translations, and derivations and was translated into almost every European vernacular and every language of the Islamic world.<ref name="auto">{{Cite book |last=Doufikar-Aerts |first=Faustina |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781118635193.ctwl0072 |title=A Companion to World Literature |date=2020 |publisher=Wiley |isbn=978-1-118-99318-7 |editor-last=Seigneurie |editor-first=Ken |pages=1–11|chapter=The Arabic ''Alexander Romance'': Mirror of a Bold, Clever, and Devout Prince |doi=10.1002/9781118635193.ctwl0072}}</ref> After the ], it was the most popular form of European literature.<ref name=":5">{{Cite book |last1=Mínguez Cornelles |first1=Víctor |title=The visual legacy of Alexander the Great from the Renaissance to the age of revolution |last2=Rodríguez Moya |first2=Inmaculada |date=2024 |publisher=Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group |isbn=978-1-032-54990-3 |series=Routledge research in art history |location=New York London |pages=22}}</ref> | |||
| '''Alexander the Great''' (]: {{Polytonic|Μέγας Ἀλέξανδρος}},<ref>The name {{Polytonic|Αλέξανδρος}} derives from the Greek words {{Polytonic|αλέξω}} (to repel, shield, protect) and {{Polytonic|ανήρ}} (man; ] {{Polytonic|ανδρός}}), and means "protector of men." For further details on the origins of the name, see ].</ref> ''Megas Alexandros''; July ]–] ]), also known as '''Alexander III''', king of ] (]–]), was one of the most successful military commanders in history. Before his death, he conquered most of the world known to the ancient ], never losing a battle. Alexander is also known in the ] ] work '']'' as "the accursed Alexander" due to his conquest of the ] and the destruction of its capital ]. He is known as '''Eskandar-e Maqduni''' (Alexander of Macedonia) in ], '']'' (the two-horned one) in ], ''Alexander Mokdon'' in ], and ''Tre-Qarnayia'' in ] (the two-horned one, apparently due to an image on coins minted during his rule that seemingly depicted him with the two ram's horns of the Egyptian god ]), ''al-Iskandar al-Kabeer'' in ], ''Sikandar-e-azam'' in ], ''Skandar'' in ]. '''Sikandar''', his name in ] and ], is also a term used as a synonym for "expert" or "extremely skilled". | |||
| {{TOC limit|3}} | |||
| Following the unification of the multiple city-states of ] under the rule of his father, ] (a labour Alexander had to repeat twice because the southern Greeks rebelled after Philip's death), Alexander conquered the ], including ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] and extended the boundaries of his own ] as far as the ]. Before his death, Alexander had already made plans to also turn west and conquer Europe. He also wanted to continue his march eastwards in order to find the end of the world, since his boyhood tutor ] told him tales about where the land ends and the Great Outer Sea begins. Alexander integrated foreigners into his army, leading some scholars to credit him with a "policy of fusion." He encouraged marriage between his army and foreigners, and practiced it himself. After twelve years of constant military campaigning, Alexander died, possibly of ], ], ], viral ], or the consequences of heavy drinking. His conquests ushered in centuries of Greek settlement and rule over distant areas, a period known as the ], a combination of Greek and Middle Eastern culture. Alexander himself lived on in the history and myth of both Greek and non-Greek cultures. After his death (and even during his life) his exploits inspired a literary tradition in which he appears as a legendary ] in the tradition of ]. | |||
| ==Early life== | ==Early life== | ||
| ] (detail). He wears a ] cape, and a ] hat. 3rd century BCE mosaic, Pella museum.]] | |||
| Born in Pella, Macedonia (modern day Greece), Alexander was the son of King ] and of his fourth wife ], an ] princess. According to ] (''Alexander'' 3.1,3), Olympias was imprengated not by Philip, who was afraid of her and her affinity for sleeping in the company of snakes, but by ]. ] relates that both Philip and Olympias dreamt of their son's future birth. Olympias dreamed of a loud burst of thunder and of lightning striking her womb. In Philip's dream, he sealed her womb with the seal of the ]. Alarmed by this, he consulted the seer ], who determined that his wife was pregnant and that the child would have the character of a lion.<ref>Plutarch, ''Alexander'' 2.2–3.</ref> Another odd coincidence is that the ] in ] was set on fire the same night of his birth. Plutarch claimed the gods were too busy watching over Alexander to care for the temple. | |||
| ===Lineage and childhood=== | |||
| ]' ], 5th century BC.]] | |||
| ] was Alexander's tutor and he gave Alexander a thorough training in ] and ] and stimulated his interest in ], ], and ]. After his visit to the ] of ] at ], according to five historians of antiquity (], ], ], ], and ]), rumors spread that the Oracle had revealed Alexander's father to be ], rather than Philip. According to Plutarch, his father descended from ] through ] and his mother descended from ] through ] and ].<ref>Plutarch, ''Alexander'' 2.1.</ref> Aristotle gave him a copy of the '']'' which he always kept with him and read frequently. | |||
| ], Greece, Alexander's birthplace]] | |||
| One time a ] brought a black horse to sell it to Philip, but the horse was wild and no man could mount him. The young Alexander went to the horse, and turned him towards the sun for he had noticed that the horse was just afraid of his own shadow, then he was able to mount it and run it. His father and other people who saw this were very impressed, and when the young Alexander returned and dismounted the horse Philip kissed him with tears of joy and said "My son, seek thee out a kingdom equal to thyself; Macedonia has not room for thee." The horse was named ] (which means "ox-head"). Bucephalus would be his companion and one of his best friends for the next two decades until the horse died (according to Plutarch due to old age, for he was already 30), other sources claimed that Bucephalus died of wounds sustained in a battle in India. Alexander then named a city after him called Bucephalia or Bucephala. | |||
| Alexander III was born in ], the capital of the ],<ref>{{cite book |last=Green |first=Peter |title=Alexander of Macedon, 356–323 B.C.: a historical biography |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=g6Wl4AKGQkIC&pg=PA559 |page=xxxiii |year=1970 |series=Hellenistic culture and society |edition=illustrated, revised reprint |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-07165-0 |quote=356 – Alexander born in Pella. The exact date is not known, but probably either 20 or 26 July. |access-date=20 June 2015}}</ref> on the sixth day of the ] of ], which probably corresponds to 20 July 356 BC (although the exact date is uncertain).<ref>Plutarch, ''Life of Alexander'' 3.5: {{cite web |url=https://www.livius.org/aj-al/alexander/alexander_t32.html#7 |title=The birth of Alexander the Great |work=Livius|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150320180439/https://www.livius.org/aj-al/alexander/alexander_t32.html|archive-date=20 March 2015|url-status = dead |access-date=16 December 2011 |quote=Alexander was born the sixth of ].}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=David George Hogarth |date=1897 |title=Philip and Alexander of Macedon : two essays in biography |url=https://archive.org/details/cu31924028251217/page/n321/mode/2up?view=theater |location=New York |publisher=Charles Scribner's Sons |pages=286–287 |access-date=9 November 2021}}</ref> He was the son of the erstwhile king of Macedon, ], and his fourth wife, ] (daughter of ], king of ]).<ref>{{harvnb|McCarty|2004|p=10}}, {{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=28}}, {{harvnb|Durant|1966|p=538}}</ref>{{Cref2|g}} Although Philip had seven or eight wives, Olympias was his principal wife for some time, likely because she gave birth to Alexander.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=171}}], Alexander's mother]]Several legends surround Alexander's birth and childhood.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=188}} According to the ] biographer ], on the eve of the consummation of her marriage to Philip, Olympias dreamed that her womb was struck by a thunderbolt that caused a flame to spread "far and wide" before dying away. Sometime after the wedding, Philip is said to have seen himself, in a dream, securing his wife's womb with a ] engraved with a lion's image.<ref name="PA2" /> Plutarch offered a variety of interpretations for these dreams: that Olympias was pregnant before her marriage, indicated by the sealing of her womb; or that Alexander's father was ]. Ancient commentators were divided about whether the ambitious Olympias promulgated the story of Alexander's divine parentage, variously claiming that she had told Alexander, or that she dismissed the suggestion as impious.<ref name="PA2" /> | |||
| On the day Alexander was born, Philip was preparing a ] on the city of ] on the peninsula of ]. That same day, Philip received news that his general ] had defeated the combined ]n and ] armies and that his horses had won at the ]. It was also said that on this day, the ] in ], one of the ], burnt down. This led ] to say that it had burnt down because ] was away, attending the birth of Alexander.<ref>{{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=28}}, {{harvnb|Bose|2003|p=21}}</ref> Such legends may have emerged when Alexander was king, and possibly at his instigation, to show that he was superhuman and destined for greatness from conception.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=188}} | |||
| ===Ascent of Macedon=== | |||
| ]. ], ].]] | |||
| When Philip led an attack on ] in ], Alexander, aged 16, was left as regent of Macedonia. In ], Philip took a fifth wife, the ]. As Alexander's mother, ], was from Epirus (a land in the western part of the Greek peninsula and not part of Macedon), and Cleopatra was a true Macedonian, this led to a dispute over Alexander's legitimacy as heir to the throne. Attalus, the uncle of the bride, supposedly gave a toast during the wedding feast giving his wish for the wedding to result in a legitimate heir to the throne of Macedon; Alexander hurled his goblet at Attalus shouting "What am I, a bastard then?" Alexander's father apparently had drawn his sword and moved towards Alexander, but then had fallen in a drunken stupor. Alexander remarked "Here is the man planning on conquering from Greece to Asia, and he cannot even move from one table to another." Alexander, his mother, and sister (also named ]) then left Macedon in anger. | |||
| In his early years, Alexander was raised by a nurse, ], sister of Alexander's future general ]. Later in his childhood, Alexander was tutored by the strict ], a relative of his mother, and by ].{{sfn|Renault|2001|pp=33–34}} Alexander was raised in the manner of noble Macedonian youths, learning to read, play the ], ride, fight, and hunt.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=186}} When Alexander was ten years old, a trader from ] brought Philip a horse, which he offered to sell for thirteen ]. The horse refused to be mounted, and Philip ordered it away. Alexander, however, detecting the horse's fear of its own shadow, asked to tame the horse, which he eventually managed.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=188}} Plutarch stated that Philip, overjoyed at this display of courage and ambition, kissed his son tearfully, declaring: "My boy, you must find a kingdom big enough for your ambitions. Macedon is too small for you", and bought the horse for him.<ref name="PA6" /> Alexander named it ], meaning "ox-head". Bucephalas carried Alexander as far as ]. When the animal died (because of old age, according to Plutarch, at age 30), Alexander named a city after him, ].<ref>{{harvnb|Durant|1966|p=538}}, {{harvnb|Lane Fox|1980|p=64}}, {{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=39}}</ref> | |||
| Eventually Philip reconciled with his son, and Alexander returned home; Olympias and Alexander's sister remained in Epirus. In ] Alexander assisted his father at the decisive ] against the city-states of Athens and ], in which the ] wing led by Alexander annihilated the ], an elite corps regarded as invincible. After the battle, Phillip led a wild celebration, from which Alexander was notably absent (it is believed he was treating the wounded and burying the dead, both of his own troops and of the enemy). It is speculated that Alexander personally treated Demades, a notable orator of Athens, who had opposed Athenian alignment against Philip. The assembled Athenian army voted on a peace plan drawn up and presented by Demades. Philip was content to deprive Thebes of its dominion over ] and leave a Macedonian garrison in the citadel. A few months later, to strengthen Macedon's control over the Greek city-states, the ] was formed. | |||
| ===Education=== | |||
| ], ]).]] | |||
| {{Alexander the Great series}} | |||
| In 336 BC Philip was assassinated at the wedding of his daughter Cleopatra of Macedonia to ]. The ] was supposedly a former lover of the king, the disgruntled young nobleman ], who held a grudge against Philip because the king had ignored a complaint he had expressed. Philip's murder was once thought to have been planned with the knowledge and involvement of Alexander or Olympias. Another possible instigator could have been ], the recently crowned King of Persia. After Philip's death, the army proclaimed Alexander, then aged 20, as the new king of Macedon. Greek cities like Athens and Thebes, which had been forced to pledge allegiance to Philip, saw in the new king an opportunity to retake their full independence. Alexander moved swiftly and Thebes, which had been most active against him, submitted when he appeared at its gates. The assembled Greeks at the ], with the exception of the ]ns, elected him to the command against Persia, which had previously been bestowed upon his father. | |||
| When Alexander was 13, Philip began to search for a ], and considered such academics as ] and ], the latter offering to resign from his stewardship of the ] to take up the post. In the end, Philip chose ] and provided the Temple of the Nymphs at ] as a classroom. In return for teaching Alexander, Philip agreed to rebuild Aristotle's hometown of ], which Philip had razed, and to repopulate it by buying and freeing the ex-citizens who were slaves, or pardoning those who were in exile.<ref>{{harvnb|Lane Fox|1980|pp=65–66}}, {{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=44}}, {{harvnb|McCarty|2004|p=15}}</ref> | |||
| Mieza was like a boarding school for Alexander and the children of Macedonian nobles, such as ], ], and ]. Many of these students would become his friends and future generals, and are often known as the "Companions". Aristotle taught Alexander and his companions about medicine, philosophy, morals, religion, logic, and art. Under Aristotle's tutelage, Alexander developed a passion for the works of ], and in particular the '']''; Aristotle gave him an annotated copy, which Alexander later carried on his campaigns.<ref>{{harvnb|Lane Fox|1980|pp=65–66}}, {{harvnb|Renault|2001|pp=45–47}}, {{harvnb|McCarty|2004|p=16}}</ref> Alexander was able to quote ] from memory.<ref name="RLF">{{cite book |last1=Lane Fox |first1=Robin |title=Alexander the Great | date=1986 |publisher=Penguin Group |isbn=978-0-14-008878-6 |page=48}}</ref> | |||
| The next year, (]), Alexander felt free to engage the ] and the ]ns in order to secure the ] as the northern boundary of the Macedonian kingdom. While he was triumphantly campaigning north, the Thebans and Athenians rebelled once again. Alexander reacted immediately and while the other cities once again hesitated, Thebes decided this time to resist with the utmost vigor. The resistance was useless; in the end, the city was conquered with great bloodshed. The Thebans encountered an even harsher fate when their city was razed to the ground and its territory divided between the other Boeotian cities. Moreover, all of the city's citizens were sold into slavery; Alexander spared only the priests, the leaders of the pro-Macedonian party, and the descendants of ], whose house was the only one left standing. The end of Thebes cowed Athens into submission, but According to ], a special Athenian embassy led by ], an opponent of the anti-Macedonian faction, was able to persuade Alexander to give up his demand for the exile of leaders of the anti-Macedonian party, particularly ].<ref name="Phocion">Plutarch, ''Phocion'', 17</ref> | |||
| In his youth, Alexander was also acquainted with Persian exiles at the Macedonian court, who received the protection of Philip II for several years as they opposed ].{{sfn|Cawthorne|2004|pp=}}<ref>{{cite book |last1=Howe |first1=Timothy |last2=Brice |first2=Lee L. |title=Brill's Companion to Insurgency and Terrorism in the Ancient Mediterranean |date=2015 |publisher=Brill |isbn=978-90-04-28473-9 |page=170 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=248DCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA170|access-date=23 February 2019}}</ref><ref name="EDC">{{cite book |last1=Carney |first1=Elizabeth Donnelly |title=Women and Monarchy in Macedonia |date=2000 |publisher=University of Oklahoma Press |isbn=978-0-8061-3212-9 |page=101 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ZbI2hZBy_EkC&pg=PA101|access-date=23 February 2019}}</ref> Among them were ] and his daughter ], possible future mistress of Alexander, who resided at the Macedonian court from 352 to 342 BC, as well as ], future ] of Alexander, and a Persian nobleman named ].{{sfn|Cawthorne|2004|pp=}}<ref name="JM">{{cite book |last1=Morgan |first1=Janett |title=Greek Perspectives on the Achaemenid Empire: Persia Through the Looking Glass |date=2016 |publisher=Edinburgh University Press |isbn=978-0-7486-4724-8 |pages=271–272 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=49JVDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA271|access-date=23 February 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Briant |first1=Pierre |title=Alexander the Great and His Empire: A Short Introduction |date=2012 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-15445-9 |page=114 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=WAW6kmL30RUC&pg=PA114|access-date=23 February 2019}}</ref><ref name="EJ">{{cite book |last1=Jensen |first1=Erik |title=Barbarians in the Greek and Roman World |date=2018 |publisher=Hackett Publishing |isbn=978-1-62466-714-5 |page=92 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QCRtDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA92|access-date=23 February 2019}}</ref> This gave the Macedonian court a good knowledge of Persian issues, and may even have influenced some of the innovations in the management of the Macedonian state.<ref name="JM"/> | |||
| ==Period of conquests== | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Fall of the Persian Empire=== | |||
| Alexander's army had crossed the ] with about 42,000 Macedonians and Greeks, more southern city-states of Greece, but also including some Thracians, ]ns and Illyrians. After an initial victory against Persian forces at the ], Alexander accepted the surrender of the Persian provincial capital and treasury of ] and proceeded down the ]n coast. At ], Alexander successfully waged the first of many ]s, eventually forcing his opponents, the mercenary captain ] and the Persian ] of ], ], to withdraw by sea. Alexander left Caria in the hands of ], who was ruler of Caria before being deposed by her brother ]. From Halicarnassus, Alexander proceeded into mountainous ] and the ]n plain, asserting control over all coastal cities and denying them to his enemy. From Pamphylia onward, the coast held no major ports and so Alexander moved inland. At ], Alexander humbled but did not storm the ]n city. At the ancient Phrygian capital of ], Alexander "undid" the tangled ], a feat said to await the future "king of ]." According to the most vivid story, Alexander proclaimed that it did not matter how the knot was undone, and he hacked it apart with his sword. Another version claims that he did not use the sword, but actually figured out how to undo the knot. | |||
| ] writes that ] was one of Alexander's teachers, and that Anaximenes also accompanied Alexander on his campaigns.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cs.uky.edu/~raphael/sol/sol-entries/alpha/1989|title=SOL Search|website=cs.uky.edu|access-date=24 August 2019|archive-date=9 August 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200809025936/https://www.cs.uky.edu/~raphael/sol/sol-entries/alpha/1989|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ]'', showing ], from the ], ]]] | |||
| ==Heir of Philip II== | |||
| Alexander's army crossed the ], met and defeated the main Persian army under the command of Darius III at the ] in ]. Darius was forced to leave the battle and left behind his wife, his two daughters, his mother ], and much of his personal treasure. Proceeding down the ] coast, he took ] and ] after famous sieges (see ]). Alexander passed through ] near ] but probably did not visit the city. | |||
| ===Regency and ascent of Macedon=== | |||
| In 332 BC–331 BC, Alexander was welcomed as a liberator in ] and was pronounced the son of Zeus by Egyptian priests of the god Ammon at the Oracle of the god at the ] in the ]n desert. Henceforth, Alexander referred to the god Zeus-Ammon as his true father, and subsequent currency featuring his head with ram horns was proof of this widespread belief. He founded ] in Egypt, which would become the prosperous capital of the ] after his death. Leaving Egypt, Alexander marched eastward into ] (now northern ]) and defeated Darius and a third Persian army at the ]. Darius was forced to leave the field after his charioteer was killed, and Alexander chased him as far as ]. While Darius fled over the mountains to ] (modern ]), Alexander marched to ]. | |||
| {{Main|Philip II of Macedon|Rise of Macedon}} | |||
| {{further|History of Macedonia (ancient kingdom)}} | |||
| ], Alexander's father]] | |||
| At the age of 16, Alexander's education under Aristotle ended. Philip II had waged war against the ] to the north, which left Alexander in charge as ] and ].{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=188}} During Philip's absence, the Thracian tribe of ] revolted against Macedonia. Alexander responded quickly and drove them from their territory. The territory was colonized, and a city, named ], was founded.<ref>{{harvnb|Lane Fox|1980|p=68}}, {{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=47}}, {{harvnb|Bose|2003|p=43}}</ref> | |||
| ], at the maximum extent of Alexander's advance in the East (], ] Museum, ]) (drawing).]] | |||
| Upon Philip's return, Alexander was dispatched with a small force to subdue the revolts in southern ]. Campaigning against the Greek city of ], Alexander reportedly saved his father's life. Meanwhile, the city of ] began to work lands that were sacred to ] near ], a sacrilege that gave Philip the opportunity to further intervene in Greek affairs. While Philip was occupied in Thrace, Alexander was ordered to muster an army for a campaign in southern Greece. Concerned that other Greek states might intervene, Alexander made it look as though he was preparing to attack Illyria instead. During this turmoil, the ] invaded Macedonia, only to be repelled by Alexander.{{sfn|Renault|2001|pp=47–49}} | |||
| From Babylon, Alexander went to ], one of the ] capitals, and captured its treasury. Sending the bulk of his army to ], the Persian capital, by the ], Alexander stormed and captured the ] (in the modern ]), then sprinted for ] before its treasury could be looted. After several months Alexander allowed the troops to loot Persepolis. A fire broke out in the eastern palace of ] and spread to the rest of the city. It was not known if it was a drunken accident or a deliberate act of revenge for the burning of the ] during the ]. The ''Book of Arda Wiraz'', a Zoroastrian work composed in the 3rd or 4th century AD, also speaks of archives containing "all the ] and Zand, written upon prepared cow-skins, and with gold ink" that were destroyed; but it must be said that this statement is often treated by scholars with a certain measure of skepticism, because it is generally thought that for many centuries the Avesta was transmitted mainly orally by the ]. | |||
| Philip and his army joined his son in 338 BC, and they marched south through ], taking it after stubborn resistance from its Theban garrison. They went on to occupy the city of ], only a few days' march from both ] and ]. The Athenians, led by ], voted to seek alliance with Thebes against Macedonia. Both Athens and Philip sent embassies to win Thebes's favour, but Athens won the contest.<ref>{{harvnb|Renault|2001|pp=50–51}}, {{harvnb|Bose|2003|pp=44–45}}, {{harvnb|McCarty|2004|p=23}}</ref> Philip marched on Amphissa (ostensibly acting on the request of the ]), capturing the mercenaries sent there by Demosthenes and accepting the city's surrender. Philip then returned to Elatea, sending a final offer of peace to Athens and Thebes, who both rejected it.<ref>{{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=51}}, {{harvnb|Bose|2003|p=47}}, {{harvnb|McCarty|2004|p=24}}</ref> | |||
| He then set off in pursuit of Darius, who was kidnapped, and then murdered by followers of ], his ]n satrap and kinsman. Bessus then declared himself Darius' successor as Artaxerxes V and retreated into ] to launch a ] campaign against Alexander. With the death of Darius, Alexander declared the war of vengeance over, and released his Greek and other allies from service in the League campaign (although he allowed those that wished to re-enlist as ] in his imperial army). | |||
| ]]] | |||
| As Philip marched south, his opponents blocked him near ], ]. During the ensuing ], Philip commanded the right wing and Alexander the left, accompanied by a group of Philip's trusted generals. According to the ancient sources, the two sides fought bitterly for some time. Philip deliberately commanded his troops to retreat, counting on the untested Athenian ] to follow, thus breaking their line. Alexander was the first to break the Theban lines, followed by Philip's generals. Having damaged the enemy's cohesion, Philip ordered his troops to press forward and quickly routed them. With the Athenians lost, the Thebans were surrounded. Left to fight alone, they were defeated.<ref name="DiodXVI" /> | |||
| After the victory at Chaeronea, Philip and Alexander marched unopposed into the ], devastating much of Laconia and ejecting the Spartans from various parts of it.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Cartledge |first1=Paul |title=Sparta and Lakonia: A Regional History, 1300-362 B.C. |date=2002 |publisher=Routledge |location=New York |isbn=0-415-26276-3 |page=273 |edition=2nd |quote=Philip laid Lakonia waste as far south as Gytheion and formally deprived Sparta of Dentheliatis (and apparently the territory on the Messenian Gulf as far as the Little Pamisos river), Belminatis, the territory of Karyai and the east Parnon foreland.}}</ref> At ], Philip established a "Hellenic Alliance" (modelled on the old ] of the ]), which included most Greek city-states except Sparta. Philip was then named '']'' (often translated as "Supreme Commander") of this league (known by modern scholars as the ]), and announced his plans to attack the ].{{sfn|Renault|2001|p=54}}{{sfn|McCarty|2004|p=26}} | |||
| His three-year campaign against first Bessus and then the satrap of ], ], took him through ], ], ] (West Afghanistan), ], ](South and Central Afghanistan), ] (North and Central Afghanistan), and ]. In the process, he captured and refounded ] and ]. Moreover, he founded a series of new cities, all called Alexandria, including modern ] in ], and ] ("The Furthest") in modern ]. In the end, both were betrayed by their men, Bessus in 329 BC and Spitamenes the year after. | |||
| === |
===Exile and return=== | ||
| When Philip returned to Pella, he fell in love with and married ] in 338 BC,<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Green |first=Peter |date=1991 |title=Alexander to Actium: The Historical Evolution of the Hellenistic Age (Hellenistic Culture and Society) |location=Berkeley & Los Angeles |publisher=University of California Press |journal=The American Historical Review |volume=1 |doi=10.1086/ahr/96.5.1515 |issn = 0002-8762}}</ref> the niece of his general ].{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=179}} The marriage made Alexander's position as heir less secure, since any son of Cleopatra Eurydice would be a fully Macedonian heir, while Alexander was only half-Macedonian.{{sfn|McCarty|2004|p=27}} During the ], a drunken Attalus publicly prayed to the gods that the union would produce a legitimate heir.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=179}} | |||
| During this time, Alexander adopted some elements of Persian dress and customs at his court, notably the custom of '']'', a symbolic kissing of the hand that Persians paid to their social superiors, but a practice of which the Greeks disapproved. The Greeks regarded the gesture as the preserve of ] and believed that Alexander meant to deify himself by requiring it. This cost him much in the sympathies of many of his countrymen. Here, too, a plot against his life was revealed, and one of his officers, ], was executed for treason for failing to bring the plot to his attention. ], Philotas' father, who had been charged with guarding the treasury at ], was assassinated by command of Alexander, who feared that Parmenion might attempt to avenge his son. Several other trials for treason followed, and many Macedonians were executed. Later on, in a drunken quarrel at ], he also killed the man who had saved his life at Granicus, ]. Later in the Central Asian campaign, a second plot against his life, this one by his own ], was revealed, and his official historian, ] of ] (who had fallen out of favor with the king by leading the opposition to his attempt to introduce ''proskynesis''), was implicated on what many historians regard as trumped-up charges. There is evidence to show that Callisthenes, the teacher of the pages, must have been the one who persuaded them to assassinate the king. | |||
| {{Blockquote|At the wedding of Cleopatra, whom Philip fell in love with and married, she being much too young for him, her uncle Attalus in his drink desired the Macedonians would implore the gods to give them a lawful successor to the kingdom by his niece. This so irritated Alexander that throwing one of the cups at his head, "You villain," said he, "what, am I then a bastard?" Then Philip, taking Attalus's part, rose up and would have run his son through; but by good fortune for them both, either his over-hasty rage, or the wine he had drunk, made his foot slip, so that he fell down on the floor, at which Alexander reproachfully insulted him: "See there," said he, "the man who makes preparations to pass out of Europe into Asia, overturned in passing from one seat to another."|Plutarch, describing the feud at Philip's wedding.<ref name="PA9" />}} | |||
| ===Invasion in India=== | |||
| ] | |||
| After the death of ] and his marriage to ] (Roshanak in ]) to cement his relations with his new Central Asian satrapies, in ] Alexander was finally free to turn his attention to ]. Alexander invited all the ]s of the former satrapy of ], in the north of present-day ], to come to him and submit to his authority. ](Greek: Omphis), ruler of ], whose kingdom extended from the ] to the ] (Greek:Hydaspes) , complied. But the chieftains of some hilly clans including the, ] and ] sections of the ] (''classical names''), known in Indian texts as ]s and ]s (''names referring to the ] nature of their society from the ] root work Ashva meaning horse''), refused to submit. | |||
| In 337 BC, Alexander fled Macedon with his mother, dropping her off with her brother, King ] in ], capital of the ].{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=180}} He continued to Illyria{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=180}} where he sought refuge with one or more Illyrian kings, perhaps with ], and was treated as a guest, despite having defeated them in battle a few years before.<ref>A History of Macedonia: Volume III: 336–167 B.C. By N. G. L. Hammond, F. W. Walbank</ref> However, it appears Philip never intended to disown his politically and militarily trained son.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=180}} Accordingly, Alexander returned to Macedon after six months due to the efforts of a family friend, ], who mediated between the two parties.<ref>{{harvnb|Bose|2003|p=75}}, {{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=56}}</ref> | |||
| Alexander personally took command of the shield-bearing guards, foot-companions, archers, Agrianians and horse-javelin-men and led them against the ] ]s—the ] of ]/] ]s, the Guraeans of the Guraeus (]) valley, and the Assakenois of the ] and ] valleys. Writes one modern historian: "They were brave people and it was hard work for Alexander to take their strongholds, of which ] and ] need special mention."<ref>Worthington, p. 162, from an extract of A. K. Narain, 'Alexander the Great', ''Greece and Rome'' '''12''' 1965, p 155–165.</ref> A fierce contest ensued with the Aspasios in which Alexander himself was wounded in the shoulder by a dart but eventually the Aspasios lost the fight; 40,000 of them were enslaved. The Assakenois faced Alexander with an army of 30,000 cavalry, 38,000 infantry and 30 ].<ref>Curtius.</ref> They had fought bravely and offered stubborn resistance to the invader in many of their strongholds like cities of ], ] and Massaga. The fort of Massaga could only be reduced after several days of bloody fighting in which Alexander himself was wounded seriously in the ankle. When the ] of Massaga fell in the battle, the supreme command of the army went to his old mother ] (q.v.) who also stood determined to defend her motherland to the last extremity. The example of Cleophis assuming the supreme command of the military also brought the entire women of the locality into the fighting.<ref>(''Ancient India'', 1971, p 99, Dr R. C. Majumdar; ''History and Culture of Indian People, The Age of Imperial Unity, Foreign Invasion'', p 46, Dr R. K Mukerjee.</ref> Alexander could only reduce Massaga by resorting to political strategem and actions of betrayal. According to ]: "Not only did Alexander slaughter the entire population of Massaga, but also did he reduce its buildings to rubbles." A similar manslaughter then followed at Ora, another stronghold of the Assakenois. | |||
| In the following year, the Persian ] (governor) of ], ], offered his eldest daughter to Alexander's half-brother, ].{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=180}} Olympias and several of Alexander's friends suggested this showed Philip intended to make Arrhidaeus his heir.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=180}} Alexander reacted by sending an actor, ] of Corinth, to tell Pixodarus that he should not offer his daughter's hand to an illegitimate son, but instead to Alexander. When Philip heard of this, he stopped the negotiations and scolded Alexander for wishing to marry the daughter of a Carian, explaining that he wanted a better bride for him.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=180}} Philip exiled four of Alexander's friends, ], ], ] and ], and had the Corinthians bring Thessalus to him in chains.<ref>{{harvnb|McCarty|2004|p=27}}, {{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=59}}, {{harvnb|Lane Fox|1980|p=71}}</ref> | |||
| ] around 323 BC.<br /> | |||
| '''Obv:''' Alexander standing, being crowned by ], fully armed and holding ]' ].<br /> | |||
| '''Rev:''' Greek rider, possibly Alexander, attacking an Indian ], possibly during the battle against ].]] | |||
| In the aftermath of general ] and ] committed by Alexander at Massaga and Ora, numerous ] people fled to a high fortress called ]. Alexander followed them close behind their heels and captured the strategic hill-fort but only after the fourth day of a bloody fight. The story of Massaga was repeated at Aornos and a similar ] on the tribal-people followed here too. | |||
| ==King of Macedon== | |||
| Writing on Alexander's campaign against the Assakenois, Victor Hanson comments: "After promising the surrounded Assacenis their lives upon capitulation, he executed all their soldiers who had surrendered. Their strongholds at Ora and Aornus were also similarly stormed. Garrisons were probably all slaughtered.”<ref>''Carnage and Culture: Landmark Battles in the Rise to Western Power'', 2002, p 86, Victor Hanson.</ref> | |||
| ===Accession=== | |||
| Sisikottos, who had helped Alexander in this campaign, was made the governor of Aornos. | |||
| {{Further|Government of Macedonia (ancient kingdom)}} | |||
| ] | |||
| In the 24th day of the ] Dios, which probably corresponds to 25 October 336 BC,<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Hammond |first=N. G. L. |date=21 December 1992 |title=The Regnal Years of Philip and Alexander |url=https://grbs.library.duke.edu/index.php/grbs/article/view/3531 |journal=Greek, Roman, and Byzantine Studies |language=en |volume=33 |issue=4 |pages=355–373 |issn=2159-3159}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Parise |first=Frank |url=https://archive.org/details/bookofcalendars0000unse_y2i4/page/10/mode/2up |title=The book of calendars |date=2002 |publisher=Gorgias Press |isbn=978-1-931956-76-5 |location=Piscataway, NJ |pages=10 |orig-date=1983}} The month of Dios started in 2 October that year.</ref> while at ] attending the wedding of his daughter ] to Olympias's brother, ], Philip was assassinated by the captain of his ], ].{{Cref2|h}} As Pausanias tried to escape, he tripped over a vine and was killed by his pursuers, including two of Alexander's companions, ] and ]. Alexander was proclaimed king on the spot by the nobles and ] at the age of 20.{{sfn|McCarty|2004|pp=30–31}}<ref>{{harvnb|Renault|2001|pp=61–62}}</ref><ref name="Fox 1980 72">{{harvnb|Lane Fox|1980|p=72}}</ref> | |||
| After reducing Aornos, Alexander crossed the Indus and fought and won an epic battle against ], a ruler of a region in the ] in the ] in 326 BC. | |||
| ===Consolidation of power=== | |||
| ] depicting Alexander and Porus during the ].]] | |||
| Alexander began his reign by eliminating potential rivals to the throne. He had his cousin, the former ], executed.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=190}} He also had two Macedonian princes from the region of ] killed for having been involved in his father's assassination, but spared a third, ]. Olympias had Cleopatra Eurydice, and Europa, her daughter by Philip, burned alive. When Alexander learned about this, he was furious. Alexander also ordered the murder of Attalus,{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=190}} who was in command of the advance guard of the army in Asia Minor and Cleopatra's uncle.<ref name="Green 2007 5–6">{{harvnb|Green|2007|pp=5–6}}</ref> | |||
| After the victory, Alexander was greatly impressed by Porus for his bravery in battle, and therefore made an alliance with him and appointed him as satrap of his own kingdom, even adding some land he did not own before. Alexander then named one of the two new cities that he founded, ], in honor of the horse who had brought him to India, who had died during the ]. Alexander continued on to conquer all the headwaters of the Indus River. | |||
| Attalus was at that time corresponding with Demosthenes, regarding the possibility of defecting to Athens. Attalus also had severely insulted Alexander, and following Cleopatra's murder, Alexander may have considered him too dangerous to be left alive.<ref name="Green 2007 5–6" /> Alexander spared Arrhidaeus, who was by all accounts mentally disabled, possibly as a result of poisoning by Olympias.{{sfn|McCarty|2004|pp=30–31}}<ref name="Fox 1980 72" /><ref>{{harvnb|Renault|2001|pp=70–71}}</ref> | |||
| East of Porus' kingdom, near the ], was the powerful empire of ] ruled by the ]. Fearing the prospects of facing another powerful Indian army and exhausted by years of campaigning, his army mutinied at the ] (the modern ]) refusing to march further east. This river thus marks the eastern-most extent of Alexander's conquests: | |||
| :"As for the Macedonians, however, their struggle with Porus blunted their courage and stayed their further advance into India. For having had all they could do to repulse an enemy who mustered only twenty thousand infantry and two thousand horse, they violently opposed Alexander when he insisted on crossing the river Ganges also, the width of which, as they learned, was thirty-two furlongs, its depth a hundred fathoms, while its banks on the further side were covered with multitudes of men-at-arms and horsemen and elephants. For they were told that the kings of the Ganderites and Praesii were awaiting them with eighty thousand horsemen, two hundred thousand footmen, eight thousand chariots, and six thousand fighting elephants." Plutarch, Vita Alexandri, 62<ref></ref> | |||
| News of Philip's death roused many states into revolt, including Thebes, Athens, Thessaly, and the Thracian tribes north of Macedon. When news of the revolts reached Alexander, he responded quickly. Though advised to use diplomacy, Alexander mustered 3,000 Macedonian cavalry and rode south towards Thessaly. He found the Thessalian army occupying the pass between ] and ], and ordered his men to ride over Mount Ossa. When the Thessalians awoke the next day, they found Alexander in their rear and promptly surrendered, adding their cavalry to Alexander's force. He then continued south towards the ].<ref>{{harvnb|McCarty|2004|p=31}}, {{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=72}}, {{harvnb|Lane Fox|1980|p=104}}, {{harvnb|Bose|2003|p=95}}</ref> | |||
| Alexander, after the meeting with his officer ], was convinced that it was better to return. Alexander was forced to turn south. Along the way his army ran into the ] clans (in modern day ]). The Malli were the most warlike clans in India during that period. Alexander's army challenged the Malli, and the ensuing battle led them to the Malli citadel. During the assault, Alexander himself was wounded seriously by a Malli arrow.<ref>Plutarch, Alexander .</ref> His forces, believing their king dead, took the citadel and unleashed their fury on the Malli who had taken refuge within it <ref></ref>. Following this, the surviving Malli surrendered to Alexander's forces, and his beleaguered army moved on <ref>,''History of Macedonia''</ref>. He sent much of his army to ] (modern southern ]) with his general ], and commissioned a fleet to explore the ] shore under his admiral ], while he led the rest of his forces back to Persia by the southern route through the ] (now part of southern ] and ] in southern ]). | |||
| Alexander stopped at Thermopylae where he was recognized as the leader of the Amphictyonic League before heading south to ]. Athens sued for peace and Alexander pardoned the rebels. The famous ] occurred during Alexander's stay in Corinth. When Alexander asked Diogenes what he could do for him, the philosopher disdainfully asked Alexander to stand a little to the side, as he was blocking the sunlight.{{sfn|Stoneman|2004|p=21}} This reply apparently delighted Alexander who is reported to have said, "But verily, if I were not Alexander, I would like to be Diogenes."{{sfn|Dillon|2004|pp=187–88}} At Corinth, Alexander took the title of ''Hegemon'' ("leader") and, like Philip, was appointed commander for the coming war against Persia. He also received news of a Thracian uprising.<ref>{{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=72}}, {{harvnb|Bose|2003|p=96}}</ref> | |||
| Alexander left forces in India however. In the territory of the Indus, he nominated his officer ] as a ], a position he would hold for the next ten years until ], and in the ] he left ] in charge of the army, at the side of the satrap ] and ]. Eudemus became ruler of the Punjab after their death. Both rulers returned to the West in 316 BC with their armies, and ] established the ] in India. | |||
| === |
===Balkan campaign=== | ||
| {{Main|Alexander's Balkan campaign}} | |||
| Discovering that many of his ]s and ] ]s had misbehaved in his absence, Alexander executed a number of them as examples on his way to ]. As a gesture of thanks, he paid off the debts of his soldiers, and announced that he would send those over-aged and disabled veterans back to Macedonia under Craterus, but his troops misunderstood his intention and mutinied at the town of ], refusing to be sent away and bitterly criticizing his adoption of Persian customs and dress and the introduction of Persian officers and soldiers into Macedonian units. Alexander executed the ringleaders of the mutiny, but forgave the rank and file. In an attempt to craft a lasting harmony between his Macedonian and Persian subjects, he held a mass marriage of his senior officers to Persian and other noblewomen at Susa, but few of those marriages seem to have lasted much beyond a year. | |||
| ] | |||
| Before crossing to Asia, Alexander wanted to safeguard his northern borders. In the spring of 335 BC, he advanced to suppress several revolts. Starting from ], he travelled east into the country of the "Independent Thracians", and at ], the Macedonian army attacked and defeated the Thracian forces manning the heights.<ref name="I, 1" /> The Macedonians marched into the country of the ] and defeated their army near the ] river<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=I, 2}}</ref> (a ]). Alexander then marched for three days to the ], encountering the ] tribe on the opposite shore. Crossing the river at night, he surprised them and forced their army to retreat after the first cavalry ].<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=I, 3–4}}, {{harvnb|Renault|2001|pp=73–74}}</ref> | |||
| News then reached Alexander that the Illyrian chieftain ] and ] of the ] were in open revolt against his authority. Marching west into Illyria, Alexander defeated each in turn, forcing the two rulers to flee with their troops. With these victories, he secured his northern frontier.<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=I, 5–6}}, {{harvnb|Renault|2001|p=77}}</ref> | |||
| His attempts to merge Persian culture with his Greek soldiers also included training a regiment of Persian boys in the ways of Macedonians. Most historians believe that Alexander adopted the Persian royal title of '']anshah'' ("great king" or "king of kings"). | |||
| === Destruction of Thebes === | |||
| It is claimed that Alexander wanted to overrun or integrate the Arabian peninsula, but this theory is widely disputed. It was assumed that Alexander would turn westwards and attack ] and ], had he conquered Arabia. | |||
| While Alexander campaigned north, the Thebans and Athenians rebelled once again. Alexander immediately headed south.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=192}} While the other cities again hesitated, Thebes decided to fight. The Theban resistance was ineffective and Alexander ] and divided its territory between the other Boeotian cities. The end of Thebes cowed Athens, leaving all of Greece temporarily at peace.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=192}} Alexander then set out on his Asian campaign, leaving ] as regent.<ref name="Roisman 2010 199">{{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=199}}</ref> | |||
| After traveling to Ecbatana to retrieve the bulk of the Persian treasure, his closest friend and possibly lover<ref>Aelian, ''Varia Historia;'' XII.7</ref> ] died of an illness, or possibly of poisoning. Alexander mourned by Hephaestion's side for six months. | |||
| ==Conquest of the Achaemenid Persian Empire== | |||
| ==Death== | |||
| {{Main|Wars of Alexander the Great|Chronology of the expedition of Alexander the Great into Asia}} | |||
| ] | |||
| On the afternoon of June 10–11, 323 BC, Alexander died in the palace of ] II of ]. He was just one month shy of attaining 33 years of age. Various theories have been proposed for the cause of his death which include ] by the sons of ] or others, sickness that followed a drinking party, or a relapse of the ] he had contracted in ]. | |||
| ===Strategy=== | |||
| It is known that on May 29, Alexander participated in a banquet organized by his friend ] of ]. After some heavy drinking, immediately before or after a bath, he was forced into bed due to severe illness. The rumors of his illness circulated with the troops causing them to be more and more anxious. On June 9, the generals decided to let the soldiers see their king alive one last time. They were admitted to his presence one at a time. While the king was too ill to speak, confined himself to move his hand. The day after, Alexander was dead. | |||
| {{Main|Military tactics of Alexander the Great#Grand strategy}} | |||
| The poisoning theory derives from the story held in antiquity by Justin and Curtius. The original story stated that ], son of Antipater, viceroy of Greece, brought the poison to Alexander in Babylon in a mule's hoof, and that Alexander's royal cupbearer, ], brother of Cassander, administered it. Many had powerful motivations for seeing Alexander gone, and were none the worse for it after his death. Deadly agents that could have killed Alexander in one or more doses include hellebore and ]. In R. Lane Fox's opinion, the strongest argument against the poison theory is the fact that twelve days had passed between the start of his illness and his death and in the ancient world, such long-acting poisons were probably not available. | |||
| Alexander's invasion of Persia as a whole has been denoted as a supreme example of a "strategic line" of conducting war, a line formed by "the chain of logic that connects operations into a single whole." In his book ''Strategy'', Soviet military officer and theorist ] delineates Alexander's strategic steps. After securing his Greek base and the Balkans by subjugating his political opponents, and securing his army's rear through the conquest of all the Afro-Asian coastline, where the Persian fleet was based and from which it was supplied, Alexander, moved to confront directly the Persians. He thus resolved the eternal problem of an army conducting operations deep into enemy territory, Svechin states, in an "exemplary manner."<ref name=svechin>{{cite book |last= Svechin|first=Alexander |author-link=Alexander Svechin|date=1991|orig-date=1927|editor-last=Lee|editor-first=Kent D.|title=Strategy|publisher=East View Information Services|page=263 |chapter=Combining Operations for Achieving the ultimate Goal of the War|isbn=1-879944-33-2}}</ref> | |||
| ===Asia Minor=== | |||
| <!-- Image with unknown copyright status removed: ] of Alexander the Great, located in ], Rome]] --> | |||
| {{Further|Battle of the Granicus|Siege of Halicarnassus|Siege of Miletus}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The warrior culture of Macedon favoured the sword over strychnine, and many ancient historians, like Plutarch and ], maintained that Alexander was not poisoned, but died of natural causes. Instead, it is likely that Alexander died of malaria or typhoid fever, which were rampant in ancient Babylon. Other illnesses could have also been the culprit, including ] or the ] virus. Recently, theories have been advanced stating that Alexander may have died from the treatment not the disease. ], believed to have been widely used as a medicine at the time but deadly in large doses, may have been overused by the impatient king to speed his recovery, with deadly results. Disease-related theories often cite the fact that Alexander's health had fallen to dangerously low levels after years of heavy drinking and suffering several appalling wounds (including one in India that nearly claimed his life), and that it was only a matter of time before one sickness or another finally killed him. | |||
| {{Campaigns of Alexander the Great}} | |||
| {{OSM Location map | |||
| | coord = {{coord|35|48}} | |||
| | zoom = 3 | |||
| | float = right | |||
| | nolabels = 1 | |||
| | width = 352 | |||
| | height = 160 | |||
| | title = | |||
| | shapeD = n-circle | |||
| No story is conclusive. Alexander's death has been reinterpreted many times over the centuries, and each generation offers a new take on it. What is certain is that Alexander died of a high fever on June 10 or 11 of ]. | |||
| | shape-colorD = navy | |||
| | shape-outlineD = white | |||
| | label-colorD = navy | |||
| | label-sizeD = 12 | |||
| | label-posD = left | |||
| | label-offset-xD = 0 | |||
| | label-offset-yD = 0 | |||
| | label1 = Pella | |||
| ], ]]] | |||
| | mark-coord1 = {{coord|40.75|22.52}} | |||
| On his death bed, his marshals asked him to whom he bequeathed his kingdom. Since Alexander had no obvious and legitimate heir (his son ] would be born after his death, and his other son was by a concubine, not a wife), it was a question of vital importance. There is some debate to what Alexander replied. Some believe that Alexander said, "Kratisto" (that is, "To the strong''est''!") or "Krat'eroi" (to the strong''er''). | |||
| | mark-title1 = Birthplace July 356 BC | |||
| | mark-description1 = ] in ] | |||
| | label-pos1 = top | |||
| | label-offset-x1 = 10 | |||
| | label2 = Granicus | |||
| Alexander may have said, "Krater'oi" (To ]). This is possible because the Greek pronunciation of "the stronger" and "Craterus" differ only by the position of the accented syllable. Most scholars believe that if Alexander did intend to choose one of his generals, his obvious choice would have been Craterus because he was the commander of the largest part of the army (infantry), because he had proven himself to be an excellent strategist, and because he displayed traits of the "ideal" Macedonian. Regardless of his reply, Craterus was eventually assassinated before he could organize a coup with the infantry and Alexander's empire was split into four kingdoms. | |||
| | mark-coord2 = {{coord|40.32|27.28}} | |||
| | mark-title2 = ] May, 334 BC | |||
| | mark-description2 = ] | |||
| | label-pos2 = right | |||
| | label-offset-y2 = -10 | |||
| | label3 = Miletus | |||
| Alexander's death has been surrounded by as much controversy as many of the events of his life. Before long, accusations of foul play were being thrown about by his generals at one another, making it incredibly hard for a modern historian to sort out the propaganda and the half-truths from the actual events. No contemporary source can be fully trusted because of the incredible level of self-serving recording, and as a result what truly happened to Alexander the Great may never be known. Most theories that he died from syphillus have been more or less discredited. | |||
| | mark-coord3 = {{coord|37.53|27.28}} | |||
| | mark-title3 = ] 334 BC<br>] 334 BC | |||
| | mark-description3 = ] | |||
| | label-pos3 = right | |||
| | label-offset-y3 = -10 | |||
| | label4 = Issus | |||
| Alexander's body was placed in a gold anthropid ], which was in turn placed in a second gold casket and covered with a purple robe. Alexander's coffin was placed, together with his armour, in a gold carriage that had a vaulted roof supported by an ] peristyle. The decoration of the carriage was very lavish and is described in great detail by Diodoros. | |||
| | mark-coord4 = {{coord|36.75|36.19}} | |||
| | mark-title4 = ] 334 BC | |||
| | mark-description4 = ] | |||
| | label5 = Tyre | |||
| ], showing himself on the obverse at the beginning of his reign, and on the reverse Alexander the Great triumphantly riding a chariot drawn by elephants, a reminder of his successful campaigns with Alexander in India.]] | |||
| | mark-coord5 = {{coord|33.27|35.2}} | |||
| According to one legend, Alexander was preserved in a clay vessel full of ] (which can act as a preservative) and interred in a glass ]. According to Aelian (''Varia Historia'' 12.64), ] stole the body and brought it to Alexandria, where it was on display until ]. It was here that ], one of the last successors of Ptolemy I, replaced Alexander's sarcophagus with a glass one, and melted the original down in order to strike emergency gold issues of his coinage. The citizens of Alexandria were outraged at this and soon after Ptolemy IX was killed. Its current whereabouts are unknown. | |||
| | mark-title5 = ] January–July 332 BC | |||
| | mark-description5 = ] | |||
| | label-offset-x5 = 2 | |||
| | label-offset-y5 = -2 | |||
| | label6 = Gaza | |||
| Roman emperor ] was said to have looted the tomb, stealing Alexander's breastplate, and wearing it. In A.D. about 200, Emperor ] closed Alexander's tomb to the public. His son and successor, ], was a great admirer of Alexander, and visited the tomb in his own reign. After this, details on the fate of the tomb are sketchy. | |||
| | mark-coord6 = {{coord|31.52|34.45}} | |||
| | mark-title6 = ] October 332 BC | |||
| | mark-description6 = ] | |||
| | label-pos6 = right | |||
| | label7 = Alexandria | |||
| The so-called "]," discovered near ] and now in the ], is now generally thought to be that of ], whom Hephaestion had appointed as the king of Sidon by Alexander's order. The sarcophagus depicts Alexander and his companions hunting and in battle with the Persians. | |||
| | mark-coord7 = {{coord|31.2|29.92}} | |||
| | mark-title7 = ] 331 BC | |||
| | mark-description7 = ] | |||
| | label-pos7 = bottom | |||
| | label-offset-y7 = -5 | |||
| | label8 = Gaugamela | |||
| ===Alexander's testament=== | |||
| | mark-coord8 = {{coord|36.56|43.44}} | |||
| Some classical authors, such as ], relate that Alexander had given detailed written instructions to ] some time before his death. Although Craterus had already started to implement Alexander's orders, such as the building of a fleet in ] for expedition against ], Alexander's successors chose not to further implement them, on the ground they were impractical and dispendious.<ref>"At the same time he had received written instructions which the king had given him for execution; nevertheless, after the death of Alexander, it seemed best to the successors not to carry out these plans." Diodorus XVIII,4</ref> | |||
| | mark-title8 = ] 1 October 331 BC | |||
| | mark-description8 = ] | |||
| | label-pos8 = right | |||
| | label-offset-y8 = -5 | |||
| | label9 = Uxians | |||
| The testament, described in Diodorus XVIII, called for military expansion into the Southern and Western Mediterranean, monumental constructions, and the intermixing of Eastern and Western populations. Its most remarkable items were: | |||
| | mark-coord9 = {{coord|32.19|48.25}} | |||
| | mark-title9 = ] December 331 BC | |||
| | mark-description9 = ] | |||
| | label-pos9 = right | |||
| | label-offset-y9 = -10 | |||
| | label10 = Persian Gate | |||
| * The completion of a pyre to ] | |||
| | mark-coord10 = {{coord|30.71|51.6}} | |||
| * The building of "a thousand warships, larger than triremes, in Phoenicia, Syria, Cilicia, and Cyprus for the campaign against the Carthaginians and the other who live along the coast of ] and ] and the adjoining coastal regions as far as ]" | |||
| | mark-title10 = ] 20 January 330 BC | |||
| * The building of a road in northern Africa as far as the ], with ports and shipyards along it. | |||
| | mark-description10 = ] | |||
| * The erection of great temples in ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| | label-pos10 = bottom | |||
| * The construction of a monumental tomb for his father Philip, "to match the greatest of the ]s of Egypt" | |||
| | label-offset-y10 = -5 | |||
| * The establishment of cities and the "transplant of populations from Asia to Europe and in the opposite direction from Europe to Asia, in order to bring the largest continent to common unity and to friendship by means of intermarriage and family ties." (], ''Bibliotheca historia'', XVIII) | |||
| | label11 = Cyropolis | |||
| ==Personal life== | |||
| | mark-coord11 = {{coord|40.28|69.63}} | |||
| {{main|Alexander the Great's personal relationships}} | |||
| | mark-title11 = ] 329 BC<br>] October 329 BC<br>] 327 BC | |||
| Alexander's lifelong companion was ], the son of a Macedonian noble. Hephaistion also held the position of second-in-command of Alexander's forces until his death, which devastated Alexander. Alexander also married two women, ], daughter of a minor noble and ], a Persian princess and the daughter of ] of Persia. Another personage from the court of Darius III with whom he was intimate was ]. His son by ], ], was killed after the death of his father, before he reached adulthood. | |||
| | mark-description11 = ] | |||
| | label-offset-x11 = 2 | |||
| | label-offset-y11 = -2 | |||
| | label12 = Cophen | |||
| Alexander was admired during his lifetime for treating all his lovers humanely. ] has argued that Alexander's love of males took an ethical approach, inspired by the teachings of his mentor, Aristotle. | |||
| | mark-coord12 = {{coord|35.2|72.48}} | |||
| | mark-title12 = ] May 327 BC – March 326 BC | |||
| | mark-description12 = ] | |||
| | label-offset-x12 = 2 | |||
| | label-offset-y12 = -2 | |||
| | label13 = Hydaspes | |||
| ==Legacy and division of the empire== | |||
| | mark-coord13 = {{coord|32.83|73.64}} | |||
| {{main|Diadochi}} | |||
| | mark-title13 = ] May 326 BC | |||
| | mark-description13 = ] | |||
| | label-offset-x13 = 2 | |||
| | label-offset-y13 = -2 | |||
| | label14 = Malavas | |||
| ] inscription.]] | |||
| | mark-coord14 = {{coord|30.7|72.3}} | |||
| | mark-title14 = ] November 326 – February 325 BC | |||
| | mark-description14 = ] | |||
| | label-offset-x14 = 2 | |||
| | label-offset-y14 = -2 | |||
| | label15 = Babylon | |||
| After Alexander's death, in 323 BC, the rule of his Empire was given to Alexander's half-brother ] and Alexander's son ]. However, since Philip was mentally ill and the son of Alexander still a baby, two regents were named in ] (who had received Alexander's ring at this death) and ] (who may have been the one mentioned as successor by Alexander), although Perdiccas quickly managed to take sole power. | |||
| | mark-coord15 = {{coord|32.54|44.42}} | |||
| | mark-title15 = ] 10 or 11 June 323 BC | |||
| | mark-description15 = ] | |||
| | label-offset-x15 = 20 | |||
| | label-offset-y15 = -10 | |||
| }} | |||
| After his victory at the ], ] began the work of establishing himself as ''hēgemṓn'' ({{langx|el|ἡγεμών}}) of a league which according to ] was to wage a campaign against the Persians for the sundry grievances Greece suffered in ] and free the Greek cities of the western coast and islands from Achaemenid rule. In 336 he sent ], ], Andromenes, Attalus, and an army of 10,000 men into ] to make preparations for an invasion.<ref name="PB">{{cite book |last1=Briant |first1=Pierre |title=From Cyrus to Alexander: A History of the Persian Empire |date=2002 |publisher=Eisenbrauns |isbn=978-1-57506-120-7 |page=817 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lxQ9W6F1oSYC&pg=PA817|access-date=21 February 2019}}</ref><ref name="WH">{{cite book |last1=Heckel |first1=Waldemar |title=Who's Who in the Age of Alexander the Great: Prosopography of Alexander's Empire |date=2008 |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |isbn=978-1-4051-5469-7 |page=205 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=NR4Wn9VU8vkC&pg=PT205|access-date=21 February 2019}}</ref> The Greek cities on the western coast of Anatolia revolted until the news arrived that Philip had been murdered and had been succeeded by his young son Alexander. The Macedonians were demoralized by Philip's death and were subsequently defeated near ] by the Achaemenids under the command of the mercenary ].<ref name="PB"/><ref name="WH"/> | |||
| Perdiccas soon eliminated several of his opponents, killing about 30 (Diodorus Siculus), and at the ] named former generals of Alexander as ]s of the various regions of his Empire. In ] Perdiccas was assassinated by his own troops during his conflict with ], leading to the ], in which ] was named as the new regent, and the satrapies again shared between the various generals. From that time, Alexander's officers were focused on the explicit formation of rival monarchies and territorial states. | |||
| Taking over the invasion project of Philip II, Alexander's army crossed the ] in 334 BC with approximately 48,100 soldiers, 6,100 cavalry, and a fleet of 120 ships with crews numbering 38,000{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=192}} drawn from Macedon and various Greek city states, mercenaries, and feudally raised soldiers from ], ], and ].<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=I, 11}}</ref>{{Cref2|i}} He showed his intent to conquer the entirety of the Persian Empire by throwing a spear into Asian soil and saying he accepted Asia as a gift from the gods. This also showed Alexander's eagerness to fight, in contrast to his father's preference for diplomacy.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=192}} | |||
| ] of ] (276-194 BC), incorporating information from the campaigns of Alexander and his successors.<ref></ref>]] | |||
| Ultimately, the conflict was settled after the ] in ] in 301 BC. Alexander's empire was divided at first into four major portions: ] ruled in ], ] in ], ] in ] and Persia, and ] in the ] and ]. ] ruled for a while in ] and ] but was eventually defeated by the other generals at Ipsus (301 BC). Control over Indian territory passed to ], the first ] emperor, who further expanded his dominions after a settlement with Seleucus. | |||
| After an initial victory against Persian forces at the ], Alexander accepted the surrender of the Persian provincial capital and treasury of ]; he then proceeded along the ]n coast, granting autonomy and democracy to the cities. ], held by Achaemenid forces, required a delicate siege operation, with Persian naval forces nearby. Further south, at ], in ], Alexander successfully waged his first large-scale ], eventually forcing his opponents, the mercenary captain ] and the Persian ] of Caria, ], to withdraw by sea.<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=I, 20–23}}</ref> Alexander left the government of Caria to a member of the Hecatomnid dynasty, ], who adopted Alexander.<ref name="Arrian 1976 loc=I, 23">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=I, 23}}</ref> | |||
| By ], the ] states were consolidated, with | |||
| ]'' by ] (1767)]] | |||
| :*The ] in Macedonia and Greece; | |||
| From Halicarnassus, Alexander proceeded into mountainous ] and the ]n plain, asserting control over all coastal cities to deny the Persians naval bases. From Pamphylia onwards, the coast held no major ports and Alexander moved inland. At ], Alexander humbled and did not storm the ]n city.<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=I, 27–28}}</ref> At the ancient Phrygian capital of ], Alexander "undid" the hitherto unsolvable ], a feat said to await the future "king of ]".<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=I, 3}}</ref> According to the story, Alexander proclaimed that it did not matter how the knot was undone, and hacked it apart with his sword.<ref>{{harvnb|Green|2007|p=351}}</ref> | |||
| :*The ] in Mesopotamia and Persia; | |||
| :*The ] in Egypt, Palestine and ] | |||
| ===The Levant and Syria=== | |||
| ] king ] (reigned c. ]-]), wearing an elephant scalp, took over Alexander's legacy in the east by again invading ] in 180 BCE, and establishing the ] (180 BC- 10 AD).]] | |||
| {{Further|Battle of Issus|Siege of Tyre (332 BC)}} | |||
| By the 1st century BC though, most of the Hellenistic territories in the West had been absorbed by the ]. In the East, they had been dramatically reduced by the expansion of the ]. The territories further east seceded to form the ] kingdom (250 BC- 140 BC), which further expanded into India to form the ] (180 BC- 10 AD). | |||
| In spring 333 BC, Alexander crossed the ] into ]. After a long pause due to an illness, he marched on towards Syria. Though outmanoeuvered by Darius's significantly larger army, he marched back to Cilicia, where he defeated Darius at ]. Darius fled the battle, causing his army to collapse, and left behind his wife, his two daughters, his mother ], and a fabulous treasure.<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=I, 11–12}}</ref> He offered a ] that included the lands he had already lost, and a ransom of 10,000 ] for his family. Alexander replied that since he was now king of Asia, it was he alone who decided territorial divisions.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.gutenberg.org/files/46976/46976-h/46976-h.htm|title=The Project Gutenberg eBook of Anabasis of Alexander, by Arrian.|via=Project Gutenberg|access-date=11 January 2018|archive-date=26 March 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180326221313/http://www.gutenberg.org/files/46976/46976-h/46976-h.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> Alexander proceeded to take possession of ], and most of the coast of the ].<ref name="Arrian 1976 loc=I, 23" /> In the following year, 332 BC, he was forced to attack ], which he captured after a long and difficult ].<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=II, 16–24}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Gunther|2007|p=84}}</ref> The men of military age were massacred and the women and children sold into ].<ref>{{harvnb|Sabin|van Wees|Whitby|2007|p=396}}</ref> | |||
| The Ptolemy dynasty persisted in ] until the time of ], best known for her alliances with ] and ], just before the Roman republic officially became the ]. | |||
| ===Egypt=== | |||
| Alexander's conquests also had long term ] effects, with the flourishing of ] throughout the ] and ], and the development of ] in the ]. ] and his successors were tolerant of non-Greek religious practices, and interesting syncretisms developed in the new Greek towns he founded in ]. The first realistic portrayals of the ] appeared at this time; they are reminiscent of Greek statues of ]. Several ] traditions may have been influenced by the ancient Greek religion; the concept of ] is reminiscent of Greek divine heroes, and some ] ceremonial practices (burning incense, gifts of flowers and food placed on altars) are similar to those practiced by the ancient Greeks. ] draws in part on the ideas of Greek ], such as ]. | |||
| {{Further|Siege of Gaza (332 BCE)}} | |||
| ] (written from right to left), {{circa|332 BC}}, Egypt. ].]] | |||
| When Alexander destroyed Tyre, most of the towns on the route to ] quickly capitulated. However, Alexander was met with resistance at ]. The stronghold was heavily fortified and built on a hill, requiring a siege. When "his engineers pointed out to him that because of the height of the mound it would be impossible... this encouraged Alexander all the more to make the attempt".<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=II, 26}}</ref> After three unsuccessful assaults, the stronghold fell, but not before Alexander had received a serious shoulder wound. As in Tyre, men of military age were put to the sword, and the women and children were sold into slavery.<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=II, 26–27}}</ref> | |||
| Among other effects, the ], or ] dialect of ] became the ] through the so-called civilized world. For instance the standard version of the ] used among the jews of the ], especially in Egypt, during the life of ] was the ] ] translation, which was compiled ca 200 BC by seventy-odd scholars under the patronage of the Macedonian ruler ]. Thus many jews from Egypt or Rome would have trouble understanding the teachings of the scholars in the Temple in ] who were using the Hebrew original text and an ] translation, being themselves only aquainted with the Greek version. There has been much speculation on the issue whether Jesus spoke Koine Greek as the Gospel-writers, themselves writing in Greek, don't say anything decisive about the matter. | |||
| Egypt was only one of a large number of territories taken by Alexander from the Persians. After his trip to Siwa, Alexander was crowned in the temple of Ptah at Memphis. It appears that the Egyptian people did not find it disturbing that he was a foreigner – nor that he was absent for virtually his entire reign.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|last=Strudwick|first=Helen|title=The Encyclopedia of Ancient Egypt|publisher=Sterling Publishing Co., Inc.|year=2006|isbn=978-1-4351-4654-9|location=New York|pages=96–97}}</ref> Alexander restored the temples neglected by the Persians and dedicated new monuments to the Egyptian gods. In the temple of Luxor, near Karnak, he built a chapel for the sacred barge. During his brief months in Egypt, he reformed the taxation system on the Greek models and organized the military occupation of the country, but in early 331 BC he left for Asia in pursuit of the Persians.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| ===Influence on Ancient Rome=== | |||
| ], depicting the marriage of Alexander to Barsine (Stateira) in 324 BC. The couple are apparently dressed as Ares and Aphrodite.]] | |||
| Alexander advanced on Egypt in later 332 BC where he was regarded as a liberator.<ref>{{harvnb|Ring|Salkin|Berney|Schellinger|1994|pp=49, 320}}</ref> To legitimize taking power and be recognized as the descendant of the long line of pharaohs, Alexander made sacrifices to the gods at Memphis and went to consult the famous oracle of Amun-Ra at the ] in the ] desert,<ref name=":0" /> at which he was pronounced the son of the deity ].{{sfn|Bosworth|1988|pp=71–74}} Henceforth, Alexander often referred to ] as his true father, and after his death, ], using the ] as a symbol of his divinity.<ref>{{harvnb|Dahmen|2007|pp=10–11}}</ref> The Greeks interpreted this message – one that the gods addressed to all pharaohs – as a prophecy.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| In the late ] and early ], educated Roman citizens used Latin only for legal, political, and ceremonial purposes, and used Greek to discuss philosophy or any other intellectual topic. No Roman wanted to hear it said that his Greek was weak. Throughout the Roman world, the one language spoken everywhere was Alexander's Greek. | |||
| During his stay in Egypt, he founded ], which would become the prosperous capital of the ] after his death.<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=III, 1}}</ref> Control of Egypt passed to Ptolemy I (son of Lagos), the founder of the Ptolemaic Dynasty (305–30 BC) after the death of Alexander.{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=616}} | |||
| Alexander and his exploits were admired by many Romans who wanted to associate themselves with his achievements, although very little is known about Roman-Macedonian diplomatic relations of that time. ] wept in Spain at the mere sight of Alexander's statue and ] rummaged through the closets of conquered nations for Alexander's 260-year-old cloak, which the Roman general then wore as the costume of greatness. However, in his zeal to honor Alexander, ] accidentally broke the nose off the Macedonian's mummified corpse while laying a wreath at the hero's shrine in Alexandria, Egypt. The unbalanced emperor ] later took the dead king's armor from that tomb and donned it for luck. The Macriani, a Roman family that rose to the imperial throne in the 3rd century A.D., always kept images of Alexander on their persons, either stamped into their bracelets and rings or stitched into their garments. Even their dinnerware bore Alexander's face, with the story of the king's life displayed around the rims of special bowls.<ref>Frank L. Holt, ''Alexander the Great and the Mystery of the Elephant Medallions'', University of California Press.</ref> | |||
| ===Assyria and Babylonia=== | |||
| In the summer of 1995, during the archaeological work of the season centered on excavating the remains of domestic architecture of early-Roman date, a statue of Alexander was recovered from the structure,<!-- what structure?! --> which was richly decorated with mosaic and marble pavements and probably was constructed in the 1st century AD and occupied until the 3rd century.<ref></ref> | |||
| {{Further|Battle of Gaugamela}} | |||
| ] (1665)|upright=1]] | |||
| Leaving Egypt in 331 BC, Alexander marched eastward into ] in ] (now northern ]) and defeated Darius again at the ].<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=III 7–15}}; also in a {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170224083355/http://www.livius.org/aj-al/alexander/alexander_t40.html |date=24 February 2017 }}</ref> Darius once more fled the field, and Alexander chased him as far as ]. Gaugamela would be the final and decisive encounter between the two.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Hanson |first=Victor Davis |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XGr16-CxpH8C |title=Carnage and Culture: Landmark Battles in the Rise to Western Power |year= 2007 |publisher=Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group |isbn=978-0-307-42518-8|access-date=5 September 2020}}</ref> Darius fled over the mountains to ] (modern ]) while Alexander captured ].<ref name="AIII16" /> | |||
| ] say that "the king of the world, Alexander" sent his scouts with a message to the people of Babylon before entering the city: "I shall not enter your houses".<ref>{{cite web| url = https://www.livius.org/sources/content/oriental-varia/a-contemporary-account-of-the-battle-of-gaugamela/| title = a contemporary account of the battle of Gaugamela| access-date = 16 July 2021| archive-date = 12 August 2021| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210812155458/https://www.livius.org/sources/content/oriental-varia/a-contemporary-account-of-the-battle-of-gaugamela/| url-status = live}}</ref> | |||
| ==General timeline== | |||
| {{atg-timeline}} | |||
| * | |||
| ===Persia=== | |||
| ==Alexander's character== | |||
| {{Further|Battle of the Persian Gate}} | |||
| ], capital of ].]] | |||
| ] in modern-day ]; the road was built in the 1990s.]] | |||
| From Babylon, Alexander went to ], one of the ] capitals, and captured its treasury.<ref name="AIII16" /> He sent the bulk of his army to the Persian ceremonial capital of ] via the Persian ]. Alexander himself took selected troops on the direct route to the city. He then stormed the pass of the ] (in the modern ]) which had been blocked by a Persian army under ] and then hurried to Persepolis before its garrison could loot the treasury.<ref>{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc=III, 18}}</ref> | |||
| Modern opinion on Alexander has run the gamut from the idea that he believed he was on a divinely-inspired mission to unite the ], to the view that he was a ]c bent on ]. Such views tend to be ], and the sources allow for a variety of interpretations. Much about Alexander's personality and aims remains enigmatic. There were no disinterested commentators in Alexander's own time or soon afterward, so all accounts need to be read with skepticism. | |||
| On entering Persepolis, Alexander allowed his troops to loot the city for several days.<ref>{{harvnb|Foreman|2004|page=152}}</ref> Alexander stayed in Persepolis for five months.{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=121}} During his stay, a fire broke out in the eastern palace of ] and spread to the rest of the city. Possible causes include a drunken accident or deliberate revenge for the burning of the ] during the ] by Xerxes;{{sfn|Hammond|1983|pp=72–73}} Plutarch and ] allege that Alexander's companion, the ] ], instigated and started the fire. Even as he watched the city burn, Alexander immediately began to regret his decision.{{Sfn |Yenne|2010 | page = }}<ref>{{cite book |last1=Freeman |first1=Philip |title=Alexander the Great |date=2011 |publisher=Simon & Schuster Paperbacks |location=New York |isbn=978-1-4391-9328-0 |page=213 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=v550aeZcGowC&pg=PA213 |access-date=21 November 2017}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Briant |first1=Pierre |title=Alexander the Great and His Empire: A Short Introduction |date=2010 |orig-year=1974 |publisher=Princeton University Press |location=Princeton, NJ |isbn=978-0-691-15445-9 |page=109 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6wl0xMQCW40C&pg=PA109 |access-date=21 November 2017}}</ref> ] claims that he ordered his men to put out the fires{{Sfn |Yenne|2010 | page = }} but the flames had already spread to most of the city.{{Sfn |Yenne|2010 | page = }} ] claims that Alexander did not regret his decision until the next morning.{{Sfn |Yenne|2010 | page = }} Plutarch recounts an anecdote in which Alexander pauses and talks to a fallen statue of Xerxes as if it were a live person: | |||
| Alexander is remembered as a legendary hero in ] and much of both ] and ], where he is known as '''Iskander''' or '''Iskandar Zulkarnain'''. To ], on the other hand, he is remembered as the destroyer of their first great empire and as the destroyer of ]. Ancient sources are generally written with an agenda of either glorifying or denigrating the man, making it difficult to evaluate his actual character. Most refer to a growing instability and megalomania in the years following Gaugamela, but it has been suggested that this simply reflects the Greek ] of an orientalizing king. The murder of his friend ], which Alexander deeply and immediately regretted, is often cited as a sign of his paranoia, as is his execution of Philotas and his general Parmenion for failure to pass along details of a plot against him. There is also the view that this may have been more prudence than paranoia. | |||
| {{blockquote|Shall I pass by and leave you lying there because of the expeditions you led against Greece, or shall I set you up again because of your magnanimity and your virtues in other respects?<ref>{{cite book |title=Alexander the Great: The Invisible Enemy: A Biography |first=John Maxwell |last=O'Brien |publisher=Psychology Press |date=1994 |page= |isbn=978-0-415-10617-7 |url=https://archive.org/details/alexandergreatin00obri_0/page/104}}</ref>}} | |||
| Modern Alexandrists continue to debate these same issues, among others, in modern times. One unresolved topic involves whether Alexander was actually attempting to better the world by his conquests, or whether his purpose was primarily to rule the world. | |||
| ===Fall of the Persian Empire and the East=== | |||
| Partially in response to the ubiquity of positive portrayals of Alexander, an alternate character is sometimes presented which emphasizes some of Alexander's negative aspects. Some proponents of this view cite the destructions of ], ], ], and ] as examples of atrocities, and argue that Alexander preferred to fight rather than negotiate. It is further claimed, in response to the view that Alexander was generally tolerant of the cultures of those whom he conquered, that his attempts at cultural fusion were severely practical and that he never actually admired Persian art or culture. To this way of thinking, Alexander was, first and foremost, a general rather than a statesman. | |||
| ] dated to the seventh year of Alexander's reign (324 BC), bearing the first known use of the "Alexandros" form of his name, ]<ref>{{Cite web|title=A Long List of Supplies Disbursed|url=https://www.khalilicollections.org/collections/aramaic-documents/khalili-collection-aramaic-documents-a-long-list-of-supplies-disbursed-ia17/|access-date=6 January 2021|website=Khalili Collections|archive-date=15 August 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190815095632/https://www.khalilicollections.org/collections/aramaic-documents/khalili-collection-aramaic-documents-a-long-list-of-supplies-disbursed-ia17/|url-status=live}}</ref>]] | |||
| Alexander then chased Darius, first into Media, and then Parthia.{{Sfn |Arrian|1976|loc= III, 19–20}} The Persian king no longer controlled his own destiny, and was taken prisoner by ], his ]n satrap and kinsman.{{Sfn |Arrian|1976| loc= III, 21}} As Alexander approached, Bessus had his men fatally stab the Great King and then declared himself Darius's successor as Artaxerxes V, before retreating into Central Asia to launch a ] campaign against Alexander.{{Sfn |Arrian|1976|loc=III, 21, 25}} Alexander buried Darius's remains next to his Achaemenid predecessors in a regal funeral.{{Sfn | Arrian| 1976 | loc = III, 22}} He claimed that, while dying, Darius had named him as his successor to the Achaemenid throne.{{sfn|Gergel|2004|p=81}} The Achaemenid Empire is normally considered to have fallen with Darius.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.livius.org/aj-al/alexander/alexander10.html |title=The end of Persia |publisher=Livius |access-date=16 November 2009 |archive-date=16 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160316211044/http://www.livius.org/aj-al/alexander/alexander10.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> However, as basic forms of community life and the general structure of government were maintained and resuscitated by Alexander under his own rule, he, in the words of the ] ] "may therefore be considered to have acted in many ways as the ''last of the Achaemenids''."{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} | |||
| Alexander viewed Bessus as a usurper and set out to defeat him. This campaign, initially against Bessus, turned into a grand tour of central Asia. Alexander founded a series of new cities, all called Alexandria, including modern ] in Afghanistan, and ] ("The Furthest") in modern ]. The campaign took Alexander through ], ], ] (West Afghanistan), ], ] (South and Central Afghanistan), ] (North and Central Afghanistan), and ].{{Sfn |Arrian|1976|loc=III, 23–25, 27–30; IV, 1–7}} | |||
| Alexander's character also suffers from the interpretation of historians who themselves are subject to the bias and idealisms of their own time. Good examples are ], who wrote during the late 19th century and early 20th century, and who saw Alexander in an extremely good light, and ], who wrote after ] and for whom Alexander did little that was not inherently selfish or ambition-driven. Tarn wrote in an age where world conquest and warrior-heroes were acceptable, even encouraged, whereas Green wrote with the backdrop of ] and ]s. | |||
| In 329 BC, ], who held an undefined position in the satrapy of Sogdiana, betrayed Bessus to ], one of Alexander's trusted companions, and Bessus was executed.{{Sfn |Arrian|1976|loc= III, 30}} However, at some point later when Alexander was on the ] dealing with an incursion by a horse nomad army, Spitamenes raised Sogdiana in revolt. Alexander personally defeated the Scythians at the ] and immediately launched a campaign against Spitamenes, defeating him in the Battle of Gabai. After the defeat, Spitamenes was killed by his own men, who then sued for peace.{{Sfn |Arrian|1976|loc = IV, 5–6, 16–17}} | |||
| ==Greek and Latin sources== | |||
| Apart from the cuneiform evidence from Babylonia that is now being disclosed, the Greek and Latin sources for Alexander's life are, from the perspective of ancient history, relatively numerous. Alexander himself left only a few inscriptions and some letter-fragments of dubious authenticity, but a large number of his contemporaries wrote full accounts. The key contemporary historians are considered ], his general ], ], ] and ]. Another influential account was penned by ], who, while not a direct witness of Alexander's expedition, used the sources which had just been published. His work was to be the backbone of that of ], who heavily influenced many surviving historians. Unfortunately, all these works were lost. Instead, the modern historian must rely on authors who used these and other early sources. | |||
| ===Problems and plots=== | |||
| The five main accounts are by Arrian, Curtius, Plutarch, Diodorus, and Justin. | |||
| ]'', by ] (1898–1899)]] | |||
| * '']'' (''The Campaigns of Alexander'' in Greek) by the Greek historian ] of ], writing in the 2nd century AD, and based largely on Ptolemy and, to a lesser extent, Aristobulus and Nearchus. It is considered generally the most trustworthy source. | |||
| * ''Historiae Alexandri Magni'', a biography of Alexander in ten books, of which the last eight survive, by the Roman historian ], written in the 1st century AD, and based largely on Cleitarchus through the mediation of Timagenes, with some material probably from Ptolemy; | |||
| * ''Life of Alexander'' (see '']'') and two orations ''On the Fortune or the Virtue of Alexander the Great'' (see '']''), by the Greek historian and biographer ] of ] in the second century, based largely on Aristobulus and especially Cleitarchus. | |||
| * ''Bibliotheca historia'' (''Library of world history''), written in Greek by the ] historian ], from which Book 17 relates the conquests of Alexander, based almost entirely on Timagenes's work. The books immediately before and after, on Philip and Alexander's "Successors," throw light on Alexander's reign. | |||
| * The ''Epitome of the Philippic History of Pompeius Trogus'' by ], which contains factual errors and is highly compressed. It is difficult in this case to understand the source, since we only have an epitome, but it is thought that also ] may have limited himself to use Timagenes for his Latin history. | |||
| During this time, Alexander adopted some elements of Persian dress and customs at his court, notably the custom of '']'', either a symbolic kissing of the hand, or prostration on the ground, that Persians showed to their social superiors.<ref name="AVII11" /> This was one aspect of Alexander's broad strategy aimed at securing the aid and support of the Iranian upper classes.{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} The Greeks however regarded the gesture of ''proskynesis'' as the province of ] and believed that Alexander meant to deify himself by requiring it. This cost him the sympathies of many of his countrymen, and he eventually abandoned it.{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=111}} | |||
| To these five main sources some like to add the '']'', an anonymous late Latin work that narrates Alexander's campaigns from ] to India. Much is also recounted incidentally in other authors, including ], ], ], ], and others. | |||
| During the long rule of the Achaemenids, the elite positions in many segments of the empire including the central government, the army, and the many satrapies were specifically reserved for ] and to a major degree, ] noblemen.{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} The latter were in many cases additionally connected through marriage alliances with the royal Achaemenid family.{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} This created a problem for Alexander as to whether he had to make use of the various segments and people that had given the empire its solidity and unity for a lengthy period of time.{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} ] explains that Alexander realized that it was insufficient to merely exploit the internal contradictions within the imperial system as in Asia Minor, Babylonia or Egypt; he also had to (re)create a central government with or without the support of the Iranians.{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} As early as 334 BC he demonstrated awareness of this, when he challenged incumbent King Darius III "by appropriating the main elements of the Achaemenid monarchy's ideology, particularly the theme of the king who protects the lands and the peasants".{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} Alexander wrote a letter in 332 BC to Darius III, wherein he argued that he was worthier than Darius "to succeed to the Achaemenid throne".{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} However, Alexander's eventual decision to burn the Achaemenid palace at ] in conjunction with the major rejection and opposition of the "entire Persian people" made it impracticable for him to pose himself as Darius' legitimate successor.{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} Against Bessus (Artaxerxes V) however, Briant adds, Alexander reasserted "his claim to legitimacy as the avenger of Darius III".{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} | |||
| The "problem of the sources" is the main concern (and chief delight) of Alexander-historians. In effect, each presents a different "Alexander", with details to suit. Arrian is mostly interested in the military aspects, while Curtius veers to a more private and darker Alexander. Plutarch can't resist a good story, light or dark. All, with the possible exception of Arrian, include a considerable level of fantasy, prompting Strabo to remark, "All who wrote about Alexander preferred the marvelous to the true." Nevertheless, the sources tell us much, and leave much to our interpretation and imagination. Perhaps Arrian's words are most appropriate: | |||
| A plot against his life was revealed, and one of his officers, ], was executed for failing to alert Alexander. The death of the son necessitated the death of the father, and thus ], who had been charged with guarding the treasury at ], was assassinated at Alexander's command, to prevent attempts at vengeance. Most infamously, Alexander personally killed the man who had saved his life at Granicus, ], during a violent drunken altercation at ] (modern day ] in ]), in which Cleitus accused Alexander of several judgmental mistakes and especially of having forgotten the Macedonian ways in favour of a corrupt oriental lifestyle.{{sfn|Gergel|2004|p=99}} | |||
| :One account says that Hephaestion laid a wreath on the tomb of Patroclus; another that Alexander laid one on the tomb of Achilles, calling him a lucky man, in that he had Homer to proclaim his deeds and preserve his memory. And well might Alexander envy Achilles this piece of good fortune; for in his own case there was no equivalent: his one failure, the single break, as it were, in the long chain of his successes, was that he had no worthy chronicler to tell the world of his exploits. | |||
| Later, in the Central Asian campaign, a second plot against his life was revealed. This one was instigated by his own royal ]. His official historian, ] of ], was implicated in the plot, and in the '']'', ] states that Callisthenes and the pages were then tortured on the ] as punishment, and likely died soon after.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://archive.org/details/cu31924026460752|title=The Anabasis of Alexander; or, The history of the wars and conquests of Alexander the Great. Literally translated, with a commentary, from the Greek of Arrian, the Nicomedian|date=18 January 1884|publisher=London, Hodder and Stoughton|via=Internet Archive}}</ref> It remains unclear if Callisthenes was actually involved in the plot, for prior to his accusation he had fallen out of favour by leading the opposition to the attempt to introduce proskynesis.<ref>{{harvnb|Heckel|Tritle|2009|pp=47–48}}</ref> | |||
| ==Alexander's legend== | |||
| Alexander was a legend in his own time. His court historian Callisthenes portrayed the sea in ] as drawing back from him in ]. Writing after Alexander's death, another participant, ], went so far as to invent a ] between Alexander and ], queen of the mythical ]. When Onesicritus read this passage to his patron, Alexander's general and later King ] reportedly quipped, "I wonder where I was at the time." | |||
| ===Macedon in Alexander's absence=== | |||
| In the first centuries after Alexander's death, probably in Alexandria, a quantity of the more legendary material coalesced into a text known as the '']'', later falsely ascribed to the historian Callisthenes and therefore known as ''Pseudo-Callisthenes''. This text underwent numerous expansions and revisions throughout Antiquity and the ], exhibiting a plasticity unseen in "higher" literary forms. Latin and ] translations were made in Late Antiquity. From these, versions were developed in all the major languages of ] and the ], including ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. The "Romance" is regarded by many Western scholars as the source of the ] (] ''The Cave''). It is the source of many incidents in ]'s "]". A ]ian version is also extant. | |||
| When Alexander set out for Asia, he left his general ], an experienced military and political leader, and part of Philip II's "Old Guard", in charge of Macedon.<ref name="Roisman 2010 199" /> Alexander's sacking of Thebes ensured that Greece remained quiet during his absence.<ref name="Roisman 2010 199" /> The one exception was a call to arms by Spartan king ] in 331 BC, whom Antipater defeated and killed in the ].<ref name="Roisman 2010 199" /> Antipater referred the Spartans' punishment to the League of Corinth, which then deferred to Alexander, who chose to pardon them.<ref>{{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=201}}</ref> There was also considerable friction between Antipater and Olympias, and each complained to Alexander about the other.<ref>{{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=202}}</ref> | |||
| In general, Greece enjoyed a period of peace and prosperity during Alexander's campaign in Asia.<ref>{{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=203}}</ref> Alexander sent back vast sums from his conquest, which stimulated the economy and increased trade across his empire.<ref>{{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=205}}</ref> However, Alexander's constant demands for troops and the migration of Macedonians throughout his empire depleted Macedon's strength, greatly weakening it in the years after Alexander, and ultimately led to its subjugation by Rome after the ] (171–168 BC).{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=186}} | |||
| Alexander is also a character of Greek folklore (and other regions), as the protagonist of 'apocryphal' tales of bravery. A maritime legend says that his sister is a ] and asks the sailors if her brother is still alive. The unsuspecting sailor who answers truthfully arises the mermaid's wrath and his boat perishes in the waves; a sailor mindful of the circumstances will answer "''He lives and reigns, and conquers the world''", and the sea about his boat will immediately calm. Alexander is also a character of a standard play in the ] repertory, "Alexander the Great and the Accursed Serpent". | |||
| === Coinage === | |||
| Some believe that, excepting certain religious texts, it is the most widely-read work of pre-modern times. | |||
| ] of Alexander the Great struck by ] or his successor ], both former '']'' (bodyguards) of Alexander, when they held the position of ] of ] in the lifetime of Alexander, {{circa|333–327 BC}}. The obverse shows ], ancestor of the Macedonian royal line and the reverse shows a seated ] Aëtophoros.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cngcoins.com/Coin.aspx?CoinID=368240|title= eAuction 430. KINGS of MACEDON. Alexander III 'the Great'. 336–323 BC. AR Tetradrachm (25mm, 17.15 g, 1h). Tarsos mint. Struck under Balakros or Menes, circa 333–327 BC.|website=CNG |access-date=17 February 2019|archive-date=18 February 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190218081840/https://www.cngcoins.com/Coin.aspx?CoinID=368240|url-status=live}}</ref>]] | |||
| The conquest by ] of ], and then of the island of ] between 356 and 342 BC brought rich gold and silver mines under Macedonian control.<ref>], Anabasis VII, 3</ref> | |||
| ===Alexander in the Qur'an=== | |||
| {{main|Alexander in the Qur'an (Theory)}} | |||
| Alexander the Great sometimes is identified in Persian and Arabic traditions sources as ], Arabic for the "Two-Horned One", possibly a reference to the appearance of a horn-headed figure that appears on coins minted during his rule and later imitated in ancient Middle Eastern coinage. If this theory is followed, accounts of the Alexander legend, can be found in ] if Alexander is the ] mentioned in the Quran. | |||
| Alexander appears to have introduced a new coinage in ] in ], after the Battle of Issus in 333 BC, which went on to become the main coinage of the empire.<ref name="LE RIDER 2003, p153-214">G. LE RIDER, Alexandre le Grand : Monnaie, finances et politique, Chapitre V, "Histoire", PUF, 2003, p153-214</ref> Alexander minted gold ]s, silver ]s and ]s, and various fractional ]. The types of these coins remained constant in his empire.<!-- But this is incorrect, because the minting of Philippeioi continued throughout Alexander's reign – see Le Rider.--> The gold series had the head of ] on the obverse and a winged ] (]) on the reverse.<ref>REBUFFAT Françoise, La monnaie dans l'Antiquité, Picard, 1996 .p204</ref> The silver coinage had a beardless head of ] wearing a lionskin headdress on the obverse and Zeus aetophoros ('eagle bearer') enthroned with a scepter in his left hand, on the reverse.<ref>Gerin, Dominique; Grandjean, Catherine; Amandry, Michel; De Callatay. ''La monnaie grecque'', "L'Antiquité : une histoire", Ellipse, 2001. pp. 117–119.</ref> There are both Greek and non-Greek aspects to this design. Heracles and ] were important deities for the Macedonians, with Heracles considered to be the ancestor of the Temenid dynasty and Zeus the patron of the main Macedonian sanctuary, ].<ref name="LE RIDER 2003, p153-214"/> The lion was also the symbolic animal of the Anatolian god ], worshipped at ].<ref name="LE RIDER 2003, p153-214"/> The reverse design of Alexander's tetradrachms is closely modelled on the depiction of the god ] (Baal of Tarsus), on the silver staters minted at Tarsus by the Persian satrap ] before Alexander's conquest.<ref name="LE RIDER 2003, p153-214"/> | |||
| It can be found in the Persian tradition too if the theory is accurate. The same traditions from the Pseudo-Callisthenes were combined in Persia with ] Persian ideas about Alexander in the ]. In this tradition, Alexander built a wall of iron and melted copper in which ] are confined. | |||
| Alexander did not attempt to impose uniform imperial coinage throughout his new conquests. Persian coins continued to circulate in all the ]ies of the empire.<ref>BRIANT Pierre, Alexandre Le Grand, "Que sais-je ?", PUF, 2011.</ref> | |||
| Some Muslim scholars disagree that Alexander was ]. There are actually some theories that ] was a Persian King with a vast Empire as well, possibly King ]. The reason being is Dhul-Qarnayn is described in the Holy Quran as a monotheist believer who worshipped Allah (God). Taking this into consideration this removes Alexander as a candidate for ] as it is well known that Alexander was a man who followed the Hellenistic traditions of Greece making him a polytheist not a monotheist. | |||
| ==Indian campaign== | |||
| ===Alexander in ancient and modern culture=== | |||
| {{ |
{{Main|Indian campaign of Alexander the Great}} | ||
| Around seventy towns or outposts are claimed to have been founded by Alexander.<ref></ref> ] credits Alexander with planning cities on a ].<ref>], ''Bibliotheca historia'', vol. 8</ref> | |||
| ===Forays into the Indian subcontinent=== | |||
| Alexander has figured in works of both "high" and popular culture from his own era to the modern day. | |||
| ] | |||
| After the death of ] and his marriage to Roxana (Raoxshna in ]) to cement relations with his new satrapies, Alexander turned to the ]. He invited the ] of the former satrapy of ] (a region presently straddling eastern Afghanistan and northern ]), to come to him and submit to his authority. ] (Indian name ]), the ruler of ], whose kingdom extended from the ] to the ] (Jhelum), complied, but the chieftains of some hill clans, including the ] and ] sections of the ] (known in Indian texts also as Ashvayanas and Ashvakayanas), refused to submit.{{sfn|Tripathi|1999|pp=118–21}} ] hastened to relieve Alexander of his apprehension and met him with valuable presents, placing himself and all his forces at his disposal. Alexander not only returned Ambhi his title and the gifts but he also presented him with a wardrobe of "Persian robes, gold and silver ornaments, 30 horses and 1,000 talents in gold". Alexander was emboldened to divide his forces, and Ambhi assisted Hephaestion and Perdiccas in constructing a bridge over the Indus where it bends at ],<ref>Lane Fox 1973</ref> supplied their troops with provisions, and he received Alexander and his whole army in his capital city of Taxila, with every demonstration of friendship and the most liberal hospitality. | |||
| ==Footnotes== | |||
| ] Attacking the Centre in the ]'' by André Castaigne (1898–1899)]] | |||
| <div class="references-small"> | |||
| <references/> | |||
| </div> | |||
| On the subsequent advance of the Macedonian king, Taxiles accompanied him with a force of 5,000 men and took part in the ]. After that victory, he was sent by Alexander in pursuit of ], to whom he was charged to offer favourable terms, but narrowly escaped losing his life at the hands of his old enemy. Subsequently, the two rivals were reconciled by the personal mediation of Alexander; Taxiles contributed zealously to the equipment of the fleet on the Hydaspes and was entrusted by Alexander with the government of the whole territory between that river and the Indus. A considerable accession of power was granted him after the death of ], son of Machatas, and he was allowed to retain his authority at the death of Alexander himself (323 BC), as well as in the subsequent partition of the provinces at ], 321 BC. | |||
| ==References== | |||
| *], ''The Campaigns of Alexander'', English translation by ] (1971, first published 1958) ] published by the Penguin Group, London ISBN 0-14-044253-7. | |||
| * ] ''Alexander of Macedon: 356–323 B.C. A Historical Biography.'' Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1992. ISBN 0-520-07166-2. | |||
| * ], ''Alexander the Great'', London (Allen Lane) 1973, ISBN 0-86007-707-1. | |||
| *Lane Fox, Robin, ''The Search for Alexander'', Little Brown & Co. Boston, 1st edition (October 1980). ISBN 0-316-29108-0. | |||
| * ]. ''The Nature of Alexander'', 1st American edition (November 12, 1979), ] ISBN 0-394-73825-X. | |||
| * Wilcken, Ulrich, ''Alexander the Great'', W. W. Norton & Company; Reissue edition (March 1997). ISBN 0-393-00381-7. | |||
| * Worthington, Ian, ''Alexander the Great'', Routledge; 1st edition (February 1, 2003). ISBN 0-415-29187-9. | |||
| In the winter of 327/326 BC, Alexander personally led a campaign against the Aspasioi of the ], the Guraeans of the ], and the Assakenoi of the ] and ].<ref>{{harvnb|Narain|1965|pp=155–65}}</ref> A fierce contest ensued with the Aspasioi in which Alexander was wounded in the shoulder by a dart, but eventually the Aspasioi lost. Alexander then faced the Assakenoi who fought against him from the strongholds of Massaga, Ora, and ].{{sfn|Tripathi|1999|pp=118–21}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| * ''Alexander the Great in Fact and Fiction'', edited by A.B. Bosworth, E.J. Baynham. New York: Oxford University Press (USA), 2002 (Paperback, ISBN 0-19-925275-0). | |||
| * Baynham, Elizabeth. ''Alexander the Great: The Unique History of Quintus Curtius''. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 1998 (hardcover, ISBN 0-472-10858-1); 2004 (paperback, ISBN 0-472-03081-7). | |||
| * ''Brill's Companion to Alexander the Great'' by Joseph Roisman (editor). Leiden: Brill Academic Publishers, 2003. | |||
| * ]. ''Alexander the Great: The Hunt for a New Past''. Woodstock, NY; New York: The Overlook Press, 2004 (hardcover, ISBN 1-58567-565-2); London: PanMacmillan, 2004 (hardcover, ISBN 1-4050-3292-8); New York: Vintage, 2005 (paperback, ISBN 1-4000-7919-5). | |||
| * Dahmen, Karsten. ''The Legend of Alexander the Great on Greek and Roman Coins''. Oxford: Routledge, 2006 (hardcover, ISBN 0-415-39451-1; paperback, ISBN 0-415-39452-X). | |||
| * De Santis, Marc G. “At The Crossroads of Conquest.” '']'', December 2001. Volume 3, No. 3: 46–55, 97 (Alexander the Great, his military, his strategy at the Battle of Gaugamela and his defeat of Darius making Alexander the King of Kings). | |||
| * ]; ''A Military History of the Western World: From the earliest times to the Battle of Lepanto''; New York: Da Capo Press, Inc., 1987 and 1988. ISBN 0-306-80304-6 | |||
| * Gergel, Tania Editor ''Alexander the Great'' (2004) published by the ], London ISBN 0-14-200140-6 Brief collection of ancient accounts translated into English | |||
| * Larsen, Jakob A. O. "Alexander at the Oracle of Ammon", ''Classical Philology'', Vol. 27, No. 1. (Jan., 1932), pp. 70–75. | |||
| * Pearson, Lionel Ignacius Cusack. ''The Lost Histories of Alexander the Great''. Chicago Ridge, IL: Ares Publishers, 2004 (paperback, ISBN 0-89005-590-4). | |||
| * Thomas, Carol G. ''Alexander the Great in his World (Blackwell Ancient Lives)''. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers, 2006 (hardcover, ISBN 0631232451; paperback, ISBN 063123246X). | |||
| The fort of Massaga was reduced after days of bloody fighting in which Alexander was seriously wounded in the ankle. According to ], "Not only did Alexander slaughter the entire population of Massaga, but also did he reduce its buildings to rubble."<ref>{{cite book |last=McCrindle |first=J. W. |chapter=Curtius |title=History of Punjab |volume=I |year=1997 |publisher=] |location=Patiala |editor1-first=Fauja |editor1-last=Singh |editor2-first=L. M. |editor2-last=Joshi |page=229}}</ref> A similar slaughter followed at Ora. In the aftermath of Massaga and Ora, numerous Assakenians fled to the fortress of ]. Alexander followed close behind and captured the strategic hill-fort after four bloody days.{{sfn|Tripathi|1999|pp=118–21}} | |||
| ===Non-Greek/Latin perspectives=== | |||
| * A. Shapur Shahbazi, "Iranians and Alexander", ''American Journal of Ancient History'' n.s. 2 (2003), 5–38: the Persian side of the story. | |||
| * R.J. van der Spek, "Darius III, Alexander the Great and Babylonian scholarship" in: ''Achaemenid History'' 13 (2003), 289–346: an overview of several Babylonian sources | |||
| * Two chapters of ]'s Dutch book ''Alexander de Grote'', which uses the cuneiform sources, are available in translation. In , he argues that at Gaugamela, Alexander attacked a Persian army that was looking for an excuse to run away; and in , he offers a Babylonian perspective on Alexander's final days. | |||
| ] surrenders to Alexander'']] | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| After Aornos, Alexander crossed the Indus and won an epic battle against King ], who ruled a region lying between the Hydaspes and the ] (Chenab), in what is now the ], in the Battle of the Hydaspes in 326 BC.{{sfn|Tripathi|1999|pp=124–25}} Alexander was impressed by Porus's bravery and made him an ally. He appointed Porus as satrap, and added to Porus's territory land that he did not previously own, towards the south-east, up to the Hyphasis (]).<ref name="ReferenceA">p. xl, Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, J, Woronoff & I. Spence</ref><ref name="ReferenceB">Arrian Anabasis of Alexander, V.29.2</ref> Choosing a local helped him control these lands that were distant from Greece.{{sfn|Tripathi|1999|pp=126–27}} Alexander founded two cities on opposite sides of the ] river, naming one ], in honour of his horse, who died around this time.{{sfn|Gergel|2004|p=120}} The other was ] (Victory), thought to be located at the site of modern-day ].<ref>{{harvnb|Worthington|2003|p=175}}</ref> ] in the '']'' writes that in the army of Porus, there was an elephant who fought bravely against Alexander's army, and Alexander dedicated it to the ] (Sun) and named it Ajax because he thought that such a great animal deserved a great name. The elephant had gold rings around its tusks and an inscription was on them written in Greek: "Alexander the son of Zeus dedicates Ajax to the Helios" (ΑΛΕΞΑΝΔΡΟΣ Ο ΔΙΟΣ ΤΟΝ ΑΙΑΝΤΑ ΤΩΙ ΗΛΙΩΙ).<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=urn:cts:greekLit:tlg0638.tlg001.perseus-grc1:2.12|title=Philostratus the Athenian, Vita Apollonii, book 2, chapter 12|website=perseus.tufts.edu|access-date=20 February 2021|archive-date=25 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210225081128/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=urn:cts:greekLit:tlg0638.tlg001.perseus-grc1:2.12|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| {{commons|Alexander the Great}} | |||
| {{wiktionary}} | |||
| {{wikiquote}} | |||
| '''Primary Sources''' | |||
| * from Livius.org | |||
| * Alexander the Great forum, articles, and referenced information. | |||
| * Wiki Classical Dictionary, and | |||
| *{{en icon}} | |||
| *{{en icon}} | |||
| *{{en icon}} | |||
| *{{la icon}} | |||
| * from Alexander the Great on the Web: 1,000 resources about Alexander the Great | |||
| * | |||
| ===Revolt of the Hellenic army=== | |||
| '''Projects''' | |||
| ] and the ] of the ], in relation to Alexander's Empire and neighbours]] | |||
| * , a comprehensive directory of some 1,000 sites | |||
| * articles on Alexander by Jona Lendering | |||
| * | |||
| * , a Mediawiki based project, with stricter guidelines and editors | |||
| * , a site dedicated to Alexander. Features Articles about Alexander, his life, armies, mysteries surrounding his death, and the Hellenistic Period that came after this great Hellenic Leader. | |||
| * from his perspective; broken down into 33 segments, covering his childhood, education, upbringing, influences, strategy, leadership, friendship as well as the numerous clashes he had against Darius of the Persian Empire. | |||
| * , a site depicting Alexander's coins and later coins featuring Alexander's image | |||
| * , entry in historical sourcebook by Mahlon H. Smith | |||
| East of Porus's kingdom, near the ], was the ] of ], and further east, the ] of ] region of the Indian subcontinent. Fearing the prospect of facing other large armies and exhausted by years of campaigning, Alexander's army mutinied at the ] (Beas), refusing to march farther east.{{sfn|Kosmin|2014|p=34}} This river thus marks the easternmost extent of Alexander's conquests.{{sfn|Tripathi|1999|pp=129–30}} | |||
| '''Narratives''' | |||
| * , a project by John J. Popovic | |||
| {{blockquote|As for the Macedonians, however, their struggle with Porus blunted their courage and stayed their further advance into India. For having had all they could do to repulse an enemy who mustered only twenty thousand infantry and two thousand horse, they violently opposed Alexander when he insisted on crossing the river Ganges also, the width of which, as they learned, was {{convert|32|furlong|km|1|spell=in|disp=sqbr}}, its depth {{convert|100|fathom|m|spell=in|disp=sqbr}}, while its banks on the further side were covered with multitudes of ] and horsemen and elephants. For they were told that the kings of the Ganderites and Praesii were awaiting them with eighty thousand horsemen, two hundred thousand footmen, eight thousand chariots, and six thousand ]s.<ref name="PA62" />}} | |||
| '''Discussion''' | |||
| * | |||
| * , a forum for Alexander the Great and the history surrounding him. | |||
| Alexander tried to persuade his soldiers to march farther, but his general ] pleaded with him to change his opinion and return; the men, he said, "longed to again see their parents, their wives and children, their homeland". Alexander eventually agreed and turned south, marching along the ]. Along the way his army conquered the ] (in modern-day ]) and other Indian tribes; while besieging the Mallian citadel, Alexander suffered a near-fatal injury when an arrow penetrated his armor and entered his lung.{{sfn|Tripathi|1999|pp=137–38}}<ref>{{Cite book |last=Dodge |first=Theodore Ayrault |url=https://catalog.hathitrust.org/Record/100769753 |title=Alexander |series=Great captains |publisher=] |year=1890 |volume=2 |pages=604–605 |author-link=Theodore Ayrault Dodge}}</ref> | |||
| '''Bibliography''' | |||
| * by Waldemar Heckel (please note that Heckel ignores the Babylonian sources and publications on these sources; cf. ) | |||
| Alexander sent much of his army to ] (modern southern ]) with general ], and commissioned a fleet to explore the ] shore under his admiral ], while he led the rest back to Persia through the more difficult southern route along the ] and ].{{sfn|Tripathi|1999|p=141}} Alexander reached Susa in 324 BC, but not before losing many men to the harsh desert.<ref>{{harvnb|Morkot|1996|p=9}}</ref> | |||
| {{start}} | |||
| {{s-hou|]||356||323}} | |||
| ==Last years in Persia== | |||
| {{s-bef|before=]}} | |||
| ]; possibly meaning his ] ]]] | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=336–323 BC}} | |||
| Discovering that many of his ]s and military governors had misbehaved in his absence, Alexander executed several of them as examples on his way to ].<ref name="AVI27" /><ref name="AVII4" /> As a gesture of thanks, he paid off the debts of his soldiers, and announced that he would send over-aged and disabled veterans back to Macedon, led by Craterus. His troops misunderstood his intention and mutinied at the town of ]. They refused to be sent away and criticized his adoption of Persian customs and dress and the introduction of Persian officers and soldiers into Macedonian units.<ref name="Worthington 2003 307">{{harvnb|Worthington|2003|pp=307–08}}</ref> | |||
| {{s-aft|rows=3|after=] & ]}} | |||
| {{s-bef|rows=2|before=]}} | |||
| After three days, unable to persuade his men to back down, Alexander gave Persians command posts in the army and conferred Macedonian military titles upon Persian units. The Macedonians quickly begged forgiveness, which Alexander accepted, and held a great banquet with several thousand of his men.<ref name="Roisman 2010 194">{{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=194}}</ref> In an attempt to craft a lasting harmony between his Macedonian and Persian subjects, Alexander ] of his senior officers to Persian and other noblewomen at Susa, but few of those marriages seem to have lasted much beyond a year.<ref name="AVII4" /> | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=330–323 BC}} | |||
| ]'', by ] (1796)]] | |||
| Meanwhile, upon his return to Persia, Alexander learned that guards of the ] in ] had desecrated it, and swiftly executed them.<ref name="AVI29" /> Alexander admired ], from an early age reading ]'s '']'', which described Cyrus's heroism in battle and governance as a king and legislator.<ref name="Ulrich">{{cite book |title=Alexander the Great |author=Ulrich Wilcken |publisher=W.W. Norton & Company |year=1967 |page=146 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=WiSZM-LYsk4C&pg=PA146 |isbn=978-0-393-00381-9 |access-date=5 September 2020}}</ref> During his visit to Pasargadae, Alexander ordered his architect ] to decorate the interior of the sepulchral chamber of Cyrus's tomb.<ref name="Ulrich" /> | |||
| Afterwards, Alexander travelled to Ecbatana to retrieve the bulk of the Persian treasure. There, his closest friend, Hephaestion, died of illness or poisoning.<ref name="AVII14" /> Hephaestion's death devastated Alexander and he ordered the preparation of an expensive ] in Babylon along with a decree for public mourning.<ref name="AVII14" /> Back in Babylon, Alexander planned a series of new campaigns, beginning with an invasion of Arabia.<ref name="AVII19" /> | |||
| ==Death and succession== | |||
| {{Main|Death of Alexander the Great}} | |||
| ] (c. 323–322 BC) recording the death of Alexander (], London)]] | |||
| On either 10 or 11 June 323 BC, Alexander died in the palace of ], in Babylon, at age 32.<ref>{{cite web |title=A contemporary account of the death of Alexander |url=https://www.livius.org/sources/content/oriental-varia/a-contemporary-account-of-the-death-of-alexander/ |access-date=5 November 2019 |publisher=]}}</ref><ref name="Depuydt" /> There are two different versions of Alexander's death, differing slightly in details. Plutarch's account is that roughly 14 days before his death, Alexander entertained admiral ] and spent the night and next day drinking with ].<ref name="P75" /> Alexander developed a fever, which worsened until he was unable to speak. The common soldiers, anxious about his health, were granted the right to file past him as he silently waved at them.{{Sfn |Wood|2001|pp= 2267–70}} In the second account, Diodorus recounts that Alexander was struck with pain after downing a large bowl of unmixed wine in honour of Heracles followed by 11 days of weakness; he did not develop a fever, instead dying after some agony.<ref name="DSXVII117" /> Arrian also mentioned this as an alternative, but Plutarch specifically denied this claim.<ref name="P75" /> | |||
| Given the propensity of the Macedonian aristocracy to assassination,{{sfn|Green|2007|pp= 1–2}} foul play featured in multiple accounts of his death. Diodorus, Plutarch, Arrian and ] all mentioned the theory that Alexander was poisoned. Justin stated that Alexander was the victim of a poisoning conspiracy, Plutarch dismissed it as a fabrication,<ref name="PA77" /> while both Diodorus and Arrian noted that they mentioned it only for the sake of completeness.<ref name="DSXVII117" /><ref name="AVII27" /> The accounts were nevertheless fairly consistent in designating ], recently removed as Macedonian viceroy, replaced by Craterus, as the head of the alleged plot.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Pitt |first1=E. M. |last2=Richardson |first2=W. P. |date=May 2017 |title=Hostile inaction? Antipater, Craterus and the Macedonian regency |journal=] |volume=67 |issue=1 |pages=77–78 |doi=10.1017/S0009838817000301 |s2cid=157417151 }}</ref> Perhaps taking his summons to Babylon as a death sentence{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=23–24}} and having seen the fate of Parmenion and Philotas,<ref name="DSXVII118" /> Antipater purportedly arranged for Alexander to be poisoned by his son Iollas, who was Alexander's wine-pourer.<ref name="AVII27" /><ref name="DSXVII118" /> There was even a suggestion that Aristotle may have participated.<ref name="AVII27" /> | |||
| The strongest argument against the poison theory is the fact that twelve days passed between the start of his illness and his death; such long-acting poisons were probably not available.{{Sfn |Lane Fox|2006|loc= chapter 32}} However, in a 2003 ] documentary investigating the death of Alexander, Leo Schep from the New Zealand National Poisons Centre proposed that the plant white hellebore ('']''), which was known in antiquity, may have been used to poison Alexander.<ref>{{cite news |date=16 October 2003 |url=http://www.royalsociety.org.nz/2003/10/16/alexander/ |title=NZ scientist's detective work may reveal how Alexander died |access-date=15 January 2014 |location=Dunedin |work=The Royal Society of New Zealand |url-status = dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140116141707/http://www.royalsociety.org.nz/2003/10/16/alexander/ |archive-date=16 January 2014}}</ref>{{Sfn |Cawthorne|2004|p= 138}}<ref>{{cite journal |last=Bursztajn |first=Harold J |title=Dead Men Talking |journal=Harvard Medical Alumni Bulletin |year=2005 |issue=Spring |url=http://www.forensic-psych.com/articles/artDeadMenTalking.php |access-date=16 December 2011 |archive-date=29 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190329124207/http://www.forensic-psych.com/articles/artDeadMenTalking.php |url-status=live }}</ref> In a 2014 manuscript in the journal '']'', Schep suggested Alexander's wine was spiked with ''Veratrum album'', and that this would produce poisoning symptoms that match the course of events described in the '']''.<ref name="schep">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schep LJ, Slaughter RJ, Vale JA, Wheatley P |title=Was the death of Alexander the Great due to poisoning? Was it Veratrum album? |journal=] |volume=52 |issue=1 |pages=72–77 |date=January 2014 |pmid=24369045 |doi=10.3109/15563650.2013.870341|doi-access=free}}</ref> ''Veratrum album'' poisoning can have a prolonged course and it was suggested that if Alexander was poisoned, ''Veratrum album'' offers the most plausible cause.<ref name="schep" /><ref>{{cite news |last=Bennett-Smith |first=Meredith |date=14 January 2014 |url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2014/01/13/alexander-the-great-poisoned-toxic-wine_n_4591553.html |title=Was Alexander The Great Poisoned By Toxic Wine? |access-date=15 January 2014 |work=The Huffington Post |archive-date=17 June 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170617050647/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2014/01/13/alexander-the-great-poisoned-toxic-wine_n_4591553.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Another poisoning explanation put forward in 2010 proposed that the circumstances of his death were compatible with poisoning by water of the river Styx (modern-day ] in Arcadia, Greece) that contained ], a dangerous compound produced by bacteria.<ref>{{cite news |last=Squires |first=Nick |date=4 August 2010 |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/europe/greece/7924855/Alexander-the-Great-poisoned-by-the-River-Styx.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220110/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/europe/greece/7924855/Alexander-the-Great-poisoned-by-the-River-Styx.html |archive-date=10 January 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |title=Alexander the Great poisoned by the River Styx |access-date=12 December 2011 |location=London |work=The Daily Telegraph}}{{cbignore}}</ref> | |||
| Several ] (diseases) have been suggested, including ] and ]. A 1998 article in the '']'' attributed his death to typhoid fever complicated by ] and ascending ].<ref name="AMD" /> A 2004 analysis suggested pyogenic (infectious) ] or ].<ref name="ashrafian" /> Other illnesses fit the symptoms, including ], ],<ref name="ref1" /><ref>{{cite journal |last=Sbarounis |first=CN |title=Did Alexander the Great die of acute pancreatitis? |journal=J Clin Gastroenterol |volume=24 |pages=294–96 |year=2007 |doi=10.1097/00004836-199706000-00031 |pmid=9252868 |issue=4}}</ref> and ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.livescience.com/64676-alexander-the-great-declared-dead-prematurely.html|title=Why Alexander the Great May Have Been Declared Dead Prematurely (It's Pretty Gruesome)|author=Owen Jarus|website=]|date=4 February 2019|access-date=3 November 2021|archive-date=27 July 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210727002144/https://www.livescience.com/64676-alexander-the-great-declared-dead-prematurely.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Natural-cause theories also tend to emphasize that Alexander's health may have been in general decline after years of heavy drinking and severe wounds. The anguish that Alexander felt after Hephaestion's death may also have contributed to his declining health.<ref name="AMD" /> | |||
