| Revision as of 21:18, 5 May 2012 edit88.224.48.12 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:48, 5 May 2012 edit undoTheShadowCrow (talk | contribs)6,258 editsmNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| '''Armenians in Azerbaijan''' are the ] who lived in great numbers in ] According to the statistics, about 400,000 Armenians lived in Azerbaijan in 1989.<ref>Memorandum from the Lawyers Committee for Human Rights to John D. Evans, Resource Information Center, 13 June 1993.</ref><ref>"Implementation of the Helsinki Accords: Human Rights and Democratization in the Newly Independent States of the former Soviet Union" (Washington, DC: U.S. Congress, Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe, January 1993), p. 118.</ref> Most of the Armenian-Azerbaijanis however had to flee the republic, like ], in the events leading up to the ], a result of the ongoing Armenian-Azerbaijani conflict. Atrocities directed against the Armenian population have reportedly taken place in ] (February 1988), ] (Kirovabad, November 1988) and ] (January 1990). Today the vast majority of Armenians in Azerbaijan live in territory controlled by the break-away region ] (120,700 as of 1999 Azerbaijani official statistics)<ref></ref><ref name="cidcm.umd.edu"></ref> which declared its unilateral act of independence in 1991 under the name ] but has not been recognised by any country, including Armenia. | '''Armenians in Azerbaijan''' are the ] who lived in great numbers in ] According to the statistics, about 400,000 Armenians lived in Azerbaijan in 1989.<ref>Memorandum from the Lawyers Committee for Human Rights to John D. Evans, Resource Information Center, 13 June 1993.</ref><ref>"Implementation of the Helsinki Accords: Human Rights and Democratization in the Newly Independent States of the former Soviet Union" (Washington, DC: U.S. Congress, Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe, January 1993), p. 118.</ref> Most of the Armenian-Azerbaijanis however had to flee the republic, like ], in the events leading up to the ], a result of the ongoing Armenian-Azerbaijani conflict. Atrocities directed against the Armenian population have reportedly taken place in ] (February 1988), ] (Kirovabad, November 1988) and ] (January 1990). Today the vast majority of Armenians in Azerbaijan live in territory controlled by the break-away region ] (120,700 as of 1999 Azerbaijani official statistics)<ref></ref><ref name="cidcm.umd.edu"></ref> which declared its unilateral act of independence in 1991 under the name ] but has not been recognised by any country, including Armenia. | ||
| Non-official sources estimate that the number Armenians living on Azerbaijani territory outside Nagorno-Karabakh is around 2,000 to 3,000 |
Non-official sources estimate that the number Armenians living on Azerbaijani territory outside Nagorno-Karabakh is around 2,000 to 3,000.<ref></ref><ref name="ecri"></ref> Armenians in ] are at a great risk as long as the ] conflict remains unsettled <ref name="CIDCM"></ref><ref>Razmik Panossian. The Armenians. Columbia University Press, 2006; p. 281</ref><ref>Mario Apostolov. The Christian-Muslim Frontier. Routledge, 2004; p. 67</ref><ref>Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. Country Reports on Human Rights Practices. 2001</ref><ref>Barbara Larkin. International Religious Freedom (2000): Report to Congress by the Department of State. DIANE Publishing, 2001; p. 256</ref>In Azerbaijan, the status of Armenians, is precarious.<ref>Azerbaijan: The status of Armenians, Russians, Jews and other minorities, report, 1993, INS Resource Information Center, p. 10</ref> Armenian churches remain closed, because of the large outmigration of Armenians and fear of Azeri attacks.<ref>United States Department of State, Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 1992 (Washington: U.S. Government Printing Office, February 1993), p. 708</ref> | ||
| In Azerbaijan, the status of Armenians, is precarious.<ref>Azerbaijan: The status of Armenians, Russians, Jews and other minorities, report, 1993, INS Resource Information Center, p. 10</ref> Armenian churches remain closed, because of the large outmigration of Armenians and fear of Azeri attacks.<ref>United States Department of State, Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 1992 (Washington: U.S. Government Printing Office, February 1993), p. 708</ref> | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
Revision as of 21:48, 5 May 2012
Armenians in Azerbaijan are the Armenians who lived in great numbers in Azerbaijan According to the statistics, about 400,000 Armenians lived in Azerbaijan in 1989. Most of the Armenian-Azerbaijanis however had to flee the republic, like Azeris in Armenia, in the events leading up to the Nagorno-Karabakh War, a result of the ongoing Armenian-Azerbaijani conflict. Atrocities directed against the Armenian population have reportedly taken place in Sumgait (February 1988), Ganja (Kirovabad, November 1988) and Baku (January 1990). Today the vast majority of Armenians in Azerbaijan live in territory controlled by the break-away region Nagorno-Karabakh (120,700 as of 1999 Azerbaijani official statistics) which declared its unilateral act of independence in 1991 under the name Nagorno-Karabakh Republic but has not been recognised by any country, including Armenia.
