| Revision as of 00:01, 8 November 2010 editVanSisean (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users572 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 00:22, 8 November 2010 edit undoScythian77 (talk | contribs)2,083 edits Re-added info removed without consensus in discussion. Please do not start an edit war based on your racist agenda.Next edit → | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
| |combatant2={{flagicon|Iraq|1963}} ]¹<br /> | |combatant2={{flagicon|Iraq|1963}} ]¹<br /> | ||
| {{flagicon image|People's Mujahedeen of Iran logo.png}} ]<br /> | {{flagicon image|People's Mujahedeen of Iran logo.png}} ]<br /> | ||
| {{flagicon|United States}} ]<br /> | |||
| |commander1={{flagicon|Iran}} ]<br /> | |commander1={{flagicon|Iran}} ]<br /> | ||
| {{flagicon|Iran}} ] <br /> | {{flagicon|Iran}} ] <br /> | ||
Revision as of 00:22, 8 November 2010
| Iran-Iraq War | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Clockwise from above: Iranian soldiers wearing gas masks to counter Iraqi chemical weapons, Iranian soldiers rejoicing after the liberation of Khorramshahr, Donald Rumsfeld and Saddam meeting in Baghdad to discuss American military aid to Iraq, Iranian oil platform burning after attack by American Navy in Operation Nimble Archer | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
600,000 soldiers, 100,000 to 150,000;Pasdaran and Basij, 100,000 militia, 1,000 tanks, 4,000 armored vehicles, 7,000 artillery pieces, 747 aircraft, 750 helicopters |
300,000 in 1980, 1,000,000 by 1988, 4,000 tanks, 4,000 armored vehicles, 7,330 artillery pieces, 500+ aircraft, 100+ helicopters | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
500,000 to 1,000,000 dead; Iranian government official figure of 188,015 soldiers, militia, and civilians killed; Economic loss of more than US$500 billion |
Estimated 300,000 soldiers, militia, and civilians killed or wounded Economic loss of more than US$500 billion | ||||||||
| ¹ With support from the U.S.S.R., France, Brazil, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, the United States, and other Arab, NATO and Warsaw Pact countries for Iraq. | |||||||||
| Persian Gulf Wars | |
|---|---|
Template:Fix bunching The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the Imposed War (جنگ تحمیلی, Jang-e-tahmīlī) and Holy Defense (دفاع مقدس, Defā'-e-moghaddas) in Iran, Saddām's Qādisiyyah (قادسيّة صدّام, Qādisiyyat Ṣaddām) in Iraq, and the (First) Gulf War, was a war between the armed forces of Iraq and Iran lasting from September 1980 to August 1988, making it the longest conventional war of the twentieth century. It was initially referred to in the western world as the "Persian Gulf War" prior to the "Gulf War" of 1990 with the invasion of Kuwait by Iraq.
The war began when Iraq invaded Iran, launching a simultaneous invasion by air and land into Iranian territory on 22 September 1980 following a long history of border disputes, and fears of Shia insurgency among Iraq's long-suppressed Shia majority influenced by the Iranian Revolution. Iraq was also aiming to replace Iran as the dominant Persian Gulf state. Although Iraq hoped to take advantage of revolutionary chaos in Iran and attacked without formal warning, they made only limited progress into Iran and within several months were repelled by the Iranians who regained virtually all lost territory by June, 1982. For the next six years, Iran was on the offensive. Despite calls for a ceasefire by the United Nations Security Council, hostilities continued until 20 August 1988. The last prisoners of war were exchanged in 2003.
The war came at a great cost in lives and economic damage - half a million Iraqi and Iranian soldiers as well as civilians are believed to have died in the war with many more injured and wounded - but brought neither reparations nor change in borders. The conflict is often compared to World War I, in that the tactics used closely mirrored those of that conflict, including large scale trench warfare, manned machine-gun posts, bayonet charges, use of barbed wire across trenches, human wave attacks across no-man's land, and extensive use of chemical weapons such as mustard gas against Iranian troops and civilians as well as Iraqi Kurds. At the time, the UN Security Council issued statements that "chemical weapons had been used in the war." However, in these UN statements Iraq was not mentioned by name, so it has been said that "the international community remained silent as Iraq used weapons of mass destruction against Iranian as well as Iraqi Kurds" and it is believed that "United States prevented the UN from condemning Iraq".
Background
History of war's name
The war was commonly referred to as the Gulf War or Persian Gulf War until the Iraq-Kuwait conflict (Operation Desert Storm Jan-Feb 1991), and for a while thereafter as the First Persian Gulf War. The Iraq-Kuwait conflict, while originally known as the Second Persian Gulf War, later became known simply as "The Gulf War." The United States-led invasion of Iraq in 2003 and the following occupation of the country from 2003-2010 has since been called the Second Persian Gulf War.
Iraqi president Saddam Hussein initially dubbed the conflict "The Whirlwind War".
Origins
Post-colonial era
On 18 December 1959, the new leader of Iraq Abdul Karim Qassim, declared: "We do not wish to refer to the history of Arab tribes residing in Al-Ahwaz and Mohammareh . The Ottomans handed over Mohammareh, which was part of Iraqi territory, to Iran." The Iraqi regime's dissatisfaction with Iran's possession of the oil-rich Khuzestan province was not limited to rhetorical statements; Iraq began supporting secessionist movements in Khuzestan, and even raised the issue of its territorial claims at the next meeting of the Arab League, without success. Iraq showed reluctance in fulfilling existing agreements with Iran—especially after the death of Egyptian President Jamal Abdel Nasser and the rise of the Ba'ath Party, when Iraq decided to take on the role of "leader of the Arab world".
In 1969, the deputy prime minister of Iraq stated: "Iraq's dispute with Iran is in connection with Arabistan (Khuzestan) which is part of Iraq's soil and was annexed to Iran during foreign rule." Soon Iraqi radio stations began exclusively broadcasting into "Arabistan", encouraging Arabs living in Iran and even Balūchīs to revolt against the Shah of Iran's government. Basra TV stations even began showing Iran's Khuzestan province as part of Iraq's new province called Nasiriyyah, renaming all Iranian cities with Arabic names.
In 1971, Iraq broke diplomatic relations with Iran after claiming sovereignty rights over the islands of Abu Musa, Greater Tunb and Lesser Tunb in the Persian Gulf, following the withdrawal of the British. Iraq then expropriated the properties of 70,000 Iraqis of Iranian origin and expelled them from its territory, after complaining to the Arab League and the UN without success. Many, if not most of those expelled were in fact Iraqi Shia who had little to no family ties with Iran, and the vast majority of whom spoke Arabic, rather than Persian . The expulsions formed part of a longstanding Iraqi Baathist tradition of marginalizing and delegitimizing the Shia majority by alleging subversive ties with Iran.
One of the factors contributing to hostility between the two powers was a dispute over full control of the Shatt al-Arab waterway (known as Arvand Rud in Iran) at the head of the Persian Gulf, an important channel for the oil exports of both countries.
In addition to Iraq's fomenting of separatism in Iran's Khuzestan and Iranian Balochistan provinces, both countries encouraged separatist activities by Kurdish nationalists in the other country. During the first few years of the 1980–1988 Iraq-Iran war, the Iraqi government tried to accommodate the Kurds in order to focus on the war against Iran. In 1984, the Patriotic Union of Kurdistan agreed to cooperate with Baghdad, but the Kurdish Democratic Party remained opposed.
In the 1975 Algiers Accord Iraq made territorial concessions — including the waterway — in exchange for normalized relations.
The relationship between Iranian and Iraqi governments briefly improved in 1978, when Iranian agents in Iraq discovered a pro-Soviet coup d'état against the Iraqi government. When informed of this plot, Saddam Hussein, who was Vice President at the time, ordered the execution of dozens of his army officers, and to return the favor, expelled Ruhollah Khomeini, an exiled leader of clerical opposition to the Shah, from Iraq.
