| Revision as of 18:14, 26 June 2005 editAceYYC (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers11,946 edits created page; now a COTW | Revision as of 18:16, 3 July 2005 edit undoAceYYC (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers11,946 edits no longer COTWNext edit → | ||
| (135 intermediate revisions by 27 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| The '''history of Scandinavia''' is the common history of the ]n countries ], ] and ]. | |||
| {{COTWSnow}} | |||
| {{Scandinavia}} | |||
| == Pre-historic age == | |||
| Throughout heavily wooded Scandinavia, there was little need to build tools out of mineral components. Consequently, little evidence remains of the Scandinavia of the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, or the Iron Age except limited numbers of tools created from stone, bronze, and iron, some jewelry and ornaments, and stone ]. One important collection that exists, however, is a widespread and rich collection of stone drawings known as ]. | |||
| ===Stone Age=== | |||
| :''Main article '']'' | |||
| Denmark has the longest known pre-history of the three countries, with the first settlers believed to have arrived in the ] of ] roughly 100,000 years ago and continuously over the past 12,000 years. The discovery of ancient human remains in Denmark's ] has served as proof of human habitation of the area at this early historical point. | |||
| The most recent ] covered the entirety of ], rendering it completely uninhabitable to human settlement; following the end of the era, ] began once again to move into the region, attracted by a wealth of game both on land and at sea, including such animals as elk, reindeer, musk ox, mammoth, wild boar, fish, seals, whales, and otters. | |||
| These earliest hunters and gatherers entered the region more than 10,000 years ago but left scant evidence of their presence in the historical record. The weather continued to warm, and the ice and snow continued to recede. As the region continued to warm and the ice receded, early settlers were drawn further north along the coasts and into the Scandinavian interior. | |||
| Utilizing fire, boats and stone tools enabled these ] inhabitants to survive life in northern ]. The northern hunter/gatherers followed the herds and the salmon runs, moving south during the winters, moving north again during the summers. These early peoples followed cultural traditions similar to those practised throughout other regions in the far north – areas including modern ], ], and across the ] into the northernmost strip of ] (containing portions of today's ] and ]). | |||
| ===Nordic Bronze Age=== | |||
| :''Main article ]'' | |||
| ] | |||
| In southern Scandinavia conditions grew favorable to encourage and support agriculture. By about ] in Denmark, southern Sweden, and southern Norway, temperatures temporarily warmed to levels similar to today’s ] climate. Farming guaranteed an annual food supply without migration and created a social stability that enabled a complex structured society to emerge. Agriculture required advanced tools and knowledge, and both came from neighbors further to the south on the European continent. Trade with these older, more advanced, southern European societies brought the lower Scandinavians many innovations, perhaps especially, by 1500 BC, bronze, and 1,000 years later, iron. | |||
| ===Pre-Roman Iron Age=== | |||
| :''Main article ]'' | |||
| The Nordic Bronze Age ended with a deteriorating, colder and wetter climate. And this period is known for being poor in archaeological finds. This is also the period when the ] are being known to the Mediterranean world, and the Romans. | |||
| ===Roman Iron Age=== | |||
| :''Main article ]'' | |||
| While many ] tribes sustained continued contact with the culture and military presence of the ], much of Scandinavia existed on the most extreme periphery of the Latin world. With the exception of the passing references to the Swedes (]) and the ] (Gautoi). The end of this period is sometimes called the ''Age of Gold'' because during the last centuries large amounts of gold found their way into Scandinavia, as well as new technology. | |||
| ===Germanic Iron Age=== | |||
| :''Main article ]'' | |||
| The period succeding the fall of the Roman Empire is known as the Germanic Iron Age, and it is divided into the early Germanic Iron and the late Germanic Iron Age, which in Sweden is known as the ], with rich burials in the basin of Lake ]. The early Germanic Iron Age is the period when the ] appears in history, and according to ], they were an offshoot of the Swedes (''suehans'', ''suetidi'') who had replaced the ]. | |||
| ==Viking Age== | |||
| ] | |||
| Main article: '']'' | |||
| The '''Viking Age''' is the name of the period between ] A.D and ] A.D in Scandinavia. This corresponds to the latter half of the early ]. During this period, the ] (Scandinavian warriors and traders) raided, colonized and explored large parts of ], the ], Northern ], and they even reached ], more specifically the modern area identified as ]. | |||
| The beginning of the Viking Age is commonly given as ], when Vikings pillaged the important British island monastery of ], and its end is marked by the unsuccessful invasion of England attempted by ] in ] and the ]. | |||
| ===Age of Settlement=== | |||
| ] | |||
| The age of settlement began around 800 AD. The Vikings invaded and eventually settled in England, ], the ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. Swedish settlers were mostly present in Rus, Livonia, and other Eastern regions while the Norwegians and the Danish were primarily concentrated in Western and Northern Europe. These eastern-traveling Scandinavian migrants were eventually known as ] (''væringjar'', meaning "sworn men") and, according to the oldest Slavic sources, these varangians founded ], the major East European state prior to the ] invasions. The western-led warriors, eventually known as Vikings, left great cultural marks on regions such as ] ], ], and ], where the city of ] was founded by Viking invaders. Iceland first became colonized in the 800s. | |||