| ===Post-death events=== | |||
| {{see also|Tomb of Alexander the Great}} | |||
| Alexander's body was laid in a gold anthropoid ] that was filled with honey, which was in turn placed in a gold casket.<ref name="sarco1" /><ref>{{cite web |url=http://casswww.ucsd.edu/archive/personal/ron/CVNC/byline/bugs_96mar.html |date=Mar 1996 |title=Bayfront Byline Bug Walk |publisher=UCSD |access-date=25 March 2013 |archive-date=3 December 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121203070121/http://casswww.ucsd.edu/archive/personal/ron/CVNC/byline/bugs_96mar.html |url-status=live }}</ref> According to ], a seer called Aristander foretold that the land where Alexander was laid to rest "would be happy and unvanquishable forever".<ref name="Aelian" /> Perhaps more likely, the successors may have seen possession of the body as a symbol of legitimacy, since burying the prior king was a ].{{Sfn |Green|2007|p= 32}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| While Alexander's funeral cortege was on its way to Macedon, Ptolemy seized it and took it temporarily to Memphis.<ref name="sarco1" /><ref name="Aelian" /> His successor, ], transferred the sarcophagus to Alexandria, where it remained until at least ]. ], one of Ptolemy's final successors, replaced Alexander's sarcophagus with a glass one so he could convert the original to coinage.<ref name="sarco2" /> The 2014 discovery of an ] in northern Greece, at ], dating from the time of Alexander the Great<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-29239529 |title=Greeks captivated by Alexander-era tomb at Amphipolis |publisher=BBC News |date=22 September 2014 |last1=Christides |first1=Giorgos |access-date=21 June 2018 |archive-date=21 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140921235011/https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-29239529 |url-status=live }}</ref> has given rise to speculation that its original intent was to be the burial place of Alexander. This would fit with the intended destination of Alexander's funeral cortege. However, the memorial was found to be dedicated to the dearest friend of Alexander the Great, Hephaestion.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.usnews.com/news/world/articles/2015/09/30/excavator-ancient-grave-in-greece-honored-alexanders-pal |title=Archaeologist claims opulent grave in Greece honored Alexander the Great's best friend |website=usnews.com |date=30 September 2015 |access-date=15 April 2020 |archive-date=5 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160305153254/http://www.usnews.com/news/world/articles/2015/09/30/excavator-ancient-grave-in-greece-honored-alexanders-pal |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://greece.greekreporter.com/2015/09/30/hephaestions-monogram-found-at-amphipolis-tomb/ |title=Hephaestion's Monogram Found at Amphipolis Tomb |newspaper=Greekreporter.com |date=30 September 2015 |access-date=15 April 2020 |archive-date=1 October 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151001135401/http://greece.greekreporter.com/2015/09/30/hephaestions-monogram-found-at-amphipolis-tomb/ |url-status=live |last1=Papapostolou |first1=Anastasios }}</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ], ] and ] all visited the tomb in Alexandria where Augustus, allegedly, accidentally knocked the nose of Alexander's mummified body off. ] was said to have taken Alexander's breastplate from the tomb for his own use. Around AD 200, Emperor ] closed Alexander's tomb to the public. His son and successor, ], a great admirer, visited the tomb during his own reign. After this, details on the fate of the tomb are hazy.<ref name="sarco2" /> | |||
| The so-called "]", discovered near ] and now in the ], is so named not because it was thought to have contained Alexander's remains, but because its ]s depict Alexander and his companions fighting the Persians and hunting. It was originally thought to have been the sarcophagus of ] (died 311 BC), the king of Sidon appointed by Alexander immediately following the ] in 331.<ref>{{harvnb|Studniczka|1894|pp=226ff}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Bieber |first=M |title=The Portraits of Alexander |journal=Greece & Rome |series=Second Series |year=1965 |pages=183–88 |volume=12 |issue=2 |doi=10.1017/s0017383500015345|s2cid=163858858 }}</ref> However, in 1969, it was suggested by ] that it may date from earlier than Abdalonymus's death.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Sismondo Ridgway |first=Brunilde |year=1969 |title=Review: Der Alexander-Sarkophag by Karl Schefold |journal=] |volume=73 |page=482 |doi=10.2307/504019 | url=https://repository.brynmawr.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1006&context=arch_pubs| jstor=504019}}</ref> | |||
| ] likened the Macedonian army, after the death of Alexander, to the blinded ] due to the many random and disorderly movements that it made.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:2008.01.0045:chapter=1:section=4|title=Plutarch, Galba, chapter 1, section 4|website=perseus.tufts.edu|access-date=20 February 2021|archive-date=27 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210227032246/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A2008.01.0045%3Achapter%3D1%3Asection%3D4|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:2008.01.0116:chapter=1:section=4|title=Plutarch, Galba, chapter 1, section 4|website=perseus.tufts.edu|access-date=20 February 2021|archive-date=24 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210224185759/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A2008.01.0116%3Achapter%3D1%3Asection%3D4|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:2008.01.0191:chapter=27|title=Plutarch, Regum et imperatorum apophthegmata, Ἀλέξανδρος|website=perseus.tufts.edu|access-date=20 February 2021|archive-date=24 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210224161752/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A2008.01.0191%3Achapter%3D27|url-status=live}}</ref> In addition, Leosthenes also likened the anarchy between the generals, after Alexander's death, to the blinded Cyclops "who after he had lost his eye went feeling and groping about with his hands before him, not knowing where to lay them".<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=urn:cts:greekLit:tlg0007.tlg087.perseus-grc1:2.4|title=Plutarch, De Alexandri magni fortuna aut virtute, chapter 2, section 4|website=perseus.tufts.edu|access-date=20 February 2021|archive-date=24 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210224150622/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=urn:cts:greekLit:tlg0007.tlg087.perseus-grc1:2.4|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Division of the Macedonian Empire=== | |||
| {{Main|Partition of Babylon|Diadochi}} | |||
| ] in 301 BC: the ] (dark blue), the ] (yellow), ] (orange), and ] (green). Also shown are the ] (light blue), the ] (purple), and the ] (red).]] | |||
| Alexander's death was so sudden that when reports of his death reached Greece, they were not immediately believed.<ref name="Roisman 2010 199" /> Alexander had no obvious or legitimate heir, his son Alexander IV by Roxane being born after Alexander's death.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=24–26}} According to Diodorus, Alexander's companions asked him on his deathbed to whom he bequeathed his kingdom; his laconic reply was "tôi kratistôi"—"to the strongest".<ref name="DSXVII117" /> Another theory is that his successors wilfully or erroneously misheard "tôi Kraterôi"—"to Craterus", the general leading his Macedonian troops home and newly entrusted with the regency of Macedonia.<ref name=Shipley>{{cite book |title=The Greek World After Alexander 323–30 BC |author=Graham Shipley |page=40 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=sAoiAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA40 |isbn=978-1-134-06531-8 |date=2014 |publisher=Routledge |access-date=9 November 2017}}</ref> Arrian and Plutarch claimed that Alexander was speechless by this time, implying that this was an apocryphal story.<ref>{{harvnb|Green|2007|p=20}}</ref> Diodorus, Curtius and Justin offered the more plausible story that Alexander passed his ] to ], a bodyguard and leader of the companion cavalry, in front of witnesses, thereby nominating him.<ref name="DSXVII117" />{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=24–26}} | |||
| Perdiccas initially did not claim power, instead suggesting that Roxane's baby would be king, if male, with himself, ], Leonnatus, and Antipater as guardians. However, the infantry, under the command of ], rejected this arrangement since they had been excluded from the discussion. Instead, they supported Alexander's half-brother Philip Arrhidaeus. Eventually, the two sides reconciled, and after the birth of Alexander IV, he and Philip III were appointed joint kings, albeit in name only.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=26–29}} Dissension and rivalry soon affected the Macedonians. The satrapies handed out by Perdiccas at the ] became power bases each general used to bid for power. After the assassination of Perdiccas in 321 BC, Macedonian unity collapsed, and 40 years of war between "The Successors" ('']'') ensued before the Hellenistic world settled into three stable power blocs: ], ], and ]. In the process, both Alexander IV and Philip III were murdered.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=29–34}} | |||
| ===Last plans=== | |||
| ] stated that Alexander had given detailed written instructions to ] some time before his death, which are known as Alexander's "last plans".<ref name="DSXVIII4" /> Craterus started to carry out Alexander's commands, but the successors chose not to further implement them, on the grounds they were impractical and extravagant.<ref name="DSXVIII4" /> Furthermore, ] had read the notebooks containing Alexander's last plans to the Macedonian troops in Babylon, who voted not to carry them out.<ref name="Roisman 2010 199" /> | |||
| According to Diodorus, Alexander's last plans called for military expansion into the southern and western Mediterranean, monumental constructions, and the intermixing of Eastern and Western populations. It included: | |||
| * Construction of 1,000 ships larger than triremes, along with harbours and a road running along the African coast all the way to the ], to be used for an invasion of ] and the western Mediterranean;<ref name=Bad/> | |||
| * Erection of great temples in ], ], ], ], ], all costing 1,500 ], and a monumental temple to ] at ]<ref name="Roisman 2010 199" /><ref name=Bad/> | |||
| * Amalgamation of small settlements into larger cities ("]s") and the "transplant of populations from Asia to Europe and in the opposite direction from Europe to Asia, in order to bring the largest continent to common unity and to friendship by means of intermarriage and family ties"<ref>{{harvnb|McKechnie|1989|p=54}}</ref><ref name=Bad/> | |||
| * Construction of a monumental tomb for his father Philip, "to match the greatest of the ]"<ref name="Roisman 2010 199" /><ref name=Bad/> | |||
| * Conquest of ]<ref name="Roisman 2010 199" /> | |||
| * Circumnavigation of Africa<ref name="Roisman 2010 199" /> | |||
| The enormous scale of these plans has led many scholars to doubt their historicity. ] argued that they were exaggerated by Perdiccas in order to ensure that the Macedonian troops voted not to carry them out.<ref name=Bad>{{cite journal |last1=Badian |first1=Erns |title=A King's Notebooks |journal=Harvard Studies in Classical Philology |date=1968 |volume=72 |pages=183–204|doi=10.2307/311079 |jstor=311079 }}</ref> Other scholars have proposed that they were invented by later authors within the tradition of the ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Tarn|first=William Woodthorpe|title=Alexander the Great |date=1948 |publisher=University Press |isbn=978-0-521-22584-7 |location=Cambridge |page=378 |oclc=606613}}</ref> | |||
| ==Character== | |||
| ===Generalship=== | |||
| {{further|Military tactics of Alexander the Great}} | |||
| Alexander perhaps earned the epithet "the Great" due to his unparalleled success as a military commander; he never lost a battle, despite typically being outnumbered.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=}} This was due to use of terrain, ] and cavalry tactics, bold strategy, and the fierce loyalty of his troops.<ref name="Roisman 2010 193">{{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=193}}, {{harvnb|Morkot|1996|p=110}}</ref> The ], armed with the ], a spear {{convert |6|m|ft}} long, had been developed and perfected by Philip II through rigorous training, and Alexander used its speed and manoeuvrability to great effect against larger but more disparate Persian forces.{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=110}} Alexander also recognized the potential for disunity among his diverse army, which employed various languages and weapons. He overcame this by being personally involved in battle,{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=121}} in the manner of a Macedonian king.<ref name="Roisman 2010 193"/> | |||
| ], 334 BC]] | |||
| In his first battle in Asia, at Granicus, Alexander used only a small part of his forces, perhaps 13,000 infantry with 5,000 cavalry, against a much larger Persian force of 40,000.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Tarn|first=William Woodthorpe|title=Alexander the Great |date=1948 |publisher=University Press |isbn=978-0-521-22584-7 |location=Cambridge |pages=361–362 |oclc=606613}}</ref> Alexander placed the phalanx at the center and cavalry and archers on the wings, so that his line matched the length of the Persian cavalry line, about {{convert|3|km|2|abbr=on}}. By contrast, the Persian infantry was stationed behind its cavalry. This ensured that Alexander would not be outflanked, while his phalanx, armed with long pikes, had a considerable advantage over the Persians' ] and ]. Macedonian losses were negligible compared to those of the Persians.{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=122}} | |||
| ], 333 BC]] | |||
| At Issus in 333 BC, his first confrontation with Darius, he used the same deployment, and again the central phalanx pushed through.{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=122}} Alexander personally led the charge in the center, routing the opposing army.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=193}} At the decisive encounter with Darius at Gaugamela, Darius equipped his chariots with scythes on the wheels to break up the phalanx and equipped his cavalry with pikes. Alexander arranged a double phalanx, with the center advancing at an angle, parting when the chariots bore down and then reforming. The advance was successful and broke Darius's center, causing the latter to flee once again.{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=122}} | |||
| When faced with opponents who used unfamiliar fighting techniques, such as in Central Asia and India, Alexander adapted his forces to his opponents' style. Thus, in ] and ], Alexander successfully used his javelin throwers and archers to prevent outflanking movements, while massing his cavalry at the center.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=193}} In India, confronted by Porus's elephant corps, the Macedonians opened their ranks to envelop the elephants and used their sarissas to strike upwards and dislodge the elephants' handlers.<ref name = "Roisman 2010 194" /> | |||
| ===Physical appearance=== | |||
| ] by ]|upright=.9]] | |||
| Historical sources frequently give conflicting accounts of Alexander's appearance, and the earliest sources are the most scant in their detail.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Stewart |first1=Andrew |title=Faces of Power : Alexander's Image and Hellenistic Politics Hellenistic Culture and Society |date=1993 |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-06851-3 |page=72}}</ref> During his lifetime, Alexander carefully curated his image by commissioning works from famous and great artists of the time. This included commissioning sculptures by ], paintings by ] and gem engravings by ].<ref name="Alexander the Great">{{cite book |last1=Nawotka |first1=Krzysztof |title=Alexander the Great |date=2010 |publisher=Cambridge Scholars Publishing |page=43}}</ref> Ancient authors recorded that Alexander was so pleased with portraits of himself created by Lysippos that he forbade other sculptors from crafting his image; scholars today, however, find the claim dubious.<ref>{{cite web |title=Images of Authority II: The Greek Example |year=2005 |publisher=SUNY Oneonta |url=http://employees.oneonta.edu/farberas/arth/arth200/politics/images_authority_2_greek.html |access-date=16 December 2011 |archive-date=4 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181004195912/http://employees.oneonta.edu/farberas/arth/arth200/politics/images_authority_2_greek.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Alexander the Great"/> Nevertheless, Andrew Stewart highlights the fact that artistic portraits, not least because of who they are commissioned by, are always partisan, and that artistic portrayals of Alexander "seek to legitimize him (or, by extension, his Successors), to interpret him to their audiences, to answer their critiques, and to persuade them of his greatness", and thus should be considered within a framework of "praise and blame", in the same way sources such as praise poetry are.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Stewart |first1=Andrew |title=Faces of Power : Alexander's Image and Hellenistic Politics Hellenistic Culture and Society |date=1993 |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-06851-3 |page=69}}</ref> Despite those caveats, Lysippos's sculpture, famous for its naturalism, as opposed to a stiffer, more static pose, is thought to be the most faithful depiction.{{Sfn |Bosworth|1988|pp = 19–20}} | |||
| ], a Roman historian from the first century AD, who wrote the '']'', gives this account of Alexander sitting on the throne of ]: | |||
| {{blockquote|Then Alexander seating himself on the royal throne, which was far too high for his bodily stature. Therefore, since his feet did not reach its lowest step, one of the royal pages placed a table under his feet.{{sfn |Rolfe |1946 |loc = 5.2.13}}}} | |||
| Both Curtius and ] report a story that when ]'s mother, ], first met Alexander and ], she assumed that the latter was Alexander because he was the taller and more handsome of the two.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Siculus |first1=Diodorus |title=Diodorus of Sicily in Twelve Volumes with an English Translation by C. H. Oldfather. Vol. 4–8. |date=1989 |publisher=Harvard University Press |url=http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.01.0084%3Abook%3D17%3Achapter%3D37 |access-date=7 July 2021 |archive-date=9 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210709192544/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.01.0084:book%3D17:chapter%3D37 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ]|left|upright]] | |||
| The Greek biographer ] ({{circa| 45|120 AD}}) discusses the accuracy of his depictions: | |||
| {{blockquote|The outward appearance of Alexander is best represented by the statues of him which Lysippus made, and it was by this artist alone that Alexander himself thought it fit that he should be modelled. For those peculiarities which many of his successors and friends afterwards tried to imitate, namely, the poise of the neck, which was bent slightly to the left, and the melting glance of his eyes, this artist has accurately observed. Apelles, however, in painting him as wielder of the thunder-bolt, did not reproduce his complexion, but made it too dark and swarthy. Whereas he was of a fair colour, as they say, and his fairness passed into ruddiness on his breast particularly, and in his face. Moreover, that a very pleasant odour exhaled from his skin and that there was a fragrance about his mouth and all his flesh, so that his garments were filled with it, this we have read in the ''Memoirs of Aristoxenus''.{{Sfn |Plutarch|1919|loc = }}}} | |||
| Historians have understood the detail of the pleasant fragrance attributed to Alexander as stemming from a belief in ancient Greece that pleasant scents are characteristic of gods and heroes.<ref name="Alexander the Great"/> | |||
| ] at ], the only known painting of Alexander made during his lifetime, 330s BC]] | |||
| The ] and contemporary coins portray Alexander with "a straight nose, a slightly protruding jaw, full lips and eyes deep set beneath a strongly pronounced forehead".<ref name="Alexander the Great"/> He is also described as having a slight upward tilt of his head to the left.{{sfn|Renault|2013|p=1}} | |||
| The ancient historian ] ({{circa|175}} – {{circa|235 AD}}), in his ''Varia Historia'' (12.14), describes Alexander's hair color as "''ξανθὴν''" (''xanthín''), which at the time, could mean blond, brown, tawny (light brown) or auburn.{{sfn|Liddell|Scott|1940|loc=}}<ref>{{Cite book |last=Woodhouse |first=Sidney Chawner |title=English–Greek Dictionary: A Vocabulary of the Attic Language |publisher=Routledge & Kegan Paul Limited |year=1910 |location=London |pages=52,84,101}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Beekes |first1=Robert Stephen Paul |title=Etymological Dictionary of Greek |last2=Beek |first2=Lucien van |publisher=Brill |year=2010 |location=Leiden; Boston |pages=1033}}</ref> It is sometimes claimed that Alexander had ],<ref>{{cite book |first=Peter |last=Green |author-link=Peter Green (historian) |title=Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic Age |publisher=Orion Publishing Co |year=2008 |pages=15–16 |isbn=978-0-7538-2413-9}}</ref> referring to the '']'', which is however a fictional account that also claims Alexander "had sharp teeth like fangs" and "did not look like Philip or Olympias". Reconstruction, based on remaining traces of paint of the original ] on his ], indicates that he was depicted with brown eyes and chestnut brown hair.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Brinkmann |first1=Vinzenz |url=https://pictures.abebooks.com/inventory/31048007537_3.jpg |title=Gods in Color: Painted Sculpture of Classical Antiquity |last2=Wunsche |first2=Raimund |publisher=Arthur M. Sackler / Harvard University Art Museum |year=2007 |pages=159 |access-date=12 April 2022 |archive-date=31 July 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220731043302/https://pictures.abebooks.com/inventory/31048007537_3.jpg |url-status=live }}</ref> While the acropolis museum suggests that trace amounts of red paint on a head statue of Alexander were most likely a base coat for golden hues to be painted over for his hair.<ref>{{cite web |title=Head of a statue of Alexander the Great {{!}} Acropolis Museum {{!}} Official website |url=https://www.theacropolismuseum.gr/en/head-statue-alexander-great |website=www.theacropolismuseum.gr |access-date=1 October 2024}}</ref> | |||
| ===Personality=== | |||
| ]'' and fighting an ] with his friend ] (detail); late 4th century BC ],<ref>] (2000). "Hephaestion's Pyre and the Royal Hunt of Alexander", in A.B. Bosworth and E.J. Baynham (eds), ''Alexander the Great in Fact and Fiction''. Oxford & New York: Oxford University Press. {{ISBN|978-0-19-815287-3}}, p. 185.</ref> ] Museum]] | |||
| Both of Alexander's parents encouraged his ambitions. His father Philip was probably Alexander's most immediate and influential role model, as the young Alexander watched him campaign practically every year, winning victory after victory while ignoring severe wounds.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=190}} Alexander's relationship with his father "forged" the competitive side of his personality; he had a need to outdo his father, illustrated by his reckless behavior in battle.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=15–16}} While Alexander worried that his father would leave him "no great or brilliant achievement to be displayed to the world",<ref name="PA5"/> he also downplayed his father's achievements to his companions.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=15–16}} Alexander's mother Olympia similarly had huge ambitions, and encouraged her son to believe it was his destiny to conquer the Persian Empire.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=15–16}} She instilled a sense of destiny in him,{{sfn|Green|2007|p=4}} and Plutarch tells how his ambition "kept his spirit serious and lofty in advance of his years".<ref name="PA4"/> | |||
| According to Plutarch, Alexander also had a violent temper and rash, impulsive nature,<ref name="AVII29"/> which could influence his decision making.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=15–16}} Although Alexander was stubborn and did not respond well to orders from his father, he was open to reasoned debate.<ref name="PA7"/> He had a calmer side—perceptive, logical, and calculating. He had a great desire for knowledge, a love for philosophy, and was an avid reader.<ref name="PA8"/> This was no doubt in part due to Aristotle's tutelage; Alexander was intelligent and quick to learn.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=15–16}} His intelligent and rational side was amply demonstrated by his ability and success as a general.<ref name="AVII29"/> He had great self-restraint in "pleasures of the body", in contrast with his lack of ] with alcohol.<ref name="AVII28">{{harvnb | Arrian|1976|loc=VII, 28}}</ref> | |||
| ] of an original 3rd century BC ] depicting Alexander the Great, ], Copenhagen]] | |||
| Alexander was erudite and patronized both arts and sciences.<ref name="PA4"/><ref name="PA8"/> However, he had little interest in sports or the ] (unlike his father), seeking only the ] ideals of honour (''timê'') and glory (''kudos'').<ref>{{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=190}}, {{harvnb|Green|2007|p=4}}</ref> He had great ] and force of personality, characteristics which made him a great leader.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=24–26}}<ref name="AVII29"/> His unique abilities were further demonstrated by the inability of any of his generals to unite Macedonia and retain the Empire after his death—only Alexander had the ability to do so.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=24–26}} | |||
| During his final years, and especially after the death of Hephaestion, Alexander began to exhibit signs of ] and ].{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=23–24}} His extraordinary achievements, coupled with his own ineffable sense of destiny and the flattery of his companions, may have combined to produce this effect.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=20–21}} His ] are readily visible in his ] and in his desire to conquer the world,{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=23–24}} in as much as he is by various sources described as having ''boundless ambition'',<ref>M Wood (edited by T Gergel) – Penguin, 2004 {{ISBN|978-0-14-101312-1}} </ref><ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TUqQbemlo80C&pg=PA7 |page=7 |title=Medieval French Alexander, the |isbn=978-0-7914-8832-4 |last1=Maddox |first1=Donald |last2=Sturm-Maddox |first2=Sara |date=February 2012 |publisher=State University of New York Press |access-date=17 October 2016}}</ref> an epithet, the meaning of which has descended into a historical cliché.<ref>G Highet<!-- taught classics at Oxford University until 1938; in 1950 he was appointed Anthon Professor of the Latin Language and Literature at Columbia University --> – , Oxford University Press, 31 December 1949 p. 68 (ed. c.f. – {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150626135648/http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/clich%C3%A9 |date=26 June 2015 }})</ref><ref>Merriam-Webster {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150326115024/http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/epithet |date=26 March 2015 }} </ref> | |||
| He appears to have believed himself a deity, or at least sought to deify himself.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=23–24}} Olympias always insisted to him that he was the son of Zeus,<ref name="PA3" /> a theory apparently confirmed to him by the oracle of Amun at ].<ref name="P27"/> He began to identify himself as the son of Zeus-Ammon.<ref name="P27"/> Alexander adopted elements of Persian dress and customs at court, notably '']'', which was one aspect of Alexander's broad strategy aimed at securing the aid and support of the Iranian upper classes;{{sfn|Briant|1985|pages=827–830}} however the practise of ''proskynesis'' was disapproved by the Macedonians, and they were unwilling to perform it.<ref name="AVII11"/> This behaviour cost him the sympathies of many of his countrymen.<ref name="PA45"/> Alexander also was a pragmatic ruler who understood the difficulties of ruling culturally disparate peoples, many of whom lived in societies where the king was treated as divine.<ref>{{harvnb|Morkot|1996|p=111}}, {{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=195}}</ref> Thus, rather than megalomania, his behaviour may have been a practical attempt at strengthening his rule and keeping his empire together.<ref>{{harvnb|Morkot|1996|p=121}}, {{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=195}}</ref> | |||
| ===Personal relationships=== | |||
| {{Main |Personal relationships of Alexander the Great}} | |||
| ], depicting the marriage of Alexander to ] in 324 BC; the couple is apparently dressed as ] and ].]] | |||
| Alexander married three times: ], daughter of the ]n nobleman ] of ],<ref>Ahmed, S. Z. (2004), ''Chaghatai: the Fabulous Cities and People of the Silk Road'', West Conshokoken: Infinity Publishing, p. 61.</ref><ref>Strachan, Edward and Roy Bolton (2008), ''Russia and Europe in the Nineteenth Century'', London: Sphinx Fine Art, p. 87, {{ISBN|978-1-907200-02-1}}.</ref><ref>Livius.org. " {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210414100829/https://www.livius.org/articles/person/roxane/ |date=14 April 2021}}." ''Articles on Ancient History''. Retrieved on 30 August 2016.</ref> out of love;{{Sfn|Plutarch|1919|loc= }} and the Persian princesses ] and ], the former a daughter of ] and the latter a daughter of ], for political reasons.<ref name="Carney">{{cite book |last=Carney |first=Elizabeth Donnelly |title=Women and Monarchy in Macedonia |date=2000 |publisher=University of Oklahoma Press |location=Norman |isbn=978-0-8061-3212-9}}</ref>{{Sfn |Plutarch|1936|loc= }} Alexander apparently had two children by Roxana: an unnamed first child, who was born in India and died in infancy in November 326 BC,<ref>Metz Epitome 70 | |||
| </ref> and ], born after his father's death. Additionally ] was claimed to be his illegitimate son born of mistress, ]. | |||
| Alexander also had a close relationship with his friend, general, and bodyguard ], the son of a Macedonian noble.<ref name="AVII14" />{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=15–16}}<ref name="DSXVII114" /> Hephaestion's death devastated Alexander.<ref name="AVII14" /><ref name="P72" /> This event may have contributed to Alexander's failing health and detached ] during his final months.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=23–24}}<ref name="AMD" /> | |||
| === Sexuality === | |||
| Alexander's sexuality has been the subject of speculation and controversy in modern times.{{sfn|Ogden|2009|p=204}} The Roman era writer ] says, based on the scholar ], who was Alexander's contemporary, that the king "was quite excessively keen on boys", and that Alexander kissed the ] ] in public.<ref>{{cite book |title=Homosexuality in Greece and Rome: A Sourcebook of Basic Documents |url=https://archive.org/details/homosexualitygre00hubb|url-access=limited |editor=Thomas K. Hubbard |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-520-23430-7 |publisher=University of California Press |page=}}</ref> This episode is also told by Plutarch, probably based on the same source. None of Alexander's contemporaries, however, are known to have explicitly described Alexander's relationship with Hephaestion as sexual, though the pair was often compared to ], who are often interpreted as a couple. Aelian writes of Alexander's visit to ] where "Alexander garlanded the tomb of Achilles, and Hephaestion that of ], the latter hinting that he was a beloved of Alexander, in just the same way as Patroclus was of Achilles."<ref name="AelXII7" /> Some modern historians (e.g., ]) believe not only that Alexander's youthful relationship with Hephaestion was sexual, but also that their sexual contacts may have continued into adulthood, which went against the social norms of at least some Greek cities, such as Athens,<ref>{{cite book |author=Marilyn Skinner |title=Sexuality in Greek and Roman Culture (Ancient Cultures) |edition=2nd |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |isbn=978-1-4443-4986-3 |page=190 |year=2013}}</ref>{{sfn|Sacks|1995|p=16}} though some modern researchers have tentatively proposed that Macedonia (or at least the Macedonian court) may have been more tolerant of homosexuality between adults.<ref>{{cite book|editor-last=Hubbard|editor-first=Thomas |title=A Companion to Greek and Roman Sexualities |date=2014 |publisher=Blackwell Publishing Ltd |isbn=978-1-4051-9572-0 |page=143 |chapter=Chapter 8: Peer Homosexuality |author=Thomas Hubbard}}</ref> | |||
| ], at the ]|left]] | |||
| ] argues that there is little evidence in ancient sources that Alexander had much sexual interest in women; he did not produce an heir until the very end of his life.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=15–16}} However, Ogden calculates that Alexander, who impregnated his partners thrice in eight years, had a higher matrimonial record than his father at the same age.{{sfn|Ogden|2009|p=208|ps=... three attested pregnancies in eight years produces an attested impregnation rate of one every 2.7 years, which is actually superior to that of his father.}} Two of these pregnancies—Stateira's and Barsine's—are of dubious legitimacy.<ref>{{cite book |title=] |author=] |quote=No record at all exists of such a woman accompanying his march; nor of any claim by her, or her powerful kin, that she had borne him offspring. Yet twelve years after his death a boy was produced, seventeen years old, born therefore five years after Damascus, her alleged son "brought up in Pergamon"; a claimant and shortlived pawn in the succession wars, chosen probably for a physical resemblance to Alexander. That he actually did marry another Barsine must have helped both to launch and preserve the story; but no source reports any notice whatever taken by him of a child who, Roxane's being posthumous, would have been during his lifetime his only son, by a near-royal mother. In a man who named cities after his horse and dog, this strains credulity. |page=110 |year=1979 |publisher=Pantheon |isbn=978-0-394-73825-3}}</ref> | |||
| According to Diodorus Siculus, Alexander accumulated a harem in the style of Persian kings, but he used it rather sparingly, "not wishing to offend the Macedonians",<ref name="DSXVII77" /> showing great self-control in "pleasures of the body".<ref name="AVII28" /> Nevertheless, Plutarch described how Alexander was infatuated by Roxana while complimenting him on not forcing himself on her.<ref>{{cite web |year=1936 |url=https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Plutarch/Moralia/Fortuna_Alexandri*/2.html |author=Plutarch |title=Moralia |id=I, 11 |publisher=University of Chicago |ref=none |access-date=19 February 2021}}</ref> Green suggested that, in the context of the period, Alexander formed quite strong friendships with women, including ], who adopted him, and even Darius's mother ], who supposedly died from grief upon hearing of Alexander's death.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=15–16}} | |||
| ==Battle record== | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable plainrowheaders" style="width:100%; font-size:90%; margin:1em auto 1em auto;" | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| !width="65"|Outcome | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=332–323 BC}} | |||
| ! style="width:140px;"|Date | |||
| {{end}} | |||
| ! style="width:110px;"|War | |||
| {{MacedonKings}} | |||
| ! style="width:auto;"|Action | |||
| {{Plutarch}} | |||
| ! style="width:170px;"|Opponent/s | |||
| !width="45"|Type | |||
| ! style="width:120px;"|Country<br>(present day) | |||
| !width="50"|Rank | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">338-08-02</span> 2 August 338 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Chaeronea</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>], ] and other Greek cities | |||
| |Battle | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">335</span> 335 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Mount Haemus</span> Battle of Mount Haemus | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>], ] | |||
| |Battle | |||
| | ] | |||
| |] | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">335-12</span> December 335 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Balkan Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Pelium</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Siege | |||
| |] | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">335-12</span> December 335 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Balkan Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Pelium</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Battle | |||
| |Greece | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">334-05</span> May 334 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Granicus</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Battle | |||
| | ] | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">334</span> 334 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Miletus</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>], ] | |||
| |Siege | |||
| | Turkey | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">334</span> 334 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Halicarnassus</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Siege | |||
| |Turkey | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">333-11-05</span> 5 November 333 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Issus</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Battle | |||
| | Turkey | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">332</span> January–July 332 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Tyre</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>], ] | |||
| |Siege | |||
| | ] | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">332-10</span> October 332 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Tyre</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Siege | |||
| | ] | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">331-10-01</span> 1 October 331 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Gaugamela</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Battle | |||
| | ] | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">331-12</span> December 331 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Uxian Defile</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Battle | |||
| | ] | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">330-01-20</span> 20 January 330 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Persian Gate</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Battle | |||
| | Iran | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">329</span> 329 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Cyropolis</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Siege | |||
| | ] | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">329-10</span> October 329 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Jaxartes</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Battle | |||
| | ] | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">327</span> 327 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Persian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Sogdian Rock</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Siege | |||
| | Uzbekistan | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">327</span> May 327 – March 326 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Cophen</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Expedition | |||
| | ] and ] | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">326-04</span> April 326 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Indian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Aornos</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Siege | |||
| | Pakistan | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">326-05</span> May 326 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Indian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Hydaspes</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Battle | |||
| |Pakistan | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{yes2}}Victory | |||
| !scope="row"|<span style="display:none">325</span> November 326 – February 325 BC | |||
| |style="background:#ACBECF"|Indian Campaign | |||
| |<span style="display:none">Aornos</span> ] | |||
| |<span style="display:none">.</span>] | |||
| |Siege | |||
| | Pakistan | |||
| |King | |||
| <span style="display:none">⁂</span> | |||
| |} | |||
| ==Legacy== | |||
| Alexander's legacy extended beyond his military conquests, and his reign marked a turning point in European and Asian history.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|title=Alexander the Great's Achievements|encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Britannica|url=https://www.britannica.com/summary/Alexander-the-Greats-Achievements|access-date=19 August 2021|archive-date=2 July 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210702234248/https://www.britannica.com/summary/Alexander-the-Greats-Achievements|url-status=live}}</ref> His campaigns greatly increased contacts and trade between ] and ], and vast areas to the east were significantly exposed to ] and influence.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=186}} Some of the cities he founded became major cultural centers, many surviving into the 21st century. His chroniclers recorded valuable information about the areas through which he marched, while the Greeks themselves got a sense of belonging to a world beyond the Mediterranean.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=186}} | |||
| ===Hellenistic kingdoms=== | |||
| {{Main|Hellenistic period}} | |||
| ] world view: ] by ] (276–194 BC), using information from the campaigns of Alexander and his successors<ref>{{cite web |title=World map according to Eratosthenes (194 B.C.) |publisher=Henry Davis Consulting |work=henry-davis.com |url=http://www.henry-davis.com/MAPS/Ancient%20Web%20Pages/112.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/19981205015304/http://www.henry-davis.com/MAPS/Ancient%20Web%20Pages/112.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=5 December 1998 |access-date=16 December 2011 }}</ref>]] | |||
| Alexander's most immediate legacy was the introduction of Macedonian rule to huge new swathes of Asia. At the time of his death, Alexander's empire covered some {{convert|5200000|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}},<ref name="uconn">Peter Turchin, Thomas D. Hall and Jonathan M. Adams, " {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070222011511/http://jwsr.ucr.edu/archive/vol12/number2/pdf/jwsr-v12n2-tah.pdf |date=22 February 2007 }}", ''Journal of World-Systems Research'' Vol. 12 (no. 2), pp. 219–29 (2006).</ref> and was the largest state of its time. Many of these areas remained in Macedonian hands or under Greek influence for the next 200–300 years. The ] that emerged were, at least initially, dominant forces, and these 300 years are often referred to as the ].{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=xii–xix}} | |||
| The eastern borders of Alexander's empire began to collapse even during his lifetime.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=24–26}} However, the power vacuum he left in the northwest of the Indian subcontinent directly gave rise to one of the most powerful Indian dynasties in history, the ]. Taking advantage of this power vacuum, ] (referred to in Greek sources as "Sandrokottos"), of relatively humble origin, took control of the ], and with that power base proceeded to conquer the ].{{sfn|Keay|2001|pp=82–85}} | |||
| ===Founding of cities=== | |||
| {{Main|List of cities founded by Alexander the Great}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Over the course of his conquests, Alexander founded ], most of them east of the ].{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=111}}<ref name="livius">{{cite web |url=https://www.livius.org/aj-al/alexander/alexander_z2.html |title=Alexander the Great: his towns |publisher=livius.org |access-date=13 December 2009 |archive-date=3 May 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150503150242/http://www.livius.org/aj-al/alexander/alexander_z2.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> The first, and greatest, was ] in Egypt, which would become one of the leading Mediterranean cities.{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=111}} The cities' locations reflected trade routes as well as defensive positions. At first, the cities must have been inhospitable, little more than defensive garrisons.{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=111}} Following Alexander's death, many Greeks who had settled there tried to return to Greece.{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=111}}<ref name="livius" /> However, a century or so after Alexander's death, many of the Alexandrias were thriving, with elaborate public buildings and substantial populations that included both Greek and local peoples.{{sfn|Morkot|1996|p=111}} | |||
| ===Funding of temples=== | |||
| ] at ], now housed in the ]<ref name="Burn"/>]] | |||
| In 334 BC, Alexander the Great donated funds for the completion of the new temple of ] in ], in modern-day western Turkey.<ref name="BritishMuseum">{{cite web |url=http://www.britishmuseum.org/research/collection_online/collection_object_details.aspx?objectId=437260&partId=1&searchText=athena+polias&people=72426&page=1 |title=Collection online |publisher=] |access-date=15 December 2017 |archive-date=15 December 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171215221426/http://www.britishmuseum.org/research/collection_online/collection_object_details.aspx?objectId=437260&partId=1&searchText=athena+polias&people=72426&page=1 |url-status=live }} "Marble wall block from the temple of Athena at Priene, inscribed on two sides. The inscription on the front records the gift of funds from Alexander the Great to complete the temple."</ref> An ], now housed in the ], declares: "King Alexander dedicated to Athena Polias."<ref name="Burn">{{cite book |last=Burn |first=Lucilla |date=2004 |title=Hellenistic Art: From Alexander the Great to Augustus |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TmhjC_AdoNsC&pg=PA10 |location=London |publisher=The British Museum Press |isbn=978-0-89236-776-4 |pages=10–11 |access-date=15 December 2017}}</ref> This inscription is one of the few independent archaeological discoveries confirming an episode from Alexander's life.<ref name="Burn"/> The temple was designed by ], one of the architects of the ].<ref name="Burn"/><ref name="BritishMuseum"/><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.britishmuseum.org/research/collection_online/collection_object_details/collection_image_gallery.aspx?partid=1&assetid=457544001&objectid=437260 |title=Priene Inscription |publisher=] |access-date=15 December 2017 |archive-date=15 December 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171215221617/http://www.britishmuseum.org/research/collection_online/collection_object_details/collection_image_gallery.aspx?partid=1&assetid=457544001&objectid=437260 |url-status=live }} "Marble wall block from the temple of Athena at Priene, inscribed. Part of the marble wall of the temple of Athena at Priene. Above: "King Alexander dedicated the temple to Athena Polias."</ref> | |||
| ] wrote that Alexander founded the temple of Zeus Bottiaios ({{langx|grc|Βοττιαίου Δῖός}}), in the place where later the city of ] was built.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://cts.perseids.org/read/greekLit/tlg2200/tlg00411/opp-grc1/88|title=Capitains Nemo|website=cts.perseids.org|access-date=23 May 2020|archive-date=15 August 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200815194836/http://cts.perseids.org/read/greekLit/tlg2200/tlg00411/opp-grc1/88|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Downey |first1=Glanville |chapter=II The City of Seleucus the Conqueror |pages=27–44 |id={{Project MUSE|1708741|type=chapter}} |title=Ancient Antioch |date=2015 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-1-4008-7671-6 }}</ref> | |||
| ] wrote that Alexander built a big temple to ].<ref>{{cite web| url = https://www.cs.uky.edu/~raphael/sol/sol-entries/sigma/117| title = Suda, sigma, 117| access-date = 12 August 2021| archive-date = 14 October 2021| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20211014070448/https://www.cs.uky.edu/~raphael/sol/sol-entries/sigma/117| url-status = live}}</ref> | |||
| In 2023, ] experts have suggested the possibility that a Greek temple at ] in ], was founded by Alexander. According to the researchers, recent discoveries suggest that "this site honours Zeus and two divine sons. The sons are Heracles and Alexander."<ref>{{cite news| url = https://www.telegraph.co.uk/world-news/2023/11/18/ancient-iraqi-civilisation-worshipped-alexander-the-great/| title = Ancient Iraqis may have worshipped Alexander the Great, says British Museum| newspaper = The Telegraph| date = 18 November 2023| access-date = 18 November 2023| archive-date = 21 November 2023| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20231121225300/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/world-news/2023/11/18/ancient-iraqi-civilisation-worshipped-alexander-the-great/| url-status = live| last1 = Simpson| first1 = Craig}}</ref> | |||
| ===Hellenization=== | |||
| {{Main|Hellenization}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ''Hellenization'' was coined by the German historian ] to denote the spread of Greek language, culture, and population into the former Persian empire after Alexander's conquest.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=xii–xix}} This process can be seen in such great Hellenistic cities as ], ]{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=56–59}} and ] (south of modern ]).<ref>{{cite web |last1=Waterman |first1=Leroy |last2=McDowell |first2=Robert H. |last3=Hopkins |first3=Clark |title=Seleucia on the Tigris, Iraq |publisher=The Kelsey Online |year=1998 |url=http://www.umich.edu/~kelseydb/Excavation/Seleucia.html |work=umich.edu |access-date=16 December 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120104113121/http://www.umich.edu/~kelseydb/Excavation/Seleucia.html |archive-date=4 January 2012 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Alexander sought to insert Greek elements into ] and to hybridize Greek and Persian culture, homogenizing the populations of Asia and Europe. Although his successors explicitly rejected such policies, Hellenization occurred throughout the region, accompanied by a distinct and opposite 'Orientalization' of the successor states.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=21, 56–59}} | |||
| The core of the Hellenistic culture promulgated by the conquests was essentially ].<ref>{{harvnb|Green|2007|pp=56–59}}, {{harvnb|McCarty|2004|p=17}}</ref> The close association of men from across Greece in Alexander's army directly led to the emergence of the largely ]-based "]", or "common" Greek dialect.{{sfn|Harrison|1971|p=51}} Koine spread throughout the Hellenistic world, becoming the ] of Hellenistic lands, and eventually the ancestor of ].{{sfn|Harrison|1971|p=51}} Furthermore, ], education, local government, and art current in the Hellenistic period were all based on Classical Greek ideals, evolving into distinct new forms commonly grouped as Hellenistic. Also, the ] was written in the ] language.{{sfn|Green|2007|pp=56–59}} Aspects of Hellenistic culture were still evident in the traditions of the Byzantine Empire in the mid-15th century.<ref>{{harvnb|Baynes|2007|p=170}}, {{harvnb|Gabriel|2002|p=277}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Hellenization in South and Central Asia ==== | |||
| {{Main|Indo-Greek Kingdom|Indo-Greek art|Greco-Buddhism}} | |||
| ], in ], 1st to 2nd century AD, ], northern Pakistan. ].]] | |||
| Some of the most pronounced effects of Hellenization can be seen in Afghanistan and India, in the region of the relatively late-rising ] (250–125 BC) (in modern ], ], and ]) and the ] (180 BC – 10 AD) in modern Afghanistan and India.{{sfn|Keay|2001|pp=101–109}} On the ] trade routes, Hellenistic culture hybridized with Iranian and ] cultures. The cosmopolitan art and mythology of ] (a region spanning the upper confluence of the Indus, Swat and Kabul rivers in modern Pakistan) of the ~3rd century BC to the ~5th century AD are most evident of the direct contact between Hellenistic civilization and South Asia, as are the ], which directly mention the Greeks within Ashoka's dominion as converting to Buddhism and the reception of Buddhist emissaries by Ashoka's contemporaries in the Hellenistic world.<ref>{{Cite book |title=The Buddhist Heritage of Pakistan: Art of Gandhara |last=Proser |first=Adriana |publisher=Asia Society |year=2011 |isbn=978-0-87848-112-5 }}</ref> The resulting ] known as ] influenced the development of Buddhism<ref>{{cite web |url=https://neosalexandria.org/syncretism/greco-buddhism-a-brief-history/ |title=Greco-Buddhism: A Brief History |website=Neosalexandria |date=11 November 2010 |access-date=19 March 2021 |archive-date=26 February 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210226133605/https://neosalexandria.org/syncretism/greco-buddhism-a-brief-history/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and created a culture of ]. These Greco-Buddhist kingdoms sent some of the first Buddhist missionaries to ], ] and Hellenistic Asia and Europe (]). | |||
| Some of the first and most influential figurative portrayals of ] appeared at this time, perhaps modelled on Greek statues of ] in the Greco-Buddhist style.{{sfn|Keay|2001|pp=101–09}} Several Buddhist traditions may have been influenced by the ]: the concept of ] is reminiscent of Greek divine heroes,<ref>{{harvnb|Luniya|1978|p=312}}</ref> and some ] ] (burning ], gifts of flowers, and food placed on altars) are similar to those practised by the ancient Greeks; however, similar practices were also observed amongst the native Indic culture. One Greek king, ], probably became Buddhist, and was immortalized in ] as 'Milinda'.{{sfn|Keay|2001|pp=101–09}} The process of Hellenization also spurred trade between the east and west.<ref name="Pingree (1978), 533, 554f.">{{harvnb|Pingree|1978|pp=533, 554ff}}</ref> For example, Greek astronomical instruments dating to the 3rd century BC were found in the ] city of ] in modern-day ],<ref>{{cite book |first1=Pierre |last1=Cambon |first2=Jean-François |last2=Jarrige |year=2006 |language=fr |title=Afghanistan, les trésors retrouvés: Collections du Musée national de Kaboul |trans-title=Afghanistan, the treasures found: collections of the Kabul national museum |publisher=Réunion des musées nationaux |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xJFtQgAACAAJ |page=269 |isbn=978-2-7118-5218-5 |access-date=5 September 2020}}</ref> while the Greek concept of a ] surrounded by the spheres of planets eventually supplanted the long-standing Indian cosmological belief of a disc consisting of four continents grouped around a central mountain (Mount Meru) like the petals of a flower.<ref name="Pingree (1978), 533, 554f." /><ref>{{harvnb|Glick|Livesey|Wallis|2005|p=463}}</ref><ref name="Hayashi08Aryabhata">Hayashi (2008), ''Aryabhata I''</ref> The ] (lit. Greek astronomical treatise) and ] texts depict the influence of Greek astronomical ideas on Indian astronomy. | |||
| Following the conquests of Alexander the Great in the east, ] was far-reaching. In ], a few examples of the ] can be found as far as ] with the ] near ]. Several examples of ] displaying Ionic influences can be seen as far as ], especially with the ], dated to the 3rd century BC.<ref>{{cite book |page=438 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7DX-CAAAQBAJ&pg=PA438 |title=A Companion to Asian Art and Architecture |isbn=978-1-119-01953-4 |last1=Brown |first1=Rebecca M. |last2=Hutton |first2=Deborah S. |year=2015 | publisher=John Wiley & Sons |access-date=3 February 2017}}</ref> The ] is also heavily represented in the ], especially through ]s. | |||
| ===Influence on Rome=== | |||
| ], demonstrating the influence of Alexander's memory. ], ].]] | |||
| Alexander and his exploits were admired by many Romans, especially generals, who wanted to associate themselves with his achievements.<ref name="Asirvatham">{{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|loc=Chapter 6, p. 114}}</ref> ] began his '']'' by reminding Romans of Alexander's achievements, and thereafter Roman leaders saw him as a role model. ] adopted the epithet "Magnus" and even Alexander's anastole-type haircut, and searched the conquered lands of the east for Alexander's 260-year-old cloak, which he then wore as a sign of greatness.<ref name="Asirvatham" /> ] dedicated a ] ] ] statue, but replaced Alexander's head with his own, while ] visited Alexander's tomb in Alexandria and temporarily changed his seal from a ] to Alexander's profile.<ref name="Asirvatham" /> The emperor ] also admired Alexander, as did ] and ].<ref name="Asirvatham" /> The Macriani, a Roman family that in the person of ] briefly ascended to the imperial throne, kept images of Alexander on their persons, either on jewellery or embroidered into their clothes.{{sfn|Holt|2003|p=3}} | |||
| On the other hand, some Roman writers, particularly Republican figures, used Alexander as a cautionary tale of how ] tendencies can be kept in check by the values of the ].<ref name="Asirvatham2">{{harvnb|Roisman|Worthington|2010|loc=Chapter 6, p. 115}}</ref> Alexander was used by these writers as an example of ruler values such as {{lang|la|amicitia}} (friendship) and {{lang|la|clementia}} (clemency), but also {{lang|la|iracundia}} (anger) and {{lang|la|cupiditas gloriae}} (over-desire for glory).<ref name="Asirvatham2" /> | |||
| ] in his satire called "The Caesars", describes a contest between the previous Roman emperors, with Alexander the Great called in as an extra contestant, in the presence of the assembled gods.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.attalus.org/translate/caesars.html|title=Julian: Caesars – translation|website=attalus.org|access-date=29 March 2020|archive-date=26 February 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200226035227/http://www.attalus.org/translate/caesars.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The ] is a 4th-century Latin description of Alexander the Great's campaigns. ] went to serve his quaestorship in Hispania after his wife's funeral, in the spring or early summer of 69 BC. While there, he encountered a statue of Alexander the Great, and realised with dissatisfaction that he was now at an age when Alexander had the world at his feet, while he had achieved comparatively little.<ref>Goldsworthy, 100</ref><ref>Plutarch 1919, XI, 2</ref> | |||
| ] posed as the "new Alexander" since he was his boyhood hero.<ref>Leach, John. Pompey the Great. p. 29.</ref> | |||
| After Caracalla concluded his campaign against the Alamanni, it became evident that he was inordinately preoccupied with Alexander the Great.<ref name=":02">{{Cite book|last=Goldsworthy|first=Adrian|url=https://archive.org/details/howromefelldeath0000gold/page/74|title=How Rome Fell: death of a superpower|publisher=New Haven: Yale University Press|year=2009|isbn=978-0-300-16426-8|pages=}}</ref><ref name=":92">{{Cite book|last=Brauer|first=G.|title=The Decadent Emperors: Power and Depravity in Third-Century Rome|year=1967|pages=75}}</ref> He began openly mimicking Alexander in his personal style. In planning his invasion of the Parthian Empire, Caracalla decided to arrange 16,000 of his men in Macedonian-style ]es, despite the Roman army having made the phalanx an obsolete tactical formation.<ref name=":02" /><ref name=":92" /><ref name=":292">{{Cite book|last=Christopher|first=Matthew|title=An Invincible Beast: Understanding the Hellenistic Pike Phalanx in Action|publisher=Casemate Publishers|year=2015|pages=403}}</ref> The historian Christopher Matthew mentions that the term ''Phalangarii'' has two possible meanings, both with military connotations. The first refers merely to the Roman battle line and does not specifically mean that the men were armed with ], and the second bears similarity to the 'Marian Mules' of the late ] who carried their equipment suspended from a long pole, which were in use until at least the 2nd century AD.<ref name=":292" /> As a consequence, the ''Phalangarii'' of ] may not have been pikemen, but rather standard battle line troops or possibly '']''.<ref name=":292" /> | |||
| Caracalla's mania for Alexander went so far that Caracalla visited Alexandria while preparing for his Persian invasion and persecuted philosophers of the ] school based on a legend that ] had poisoned Alexander. This was a sign of Caracalla's increasingly erratic behaviour. But this mania for Alexander, strange as it was, was overshadowed by subsequent events in Alexandria.<ref name=":92" /> | |||
| In 39, Caligula performed a spectacular stunt by ordering a temporary ] to be built using ships as ], stretching for over two miles from the resort of ] to the neighbouring port of ].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Wardle |first1=David |title=Caligula's Bridge of Boats – AD 39 or 40? |journal=Historia |date=2007 |volume=56 |issue=1 |pages=118–120 |doi=10.25162/historia-2007-0009 |jstor=25598379 |s2cid=164017284 }}</ref><ref name="seutonius-calig-19">Suetonius, ''The Lives of Twelve Caesars'', Life of Caligula .</ref> It was said that the bridge was to rival the Persian king ] crossing of the Hellespont.<ref name="seutonius-calig-19" /> Caligula, who could not swim,<ref>Suetonius, ''The Lives of Twelve Caesars'', Life of Caligula .</ref> then proceeded to ride his favourite horse ] across, wearing the breastplate of ].<ref name="seutonius-calig-19" /> This act was in defiance of a prediction by Tiberius's soothsayer ] that Caligula had "no more chance of becoming emperor than of riding a horse across the Bay of Baiae".<ref name="seutonius-calig-19" /> | |||
| The diffusion of Greek culture and language cemented by Alexander's conquests in West Asia and North Africa served as a "precondition" for the ] into these territories and ] for the ], according to ].<ref>{{harvnb|Errington|1990|p=249}}.</ref> | |||
| ===Letters=== | |||
| {{main|Letters of Alexander the Great}} | |||
| Alexander wrote and received numerous letters, but no ] survive. A few official letters addressed to the Greek cities survive in copies inscribed in stone and the content of others is sometimes reported in historical sources. These only occasionally quote the letters and it is an open question how reliable such quotations are. Several fictitious letters, some perhaps based on actual letters, made their way into the ''Romance'' tradition.<ref name=LICP>{{cite journal |last1=Pearson |first1=Lionel |title=The Diary and the Letters of Alexander the Great |journal=Historia |date=1955 |volume=3 |issue=4 |pages=429–455 |jstor=4434421 }}</ref> | |||
| ===In legend=== | |||
| {{Main|Alexander the Great in legend}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Many of the legends about Alexander derive from his own lifetime, probably encouraged by Alexander himself.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=187}} His court historian Callisthenes portrayed the sea in ] as drawing back from him in proskynesis. Writing shortly after Alexander's death, ] invented a tryst between Alexander and ], queen of the mythical ]. He reportedly read this passage to his patron King ], who had been one of Alexander's generals and who quipped, "I wonder where I was at the time."<ref name="PA46" /> | |||
| In the first centuries after Alexander's death, probably in Alexandria, a quantity of the legendary material coalesced into a text known as the '']'', later falsely ascribed to Callisthenes and therefore known as ''Pseudo-Callisthenes''. This text underwent over one hundred recensions, translations, and derivations throughout the Islamic and European worlds in premodern times,<ref>{{harvnb|Stoneman|1996|loc=''passim''}}</ref> containing many dubious stories,{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=187}} and was translated into twenty-five languages,{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=117}} for example ], ] and ].<ref>{{harvnb|Darvishi|2022|loc=''117–152''}}</ref><ref name="auto"/> | |||
| ===In ancient and modern culture=== | |||
| {{Main|Cultural depictions of Alexander the Great|Alexander the Great in Islamic tradition|Alexander the Great in the Quran}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Alexander the Great's accomplishments and legacy have been depicted in many cultures. Alexander has featured in both high and popular culture, beginning from his own era to the present day. The ''Alexander Romance'', in particular, has had a significant impact on portrayals of Alexander in later cultures, from Persian to medieval European, to modern Greek.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=117}} | |||
| Alexander features prominently in modern Greek folklore, more than any other ancient figure.<ref name="Fermor">{{harvnb|Fermor|2006|page=215}}</ref> The colloquial form of his name in modern Greek ("O Megalexandros") is a household name, and he is the only ancient hero to appear in the ] shadow play.<ref name="Fermor" /> One well-known fable among Greek seamen involves a solitary ] who would grasp a ship's prow during a storm and ask the captain, "Is King Alexander alive?" The answer should be "He is alive and well and rules the world!" causing the mermaid to vanish and the sea to calm. Any other answer would cause the mermaid to turn into a raging ] who would drag the ship to the bottom of the sea, all hands aboard.<ref name="Fermor" /> | |||
| ]'' showing Alexander praying at the ], mid-16th century]] | |||
| In pre-Islamic ] (]) literature, Alexander is referred to by the epithet ''gujastak'', meaning "accursed", and is accused of destroying temples and burning the sacred texts of Zoroastrianism.<ref>{{harvnb|Curtis|Tallis|Andre-Salvini|2005|p=154}}</ref> In ]ic Persia, under the influence of the '']'' (in {{langx|fa|اسکندرنامه}} '']''), a more positive portrayal of Alexander emerges.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=120}} ]'s '']'' ("The Book of Kings") ] in a line of legitimate Persian ]s, a mythical figure who explored the far reaches of the world in search of the ].<ref>{{harvnb|Fischer|2004|p=66}}</ref> In the ''Shahnameh'', Alexander's first journey is to ] to pray at the ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Kennedy|first=Hugh|title=Hajj : journey to the heart of Islam|publisher=The British Museum|year=2012|isbn=978-0-674-06218-4|editor-last=Porter|editor-first=Venetia|location=Cambridge, Mass.|pages=131|chapter=Journey to Mecca: A History|oclc=709670348}}</ref> Alexander was depicted as performing a ] (pilgrimage to Mecca) many times in subsequent Islamic art and literature.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Webb|first=Peter|title=The Hajj : collected essays|publisher=The British Museum|year=2013|isbn=978-0-86159-193-0|editor-last=Porter|editor-first=Venetia|location=London|pages=14 footnote 72|chapter=The Hajj before Muhammad: Journeys to Mecca in Muslim Narratives of Pre-Islamic History|oclc=857109543|editor2-last=Saif|editor2-first=Liana}}</ref> Later Persian writers associate him with philosophy, portraying him at a symposium with figures such as ], ] and Aristotle, in search of immortality.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=120}} | |||
| ] depicting Alexander being lowered in a glass ]]] | |||
| The figure of ] (]: ذو القرنين; lit. "The Two-Horned One") is believed by the majority of modern researchers of the ] as well as Islamic commentators to be a reference to Alexander.<ref name=":1">{{cite journal |last1=Griffith |first1=Sidney |title=Narratives of 'the Companions of the Cave,' Moses and His Servant, and Dhū 'l-Qarnayn in Sūrat al-Kahf: Late Antique Lore within the Purview of the Qurʾān |journal=Journal of the International Qur'anic Studies Association |date=15 March 2022 |volume=6 |issue=1 |doi=10.5913/jiqsa.6.2021.a005 |s2cid=251486595 }}</ref> The figure is also believed by scholars to be based on later legends of Alexander.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=120}} In this tradition, he was a heroic figure who ] to defend against the nations of ].{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=122}} He also travelled the known world in search of the Water of Life and Immortality, eventually becoming a prophet.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=122}} | |||
| The ] version of the ''Alexander Romance'' portrays him as an ideal Christian world conqueror who prayed to "the one true God".{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=120}} In Egypt, Alexander was portrayed as the son of ], the last ] before the Persian conquest.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=122}} His defeat of Darius was depicted as Egypt's salvation, "proving" Egypt was still ruled by an Egyptian.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=120}} | |||
| According to ], Alexander was shown the ] when he entered Jerusalem, which described a mighty Greek king who would conquer the Persian Empire. This is cited as a reason for sparing Jerusalem.<ref>Josephus, ], XI, 337 </ref> | |||
| ], ''Les faits et conquêtes d'Alexandre le Grand'', 1448–1449]] | |||
| In ] and ], the name "]", derived from the Persian name for Alexander, denotes a rising young talent, and the ] ruler ] stylized himself as "Sikandar-i-Sani" (the Second Alexander the Great).<ref>{{harvnb|Connerney|2009|p=68}}</ref> In ], Turkic and Afghan sovereigns from the Iranian-cultured region of Central Asia brought positive cultural connotations of Alexander to the Indian subcontinent, resulting in the efflorescence of ''Sikandernameh'' (]) written by Indo-Persian poets such as ] and the prominence of Alexander the Great as a popular subject in Mughal-era Persian miniatures.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Donde |first=Dipanwita |date=2014 |title=The Mughal Sikander: Influence of the Romance of Alexander on Mughal Manuscript Painting |url=https://www.academia.edu/6097802 |journal=International Conference of Greek Studies: An Asian Perspective |via=Academia |access-date=19 April 2019 |archive-date=12 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210812151906/https://www.academia.edu/6097802 |url-status=live }}</ref> In ], Alexander the Great was revered as a member of the ]; a group of heroes whose lives were believed to encapsulate all the ideal qualities of ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Noll |first1=Thomas |article=The Visual Image of Alexander the Great |title=Alexander the Great in the Middle Ages: Transcultural Perspectives |editor-last=Stock |editor-first=Markus |translator-last=Boettcher |translator-first=Susan |date=2016 |publisher=University of Toronto Press |location=Toronto |isbn=978-1-4426-4466-3 |page=258 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2nqMCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA258 |access-date=21 November 2017}}</ref> During the first ], in a question from ], asking whether he gave his preference to Alexander or Caesar, ] said that he places Alexander The Great in the first rank, the main reason being his campaign on Asia.<ref>Louis Antoine Fauvelet de Bourrienne, Memoirs of Napoleon Bonaparte, pp 158</ref> | |||
| In the '']'', there are poems referring to Alexander.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://topostext.org/work/534#9.699|title=ToposText|website=topostext.org|access-date=18 August 2019|archive-date=1 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210201022239/https://topostext.org/work/534#9.699|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://topostext.org/work/748#122|title=ToposText|website=topostext.org|access-date=18 August 2019|archive-date=1 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210201022206/https://topostext.org/work/748#122|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Throughout time, art objects related to Alexander were being created. In addition to speech works, sculptures and paintings, in modern times Alexander is still the subject of musical and cinematic works. The song 'Alexander the Great' by the British heavy metal band ] is indicative. Some films that have been shot with the theme of Alexander are: | |||
| * '']'' (1941), an Indian production directed by ] about the conquest of India by Alexander<ref>{{cite book|title=100 Bollywood Films|isbn=978-81-7436-990-1|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=tk5gBAAAQBAJ&q=Sikandar+1941+Prithviraj+Kapoor&pg=PT165|last1=Dwyer|first1=Rachel|date=December 2005|publisher=Roli Books |access-date=6 April 2021}}</ref> | |||
| * '']'' (1956), produced by MGM and starring ] | |||
| * ''Sikandar-e-Azam'' (1965), an Indian production directed by Kedar Kapoor | |||
| * '']'' (2004), directed by ], starring ] | |||
| There are also many references to other movies and TV series. | |||
| Newer novels about Alexander are: | |||
| The trilogy "Alexander the Great" by ] consisting of "The son of the dream", "The sand of Amon", and "The ends of the world". | |||
| The trilogy of ] consisting of "]", "]" and "]". | |||
| * '']'', about Alexander the Great (2004), {{ISBN|978-0-385-50099-9}} and "* '']'', about Alexander the Great's conquests in Afghanistan (2006), {{ISBN|978-0-385-51641-9}}" by ]. | |||
| Irish playwright ] wrote '']''. | |||
| ==Historiography== | |||
| {{Main|Historiography of Alexander the Great}} | |||
| Apart from a few inscriptions and fragments, texts written by people who actually knew Alexander or who gathered information from men who served with Alexander were all lost.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=186}} Contemporaries who wrote accounts of his life included Alexander's campaign historian Callisthenes, Alexander's generals; Ptolemy and ], ], a junior officer on the campaigns, and Onesicritus, Alexander's chief helmsman. Their works are lost, but later works based on these ] have survived. The earliest of these is ] (1st century BC), followed by Quintus Curtius Rufus (mid-to-late 1st century AD), ] (1st to 2nd century AD), the biographer Plutarch (1st to 2nd century AD), and finally ], whose work dated as late as the 4th century.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=186}} Of these, Arrian is generally considered the most reliable, given that he used Ptolemy and Aristobulus as his sources, closely followed by Diodorus.{{sfn|Roisman|Worthington|2010|p=186}} | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Portal|History|Greece|Iran|Egypt}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| ===Notes=== | |||
| {{Cnote2 Begin|liststyle=upper-alpha}} | |||
| {{Cnote2|a| Heracles was Alexander's alleged illegitimate son.}} | |||
| {{Cnote2|b| The name {{lang|grc|Ἀλέξανδρος}} derives from the Greek verb {{lang|grc|ἀλέξω}} ({{transliteration|grc|aléxō}}, {{Literal translation|ward off, avert, defend|lk=on}}){{Sfn |Plutarch|1919|loc= | ps =: '{{lang|grc|ἀλέξω}}'.}}{{Sfn | Liddell | Scott | 1940}} and {{lang|grc|ἀνδρ-}} ({{transliteration|grc|andr-}}), the stem of {{lang|grc|ἀνήρ}} ({{transliteration|grc|anḗr}}, {{Literal translation|man}}),{{Sfn |Plutarch|1919|loc = | ps =: '{{lang|grc|ἀνήρ}}'.}}{{Sfn |Liddell|Scott|1940}} and means "protector of men".<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |access-date=11 December 2009 |url=http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?search=Alexander&searchmode=none |title=Alexander |dictionary=] |archive-date=20 September 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090920175420/http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?search=Alexander&searchmode=none |url-status=live }}</ref> }} | |||
| {{Cnote2|c|The first known person to call Alexander "the Great" was a Roman playwright named ] (254–184 BC) in his play '']''.<ref>{{Cite book|author=Diana Spencer|title=Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Classics|year= 2019|chapter=Alexander the Great, reception of|chapter-url=https://oxfordre.com/classics/view/10.1093/acrefore/9780199381135.001.0001/acrefore-9780199381135-e-8048|series=Oxford Research Encyclopedias|doi=10.1093/acrefore/9780199381135.013.8048|isbn=978-0-19-938113-5|access-date=9 November 2021|quote=Alexander enjoys the epithet ''the Great'' for the first time in Plautus's Roman comedy ''Mostellaria'' (775–777).|archive-date=10 November 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211110030827/https://oxfordre.com/classics/view/10.1093/acrefore/9780199381135.001.0001/acrefore-9780199381135-e-8048|url-status=live}}</ref>}} | |||
| {{Cnote2|d|Macedon was an Ancient Greek polity; the Macedonians were a Greek tribe.<ref name="Macedonians">{{harvnb|Hornblower|2008|pp=55–58}}; {{harvnb|Joint Association of Classical Teachers|1984|pp=50–51}}; {{harvnb|Errington|1990|pp=3–4}}; {{harvnb|Fine|1983|pp=607–08}}; {{harvnb|Hammond|Walbank|2001|p=11}}; {{harvnb|Jones|2001|p=21}}; {{harvnb|Osborne|2004|p=127}}; {{harvnb|Hammond|1989|pp=12–13}}; {{harvnb|Hammond|1993|p=97}}; {{harvnb|Starr|1991|pp=260, 367}}; {{harvnb|Toynbee|1981|p=67}}; {{harvnb|Worthington|2008|pp=8, 219}}; {{harvnb|Cawkwell|1978|p=22}}; {{harvnb|Perlman|1973|p=78}}; {{harvnb|Hamilton|1974|p=23}}; {{harvnb|Bryant|1996|p=306}}; {{harvnb|O'Brien|1994|p=25}}.</ref>}} | |||
| {{Cnote2|e| By the time of his death, he had conquered the entire ], adding it to Macedon's European territories; according to some modern writers, this was most of the world then known to the ancient Greeks (the ']').{{sfn|Danforth|1997|pp=38, 49, 167}}{{sfn|Stoneman|2004|p=2}} An approximate view of the world known to Alexander can be seen in ]'s map; see ]. }} | |||
| {{Cnote2|f| For instance, ] supposedly ranked Alexander as the greatest general;{{Sfn | Goldsworthy |2003|pp=327–28}} ] wept on seeing a statue of Alexander, since he had achieved so little by the same age;<ref name="Plutarch, Caesar, 11" /> ] and ] consciously posed as the 'new Alexander';{{sfn|Holland|2003|pp=176–83}} the young ] Bonaparte also encouraged comparisons with Alexander. Napoleon also placed Alexander in the first rank.{{sfn|Barnett|1997|p=45}} ] believed himself to be the actual reincarnation of Alexander.<ref>Ronald H. Fritze, Egyptomania: A History of Fascination, Obsession and Fantasy, p. 103.</ref><ref>Goldsworthy, Adrian (2009). How Rome Fell: death of a superpower. New Haven: Yale University Press. pp. 74. {{ISBN|978-0-300-16426-8}}.</ref><ref>Brauer, G. (1967). The Decadent Emperors: Power and Depravity in Third-Century Rome. p. 75.</ref> ] wore the breastplate of Alexander in order to show his power.<ref>Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 19.</ref><ref>Geoff W. Adams, The Roman Emperor Gaius "Caligula" and His Hellenistic Aspirations, pp 46</ref> ]'s hero was Alexander the Great, whose Spanish equivalent ''Alejandro'' he adopted as his ''nom de guerre''.<ref>Leycester Coltman, The Real Fidel Castro, p 220.</ref> Among ], ]'s heroes were Alexander and ].<ref>Nicolle, David (2000). Constantinople 1453: The End of Byzantium. Osprey Publishing. {{ISBN|978-1-84176-091-9}}.</ref> In a letter to his rival, ], while equating himself with Alexander, compares ] as "Darius of our days".<ref>{{cite book|title=Imperial Citizen: Marriage and Citizenship in the Ottoman Frontier Provinces of Iraq|page=39|year=2011|author=Karen M. Kern}}</ref> ], in a work written for ], says that Selim holds Alexander the Great and Julius Caesar in the highest esteem above all the generals of old.<ref>{{cite book|author=Donald Presgrave Little|year=1976|page=227|title=Essays on Islamic civilization presented to Niyazi Berkes}}</ref>}} | |||
| {{Cnote2|g|In ancient historiography, the ] was traditionally regarded as having originated from ]. The Argeads themselves claimed Argive Greek descent from the hero ]. Through his parents' genealogy, ancient authors traced Alexander's descent back to heroes and other legendary figures from ], such as ] and ].<ref>Diodorus, '']'' , ; Plutarch, '']'' ; Pausanias, '']'' , , ; Arrian, '']'' ; Herodotus, '']'' , ; Isocrates, ''To Philip'' ; Thucydides, </ref><ref>{{harvnb|Errington|1990|p=3}}; {{harvnb|Hornblower|2008|pp=55–58}}</ref>}} | |||
| {{Cnote2|h| There have been, since the time, many suspicions that Pausanias was actually hired to murder Philip. Suspicion has fallen upon Alexander, Olympias and even the newly crowned Persian Emperor, Darius III. All three of these people had motive to have Philip murdered.{{sfn|Lane Fox|1980|pp=72–73}} }} | |||
| {{Cnote2|i| However, ], who used ] as a source, said that Alexander crossed with more than 5,000 horse and 30,000 foot; ] quoted the same totals, but listed 5,100 horse and 32,000 foot. Diodorus also referred to an advance force already present in Asia, which ], in his Stratagems of War (5.44.4), said numbered 10,000 men.}} | |||
| {{Cnote2 End}} | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| ===Citations=== | |||
| {{reflist|refs = | |||
| <!-- List of named references in alphabetic order (grouped by 1st letter) --> | |||
| <ref name="Aelian">{{Citation |last=Aelian | chapter-url = http://penelope.uchicago.edu/aelian/varhist12.xhtml#chap64 |title=Varia Historia |volume=XII |chapter=64}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AelXII7">{{Citation |last=Aelian |title=Varia Historia | chapter-url = http://penelope.uchicago.edu/aelian/varhist12.xhtml#chap7 |volume=XII |chapter=7}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AIII16">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AMD">{{cite journal |last1=Oldach |first1=DW |last2=Richard |first2=RE |last3=Borza |first3=EN |last4=Benitez |first4=RM |title=A mysterious death |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=338 |issue=24 |pages=1764–69 |date=June 1998 |pmid=9625631 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199806113382411}}</ref> | |||
| <!--<ref name="appian">{{Citation |last=Appian |title=History of the Syrian Wars |at=§10 and §11 |url=https://www.livius.org/ap-ark/appian/appian_syriaca_02.html |publisher=Livius}}.</ref>--> | |||
| <ref name="ashrafian">{{cite journal |last=Ashrafian |first=H |title=The death of Alexander the Great – a spinal twist of fate |journal=J Hist Neurosci |volume=13 |pages=138–42 |year=2004 |doi=10.1080/0964704049052157 |pmid=15370319 |issue=2 |s2cid=36601180}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AVI27">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AVI29">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AVII11">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AVII14">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AVII19">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AVII27">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AVII29">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AVII4">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="Depuydt">{{Cite journal |last=Depuydt |first=Leo |date=1997 |title=The Time of Death of Alexander the Great: 11 June 323 B.C. (–322), ca. 4:00–5:00 PM |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/25683643 |journal=Die Welt des Orients |volume=28 |pages=117–135 |jstor=25683643 |issn=0043-2547}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="DiodXVI">{{harvnb|Diodorus Siculus|1989|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="DSXVII77">{{harvnb|Diodorus Siculus|1989|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="DSXVII114">{{harvnb|Diodorus Siculus|1989|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="DSXVII117">{{harvnb|Diodorus Siculus|1989|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="DSXVII118">{{harvnb|Diodorus Siculus|1989|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="DSXVIII4">{{harvnb|Diodorus Siculus|1989|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="I, 1">{{harvnb|Arrian|1976|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="P27">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="P72">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="P75">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA2">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA3">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA4">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA5">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA6">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA7">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA8">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA9">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA62">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA46">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA77">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PA45">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="Plutarch, Caesar, 11">{{harvnb|Plutarch|1919|loc= }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="ref1">{{cite journal |last1=Marr |first1=John S|author2-link=Charles Calisher |last2=Calisher |first2=Charles H |year=2003 |title=Alexander the Great and West Nile Virus Encephalitis |journal=Emerging Infectious Diseases |volume=9 |issue=12 |pages=1599–1603 |doi=10.3201/eid0912.030288 |pmc=3034319 |pmid=14725285}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="sarco1">{{cite web |last=Kosmetatou |first=Elizabeth |title=The Location of the Tomb: Facts and Speculation |work=Hellenic Electronic Center |year=1998 |publisher=Greece.org |url=http://www.greece.org/alexandria/alexander/pages/location.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040531025749/http://www.greece.org/alexandria/alexander/pages/location.html |archive-date=31 May 2004 |access-date=16 December 2011}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="sarco2">{{cite web |last=Kosmetatou |first=Elizabeth |title=The Aftermath: The Burial of Alexander the Great |work=Hellenic Electronic Center |year=1998 |publisher=Greece.org |url=http://www.greece.org/alexandria/alexander/pages/aftermath.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040827134332/http://www.greece.org/alexandria/alexander/pages/aftermath.html |archive-date=27 August 2004 |access-date=16 December 2011}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| ===Sources=== | |||
| ====Primary sources==== | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{cite book |isbn=978-0-14-044253-3 |author-link=Arrian |last=Arrian |title=Anabasis Alexandri (The Campaigns of Alexander) |editor1-first=Aubrey |editor1-last=de Sélincourt |editor1-link=Aubrey de Sélincourt |year=1976 |publisher=Penguin Books |title-link=Anabasis Alexandri}} | |||
| * {{cite book |url=http://www.attalus.org/info/curtius.html |title=History of Alexander |editor-first=John |editor-last=Rolfe |chapter=] |year=1946 |publisher=] |access-date=28 April 2015 |archive-date=23 September 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923180024/http://www.attalus.org/info/curtius.html |url-status=live}} | |||
| * {{cite web |last=Siculus |first=Diodorus |author-link=Diodorus Siculus |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=urn:cts:greekLit:tlg0060.tlg001.perseus-grc2:18.4.4 |title=Library of History |publisher=] |access-date=14 November 2009 |year=1989 |ref={{SfnRef|Diodorus Siculus|1989}} |others=CH Oldfather, translator |archive-date=24 September 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924214821/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=urn:cts:greekLit:tlg0060.tlg001.perseus-grc2:18.4.4 |url-status=live}} | |||
| * {{cite book |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.01.0243 |title=Plutarch, Alexander |editor-first=Bernadotte |editor-last=Perrin |last=] |year=1919 |publisher=Perseus Project |access-date=6 December 2011 |archive-date=21 October 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111021034907/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3atext%3a1999.01.0243 |url-status=live}} | |||
| * {{cite book |url=https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Plutarch/Moralia/Fortuna_Alexandri*/ |title=On the Fortune of Alexander |last=Plutarch |publisher=] |editor-first=Frank Cole |editor-last=Babbitt |access-date=26 November 2011 |volume=IV |year=1936 |pages=379–487}} | |||
| * {{cite web |first=Pompeius |last=Trogus |year=1853 |url=http://www.forumromanum.org/literature/justin/english/ |editor-last=Justin |title=Epitome of the Philippic History |access-date=14 November 2009 |website=Corpus Scriptorum Latinorum |others=Rev. John Selby Watson, translator |archive-date=8 November 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131108235820/http://www.forumromanum.org/literature/justin/english/ |url-status=usurped}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ====Secondary sources==== | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Barnett |first=C. |title=Bonaparte |publisher=Wordsworth |year=1997 |isbn=978-1-85326-678-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Baynes |first=Norman G |year=2007 |title=Byzantium: An Introduction to East Roman Civilization |publisher=Baynes |page=170 |chapter=Byzantine art |isbn=978-1-4067-5659-3 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HdHiVlZ3ErIC |access-date=5 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Berkley |first=Grant |year=2006 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=N7mj2NhCGNYC |title=Moses in the Hieroglyphs |publisher=Trafford |isbn=978-1-4120-5600-7 |access-date=13 January 2011}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Bose |first=Partha |title=Alexander the Great's Art of Strategy |publisher=Allen & Unwin |location=Crows Nest, NSW |isbn=978-1-74114-113-9 |year=2003}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Bosworth |first=A. B. |year=1988 |title=Conquest and Empire: The Reign of Alexander the Great |url=https://archive.org/details/conquestempire00abbo |url-access=registration |location=New York |publisher=Cambridge University Press}} | |||
| * {{Encyclopaedia Iranica|last=Briant|first=P.|author-link=Pierre Briant|title=ALEXANDER THE GREAT|volume=1|fascicle=8|url=https://iranicaonline.org/articles/alexander-the-great-356-23-bc|pages=827–830}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Bryant |first=Joseph M. |year=1996 |title=Moral Codes and Social Structure in Ancient Greece: A Sociology of Greek Ethics from Homer to the Epicureans and Stoics |publisher=] |location=Albany, NY |isbn=978-0-7914-3042-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bCM9D9fyCoQC |access-date=3 October 2020 |archive-date=9 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201109042906/https://books.google.com/books?id=bCM9D9fyCoQC |url-status=live}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Cawkwell |first=George |author-link=George Cawkwell |year=1978 |title=Philip of Macedon |publisher=] |location=London |isbn=978-0-571-10958-6 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=k-mUQgAACAAJ |access-date=3 October 2020 |archive-date=17 September 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200917114805/https://books.google.com/books?id=k-mUQgAACAAJ |url-status=live}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Cawthorne |first=Nigel |year=2004 |title=Alexander the Great |publisher=Haus |isbn=978-1-904341-56-7}} | |||
| * {{EB1911 |wstitle = Ptolemies |volume = 22 |pages = 616–618 }} <!-- Chisholm 1911 --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Connerney |first=R. D. |year=2009 |title=The upside-down tree: India's changing culture |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4WadcncjsRUC |publisher=Algora |isbn=978-0-87586-649-9 |page=214 |access-date=5 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Curtis |first1=J. |last2=Tallis |first2=N |last3=Andre-Salvini |first3=B |year=2005 |title=Forgotten empire: the world of ancient Persia |page=154 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kJnaKu9DdNEC |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-24731-4 |access-date=20 June 2015}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Dahmen |first=Karsten |year=2007 |title=The Legend of Alexander the Great on Greek and Roman Coins |publisher=Taylor & Francis |isbn=978-0-415-39451-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Danforth |first=Loring M. |year=1997 |title=The Macedonian Conflict: Ethnic Nationalism in a Transnational World |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-04356-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Darvishi |first=Dariush |year=2022 |title=The Alexander Romance |publisher=Negah-e Moaser |location=Tehran |isbn=978-622-290-118-9 |url=https://www.academia.edu/95955711 |access-date=5 May 2023}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Dillon |first=John M. |year=2004 |title=Morality and custom in ancient Greece |publisher=Indiana University Press |isbn=978-0-253-34526-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Durant |first=Will |author-link=Will Durant |year=1966 |title=The Story of Civilization: The Life of Greece |publisher=Simon & Schuster |isbn=978-0-671-41800-7 |url=https://archive.org/details/lifeofgreece02dura}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Errington |first=Robert Malcolm |author-link=Robert Malcolm Errington |year=1990 |title=A History of Macedonia |publisher=University of California Press |location=Berkeley |translator=Catherine Errington |isbn=978-0-520-06319-8 |url=https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_PYgkqP_s1PQC}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Fine |first=John Van Antwerp |year=1983 |title=The Ancient Greeks: A Critical History |publisher=] |location=Cambridge, MA |url=https://archive.org/details/ancientgreeks00john |url-access=registration |isbn=978-0-674-03314-6}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Fermor |first=Patrick Leigh |year=2006 |title=Mani: Travels in the Southern Peloponnese |publisher=] |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8V5QBkD7IIYC |isbn=978-1-59017-188-2 |page=358 |access-date=5 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Fischer |first=M. M. J. |year=2004 |title=Mute dreams, blind owls, and dispersed knowledges: Persian poesis in the transnational circuitry |page=66 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KibBH6cI8BgC |publisher=Duke University Press |isbn=978-0-8223-3298-5 |access-date=5 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Fletcher |first=Joann |author-link=Joann Fletcher |year=2008 |title=Cleopatra the Great: The Woman Behind the Legend |publisher=Harper |location=New York |isbn=978-0-06-058558-7 |url=https://archive.org/details/cleopatragreatwo00flet}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Foreman |first=Laura |year=2004 |title=Alexander the conqueror: the epic story of the warrior king |publisher=] |page=217 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rVEa4nzLkT4C |isbn=978-0-306-81293-4 |access-date=20 June 2015}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gabriel |first=Richard A |year=2002 |title=The Great Armies of Antiquity |publisher=Greenwood |page=277 |chapter=The army of Byzantium |isbn=978-0-275-97809-9 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=y1ngxn_xTOIC |access-date=5 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Gergel |editor-first=Tania |year=2004 |title=The Brief Life and Towering Exploits of History's Greatest Conqueror as Told By His Original Biographers |publisher=Penguin |isbn=978-0-14-200140-0 |url=https://archive.org/details/alexandergreatse00gerg}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Gerin |first1=Dominique |last2=Grandjean |first2=Catherine |last3=Amandry |first3=Michel |author-link3=Michel Amandry |last4=de Callatay |first4=François |author-link4=François de Callataÿ |title=La monnaie grecque |date=2001 |edition=Ellipse, "L'Antiquité : une histoire"}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Glick |editor1-first=Thomas F. |editor2-last=Livesey |editor2-first=Steven John |editor3-last=Wallis |editor3-first=Faith |year=2005 |title=Medieval Science, Technology, and Medicine: An Encyclopedia |publisher=Routledge |location=New York |isbn=978-0-415-96930-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Goldsworthy |first=A. |year=2003 |title=The Fall of Carthage |publisher=Cassel |isbn=978-0-304-36642-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first1=Anthony |last1=Grafton |year=2010 |editor1-last=Most |editor1-first=Glenn W |editor2-last=Settis |editor2-first=Salvatore |title=The Classical Tradition |publisher=Harvard University Press |isbn=978-0-674-03572-0}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Green |first=Peter |author-link=Peter Green (historian) |year=2007 |title=Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic Age |publisher=Phoenix |location=London |isbn=978-0-7538-2413-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gunther |first=John |year=2007 |title=Alexander the Great |publisher=Sterling |isbn=978-1-4027-4519-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hamilton |first=J.R. |year=1974 |title=Alexander the Great |publisher=] |location=Pittsburgh |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qi0iL6r7v2IC |isbn=978-0-8229-6084-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |author-link=N. G. L. Hammond |last=Hammond |first=NGL |year=1983 |title=Sources for Alexander the Great |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-521-71471-6 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gay_i14p9oEC |access-date=5 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hammond |first=Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière |year=1986 |title=A History of Greece to 323 BC |publisher=Cambridge University |author-link=N. G. L. Hammond |author-mask=3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hammond |first=Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière |year=1993 |title=Studies concerning Epirus and Macedonia before Alexander |publisher=Hakkert |location=Amsterdam |isbn=978-90-256-1050-0 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TWwiAQAAIAAJ |access-date=3 October 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Hammond |first1=Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière |author-link1=N. G. L. Hammond |last2=Walbank |first2=Frank William |author-link2=F. W. Walbank |year=2001 |title=A History of Macedonia: 336–167 B.C. |volume=3 |edition=reprint |publisher=] of the ] |location=Oxford |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qpb3JdwuDQIC |isbn=978-0-19-814815-9 |access-date=3 October 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Harrison |first=E. F. |year=1971 |title=The language of the New Testament |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qh7b4o6JQpIC |publisher=Wm B Eerdmans |page=508 |isbn=978-0-8028-4786-7 |access-date=5 September 2020 |archive-date=14 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210414133402/https://books.google.com/books?id=qh7b4o6JQpIC |url-status=live}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Heckel |editor1-first=Waldemar |editor2-first=Lawrence A |editor2-last=Tritle |year=2009 |title=Alexander the Great: A New History |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |isbn=978-1-4051-3082-0 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jbaPwpvt8ZQC |access-date=5 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Holland |first=Tom |title=Rubicon: Triumph and Tragedy in the Roman Republic |year=2003 |publisher=Abacus |isbn=978-0-349-11563-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Holt |first=Frank Lee |title=Alexander the Great and The Mystery of the Elephant Medallions |year=2003 |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-23881-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hornblower |first=Simon |chapter=Greek Identity in the Archaic and Classical Periods |title=Hellenisms: Culture, Identity and Ethnicity from Antiquity to Modernity |url=https://archive.org/details/hellenismscultur00zach |url-access=limited |pages=–58 |editor-last=Zacharia |editor-first=K. |publisher=Ashgate |isbn=978-0-7546-6525-0 |year=2008}} | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Joint Association of Classical Teachers|title=The World of Athens: An Introduction to Classical Athenian Culture|location=Cambridge, UK |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1984|isbn=0-521-27389-7|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VgDKeqi4or8C}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Jones |first=Archer |year=2001 |title=The Art of War in the Western World |publisher=] |location=Champaign |isbn=978-0-252-06966-6 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=z2FRzcz2W0oC |access-date=3 October 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Keay |first=John |title=India: A History |publisher=Grove Press |year=2001 |isbn=978-0-8021-3797-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kosmin |first=Paul J. |author-link=Paul J. Kosmin |title=The Land of the Elephant Kings: Space, Territory, and Ideology in Seleucid Empire |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9UWdAwAAQBAJ |publisher=Harvard University Press |date=2014 |isbn=978-0-674-72882-0 |access-date=24 August 2017}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lane Fox |first=Robin |year=1980 |title=The Search for Alexander |publisher=Little Brown & Co |place=Boston |isbn=978-0-316-29108-8 |url=https://archive.org/details/searchforalexand00lane}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lane Fox |first=Robin |author-link=Robin Lane Fox |year=2006 |title=Alexander the Great |publisher=ePenguin |asin=B002RI9DYW |author-mask=3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=LE RIDER |first1=George |title=Alexandre le Grand : Monnaie, finances et politique |date=2003 |publisher=PUF |page=Chapter V |edition=Histoire}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Liddell |first1=Henry George |first2=Robert |last2=Scott |title=A Greek-English Lexicon on Perseus Digital Library |editor1-first=Sir Henry Stuart |editor1-last=Jones |editor2-first=Roderick |editor2-last=McKenzie |location=Oxford |publisher=Clarendon Press |year=1940}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Luniya |first=Bhanwarlal Nathuram |title=Life and Culture in Ancient India: From the Earliest Times to 1000 AD |year=1978 |publisher=Lakshmi Narain Agarwal |lccn=78907043}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=McCarty |first=Nick |title=Alexander the Great |publisher=Penguin |location=Camberwell, Victoria |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-670-04268-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lMoOAAAAQAAJ |title=Outsiders in the Greek cities in the fourth century BC |last=McKechnie |first=Paul |page=54 |publisher=Taylor & Francis |year=1989 |isbn=978-0-415-00340-7 |access-date=20 June 2015}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Morkot |first=Robert |title=The Penguin Historical Atlas of Ancient Greece |publisher=Penguin |year=1996}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Narain |first=A. K. |title=Alexander the Great: Greece and Rome–12 |year=1965}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Ogden |first=Daniel |chapter=Alexander's Sex Life |title=Alexander the Great: A New History |editor1-first=Alice |editor1-last=Heckel |editor2-first=Waldemar |editor2-last=Heckel |editor3-first=Lawrence A |editor3-last=Tritle |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |year=2009 |isbn=978-1-4051-3082-0}} | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Osborne|first=Robin|title=Greek History|location=New York, New York and London, UK |publisher=Routledge|year=2004|isbn=0-415-31717-7|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jXve_I_7u8QC}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Perlman |first=Samuel |year=1973 |title=Philip and Athens |publisher=Heffer |location=Cambridge |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=s5sgAAAAMAAJ |isbn=978-0-85270-076-1}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Pingree |first=D. |volume=15 |year=1978 |pages=533–633 |chapter=History of Mathematical Astronomy in India |title=Dictionary of Scientific Biography}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Pratt |first=James Bissett |title=The Pilgrimage of Buddhism and a Buddhist Pilgrimage |year=1996 |publisher=Laurier Books |isbn=978-81-206-1196-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Rebuffat |first1=Françoise |title=La monnaie dans l'Antiquité |date=1996 |publisher=Picard}} | |||
| <!-- Both version are in use, d not remove either until the reference are all corrected --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Renault |first=Mary |title=The Nature of Alexander the Great |publisher=Penguin |year=2001 |isbn=978-0-14-139076-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Renault |first=Mary |title=The Nature of Alexander |publisher=Open Road Media |year=2013 |isbn=978-1480432949}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Ring |editor1-first=Trudy |editor2-last=Salkin |editor2-first=Robert M |editor3-last=Berney |editor3-first=KA |editor4-last=Schellinger |editor4-first=Paul E |title=International dictionary of historic places |year=1994 |isbn=978-1-884964-04-6 |location=Chicago |publisher=Fitzroy Dearborn, 1994–1996}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Roisman |first1=Joseph |last2=Worthington |first2=Ian |title=A Companion to Ancient Macedonia |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |year=2010 |isbn=978-1-4051-7936-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lkYFVJ3U-BIC |access-date=20 June 2015}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Sabin |first1=P |last2=van Wees |first2=H |last3=Whitby |first3=M |title=The Cambridge History of Greek and Roman Warfare: Greece, the Hellenistic World and the Rise of Rome |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-521-78273-9 |year=2007}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Sacks |first=David |title=Encyclopedia of the Ancient Greek World |publisher=Constable & Co |isbn=978-0-09-475270-2 |year=1995}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Starr |first=Chester G. |year=1991 |title=A History of the Ancient World |publisher=Oxford University Press |location=New York |isbn=978-0-19-506628-9 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bA3kgtZU1iMC |access-date=3 October 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Stoneman |first=Richard |title=Alexander the Great |url=https://archive.org/details/alexandergreat0000ston |url-access=registration |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-0-415-31932-4 |year=2004}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Stoneman |first=Richard |title=The Novel in the Ancient World |url=https://archive.org/details/novelancientworl00schm |url-access=limited |editor-last=Schmeling |editor-first=Gareth L |chapter=The Metamorphoses of Alexander Romance |pages=–12 |publisher=Brill |year=1996 |isbn=978-90-04-09630-1}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Studniczka |first=Franz |title=Achäologische Jahrbook 9 |year=1894}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Tripathi |first=Rama Shankar |title=History of Ancient India |year=1999 |publisher=Motilal Banarsidass Publ. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=WbrcVcT-GbUC |isbn=978-81-208-0018-2 |access-date=5 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Toynbee |first=Arnold Joseph |year=1981 |title=The Greeks and Their Heritages |publisher=Oxford University Press |location=Oxford |isbn=978-0-19-215256-5 |url=https://archive.org/details/greekstheirheri00toyn |url-access=registration}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Wood |first=Michael |year=2001 |title=In the Footsteps of Alexander the Great: A Journey from Greece to Asia |publisher=University of California Press |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5wDWn1dL6HMC |isbn=978-0-520-23192-4 |access-date=5 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Worthington |first=Ian |year=2003 |title=Alexander the Great: A Reader |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OiM51I7_A1gC |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-0-415-29187-3 |page=332 |access-date=5 September 2020}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Worthington |first=Ian |year=2008 |title=Philip II of Macedonia |publisher=] |location=New Haven, CT |isbn=978-0-300-12079-0 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CZsTAQAAIAAJ |access-date=20 June 2015}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Yenne |first=Bill |year=2010 |title=Alexander the Great: Lessons From History's Undefeated General |publisher=Palgrave MacMillan |isbn=978-0-230-61915-9}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Badian |first=Ernst |author-link=Ernst Badian |year=1958 |title=Alexander the Great and the Unity of Mankind |journal=Historia |volume=7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Beazley |first1=JD |author1-link=J. D. Beazley |last2=Ashmole |first2=B |author2-link=Bernard Ashmole |year=1932 |title=Greek Sculpture and Painting |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-521-04131-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Bowra |first=Maurice |author-link=Maurice Bowra |year=1994 |title=The Greek Experience |publisher=Phoenix |isbn=978-1-85799-122-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Boardman |first=John |author-link=John Boardman (art historian) |year=2019 |title=Alexander the Great: From His Death to the Present Day |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-18175-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Burn |first=AR |year=1951 |title=Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic Empire |edition=2nd |location=London |publisher=English Universities Press}} | |||
| * {{cite web |language=la |url=https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Curtius/home.html |last=Rufus |first=Quintus Curtius |title=Quintus Curtius Rufus, History of Alexander the Great |publisher=U Chicago |access-date=16 November 2009}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Cartledge |first=Paul |author-link=Paul Cartledge |year=2004 |title=Alexander the Great |url=https://archive.org/details/alexandergreatth00cart |url-access=registration |publisher=Overlook |isbn=978-1-58567-565-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Doherty |first=Paul |author-link=Paul C. Doherty |year=2004 |title=The Death of Alexander the Great |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780786713400 |url-access=registration |publisher=Carroll & Graf |isbn=978-0-7867-1340-0}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Engels |first=Donald W |year=1978 |title=Alexander the Great and the Logistics of the Macedonian Army |location=Berkeley |publisher=University of California Press}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Fawcett |editor-first=Bill |year=2006 |title=How To Lose A Battle: Foolish Plans and Great Military Blunders |publisher=Harper |isbn=978-0-06-076024-3 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/howtolosebattlef0000unse}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Fuller |first=JFC |author-link=J. F. C. Fuller |year=1958 |title=The Generalship of Alexander the Great |location=London |publisher=Eyre & Spottiswoode |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=q3M0NE2RJgYC |isbn=978-0-306-80371-0 |access-date=20 June 2015}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Goldsworthy |first=Adrian |author-link=Adrian Goldsworthy |title=] |publisher=] |date=2020 |location=London |isbn=978-1-78497-869-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Green |first=Peter |author-link=Peter Green (historian) |year=1992 |title=Alexander of Macedon: 356–323 BC. A Historical Biography |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-07166-7 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/alexanderofmaced0000gree}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Greene |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Greene (American author) |year=2000 |title=The 48 Laws of Power |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780670881468 |url-access=registration |publisher=Penguin |page= |isbn=978-0-14-028019-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hammond |first=NGL |author-link=N. G. L. Hammond |year=1989 |title=The Macedonian State: Origins, Institutions, and History |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-814883-8}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hammond |first=NGL |year=1994 |title=Alexander the Great: King, Commander, and Statesman |edition=3rd |location=London |publisher=Bristol Classical Press}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hammond |first=NGL |year=1997 |title=The Genius of Alexander the Great |url=https://archive.org/details/geniusofalexande00nglh |url-access=registration |location=Chapel Hill |publisher=University of North Carolina Press}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lane Fox |first=Robin |author-link=Robin Lane Fox |year=1973 |title=Alexander the Great |location=London |publisher=Allen Lane |isbn=978-0-14-008878-6}}, also (1974) New York: E. P. Dutton and (1986) London: ]. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Mercer |first=Charles |year=1962 |title=The Way of Alexander the Great |location=Boston |publisher=American Heritage Inc.}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=McCrindle |first=J. W. |year=1893 |title=The Invasion of India by Alexander the Great as Described by Arrian, Q Curtius, Diodorus, Plutarch, and Justin |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=A9YNAAAAIAAJ |location=Westminster |publisher=Archibald Constable & Co |access-date=20 June 2015}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Monti |first1=Giustina |title=Alexander the Great: letters: a selection |date=2023 |publisher=Liverpool University Press |location=Liverpool |isbn=9781800348622}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Murphy |first1=James Jerome |last2=Katula |first2=Richard A |last3=Hill |first3=Forbes I |last4=Ochs |first4=Donovan J |year=2003 |title=A Synoptic History of Classical Rhetoric |publisher=Lawrence Erlbaum Associates |page=17 |isbn=978-1-880393-35-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Nandan |first1=Y |last2=Bhavan |first2=BV |year=2003 |title=British Death March Under Asiatic Impulse: Epic of Anglo-Indian Tragedy in Afghanistan |isbn=978-81-7276-301-5 |publisher=Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan |location=Mumbai}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=O'Brien |first=John Maxwell |year=1992 |title=Alexander the Great: The Invisible Enemy |location=London |publisher=Routledge}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Pomeroy |first1=S |last2=Burstein |first2=S |last3=Dolan |first3=W |last4=Roberts |first4=J |year=1998 |title=Ancient Greece: A Political, Social, and Cultural History |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-509742-9 |url=https://archive.org/details/ancientgreecepol00sara}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Prevas |first=John |author-link=John Prevas |year=2004 |title=Envy of the Gods: Alexander the Great's Ill-Fated Journey Across Asia |url=https://archive.org/details/envyofgodsalexan00prev |url-access=registration |edition=3rd |publisher=Da Capo Press |isbn=978-0-306-81268-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Roisman |editor-first=Joseph |year=1995 |title=Alexander the Great Ancient and Modern Perspectives |series=Problems in European Civilization |location=Lexington, MA |publisher=DC Heath}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Rowson |first=Alex |year=2022 |title=The Young Alexander: The Making of Alexander the Great |location=London |publisher=William Collins |type=Hardcover |isbn=978-0-00-828439-8}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Savill |first=Agnes |author-link=l |year=1959 |title=Alexander the Great and His Time |url=https://archive.org/details/alexandergreathi0000savi_n3m7 |url-access=registration |edition=3rd |location=London |publisher=Barrie & Rockliff}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Stewart |first=Andrew |year=1993 |series=Hellenistic Culture and Society |title=Faces of Power: Alexander's Image and Hellenistic Politics |volume=11 |location=Berkeley |publisher=University of California Press}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Stoneman |first=Richard |year=2008 |title=Alexander the Great: A Life in Legend |publisher=Yale University Press |isbn=978-0-300-11203-0 |url=https://archive.org/details/alexandergreatli00ston}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Tarn |first=WW |author-link=William Woodthorpe Tarn |year=1948 |title=Alexander the Great |url=https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.499219 |location=Cambridge |publisher=Cambridge University Press}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Wheeler |first=Benjamin Ide |author-link=Benjamin Ide Wheeler |year=1900 |title=Alexander the Great; the merging of East and West in universal history |url=https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.173405 |location=New York |publisher=GP Putnam's sons}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Wilcken |first=Ulrich |year=1997 |author-link=Ulrich Wilcken |orig-year=1932 |title=Alexander the Great |location=New York |publisher=WW Norton & Co |isbn=978-0-393-00381-9 |url=https://archive.org/details/alexandergreat00wilc}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Worthington |first=Ian |year=2004 |title=Alexander the Great: Man And God |publisher=Pearson |isbn=978-1-4058-0162-1}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{Sister project links |s=Author:Alexander III of Macedon |n=no |voy=On the trail of Alexander the Great}} | |||
| {{Library resources box |by=no |onlinebooks=yes |others=yes |about=yes |label=Alexander the Great | |||
| |viaf= |lccn= |lcheading= |wikititle= }} | |||
| * {{cite map |url=http://www.wdl.org/en/item/11738/ |title=The Empire and Expeditions of Alexander the Great |first=Félix |last=Delamarche |author-link=Félix Delamarche |year=1833}} | |||
| * {{cite news |title=Two Great Historians on Alexander the Great |type=conversations |first1=James |last1=Romm |first2=Paul |last2=Cartledge |author2-link=Paul Cartledge |newspaper=Forbes}} , , , , , . | |||
| * . Livius. Archived from on 4 December 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2020. | |||
| * {{snd}}BBC discussion with Paul Cartledge, Diana Spencer and Rachel Mairs hosted by Melvyn Bragg, first broadcast 1 October 2015. | |||
| {{S-start}} | |||
| {{S-hou|]||356 BC||323 BC}} | |||
| {{s-reg}} | |||
| {{S-bef|before=]}} | |||
| {{S-ttl|title=]|years=336–323 BC}} | |||
| {{S-aft|rows=4|after=]|after2=]}} | |||
| {{S-bef|rows=2|before=]}} | |||
| {{S-ttl|title=]|years=330–323 BC}} | |||
| {{S-break}} | |||
| {{S-ttl|title=]|years=332–323 BC}} | |||
| {{S-new|creation}} | |||
| {{S-ttl|title=Lord of Asia|years=331–323 BC}} | |||
| {{S-end}} | |||
| {{Kings of Macedon}} | |||
| {{Hellenistic rulers}} | |||
| {{Pharaohs |late}} | |||
| {{Babylonian kings|state=collapsed}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| {{Link FA|fi}} | |||
| {{Link FA|it}} | |||
| {{Link FA|mk}} | |||
| {{Link FA|no}} | |||
| {{Link FA|sk}} | |||
| {{Link FA|he}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:25, 20 January 2025
Military commander and king of Macedon (356–323 BC) This article is about the ancient king of Macedon. For other uses, see Alexander the Great (disambiguation).
| Alexander the Great | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basileus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Alexander in the Alexander Mosaic Alexander in the Alexander Mosaic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| King of Macedon | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reign | October 336 – June 323 BC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predecessor | Philip II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Successor | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hegemon of the Hellenic League | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reign | 336–323 BC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predecessor | Philip II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Successor | Demetrius I of Macedon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharaoh of Egypt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reign | 332–323 BC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predecessor | Darius III | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Successor |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Royal titulary
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| King of Persia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reign | 330–323 BC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predecessor | Darius III | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Successor |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Born | 20 or 21 July 356 BC Pella, Macedon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Died | 10 or 11 June 323 BC (aged 32) Babylon, Macedon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spouse | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issue | 3, including | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greek | Ἀλέξανδρος | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dynasty | Argead | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Father | Philip II of Macedon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mother | Olympias of Epirus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Ancient Greek religion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Alexander III of Macedon (Ancient Greek: Ἀλέξανδρος, romanized: Aléxandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia, Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and Egypt. By the age of 30, he had created one of the largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders.
Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he campaigned in the Balkans and reasserted control over Thrace and parts of Illyria before marching on the city of Thebes, which was subsequently destroyed in battle. Alexander then led the League of Corinth, and used his authority to launch the pan-Hellenic project envisaged by his father, assuming leadership over all Greeks in their conquest of Persia.
In 334 BC, he invaded the Achaemenid Persian Empire and began a series of campaigns that lasted for 10 years. Following his conquest of Asia Minor, Alexander broke the power of Achaemenid Persia in a series of decisive battles, including those at Issus and Gaugamela; he subsequently overthrew Darius III and conquered the Achaemenid Empire in its entirety. After the fall of Persia, the Macedonian Empire held a vast swath of territory between the Adriatic Sea and the Indus River. Alexander endeavored to reach the "ends of the world and the Great Outer Sea" and invaded India in 326 BC, achieving an important victory over Porus, an ancient Indian king of present-day Punjab, at the Battle of the Hydaspes. Due to the mutiny of his homesick troops, he eventually turned back at the Beas River and later died in 323 BC in Babylon, the city of Mesopotamia that he had planned to establish as his empire's capital. Alexander's death left unexecuted an additional series of planned military and mercantile campaigns that would have begun with a Greek invasion of Arabia. In the years following his death, a series of civil wars broke out across the Macedonian Empire, eventually leading to its disintegration at the hands of the Diadochi.
With his death marking the start of the Hellenistic period, Alexander's legacy includes the cultural diffusion and syncretism that his conquests engendered, such as Greco-Buddhism and Hellenistic Judaism. He founded more than twenty cities, with the most prominent being the city of Alexandria in Egypt. Alexander's settlement of Greek colonists and the resulting spread of Greek culture led to the overwhelming dominance of Hellenistic civilization and influence as far east as the Indian subcontinent. The Hellenistic period developed through the Roman Empire into modern Western culture; the Greek language became the lingua franca of the region and was the predominant language of the Byzantine Empire until its collapse in the mid-15th century AD.
Alexander became legendary as a classical hero in the mould of Achilles, featuring prominently in the historical and mythical traditions of both Greek and non-Greek cultures. His military achievements and unprecedented enduring successes in battle made him the measure against which many later military leaders would compare themselves, and his tactics remain a significant subject of study in military academies worldwide. Legends of Alexander's exploits coalesced into the third-century Alexander Romance which, in the premodern period, went through over one hundred recensions, translations, and derivations and was translated into almost every European vernacular and every language of the Islamic world. After the Bible, it was the most popular form of European literature.
Early life
Lineage and childhood