Non-official sources estimate that the number Armenians living on Azerbaijani territory outside Nagorno-Karabakh is around 2,000 to 3,000. Armenians in Azerbaijan are at a great risk as long as the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict remains unsettled In Azerbaijan, the status of Armenians, is precarious. Armenian churches remain closed, because of the large outmigration of Armenians and fear of Azeri attacks.
History
Armenians in Baku
Main article: Armenians in BakuArmenians in Nagorno-Karabakh
Main articles: Nagorno-Karabakh Republic, Artsakh, and Nagorno-Karabakh

Armenians have lived in the Karabakh region since the period of antiquity. In the beginning of the 2 century B.C. Karabakh became a part of Armenian Kingdom as province of Artsakh. In the 14th century, a local Armenian leadership emerged, consisting of five noble dynasties led by princes, who held the titles of meliks and were referred to as Khamsa (five in Arabic). The Armenian meliks maintained control over the region until the 18th century. In the early 16th century, control of the region passed to the Safavid dynasty, which created the Ganja-Karabakh province (beglarbekdom, bəylərbəylik). Despite these conquests, the population of Upper Karabakh remained largely Armenian.
Karabakh passed to Imperial Russia by the Kurekchay Treaty, signed between the Khan of Karabakh and Tsar Alexander I of Russia in 1805, and later further formalized by the Russo-Persian Treaty of Gulistan in 1813, before the rest of Transcaucasia was incorporated into the Empire in 1828 by the Treaty of Turkmenchay. In 1822, the Karabakh khanate was dissolved, and the area became part of the Elisabethpol Governorate within the Russian Empire.
After the Russian Revolution of 1917, Karabakh became part of the Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic, but this soon dissolved into separate Armenian, Azerbaijani, and Georgian states. Over the next two years (1918–1920), there were a series of short wars between Armenia and Azerbaijan over several regions, including Karabakh. In July 1918, the First Armenian Assembly of Nagorno-Karabakh declared the region self-governing and created a National Council and government. Later, Ottoman troops entered Karabakh, meeting armed resistance by Armenians.
In April 1920, while the Azerbaijani army was locked in Karabakh fighting local Armenian forces, Azerbaijan was taken over by Bolsheviks. Subsequently, the disputed areas of Karabakh, Zangezur, and Nakhchivan came under the control of Armenia. During July and August 1920, however, the Red Army occupied mountainous Karabakh, Zangezur, and part of Nakhchivan. Later on, for basically political reasons, the Soviet Union agreed to a division under which Zangezur would fall under the control of Armenia, while Karabakh and Nakhchivan would be under the control of Azerbaijan. In addition, the mountainous part of Karabakh that had come to be named Nagorno-Karabakh was granted an autonomous status as the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast, giving Armenians more rights than were given to Azeris in Armenia and enabling Armenians to be appointed to key positions and attend schools in their first language.
With the Soviet Union firmly in control of the region, the conflict over the region died down for several decades. The Armenians in Karabakh were not repressed to a substantial extent. Their situation was undoubtedly better than of the Azeris in Armenia who lived in Zangezur in an equally concentrated manner, though without possessing any autonomy. Local schools offered education in Armenian but taught Azerbaijani history and not the history of the Armenian people; the population had access to Armenian-language television broadcast by a Stepanakert-based channel controlled from Baku, and later directly from Armenia as well, though in an unfavourable manner. The autonomy of Nagorno-Karabakh led to the rise of Armenian nationalism and the Armenians' determination in claiming independence. With the beginning of the dissolution of the Soviet Union in the late 1980s and early 1990s, the question of Nagorno-Karabakh re-emerged.
Armenians allege that this followed the Azerbaijani and Soviet military forces jointly starting "a campaign of violence to disperse Armenian villagers from areas north and south of Nagorno-Karabakh, a territorial enclave in Azerbaijan where Armenian communities have lived for centuries".