| ] remains a major figure in ] and ] history, becoming one of the first recorded Europeans to reach ]. Eriksson sailed across the ] and landed in ], christening the region ]. However, he showed little interest in setting up a permanent colony in the far western territory, instead claiming the nearby island of ] in the name of the Norse pantheon and encouraging the establishment of communities there instead of on the American landfall. Proof of Viking presence in Newfoundland was substantiated by the discovery of Viking relics and dwellings in the area, after a joint team of archaeologists unearthed runic treasure and found a Viking village in ] in ]. Gradual successions of voyages to ] by the Vikings formed the initial core of the island's population, but migration remained low. The island later came to be inhabited by ] and other indigenous peoples from the Canadian mainland. | |||
| The Vikings considered these colonies to be merely extensions of their own homeland, and notions about a different world only arose after interaction with indigenous peoples of the settled areas. | |||
| See also: | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| === Christianisation === | |||
| ] (]) tied and left on a skerry at ebb, resulting in a protracted death by drowning and the securing of Christian hegemony in the Norwegian kingdom.]] | |||
| Viking religious beliefs were heavily connected to ]. Viking religious beliefs placed heavy emphasis on battle, honor and focused on the idea of ], a mythical home with the gods for fallen warriors. | |||
| Christianization of Scandinavia came later than most parts of Europe. In Denmark ] christianized the country around ]. The process of Christianization began in Norway during the reigns of ] (reigned 995 AD-c.1000 AD) and ] (reigned 1015 AD-1030 AD). Olaf and Olaf II had been baptized voluntarily outside of Norway. Olaf II managed to bring English clergy to his country. Norway's conversion from the ] to Christianity was mostly the result of English missionaries. As a result of the adoption of ] by the monarchy and eventually the entirety of the country, traditional ] practices were marginalized and eventually persecuted. ], practioners of ], a Scandinavian pre-Christian tradition, were executed or exiled under newly Christianized governments in the eleventh and twelfth centuries. | |||
| Sweden required a little more time to transition to Christianity, with indigenous religous practices commonly held in localized communities well until the end of the eleventh century. A brief Swedish ] ensued in ] primarily reflecting the divisions between practitioners of indigenous religions and advocates of Christianity; by the mid-twelfth century, the Christian faction appeared to have triumphed; the once resistant center of ] became the seat of the ] in ]. The Christianization of Scandinavia occurred nearly simultaneously with the end of the Viking era. The adoption of Christianity is believed to have aided in the absorption of Viking communities into the greater religious and cultural framework of the European continent. | |||
| See also: | |||
| * | |||
| == 1100 - 1600 == | |||
| === Kalmar Union === | |||
| Main article: '']'' | |||
| The '''Kalmar Union''' (]/]/]: ''Kalmarunionen'') was a series of ]s (]–]<!-- Election of Christian II as king was 1513 in Denmark and Norway, 1520 in Sweden -->) that united the three kingdoms of ], ] and ] under a single ]. The countries had given up their ], but not their ], and diverging interests (especially Swedish dissatisfaction over the Danish and ]ish dominance) gave rise to a conflict that would hamper it from the ] until it's final dissolution in ]. | |||
| The ] is said to have finally broken the union and established Sweden's status as one of Europe's great powers. | |||
| ===Reformation=== | |||
| The reformation came to Scandinavia in the 1530s. Scandinavia soon became one of the heartlands of ]. | |||
| See also: ] | |||
| ==1600s== | |||
| === Rise of Sweden and the Swedish Empire=== | |||
| ''Main Articles: ]-]'' | |||
| ] in ]. The yellow coloured area shows the extent of modern Sweden.]] | |||
| The Swedish power began under the rule of Charles IX. During the ] Sweden expanded its territories eastward. Several other wars with Poland, Denmark-Norway, and German countries continued to expand Sweden. Sweden began consolidating its Empire. Several other wars followed soon after including the ] and the ]. Denmark suffered many defeats during this period. Finally under the rule of ] the empire was consolidated under a semi-absolute monarchy. | |||
| ===Thirty Years War=== | |||
| The ] was a conflict fought between the years 1618 and 1648, principally in the Central European territory of the ], but also involving most of the major continental powers. It occurred for a number of reasons. Although it was from its outset a religious conflict between ] and ], the self-preservation of the ] was also a central motive. The Danes and then Swedes intervened at various points to protect their interests. | |||
| ] | |||
| The Danish intervention began when ] (1577-1648) the King of Denmark, himself a Lutheran, helped the Germans by leading an army against the Holy Roman Empire, fearing that Denmark's sovereignty as a Protestant nation was being threatened. The period began in ] and lasted till ] Christian IV had profited greatly from his policies in northern Germany (Hamburg had been forced to accept Danish sovereignty in 1621, and in 1623 the Danish heir apparent was made bishop of Bremen-Verden.) As an administrator, Christian IV had done remarkably well, obtaining for his kingdom a level of stability and wealth that was virtually unmatched elsewhere in Europe, paid for by the ] toll and extensive war reparations from Sweden. The only country in Europe with a comparably strong financial position was, ironically, Bavaria. It also helped that the French regent] was willing to pay for a Danish incursion into Germany. Christian invaded at the head of a mercenary army of 20,000 men. | |||
| ].]] | |||
| The Swedish intervention began in ] and lasted until ] Some within ]'s court believed that ] wanted to take control of the German Princes and thus gain influence over the Emperor. Ferdinand II dismissed Wallenstein in 1630. He was to later recall him after the Swedes, led by ], attacked the Empire and prevailed in a number of significant battles. | |||
| Gustavus Adolphus, like Christian IV before him, came to aid the German Lutherans, to forestall Catholic aggression against their homeland and to obtain economic influence in the German states around the ]. Also like Christian IV, Adolphus was subsidized by Richelieu, the Chief Minister of] of France, and by the ]. From 1630-1634, they drove the Catholic forces back and regained much of the occupied Protestant lands | |||