Alexander III was born in Pella, the capital of the Kingdom of Macedon, on the sixth day of the ancient Greek month of Hekatombaion, which probably corresponds to 20 July 356 BC (although the exact date is uncertain). He was the son of the erstwhile king of Macedon, Philip II, and his fourth wife, Olympias (daughter of Neoptolemus I, king of Epirus). Although Philip had seven or eight wives, Olympias was his principal wife for some time, likely because she gave birth to Alexander.

Several legends surround Alexander's birth and childhood. According to the ancient Greek biographer Plutarch, on the eve of the consummation of her marriage to Philip, Olympias dreamed that her womb was struck by a thunderbolt that caused a flame to spread "far and wide" before dying away. Sometime after the wedding, Philip is said to have seen himself, in a dream, securing his wife's womb with a seal engraved with a lion's image. Plutarch offered a variety of interpretations for these dreams: that Olympias was pregnant before her marriage, indicated by the sealing of her womb; or that Alexander's father was Zeus. Ancient commentators were divided about whether the ambitious Olympias promulgated the story of Alexander's divine parentage, variously claiming that she had told Alexander, or that she dismissed the suggestion as impious.
On the day Alexander was born, Philip was preparing a siege on the city of Potidea on the peninsula of Chalcidice. That same day, Philip received news that his general Parmenion had defeated the combined Illyrian and Paeonian armies and that his horses had won at the Olympic Games. It was also said that on this day, the Temple of Artemis in Ephesus, one of the Seven Wonders of the World, burnt down. This led Hegesias of Magnesia to say that it had burnt down because Artemis was away, attending the birth of Alexander. Such legends may have emerged when Alexander was king, and possibly at his instigation, to show that he was superhuman and destined for greatness from conception.
In his early years, Alexander was raised by a nurse, Lanike, sister of Alexander's future general Cleitus the Black. Later in his childhood, Alexander was tutored by the strict Leonidas, a relative of his mother, and by Lysimachus of Acarnania. Alexander was raised in the manner of noble Macedonian youths, learning to read, play the lyre, ride, fight, and hunt. When Alexander was ten years old, a trader from Thessaly brought Philip a horse, which he offered to sell for thirteen talents. The horse refused to be mounted, and Philip ordered it away. Alexander, however, detecting the horse's fear of its own shadow, asked to tame the horse, which he eventually managed. Plutarch stated that Philip, overjoyed at this display of courage and ambition, kissed his son tearfully, declaring: "My boy, you must find a kingdom big enough for your ambitions. Macedon is too small for you", and bought the horse for him. Alexander named it Bucephalas, meaning "ox-head". Bucephalas carried Alexander as far as India. When the animal died (because of old age, according to Plutarch, at age 30), Alexander named a city after him, Bucephala.
Education
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Early rule Conquest of the Persian Empire Expedition into India Death and legacy Cultural impact |
||
When Alexander was 13, Philip began to search for a tutor, and considered such academics as Isocrates and Speusippus, the latter offering to resign from his stewardship of the Academy to take up the post. In the end, Philip chose Aristotle and provided the Temple of the Nymphs at Mieza as a classroom. In return for teaching Alexander, Philip agreed to rebuild Aristotle's hometown of Stageira, which Philip had razed, and to repopulate it by buying and freeing the ex-citizens who were slaves, or pardoning those who were in exile.
Mieza was like a boarding school for Alexander and the children of Macedonian nobles, such as Ptolemy, Hephaistion, and Cassander. Many of these students would become his friends and future generals, and are often known as the "Companions". Aristotle taught Alexander and his companions about medicine, philosophy, morals, religion, logic, and art. Under Aristotle's tutelage, Alexander developed a passion for the works of Homer, and in particular the Iliad; Aristotle gave him an annotated copy, which Alexander later carried on his campaigns. Alexander was able to quote Euripides from memory.
In his youth, Alexander was also acquainted with Persian exiles at the Macedonian court, who received the protection of Philip II for several years as they opposed Artaxerxes III. Among them were Artabazos II and his daughter Barsine, possible future mistress of Alexander, who resided at the Macedonian court from 352 to 342 BC, as well as Amminapes, future satrap of Alexander, and a Persian nobleman named Sisines. This gave the Macedonian court a good knowledge of Persian issues, and may even have influenced some of the innovations in the management of the Macedonian state.
Suda writes that Anaximenes of Lampsacus was one of Alexander's teachers, and that Anaximenes also accompanied Alexander on his campaigns.
Heir of Philip II
Regency and ascent of Macedon
Main articles: Philip II of Macedon and Rise of Macedon Further information: History of Macedonia (ancient kingdom)
At the age of 16, Alexander's education under Aristotle ended. Philip II had waged war against the Thracians to the north, which left Alexander in charge as regent and heir apparent. During Philip's absence, the Thracian tribe of Maedi revolted against Macedonia. Alexander responded quickly and drove them from their territory. The territory was colonized, and a city, named Alexandropolis, was founded.
Upon Philip's return, Alexander was dispatched with a small force to subdue the revolts in southern Thrace. Campaigning against the Greek city of Perinthus, Alexander reportedly saved his father's life. Meanwhile, the city of Amphissa began to work lands that were sacred to Apollo near Delphi, a sacrilege that gave Philip the opportunity to further intervene in Greek affairs. While Philip was occupied in Thrace, Alexander was ordered to muster an army for a campaign in southern Greece. Concerned that other Greek states might intervene, Alexander made it look as though he was preparing to attack Illyria instead. During this turmoil, the Illyrians invaded Macedonia, only to be repelled by Alexander.
Philip and his army joined his son in 338 BC, and they marched south through Thermopylae, taking it after stubborn resistance from its Theban garrison. They went on to occupy the city of Elatea, only a few days' march from both Athens and Thebes. The Athenians, led by Demosthenes, voted to seek alliance with Thebes against Macedonia. Both Athens and Philip sent embassies to win Thebes's favour, but Athens won the contest. Philip marched on Amphissa (ostensibly acting on the request of the Amphictyonic League), capturing the mercenaries sent there by Demosthenes and accepting the city's surrender. Philip then returned to Elatea, sending a final offer of peace to Athens and Thebes, who both rejected it.