After the Islamic Revolution
See also: Islamic Revolution, Iranian Embassy Siege, and Modern usage of al-QādisiyyahThe Pan-Islamism and revolutionary Shia Islamism of Ayatollah Khomeini and the Islamic Republic of Iran; and the Arab nationalism of Saddam Hussein's Iraqi regime were central to the conflict.
Saddam Hussein was keenly interested in elevating Iraq to a strong regional power. A successful invasion of Iran would enlarge Iraq's oil reserves and make Iraq the dominant power in the Persian Gulf region.
On several occasions Saddam alluded to the Islamic conquest of Iran in propagating his position against Iran. For example, on 2 April 1980, half a year before the outbreak of the war, in a visit by Saddam to al-Mustansiriyyah University in Baghdad, drawing parallels with the 7th century defeat of Persia in the Battle of al-Qādisiyyah, he announced:
In your name, brothers, and on behalf of the Iraqis and Arabs everywhere we tell those Persian cowards and dwarfs who try to avenge Al-Qadisiyah that the spirit of Al-Qadisiyah as well as the blood and honor of the people of Al-Qadisiyah who carried the message on their spearheads are greater than their attempts."
In turn the Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini believed Muslims, particularly the Shias in Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and Kuwait, whom he saw as oppressed, could and should follow the Iranian example, rise up against their governments to join a united Islamic republic. Khomeini and Iran's Islamic revolutionaries despised Saddam's secularist, Arab nationalist Ba'athist regime in particular as un-Islamic and "a puppet of Satan," and called on Iraqis to overthrow Saddam and his regime. At the same time severe officer purges (including several executions ordered by Sadegh Khalkhali, the post-revolution sharia ruler), and spare parts shortages for Iran's American-made equipment, had crippled Iran's once mighty military. The bulk of the Iranian military was made up of poorly armed, though committed, militias. Iran had minimal defenses in the Shatt al-Arab river.
The UN Secretary General report dated 9 December 1991 (S/23273) explicitly cites "Iraq's aggression against Iran" in starting the war and breaching International security and peace.
War
Iraqi pretext for war and Iraqi war aims
Iraq's pretext was an alleged assassination attempt on Foreign Minister Tariq Aziz in southern Iraq, which Saddam Hussein blamed on "Iranian agents", in one of his speeches.

"Relations deteriorated rapidly until in March 1980, Iran unilaterally downgraded its diplomatic ties to the charge d'affaires level, withdrew its ambassador, and demanded that Iraq do the same. The tension increased in April following the attempted assassination of Iraqi Deputy Prime Minister Tariq Aziz and, three days later, the bombing of a funeral procession being held to bury students who had died in an earlier attack. Iraq blamed Iran, and in September, attacked.
On 17 September, in a statement addressed to the Iraqi parliament, Saddam Hussein stated that "The frequent and blatant Iranian violations of Iraqi sovereignty...have rendered the 1975 Algiers Agreement null and void... This river...must have its Iraqi-Arab identity restored as it was throughout history in name and in reality with all the disposal rights emanating from full sovereignty over the river.",
The objectives of Iraq's invasion of Iran were:
- Control of the Shatt al-Arab waterway by Iraqis
- Acquisition of the three islands of Abu Musa and the Greater and Lesser Tunbs, on behalf of the UAE.
- Annexation of Khuzestan to Iraq
- Prevent the spread of the Islamic Revolution in the region
September 1980: Iraqi invasion
Iraq launched a full-scale invasion of Iran on 22 September 1980. On 22 September 1980, the Iraqi air force attacked Iran, attacking ten airfields inside Iran, but failed to achieve their objective of destroying the Iranian air force on the ground. The next day Iraq initiated a ground invasion of Iran along a front measuring 644 kilometres, in three simultaneous thrusts. The purpose of the invasion, according to Saddam Hussein, was to blunt the edge of Khomeini's movement and to thwart his attempt to export his Islamic revolution to Iraq and the Persian Gulf states."
Of the six Iraqi divisions that were invading, four were sent against the Iranian province of Khuzestan, which was located near the southern end of the border, to cut off the Shatt al-Arab from the rest of Iran, and to establish a territorial security zone. The other two divisions invaded through the northern and central part of the border, to prevent an Iranian counter-attack into Iraq. Two of the four Iraqi divisions operating near the southern end, one mechanized and one armored, began a siege of the strategically important towns of Abadan and Khorramshahr.
The other two divisions, both armoured, secured the territory bounded by the line Khorramshahr-Ahvaz-Susangerd-Musian, due to an enveloping movement. On the central front, the Iraqis occupied Mehran, advanced towards the foothills of the Zagros Mountains; and were able to block the traditional Tehran–Baghdad invasion route by securing some territory forward of Qasr-e-Shirin. On the northern front, the Iraqis attempted to establish a strong defensive position opposite Suleimaniya to protect the Iraqi Kirkuk oil complex.
Since the Iranian regular military and the Pasdaran conducted their operations separately, the Iraqi invading forces did not face co-ordinated resistance. On 24 September, though, the Iranian navy attacked Basra and, on the way, had destroyed two oil terminals near the Iraqi port of Fao, which reduced Iraq's ability to export oil. The Iranian air force also began air strikes in September against strategically important Iraqi targets, including oil facilities, dams, petrochemical plants, and a nuclear reactor near Baghdad.
On September 28, the UN Security Council adopted a resolution urging Iran and Iraq to stop the fighting and accept mediation.
Baghdad was subjected to eight air raids by 1 October. In response to these air attacks, Iraq launched a number of aerial strikes against Iranian targets. The Pasdaran fought against the Iraqi invasion with "great fervour and tenacity", and bore the brunt of the invasion. On 24 October, Khorramshahr was captured and by November Saddam ordered his forces to advance towards Dezful and Ahvaz, but they were not successful in occupying these two settlements.
Iraq had mobilized 21 divisions for the invasion, while Iran countered with only 13 regular army divisions and one brigade. Of these divisions, only seven were deployed to the border.
The surprise offensive advanced quickly against the still disorganized Iranian forces, advancing on a wide front into Iranian territory along the Mehran–Khorramabad axis in central Iran and towards Ahvaz in the oil-rich southern province of Khuzestan.
The invasion stalls
The Iraqi invasion soon encountered unexpected resistance, however, and around March 1981 it stalled. A preemptive strike executed by the Iraqi Air Force on the first day of the war successfully destroyed parts of Iran's airbase infrastructure, but failed to destroy a significant number of aircraft. The IQAF was only able to strike in depth with a few MiG-23BN, Tu-22 and Su-20 aircraft, ineffective in a country as large as Iran. When three MiG-23BN's flew over Tehran, they attacked its airport but damaged only a few aircraft. Over the next day dozens of Iranian F-4s attacked Iraqi targets, and in a few days the IRIAF gained air superiority over IQAF, allowing them to conduct ground attack missions with fighter-bombers and helicopters.
Also, rather than turning against the Ayatollah's government as exiles had promised, the people of Iran rallied around their country and mounted a stiff resistance. An estimated 200,000 additional troops arrived at the front by November, many of them "ideologically committed" volunteers. The Iraqis soon found the Iranian military was not nearly as depleted as they had thought.
For about a year after the Iraqi offensive stalled in March 1981 there was little change in the front, but in mid-March 1982 Iran took the offensive and the Iraqi military was forced to retreat. By June 1982, an Iranian counter-offensive had recovered the areas lost to Iraq earlier in the war. An especially significant battle of this counter-offensive in the Khuzestan province was the Liberation of Khorramshahr from the Iraqis on 24 May 1982. A total of 7,000 Iraqis had been killed or wounded in Khorramshahr and 19,000 taken prisoner, while the Iranians had suffered 10,000 casualties.