| ==1700s== | |||
| === Great Northern War === | |||
| Main article: '']'' | |||
| ] | |||
| The '''Great Northern War''' was the war fought between a coalition of ], ] and ]-] (from ] also ] and ]) on one side and ] on the other side from ] to ]. It started by a coordinated attack on Sweden by the coalition in ], and ended ] with the conclusion of the ], and the ]. As a result of the war, Russia supplanted Sweden as the dominant ] on the ] and became a major player in European politics. | |||
| === Colonialism=== | |||
| Main article: '']; ]'' | |||
| Both Sweden and Denmark maintained a number of ] outside Scandinavia starting in the 17th century lasting until the 20th century. Denmark had colonies in Greenland and Iceland in the north Atlantic. In the ] Denmark started a colony on ] in ], ] in ], and purchased ] from France in ]. Denmark also maintained a colony, ], in India. The Danish East India Company operated out of Tranquebar. Sweden also chartered a ]. During its heyday, the Danish and Swedish East India Company imported more tea than the British East India Company - and smuggled 90% of it into Britain, where it could be sold at a huge profit. Both East India Companies folded over the course of the Napoleonic Wars. Sweden had a short lived colony in North America and ] (1785-1878) and ] in the Caribbean. | |||
| ==1800== | |||
| ===Napoleonic Wars=== | |||
| {{Seemain|Napoleonic Wars}} | |||
| Scandinavia was divided during the Napoleonic Wars. Sweden joined the Third Coalition in 1805 against Napoleon however the alliance fell apart after Russia abadoned the alliance and invaded Finland which forced Sweden to cede the territory. During this time it was also decided that since ] was childless, Marshal ] would be named the next king. Bernadotte was originally one of Napoleon's eighteen generals, however he decided to continue fighting France in favour of Sweden throughout 1813-1814. ], a prominent Swedish baron was the one who initially extended the offer of the Swedish crown to the young soldier. | |||
| Denmark-Norway became involved in the conflict after Danish ports were being blockaded by the British navy. Britain thereafter ] and ]. The Danish fleet was destroyed in 1801, but was rebuilt and captured or destroyed in 1807. After the war, Denmark was forced to cede ] to Britain and Norway to Sweden. | |||
| ===Sweden-Norway=== | |||
| Main article: '']; ]'' | |||
| On ], 1814, at the ], Norway was ceded by Denmark to Sweden. In an attempt to take control of its destiny the Norwegians convened a ] at ] and on ], 1814 signed the ]. A Danish prince, ] was elected by the assembly as king. | |||
| The Swedish king rejected the premise of an independent Norway and launched a military campaign on ] 1814 with an attack on the ] islands and the city of ]. The Swedish army was superior in numbers, was better equipped and trained, and was led by one of Napoleon's foremost generals, the newly elected Swedish crown prince, ]. Battles were short and decisively won by the Swedes. Armistice negotiations concluded on August 14, 1814. | |||
| In the peace negotiations, Christian Frederik agreed to relinquish claims to the Norwegian crown and return to Denmark if Sweden would accept the ] Norwegian constitution and a ]. | |||
| Following growing dissatisfaction with the union in Norway, the parliament unanimously declared its dissolution on ], ]. This unilateral action met with Swedish threats of war. A ] on ] confirmed the parliamentary decision by a majority of 368,208 to 184. Negotiations in ] led to agreement with Sweden on ] and mutual demobilization. Both parliaments revoked the Act of Union ], and the deposed king ] of Sweden renounced his claim to the Norwegian throne and recognized Norway as an independent kingdom on ]. The Norwegian parliament offered the vacant throne to Prince Carl of ], who accepted after another plebiscite had confirmed the monarchy. He arrived in Norway on ], ], taking the name ]. | |||
| ===Finnish War=== | |||
| The ] was fought between ] and ] from February ] to September ]. As a result of the war, ] which formed the eastern third of Swedish Empire became the semi-autonomous ], according to the Finns in ] with ]. Finland remained as a part of Russian Empire until 1917 at which point it became independent. Another notable effect was the Swedish parliament's adoption of a new constitution and a new royal house, that of ]. | |||
| ===Industrialisation=== | |||
| ] began in the mid ] in Scandinavia. | |||
| ===Monetary Union=== | |||
| See also: '']'' | |||
| ] | |||
| The Scandinavian Monetary Union was a ] formed by Sweden and Denmark on ], ] by fixing their ] against ] at par to each other. ], which was in union with Sweden entered the union two years later, in ] by pegging its currency to gold at the same level as Denmark and Sweden (.403 grams ). The monetary union was one of the few tangible results of the ]n political movement of the ]. | |||
| The union provided fixed exchange rates and stability in monetary terms, but the member countries continued to issue their own separate currencies. Even if it was not initially foreseen, the perceived security led to a situation where the formally separate currencies were accepted on a basis of "as good as" the ] virtually throughout the entire area. | |||
| The outbreak of ], in ] brought an end to the monetary union. Sweden abandoned the tie to gold on ], 1914 and without a fixed exchange rate the free circulation came to an end. | |||
| ==1900s== | |||
| ===Development of the Welfare State=== | |||
| All three countries developed social welfare states in the early to mid ]. This came about partially because of the domination of the social-democrats in Sweden and Denmark, and the Labour party in Norway. | |||
| ===Second World War=== | |||
| ''Main articles: ]; ]; ]; ]; ]; ]; ]; ]; ]'' | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Near the beginning of ], both the ] and the ] powers feared their enemies gaining power in Scandanavia. Britain believed Germany was planning to invade, and was not eager to do battle there. At the same time, Germany feared that Britain could gain bases in the area and claimed they suspected an outright invasion. In addition, Germany highly valued the iron ore they received through Norway and could not afford to lose it. They also desired Norway for its ice-free ports. This made it a primary target, with Denmark a secondary goal mainly needed for facilitating the Norwegian invasion. After planning for months, Germany invaded both Denmark and Norway the same day, ], ]. | |||