"However, the unstated goal was to "convince" the villagers half are pensioners to relocate permanently in Armenia." This military action was officially called "Operation Ring," because its basic strategy consists of surrounding villages (included Martunashen and Chaykand) with tanks and armored personnel carriers and shelling them. Azerbaijani villagers were allowed to come and loot the empty Armenian villages, while more than ten thousand Armenian villagers have been forced to leave Azerbaijan.
The majority Armenian population started a movement that culminated in the unilateral declaration of independence.
Armenians in Nakhchivan
Main articles: Armenians in Nakhchivan, Nakhchivan, and Khachkar destruction in Nakhchivan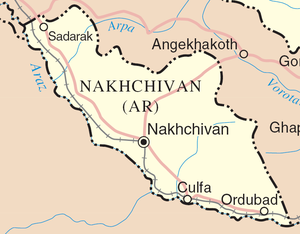

Armenians had a historic presence in Nakhchivan (In Armenian Նախիջևան). According to an Armenian tradition, Nakhchivan was founded by Noah, of the Abrahamic religions. It became part of the Satrapy of Armenia under Achaemenid Persia circa 521 BC. In 189 BC, Nakhchivan was part of the new Kingdom of Armenia established by Artaxias I. In 428, the Armenian Arshakuni monarchy was abolished and Nakhchivan was annexed by Sassanid Persia. In 623 AD, possession of the region passed to the Byzantine Empire. Nakhchivan itself became part of the autonomous Principality of Armenia under Arab control. After the fall of the Arab rule in the 9th century, the area became the domain of several Muslim emirates of Arran and Azerbaijan. Nakhchivan became part of the Seljuk Empire in the 11th century, followed by becoming the capital of the Atabegs of Azerbaijan in the 12th century. In the 1220s it was plundered by Khwarezmians and Mongols. In the 15th century, the weakening Mongol rule in Nakhchivan was forced out by the Turcoman dynasties of Kara Koyunlu and Ak Koyunlu.
In the 16th century, control of Nakhchivan passed to the Safavid dynasty of Persia. In 1604, Shah Abbas I Safavi, concerned that the lands of Nakhchivan and the surrounding areas would pass into Ottoman hands, decided to institute a scorched earth policy. He forced the entire local population, Armenians, Jews and Muslims alike, to leave their homes and move to the Persian provinces south of the Aras River. Many of the deportees were settled in the neighborhood of Isfahan that was named New Julfa since most of the residents were from the original Julfa (a predominantly Armenian town).
After the last Russo-Persian War and the Treaty of Turkmenchay, the Nakhchivan khanate passed into Russian possession in 1828. The Nakhchivan khanate was dissolved, and its territory was merged with the territory of the Erivan khanate and the area became the Nakhchivan uyezd of the new Armenian Oblast, which was reformed into the Erivan Governorate in 1849. A resettlement policy implemented by the Russian authorities encouraged massive Armenian immigration to Nakhchivan from various parts of the Ottoman Empire and Persia. According to official statistics of the Russian Empire, by the turn of the 20th century Azerbaijanis made up 57% of the uyezd's population, while Armenians constituted 42%.
During the Russian Revolution of 1905, conflict erupted between the Armenians and the Azeris, culminating in the Armenian-Tatar massacres. In the final year of World War I, Nakhchivan was the scene of more bloodshed between Armenians and Azerbaijanis, who both laid claim to the area. By 1914, the Armenian population was at 40% while the Azeri population increased to roughly 60%. After the February Revolution, the region was under the authority of the Special Transcaucasian Committee of the Russian Provisional Government and subsequently of the short-lived Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic. When the TDFR was dissolved in May 1918, Nakhchivan, Nagorno-Karabakh, Zangezur (today the Armenian province of Syunik), and Qazakh were heavily contested between the newly formed and short-lived states of the Democratic Republic of Armenia (DRA) and the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic (ADR). In June 1918, the region came under Ottoman occupation. Under the terms of the Armistice of Mudros, the Ottomans agreed to pull their troops out of the Transcaucasus to make way for the forthcoming British military presence.