As Philip marched south, his opponents blocked him near Chaeronea, Boeotia. During the ensuing Battle of Chaeronea, Philip commanded the right wing and Alexander the left, accompanied by a group of Philip's trusted generals. According to the ancient sources, the two sides fought bitterly for some time. Philip deliberately commanded his troops to retreat, counting on the untested Athenian hoplites to follow, thus breaking their line. Alexander was the first to break the Theban lines, followed by Philip's generals. Having damaged the enemy's cohesion, Philip ordered his troops to press forward and quickly routed them. With the Athenians lost, the Thebans were surrounded. Left to fight alone, they were defeated.
After the victory at Chaeronea, Philip and Alexander marched unopposed into the Peloponnese, devastating much of Laconia and ejecting the Spartans from various parts of it. At Corinth, Philip established a "Hellenic Alliance" (modelled on the old anti-Persian alliance of the Greco-Persian Wars), which included most Greek city-states except Sparta. Philip was then named Hegemon (often translated as "Supreme Commander") of this league (known by modern scholars as the League of Corinth), and announced his plans to attack the Persian Empire.
Exile and return
When Philip returned to Pella, he fell in love with and married Cleopatra Eurydice in 338 BC, the niece of his general Attalus. The marriage made Alexander's position as heir less secure, since any son of Cleopatra Eurydice would be a fully Macedonian heir, while Alexander was only half-Macedonian. During the wedding banquet, a drunken Attalus publicly prayed to the gods that the union would produce a legitimate heir.
At the wedding of Cleopatra, whom Philip fell in love with and married, she being much too young for him, her uncle Attalus in his drink desired the Macedonians would implore the gods to give them a lawful successor to the kingdom by his niece. This so irritated Alexander that throwing one of the cups at his head, "You villain," said he, "what, am I then a bastard?" Then Philip, taking Attalus's part, rose up and would have run his son through; but by good fortune for them both, either his over-hasty rage, or the wine he had drunk, made his foot slip, so that he fell down on the floor, at which Alexander reproachfully insulted him: "See there," said he, "the man who makes preparations to pass out of Europe into Asia, overturned in passing from one seat to another."
— Plutarch, describing the feud at Philip's wedding.
In 337 BC, Alexander fled Macedon with his mother, dropping her off with her brother, King Alexander I of Epirus in Dodona, capital of the Molossians. He continued to Illyria where he sought refuge with one or more Illyrian kings, perhaps with Glaucias, and was treated as a guest, despite having defeated them in battle a few years before. However, it appears Philip never intended to disown his politically and militarily trained son. Accordingly, Alexander returned to Macedon after six months due to the efforts of a family friend, Demaratus, who mediated between the two parties.
In the following year, the Persian satrap (governor) of Caria, Pixodarus, offered his eldest daughter to Alexander's half-brother, Philip Arrhidaeus. Olympias and several of Alexander's friends suggested this showed Philip intended to make Arrhidaeus his heir. Alexander reacted by sending an actor, Thessalus of Corinth, to tell Pixodarus that he should not offer his daughter's hand to an illegitimate son, but instead to Alexander. When Philip heard of this, he stopped the negotiations and scolded Alexander for wishing to marry the daughter of a Carian, explaining that he wanted a better bride for him. Philip exiled four of Alexander's friends, Harpalus, Nearchus, Ptolemy and Erigyius, and had the Corinthians bring Thessalus to him in chains.
King of Macedon
Accession
Further information: Government of Macedonia (ancient kingdom)
In the 24th day of the Macedonian month Dios, which probably corresponds to 25 October 336 BC, while at Aegae attending the wedding of his daughter Cleopatra to Olympias's brother, Alexander I of Epirus, Philip was assassinated by the captain of his bodyguards, Pausanias. As Pausanias tried to escape, he tripped over a vine and was killed by his pursuers, including two of Alexander's companions, Perdiccas and Leonnatus. Alexander was proclaimed king on the spot by the nobles and army at the age of 20.
Consolidation of power
Alexander began his reign by eliminating potential rivals to the throne. He had his cousin, the former Amyntas IV, executed. He also had two Macedonian princes from the region of Lyncestis killed for having been involved in his father's assassination, but spared a third, Alexander Lyncestes. Olympias had Cleopatra Eurydice, and Europa, her daughter by Philip, burned alive. When Alexander learned about this, he was furious. Alexander also ordered the murder of Attalus, who was in command of the advance guard of the army in Asia Minor and Cleopatra's uncle.
Attalus was at that time corresponding with Demosthenes, regarding the possibility of defecting to Athens. Attalus also had severely insulted Alexander, and following Cleopatra's murder, Alexander may have considered him too dangerous to be left alive. Alexander spared Arrhidaeus, who was by all accounts mentally disabled, possibly as a result of poisoning by Olympias.
News of Philip's death roused many states into revolt, including Thebes, Athens, Thessaly, and the Thracian tribes north of Macedon. When news of the revolts reached Alexander, he responded quickly. Though advised to use diplomacy, Alexander mustered 3,000 Macedonian cavalry and rode south towards Thessaly. He found the Thessalian army occupying the pass between Mount Olympus and Mount Ossa, and ordered his men to ride over Mount Ossa. When the Thessalians awoke the next day, they found Alexander in their rear and promptly surrendered, adding their cavalry to Alexander's force. He then continued south towards the Peloponnese.
Alexander stopped at Thermopylae where he was recognized as the leader of the Amphictyonic League before heading south to Corinth. Athens sued for peace and Alexander pardoned the rebels. The famous encounter between Alexander and Diogenes the Cynic occurred during Alexander's stay in Corinth. When Alexander asked Diogenes what he could do for him, the philosopher disdainfully asked Alexander to stand a little to the side, as he was blocking the sunlight. This reply apparently delighted Alexander who is reported to have said, "But verily, if I were not Alexander, I would like to be Diogenes." At Corinth, Alexander took the title of Hegemon ("leader") and, like Philip, was appointed commander for the coming war against Persia. He also received news of a Thracian uprising.
Balkan campaign
Main article: Alexander's Balkan campaign
Before crossing to Asia, Alexander wanted to safeguard his northern borders. In the spring of 335 BC, he advanced to suppress several revolts. Starting from Amphipolis, he travelled east into the country of the "Independent Thracians", and at Mount Haemus, the Macedonian army attacked and defeated the Thracian forces manning the heights. The Macedonians marched into the country of the Triballi and defeated their army near the Lyginus river (a tributary of the Danube). Alexander then marched for three days to the Danube, encountering the Getae tribe on the opposite shore. Crossing the river at night, he surprised them and forced their army to retreat after the first cavalry skirmish.
News then reached Alexander that the Illyrian chieftain Cleitus and King Glaukias of the Taulantii were in open revolt against his authority. Marching west into Illyria, Alexander defeated each in turn, forcing the two rulers to flee with their troops. With these victories, he secured his northern frontier.
Destruction of Thebes
While Alexander campaigned north, the Thebans and Athenians rebelled once again. Alexander immediately headed south. While the other cities again hesitated, Thebes decided to fight. The Theban resistance was ineffective and Alexander razed the city and divided its territory between the other Boeotian cities. The end of Thebes cowed Athens, leaving all of Greece temporarily at peace. Alexander then set out on his Asian campaign, leaving Antipater as regent.
Conquest of the Achaemenid Persian Empire
Main articles: Wars of Alexander the Great and Chronology of the expedition of Alexander the Great into AsiaStrategy
Main article: Military tactics of Alexander the Great § Grand strategyAlexander's invasion of Persia as a whole has been denoted as a supreme example of a "strategic line" of conducting war, a line formed by "the chain of logic that connects operations into a single whole." In his book Strategy, Soviet military officer and theorist Alexander Svechin delineates Alexander's strategic steps. After securing his Greek base and the Balkans by subjugating his political opponents, and securing his army's rear through the conquest of all the Afro-Asian coastline, where the Persian fleet was based and from which it was supplied, Alexander, moved to confront directly the Persians. He thus resolved the eternal problem of an army conducting operations deep into enemy territory, Svechin states, in an "exemplary manner."
Asia Minor
Further information: Battle of the Granicus, Siege of Halicarnassus, and Siege of Miletus
| Campaigns of Alexander the Great | |
|---|---|
|
820miles Babylon15
After his victory at the Battle of Chaeronea (338 BC), Philip II began the work of establishing himself as hēgemṓn (Greek: ἡγεμών) of a league which according to Diodorus was to wage a campaign against the Persians for the sundry grievances Greece suffered in 480 and free the Greek cities of the western coast and islands from Achaemenid rule. In 336 he sent Parmenion, Amyntas, Andromenes, Attalus, and an army of 10,000 men into Anatolia to make preparations for an invasion. The Greek cities on the western coast of Anatolia revolted until the news arrived that Philip had been murdered and had been succeeded by his young son Alexander. The Macedonians were demoralized by Philip's death and were subsequently defeated near Magnesia by the Achaemenids under the command of the mercenary Memnon of Rhodes.
Taking over the invasion project of Philip II, Alexander's army crossed the Hellespont in 334 BC with approximately 48,100 soldiers, 6,100 cavalry, and a fleet of 120 ships with crews numbering 38,000 drawn from Macedon and various Greek city states, mercenaries, and feudally raised soldiers from Thrace, Paionia, and Illyria. He showed his intent to conquer the entirety of the Persian Empire by throwing a spear into Asian soil and saying he accepted Asia as a gift from the gods. This also showed Alexander's eagerness to fight, in contrast to his father's preference for diplomacy.
After an initial victory against Persian forces at the Battle of the Granicus, Alexander accepted the surrender of the Persian provincial capital and treasury of Sardis; he then proceeded along the Ionian coast, granting autonomy and democracy to the cities. Miletus, held by Achaemenid forces, required a delicate siege operation, with Persian naval forces nearby. Further south, at Halicarnassus, in Caria, Alexander successfully waged his first large-scale siege, eventually forcing his opponents, the mercenary captain Memnon of Rhodes and the Persian satrap of Caria, Orontobates, to withdraw by sea. Alexander left the government of Caria to a member of the Hecatomnid dynasty, Ada, who adopted Alexander.