| The nations reacted quite differently. Denmark surrendered a mere two hours after invasion, having lost just sixteen men. They sought to avoid civillian casualties and receive favourable treatment from Germany. Norway however, refused to give in and fought with their full strength. The Western allies sent military assistance, but the campaign was not effectively run. By ], ] Norway too had submitted to their attackers completely. | |||
| Denmark's strategy proved the more beneficial in the long run. It was one of the factors that led Germany to grant them a high degree of autonomy. Another reason was that they had no real agenda in Denmark. After invading, they simply didn't want to relinquish it, seeing it as a permanent part of their empire. Also, Danes were considered fellow Nordics by Nazi ideologues, which further helped the country. For all these reasons, Denmark was able to retain their parliament, king, and much of their normal domestic function. However, bitterness towards Germany grew and small sabatoges directed against Germany became commonplace. Germany eventually reacted by eliminating Denmark's representative government and imposing martial law. | |||
| Norway was treated much more harshly throughout their occupation. Opposition parties were eliminated and National Gathering(the Norwegian Nazi party) appointed all government officials. ] was installed as the new dictator. Labor unions could only exist if they accepted Nazi control. Despite these repressive measures, there was still a fairly high degree of cooperation. About ten precent supported the Nazi party, and others supported some of their programs. Nevertheless, there was a hostile relationship, with 8 German soldiers for every Norwegian. | |||
| Denmark and Norway were also unalike in their cooperation with Germany's genocidal policy. Danes were notable for their devoted efforts to protect Danish ]. More than 96% of the Jewish population was boated to safety in Sweden, while others found refuge with Christian Danish families and organizations. Norwegian police, however, aided in the capture of Norwegian Jews. This helped allow 40% of Norwegian Jews to be murdered in ]s. | |||
| Alone out of the three Scandanavian countries, Sweden was not invaded and remained nominally neutral during the war. They successfully cultivated peace with the Germans, supplying them with needed raw materials. The Swedish government was very careful to avoid inflaming the Nazis, going so far as to persuade newspaper editors to censor articles. However, there were exceptions to their neutrality. For example, they granted the Jews that escaped from Denmark asylum and gave minor aid to Finland during the ]. | |||
| ===Post-war=== | |||
| See also: '']'' | |||
| After the second world war, all of the Scandinavian countries agreed that some form of mutual defense policy was necessary. They began to discuss a Scandinavian defense union. The three Scandinavian countries would, if they had entered into an alliance, have remained separate ] countries but acted as a single bloc in foreign policy and security issues. The proposed union was being discussed by a joint Scandinavian committee during the winter of ]-], but the ] tension between the ] and the ], and preparations for a western alliance that would result in the ] overshadowed the effort. When it became known that the western alliance would not be able to supply the Scandinavian countries with armaments before meeting their own pressing needs, this issue ultimately proved to be the turning point for Norway, which resigned from the talks. Denmark was still willing to enter into an alliance with Sweden, but the Swedes saw few advantages in this and the proposal fell. Norway and Denmark subsequently became signatory parties of the North Atlantic Treaty and members of ]. Sweden remained neutral after a heated debate. Some people credit the Swedish stance for allowing Finland to remain outside the ], as the USSR might have felt threatened by a NATO member so close by. | |||
| ===European integration=== | |||
| The Nordic countries established the ] in 1952 and the ] ]. | |||
| After a 1972 referendum, Denmark became the first Scandinavian member of the ], which later paved the way for the ], in ]. Sweden joined the EU in ]; after the fall of the Soviet Union, Sweden felt it could do so without being provocative. Norway remains outside the European Union to this day after ] and ], although it is a signatory of the ] and a member of the ]. None of the Scandinavian countries have joined the ], membership being rejected by referendum in both Denmark and Sweden. All of the Scandinavian countries have shown high degrees of Euro-scepticism, despite their enthusiasm for cooperation and ]. Denmark voted no to the ] in 1992, causing uproar across the community, and forcing a renegotiation, including "opting-out" of the proposed unified currency. | |||
| == See also == | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| #{{Web reference | title=Ukrainian Net | work=The Outcomes Of Establishment Of Roman Catholic Church Structures And Church Power In Norway And Scandinavia| URL=http://www.personal.ceu.hu/students/97/Roman_Zakharii/norway-church.htm | date=June 28 | year=2005}} | |||
| #{{Web reference | title=Decision to Invade Norway and Denmark | work=The German Decision to Invade Norway and Denmark|URL=http://www.army.mil/cmh-pg/books/70-7_02.htm|date=July 2|year=2005}} | |||
| # | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Revision as of 18:16, 3 July 2005
The history of Scandinavia is the common history of the Scandinavian countries Denmark, Norway and Sweden.
| Part of a series on |
| Scandinavia |
|---|
 |
|
Countries
|
|
HistoryHistory by country
Chronological history
|
|
Geography
|
|
Economy
|
| Related |
Pre-historic age
Throughout heavily wooded Scandinavia, there was little need to build tools out of mineral components. Consequently, little evidence remains of the Scandinavia of the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, or the Iron Age except limited numbers of tools created from stone, bronze, and iron, some jewelry and ornaments, and stone burial cairns. One important collection that exists, however, is a widespread and rich collection of stone drawings known as petroglyphs.