Iraq retreats but the war continues

Saddam decided to withdraw his armed forces completely from Iran, and that they should be deployed along the international border between Iraq and Iran. Efraim Karsh states that Saddam made this choice because the Iraqi leader believed that his army was now too demoralised and damaged to hold onto any territory in Iran, and that Iran could be successfully resisted through a line of defence on Iraqi land near the border.
Iranian offensive, blunders, and hardening of Iraqi resolve
Under the slogans "War, War until Victory" and "The Road to Jerusalem Goes through Karbala", Iran advanced. A tactic used in this advance noted throughout the world was the encouragement of heroism among young Iranian basij volunteers who sought martyrdom in human wave attacks on Iraqi positions. The volunteers were inspired before battle by tales of Ashura, the Battle of Karbala, and the supreme glory of martyrdom, and sometimes by an actor (usually a more mature soldier), playing the part of Imam Hossein himself riding a white horse, galloping along the lines, providing the inexperienced soldiers a vision of "the hero who would lead them into their fateful battle before they met their God."
On 13 July, the Iranian units crossed the border in force, aiming towards the city of Basra, the second most important city in Iraq. However, the enemy they encountered had entrenched itself in formidable defenses. Unlike the hastily improvised defenses that the Iraqis had manned in Iran during the 1980–1981 occupation of the conquered territories, the border defenses were, by necessity, well developed even before the war, and the Iraqis were able to utilize a highly-developed network of bunkers and artillery fire-bases. Saddam had also more than doubled the size of the Iraqi army from 1981's 500,000 soldiers (26 divisions and 3 independent brigades) to 1985's 1,050,000 (55 divisions and nine brigades).
Saddam's efforts bore fruit. Iran had been using combined-arms operations to great effect when it was attacking the Iraqi troops in its country, and had launched the iconic human-wave attacks with great support from artillery, aircraft, and tanks. However, lack of ammunition meant that the Iranians were now launching human-wave assaults with no support from other branches of the military. The superior defenses of the Iraqis meant that tens of thousands of Iranian soldiers were lost in most operations after 1982, and the Iraqi defenses would continue to hold in most sectors.
In the Basra offensive, or Operation Ramadan, five human-wave attacks were met with withering fire from the Iraqis. The boy-soldiers of Iran were particularly hard-hit, especially since they volunteered to run into minefields, in order to clear the way for the Iranian soldiers behind them. The Iranians were also hard-hit by the employment of chemical weapons and mustard gas by the Iraqis.
1983–1985: Further Iranian offensives fail to break strategic stalemate
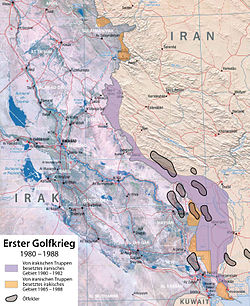
After the failure of their 1982 summer offensives, Iran believed that a major effort along the entire breadth of the front would yield the victory that they desired. Iranian numerical superiority might have achieved a break-through if they had attacked across all parts of the front at the same time, but they still lacked the organization for that type of assault. Iran was getting supplies from countries such as North Korea, Libya, and China. The Iraqis had more suppliers such as the USSR, the NATO nations, France, United Kingdom, Brazil, Yugoslavia, Spain, Italy, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Germany, and the United States.
During the course of 1983, the Iranians launched five major assaults along the front. None met with substantial success. Khomeini's position on a truce remained unchanged.
In February 1984, Saddam ordered aerial and missile attacks against the eleven cities that he had designated. The bombardment ceased on 22 February 1984. Iran soon retaliated against urban centers, and these exchanges become known as the first "war of the cities". There would be five such exchanges throughout the course of the war.
The attacks on the Iranian cities did not destroy the Iranian government's resolve to fight. On 15 February, the Iranians launched a major attack against the central section of the front where the Second Iraqi Army Corps was deployed. 250,000 Iranians faced 250,000 Iraqis.
From 15 to 22 February, in Operation Dawn 5, and 22 to 24 February, in Operation Dawn 6, the Iranians attempted to capture the vital town of Kut al-Amara and to cut the key highway linking Baghdad and Basra. Capture of this road would have made it extremely difficult for the Iraqis to supply and co-ordinate the defenses, but the Iranian forces only came within 15 miles (24 km) of the highway.
However, Operation Khaibar met with much greater success. Involving a number of thrusts towards the key Iraqi city of Basra, the operation started on the 24 February and lasted until 19 March. The Iraqi defenses, under continuous strain since 15 February, seemed close to breaking conclusively. The Iraqis successfully stabilized the front but not before the Iranians captured part of the Majnun Islands. Despite a heavy Iraqi counterattack coupled with the use of mustard gas and sarin nerve gas, the Iranians held their gains and would continue to hold them almost until the end of the war.
'Tanker War' in the Persian Gulf 1984
The Tanker War started when Iraq attacked Iranian tankers and the oil terminal at Kharg island in 1984. Iran struck back by attacking tankers carrying Iraqi oil from Kuwait and then any tanker of the Persian Gulf states supporting Iraq. Both nations attacked oil tankers and merchant ships, including those of neutral nations, in an effort to deprive the opponent of trade. Iraq declared that all ships going to or from Iranian ports in the northern zone of the Gulf were subject to attack.
Iraq used its air power to enforce its threats, primarily helicopters, F-1 Mirage and MiG-23 fighters armed with Exocet anti-ship missiles. After repeated Iraqi attacks on Iran's main exporting facility on Khark Island, Iran attacked a Kuwaiti tanker near Bahrain on May 13, 1984, and a Saudi tanker in Saudi waters on May 16. Attacks on ships of noncombatant nations in the Persian Gulf sharply increased thereafter, and this phase of the Iraq-Iran war was dubbed the "Tanker War."
A US Navy ship, the USS Stark was struck on May 17, 1987, by two Exocet antiship missiles fired from an Iraqi F-1 Mirage plane. The Iraqi fighter fired the Exocet missiles at about the time the fighter was given a routine radio warning by the Stark. The frigate did not detect the missiles with radar and warning was given by the lookout only moments before the missiles struck. The missiles hit the ship and one exploded in crew quarters and 37 sailors were killed and 21 were injured.
January 1985 - February 1986: Abortive offensives by Iran
With his armed forces now benefiting from financial support from Saudi Arabia, Kuwait and other Persian Gulf states, and substantial arms purchases from the Soviet Union, China and France (among others), Saddam went on the offensive on 28 January 1985, for the first time since early 1980. This offensive, however, did not produce any significant gains, and the Iranians responded in kind with their own offensive directed against Basra, codenamed Operation Badr, on 11 March 1985. The Imam Khomeini urged Iranians on saying, "It is our belief that Saddam wishes to return Islam to blasphemy and polytheism. ... if America becomes victorious ... and grants victory to Saddam, Islam will receive such a blow that it will not be able to raise its head for a long time ... The issue is one of Islam versus blasphemy, and not of Iran versus Iraq."
By this time, the failure of the unsupported human wave attacks during 1984 meant that Iran was trying to develop a better working relationship between the army and the Pasdaran. The Iranian government also worked on molding the Pasdaran units into a much more conventional fighting force. The attack did succeed in capturing a part of the Baghdad-Basra highway that had proven elusive during Operation Dawn 5 and Operation Dawn 6. Saddam responded to this strategic emergency by launching chemical attacks against the Iranian positions along the highway and by initiating the second 'war of the cities' with a massive air and missile campaign against twenty Iranian towns, including Tehran.
The Tanker War and U.S. support for Iraq
The Tanker War started when Iraq attacked Iranian tankers and the oil terminal at Kharg island in 1984. Iran struck back by attacking tankers carrying Iraqi oil from Kuwait and then any tanker of the Persian Gulf states supporting Iraq. The air and small boat attacks did very little damage to Persian Gulf state economies and Iran just moved its shipping port to Larak Island in the strait of Hormuz.