From Halicarnassus, Alexander proceeded into mountainous Lycia and the Pamphylian plain, asserting control over all coastal cities to deny the Persians naval bases. From Pamphylia onwards, the coast held no major ports and Alexander moved inland. At Termessos, Alexander humbled and did not storm the Pisidian city. At the ancient Phrygian capital of Gordium, Alexander "undid" the hitherto unsolvable Gordian Knot, a feat said to await the future "king of Asia". According to the story, Alexander proclaimed that it did not matter how the knot was undone, and hacked it apart with his sword.
The Levant and Syria
Further information: Battle of Issus and Siege of Tyre (332 BC)In spring 333 BC, Alexander crossed the Taurus into Cilicia. After a long pause due to an illness, he marched on towards Syria. Though outmanoeuvered by Darius's significantly larger army, he marched back to Cilicia, where he defeated Darius at Issus. Darius fled the battle, causing his army to collapse, and left behind his wife, his two daughters, his mother Sisygambis, and a fabulous treasure. He offered a peace treaty that included the lands he had already lost, and a ransom of 10,000 talents for his family. Alexander replied that since he was now king of Asia, it was he alone who decided territorial divisions. Alexander proceeded to take possession of Syria, and most of the coast of the Levant. In the following year, 332 BC, he was forced to attack Tyre, which he captured after a long and difficult siege. The men of military age were massacred and the women and children sold into slavery.
Egypt
Further information: Siege of Gaza (332 BCE)
When Alexander destroyed Tyre, most of the towns on the route to Egypt quickly capitulated. However, Alexander was met with resistance at Gaza. The stronghold was heavily fortified and built on a hill, requiring a siege. When "his engineers pointed out to him that because of the height of the mound it would be impossible... this encouraged Alexander all the more to make the attempt". After three unsuccessful assaults, the stronghold fell, but not before Alexander had received a serious shoulder wound. As in Tyre, men of military age were put to the sword, and the women and children were sold into slavery.
Egypt was only one of a large number of territories taken by Alexander from the Persians. After his trip to Siwa, Alexander was crowned in the temple of Ptah at Memphis. It appears that the Egyptian people did not find it disturbing that he was a foreigner – nor that he was absent for virtually his entire reign. Alexander restored the temples neglected by the Persians and dedicated new monuments to the Egyptian gods. In the temple of Luxor, near Karnak, he built a chapel for the sacred barge. During his brief months in Egypt, he reformed the taxation system on the Greek models and organized the military occupation of the country, but in early 331 BC he left for Asia in pursuit of the Persians.
Alexander advanced on Egypt in later 332 BC where he was regarded as a liberator. To legitimize taking power and be recognized as the descendant of the long line of pharaohs, Alexander made sacrifices to the gods at Memphis and went to consult the famous oracle of Amun-Ra at the Siwa Oasis in the Libyan desert, at which he was pronounced the son of the deity Amun. Henceforth, Alexander often referred to Zeus-Ammon as his true father, and after his death, currency depicted him adorned with horns, using the Horns of Ammon as a symbol of his divinity. The Greeks interpreted this message – one that the gods addressed to all pharaohs – as a prophecy.
During his stay in Egypt, he founded Alexandria, which would become the prosperous capital of the Ptolemaic Kingdom after his death. Control of Egypt passed to Ptolemy I (son of Lagos), the founder of the Ptolemaic Dynasty (305–30 BC) after the death of Alexander.
Assyria and Babylonia
Further information: Battle of Gaugamela
Leaving Egypt in 331 BC, Alexander marched eastward into Achaemenid Assyria in Upper Mesopotamia (now northern Iraq) and defeated Darius again at the Battle of Gaugamela. Darius once more fled the field, and Alexander chased him as far as Arbela. Gaugamela would be the final and decisive encounter between the two. Darius fled over the mountains to Ecbatana (modern Hamadan) while Alexander captured Babylon.
Babylonian astronomical diaries say that "the king of the world, Alexander" sent his scouts with a message to the people of Babylon before entering the city: "I shall not enter your houses".
Persia
Further information: Battle of the Persian Gate
From Babylon, Alexander went to Susa, one of the Achaemenid capitals, and captured its treasury. He sent the bulk of his army to the Persian ceremonial capital of Persepolis via the Persian Royal Road. Alexander himself took selected troops on the direct route to the city. He then stormed the pass of the Persian Gates (in the modern Zagros Mountains) which had been blocked by a Persian army under Ariobarzanes and then hurried to Persepolis before its garrison could loot the treasury.
On entering Persepolis, Alexander allowed his troops to loot the city for several days. Alexander stayed in Persepolis for five months. During his stay, a fire broke out in the eastern palace of Xerxes I and spread to the rest of the city. Possible causes include a drunken accident or deliberate revenge for the burning of the Acropolis of Athens during the Second Persian War by Xerxes; Plutarch and Diodorus allege that Alexander's companion, the hetaera Thaïs, instigated and started the fire. Even as he watched the city burn, Alexander immediately began to regret his decision. Plutarch claims that he ordered his men to put out the fires but the flames had already spread to most of the city. Curtius claims that Alexander did not regret his decision until the next morning. Plutarch recounts an anecdote in which Alexander pauses and talks to a fallen statue of Xerxes as if it were a live person:
Shall I pass by and leave you lying there because of the expeditions you led against Greece, or shall I set you up again because of your magnanimity and your virtues in other respects?
Fall of the Persian Empire and the East