Stone Age
- Main article Stone Age
Denmark has the longest known pre-history of the three countries, with the first settlers believed to have arrived in the peninsula of Jutland roughly 100,000 years ago and continuously over the past 12,000 years. The discovery of ancient human remains in Denmark's local bogs has served as proof of human habitation of the area at this early historical point.
The most recent Ice Age covered the entirety of Scandinavia, rendering it completely uninhabitable to human settlement; following the end of the era, settlers began once again to move into the region, attracted by a wealth of game both on land and at sea, including such animals as elk, reindeer, musk ox, mammoth, wild boar, fish, seals, whales, and otters.
These earliest hunters and gatherers entered the region more than 10,000 years ago but left scant evidence of their presence in the historical record. The weather continued to warm, and the ice and snow continued to recede. As the region continued to warm and the ice receded, early settlers were drawn further north along the coasts and into the Scandinavian interior.
Utilizing fire, boats and stone tools enabled these Stone Age inhabitants to survive life in northern Europe. The northern hunter/gatherers followed the herds and the salmon runs, moving south during the winters, moving north again during the summers. These early peoples followed cultural traditions similar to those practised throughout other regions in the far north – areas including modern Finland, Russia, and across the Bering Strait into the northernmost strip of North America (containing portions of today's Alaska and Canada).
Nordic Bronze Age
- Main article Nordic Bronze Age

In southern Scandinavia conditions grew favorable to encourage and support agriculture. By about 1500 BC in Denmark, southern Sweden, and southern Norway, temperatures temporarily warmed to levels similar to today’s Mediterranean climate. Farming guaranteed an annual food supply without migration and created a social stability that enabled a complex structured society to emerge. Agriculture required advanced tools and knowledge, and both came from neighbors further to the south on the European continent. Trade with these older, more advanced, southern European societies brought the lower Scandinavians many innovations, perhaps especially, by 1500 BC, bronze, and 1,000 years later, iron.
Pre-Roman Iron Age
- Main article Pre-Roman Iron Age
The Nordic Bronze Age ended with a deteriorating, colder and wetter climate. And this period is known for being poor in archaeological finds. This is also the period when the Germanic tribes are being known to the Mediterranean world, and the Romans.
Roman Iron Age
- Main article Roman Iron Age
While many Germanic tribes sustained continued contact with the culture and military presence of the Roman Empire, much of Scandinavia existed on the most extreme periphery of the Latin world. With the exception of the passing references to the Swedes (Suiones) and the Geats (Gautoi). The end of this period is sometimes called the Age of Gold because during the last centuries large amounts of gold found their way into Scandinavia, as well as new technology.
Germanic Iron Age
- Main article Germanic Iron Age
The period succeding the fall of the Roman Empire is known as the Germanic Iron Age, and it is divided into the early Germanic Iron and the late Germanic Iron Age, which in Sweden is known as the Vendel Age, with rich burials in the basin of Lake Mälaren. The early Germanic Iron Age is the period when the Danes appears in history, and according to Jordanes, they were an offshoot of the Swedes (suehans, suetidi) who had replaced the Heruls.
Viking Age
Main article: Viking Age
The Viking Age is the name of the period between 793 A.D and 1066 A.D in Scandinavia. This corresponds to the latter half of the early Iron Age. During this period, the Vikings (Scandinavian warriors and traders) raided, colonized and explored large parts of Europe, the Middle East, Northern Africa, and they even reached North America, more specifically the modern area identified as Newfoundland.
The beginning of the Viking Age is commonly given as 793, when Vikings pillaged the important British island monastery of Lindisfarne, and its end is marked by the unsuccessful invasion of England attempted by Harald Hårdråde in 1066 and the Norman conquest.
Age of Settlement

The age of settlement began around 800 AD. The Vikings invaded and eventually settled in England, Greenland, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Ireland, Livonia, Normandy, the Shetland Islands, Sicily, Rus' and Vinland. Swedish settlers were mostly present in Rus, Livonia, and other Eastern regions while the Norwegians and the Danish were primarily concentrated in Western and Northern Europe. These eastern-traveling Scandinavian migrants were eventually known as Varangians (væringjar, meaning "sworn men") and, according to the oldest Slavic sources, these varangians founded Kievan Rus, the major East European state prior to the Mongol invasions. The western-led warriors, eventually known as Vikings, left great cultural marks on regions such as French Normandy, England, and Ireland, where the city of Dublin was founded by Viking invaders. Iceland first became colonized in the 800s.
Leif Eriksson remains a major figure in Viking and Scandinavian history, becoming one of the first recorded Europeans to reach North America. Eriksson sailed across the Atlantic Ocean and landed in Newfoundland, christening the region Vinland. However, he showed little interest in setting up a permanent colony in the far western territory, instead claiming the nearby island of Greenland in the name of the Norse pantheon and encouraging the establishment of communities there instead of on the American landfall. Proof of Viking presence in Newfoundland was substantiated by the discovery of Viking relics and dwellings in the area, after a joint team of archaeologists unearthed runic treasure and found a Viking village in L'Anse aux Meadows in 1960. Gradual successions of voyages to Greenland by the Vikings formed the initial core of the island's population, but migration remained low. The island later came to be inhabited by Inuit and other indigenous peoples from the Canadian mainland.