In 1982 with Iranian success on the battlefield, the U.S. made its backing of Iraq more pronounced, supplying it with intelligence, economic aid, normalizing relations with the government (broken during the 1967 Six-Day War), and also supplying "dual-use" equipment and vehicles. Dual use items are civilian items such as heavy trucks, armored ambulances and communications gear as well as industrial technology that can have a military application. President Ronald Reagan decided that the United States "could not afford to allow Iraq to lose the war to Iran", and that the United States "would do whatever was necessary to prevent Iraq from losing the war with Iran." President Reagan formalized this policy by issuing a National Security Decision Directive ("NSDD") to this effect in June, 1982. The Security Council passed Resolution 552 condemning attacks on commercial ships in the region.
Attacks on shipping
Lloyd's of London, a British insurance market, estimated that the Tanker War damaged 546 commercial vessels and killed about 430 civilian mariners. The largest portion of the attacks were directed by Iran against Kuwaiti vessels, and on 1 November 1986, Kuwait formally petitioned foreign powers to protect its shipping. The Soviet Union agreed to charter tankers starting in 1987, and the United States offered to provide protection for tankers flying the U.S. flag on 7 March 1987 (Operation Earnest Will and Operation Prime Chance). Under international law, an attack on such ships would be treated as an attack on the United States, allowing the U.S. Navy to retaliate. This support would protect neutral ships headed to Iraqi ports, effectively guaranteeing Iraq's revenue stream for the duration of the war. During the course of the war Iran attacked two Soviet Navy ships which were protecting Kuwaiti tankers. One of the ships which was damaged as a result of an attack during the war was the Seawise Giant carrying Iranian crude which was struck by French Exocet missiles fired by Iraqi air force resulting in sinking of the largest ship ever built in history.
Iraqi attack on US warship

On 17 May 1987, an Iraqi Mirage F1 attack aircraft launched two Exocet missiles at the USS Stark (FFG 31), a Perry class frigate. The first struck the port side of the ship and failed to explode, though it left burning propellant in its wake; the second struck moments later in approximately the same place and penetrated through to crew quarters, where it exploded. The detonation killed 37 crewmembers and left 21 injured. The question of whether or not Iraqi leadership authorized the attack is still unanswered. Initial claims by the Iraqi government (that Stark was inside the Iran–Iraq War zone) were shown to be false, so the motives and orders of the pilot remain unanswered. Though American officials claimed he had been executed, an ex-Iraqi Air Force commander since stated that the pilot who attacked Stark was not punished, and was still alive at the time. The attack remains the only successful anti-ship missile strike on an American warship.
US military actions toward Iran
However, U.S. attention was focused on isolating Iran as well as maintaining freedom of navigation, criticizing Iran's mining of international waters, and sponsored UN Security Council Resolution 598, which passed unanimously on 20 July, under which it skirmished with Iranian forces during Operation Earnest Will. During the Operation Nimble Archer in October 1987, the U.S. attacked Iranian oil platforms in retaliation for an Iranian attack on the U.S.-flagged Kuwaiti tanker Sea Isle City.
On 14 April 1988, the frigate USS Samuel B. Roberts was badly damaged by an Iranian mine,10 wounded but none dead. U.S. forces responded with Operation Praying Mantis on 18 April, the United States Navy's largest engagement of surface warships since World War II. Two Iranian oil platforms, two Iranian ships and six Iranian gunboats were destroyed. An American helicopter also crashed. (see also Oil Platforms (Iran v. United States))
US shoots down civilian airliner

In the course of these escorts by the U.S. Navy, the cruiser USS Vincennes shot down Iran Air Flight 655 with the loss of all 290 passengers and crew on 3 July 1988. The American government claimed that the airliner had been mistaken for an Iranian F-14 Tomcat, and that the Vincennes was operating in international waters at the time and feared that it was under attack, which later appeared to be untrue. The Iranians, however, maintain that the Vincennes was in fact in Iranian territorial waters, and that the Iranian passenger jet was turning away and increasing altitude after take-off. U.S. Admiral William J. Crowe also admitted on Nightline that the Vincennes was inside Iranian territorial waters when it launched the missiles. At the time, the captain of the Vincennes claimed that the Iranian plane did not identify itself and sent no response to warning signals from the Vincennes. Apart from Iran, other independent sources, for example the airport of Dubai, have confirmed that the plane did indeed identify itself to the American naval ship and also confirmed that "the civilian aircraft was ascending and therefore could not have posed a threat," agreeing with Iranian officials.
According to an investigation conducted by ABC News' Nightline, decoys were set during the war by the US Navy inside the Persian Gulf to lure out the Iranian gunboats and destroy them, and at the time USS Vincennes shot down the Iranian airliner, it was performing such an operation.
In 1996 the U.S. expressed regret only for the loss of innocent life, and did not make a specific apology to the Iranian government.
The shooting down of a civilian Iranian passenger plane Iran Air Flight 655 by the American cruiser USS Vincennes, was cited by an Iranian scholar as apparently giving Ruhollah Khomeini reason to withdraw from the conflict:
An Iranian scholar present at the conference said a turning point in Iran's thinking came with the shooting down of an Iranian passenger plane in July 1988 by the American cruiser USS Vincennes. That incident apparently led Ayatollah Khomeini to conclude that Iran could not risk the possibility of U.S. open combat operations against Iran and he decided it was time to end the conflict.
"War of the Cities"
Toward the end of the war, the land conflict regressed into stalemate largely because neither side had enough self-propelled artillery or air power to support ground advances.
The relatively professional Iraqi armed forces could not make headway against the far more numerous Iranian infantry. The Iranians were outmatched in towed and self-propelled artillery, which left their tanks and troops vulnerable. What followed was the Iranians substituting infantry for artillery.
Iraq's air force soon began strategic bombing against Iranian cities, chiefly Tehran, in 1985. To minimize losses from the superior Iranian Air Force, Iraq rapidly switched to Scud and Al-Hussein improved Scud launches. In retaliation, Iran fired Scud missiles acquired from Libya and Syria against Baghdad. In all, Iraq launched 520 Scuds and Al-Husseins against Iran and received only 177 in exchange.
In retaliation for the Iranian Operation Karbala-5, an early 1987 attempt to capture Basra, Iraq attacked 65 cities in 226 sorties over 42 days, bombing civilian neighborhoods. Eight Iranian cities came under attack from Iraqi missiles. The bombings killed 65 children in an elementary school in Borujerd alone. The Iranians also responded with Scud missile attacks on Baghdad and struck a primary school there. These events became known as "the war of the cities".
Towards a ceasefire

1987 saw a renewed wave of Iranian offensives against targets in both the north and south of Iraq. Iranian troops were stopped by Iraqi prepared defenses in the south in a month-and-a-half long battle for Basra (Operation Karbala-5), but met with more success later in the year in the north as Operations Nasr 4 and Karbala-10 threatened to capture the oil-rich Iraqi city of Kirkuk and other northern oilfields. However, the Iranian forces were unable to consolidate their gains and continue their advance, and so 1987 saw little land change hands. On 20 July, the Security Council of the United Nations passed the US-sponsored Resolution 598, which called for an end to fighting and a return to pre-war boundaries.
By April 1988, however, the Iraqi forces had regrouped sufficiently to begin a new series of devastating attacks on the Iranians, and in quick succession recaptured the strategic al-Faw peninsula (lost in 1986 in Operation Dawn-8) and territory around Basra and also struck deep into the Iranian north, capturing much matériel. In July 1988 Iraqi airplanes dropped chemical cyanide bombs on the Iranian Kurdish village of Zardan (as they had done four months earlier at their own Kurdish village of Halabja). Hundreds were killed at once, and the survivors are still suffering from a variety of physical and mental disorders. Following these major setbacks, Iran accepted the terms of U.N. Security Council Resolution 598 and on 20 August 1988 peace was restored.