After a brief British occupation and the fragile peace they tried to impose, in December 1918, with the support of Azerbaijan's Musavat Party, Jafar Gulu Khan Nakhchivanski declared the Republic of Aras in the Nakhchivan uyezd of the former Yerevan Governorate assigned to Armenia by Wardrop. The Armenian government did not recognize the new state and sent its troops into the region to take control of it. The conflict soon erupted into the violent Aras War. By mid-June 1919, however, Armenia succeeded in establishing control over Nakhchivan and the whole territory of the self-proclaimed republic. The fall of the Aras republic triggered an invasion by the regular Azerbaijani army and by the end of July, Armenian troops were forced to leave Nakhchivan City to the Azeris. In mid-March 1920, Armenian forces launched an offensive on all of the disputed territories, and by the end of the month both the Nakhchivan and Zangezur regions came under stable but temporary Armenian control. In July 1920, the 11th Soviet Red Army invaded and occupied the region and on July 28, declared the Nakhchivan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic with "close ties" to the Azerbaijan SSR. A referendum was called for the people of Nakhchivan to be consulted. According to the formal figures of this referendum, held at the beginning of 1921, 90% of Nakhchivan's population wanted to be included in the Azerbaijan SSR "with the rights of an autonomous republic." The decision to make Nakhchivan a part of modern-day Azerbaijan was cemented March 16, 1921 in the Treaty of Moscow between Bolshevist Russia and Turkey. The agreement between the Soviet Russia and Turkey also called for attachment of the former Sharur-Daralagez uyezd (which had a solid Azeri majority) to Nakhchivan, thus allowing Turkey to share a border with the Azerbaijan SSR. This deal was reaffirmed on October 23, in the Treaty of Kars.
In the years following the establishment of Soviet rule, Nakhchivan saw a significant demographic shift. Its Armenian population gradually decreased as many emigrated. According to statistics published by the Imperial Russian government in 1916, Armenians made up 40% of the population of the Nakhchivan uyezd. The borders of the uyezd were redrawn and in the 1926 all-Soviet census 11% of region's population was Armenian,. By 1979 this number had shrunk to 1.4%. The Azeri population, meanwhile increased substantially with both a higher birth rate and immigration (growing from 85% in 1926 to 96% by 1979). The Armenian population saw a great reduction in their numbers throughout the years repatriating to Armenia and elsewhere.
Some Armenian political groupings of the Republic of Armenia and the Armenian diaspora, among them most notably the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (ARF) claim that Nakhchivan should belong to Armenia. However, Nakhchivan is not officially claimed by the government of Armenia. But huge Armenian religious and cultural remnants are witness of the historic presence of Armenians in the Nakhcivan region (Nakichevan, sometimes Nakhijevan in Armenian). Recently the Medieval Armenian cemetery of Jugha (Julfa) in Nakhchivan, regarded by Armenians as the biggest and most precious repository of medieval headstones marked with Christian crosses – khachkars (of which more than 2,000 were still there in the late 1980s), has completely vanished in 2006.
Conditions today
The Armenians still remaining in Azerbaijan practically live in virtual hiding, and have also changed their Armenian names and surnames to Azerbaijani names and surnames because they have to maintain an extremely low profile to avoid harassment and physical attacks. They have continued to complain (in private due to fear of attacks) that they remain subject to harassmant and human rights violations and therefore have to hide their identity. According to a 1993 United States Immigration and naturalization service report:
It is clear that Armenians are the target of violence from societal forces and that the Azerbaijani government is unable or in some instances unwilling to control the violence or acts of discrimination and harassment. Some sectors of the government, such as the Department of Visas and Registrations mentioned above, appear unwilling to enforce the governments stated policy on minorities. As long as the Armenian-Azeri conflict over the fate of Karabakh continues, and possibly long after a settlement is reached, Armenian inhabitants of Azerbaijan will have no guarantees of physical safety.
A report by the European Commission against Racism and Intolerance (ECRI) released in May 2011 found that their conditions had barely improved. It found that:
...people of Armenian origin are at risk of being discriminated against in their daily lives. Certain people born of mixed Armenian-Azerbaijani marriages choose to use the name of their Azerbaijani parent so as to avoid problems in their contacts with officialdom; others who did not immediately apply for Azerbaijani identity documents when the former Soviet passports were done away with today encounter difficulties in obtaining identity papers.
It further expressed concern over the "fact that the constant negative official and media discourse concerning the Republic of Armenia helps to sustain a negative climate of opinion regarding people of Armenian origin coming under the Azerbaijani authorities' jurisdiction." It recommended that the government "work actively to improve the climate of opinion concerning Armenians coming under Azerbaijan’s jurisdiction."