The Vikings considered these colonies to be merely extensions of their own homeland, and notions about a different world only arose after interaction with indigenous peoples of the settled areas.
See also:
Christianisation

Viking religious beliefs were heavily connected to Norse Mythology. Viking religious beliefs placed heavy emphasis on battle, honor and focused on the idea of Valhalla, a mythical home with the gods for fallen warriors.
Christianization of Scandinavia came later than most parts of Europe. In Denmark Harald Bluetooth christianized the country around 980. The process of Christianization began in Norway during the reigns of Olaf Tryggvason (reigned 995 AD-c.1000 AD) and Olaf II Haraldsson (reigned 1015 AD-1030 AD). Olaf and Olaf II had been baptized voluntarily outside of Norway. Olaf II managed to bring English clergy to his country. Norway's conversion from the Norse religion to Christianity was mostly the result of English missionaries. As a result of the adoption of Christianity by the monarchy and eventually the entirety of the country, traditional shamanistic practices were marginalized and eventually persecuted. Völvas, practioners of seid, a Scandinavian pre-Christian tradition, were executed or exiled under newly Christianized governments in the eleventh and twelfth centuries.
Sweden required a little more time to transition to Christianity, with indigenous religous practices commonly held in localized communities well until the end of the eleventh century. A brief Swedish civil war ensued in 1066 primarily reflecting the divisions between practitioners of indigenous religions and advocates of Christianity; by the mid-twelfth century, the Christian faction appeared to have triumphed; the once resistant center of Uppsala became the seat of the Swedish Archbishop in 1164. The Christianization of Scandinavia occurred nearly simultaneously with the end of the Viking era. The adoption of Christianity is believed to have aided in the absorption of Viking communities into the greater religious and cultural framework of the European continent.
See also:
1100 - 1600
Kalmar Union
Main article: Kalmar Union
The Kalmar Union (Danish/Norwegian/Swedish: Kalmarunionen) was a series of personal unions (1397–1520) that united the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden under a single monarch. The countries had given up their sovereignty, but not their independence, and diverging interests (especially Swedish dissatisfaction over the Danish and Holsteinish dominance) gave rise to a conflict that would hamper it from the 1430s until it's final dissolution in 1523.
The Nordic Seven Years' War is said to have finally broken the union and established Sweden's status as one of Europe's great powers.
Reformation
The reformation came to Scandinavia in the 1530s. Scandinavia soon became one of the heartlands of lutheranism.
See also: The Danish Reformation
1600s
Rise of Sweden and the Swedish Empire
Main Articles: Rise of Sweden as a Great Power-Swedish Empire
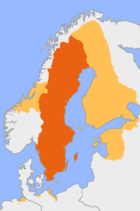
The Swedish power began under the rule of Charles IX. During the Ingrian War Sweden expanded its territories eastward. Several other wars with Poland, Denmark-Norway, and German countries continued to expand Sweden. Sweden began consolidating its Empire. Several other wars followed soon after including the Northern Wars and the Scanian War. Denmark suffered many defeats during this period. Finally under the rule of Charles XI the empire was consolidated under a semi-absolute monarchy.
Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years War was a conflict fought between the years 1618 and 1648, principally in the Central European territory of the Holy Roman Empire, but also involving most of the major continental powers. It occurred for a number of reasons. Although it was from its outset a religious conflict between Protestants and Catholics, the self-preservation of the Habsburg dynasty was also a central motive. The Danes and then Swedes intervened at various points to protect their interests.

The Danish intervention began when Christian IV of Denmark (1577-1648) the King of Denmark, himself a Lutheran, helped the Germans by leading an army against the Holy Roman Empire, fearing that Denmark's sovereignty as a Protestant nation was being threatened. The period began in 1625 and lasted till 1629 Christian IV had profited greatly from his policies in northern Germany (Hamburg had been forced to accept Danish sovereignty in 1621, and in 1623 the Danish heir apparent was made bishop of Bremen-Verden.) As an administrator, Christian IV had done remarkably well, obtaining for his kingdom a level of stability and wealth that was virtually unmatched elsewhere in Europe, paid for by the Oresund toll and extensive war reparations from Sweden. The only country in Europe with a comparably strong financial position was, ironically, Bavaria. It also helped that the French regentCardinal Richelieu was willing to pay for a Danish incursion into Germany. Christian invaded at the head of a mercenary army of 20,000 men.

The Swedish intervention began in 1630 and lasted until 1635 Some within Ferdinand II's court believed that Wallenstein wanted to take control of the German Princes and thus gain influence over the Emperor. Ferdinand II dismissed Wallenstein in 1630. He was to later recall him after the Swedes, led by Gustavus Adolphus, attacked the Empire and prevailed in a number of significant battles.