The People's Mujahedin of Iran started their ten-day operation after the Iranian government accepted UN Resolution 598. While Iraqi forces attacked Khuzestan, the Mujahedin attacked western Iran and battled the Pasdaran for Kermanshah. Close air support from the Iraqis contributed to whatever gains the Mojahedin made. However, under heavy international pressure for ending the war, Saddam Hussein withdrew his fighter aircraft and the sky opened for the Iranian airborne forces to be deployed behind Mojahedin lines. The operation ended in a defeat for the Mojahedin. Casualty figures range from 2,000 to as high as 10,000.
See also: Operation MersadComparison of Iraqi and Iranian military strength
Main article: Order of battle during the Iran–Iraq WarAt the commencement of hostilities, Iraq held a clear advantage in armour, while both nations were roughly at parity with artillery. The gap only widened as the war went on. Iran started with a stronger air force, but over time, the balance of power flipped towards favoring Iraq. By the end of the war, Iraq enjoyed an immense numerical superiority over Iran's forces in every category. The Economist estimates for 1980 and 1987 were:
| Imbalance of Power (1980–1987) | Iraq | Iran |
|---|---|---|
| Tanks in 1980 | 2700 | 1740 |
| Tanks in 1987 | 4500 | 1000 |
| Fighter Aircraft in 1980 | 332 | 445 |
| Fighter Aircraft in 1987 | 500+ | 65 (serviceable) |
| Helicopters in 1980 | 40 | 500 |
| Helicopters in 1987 | 150 | 60 |
| Artillery in 1980 | 1000 | 1000+ |
| Artillery in 1987 | 4000+ | 1000+ |
Foreign support to Iraq and Iran
Main article: International aid to combatants in the Iran–Iraq WarDuring the war, Iraq was regarded by the West (and specifically the United States) as a counterbalance to post-revolutionary Iran. The support of Iraq took the form of technological aid, intelligence, the sale of dual-use and military equipment and satellite intelligence to Iraq. While there was direct combat between Iran and the United States, it is not universally agreed that the fighting between the U.S. and Iran was specifically to benefit Iraq, or for separate, although occurring at the same time, issues between the U.S. and Iran. American ambiguity towards which side to support was summed up by Henry Kissinger when the American statesman remarked that "it's a pity they both can't lose." More than 30 countries provided support to Iraq, Iran, or both. Iraq, in particular, had a complex clandestine procurement network to obtain munitions and critical materials, which, in some transactions, involved 10-12 countries. Also, a number of Arab mercenaries and volunteers from Egypt and Jordan (called the Yarmouk Brigade) participated in the war alongside Iraqis.
Iraq
See also: United States support for Iraq during the Iran–Iraq warAmong major powers, the United States' policy was to "tilt" toward Iraq by reopening diplomatic channels, lifting restrictions on the export of dual-use technology, overseeing the transfer of third party military hardware, and providing operational intelligence on the battlefield.
As will be seen in some of the country-specific sub-articles of this page, Iraq made extensive use of front companies, middlemen, secret ownership of all or part of companies all over the world, forged end user certificates and other methods to hide what it was acquiring. At this time, the country-level sub-articles emphasize the country in which the procurement started, but also illustrate how procurement infrastructure was established in different countries. Some transactions may have involved people, shipping, and manufacturing in as many as 10 countries.
In their documentary Saddam Hussein-The Trial You Will Never See, made for European audience, Barry Lando and Michel Despratx claim that United States secretary of state Alexander Meigs Haig Jr. wrote in a secret memo to President Ronald Reagan, about United States previous president Jimmy Carter's green light to Saddam Hussein for launching a war against Iran using Saudi Arabia delivering the go ahead message to Iraqis. British support for Iraq during the Iran–Iraq war especially illustrated the ways by which Iraq would circumvent export controls. Iraq bought at least one British company with operations in the U.K. and the U.S.
Iraq had a complex relationship with France and the Soviet Union, its major suppliers of actual weapons, to some extent having the two nations compete for its business.
Singapore support for Iraq during the Iran–Iraq war discusses land mines assembled there, as well as chemical warfare precursors shipped from Singapore, possibly by an Iraqi front company.
Another country that had an important role in arming Iraq was Italy, whose greatest impact was financial, through the U.S. branch of the state-owned largest bank in Italy. The Italian article is one example of how Iraq circumvented a national embargo, by, as one example, moving land and sea mine production to Singapore.
Additional country details will be added as the articles become available, in some cases in stub format for individual yet significant support, such as providing the largest amount of precursor chemicals from which chemical weapons were produced.
Although the United Nations Security Council called for a cease-fire after a week of fighting and renewed the call on later occasions, the initial call was made while Iraq occupied Iranian territory. Moreover, the UN refused to come to Iran's aid to repel the Iraqi invasion. The Iranians thus interpreted the UN as subtly biased in favor of Iraq.
Iran
While the United States directly fought Iran, citing freedom of navigation as a major casus belli, as part of a complex and partially illegal program (see Iran-Contra Affair), it also indirectly supplied weapons to Iran.
North Korea was a major arms supplier to Iran, often acting as a third party in arms deals between Iran and the Communist bloc.. DPRK support included domestically manufactured arms and Eastern-Bloc weapons for which the major powers wanted deniability.. Libya and China were arms suppliers and supporters of Iran as well.
Both countries
Besides the US and the Soviet Union, Yugoslavia also sold weapons to both countries for the entire duration of the conflict. Likewise, Portugal helped both countries: it was not unusual seeing Iranian and Iraqi flagged ships moored side-by-side at the port of Sines.
From 1980 to 1987 Spain sold €458 million in weapons to Iran and €172 million in weapons to Iraq. Spain sold to Iraq 4x4 vehicles, BO-105 Helicopters, explosives and ammunition. A research party discovered that an unexploded chemical Iraqi warhead in Iran was manufactured in Spain.
Although neither side did acquire any weapons from Turkey, both sides enjoyed Turkish civilian help during conflict. Having managed to remain neutral and refused to support trade embargo imposed by US, Ankara turned out to be the one upon whom both warring sides developed high degree of economic dependancy, since Turkey was one of their few outlets to the west and source of local goods. Turkey's export jumped from $220 million in 1981 to $2 billion in 1985, making up 25% of Turkey's overall exports. Additionally, Turkish construction projects in Iraq totaled $2.5 billion between 1974 and 1990. These benefits helped Turkey to offset the ongoing Turkish economic crisis, though they decreased with the end of the war and vanished thanks to Invasion of Kuwait by Iraq and Turkish response to it.
Financial support
Iraq's main financial backers were the oil-rich Persian Gulf states, most notably Saudi Arabia ($30.9 billion), Kuwait ($8.2 billion) and the United Arab Emirates ($8 billion).
The Iraqgate scandal revealed that an Atlanta branch of Italy's largest bank, Banca Nazionale del Lavoro, relying partially on U.S. taxpayer-guaranteed loans, funneled $5 billion to Iraq from 1985 to 1989. In August 1989, when FBI agents finally raided the Atlanta branch of BNL, the branch manager, Christopher Drogoul, was charged with making unauthorized, clandestine, and illegal loans to Iraq — some of which, according to his indictment, were used to purchase arms and weapons technology.
The New York Times, the Los Angeles Times, and ABC's Ted Koppel, covered the Iraq-gate story, and the investigation by the U.S. Congress. This scandal is covered in Alan Friedman's book The Spider's Web: The Secret History of How the White House Illegally Armed Iraq.
Beginning in September 1989, the Financial Times laid out the first charges that BNL, relying heavily on U.S. government-guaranteed loans, was funding Iraqi chemical and nuclear weapons work. For the next two and a half years, the Financial Times provided the only continuous newspaper reportage (over 300 articles) on the subject. Among the companies shipping militarily useful technology to Iraq under the eye of the U.S. government, according to the Financial Times, were Hewlett-Packard, Tektronix, and Matrix Churchill, through its Ohio branch.