Alexander then chased Darius, first into Media, and then Parthia. The Persian king no longer controlled his own destiny, and was taken prisoner by Bessus, his Bactrian satrap and kinsman. As Alexander approached, Bessus had his men fatally stab the Great King and then declared himself Darius's successor as Artaxerxes V, before retreating into Central Asia to launch a guerrilla campaign against Alexander. Alexander buried Darius's remains next to his Achaemenid predecessors in a regal funeral. He claimed that, while dying, Darius had named him as his successor to the Achaemenid throne. The Achaemenid Empire is normally considered to have fallen with Darius. However, as basic forms of community life and the general structure of government were maintained and resuscitated by Alexander under his own rule, he, in the words of the Iranologist Pierre Briant "may therefore be considered to have acted in many ways as the last of the Achaemenids."
Alexander viewed Bessus as a usurper and set out to defeat him. This campaign, initially against Bessus, turned into a grand tour of central Asia. Alexander founded a series of new cities, all called Alexandria, including modern Kandahar in Afghanistan, and Alexandria Eschate ("The Furthest") in modern Tajikistan. The campaign took Alexander through Media, Parthia, Aria (West Afghanistan), Drangiana, Arachosia (South and Central Afghanistan), Bactria (North and Central Afghanistan), and Scythia.
In 329 BC, Spitamenes, who held an undefined position in the satrapy of Sogdiana, betrayed Bessus to Ptolemy, one of Alexander's trusted companions, and Bessus was executed. However, at some point later when Alexander was on the Jaxartes dealing with an incursion by a horse nomad army, Spitamenes raised Sogdiana in revolt. Alexander personally defeated the Scythians at the Battle of Jaxartes and immediately launched a campaign against Spitamenes, defeating him in the Battle of Gabai. After the defeat, Spitamenes was killed by his own men, who then sued for peace.
Problems and plots

During this time, Alexander adopted some elements of Persian dress and customs at his court, notably the custom of proskynesis, either a symbolic kissing of the hand, or prostration on the ground, that Persians showed to their social superiors. This was one aspect of Alexander's broad strategy aimed at securing the aid and support of the Iranian upper classes. The Greeks however regarded the gesture of proskynesis as the province of deities and believed that Alexander meant to deify himself by requiring it. This cost him the sympathies of many of his countrymen, and he eventually abandoned it.
During the long rule of the Achaemenids, the elite positions in many segments of the empire including the central government, the army, and the many satrapies were specifically reserved for Iranians and to a major degree, Persian noblemen. The latter were in many cases additionally connected through marriage alliances with the royal Achaemenid family. This created a problem for Alexander as to whether he had to make use of the various segments and people that had given the empire its solidity and unity for a lengthy period of time. Pierre Briant explains that Alexander realized that it was insufficient to merely exploit the internal contradictions within the imperial system as in Asia Minor, Babylonia or Egypt; he also had to (re)create a central government with or without the support of the Iranians. As early as 334 BC he demonstrated awareness of this, when he challenged incumbent King Darius III "by appropriating the main elements of the Achaemenid monarchy's ideology, particularly the theme of the king who protects the lands and the peasants". Alexander wrote a letter in 332 BC to Darius III, wherein he argued that he was worthier than Darius "to succeed to the Achaemenid throne". However, Alexander's eventual decision to burn the Achaemenid palace at Persepolis in conjunction with the major rejection and opposition of the "entire Persian people" made it impracticable for him to pose himself as Darius' legitimate successor. Against Bessus (Artaxerxes V) however, Briant adds, Alexander reasserted "his claim to legitimacy as the avenger of Darius III".
A plot against his life was revealed, and one of his officers, Philotas, was executed for failing to alert Alexander. The death of the son necessitated the death of the father, and thus Parmenion, who had been charged with guarding the treasury at Ecbatana, was assassinated at Alexander's command, to prevent attempts at vengeance. Most infamously, Alexander personally killed the man who had saved his life at Granicus, Cleitus the Black, during a violent drunken altercation at Maracanda (modern day Samarkand in Uzbekistan), in which Cleitus accused Alexander of several judgmental mistakes and especially of having forgotten the Macedonian ways in favour of a corrupt oriental lifestyle.
Later, in the Central Asian campaign, a second plot against his life was revealed. This one was instigated by his own royal pages. His official historian, Callisthenes of Olynthus, was implicated in the plot, and in the Anabasis of Alexander, Arrian states that Callisthenes and the pages were then tortured on the rack as punishment, and likely died soon after. It remains unclear if Callisthenes was actually involved in the plot, for prior to his accusation he had fallen out of favour by leading the opposition to the attempt to introduce proskynesis.
Macedon in Alexander's absence
When Alexander set out for Asia, he left his general Antipater, an experienced military and political leader, and part of Philip II's "Old Guard", in charge of Macedon. Alexander's sacking of Thebes ensured that Greece remained quiet during his absence. The one exception was a call to arms by Spartan king Agis III in 331 BC, whom Antipater defeated and killed in the battle of Megalopolis. Antipater referred the Spartans' punishment to the League of Corinth, which then deferred to Alexander, who chose to pardon them. There was also considerable friction between Antipater and Olympias, and each complained to Alexander about the other.
In general, Greece enjoyed a period of peace and prosperity during Alexander's campaign in Asia. Alexander sent back vast sums from his conquest, which stimulated the economy and increased trade across his empire. However, Alexander's constant demands for troops and the migration of Macedonians throughout his empire depleted Macedon's strength, greatly weakening it in the years after Alexander, and ultimately led to its subjugation by Rome after the Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC).
Coinage

The conquest by Philip II of Pangaeum, and then of the island of Thasos between 356 and 342 BC brought rich gold and silver mines under Macedonian control.
Alexander appears to have introduced a new coinage in Cilicia in Tarsus, after the Battle of Issus in 333 BC, which went on to become the main coinage of the empire. Alexander minted gold staters, silver tetradrachms and drachims, and various fractional bronze coins. The types of these coins remained constant in his empire. The gold series had the head of Athena on the obverse and a winged Nike (Victory) on the reverse. The silver coinage had a beardless head of Heracles wearing a lionskin headdress on the obverse and Zeus aetophoros ('eagle bearer') enthroned with a scepter in his left hand, on the reverse. There are both Greek and non-Greek aspects to this design. Heracles and Zeus were important deities for the Macedonians, with Heracles considered to be the ancestor of the Temenid dynasty and Zeus the patron of the main Macedonian sanctuary, Dium. The lion was also the symbolic animal of the Anatolian god Sandas, worshipped at Tarsus. The reverse design of Alexander's tetradrachms is closely modelled on the depiction of the god Baaltars (Baal of Tarsus), on the silver staters minted at Tarsus by the Persian satrap Mazaeus before Alexander's conquest.
Alexander did not attempt to impose uniform imperial coinage throughout his new conquests. Persian coins continued to circulate in all the satrapies of the empire.
Indian campaign
Main article: Indian campaign of Alexander the GreatForays into the Indian subcontinent

After the death of Spitamenes and his marriage to Roxana (Raoxshna in Old Iranian) to cement relations with his new satrapies, Alexander turned to the Indian subcontinent. He invited the chieftains of the former satrapy of Gandhara (a region presently straddling eastern Afghanistan and northern Pakistan), to come to him and submit to his authority. Omphis (Indian name Ambhi), the ruler of Taxila, whose kingdom extended from the Indus to the Hydaspes (Jhelum), complied, but the chieftains of some hill clans, including the Aspasioi and Assakenoi sections of the Kambojas (known in Indian texts also as Ashvayanas and Ashvakayanas), refused to submit. Ambhi hastened to relieve Alexander of his apprehension and met him with valuable presents, placing himself and all his forces at his disposal. Alexander not only returned Ambhi his title and the gifts but he also presented him with a wardrobe of "Persian robes, gold and silver ornaments, 30 horses and 1,000 talents in gold". Alexander was emboldened to divide his forces, and Ambhi assisted Hephaestion and Perdiccas in constructing a bridge over the Indus where it bends at Hund, supplied their troops with provisions, and he received Alexander and his whole army in his capital city of Taxila, with every demonstration of friendship and the most liberal hospitality.

On the subsequent advance of the Macedonian king, Taxiles accompanied him with a force of 5,000 men and took part in the Battle of the Hydaspes. After that victory, he was sent by Alexander in pursuit of Porus, to whom he was charged to offer favourable terms, but narrowly escaped losing his life at the hands of his old enemy. Subsequently, the two rivals were reconciled by the personal mediation of Alexander; Taxiles contributed zealously to the equipment of the fleet on the Hydaspes and was entrusted by Alexander with the government of the whole territory between that river and the Indus. A considerable accession of power was granted him after the death of Philip, son of Machatas, and he was allowed to retain his authority at the death of Alexander himself (323 BC), as well as in the subsequent partition of the provinces at Triparadisus, 321 BC.
In the winter of 327/326 BC, Alexander personally led a campaign against the Aspasioi of the Kunar Valley, the Guraeans of the Guraeus Valley, and the Assakenoi of the Swat and Buner Valleys. A fierce contest ensued with the Aspasioi in which Alexander was wounded in the shoulder by a dart, but eventually the Aspasioi lost. Alexander then faced the Assakenoi who fought against him from the strongholds of Massaga, Ora, and Aornos.
The fort of Massaga was reduced after days of bloody fighting in which Alexander was seriously wounded in the ankle. According to Curtius, "Not only did Alexander slaughter the entire population of Massaga, but also did he reduce its buildings to rubble." A similar slaughter followed at Ora. In the aftermath of Massaga and Ora, numerous Assakenians fled to the fortress of Aornos. Alexander followed close behind and captured the strategic hill-fort after four bloody days.

After Aornos, Alexander crossed the Indus and won an epic battle against King Porus, who ruled a region lying between the Hydaspes and the Acesines (Chenab), in what is now the Punjab, in the Battle of the Hydaspes in 326 BC. Alexander was impressed by Porus's bravery and made him an ally. He appointed Porus as satrap, and added to Porus's territory land that he did not previously own, towards the south-east, up to the Hyphasis (Beas). Choosing a local helped him control these lands that were distant from Greece. Alexander founded two cities on opposite sides of the Hydaspes river, naming one Bucephala, in honour of his horse, who died around this time. The other was Nicaea (Victory), thought to be located at the site of modern-day Mong, Punjab. Philostratus the Elder in the Life of Apollonius of Tyana writes that in the army of Porus, there was an elephant who fought bravely against Alexander's army, and Alexander dedicated it to the Helios (Sun) and named it Ajax because he thought that such a great animal deserved a great name. The elephant had gold rings around its tusks and an inscription was on them written in Greek: "Alexander the son of Zeus dedicates Ajax to the Helios" (ΑΛΕΞΑΝΔΡΟΣ Ο ΔΙΟΣ ΤΟΝ ΑΙΑΝΤΑ ΤΩΙ ΗΛΙΩΙ).
Revolt of the Hellenic army
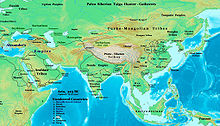
East of Porus's kingdom, near the Ganges River, was the Nanda Empire of Magadha, and further east, the Gangaridai Empire of Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent. Fearing the prospect of facing other large armies and exhausted by years of campaigning, Alexander's army mutinied at the Hyphasis River (Beas), refusing to march farther east. This river thus marks the easternmost extent of Alexander's conquests.
As for the Macedonians, however, their struggle with Porus blunted their courage and stayed their further advance into India. For having had all they could do to repulse an enemy who mustered only twenty thousand infantry and two thousand horse, they violently opposed Alexander when he insisted on crossing the river Ganges also, the width of which, as they learned, was thirty-two furlongs , its depth one hundred fathoms , while its banks on the further side were covered with multitudes of men-at-arms and horsemen and elephants. For they were told that the kings of the Ganderites and Praesii were awaiting them with eighty thousand horsemen, two hundred thousand footmen, eight thousand chariots, and six thousand war elephants.
Alexander tried to persuade his soldiers to march farther, but his general Coenus pleaded with him to change his opinion and return; the men, he said, "longed to again see their parents, their wives and children, their homeland". Alexander eventually agreed and turned south, marching along the Indus. Along the way his army conquered the Malhi (in modern-day Multan) and other Indian tribes; while besieging the Mallian citadel, Alexander suffered a near-fatal injury when an arrow penetrated his armor and entered his lung.
Alexander sent much of his army to Carmania (modern southern Iran) with general Craterus, and commissioned a fleet to explore the Persian Gulf shore under his admiral Nearchus, while he led the rest back to Persia through the more difficult southern route along the Gedrosian Desert and Makran. Alexander reached Susa in 324 BC, but not before losing many men to the harsh desert.
Last years in Persia

Discovering that many of his satraps and military governors had misbehaved in his absence, Alexander executed several of them as examples on his way to Susa. As a gesture of thanks, he paid off the debts of his soldiers, and announced that he would send over-aged and disabled veterans back to Macedon, led by Craterus. His troops misunderstood his intention and mutinied at the town of Opis. They refused to be sent away and criticized his adoption of Persian customs and dress and the introduction of Persian officers and soldiers into Macedonian units.
After three days, unable to persuade his men to back down, Alexander gave Persians command posts in the army and conferred Macedonian military titles upon Persian units. The Macedonians quickly begged forgiveness, which Alexander accepted, and held a great banquet with several thousand of his men. In an attempt to craft a lasting harmony between his Macedonian and Persian subjects, Alexander held a mass marriage of his senior officers to Persian and other noblewomen at Susa, but few of those marriages seem to have lasted much beyond a year.

Meanwhile, upon his return to Persia, Alexander learned that guards of the tomb of Cyrus the Great in Pasargadae had desecrated it, and swiftly executed them. Alexander admired Cyrus the Great, from an early age reading Xenophon's Cyropaedia, which described Cyrus's heroism in battle and governance as a king and legislator. During his visit to Pasargadae, Alexander ordered his architect Aristobulus to decorate the interior of the sepulchral chamber of Cyrus's tomb.
Afterwards, Alexander travelled to Ecbatana to retrieve the bulk of the Persian treasure. There, his closest friend, Hephaestion, died of illness or poisoning. Hephaestion's death devastated Alexander and he ordered the preparation of an expensive funeral pyre in Babylon along with a decree for public mourning. Back in Babylon, Alexander planned a series of new campaigns, beginning with an invasion of Arabia.
Death and succession
Main article: Death of Alexander the Great
On either 10 or 11 June 323 BC, Alexander died in the palace of Nebuchadnezzar II, in Babylon, at age 32. There are two different versions of Alexander's death, differing slightly in details. Plutarch's account is that roughly 14 days before his death, Alexander entertained admiral Nearchus and spent the night and next day drinking with Medius of Larissa. Alexander developed a fever, which worsened until he was unable to speak. The common soldiers, anxious about his health, were granted the right to file past him as he silently waved at them. In the second account, Diodorus recounts that Alexander was struck with pain after downing a large bowl of unmixed wine in honour of Heracles followed by 11 days of weakness; he did not develop a fever, instead dying after some agony. Arrian also mentioned this as an alternative, but Plutarch specifically denied this claim.
Given the propensity of the Macedonian aristocracy to assassination, foul play featured in multiple accounts of his death. Diodorus, Plutarch, Arrian and Justin all mentioned the theory that Alexander was poisoned. Justin stated that Alexander was the victim of a poisoning conspiracy, Plutarch dismissed it as a fabrication, while both Diodorus and Arrian noted that they mentioned it only for the sake of completeness. The accounts were nevertheless fairly consistent in designating Antipater, recently removed as Macedonian viceroy, replaced by Craterus, as the head of the alleged plot. Perhaps taking his summons to Babylon as a death sentence and having seen the fate of Parmenion and Philotas, Antipater purportedly arranged for Alexander to be poisoned by his son Iollas, who was Alexander's wine-pourer. There was even a suggestion that Aristotle may have participated. The strongest argument against the poison theory is the fact that twelve days passed between the start of his illness and his death; such long-acting poisons were probably not available. However, in a 2003 BBC documentary investigating the death of Alexander, Leo Schep from the New Zealand National Poisons Centre proposed that the plant white hellebore (Veratrum album), which was known in antiquity, may have been used to poison Alexander. In a 2014 manuscript in the journal Clinical Toxicology, Schep suggested Alexander's wine was spiked with Veratrum album, and that this would produce poisoning symptoms that match the course of events described in the Alexander Romance. Veratrum album poisoning can have a prolonged course and it was suggested that if Alexander was poisoned, Veratrum album offers the most plausible cause. Another poisoning explanation put forward in 2010 proposed that the circumstances of his death were compatible with poisoning by water of the river Styx (modern-day Mavroneri in Arcadia, Greece) that contained calicheamicin, a dangerous compound produced by bacteria.
Several natural causes (diseases) have been suggested, including malaria and typhoid fever. A 1998 article in the New England Journal of Medicine attributed his death to typhoid fever complicated by bowel perforation and ascending paralysis. A 2004 analysis suggested pyogenic (infectious) spondylitis or meningitis. Other illnesses fit the symptoms, including acute pancreatitis, West Nile virus, and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Natural-cause theories also tend to emphasize that Alexander's health may have been in general decline after years of heavy drinking and severe wounds. The anguish that Alexander felt after Hephaestion's death may also have contributed to his declining health.
Post-death events
See also: Tomb of Alexander the GreatAlexander's body was laid in a gold anthropoid sarcophagus that was filled with honey, which was in turn placed in a gold casket. According to Aelian, a seer called Aristander foretold that the land where Alexander was laid to rest "would be happy and unvanquishable forever". Perhaps more likely, the successors may have seen possession of the body as a symbol of legitimacy, since burying the prior king was a royal prerogative.

While Alexander's funeral cortege was on its way to Macedon, Ptolemy seized it and took it temporarily to Memphis. His successor, Ptolemy II Philadelphus, transferred the sarcophagus to Alexandria, where it remained until at least late antiquity. Ptolemy IX Lathyros, one of Ptolemy's final successors, replaced Alexander's sarcophagus with a glass one so he could convert the original to coinage. The 2014 discovery of an enormous tomb in northern Greece, at Amphipolis, dating from the time of Alexander the Great has given rise to speculation that its original intent was to be the burial place of Alexander. This would fit with the intended destination of Alexander's funeral cortege. However, the memorial was found to be dedicated to the dearest friend of Alexander the Great, Hephaestion.

Pompey, Julius Caesar and Augustus all visited the tomb in Alexandria where Augustus, allegedly, accidentally knocked the nose of Alexander's mummified body off. Caligula was said to have taken Alexander's breastplate from the tomb for his own use. Around AD 200, Emperor Septimius Severus closed Alexander's tomb to the public. His son and successor, Caracalla, a great admirer, visited the tomb during his own reign. After this, details on the fate of the tomb are hazy.
The so-called "Alexander Sarcophagus", discovered near Sidon and now in the Istanbul Archaeology Museum, is so named not because it was thought to have contained Alexander's remains, but because its bas-reliefs depict Alexander and his companions fighting the Persians and hunting. It was originally thought to have been the sarcophagus of Abdalonymus (died 311 BC), the king of Sidon appointed by Alexander immediately following the battle of Issus in 331. However, in 1969, it was suggested by Karl Schefold that it may date from earlier than Abdalonymus's death.
Demades likened the Macedonian army, after the death of Alexander, to the blinded Cyclops due to the many random and disorderly movements that it made. In addition, Leosthenes also likened the anarchy between the generals, after Alexander's death, to the blinded Cyclops "who after he had lost his eye went feeling and groping about with his hands before him, not knowing where to lay them".
Division of the Macedonian Empire
Main articles: Partition of Babylon and Diadochi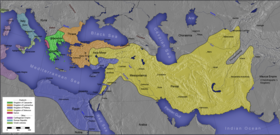
Alexander's death was so sudden that when reports of his death reached Greece, they were not immediately believed. Alexander had no obvious or legitimate heir, his son Alexander IV by Roxane being born after Alexander's death. According to Diodorus, Alexander's companions asked him on his deathbed to whom he bequeathed his kingdom; his laconic reply was "tôi kratistôi"—"to the strongest". Another theory is that his successors wilfully or erroneously misheard "tôi Kraterôi"—"to Craterus", the general leading his Macedonian troops home and newly entrusted with the regency of Macedonia. Arrian and Plutarch claimed that Alexander was speechless by this time, implying that this was an apocryphal story. Diodorus, Curtius and Justin offered the more plausible story that Alexander passed his signet ring to Perdiccas, a bodyguard and leader of the companion cavalry, in front of witnesses, thereby nominating him.
Perdiccas initially did not claim power, instead suggesting that Roxane's baby would be king, if male, with himself, Craterus, Leonnatus, and Antipater as guardians. However, the infantry, under the command of Meleager, rejected this arrangement since they had been excluded from the discussion. Instead, they supported Alexander's half-brother Philip Arrhidaeus. Eventually, the two sides reconciled, and after the birth of Alexander IV, he and Philip III were appointed joint kings, albeit in name only. Dissension and rivalry soon affected the Macedonians. The satrapies handed out by Perdiccas at the Partition of Babylon became power bases each general used to bid for power. After the assassination of Perdiccas in 321 BC, Macedonian unity collapsed, and 40 years of war between "The Successors" (Diadochi) ensued before the Hellenistic world settled into three stable power blocs: Ptolemaic Egypt, Seleucid Syria and East, and Antigonid Macedonia. In the process, both Alexander IV and Philip III were murdered.
Last plans
Diodorus stated that Alexander had given detailed written instructions to Craterus some time before his death, which are known as Alexander's "last plans". Craterus started to carry out Alexander's commands, but the successors chose not to further implement them, on the grounds they were impractical and extravagant. Furthermore, Perdiccas had read the notebooks containing Alexander's last plans to the Macedonian troops in Babylon, who voted not to carry them out.
According to Diodorus, Alexander's last plans called for military expansion into the southern and western Mediterranean, monumental constructions, and the intermixing of Eastern and Western populations. It included:
- Construction of 1,000 ships larger than triremes, along with harbours and a road running along the African coast all the way to the Pillars of Hercules, to be used for an invasion of Carthage and the western Mediterranean;
- Erection of great temples in Delos, Delphi, Dodona, Dium, Amphipolis, all costing 1,500 talents, and a monumental temple to Athena at Troy
- Amalgamation of small settlements into larger cities ("synoecisms") and the "transplant of populations from Asia to Europe and in the opposite direction from Europe to Asia, in order to bring the largest continent to common unity and to friendship by means of intermarriage and family ties"
- Construction of a monumental tomb for his father Philip, "to match the greatest of the pyramids of Egypt"
- Conquest of Arabia
- Circumnavigation of Africa
The enormous scale of these plans has led many scholars to doubt their historicity. Ernst Badian argued that they were exaggerated by Perdiccas in order to ensure that the Macedonian troops voted not to carry them out. Other scholars have proposed that they were invented by later authors within the tradition of the Alexander Romance.
Character
Generalship
Further information: Military tactics of Alexander the GreatAlexander perhaps earned the epithet "the Great" due to his unparalleled success as a military commander; he never lost a battle, despite typically being outnumbered. This was due to use of terrain, phalanx and cavalry tactics, bold strategy, and the fierce loyalty of his troops. The Macedonian phalanx, armed with the sarissa, a spear 6 metres (20 ft) long, had been developed and perfected by Philip II through rigorous training, and Alexander used its speed and manoeuvrability to great effect against larger but more disparate Persian forces. Alexander also recognized the potential for disunity among his diverse army, which employed various languages and weapons. He overcame this by being personally involved in battle, in the manner of a Macedonian king.