Gustavus Adolphus, like Christian IV before him, came to aid the German Lutherans, to forestall Catholic aggression against their homeland and to obtain economic influence in the German states around the Baltic Sea. Also like Christian IV, Adolphus was subsidized by Richelieu, the Chief Minister ofKing Louis XIII of France, and by the Dutch. From 1630-1634, they drove the Catholic forces back and regained much of the occupied Protestant lands
1700s
Great Northern War
Main article: Great Northern War

The Great Northern War was the war fought between a coalition of Russia, Denmark-Norway and Saxony-Poland (from 1715 also Prussia and Hanover) on one side and Sweden on the other side from 1700 to 1721. It started by a coordinated attack on Sweden by the coalition in 1700, and ended 1721 with the conclusion of the Treaty of Nystad, and the Stockholm treaties. As a result of the war, Russia supplanted Sweden as the dominant Power on the Baltic Sea and became a major player in European politics.
Colonialism
Main article: Danish colonization of the Americas; Swedish colonization of the Americas
Both Sweden and Denmark maintained a number of colonies outside Scandinavia starting in the 17th century lasting until the 20th century. Denmark had colonies in Greenland and Iceland in the north Atlantic. In the Caribbean Denmark started a colony on St Thomas in 1671, St John in 1718, and purchased Saint Croix from France in 1733. Denmark also maintained a colony, Tranquebar, in India. The Danish East India Company operated out of Tranquebar. Sweden also chartered a Swedish East India Company. During its heyday, the Danish and Swedish East India Company imported more tea than the British East India Company - and smuggled 90% of it into Britain, where it could be sold at a huge profit. Both East India Companies folded over the course of the Napoleonic Wars. Sweden had a short lived colony in North America and Saint-Barthélemy (1785-1878) and Guadeloupe in the Caribbean.
1800
Napoleonic Wars
Main article: Napoleonic WarsScandinavia was divided during the Napoleonic Wars. Sweden joined the Third Coalition in 1805 against Napoleon however the alliance fell apart after Russia abadoned the alliance and invaded Finland which forced Sweden to cede the territory. During this time it was also decided that since Charles XIII was childless, Marshal Jean-Baptiste Jules Bernadotte would be named the next king. Bernadotte was originally one of Napoleon's eighteen generals, however he decided to continue fighting France in favour of Sweden throughout 1813-1814. Karl Otto Mörner, a prominent Swedish baron was the one who initially extended the offer of the Swedish crown to the young soldier.
Denmark-Norway became involved in the conflict after Danish ports were being blockaded by the British navy. Britain thereafter attacked the Danish fleet at Copenhagen in 1801 and bombarded the city in 1807. The Danish fleet was destroyed in 1801, but was rebuilt and captured or destroyed in 1807. After the war, Denmark was forced to cede Heligoland to Britain and Norway to Sweden.
Sweden-Norway
Main article: Sweden-Norway; Convention of Moss
On January 14, 1814, at the Treaty of Kiel, Norway was ceded by Denmark to Sweden. In an attempt to take control of its destiny the Norwegians convened a constitutional assembly at Eidsvoll and on May 17, 1814 signed the Constitution of Norway. A Danish prince, Christian Frederik was elected by the assembly as king.
The Swedish king rejected the premise of an independent Norway and launched a military campaign on 27 July 1814 with an attack on the Hvaler islands and the city of Fredrikstad. The Swedish army was superior in numbers, was better equipped and trained, and was led by one of Napoleon's foremost generals, the newly elected Swedish crown prince, Jean Baptiste Bernadotte. Battles were short and decisively won by the Swedes. Armistice negotiations concluded on August 14, 1814.
In the peace negotiations, Christian Frederik agreed to relinquish claims to the Norwegian crown and return to Denmark if Sweden would accept the democratic Norwegian constitution and a loose personal union.
Following growing dissatisfaction with the union in Norway, the parliament unanimously declared its dissolution on June 7, 1905. This unilateral action met with Swedish threats of war. A plebiscite on August 13 confirmed the parliamentary decision by a majority of 368,208 to 184. Negotiations in Karlstad led to agreement with Sweden on September 23 and mutual demobilization. Both parliaments revoked the Act of Union October 16, and the deposed king Oscar II of Sweden renounced his claim to the Norwegian throne and recognized Norway as an independent kingdom on October 26. The Norwegian parliament offered the vacant throne to Prince Carl of Denmark, who accepted after another plebiscite had confirmed the monarchy. He arrived in Norway on November 25, 1905, taking the name Haakon VII.
Finnish War
The Finnish War was fought between Sweden and Russia from February 1808 to September 1809. As a result of the war, Finland which formed the eastern third of Swedish Empire became the semi-autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland, according to the Finns in personal union with Imperial Russia. Finland remained as a part of Russian Empire until 1917 at which point it became independent. Another notable effect was the Swedish parliament's adoption of a new constitution and a new royal house, that of Bernadotte.
Industrialisation
Industrialisation began in the mid 19th century in Scandinavia.
Monetary Union
See also: Scandinavian Monetary Union

The Scandinavian Monetary Union was a monetary union formed by Sweden and Denmark on May 5, 1873 by fixing their currencies against gold at par to each other. Norway, which was in union with Sweden entered the union two years later, in 1875 by pegging its currency to gold at the same level as Denmark and Sweden (.403 grams ). The monetary union was one of the few tangible results of the Scandinavian political movement of the 19th century.
The union provided fixed exchange rates and stability in monetary terms, but the member countries continued to issue their own separate currencies. Even if it was not initially foreseen, the perceived security led to a situation where the formally separate currencies were accepted on a basis of "as good as" the legal tender virtually throughout the entire area.
The outbreak of World War I, in 1914 brought an end to the monetary union. Sweden abandoned the tie to gold on August 2, 1914 and without a fixed exchange rate the free circulation came to an end.