In all, Iraq received $35 billion in loans from the West and between $30 and $40 billion from the Persian Gulf states during the 1980s.
Use of chemical weapons
See also: Halabja poison gas attackWith more than 100,000 Iranian victims of Iraq's chemical weapons during the eight-year war, Iran is one of the countries most severely afflicted by "weapons of mass destruction". In a declassified report, the CIA estimated in 1991 that Iran had suffered more than 50,000 casualties from Iraq's use of several chemical weapons, but today the actual number of victims is estimated to more than 100,000, since the long term effects still causes casualties to this day.
The official estimate does not include the civilian population contaminated in bordering towns or the children and relatives of veterans, many of whom have developed blood, lung and skin complications, according to the Organization for Veterans of Iran. According to a 2002 article in the Star-Ledger:
"Nerve gas killed about 20,000 Iranian soldiers immediately, according to official reports. Of the 90,000 survivors, some 5,000 seek medical treatment regularly and about 1,000 are still hospitalized with severe, chronic conditions."
On 21 March 1986, the United Nations Security Council made a declaration stating that "members are profoundly concerned by the unanimous conclusion of the specialists that chemical weapons on many occasions have been used by Iraqi forces against Iranian troops and the members of the Council strongly condemn this continued use of chemical weapons in clear violation of the Geneva Protocol of 1925 which prohibits the use in war of chemical weapons." The United States was the only member who voted against the issuance of this statement. A mission to the region in 1988 found evidence of the use of chemical weapons, and was condemned in Security Council Resolution 612.
According to retired Colonel Walter Lang, senior defense intelligence officer for the United States Defense Intelligence Agency at the time, "the use of gas on the battlefield by the Iraqis was not a matter of deep strategic concern" to Reagan and his aides, because they "were desperate to make sure that Iraq did not lose." He claimed that the Defense Intelligence Agency "would have never accepted the use of chemical weapons against civilians, but the use against military objectives was seen as inevitable in the Iraqi struggle for survival", The Reagan administration did not stop aiding Iraq after receiving reports of the use of poison gas on Kurdish civilians. There is great resentment in Iran that the international community helped Iraq develop its chemical weapons arsenal and armed forces, and also that the world did nothing to punish Saddam's Ba'athist regime for its use of chemical weapons against Iran throughout the war — particularly since the US and other western powers soon felt obliged to oppose the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait and eventually invade Iraq itself to remove Saddam Hussein.
The U.S. also accused Iran of using chemical weapons. These allegations however, have been disputed. Joost Hiltermann, who was the principal researcher for Human Rights Watch between 1992–1994, conducted a two year study, including a field investigation in Iraq, capturing Iraqi government documents in the process. According to Hiltermann, the literature on the Iran–Iraq War reflects a number of allegations of chemical weapons use by Iran, but these are "marred by a lack of specificity as to time and place, and the failure to provide any sort of evidence".
Gary Sick and Lawrence Potter call the allegations against Iran "mere assertions" and state: "no persuasive evidence of the claim that Iran was the primary culprit was ever presented". Policy consultant and author Joseph Tragert also states: "Iran did not retaliate with chemical weapons, probably because it did not possess any at the time".
At his trial in December 2006, Saddam Hussein said he would take responsibility "with honour" for any attacks on Iran using conventional or chemical weapons during the 1980–1988 war but he took issue with charges he ordered attacks on Iraqis. A medical analysis of the effects of Iraqi mustard gas is described a U.S. military textbook, and contrasted with slightly different effects in the First World War.
Distinctions and Peculiarity
Iran attacked and partially damaged the Osirak nuclear reactor on September 30, 1980 with two F-4 Phantoms, shortly after the outbreak of the Iran-Iraq War. This was the first attack on a nuclear reactor and only the third on a nuclear facility in history of the world. It was also the first instance of a pre-emptive attack on a nuclear reactor to forestall the development of a nuclear weapon, though it did not achieve its objective as France repaired the reactor after the Iranian attack. It took a second pre-emptive strike by the Israeli Airforce to disable the reactor, in the process killing a French engineer and causing France to pull out of Osirak. The decommissioning of Osirak has been cited as causing a substantial delay to Iraqi acquisition of nuclear weapons, which Saddam announced an intention to develop in response to the Iranian revolution.
The Iran-Iraq War was also the first and only conflict in the history of warfare in which both forces used Ballistic Missiles against each other.
This war also saw the only confirmed air-to-air helicopter battles in history of warfare with the Iraqi Mi-25s flying against Iranian AH-1 SuperCobra on numerous occasions. The first instance of these helicopter "dogfights" happened when on the starting day of the war (22 September 1980), two Iranian SuperCobras crept up on two Mi-25s and hit them with TOW wire-guided antitank missiles. One Mi-25 went down immediately, the other was badly damaged and crashed before reaching base. The Iranians pulled off a repeat performance on 24 April 1981, destroying two Mi-25s without incurring losses to themselves. According to some unclassified documents, Iranian pilots achieved a 10 to 1 kill ratio over the Iraqi helicopter pilots during these engagements and even engaged Iraqi fixed wing aircraft.
Aftermath


The Iran–Iraq War was extremely costly in lives and material, one of the deadliest wars since World War II. Both countries were devastated by the effect of the war. It cost Iran an estimated 1 million casualties, killed or wounded, and Iranians continue to suffer and die as a consequence of Iraq's use of chemical weapons. Iraqi casualties are estimated at 250,000-500,000 killed or wounded. Thousands of civilians died on both sides in air raids and ballistic missile attacks.
The financial loss was also enormous, at the time exceeding US$600 billion for each country (US$1.2 trillion in total). But shortly after the war it turned out that the economic cost of war is more profound and long-lasting than the estimates right after the war suggested. Economic development was stalled and oil exports disrupted. These economic woes were of a more serious nature for Iraq that had to incur huge debts during the war as compared to the very small debt of Iran, as Iranians had used bloodier but economically cheaper tactics during the war, in effect substituting soldiers lives for lack of financial funding during their defense. This put Saddam in a difficult position, particularly with his war-time allies, as by then Iraq was under more than $130 billion of international debt, excluding the interest in an after war economy with a slowed GDP growth. A large portion of this debt was loaned by Paris Club amounting to $21 billion, 85% of which had originated from seven countries of Japan, Russia, France, Germany, United States, Italy and United Kingdom. But the largest portion of $130 billion debt was to Iraq's former Arab backers of the war including the US$67 billion loaned by Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, UAE and Jordan.
After the war, Kuwait started to over-produce oil, which to keep Iraq's economy down. Iraq also accused Kuwait of sland drilling and stealing oil which lead to the invasion of Kuwait which made it worse to Iraq's financial situation, but it also made it much worse as United Nations Compensation Commission awarded reparations amounting more than $200 billion dollars to victims of the invasion including Kuwait, United States, individuals and companies among others, to be paid by Iraq in oil commodity as well as putting Iraq under a complete international embargo. This put further strain on Iraqi economy pushing its external debt and international liabilities to private and public sectors including the interests on them by the end of Saddam's rule, to more than $500 billion which combined with negative economic growth of Iraq after the prolonged international sanctions produced a Debt-to-GDP ratio of more than 1,000% (10 Years), making Iraq the most indebted poor country in the world. This unsustainable economic situation compelled the new Iraqi government formed after the fall of Saddam to request the forgiveness of a considerable portion of loans incurred during Iran Iraq war.
Among the other outcomes of the war is the different ways by which the countries involved responded in their scientific and technological advancement. In case of Iraq, after the war, its scientific and technological productivity collapsed and has not yet recovered. Kuwait's scientific output on the other hand was slowed initially due to the funding it extended to Saddam and later on became stagnant. Iran on the other hand experienced a scientific revival due to the war and has the fastest scientific growth rate in the world today.