Famous Armenians from Azerbaijan
- Hovhannes Bagramyan Army Commander, Marshal of the Soviet Union
- Hovannes Adamian, designer of color television
- Alexander Shirvanzade, playwright and novelist, awarded by the "People's Writer of Armenia" and "People's Writer of Azerbaijan" titles
- Boris Babaian, pioneering creator of supercomputers in the Soviet Union
- Armen Ohanian, an Armenian dancer, actress, writer and translator
- Alexey Ekimyan, composer and police general
- Garri Kasparov, grandmaster and world champion
- Vladimir Akopian, chess player
- Ashot Nadanian, chess player
- Vladimir Bagirov, chess player
- Yevgeny Petrosyan, comedian
- Georgy Shakhnazarov, political scientist
- Rafael Kapreliants, Hero of the Soviet Union.
- Avet Terterian, composer
- Sergey Petrosyan, weightlifter
- Karina Aznavourian, épée fencer
See also
- List of Azerbaijani Armenians
- Armenian–Azerbaijani War
- Armenian National Council of Baku
- Anti-Armenianism#Persecution in the Republic of Azerbaijan
- Armenia–Azerbaijan relations
Notes
- Memorandum from the Lawyers Committee for Human Rights to John D. Evans, Resource Information Center, 13 June 1993.
- "Implementation of the Helsinki Accords: Human Rights and Democratization in the Newly Independent States of the former Soviet Union" (Washington, DC: U.S. Congress, Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe, January 1993), p. 118.
- Demographic indicators: Population by ethnic groups
- Assessment for Armenians in Azerbaijan, Minorities At Risk Project
- Definitions of national identity, nationalism and ethnicity in post-Soviet Azerbaijan in the 1990s
- European Commission Against Racism and Intolerance (ECRI), Second Report on Azerbajan, CRI(2007)22, May 24, 2007
- University of Maryland Center for International Development and Conflict Management. Minorities at Risk: Assessment of Armenians in Azerbaijan, Online Report, 2004
- Razmik Panossian. The Armenians. Columbia University Press, 2006; p. 281
- Mario Apostolov. The Christian-Muslim Frontier. Routledge, 2004; p. 67
- Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. Country Reports on Human Rights Practices. 2001
- Barbara Larkin. International Religious Freedom (2000): Report to Congress by the Department of State. DIANE Publishing, 2001; p. 256
- Azerbaijan: The status of Armenians, Russians, Jews and other minorities, report, 1993, INS Resource Information Center, p. 10
- United States Department of State, Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 1992 (Washington: U.S. Government Printing Office, February 1993), p. 708
- ^ Hewsen, Robert H. Armenia: A Historical Atlas. Chicago: Chicago University Press, 2001.
- ^ Cornell, Svante E. The Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict. Uppsala: Department of East European Studies, April 1999.
- The Nagorno-Karabagh Crisis: A Blueprint for Resolution, New England Center for International Law & Policy
- ^ Tobias Debiel, Axel Klein, Stiftung Entwicklung und Frieden. . Zed Books, 2002; p.94
- T.K.Oommen. Citizenship, nationality, and ethnicity. Wiley-Blackwell, 1997; p. 131
- ^ HRW Report on Soviet Union Human Rights Developments, 1992
- Hovannisian, Richard G. (1971). The Republic of Armenia: The First Year, 1918-1919, Vol. I. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 58–62. ISBN 0-5200-1984-9.
- Hovannisian. Republic of Armenia, vol. I, p. 91.
- Nakhchivan ASSR in the 1926 All-Soviet Census
- "Implementation of the Helsinki Accords: Human Rights and Democratization in the Newly Independent States of the former Soviet Union" (Washington, DC: U.S. Congress, Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe, January 1993), p. 118
- "AZERBAIJAN: THE STATUS OF ARMENIANS, RUSSIANS, JEWS AND OTHER MINORITIES", INS resource information center, 1993
- ^ European Commission against Racism and Intolerance "ECRI REPORT ON AZERBAIJAN (fourth monitoring cycle)." May 31, 2011. p. 30.
External links
- Armenia.az Azerbaijan's Armenia site in Armenian
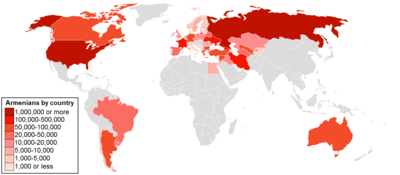
| Armenian diaspora | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Historic areas of Armenian settlement | ||
| Caucasus | ||
| Former Soviet Union | ||
| Americas | ||
| Europe | ||
| Middle East | ||
| Asia | ||
| Africa | ||
| Oceania | ||