1900s
Development of the Welfare State
All three countries developed social welfare states in the early to mid 20th century. This came about partially because of the domination of the social-democrats in Sweden and Denmark, and the Labour party in Norway.
Second World War
Main articles: Operation Weserübung; Occupation of Norway by Nazi Germany; Occupation of Denmark; Sweden during World War II; Sweden and the Winter War; Norwegian Campaign; Norwegian resistance movement; Danish resistance movement; Rescue of the Danish Jews

Near the beginning of World War II, both the Allies and the Axis powers feared their enemies gaining power in Scandanavia. Britain believed Germany was planning to invade, and was not eager to do battle there. At the same time, Germany feared that Britain could gain bases in the area and claimed they suspected an outright invasion. In addition, Germany highly valued the iron ore they received through Norway and could not afford to lose it. They also desired Norway for its ice-free ports. This made it a primary target, with Denmark a secondary goal mainly needed for facilitating the Norwegian invasion. After planning for months, Germany invaded both Denmark and Norway the same day, April 9th, 1940.
The nations reacted quite differently. Denmark surrendered a mere two hours after invasion, having lost just sixteen men. They sought to avoid civillian casualties and receive favourable treatment from Germany. Norway however, refused to give in and fought with their full strength. The Western allies sent military assistance, but the campaign was not effectively run. By June 10, 1940 Norway too had submitted to their attackers completely.
Denmark's strategy proved the more beneficial in the long run. It was one of the factors that led Germany to grant them a high degree of autonomy. Another reason was that they had no real agenda in Denmark. After invading, they simply didn't want to relinquish it, seeing it as a permanent part of their empire. Also, Danes were considered fellow Nordics by Nazi ideologues, which further helped the country. For all these reasons, Denmark was able to retain their parliament, king, and much of their normal domestic function. However, bitterness towards Germany grew and small sabatoges directed against Germany became commonplace. Germany eventually reacted by eliminating Denmark's representative government and imposing martial law.
Norway was treated much more harshly throughout their occupation. Opposition parties were eliminated and National Gathering(the Norwegian Nazi party) appointed all government officials. Vidkun Quisling was installed as the new dictator. Labor unions could only exist if they accepted Nazi control. Despite these repressive measures, there was still a fairly high degree of cooperation. About ten precent supported the Nazi party, and others supported some of their programs. Nevertheless, there was a hostile relationship, with 8 German soldiers for every Norwegian.
Denmark and Norway were also unalike in their cooperation with Germany's genocidal policy. Danes were notable for their devoted efforts to protect Danish Jews. More than 96% of the Jewish population was boated to safety in Sweden, while others found refuge with Christian Danish families and organizations. Norwegian police, however, aided in the capture of Norwegian Jews. This helped allow 40% of Norwegian Jews to be murdered in Nazi death camps.
Alone out of the three Scandanavian countries, Sweden was not invaded and remained nominally neutral during the war. They successfully cultivated peace with the Germans, supplying them with needed raw materials. The Swedish government was very careful to avoid inflaming the Nazis, going so far as to persuade newspaper editors to censor articles. However, there were exceptions to their neutrality. For example, they granted the Jews that escaped from Denmark asylum and gave minor aid to Finland during the Winter War.
Post-war
See also: Scandinavian defense union
After the second world war, all of the Scandinavian countries agreed that some form of mutual defense policy was necessary. They began to discuss a Scandinavian defense union. The three Scandinavian countries would, if they had entered into an alliance, have remained separate sovereign countries but acted as a single bloc in foreign policy and security issues. The proposed union was being discussed by a joint Scandinavian committee during the winter of 1948-1949, but the Cold War tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, and preparations for a western alliance that would result in the North Atlantic Treaty overshadowed the effort. When it became known that the western alliance would not be able to supply the Scandinavian countries with armaments before meeting their own pressing needs, this issue ultimately proved to be the turning point for Norway, which resigned from the talks. Denmark was still willing to enter into an alliance with Sweden, but the Swedes saw few advantages in this and the proposal fell. Norway and Denmark subsequently became signatory parties of the North Atlantic Treaty and members of NATO. Sweden remained neutral after a heated debate. Some people credit the Swedish stance for allowing Finland to remain outside the Iron Curtain, as the USSR might have felt threatened by a NATO member so close by.
European integration
The Nordic countries established the Nordic Council in 1952 and the Nordic passport union two years later.
After a 1972 referendum, Denmark became the first Scandinavian member of the EEC, which later paved the way for the EU, in 1973. Sweden joined the EU in 1995; after the fall of the Soviet Union, Sweden felt it could do so without being provocative. Norway remains outside the European Union to this day after referendums on membership in 1972 and 1994, although it is a signatory of the Schengen treaty and a member of the European Economic Area. None of the Scandinavian countries have joined the Euro, membership being rejected by referendum in both Denmark and Sweden. All of the Scandinavian countries have shown high degrees of Euro-scepticism, despite their enthusiasm for cooperation and multilateralism. Denmark voted no to the Maastricht Treaty in 1992, causing uproar across the community, and forcing a renegotiation, including "opting-out" of the proposed unified currency.
See also
References
- "Ukrainian Net". The Outcomes Of Establishment Of Roman Catholic Church Structures And Church Power In Norway And Scandinavia. June 28.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - "Decision to Invade Norway and Denmark". The German Decision to Invade Norway and Denmark. July 2.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - BYU History of Scandinavia