Much of the oil industry in both countries was damaged in air raids. Iran's production capacity has yet to fully recover from the damages of the war. 10 million shells had landed in Iraq's oil fields at Basra, seriously damaging Iraq's oil production. Prisoners taken by both sides were not released until more than 10 years after the end of the conflict. Cities on both sides had also been considerably damaged. Not all saw the war in negative terms. The Islamic Revolution of Iran was strengthened and radicalized. The Iranian government-owned Etelaat newspaper wrote:
"There is not a single school or town that is excluded from the happiness of "holy defence" of the nation, from drinking the exquisite elixir of martyrdom, or from the sweet death of the martyr, who dies in order to live forever in paradise."
The Iraqi government commemorated the war with various monuments, including the Hands of Victory and the Al-Shaheed Monument, both in Baghdad.
The war left the borders unchanged. Two years later, as war with the western powers loomed, Saddam recognized Iranian rights over the eastern half of the Shatt al-Arab, a reversion to the status quo ante bellum that he had repudiated a decade earlier.
Declassified US intelligence available has explored both the domestic and foreign implications of Iran's apparent (in 1982) victory over Iraq in their then two-year old war.
On 9 December 1991, the UN Secretary-General reported the following to the UN Security Council:
"That Iraq's explanations do not appear sufficient or acceptable to the international community is a fact. Accordingly, the outstanding event under the violations referred to is the attack of 22 September 1980, against Iran, which cannot be justified under the charter of the United Nations, any recognized rules and principles of international law or any principles of international morality and entails the responsibility for conflict."
"Even if before the outbreak of the conflict there had been some encroachment by Iran on Iraqi territory, such encroachment did not justify Iraq's aggression against Iran—which was followed by Iraq's continuous occupation of Iranian territory during the conflict—in violation of the prohibition of the use of force, which is regarded as one of the rules of jus cogens."
"On one occasion I had to note with deep regret the experts' conclusion that "chemical weapons had been used against Iranian civilians in an area adjacent to an urban center lacking any protection against that kind of attack" (s/20134, annex). The Council expressed its dismay on the matter and its condemnation in Resolution 620 (1988), adopted on 26 August 1988."
In 2005, the new government of Iraq apologized to Iran for starting the war.
See also
- Halabja poison gas attack
- Arms-to-Iraq
- Ali Sayad Shirazi
- Baluchi Autonomist Movement
- British support for Iraq during the Iran–Iraq war
- Frans Van Anraat
- French support for Iraq during the Iran-Iraq war
- Iran Ajr, the minelaying ship captured by the U.S.
- Kaveh Golestan
- List of Iranian commanders in the Iran–Iraq War
- Morteza Avini, prominent photographer of the Iran–Iraq War
- Operation Mersad
- Osirak
- People's Mujahedin of Iran
- Persepolis
- Reagan Doctrine
- Saddam Hussein – United States relations
- Saddam's Trial and Iran-Iraq War
- Scott Report
- The Night Bus (film)
- United States support for Iraq during the Iran–Iraq war
- Iran–Iraq War in the Air 1980–1988
General:
- History of Iran
- History of Iraq
- Composite Index of National Capability
- Iran–Iraq relations
- Iran-Israel relations
- Military history of Iran
- Military of Iran
- Military of Iraq
- US-Iran relations
- List of modern conflicts in the Middle East
- Post-World War II air-to-air combat losses
References
- ^ http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/war/iran-iraq.htm
- http://i-cias.com/e.o/iranirqw.htm
- http://www.infoplease.com/ce6/history/A0825449.html#axzz0xO29RbVf
- Federal Research Division. "Country Study: Iran" (Document). Library of Congress.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help) - ^ "Iran–Iraq War (1980–1988)". Globalsecurity.org (John Pike). Cite error: The named reference "GlobalSecIIWar" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- "Twentieth Century Atlas - Death Tolls". Users.erols.com. Retrieved 2009-03-01.
- John Pike. "Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988)". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 2009-03-01.
- ^ Iran-Iraq War - MSN Encarta. Encarta.msn.com. 1988-08-20. Retrieved 2009-03-01.
- "Iran Chamber Society: History of Iran: Iran-Iraq War 1980-1988". Iranchamber.com. Retrieved 2009-03-01.
- "Iran-Iraq War 1980-1988". Historyofwar.org. Retrieved 2009-03-01.
- Hamsharionline.ir, Hamshahri Newspaper: "مدير كل آمار و اطلاعات بنياد شهيد اعلام كرد: ۱۸۸ هزار و ۱۵ تن از بهترين مردان و زنان ايران اسلامي در دوران هشت سال دفاع مقدس به درجه رفيع شهادت نايل شدند."
- EùmadBaghi.com, امار شهداي جنگ جامعه شناسي جنگ, from the website of Iranian journalist and activist Emadeddin Baghi
- "Iran-Iraq War". Infoplease.com. 1980-09-22. Retrieved 2009-03-01.
- "The Iran-Iraq War". Jewishvirtuallibrary.org. Retrieved 2009-03-01.
- http://www.amazon.com/Longest-War-Iran-Iraq-Military-Conflict/product-reviews/0415904072
- http://www.iranian.com/main/blog/fair/longest-war-never-again
- http://www.safehaven.com/article/7228/war-of-blackmail
- ^ Molavi, Afshin (2005). "The Soul of Iran" (Document). Norton. p. 152.
- "Threats and Responses: Briefly Noted; Iran-Iraq Prisoner Deal", by Nazila Fathi, New York Times, 14 March 2003
- Abrahamian, Ervand, A History of Modern Iran, Cambridge, 2008, p.171
- ^ S. M. Gieling, Iran-Iraq War, in Encyclopaedia Iranica, 2006.
- Hiltermann, Joost (January 17, 2003). "America Didn't Seem to Mind Poison Gas". International Herald Tribune.
- King, John (31 March 2003). "Arming Iraq and the Path to War". U.N. Observer & International Report.
- Fisk, Robert. The Great War for Civilisation: The Conquest of the Middle East. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2005, p. 219. ISBN 1-84115-007-X.
- Fendereski, Guive (2005). "2005: Tonb (Greater and Lesser)". www.iranica.com Eisenbrauns Inc.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - News.BBC.co.uk, "Iraq's rich mosaic of people", 2003
- CRS Report for Congress: The Kurds in Post-Saddam Iraq(Page 2)
- Speech made by Saddam Hussein. Baghdad, Voice of the Masses in Arabic, 1200 GMT 2 April 1980. FBIS-MEA-80-066. 3 April 1980, E2-3. E3
- Khomeini,Ruhollah and Algar, Hamid (translator) (1981). Islam and Revolution: Writing and Declarations of Imam Khomeini. Mizan Press. p. 122.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Mackey, Sandra (1996). The Iranians: Persia, Islam and the Soul of a Nation. Dutton. p. 317.
- "Who started the Iran–Iraq War?". Virginia Journal of International Law. 33: 69–89. Fall 1992.
{{cite journal}}:|first=missing|last=(help) - ^ Cruze, Gregory S. (Spring 1988). "Iran and Iraq: Perspectives in Conflict" (Document). U.S. Marine Corps Command and Staff College.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|volume=ignored (help) - Karsh, Efraim (2002). The Iran–Iraq War, 1980–1988. Osprey Publishing. p. 22.
- ^ The Iran–Iraq War: 1980–1988. p. 22.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ The Iran–Iraq War: 1980–1988. p. 23.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ The Iran–Iraq War: 1980–1988. p. 29.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ The Iran–Iraq War: 1980–1988. p. 27.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - The Iran–Iraq War: 1980–1988. p. 25.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Cordesman, Anthony and Wagner,Abraham R. (1990). The Lessons of Modern War: Volume Two - The Iran-Iraq Conflict. Westview. p. 102.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - John Keegan:The Iraq War
- Abrahamian, History of Modern Iran, pp. 171, 175.