In his first battle in Asia, at Granicus, Alexander used only a small part of his forces, perhaps 13,000 infantry with 5,000 cavalry, against a much larger Persian force of 40,000. Alexander placed the phalanx at the center and cavalry and archers on the wings, so that his line matched the length of the Persian cavalry line, about 3 km (1.86 mi). By contrast, the Persian infantry was stationed behind its cavalry. This ensured that Alexander would not be outflanked, while his phalanx, armed with long pikes, had a considerable advantage over the Persians' scimitars and javelins. Macedonian losses were negligible compared to those of the Persians.
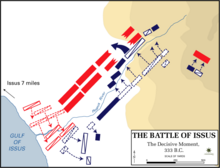
At Issus in 333 BC, his first confrontation with Darius, he used the same deployment, and again the central phalanx pushed through. Alexander personally led the charge in the center, routing the opposing army. At the decisive encounter with Darius at Gaugamela, Darius equipped his chariots with scythes on the wheels to break up the phalanx and equipped his cavalry with pikes. Alexander arranged a double phalanx, with the center advancing at an angle, parting when the chariots bore down and then reforming. The advance was successful and broke Darius's center, causing the latter to flee once again.
When faced with opponents who used unfamiliar fighting techniques, such as in Central Asia and India, Alexander adapted his forces to his opponents' style. Thus, in Bactria and Sogdiana, Alexander successfully used his javelin throwers and archers to prevent outflanking movements, while massing his cavalry at the center. In India, confronted by Porus's elephant corps, the Macedonians opened their ranks to envelop the elephants and used their sarissas to strike upwards and dislodge the elephants' handlers.
Physical appearance

Historical sources frequently give conflicting accounts of Alexander's appearance, and the earliest sources are the most scant in their detail. During his lifetime, Alexander carefully curated his image by commissioning works from famous and great artists of the time. This included commissioning sculptures by Lysippos, paintings by Apelles and gem engravings by Pyrgoteles. Ancient authors recorded that Alexander was so pleased with portraits of himself created by Lysippos that he forbade other sculptors from crafting his image; scholars today, however, find the claim dubious. Nevertheless, Andrew Stewart highlights the fact that artistic portraits, not least because of who they are commissioned by, are always partisan, and that artistic portrayals of Alexander "seek to legitimize him (or, by extension, his Successors), to interpret him to their audiences, to answer their critiques, and to persuade them of his greatness", and thus should be considered within a framework of "praise and blame", in the same way sources such as praise poetry are. Despite those caveats, Lysippos's sculpture, famous for its naturalism, as opposed to a stiffer, more static pose, is thought to be the most faithful depiction.
Curtius Rufus, a Roman historian from the first century AD, who wrote the Histories of Alexander the Great, gives this account of Alexander sitting on the throne of Darius III:
Then Alexander seating himself on the royal throne, which was far too high for his bodily stature. Therefore, since his feet did not reach its lowest step, one of the royal pages placed a table under his feet.
Both Curtius and Diodorus report a story that when Darius III's mother, Sisygambis, first met Alexander and Hephaestion, she assumed that the latter was Alexander because he was the taller and more handsome of the two.

The Greek biographer Plutarch (c. 45 – c. 120 AD) discusses the accuracy of his depictions:
The outward appearance of Alexander is best represented by the statues of him which Lysippus made, and it was by this artist alone that Alexander himself thought it fit that he should be modelled. For those peculiarities which many of his successors and friends afterwards tried to imitate, namely, the poise of the neck, which was bent slightly to the left, and the melting glance of his eyes, this artist has accurately observed. Apelles, however, in painting him as wielder of the thunder-bolt, did not reproduce his complexion, but made it too dark and swarthy. Whereas he was of a fair colour, as they say, and his fairness passed into ruddiness on his breast particularly, and in his face. Moreover, that a very pleasant odour exhaled from his skin and that there was a fragrance about his mouth and all his flesh, so that his garments were filled with it, this we have read in the Memoirs of Aristoxenus.
Historians have understood the detail of the pleasant fragrance attributed to Alexander as stemming from a belief in ancient Greece that pleasant scents are characteristic of gods and heroes.

The Alexander Mosaic and contemporary coins portray Alexander with "a straight nose, a slightly protruding jaw, full lips and eyes deep set beneath a strongly pronounced forehead". He is also described as having a slight upward tilt of his head to the left.
The ancient historian Aelian (c. 175 – c. 235 AD), in his Varia Historia (12.14), describes Alexander's hair color as "ξανθὴν" (xanthín), which at the time, could mean blond, brown, tawny (light brown) or auburn. It is sometimes claimed that Alexander had one blue and one brown eye, referring to the Alexander Romance, which is however a fictional account that also claims Alexander "had sharp teeth like fangs" and "did not look like Philip or Olympias". Reconstruction, based on remaining traces of paint of the original polychromy on his sarcophagus, indicates that he was depicted with brown eyes and chestnut brown hair. While the acropolis museum suggests that trace amounts of red paint on a head statue of Alexander were most likely a base coat for golden hues to be painted over for his hair.
Personality

Both of Alexander's parents encouraged his ambitions. His father Philip was probably Alexander's most immediate and influential role model, as the young Alexander watched him campaign practically every year, winning victory after victory while ignoring severe wounds. Alexander's relationship with his father "forged" the competitive side of his personality; he had a need to outdo his father, illustrated by his reckless behavior in battle. While Alexander worried that his father would leave him "no great or brilliant achievement to be displayed to the world", he also downplayed his father's achievements to his companions. Alexander's mother Olympia similarly had huge ambitions, and encouraged her son to believe it was his destiny to conquer the Persian Empire. She instilled a sense of destiny in him, and Plutarch tells how his ambition "kept his spirit serious and lofty in advance of his years".
According to Plutarch, Alexander also had a violent temper and rash, impulsive nature, which could influence his decision making. Although Alexander was stubborn and did not respond well to orders from his father, he was open to reasoned debate. He had a calmer side—perceptive, logical, and calculating. He had a great desire for knowledge, a love for philosophy, and was an avid reader. This was no doubt in part due to Aristotle's tutelage; Alexander was intelligent and quick to learn. His intelligent and rational side was amply demonstrated by his ability and success as a general. He had great self-restraint in "pleasures of the body", in contrast with his lack of self-control with alcohol.

Alexander was erudite and patronized both arts and sciences. However, he had little interest in sports or the Olympic Games (unlike his father), seeking only the Homeric ideals of honour (timê) and glory (kudos). He had great charisma and force of personality, characteristics which made him a great leader. His unique abilities were further demonstrated by the inability of any of his generals to unite Macedonia and retain the Empire after his death—only Alexander had the ability to do so.
During his final years, and especially after the death of Hephaestion, Alexander began to exhibit signs of megalomania and paranoia. His extraordinary achievements, coupled with his own ineffable sense of destiny and the flattery of his companions, may have combined to produce this effect. His delusions of grandeur are readily visible in his will and in his desire to conquer the world, in as much as he is by various sources described as having boundless ambition, an epithet, the meaning of which has descended into a historical cliché.
He appears to have believed himself a deity, or at least sought to deify himself. Olympias always insisted to him that he was the son of Zeus, a theory apparently confirmed to him by the oracle of Amun at Siwa. He began to identify himself as the son of Zeus-Ammon. Alexander adopted elements of Persian dress and customs at court, notably proskynesis, which was one aspect of Alexander's broad strategy aimed at securing the aid and support of the Iranian upper classes; however the practise of proskynesis was disapproved by the Macedonians, and they were unwilling to perform it. This behaviour cost him the sympathies of many of his countrymen. Alexander also was a pragmatic ruler who understood the difficulties of ruling culturally disparate peoples, many of whom lived in societies where the king was treated as divine. Thus, rather than megalomania, his behaviour may have been a practical attempt at strengthening his rule and keeping his empire together.
Personal relationships
Main article: Personal relationships of Alexander the Great
Alexander married three times: Roxana, daughter of the Sogdian nobleman Oxyartes of Bactria, out of love; and the Persian princesses Stateira and Parysatis, the former a daughter of Darius III and the latter a daughter of Artaxerxes III, for political reasons. Alexander apparently had two children by Roxana: an unnamed first child, who was born in India and died in infancy in November 326 BC, and Alexander IV of Macedon, born after his father's death. Additionally Heracles of Macedon was claimed to be his illegitimate son born of mistress, Barsine.
Alexander also had a close relationship with his friend, general, and bodyguard Hephaestion, the son of a Macedonian noble. Hephaestion's death devastated Alexander. This event may have contributed to Alexander's failing health and detached mental state during his final months.
Sexuality
Alexander's sexuality has been the subject of speculation and controversy in modern times. The Roman era writer Athenaeus says, based on the scholar Dicaearchus, who was Alexander's contemporary, that the king "was quite excessively keen on boys", and that Alexander kissed the eunuch Bagoas in public. This episode is also told by Plutarch, probably based on the same source. None of Alexander's contemporaries, however, are known to have explicitly described Alexander's relationship with Hephaestion as sexual, though the pair was often compared to Achilles and Patroclus, who are often interpreted as a couple. Aelian writes of Alexander's visit to Troy where "Alexander garlanded the tomb of Achilles, and Hephaestion that of Patroclus, the latter hinting that he was a beloved of Alexander, in just the same way as Patroclus was of Achilles." Some modern historians (e.g., Robin Lane Fox) believe not only that Alexander's youthful relationship with Hephaestion was sexual, but also that their sexual contacts may have continued into adulthood, which went against the social norms of at least some Greek cities, such as Athens, though some modern researchers have tentatively proposed that Macedonia (or at least the Macedonian court) may have been more tolerant of homosexuality between adults.

Peter Green argues that there is little evidence in ancient sources that Alexander had much sexual interest in women; he did not produce an heir until the very end of his life. However, Ogden calculates that Alexander, who impregnated his partners thrice in eight years, had a higher matrimonial record than his father at the same age. Two of these pregnancies—Stateira's and Barsine's—are of dubious legitimacy.
According to Diodorus Siculus, Alexander accumulated a harem in the style of Persian kings, but he used it rather sparingly, "not wishing to offend the Macedonians", showing great self-control in "pleasures of the body". Nevertheless, Plutarch described how Alexander was infatuated by Roxana while complimenting him on not forcing himself on her. Green suggested that, in the context of the period, Alexander formed quite strong friendships with women, including Ada of Caria, who adopted him, and even Darius's mother Sisygambis, who supposedly died from grief upon hearing of Alexander's death.
Battle record
| Outcome | Date | War | Action | Opponent/s | Type | Country (present day) |
Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Victory | 338-08-02 2 August 338 BC | Philip II's submission of Greece | Chaeronea Battle of Chaeronea | .Thebans, Athenians and other Greek cities | Battle | Greece | Prince
⁂ |
| Victory | 335 335 BC | Balkan Campaign | Mount Haemus Battle of Mount Haemus | .Getae, Thracians | Battle | Bulgaria | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 335-12 December 335 BC | Balkan Campaign | Pelium Siege of Pelium | .Illyrians | Siege | Albania | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 335-12 December 335 BC | Balkan Campaign | Pelium Battle of Thebes | .Thebans | Battle | Greece | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 334-05 May 334 BC | Persian Campaign | Granicus Battle of the Granicus | .Achaemenid Empire | Battle | Turkey | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 334 334 BC | Persian Campaign | Miletus Siege of Miletus | .Achaemenid Empire, Milesians | Siege | Turkey | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 334 334 BC | Persian Campaign | Halicarnassus Siege of Halicarnassus | .Achaemenid Empire | Siege | Turkey | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 333-11-05 5 November 333 BC | Persian Campaign | Issus Battle of Issus | .Achaemenid Empire | Battle | Turkey | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 332 January–July 332 BC | Persian Campaign | Tyre Siege of Tyre | .Achaemenid Empire, Tyrians | Siege | Lebanon | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 332-10 October 332 BC | Persian Campaign | Tyre Siege of Gaza | .Achaemenid Empire | Siege | Palestine | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 331-10-01 1 October 331 BC | Persian Campaign | Gaugamela Battle of Gaugamela | .Achaemenid Empire | Battle | Iraq | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 331-12 December 331 BC | Persian Campaign | Uxian Defile Battle of the Uxian Defile | .Uxians | Battle | Iran | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 330-01-20 20 January 330 BC | Persian Campaign | Persian Gate Battle of the Persian Gate | .Achaemenid Empire | Battle | Iran | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 329 329 BC | Persian Campaign | Cyropolis Siege of Cyropolis | .Sogdians | Siege | Turkmenistan | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 329-10 October 329 BC | Persian Campaign | Jaxartes Battle of Jaxartes | .Scythians | Battle | Uzbekistan | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 327 327 BC | Persian Campaign | Sogdian Rock Siege of the Sogdian Rock | .Sogdians | Siege | Uzbekistan | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 327 May 327 – March 326 BC | Indian Campaign | Cophen Cophen campaign | .Aspasians | Expedition | Afghanistan and Pakistan | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 326-04 April 326 BC | Indian Campaign | Aornos Siege of Aornos | .Aśvaka | Siege | Pakistan | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 326-05 May 326 BC | Indian Campaign | Hydaspes Battle of the Hydaspes | .Porus | Battle | Pakistan | King
⁂ |
| Victory | 325 November 326 – February 325 BC | Indian Campaign | Aornos Siege of Multan | .Malli | Siege | Pakistan | King
⁂ |
Legacy
Alexander's legacy extended beyond his military conquests, and his reign marked a turning point in European and Asian history. His campaigns greatly increased contacts and trade between East and West, and vast areas to the east were significantly exposed to Greek civilization and influence. Some of the cities he founded became major cultural centers, many surviving into the 21st century. His chroniclers recorded valuable information about the areas through which he marched, while the Greeks themselves got a sense of belonging to a world beyond the Mediterranean.
Hellenistic kingdoms
Main article: Hellenistic period
Alexander's most immediate legacy was the introduction of Macedonian rule to huge new swathes of Asia. At the time of his death, Alexander's empire covered some 5,200,000 km (2,000,000 sq mi), and was the largest state of its time. Many of these areas remained in Macedonian hands or under Greek influence for the next 200–300 years. The successor states that emerged were, at least initially, dominant forces, and these 300 years are often referred to as the Hellenistic period.
The eastern borders of Alexander's empire began to collapse even during his lifetime. However, the power vacuum he left in the northwest of the Indian subcontinent directly gave rise to one of the most powerful Indian dynasties in history, the Maurya Empire. Taking advantage of this power vacuum, Chandragupta Maurya (referred to in Greek sources as "Sandrokottos"), of relatively humble origin, took control of the Punjab, and with that power base proceeded to conquer the Nanda Empire.
Founding of cities
Main article: List of cities founded by Alexander the Great
Over the course of his conquests, Alexander founded many cities that bore his name, most of them east of the Tigris. The first, and greatest, was Alexandria in Egypt, which would become one of the leading Mediterranean cities. The cities' locations reflected trade routes as well as defensive positions. At first, the cities must have been inhospitable, little more than defensive garrisons. Following Alexander's death, many Greeks who had settled there tried to return to Greece. However, a century or so after Alexander's death, many of the Alexandrias were thriving, with elaborate public buildings and substantial populations that included both Greek and local peoples.
Funding of temples

In 334 BC, Alexander the Great donated funds for the completion of the new temple of Athena Polias in Priene, in modern-day western Turkey. An inscription from the temple, now housed in the British Museum, declares: "King Alexander dedicated to Athena Polias." This inscription is one of the few independent archaeological discoveries confirming an episode from Alexander's life. The temple was designed by Pytheos, one of the architects of the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus.
Libanius wrote that Alexander founded the temple of Zeus Bottiaios (Ancient Greek: Βοττιαίου Δῖός), in the place where later the city of Antioch was built.
Suda wrote that Alexander built a big temple to Sarapis.
In 2023, British Museum experts have suggested the possibility that a Greek temple at Girsu in Iraq, was founded by Alexander. According to the researchers, recent discoveries suggest that "this site honours Zeus and two divine sons. The sons are Heracles and Alexander."
Hellenization
Main article: Hellenization
Hellenization was coined by the German historian Johann Gustav Droysen to denote the spread of Greek language, culture, and population into the former Persian empire after Alexander's conquest. This process can be seen in such great Hellenistic cities as Alexandria, Antioch and Seleucia (south of modern Baghdad). Alexander sought to insert Greek elements into Persian culture and to hybridize Greek and Persian culture, homogenizing the populations of Asia and Europe. Although his successors explicitly rejected such policies, Hellenization occurred throughout the region, accompanied by a distinct and opposite 'Orientalization' of the successor states.
The core of the Hellenistic culture promulgated by the conquests was essentially Athenian. The close association of men from across Greece in Alexander's army directly led to the emergence of the largely Attic-based "koine", or "common" Greek dialect. Koine spread throughout the Hellenistic world, becoming the lingua franca of Hellenistic lands, and eventually the ancestor of modern Greek. Furthermore, town planning, education, local government, and art current in the Hellenistic period were all based on Classical Greek ideals, evolving into distinct new forms commonly grouped as Hellenistic. Also, the New Testament was written in the Koine Greek language. Aspects of Hellenistic culture were still evident in the traditions of the Byzantine Empire in the mid-15th century.
Hellenization in South and Central Asia
Main articles: Indo-Greek Kingdom, Indo-Greek art, and Greco-Buddhism
Some of the most pronounced effects of Hellenization can be seen in Afghanistan and India, in the region of the relatively late-rising Greco-Bactrian Kingdom (250–125 BC) (in modern Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Tajikistan) and the Indo-Greek Kingdom (180 BC – 10 AD) in modern Afghanistan and India. On the Silk Road trade routes, Hellenistic culture hybridized with Iranian and Buddhist cultures. The cosmopolitan art and mythology of Gandhara (a region spanning the upper confluence of the Indus, Swat and Kabul rivers in modern Pakistan) of the ~3rd century BC to the ~5th century AD are most evident of the direct contact between Hellenistic civilization and South Asia, as are the Edicts of Ashoka, which directly mention the Greeks within Ashoka's dominion as converting to Buddhism and the reception of Buddhist emissaries by Ashoka's contemporaries in the Hellenistic world. The resulting syncretism known as Greco-Buddhism influenced the development of Buddhism and created a culture of Greco-Buddhist art. These Greco-Buddhist kingdoms sent some of the first Buddhist missionaries to China, Sri Lanka and Hellenistic Asia and Europe (Greco-Buddhist monasticism).
Some of the first and most influential figurative portrayals of The Buddha appeared at this time, perhaps modelled on Greek statues of Apollo in the Greco-Buddhist style. Several Buddhist traditions may have been influenced by the ancient Greek religion: the concept of Boddhisatvas is reminiscent of Greek divine heroes, and some Mahayana ceremonial practices (burning incense, gifts of flowers, and food placed on altars) are similar to those practised by the ancient Greeks; however, similar practices were also observed amongst the native Indic culture. One Greek king, Menander I, probably became Buddhist, and was immortalized in Buddhist literature as 'Milinda'. The process of Hellenization also spurred trade between the east and west. For example, Greek astronomical instruments dating to the 3rd century BC were found in the Greco-Bactrian city of Ai Khanoum in modern-day Afghanistan, while the Greek concept of a spherical Earth surrounded by the spheres of planets eventually supplanted the long-standing Indian cosmological belief of a disc consisting of four continents grouped around a central mountain (Mount Meru) like the petals of a flower. The Yavanajataka (lit. Greek astronomical treatise) and Paulisa Siddhanta texts depict the influence of Greek astronomical ideas on Indian astronomy.
Following the conquests of Alexander the Great in the east, Hellenistic influence on Indian art was far-reaching. In architecture, a few examples of the Ionic order can be found as far as Pakistan with the Jandial temple near Taxila. Several examples of capitals displaying Ionic influences can be seen as far as Patna, especially with the Pataliputra capital, dated to the 3rd century BC. The Corinthian order is also heavily represented in the art of Gandhara, especially through Indo-Corinthian capitals.
Influence on Rome

Alexander and his exploits were admired by many Romans, especially generals, who wanted to associate themselves with his achievements. Polybius began his Histories by reminding Romans of Alexander's achievements, and thereafter Roman leaders saw him as a role model. Pompey the Great adopted the epithet "Magnus" and even Alexander's anastole-type haircut, and searched the conquered lands of the east for Alexander's 260-year-old cloak, which he then wore as a sign of greatness. Julius Caesar dedicated a Lysippean equestrian bronze statue, but replaced Alexander's head with his own, while Octavian visited Alexander's tomb in Alexandria and temporarily changed his seal from a sphinx to Alexander's profile. The emperor Trajan also admired Alexander, as did Nero and Caracalla. The Macriani, a Roman family that in the person of Macrinus briefly ascended to the imperial throne, kept images of Alexander on their persons, either on jewellery or embroidered into their clothes.
On the other hand, some Roman writers, particularly Republican figures, used Alexander as a cautionary tale of how autocratic tendencies can be kept in check by the values of the Roman Republic. Alexander was used by these writers as an example of ruler values such as amicitia (friendship) and clementia (clemency), but also iracundia (anger) and cupiditas gloriae (over-desire for glory).
Emperor Julian in his satire called "The Caesars", describes a contest between the previous Roman emperors, with Alexander the Great called in as an extra contestant, in the presence of the assembled gods.
The Itinerarium Alexandri is a 4th-century Latin description of Alexander the Great's campaigns. Julius Caesar went to serve his quaestorship in Hispania after his wife's funeral, in the spring or early summer of 69 BC. While there, he encountered a statue of Alexander the Great, and realised with dissatisfaction that he was now at an age when Alexander had the world at his feet, while he had achieved comparatively little.
Pompey posed as the "new Alexander" since he was his boyhood hero.
After Caracalla concluded his campaign against the Alamanni, it became evident that he was inordinately preoccupied with Alexander the Great. He began openly mimicking Alexander in his personal style. In planning his invasion of the Parthian Empire, Caracalla decided to arrange 16,000 of his men in Macedonian-style phalanxes, despite the Roman army having made the phalanx an obsolete tactical formation. The historian Christopher Matthew mentions that the term Phalangarii has two possible meanings, both with military connotations. The first refers merely to the Roman battle line and does not specifically mean that the men were armed with pikes, and the second bears similarity to the 'Marian Mules' of the late Roman Republic who carried their equipment suspended from a long pole, which were in use until at least the 2nd century AD. As a consequence, the Phalangarii of Legio II Parthica may not have been pikemen, but rather standard battle line troops or possibly Triarii.
Caracalla's mania for Alexander went so far that Caracalla visited Alexandria while preparing for his Persian invasion and persecuted philosophers of the Aristotelian school based on a legend that Aristotle had poisoned Alexander. This was a sign of Caracalla's increasingly erratic behaviour. But this mania for Alexander, strange as it was, was overshadowed by subsequent events in Alexandria.
In 39, Caligula performed a spectacular stunt by ordering a temporary floating bridge to be built using ships as pontoons, stretching for over two miles from the resort of Baiae to the neighbouring port of Puteoli. It was said that the bridge was to rival the Persian king Xerxes' pontoon bridge crossing of the Hellespont. Caligula, who could not swim, then proceeded to ride his favourite horse Incitatus across, wearing the breastplate of Alexander the Great. This act was in defiance of a prediction by Tiberius's soothsayer Thrasyllus of Mendes that Caligula had "no more chance of becoming emperor than of riding a horse across the Bay of Baiae".
The diffusion of Greek culture and language cemented by Alexander's conquests in West Asia and North Africa served as a "precondition" for the later Roman expansion into these territories and entire basis for the Byzantine Empire, according to Errington.
Letters
Main article: Letters of Alexander the GreatAlexander wrote and received numerous letters, but no originals survive. A few official letters addressed to the Greek cities survive in copies inscribed in stone and the content of others is sometimes reported in historical sources. These only occasionally quote the letters and it is an open question how reliable such quotations are. Several fictitious letters, some perhaps based on actual letters, made their way into the Romance tradition.
In legend
Main article: Alexander the Great in legend
Many of the legends about Alexander derive from his own lifetime, probably encouraged by Alexander himself. His court historian Callisthenes portrayed the sea in Cilicia as drawing back from him in proskynesis. Writing shortly after Alexander's death, Onesicritus invented a tryst between Alexander and Thalestris, queen of the mythical Amazons. He reportedly read this passage to his patron King Lysimachus, who had been one of Alexander's generals and who quipped, "I wonder where I was at the time."
In the first centuries after Alexander's death, probably in Alexandria, a quantity of the legendary material coalesced into a text known as the Alexander Romance, later falsely ascribed to Callisthenes and therefore known as Pseudo-Callisthenes. This text underwent over one hundred recensions, translations, and derivations throughout the Islamic and European worlds in premodern times, containing many dubious stories, and was translated into twenty-five languages, for example Middle Persian, Syriac and Arabic.
In ancient and modern culture
Main articles: Cultural depictions of Alexander the Great, Alexander the Great in Islamic tradition, and Alexander the Great in the Quran
Alexander the Great's accomplishments and legacy have been depicted in many cultures. Alexander has featured in both high and popular culture, beginning from his own era to the present day. The Alexander Romance, in particular, has had a significant impact on portrayals of Alexander in later cultures, from Persian to medieval European, to modern Greek.
Alexander features prominently in modern Greek folklore, more than any other ancient figure. The colloquial form of his name in modern Greek ("O Megalexandros") is a household name, and he is the only ancient hero to appear in the Karagiozis shadow play. One well-known fable among Greek seamen involves a solitary mermaid who would grasp a ship's prow during a storm and ask the captain, "Is King Alexander alive?" The answer should be "He is alive and well and rules the world!" causing the mermaid to vanish and the sea to calm. Any other answer would cause the mermaid to turn into a raging Gorgon who would drag the ship to the bottom of the sea, all hands aboard.

In pre-Islamic Middle Persian (Zoroastrian) literature, Alexander is referred to by the epithet gujastak, meaning "accursed", and is accused of destroying temples and burning the sacred texts of Zoroastrianism. In Islamic Persia, under the influence of the Alexander Romance (in Persian: اسکندرنامه Iskandarnameh), a more positive portrayal of Alexander emerges. Firdausi's Shahnameh ("The Book of Kings") includes Alexander in a line of legitimate Persian shahs, a mythical figure who explored the far reaches of the world in search of the Fountain of Youth. In the Shahnameh, Alexander's first journey is to Mecca to pray at the Kaaba. Alexander was depicted as performing a Hajj (pilgrimage to Mecca) many times in subsequent Islamic art and literature. Later Persian writers associate him with philosophy, portraying him at a symposium with figures such as Socrates, Plato and Aristotle, in search of immortality.

The figure of Dhu al-Qarnayn (Arabic: ذو القرنين; lit. "The Two-Horned One") is believed by the majority of modern researchers of the Qur'an as well as Islamic commentators to be a reference to Alexander. The figure is also believed by scholars to be based on later legends of Alexander. In this tradition, he was a heroic figure who built a wall to defend against the nations of Gog and Magog. He also travelled the known world in search of the Water of Life and Immortality, eventually becoming a prophet.
The Syriac version of the Alexander Romance portrays him as an ideal Christian world conqueror who prayed to "the one true God". In Egypt, Alexander was portrayed as the son of Nectanebo II, the last pharaoh before the Persian conquest. His defeat of Darius was depicted as Egypt's salvation, "proving" Egypt was still ruled by an Egyptian.
According to Josephus, Alexander was shown the Book of Daniel when he entered Jerusalem, which described a mighty Greek king who would conquer the Persian Empire. This is cited as a reason for sparing Jerusalem.

In Hindi and Urdu, the name "Sikandar", derived from the Persian name for Alexander, denotes a rising young talent, and the Delhi Sultanate ruler Alauddin Khalji stylized himself as "Sikandar-i-Sani" (the Second Alexander the Great). In medieval India, Turkic and Afghan sovereigns from the Iranian-cultured region of Central Asia brought positive cultural connotations of Alexander to the Indian subcontinent, resulting in the efflorescence of Sikandernameh (Alexander Romances) written by Indo-Persian poets such as Amir Khusrau and the prominence of Alexander the Great as a popular subject in Mughal-era Persian miniatures. In medieval Europe, Alexander the Great was revered as a member of the Nine Worthies; a group of heroes whose lives were believed to encapsulate all the ideal qualities of chivalry. During the first Italian campaign of the French Revolutionary Wars, in a question from Bourrienne, asking whether he gave his preference to Alexander or Caesar, Napoleon said that he places Alexander The Great in the first rank, the main reason being his campaign on Asia.
In the Greek Anthology, there are poems referring to Alexander.
Throughout time, art objects related to Alexander were being created. In addition to speech works, sculptures and paintings, in modern times Alexander is still the subject of musical and cinematic works. The song 'Alexander the Great' by the British heavy metal band Iron Maiden is indicative. Some films that have been shot with the theme of Alexander are:
- Sikandar (1941), an Indian production directed by Sohrab Modi about the conquest of India by Alexander
- Alexander the Great (1956), produced by MGM and starring Richard Burton
- Sikandar-e-Azam (1965), an Indian production directed by Kedar Kapoor
- Alexander (2004), directed by Oliver Stone, starring Colin Farrell
There are also many references to other movies and TV series.
Newer novels about Alexander are: The trilogy "Alexander the Great" by Valerio Massimo Manfredi consisting of "The son of the dream", "The sand of Amon", and "The ends of the world". The trilogy of Mary Renault consisting of "Fire from Heaven", "The Persian Boy" and "Funeral Games".
- The Virtues of War, about Alexander the Great (2004), ISBN 978-0-385-50099-9 and "* The Afghan Campaign, about Alexander the Great's conquests in Afghanistan (2006), ISBN 978-0-385-51641-9" by Steven Pressfield.
Irish playwright Aubrey Thomas de Vere wrote Alexander the Great, a Dramatic Poem.
Historiography
Main article: Historiography of Alexander the GreatApart from a few inscriptions and fragments, texts written by people who actually knew Alexander or who gathered information from men who served with Alexander were all lost. Contemporaries who wrote accounts of his life included Alexander's campaign historian Callisthenes, Alexander's generals; Ptolemy and Nearchus, Aristobulus, a junior officer on the campaigns, and Onesicritus, Alexander's chief helmsman. Their works are lost, but later works based on these original sources have survived. The earliest of these is Diodorus Siculus (1st century BC), followed by Quintus Curtius Rufus (mid-to-late 1st century AD), Arrian (1st to 2nd century AD), the biographer Plutarch (1st to 2nd century AD), and finally Justin, whose work dated as late as the 4th century. Of these, Arrian is generally considered the most reliable, given that he used Ptolemy and Aristobulus as his sources, closely followed by Diodorus.
See also
- Alexander the Great in Islamic tradition
- Ancient Macedonian army
- Bucephalus
- Chronology of European exploration of Asia
- Horns of Alexander
- List of biblical figures identified in extra-biblical sources
- List of people known as The Great
- Gates of Alexander
- Military tactics of Alexander the Great
- Ptolemaic cult of Alexander the Great
- Theories about Alexander the Great in the Quran
References
Notes
- Heracles was Alexander's alleged illegitimate son.
- The name Ἀλέξανδρος derives from the Greek verb ἀλέξω (aléxō, lit. 'ward off, avert, defend') and ἀνδρ- (andr-), the stem of ἀνήρ (anḗr, lit. 'man'), and means "protector of men".
- The first known person to call Alexander "the Great" was a Roman playwright named Plautus (254–184 BC) in his play Mostellaria.
- Macedon was an Ancient Greek polity; the Macedonians were a Greek tribe.
- By the time of his death, he had conquered the entire Achaemenid Persian Empire, adding it to Macedon's European territories; according to some modern writers, this was most of the world then known to the ancient Greeks (the 'Ecumene'). An approximate view of the world known to Alexander can be seen in Hecataeus of Miletus's map; see Hecataeus world map.
- For instance, Hannibal supposedly ranked Alexander as the greatest general; Julius Caesar wept on seeing a statue of Alexander, since he had achieved so little by the same age; Pompey and Alauddin Khalji consciously posed as the 'new Alexander'; the young Napoleon Bonaparte also encouraged comparisons with Alexander. Napoleon also placed Alexander in the first rank. Caracalla believed himself to be the actual reincarnation of Alexander. Caligula wore the breastplate of Alexander in order to show his power. Fidel Castro's hero was Alexander the Great, whose Spanish equivalent Alejandro he adopted as his nom de guerre. Among Ottoman sultans, Mehmed II's heroes were Alexander and Achilles. In a letter to his rival, Selim I, while equating himself with Alexander, compares Ismail I as "Darius of our days". Paolo Giovio, in a work written for Charles V, says that Selim holds Alexander the Great and Julius Caesar in the highest esteem above all the generals of old.
- In ancient historiography, the Argead dynasty was traditionally regarded as having originated from Argos. The Argeads themselves claimed Argive Greek descent from the hero Temenus. Through his parents' genealogy, ancient authors traced Alexander's descent back to heroes and other legendary figures from Greek mythology, such as Heracles and Achilles.
- There have been, since the time, many suspicions that Pausanias was actually hired to murder Philip. Suspicion has fallen upon Alexander, Olympias and even the newly crowned Persian Emperor, Darius III. All three of these people had motive to have Philip murdered.
- However, Arrian, who used Ptolemy as a source, said that Alexander crossed with more than 5,000 horse and 30,000 foot; Diodorus quoted the same totals, but listed 5,100 horse and 32,000 foot. Diodorus also referred to an advance force already present in Asia, which Polyaenus, in his Stratagems of War (5.44.4), said numbered 10,000 men.
Citations
- Bloom, Jonathan M.; Blair, Sheila S. (2009), The Grove Encyclopedia of Islamic Art and Architecture: Mosul to Zirid, Volume 3. (Oxford University Press Incorporated, 2009), 385; "; As the easternmost outpost of the empire of Alexander the Great, the city was renamed Alexandria Eschate ("furthest Alexandria") in 329 BCE."Golden, Peter B. Central Asia in World History (Oxford University Press, 2011), 25;" his campaigns in Central Asia brought Khwarazm, Sogdia, and Bactria under Graeco-Macedonian rule. As elsewhere, Alexander founded or renamed a number of cities, such as Alexandria Eschate ("Outernmost Alexandria," near modern Khojent in Tajikistan)."
- Yenne 2010, p. 159.
- Grant, R.G. (2011). Commanders: History's Greatest Military Leaders. DK Publishing. p. 18. ISBN 978-1-4053-3696-3.
- Beaton, Roderick (2021). The Greeks: A Global History (1st ed.). New York: Basic Books. p. 163. ISBN 9781541618299.
- Heckel & Tritle 2009, p. 99.
- Burger, Michael (2008). The Shaping of Western Civilization: From Antiquity to the Enlightenment. University of Toronto Press. p. 76. ISBN 978-1-55111-432-3.
- Yenne 2010, p. viii.
- ^ Doufikar-Aerts, Faustina (2020). "The Arabic Alexander Romance: Mirror of a Bold, Clever, and Devout Prince". In Seigneurie, Ken (ed.). A Companion to World Literature. Wiley. pp. 1–11. doi:10.1002/9781118635193.ctwl0072. ISBN 978-1-118-99318-7.
- Mínguez Cornelles, Víctor; Rodríguez Moya, Inmaculada (2024). The visual legacy of Alexander the Great from the Renaissance to the age of revolution. Routledge research in art history. New York London: Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group. p. 22. ISBN 978-1-032-54990-3.
- Green, Peter (1970). Alexander of Macedon, 356–323 B.C.: a historical biography. Hellenistic culture and society (illustrated, revised reprint ed.). University of California Press. p. xxxiii. ISBN 978-0-520-07165-0. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
356 – Alexander born in Pella. The exact date is not known, but probably either 20 or 26 July.
- Plutarch, Life of Alexander 3.5: "The birth of Alexander the Great". Livius. Archived from the original on 20 March 2015. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
Alexander was born the sixth of Hekatombaion.
- David George Hogarth (1897). Philip and Alexander of Macedon : two essays in biography. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 286–287. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- McCarty 2004, p. 10, Renault 2001, p. 28, Durant 1966, p. 538
- Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 171.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 188.
- ^ Plutarch 1919, III, 2
- Renault 2001, p. 28, Bose 2003, p. 21
- Renault 2001, pp. 33–34.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 186.
- Plutarch 1919, VI, 5
- Durant 1966, p. 538, Lane Fox 1980, p. 64, Renault 2001, p. 39
- Lane Fox 1980, pp. 65–66, Renault 2001, p. 44, McCarty 2004, p. 15
- Lane Fox 1980, pp. 65–66, Renault 2001, pp. 45–47, McCarty 2004, p. 16
- Lane Fox, Robin (1986). Alexander the Great. Penguin Group. p. 48. ISBN 978-0-14-008878-6.
- ^ Cawthorne 2004, pp. 42–43.
- Howe, Timothy; Brice, Lee L. (2015). Brill's Companion to Insurgency and Terrorism in the Ancient Mediterranean. Brill. p. 170. ISBN 978-90-04-28473-9. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- Carney, Elizabeth Donnelly (2000). Women and Monarchy in Macedonia. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 101. ISBN 978-0-8061-3212-9. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- ^ Morgan, Janett (2016). Greek Perspectives on the Achaemenid Empire: Persia Through the Looking Glass. Edinburgh University Press. pp. 271–272. ISBN 978-0-7486-4724-8. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- Briant, Pierre (2012). Alexander the Great and His Empire: A Short Introduction. Princeton University Press. p. 114. ISBN 978-0-691-15445-9. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- Jensen, Erik (2018). Barbarians in the Greek and Roman World. Hackett Publishing. p. 92. ISBN 978-1-62466-714-5. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- "SOL Search". cs.uky.edu. Archived from the original on 9 August 2020. Retrieved 24 August 2019.
- Lane Fox 1980, p. 68, Renault 2001, p. 47, Bose 2003, p. 43
- Renault 2001, pp. 47–49.
- Renault 2001, pp. 50–51, Bose 2003, pp. 44–45, McCarty 2004, p. 23
- Renault 2001, p. 51, Bose 2003, p. 47, McCarty 2004, p. 24
- Diodorus Siculus 1989, XVI, 86
- Cartledge, Paul (2002). Sparta and Lakonia: A Regional History, 1300-362 B.C. (2nd ed.). New York: Routledge. p. 273. ISBN 0-415-26276-3.
Philip laid Lakonia waste as far south as Gytheion and formally deprived Sparta of Dentheliatis (and apparently the territory on the Messenian Gulf as far as the Little Pamisos river), Belminatis, the territory of Karyai and the east Parnon foreland.
- Renault 2001, p. 54.
- McCarty 2004, p. 26.
- Green, Peter (1991). "Alexander to Actium: The Historical Evolution of the Hellenistic Age (Hellenistic Culture and Society)". The American Historical Review. 1. Berkeley & Los Angeles: University of California Press. doi:10.1086/ahr/96.5.1515. ISSN 0002-8762.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 179.
- McCarty 2004, p. 27.
- Plutarch 1919, IX, 1
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 180.
- A History of Macedonia: Volume III: 336–167 B.C. By N. G. L. Hammond, F. W. Walbank
- Bose 2003, p. 75, Renault 2001, p. 56
- McCarty 2004, p. 27, Renault 2001, p. 59, Lane Fox 1980, p. 71
- Hammond, N. G. L. (21 December 1992). "The Regnal Years of Philip and Alexander". Greek, Roman, and Byzantine Studies. 33 (4): 355–373. ISSN 2159-3159.
- Parise, Frank (2002) . The book of calendars. Piscataway, NJ: Gorgias Press. p. 10. ISBN 978-1-931956-76-5. The month of Dios started in 2 October that year.
- ^ McCarty 2004, pp. 30–31.
- Renault 2001, pp. 61–62
- ^ Lane Fox 1980, p. 72
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 190.
- ^ Green 2007, pp. 5–6
- Renault 2001, pp. 70–71
- McCarty 2004, p. 31, Renault 2001, p. 72, Lane Fox 1980, p. 104, Bose 2003, p. 95
- Stoneman 2004, p. 21.
- Dillon 2004, pp. 187–88.
- Renault 2001, p. 72, Bose 2003, p. 96
- Arrian 1976, I, 1
- Arrian 1976, I, 2
- Arrian 1976, I, 3–4, Renault 2001, pp. 73–74
- Arrian 1976, I, 5–6, Renault 2001, p. 77
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 192.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 199
- Svechin, Alexander (1991) . "Combining Operations for Achieving the ultimate Goal of the War". In Lee, Kent D. (ed.). Strategy. East View Information Services. p. 263. ISBN 1-879944-33-2.
- ^ Briant, Pierre (2002). From Cyrus to Alexander: A History of the Persian Empire. Eisenbrauns. p. 817. ISBN 978-1-57506-120-7. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- ^ Heckel, Waldemar (2008). Who's Who in the Age of Alexander the Great: Prosopography of Alexander's Empire. John Wiley & Sons. p. 205. ISBN 978-1-4051-5469-7. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- Arrian 1976, I, 11
- Arrian 1976, I, 20–23
- ^ Arrian 1976, I, 23
- Arrian 1976, I, 27–28
- Arrian 1976, I, 3
- Green 2007, p. 351
- Arrian 1976, I, 11–12
- "The Project Gutenberg eBook of Anabasis of Alexander, by Arrian". Archived from the original on 26 March 2018. Retrieved 11 January 2018 – via Project Gutenberg.
- Arrian 1976, II, 16–24
- Gunther 2007, p. 84
- Sabin, van Wees & Whitby 2007, p. 396
- Arrian 1976, II, 26
- Arrian 1976, II, 26–27
- ^ Strudwick, Helen (2006). The Encyclopedia of Ancient Egypt. New York: Sterling Publishing Co., Inc. pp. 96–97. ISBN 978-1-4351-4654-9.
- Ring et al. 1994, pp. 49, 320
- Bosworth 1988, pp. 71–74.
- Dahmen 2007, pp. 10–11
- Arrian 1976, III, 1
- Chisholm 1911, p. 616.
- Arrian 1976, III 7–15; also in a contemporary Babylonian account of the battle of Gaugamela Archived 24 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- Hanson, Victor Davis (2007). Carnage and Culture: Landmark Battles in the Rise to Western Power. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-307-42518-8. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ Arrian 1976, III, 16
- "a contemporary account of the battle of Gaugamela". Archived from the original on 12 August 2021. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- Arrian 1976, III, 18
- Foreman 2004, p. 152
- ^ Morkot 1996, p. 121.
- Hammond 1983, pp. 72–73.
- ^ Yenne 2010, p. 99.
- Freeman, Philip (2011). Alexander the Great. New York: Simon & Schuster Paperbacks. p. 213. ISBN 978-1-4391-9328-0. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- Briant, Pierre (2010) . Alexander the Great and His Empire: A Short Introduction. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. p. 109. ISBN 978-0-691-15445-9. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- O'Brien, John Maxwell (1994). Alexander the Great: The Invisible Enemy: A Biography. Psychology Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-415-10617-7.
- "A Long List of Supplies Disbursed". Khalili Collections. Archived from the original on 15 August 2019. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
- Arrian 1976, III, 19–20.
- Arrian 1976, III, 21.
- Arrian 1976, III, 21, 25.
- Arrian 1976, III, 22.
- Gergel 2004, p. 81.
- "The end of Persia". Livius. Archived from the original on 16 March 2016. Retrieved 16 November 2009.
- ^ Briant 1985, pp. 827–830.
- Arrian 1976, III, 23–25, 27–30; IV, 1–7.
- Arrian 1976, III, 30.
- Arrian 1976, IV, 5–6, 16–17.
- ^ Arrian 1976, VII, 11
- ^ Morkot 1996, p. 111.
- Gergel 2004, p. 99.
- "The Anabasis of Alexander; or, The history of the wars and conquests of Alexander the Great. Literally translated, with a commentary, from the Greek of Arrian, the Nicomedian". London, Hodder and Stoughton. 18 January 1884 – via Internet Archive.
- Heckel & Tritle 2009, pp. 47–48
- Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 201
- Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 202
- Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 203
- Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 205
- "eAuction 430. KINGS of MACEDON. Alexander III 'the Great'. 336–323 BC. AR Tetradrachm (25mm, 17.15 g, 1h). Tarsos mint. Struck under Balakros or Menes, circa 333–327 BC". CNG. Archived from the original on 18 February 2019. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- Arrian, Anabasis VII, 3
- ^ G. LE RIDER, Alexandre le Grand : Monnaie, finances et politique, Chapitre V, "Histoire", PUF, 2003, p153-214
- REBUFFAT Françoise, La monnaie dans l'Antiquité, Picard, 1996 .p204
- Gerin, Dominique; Grandjean, Catherine; Amandry, Michel; De Callatay. La monnaie grecque, "L'Antiquité : une histoire", Ellipse, 2001. pp. 117–119.
- BRIANT Pierre, Alexandre Le Grand, "Que sais-je ?", PUF, 2011.
- ^ Tripathi 1999, pp. 118–21.
- Lane Fox 1973
- Narain 1965, pp. 155–65
- McCrindle, J. W. (1997). "Curtius". In Singh, Fauja; Joshi, L. M. (eds.). History of Punjab. Vol. I. Patiala: Punjabi University. p. 229.
- Tripathi 1999, pp. 124–25.
- p. xl, Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, J, Woronoff & I. Spence
- Arrian Anabasis of Alexander, V.29.2
- Tripathi 1999, pp. 126–27.
- Gergel 2004, p. 120.
- Worthington 2003, p. 175
- "Philostratus the Athenian, Vita Apollonii, book 2, chapter 12". perseus.tufts.edu. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- Kosmin 2014, p. 34.
- Tripathi 1999, pp. 129–30.
- Plutarch 1919, LXII, 1
- Tripathi 1999, pp. 137–38.
- Dodge, Theodore Ayrault (1890). Alexander. Great captains. Vol. 2. Houghton Mifflin. pp. 604–605.
- Tripathi 1999, p. 141.
- Morkot 1996, p. 9
- Arrian 1976, VI, 27
- ^ Arrian 1976, VII, 4
- Worthington 2003, pp. 307–08
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 194
- Arrian 1976, II, 29
- ^ Ulrich Wilcken (1967). Alexander the Great. W.W. Norton & Company. p. 146. ISBN 978-0-393-00381-9. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ Arrian 1976, VII, 14
- Arrian 1976, VII, 19
- "A contemporary account of the death of Alexander". Livius.org. Retrieved 5 November 2019.
- Depuydt, Leo (1997). "The Time of Death of Alexander the Great: 11 June 323 B.C. (–322), ca. 4:00–5:00 PM". Die Welt des Orients. 28: 117–135. ISSN 0043-2547. JSTOR 25683643.
- ^ Plutarch 1919, LXXV, 1
- Wood 2001, pp. 2267–70.
- ^ Diodorus Siculus 1989, XVII, 117
- Green 2007, pp. 1–2.
- Plutarch 1919, LXXVII, 1
- ^ Arrian 1976, VII, 27
- Pitt, E. M.; Richardson, W. P. (May 2017). "Hostile inaction? Antipater, Craterus and the Macedonian regency". The Classical Quarterly. 67 (1): 77–78. doi:10.1017/S0009838817000301. S2CID 157417151.
- ^ Green 2007, pp. 23–24.
- ^ Diodorus Siculus 1989, XVII, 118
- Lane Fox 2006, chapter 32.
- "NZ scientist's detective work may reveal how Alexander died". The Royal Society of New Zealand. Dunedin. 16 October 2003. Archived from the original on 16 January 2014. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- Cawthorne 2004, p. 138.
- Bursztajn, Harold J (2005). "Dead Men Talking". Harvard Medical Alumni Bulletin (Spring). Archived from the original on 29 March 2019. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- ^ Schep LJ, Slaughter RJ, Vale JA, Wheatley P (January 2014). "Was the death of Alexander the Great due to poisoning? Was it Veratrum album?". Clinical Toxicology. 52 (1): 72–77. doi:10.3109/15563650.2013.870341. PMID 24369045.
- Bennett-Smith, Meredith (14 January 2014). "Was Alexander The Great Poisoned By Toxic Wine?". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 17 June 2017. Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- Squires, Nick (4 August 2010). "Alexander the Great poisoned by the River Styx". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 12 December 2011.
- ^ Oldach, DW; Richard, RE; Borza, EN; Benitez, RM (June 1998). "A mysterious death". N. Engl. J. Med. 338 (24): 1764–69. doi:10.1056/NEJM199806113382411. PMID 9625631.
- Ashrafian, H (2004). "The death of Alexander the Great – a spinal twist of fate". J Hist Neurosci. 13 (2): 138–42. doi:10.1080/0964704049052157. PMID 15370319. S2CID 36601180.
- Marr, John S; Calisher, Charles H (2003). "Alexander the Great and West Nile Virus Encephalitis". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 9 (12): 1599–1603. doi:10.3201/eid0912.030288. PMC 3034319. PMID 14725285.
- Sbarounis, CN (2007). "Did Alexander the Great die of acute pancreatitis?". J Clin Gastroenterol. 24 (4): 294–96. doi:10.1097/00004836-199706000-00031. PMID 9252868.
- Owen Jarus (4 February 2019). "Why Alexander the Great May Have Been Declared Dead Prematurely (It's Pretty Gruesome)". Live Science. Archived from the original on 27 July 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2021.
- ^ Kosmetatou, Elizabeth (1998). "The Location of the Tomb: Facts and Speculation". Hellenic Electronic Center. Greece.org. Archived from the original on 31 May 2004. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- "Bayfront Byline Bug Walk". UCSD. March 1996. Archived from the original on 3 December 2012. Retrieved 25 March 2013.
- ^ Aelian, "64", Varia Historia, vol. XII
- Green 2007, p. 32.
- ^ Kosmetatou, Elizabeth (1998). "The Aftermath: The Burial of Alexander the Great". Hellenic Electronic Center. Greece.org. Archived from the original on 27 August 2004. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- Christides, Giorgos (22 September 2014). "Greeks captivated by Alexander-era tomb at Amphipolis". BBC News. Archived from the original on 21 September 2014. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- "Archaeologist claims opulent grave in Greece honored Alexander the Great's best friend". usnews.com. 30 September 2015. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- Papapostolou, Anastasios (30 September 2015). "Hephaestion's Monogram Found at Amphipolis Tomb". Greekreporter.com. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- Studniczka 1894, pp. 226ff
- Bieber, M (1965). "The Portraits of Alexander". Greece & Rome. Second Series. 12 (2): 183–88. doi:10.1017/s0017383500015345. S2CID 163858858.
- Sismondo Ridgway, Brunilde (1969). "Review: Der Alexander-Sarkophag by Karl Schefold". American Journal of Archaeology. 73: 482. doi:10.2307/504019. JSTOR 504019.
- "Plutarch, Galba, chapter 1, section 4". perseus.tufts.edu. Archived from the original on 27 February 2021. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "Plutarch, Galba, chapter 1, section 4". perseus.tufts.edu. Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "Plutarch, Regum et imperatorum apophthegmata, Ἀλέξανδρος". perseus.tufts.edu. Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- "Plutarch, De Alexandri magni fortuna aut virtute, chapter 2, section 4". perseus.tufts.edu. Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- ^ Green 2007, pp. 24–26.
- Graham Shipley (2014). The Greek World After Alexander 323–30 BC. Routledge. p. 40. ISBN 978-1-134-06531-8. Retrieved 9 November 2017.
- Green 2007, p. 20
- Green 2007, pp. 26–29.
- Green 2007, pp. 29–34.
- ^ Diodorus Siculus 1989, XVIII, 4
- ^ Badian, Erns (1968). "A King's Notebooks". Harvard Studies in Classical Philology. 72: 183–204. doi:10.2307/311079. JSTOR 311079.
- McKechnie 1989, p. 54
- Tarn, William Woodthorpe (1948). Alexander the Great. Cambridge : University Press. p. 378. ISBN 978-0-521-22584-7. OCLC 606613.
- Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 192.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 193, Morkot 1996, p. 110
- Morkot 1996, p. 110.
- Tarn, William Woodthorpe (1948). Alexander the Great. Cambridge : University Press. pp. 361–362. ISBN 978-0-521-22584-7. OCLC 606613.
- ^ Morkot 1996, p. 122.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 193.
- Stewart, Andrew (1993). Faces of Power : Alexander's Image and Hellenistic Politics Hellenistic Culture and Society. University of California Press. p. 72. ISBN 978-0-520-06851-3.
- ^ Nawotka, Krzysztof (2010). Alexander the Great. Cambridge Scholars Publishing. p. 43.
- "Images of Authority II: The Greek Example". SUNY Oneonta. 2005. Archived from the original on 4 October 2018. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- Stewart, Andrew (1993). Faces of Power : Alexander's Image and Hellenistic Politics Hellenistic Culture and Society. University of California Press. p. 69. ISBN 978-0-520-06851-3.
- Bosworth 1988, pp. 19–20.
- Rolfe 1946, 5.2.13.
- Siculus, Diodorus (1989). Diodorus of Sicily in Twelve Volumes with an English Translation by C. H. Oldfather. Vol. 4–8. Harvard University Press. Archived from the original on 9 July 2021. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- Plutarch 1919, IV, 1.
- Renault 2013, p. 1.
- Liddell & Scott 1940, ξανθός.
- Woodhouse, Sidney Chawner (1910). English–Greek Dictionary: A Vocabulary of the Attic Language. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul Limited. pp. 52, 84, 101.
- Beekes, Robert Stephen Paul; Beek, Lucien van (2010). Etymological Dictionary of Greek. Leiden; Boston: Brill. p. 1033.
- Green, Peter (2008). Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic Age. Orion Publishing Co. pp. 15–16. ISBN 978-0-7538-2413-9.
- Brinkmann, Vinzenz; Wunsche, Raimund (2007). Gods in Color: Painted Sculpture of Classical Antiquity. Arthur M. Sackler / Harvard University Art Museum. p. 159. Archived from the original on 31 July 2022. Retrieved 12 April 2022.
- "Head of a statue of Alexander the Great | Acropolis Museum | Official website". www.theacropolismuseum.gr. Retrieved 1 October 2024.
- Olga Palagia (2000). "Hephaestion's Pyre and the Royal Hunt of Alexander", in A.B. Bosworth and E.J. Baynham (eds), Alexander the Great in Fact and Fiction. Oxford & New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-815287-3, p. 185.
- ^ Green 2007, pp. 15–16.
- Plutarch 1919, V, 2
- Green 2007, p. 4.
- ^ Plutarch 1919, IV, 4
- ^ Arrian 1976, VII, 29
- Plutarch 1919, VII, 1
- ^ Plutarch 1919, VIII, 1
- ^ Arrian 1976, VII, 28
- Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 190, Green 2007, p. 4
- Green 2007, pp. 20–21.
- M Wood (edited by T Gergel) – Alexander: Selected Texts from Arrian, Curtius and Plutarch Penguin, 2004 ISBN 978-0-14-101312-1
- Maddox, Donald; Sturm-Maddox, Sara (February 2012). Medieval French Alexander, the. State University of New York Press. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-7914-8832-4. Retrieved 17 October 2016.
- G Highet – The Classical Tradition: Greek and Roman Influences on Western Literature: Greek and Roman Influences on Western Literature, Oxford University Press, 31 December 1949 p. 68 (ed. c.f. – Merriam-webster.com Archived 26 June 2015 at the Wayback Machine)
- Merriam-Webster – epithet Archived 26 March 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- Plutarch 1919, IX, IV
- ^ Plutarch 1919, XXVII, 1
- Plutarch 1919, LXV, 1
- Morkot 1996, p. 111, Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 195
- Morkot 1996, p. 121, Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 195
- Ahmed, S. Z. (2004), Chaghatai: the Fabulous Cities and People of the Silk Road, West Conshokoken: Infinity Publishing, p. 61.
- Strachan, Edward and Roy Bolton (2008), Russia and Europe in the Nineteenth Century, London: Sphinx Fine Art, p. 87, ISBN 978-1-907200-02-1.
- Livius.org. "Roxane Archived 14 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine." Articles on Ancient History. Retrieved on 30 August 2016.
- Plutarch 1919, LXVII, 1.
- Carney, Elizabeth Donnelly (2000). Women and Monarchy in Macedonia. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0-8061-3212-9.
- Plutarch 1936, II, 6.
- Metz Epitome 70
- Diodorus Siculus 1989, XVII, 114
- Plutarch 1919, LXXII, 1
- Ogden 2009, p. 204.
- Thomas K. Hubbard, ed. (2003). Homosexuality in Greece and Rome: A Sourcebook of Basic Documents. University of California Press. p. 79. ISBN 978-0-520-23430-7.
- Aelian, "7", Varia Historia, vol. XII
- Marilyn Skinner (2013). Sexuality in Greek and Roman Culture (Ancient Cultures) (2nd ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. p. 190. ISBN 978-1-4443-4986-3.
- Sacks 1995, p. 16.
- Thomas Hubbard (2014). "Chapter 8: Peer Homosexuality". In Hubbard, Thomas (ed.). A Companion to Greek and Roman Sexualities. Blackwell Publishing Ltd. p. 143. ISBN 978-1-4051-9572-0.
- Ogden 2009, p. 208... three attested pregnancies in eight years produces an attested impregnation rate of one every 2.7 years, which is actually superior to that of his father.
- Mary Renault (1979). The Nature of Alexander. Pantheon. p. 110. ISBN 978-0-394-73825-3.
No record at all exists of such a woman accompanying his march; nor of any claim by her, or her powerful kin, that she had borne him offspring. Yet twelve years after his death a boy was produced, seventeen years old, born therefore five years after Damascus, her alleged son "brought up in Pergamon"; a claimant and shortlived pawn in the succession wars, chosen probably for a physical resemblance to Alexander. That he actually did marry another Barsine must have helped both to launch and preserve the story; but no source reports any notice whatever taken by him of a child who, Roxane's being posthumous, would have been during his lifetime his only son, by a near-royal mother. In a man who named cities after his horse and dog, this strains credulity.
- Diodorus Siculus 1989, XVII, 77
- Plutarch (1936). "Moralia". University of Chicago. I, 11. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- "Alexander the Great's Achievements". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 2 July 2021. Retrieved 19 August 2021.
- "World map according to Eratosthenes (194 B.C.)". henry-davis.com. Henry Davis Consulting. Archived from the original on 5 December 1998. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- Peter Turchin, Thomas D. Hall and Jonathan M. Adams, "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires Archived 22 February 2007 at the Wayback Machine", Journal of World-Systems Research Vol. 12 (no. 2), pp. 219–29 (2006).
- ^ Green 2007, pp. xii–xix.
- Keay 2001, pp. 82–85.
- ^ "Alexander the Great: his towns". livius.org. Archived from the original on 3 May 2015. Retrieved 13 December 2009.
- ^ Burn, Lucilla (2004). Hellenistic Art: From Alexander the Great to Augustus. London: The British Museum Press. pp. 10–11. ISBN 978-0-89236-776-4. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Collection online". British Museum. Archived from the original on 15 December 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017. "Marble wall block from the temple of Athena at Priene, inscribed on two sides. The inscription on the front records the gift of funds from Alexander the Great to complete the temple."
- "Priene Inscription". British Museum. Archived from the original on 15 December 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017. "Marble wall block from the temple of Athena at Priene, inscribed. Part of the marble wall of the temple of Athena at Priene. Above: "King Alexander dedicated the temple to Athena Polias."
- "Capitains Nemo". cts.perseids.org. Archived from the original on 15 August 2020. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- Downey, Glanville (2015). "II The City of Seleucus the Conqueror". Ancient Antioch. Princeton University Press. pp. 27–44. ISBN 978-1-4008-7671-6. Project MUSE chapter 1708741.
- "Suda, sigma, 117". Archived from the original on 14 October 2021. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- Simpson, Craig (18 November 2023). "Ancient Iraqis may have worshipped Alexander the Great, says British Museum". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 21 November 2023. Retrieved 18 November 2023.
- ^ Green 2007, pp. 56–59.
- Waterman, Leroy; McDowell, Robert H.; Hopkins, Clark (1998). "Seleucia on the Tigris, Iraq". umich.edu. The Kelsey Online. Archived from the original on 4 January 2012. Retrieved 16 December 2011.
- Green 2007, pp. 21, 56–59.
- Green 2007, pp. 56–59, McCarty 2004, p. 17
- ^ Harrison 1971, p. 51.
- Baynes 2007, p. 170, Gabriel 2002, p. 277
- Keay 2001, pp. 101–109.
- Proser, Adriana (2011). The Buddhist Heritage of Pakistan: Art of Gandhara. Asia Society. ISBN 978-0-87848-112-5.
- "Greco-Buddhism: A Brief History". Neosalexandria. 11 November 2010. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ Keay 2001, pp. 101–09.
- Luniya 1978, p. 312
- ^ Pingree 1978, pp. 533, 554ff
- Cambon, Pierre; Jarrige, Jean-François (2006). Afghanistan, les trésors retrouvés: Collections du Musée national de Kaboul [Afghanistan, the treasures found: collections of the Kabul national museum] (in French). Réunion des musées nationaux. p. 269. ISBN 978-2-7118-5218-5. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Glick, Livesey & Wallis 2005, p. 463
- Hayashi (2008), Aryabhata I
- Brown, Rebecca M.; Hutton, Deborah S. (2015). A Companion to Asian Art and Architecture. John Wiley & Sons. p. 438. ISBN 978-1-119-01953-4. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, Chapter 6, p. 114
- Holt 2003, p. 3.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, Chapter 6, p. 115
- "Julian: Caesars – translation". attalus.org. Archived from the original on 26 February 2020. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- Goldsworthy, 100
- Plutarch 1919, XI, 2
- Leach, John. Pompey the Great. p. 29.
- ^ Goldsworthy, Adrian (2009). How Rome Fell: death of a superpower. New Haven: Yale University Press. pp. 74. ISBN 978-0-300-16426-8.
- ^ Brauer, G. (1967). The Decadent Emperors: Power and Depravity in Third-Century Rome. p. 75.
- ^ Christopher, Matthew (2015). An Invincible Beast: Understanding the Hellenistic Pike Phalanx in Action. Casemate Publishers. p. 403.
- Wardle, David (2007). "Caligula's Bridge of Boats – AD 39 or 40?". Historia. 56 (1): 118–120. doi:10.25162/historia-2007-0009. JSTOR 25598379. S2CID 164017284.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 19.
- Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 54.
- Errington 1990, p. 249.
- Pearson, Lionel (1955). "The Diary and the Letters of Alexander the Great". Historia. 3 (4): 429–455. JSTOR 4434421.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 187.
- Plutarch 1919, LXVI, 1
- Stoneman 1996, passim
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 117.
- Darvishi 2022, 117–152
- ^ Fermor 2006, p. 215
- Curtis, Tallis & Andre-Salvini 2005, p. 154
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 120.
- Fischer 2004, p. 66
- Kennedy, Hugh (2012). "Journey to Mecca: A History". In Porter, Venetia (ed.). Hajj : journey to the heart of Islam. Cambridge, Mass.: The British Museum. p. 131. ISBN 978-0-674-06218-4. OCLC 709670348.
- Webb, Peter (2013). "The Hajj before Muhammad: Journeys to Mecca in Muslim Narratives of Pre-Islamic History". In Porter, Venetia; Saif, Liana (eds.). The Hajj : collected essays. London: The British Museum. pp. 14 footnote 72. ISBN 978-0-86159-193-0. OCLC 857109543.
- Griffith, Sidney (15 March 2022). "Narratives of 'the Companions of the Cave,' Moses and His Servant, and Dhū 'l-Qarnayn in Sūrat al-Kahf: Late Antique Lore within the Purview of the Qurʾān". Journal of the International Qur'anic Studies Association. 6 (1). doi:10.5913/jiqsa.6.2021.a005. S2CID 251486595.
- ^ Roisman & Worthington 2010, p. 122.
- Josephus, Jewish Antiquities, XI, 337 viii, 5
- Connerney 2009, p. 68
- Donde, Dipanwita (2014). "The Mughal Sikander: Influence of the Romance of Alexander on Mughal Manuscript Painting". International Conference of Greek Studies: An Asian Perspective. Archived from the original on 12 August 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2019 – via Academia.
- Noll, Thomas (2016). "The Visual Image of Alexander the Great". In Stock, Markus (ed.). Alexander the Great in the Middle Ages: Transcultural Perspectives. Translated by Boettcher, Susan. Toronto: University of Toronto Press. p. 258. ISBN 978-1-4426-4466-3. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- Louis Antoine Fauvelet de Bourrienne, Memoirs of Napoleon Bonaparte, pp 158
- "ToposText". topostext.org. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- "ToposText". topostext.org. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- Dwyer, Rachel (December 2005). 100 Bollywood Films. Roli Books. ISBN 978-81-7436-990-1. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- Plutarch 1919, IV, 57: 'ἀλέξω'.
- ^ Liddell & Scott 1940.
- Plutarch 1919, IV, 57: 'ἀνήρ'.
- "Alexander". Online Etymology Dictionary. Archived from the original on 20 September 2009. Retrieved 11 December 2009.
- Diana Spencer (2019). "Alexander the Great, reception of". Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Classics. Oxford Research Encyclopedias. doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780199381135.013.8048. ISBN 978-0-19-938113-5. Archived from the original on 10 November 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
Alexander enjoys the epithet the Great for the first time in Plautus's Roman comedy Mostellaria (775–777).
- Hornblower 2008, pp. 55–58; Joint Association of Classical Teachers 1984, pp. 50–51; Errington 1990, pp. 3–4; Fine 1983, pp. 607–08; Hammond & Walbank 2001, p. 11; Jones 2001, p. 21; Osborne 2004, p. 127; Hammond 1989, pp. 12–13; Hammond 1993, p. 97; Starr 1991, pp. 260, 367; Toynbee 1981, p. 67; Worthington 2008, pp. 8, 219; Cawkwell 1978, p. 22; Perlman 1973, p. 78; Hamilton 1974, p. 23; Bryant 1996, p. 306; O'Brien 1994, p. 25.
- Danforth 1997, pp. 38, 49, 167.
- Stoneman 2004, p. 2.
- Goldsworthy 2003, pp. 327–28.
- Plutarch 1919, XI, 2
- Holland 2003, pp. 176–83.
- Barnett 1997, p. 45.
- Ronald H. Fritze, Egyptomania: A History of Fascination, Obsession and Fantasy, p. 103.
- Goldsworthy, Adrian (2009). How Rome Fell: death of a superpower. New Haven: Yale University Press. pp. 74. ISBN 978-0-300-16426-8.
- Brauer, G. (1967). The Decadent Emperors: Power and Depravity in Third-Century Rome. p. 75.
- Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 19.
- Geoff W. Adams, The Roman Emperor Gaius "Caligula" and His Hellenistic Aspirations, pp 46
- Leycester Coltman, The Real Fidel Castro, p 220.
- Nicolle, David (2000). Constantinople 1453: The End of Byzantium. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84176-091-9.
- Karen M. Kern (2011). Imperial Citizen: Marriage and Citizenship in the Ottoman Frontier Provinces of Iraq. p. 39.
- Donald Presgrave Little (1976). Essays on Islamic civilization presented to Niyazi Berkes. p. 227.
- Diodorus, Bibliotheca Historica 17.1.5, 17.4; Plutarch, Life of Alexander 2.1; Pausanias, Description of Greece 1.9.8, 1.11.1, 7.8.9; Arrian, Anabasis of Alexander 2.7.4; Herodotus, Histories 5.22.1, 5.22.2; Isocrates, To Philip 32; Thucydides, 2.99,3
- Errington 1990, p. 3; Hornblower 2008, pp. 55–58
- Lane Fox 1980, pp. 72–73.
Sources
Primary sources
- Arrian (1976). de Sélincourt, Aubrey (ed.). Anabasis Alexandri (The Campaigns of Alexander). Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-044253-3.
- Rolfe, John, ed. (1946). "Quintus Curtius Rufus". History of Alexander. Loeb Classical Library. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- Siculus, Diodorus (1989). "Library of History". CH Oldfather, translator. Perseus Project. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 14 November 2009.
- Plutarch (1919). Perrin, Bernadotte (ed.). Plutarch, Alexander. Perseus Project. Archived from the original on 21 October 2011. Retrieved 6 December 2011.
- Plutarch (1936). Babbitt, Frank Cole (ed.). On the Fortune of Alexander. Vol. IV. Loeb Classical Library. pp. 379–487. Retrieved 26 November 2011.
- Trogus, Pompeius (1853). Justin (ed.). "Epitome of the Philippic History". Corpus Scriptorum Latinorum. Rev. John Selby Watson, translator. Archived from the original on 8 November 2013. Retrieved 14 November 2009.
Secondary sources
- Barnett, C. (1997). Bonaparte. Wordsworth. ISBN 978-1-85326-678-2.
- Baynes, Norman G (2007). "Byzantine art". Byzantium: An Introduction to East Roman Civilization. Baynes. p. 170. ISBN 978-1-4067-5659-3. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Berkley, Grant (2006). Moses in the Hieroglyphs. Trafford. ISBN 978-1-4120-5600-7. Retrieved 13 January 2011.
- Bose, Partha (2003). Alexander the Great's Art of Strategy. Crows Nest, NSW: Allen & Unwin. ISBN 978-1-74114-113-9.
- Bosworth, A. B. (1988). Conquest and Empire: The Reign of Alexander the Great. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Briant, P. (1985). "ALEXANDER THE GREAT". In Yarshater, Ehsan (ed.). Encyclopædia Iranica. Vol. I/8: Alafrank–Alp Arslan. London and New York: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 827–830. ISBN 978-0-71009-097-3.
- Bryant, Joseph M. (1996). Moral Codes and Social Structure in Ancient Greece: A Sociology of Greek Ethics from Homer to the Epicureans and Stoics. Albany, NY: State University of New York Press. ISBN 978-0-7914-3042-2. Archived from the original on 9 November 2020. Retrieved 3 October 2020.
- Cawkwell, George (1978). Philip of Macedon. London: Faber and Faber. ISBN 978-0-571-10958-6. Archived from the original on 17 September 2020. Retrieved 3 October 2020.
- Cawthorne, Nigel (2004). Alexander the Great. Haus. ISBN 978-1-904341-56-7.
- [REDACTED] This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Ptolemies". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 22 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 616–618.
- Connerney, R. D. (2009). The upside-down tree: India's changing culture. Algora. p. 214. ISBN 978-0-87586-649-9. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Curtis, J.; Tallis, N; Andre-Salvini, B (2005). Forgotten empire: the world of ancient Persia. University of California Press. p. 154. ISBN 978-0-520-24731-4. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Dahmen, Karsten (2007). The Legend of Alexander the Great on Greek and Roman Coins. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-415-39451-2.
- Danforth, Loring M. (1997). The Macedonian Conflict: Ethnic Nationalism in a Transnational World. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-04356-2.
- Darvishi, Dariush (2022). The Alexander Romance. Tehran: Negah-e Moaser. ISBN 978-622-290-118-9. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- Dillon, John M. (2004). Morality and custom in ancient Greece. Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-34526-4.
- Durant, Will (1966). The Story of Civilization: The Life of Greece. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-671-41800-7.
- Errington, Robert Malcolm (1990). A History of Macedonia. Translated by Catherine Errington. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-06319-8.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (1983). The Ancient Greeks: A Critical History. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-03314-6.
- Fermor, Patrick Leigh (2006). Mani: Travels in the Southern Peloponnese. New York Book Review. p. 358. ISBN 978-1-59017-188-2. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Fischer, M. M. J. (2004). Mute dreams, blind owls, and dispersed knowledges: Persian poesis in the transnational circuitry. Duke University Press. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-8223-3298-5. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Fletcher, Joann (2008). Cleopatra the Great: The Woman Behind the Legend. New York: Harper. ISBN 978-0-06-058558-7.
- Foreman, Laura (2004). Alexander the conqueror: the epic story of the warrior king. Da Capo Press. p. 217. ISBN 978-0-306-81293-4. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Gabriel, Richard A (2002). "The army of Byzantium". The Great Armies of Antiquity. Greenwood. p. 277. ISBN 978-0-275-97809-9. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Gergel, Tania, ed. (2004). The Brief Life and Towering Exploits of History's Greatest Conqueror as Told By His Original Biographers. Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-200140-0.
- Gerin, Dominique; Grandjean, Catherine; Amandry, Michel; de Callatay, François (2001). La monnaie grecque (Ellipse, "L'Antiquité : une histoire" ed.).
- Glick, Thomas F.; Livesey, Steven John; Wallis, Faith, eds. (2005). Medieval Science, Technology, and Medicine: An Encyclopedia. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-96930-7.
- Goldsworthy, A. (2003). The Fall of Carthage. Cassel. ISBN 978-0-304-36642-2.
- Grafton, Anthony (2010). Most, Glenn W; Settis, Salvatore (eds.). The Classical Tradition. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-03572-0.
- Green, Peter (2007). Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic Age. London: Phoenix. ISBN 978-0-7538-2413-9.
- Gunther, John (2007). Alexander the Great. Sterling. ISBN 978-1-4027-4519-5.
- Hamilton, J.R. (1974). Alexander the Great. Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press. ISBN 978-0-8229-6084-3.
- Hammond, NGL (1983). Sources for Alexander the Great. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-71471-6. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ——— (1986). A History of Greece to 323 BC. Cambridge University.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1993). Studies concerning Epirus and Macedonia before Alexander. Amsterdam: Hakkert. ISBN 978-90-256-1050-0. Retrieved 3 October 2020.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière; Walbank, Frank William (2001). A History of Macedonia: 336–167 B.C. Vol. 3 (reprint ed.). Oxford: Clarendon Press of the Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-814815-9. Retrieved 3 October 2020.
- Harrison, E. F. (1971). The language of the New Testament. Wm B Eerdmans. p. 508. ISBN 978-0-8028-4786-7. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Heckel, Waldemar; Tritle, Lawrence A, eds. (2009). Alexander the Great: A New History. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-3082-0. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Holland, Tom (2003). Rubicon: Triumph and Tragedy in the Roman Republic. Abacus. ISBN 978-0-349-11563-4.
- Holt, Frank Lee (2003). Alexander the Great and The Mystery of the Elephant Medallions. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-23881-7.
- Hornblower, Simon (2008). "Greek Identity in the Archaic and Classical Periods". In Zacharia, K. (ed.). Hellenisms: Culture, Identity and Ethnicity from Antiquity to Modernity. Ashgate. pp. 37–58. ISBN 978-0-7546-6525-0.
- Joint Association of Classical Teachers (1984). The World of Athens: An Introduction to Classical Athenian Culture. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-27389-7.
- Jones, Archer (2001). The Art of War in the Western World. Champaign: University of Illinois Press. ISBN 978-0-252-06966-6. Retrieved 3 October 2020.
- Keay, John (2001). India: A History. Grove Press. ISBN 978-0-8021-3797-5.
- Kosmin, Paul J. (2014). The Land of the Elephant Kings: Space, Territory, and Ideology in Seleucid Empire. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-72882-0. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- Lane Fox, Robin (1980). The Search for Alexander. Boston: Little Brown & Co. ISBN 978-0-316-29108-8.
- ——— (2006). Alexander the Great. ePenguin. ASIN B002RI9DYW.
- LE RIDER, George (2003). Alexandre le Grand : Monnaie, finances et politique (Histoire ed.). PUF. p. Chapter V.
- Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert (1940). Jones, Sir Henry Stuart; McKenzie, Roderick (eds.). A Greek-English Lexicon on Perseus Digital Library. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Luniya, Bhanwarlal Nathuram (1978). Life and Culture in Ancient India: From the Earliest Times to 1000 AD. Lakshmi Narain Agarwal. LCCN 78907043.
- McCarty, Nick (2004). Alexander the Great. Camberwell, Victoria: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-670-04268-5.
- McKechnie, Paul (1989). Outsiders in the Greek cities in the fourth century BC. Taylor & Francis. p. 54. ISBN 978-0-415-00340-7. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Morkot, Robert (1996). The Penguin Historical Atlas of Ancient Greece. Penguin.
- Narain, A. K. (1965). Alexander the Great: Greece and Rome–12.
- Ogden, Daniel (2009). "Alexander's Sex Life". In Heckel, Alice; Heckel, Waldemar; Tritle, Lawrence A (eds.). Alexander the Great: A New History. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-3082-0.
- Osborne, Robin (2004). Greek History. New York, New York and London, UK: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-31717-7.
- Perlman, Samuel (1973). Philip and Athens. Cambridge: Heffer. ISBN 978-0-85270-076-1.
- Pingree, D. (1978). "History of Mathematical Astronomy in India". Dictionary of Scientific Biography. Vol. 15. pp. 533–633.
- Pratt, James Bissett (1996). The Pilgrimage of Buddhism and a Buddhist Pilgrimage. Laurier Books. ISBN 978-81-206-1196-2.
- Rebuffat, Françoise (1996). La monnaie dans l'Antiquité. Picard.
- Renault, Mary (2001). The Nature of Alexander the Great. Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-139076-5.
- Renault, Mary (2013). The Nature of Alexander. Open Road Media. ISBN 978-1480432949.
- Ring, Trudy; Salkin, Robert M; Berney, KA; Schellinger, Paul E, eds. (1994). International dictionary of historic places. Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn, 1994–1996. ISBN 978-1-884964-04-6.
- Roisman, Joseph; Worthington, Ian (2010). A Companion to Ancient Macedonia. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4051-7936-2. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Sabin, P; van Wees, H; Whitby, M (2007). The Cambridge History of Greek and Roman Warfare: Greece, the Hellenistic World and the Rise of Rome. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-78273-9.
- Sacks, David (1995). Encyclopedia of the Ancient Greek World. Constable & Co. ISBN 978-0-09-475270-2.
- Starr, Chester G. (1991). A History of the Ancient World. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-506628-9. Retrieved 3 October 2020.
- Stoneman, Richard (2004). Alexander the Great. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-31932-4.
- Stoneman, Richard (1996). "The Metamorphoses of Alexander Romance". In Schmeling, Gareth L (ed.). The Novel in the Ancient World. Brill. pp. 601–12. ISBN 978-90-04-09630-1.
- Studniczka, Franz (1894). Achäologische Jahrbook 9.
- Tripathi, Rama Shankar (1999). History of Ancient India. Motilal Banarsidass Publ. ISBN 978-81-208-0018-2. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Toynbee, Arnold Joseph (1981). The Greeks and Their Heritages. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-215256-5.
- Wood, Michael (2001). In the Footsteps of Alexander the Great: A Journey from Greece to Asia. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-23192-4. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Worthington, Ian (2003). Alexander the Great: A Reader. Routledge. p. 332. ISBN 978-0-415-29187-3. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- Worthington, Ian (2008). Philip II of Macedonia. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-12079-0. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Yenne, Bill (2010). Alexander the Great: Lessons From History's Undefeated General. Palgrave MacMillan. ISBN 978-0-230-61915-9.
Further reading
- Badian, Ernst (1958). "Alexander the Great and the Unity of Mankind". Historia. 7.
- Beazley, JD; Ashmole, B (1932). Greek Sculpture and Painting. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-04131-7.
- Bowra, Maurice (1994). The Greek Experience. Phoenix. ISBN 978-1-85799-122-2.
- Boardman, John (2019). Alexander the Great: From His Death to the Present Day. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-18175-2.
- Burn, AR (1951). Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic Empire (2nd ed.). London: English Universities Press.
- Rufus, Quintus Curtius. "Quintus Curtius Rufus, History of Alexander the Great" (in Latin). U Chicago. Retrieved 16 November 2009.
- Cartledge, Paul (2004). Alexander the Great. Overlook. ISBN 978-1-58567-565-4.
- Doherty, Paul (2004). The Death of Alexander the Great. Carroll & Graf. ISBN 978-0-7867-1340-0.
- Engels, Donald W (1978). Alexander the Great and the Logistics of the Macedonian Army. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Fawcett, Bill, ed. (2006). How To Lose A Battle: Foolish Plans and Great Military Blunders. Harper. ISBN 978-0-06-076024-3.
- Fuller, JFC (1958). The Generalship of Alexander the Great. London: Eyre & Spottiswoode. ISBN 978-0-306-80371-0. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Goldsworthy, Adrian (2020). Philip and Alexander: Kings and Conquerors. London: Head of Zeus. ISBN 978-1-78497-869-3.
- Green, Peter (1992). Alexander of Macedon: 356–323 BC. A Historical Biography. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-07166-7.
- Greene, Robert (2000). The 48 Laws of Power. Penguin. p. 351. ISBN 978-0-14-028019-7.
- Hammond, NGL (1989). The Macedonian State: Origins, Institutions, and History. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-814883-8.
- Hammond, NGL (1994). Alexander the Great: King, Commander, and Statesman (3rd ed.). London: Bristol Classical Press.
- Hammond, NGL (1997). The Genius of Alexander the Great. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
- Lane Fox, Robin (1973). Alexander the Great. London: Allen Lane. ISBN 978-0-14-008878-6., also (1974) New York: E. P. Dutton and (1986) London: Penguin Books.
- Mercer, Charles (1962). The Way of Alexander the Great. Boston: American Heritage Inc.
- McCrindle, J. W. (1893). The Invasion of India by Alexander the Great as Described by Arrian, Q Curtius, Diodorus, Plutarch, and Justin. Westminster: Archibald Constable & Co. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Monti, Giustina (2023). Alexander the Great: letters: a selection. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. ISBN 9781800348622.
- Murphy, James Jerome; Katula, Richard A; Hill, Forbes I; Ochs, Donovan J (2003). A Synoptic History of Classical Rhetoric. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. p. 17. ISBN 978-1-880393-35-2.
- Nandan, Y; Bhavan, BV (2003). British Death March Under Asiatic Impulse: Epic of Anglo-Indian Tragedy in Afghanistan. Mumbai: Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan. ISBN 978-81-7276-301-5.
- O'Brien, John Maxwell (1992). Alexander the Great: The Invisible Enemy. London: Routledge.
- Pomeroy, S; Burstein, S; Dolan, W; Roberts, J (1998). Ancient Greece: A Political, Social, and Cultural History. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-509742-9.
- Prevas, John (2004). Envy of the Gods: Alexander the Great's Ill-Fated Journey Across Asia (3rd ed.). Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0-306-81268-2.
- Roisman, Joseph, ed. (1995). Alexander the Great Ancient and Modern Perspectives. Problems in European Civilization. Lexington, MA: DC Heath.
- Rowson, Alex (2022). The Young Alexander: The Making of Alexander the Great (Hardcover). London: William Collins. ISBN 978-0-00-828439-8.
- Savill, Agnes (1959). Alexander the Great and His Time (3rd ed.). London: Barrie & Rockliff.
- Stewart, Andrew (1993). Faces of Power: Alexander's Image and Hellenistic Politics. Hellenistic Culture and Society. Vol. 11. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Stoneman, Richard (2008). Alexander the Great: A Life in Legend. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-11203-0.
- Tarn, WW (1948). Alexander the Great. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Wheeler, Benjamin Ide (1900). Alexander the Great; the merging of East and West in universal history. New York: GP Putnam's sons.
- Wilcken, Ulrich (1997) . Alexander the Great. New York: WW Norton & Co. ISBN 978-0-393-00381-9.
- Worthington, Ian (2004). Alexander the Great: Man And God. Pearson. ISBN 978-1-4058-0162-1.
External links
Library resources aboutAlexander the Great
- Delamarche, Félix (1833). The Empire and Expeditions of Alexander the Great (Map).
- Romm, James; Cartledge, Paul. "Two Great Historians on Alexander the Great". Forbes (conversations). Part 1, Part 2, Part 3, Part 4, Part 5, Part 6.
- Alexander the Great: An annotated list of primary sources. Livius. Archived from the original on 4 December 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- In Our Time: "Alexander the Great" – BBC discussion with Paul Cartledge, Diana Spencer and Rachel Mairs hosted by Melvyn Bragg, first broadcast 1 October 2015.
| Alexander the Great Argead dynastyBorn: 356 BC Died: 323 BC | ||
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded byPhilip II | King of Macedon 336–323 BC |
Succeeded byPhilip III Alexander IV |
| Preceded byDarius III | King of Persia 330–323 BC | |
| Pharaoh of Egypt 332–323 BC | ||
| New creation | Lord of Asia 331–323 BC | |
| Kings of Macedon | ||
|---|---|---|
| Legendary |  | |
| Argead dynasty | ||
| Antipatrid dynasty | ||
| Dynastic conflict | ||
| Antigonid dynasty | ||
| Post-Conquest Rebel Kings |
| |
| Debatable or disputed rulers are in italics. | ||
| Kings of Babylon | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Alexander the Great
- Ancient Persia
- 356 BC births
- 323 BC deaths
- 4th-century BC Macedonian monarchs
- 4th-century BC pharaohs
- Ancient Macedonian generals
- Ancient Pellaeans
- Argead kings of Macedonia
- City founders
- Deified Greek people
- Deified male monarchs
- Hellenistic-era people
- Kayanians
- Monarchs of Persia
- People in the deuterocanonical books
- Pharaohs of the Argead dynasty
- Shahnameh characters
- Temple of Artemis