- Majd, Hooman, The Ayatollah Begs to Differ: The Paradox of Modern Iran, by Hooman Majd, Doubleday, 2008, page 146
- The Iran–Iraq War: 1980–1988. p. 41.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - http://www.jag.navy.mil/library/investigations/USS%20STARK%20BASIC.pdf
- Desert Storm at sea: what the Navy really did by Marvin Pokrant, P 43.
- Stephen Andrew Kelley (June 2007). "Better Lucky Than Good: Operation Earnest Will as Gunboat Diplomacy" (Document). Naval Postgraduate School.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|accessdate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|format=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help) - ^ Formal Investigation into the Circumstances Surrounding the Attack of the USS Stark in 1987
- `Further on Khomenyni 4 April Speech on War,` broadcast 4 April 1985, quoted in Reinventing Khomeini: The Struggle for Reform in Iran by Daniel Brumberg University of Chicago Press, 2001, pages 132-34
- Dugdale-Pointon, TDP (27 October 2002). "Tanker War 1984–1988,".
- King, John (March 2003). "Arming Iraq: A Chronology of U.S. Involvement" (Document). Iran Chamber Society.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help) - Statement by former NSC official Howard Teicher to the U.S. District Court, Southern District of Florida. Plain text version
- ^ Kelley, Stephen Andrew (June 2007). "Better Lucky than Good: Operation Earnest Will as Gunboat Diplomacy" (Document). U.S. Naval Postgraduate School.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|volume=ignored (help) - http://reference.allrefer.com/country-guide-study/iran/iran172.html
- http://www.relevantsearchscotland.co.uk/ships/jahre.html
- Fisk. The Great War for Civilisation, p. 221.
- ^ Martins, Mark S. (Winter 1994). "Rules of Engagement for Land Forces: A Matter of Training, Not Lawyering" (PDF). Military Law Review. 143: 43–46.
- Peniston, Bradley (2006). No Higher Honor: Saving the USS Samuel B. Roberts in the Persian Gulf. Persian Gulf: Naval Institute Press. pp. 61–63. ISBN 1591146615..
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - See Fisk. The Great War for Civilisation, pp. 260-273.
- ^ Rajaee, Farhang. The Iran–Iraq War: The Politics of Aggression. University Press of Florida.
- "The 1980–1988 Iran–Iraq War: A CWIHP Critical Oral History Conference", Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars, 11 August 2004
- "The Arming, and Disarming, of Iran's Revolution," The Economist, International Edition, 19 September 1987, 56-57.
- "Like the Iran-Iraq war. | Goliath Business News". Goliath.ecnext.com. 2007-04-30. Retrieved 2009-03-01.
- http://books.google.ee/books?id=BABAZqVgfq0C&pg=PA17#v=onepage&q&f=false
- http://books.google.ee/books?id=jh3Q5F7BaB8C&pg=PA368#v=onepage&q&f=false
- United Nations Special Commission. "UNSCOM's Comprehensive Review" (Document). James Martin Center for Nonproliferation Studies.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|contribution=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|format=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help) - InformationClearinghouse.info
- YouTube.com
- "Iran–Iraq War," Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2008 encarta.msn.com © 1997–2008 Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved
- El Mundo (Spain) book. El Camino de la Libertad. La democracia año a año. 1986 ISBN 978-84-92540-09-9. Page 27-32.
- Fuller, Graham E. 2008 "The new Turkish Republic, Turkey as a pivotal state in the Muslim world" ISBN 978-1-60127-019-1 Page 40,98
- Iraq debt: non-Paris Club creditors
- Lantos, Tom (19 May 1992). "The Administration's Iraq Gate Scandal, by William Safire" (Document). Congressional Record.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help) - "Annex D, Iraq Economic Data (1989–2003)". Comprehensive Report of the Special Advisor to the DCI [Director of Central Intelligence] on Iraq's WMD. Vol. 1 of 3. GlobalSecurity.org. 30 September 2004.
- Center for Documents of The Imposed War, Tehran. (مرکز مطالعات و تحقیقات جنگ)
- Iran's weapons of mass destruction: the real and potential threat by Anthony H. Cordesman - p. 27
- Wright, Robin, Dreams and Shadows : the Future of the Middle East, Penguin Press, 2008, p.438
- History's Greatest War by Terry Bryant, 2007
- The Iran-Iraq War: The Politics of Aggression by Farhang Rajaee, University Press of Florida
- Fassihi, Farnaz (27 October 2002). "In Iran, grim reminders of Saddam's arsenal". New Jersey Star-Ledger.
- S/17911 and Add. 1, 21 March 1986. Note that this is a "decision" and not a resolution.
- Officers Say U.S. Aided Iraq in War Despite Use of Gas, New York Times, 18 August 2002.
- Galbraith, Peter W.; Van Hollen, Christopher Jr. (21 September 1988). "Chemical Weapons Use in Kurdistan: Iraq's Final Offensive". staff report to the U.S. Senate Committee on Foreign Relations: 30.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Pear, Robert (15 September 1988). "U.S. Says It Monitored Iraqi Messages on Gas". The New York Times.
- Fisk. The Great War for Civilisation, p. 214.
- Potter, Gary; Sick (2004). Iran, Iraq, and the legacies of war. MacMillan. p. 153. ISBN 1-4039-6450-5.
{{cite book}}: More than one of|first1=and|first=specified (help) - Potter, Gary; Sick (2004). Iran, Iraq, and the legacies of war. MacMillan. p. 156. ISBN 1-4039-6450-5.
{{cite book}}: More than one of|first1=and|first=specified (help) - Tragert, Joseph (2003). Understanding Iran. Indianapolis., Indiana: Alpha. p. 190. ISBN 1-59257-141-7.
- Rasheed, Ahmed (19 December 2006). "Saddam admits Iran gas attacks]". The Australian.
- Sidell, Frederick R.; Urbanetti, John S.; Smith, William J.; Hurst, Charles G. "Medical Aspects of Chemical and Biological Warfare" (Document). Office of The Surgeon General, Department of the Army, United States of America.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|contribution=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help) - http://www.ipsnews.net/news.asp?idnews=52412
- AF.mil
- ^ AF.mil
- McNair Paper 41, Radical Responses to Radical Regimes: Evaluating Preemptive Counter-Proliferation, May 1995
- FAS.org
- ^ Google.com
- Docs.Google.com
- Blogfa.com
- ACIG.org
- Vectorsite.net
- Docs.Google.com
- IIE.com
- Mees.com
- News.BBC.co.uk
- Reuters.com
- JubileeIraq.org
- ProbeInternational.org
- Memri.org
- InvestorsIraq.com
- JubileeIraq.org
- http://www.science-metrix.com/30years-Paper.pdf
- Nasr, Vali, The Shia Revival, Norton, (2006), pages 140
- Column in Etelaat, 4 April 1983, quoted in Molavi, Afshin, The Soul of Iran (Norton), (2006)
- SNIE 34/36.2-82 link: Intelligence Reports on Saddam Hussein's Reign
- See items 6, 7, and 8 of the UN Secretary General's report to the UN Security Council on 9 December 1991: Iranian.com
- http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2010/sep/23/iran-iraq-war-anniversary
External links
- Documentary about the war (on Google Video)
- Template:Dmoz
- Attack on Osirak: Persian
- FMFRP 3-203 - Lessons Learned: Iran–Iraq War, 10 December 1990.
- Dutchman charged for selling chemicals to Saddam, BBC, 18 March 2005.
- Sasan Fayazmanesh, Historical Amnesia: The Shoot Down of Iran Air Flight 655, Counterpunch, 11 July 2008, Counterpunch.org.
- Global Security: Iran-Iraq war
- Bibliography: The Iran-Iraq War, and U.S. Involvement in It.
Photo Galleries
- Pictures Iran-Iraq War Times Online Photo Gallery
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Template:Link GA Template:Link GA Template:Link GA Template:Link GA
Categories: