| Revision as of 21:39, 23 May 2021 view source99.23.32.49 (talk) →Related charactersTag: Visual edit← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 14:32, 13 January 2025 view source Burzuchius (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users4,566 editsNo edit summary | ||
| (345 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description| |
{{short description|10th letter of the Latin alphabet}} | ||
| {{About|the letter of the alphabet}} | {{About|the tenth letter of the Latin alphabet}} | ||
| {{Technical reasons|J#|the programming language|J Sharp}} | {{Technical reasons|J#|the programming language|J Sharp}} | ||
| {{About||the Cyrillic letter Ј|Je (Cyrillic)}} | |||
| {{pp-move-indef}} | {{pp-move-indef}} | ||
| {{pp |
{{pp|small=yes}} | ||
| {{Infobox grapheme | {{Infobox grapheme | ||
| |name=J | |name=J | ||
| |letter=J j |
|letter=J j | ||
| |variations=(]) | |||
| |image=File:J cursiva.gif | |||
| |imagesize=200px | |||
| |imagealt=Writing cursive forms of J | |||
| |script=] | |script=] | ||
| |type=] | |type=] | ||
| |typedesc=ic | |typedesc=ic | ||
| |language=] | |language=] | ||
| |phonemes={{grid list| | |||
| |phonemes=<br>~<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>~<br><br><br><br><br>{{IPAc-en|dʒ|eɪ}}<br>{{IPAc-en|dʒ|aɪ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |~ | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |{{IPAc-en|dʒ|eɪ}} | |||
| |{{IPAc-en|dʒ|aɪ}}}} | |||
| |unicode=U+004A, U+006A, U+0237 | |unicode=U+004A, U+006A, U+0237 | ||
| |alphanumber=10 | |alphanumber=10 | ||
| Line 26: | Line 40: | ||
| |fam7=] | |fam7=] | ||
| |fam8=] | |fam8=] | ||
| |fam9=] ] ] | |fam9=] ] | ||
| |usageperiod=14th century<ref>{{cite web |title=J-letter |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/J-letter |website=Encyclopedia Britannica}}</ref> to present | |||
| |usageperiod=1524 to present | |||
| |children={{bull}}]<br>{{bull}}]<br>{{bull}}] | |children={{bull}}]<br>{{bull}}]<br>{{bull}}] | ||
| |sisters={{grid list| | |||
| |sisters=]<br>]<br>]<br>]<br>]<br>]<br>]<br>]<br>]<br>]<br>]<br>] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |]}} | |||
| |equivalents= | |equivalents= | ||
| |associates=], ] | |associates=], ] | ||
| |direction=Left-to- |
|direction=Left-to-right | ||
| |image=File:Latin_letter_J.svg}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Latin letter info|j}} | {{Latin letter info|j}} | ||
| '''J''' |
'''J''' or '''j''' is the tenth ] of the ], used in the ], the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual name in English is ] (pronounced {{IPAc-en|'|dʒ|eɪ}}), with a now-uncommon variant ''jy'' {{IPAc-en|'|dʒ|aɪ}}.<ref name="j-oed">"J", ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989)</ref><ref>"J" and "jay", ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993)</ref> | ||
| When used in the ] for the ] (the sound of "y" in "yes") it may be called ''yod'' or ''jod'' (pronounced {{IPAc-en|'|j|ɒ|d}} or {{IPAc-en|'|j|oʊ|d}}).<ref>{{OED|yod}}</ref> | |||
| == History == | |||
| == History == | |||
| ] | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| ! Egyptian hieroglyph ꜥ | |||
| ! Phoenician <br/>] | |||
| ! Western Greek<br/>] | |||
| ! Etruscan<br>I | |||
| ! Latin<br/>I | |||
| ! Latin<br/>J | |||
| |--- align=center | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |} | |||
| ] | |||
| The letter ''J'' used to be used as the ] letter ''I'', used for the letter I at the end of ] when following another I, as in XXIIJ or xxiij instead of XXIII or xxiii for the Roman numeral |
The letter ''J'' used to be used as the ] letter ''I'', used for the letter I at the end of ] when following another I, as in XXIIJ or xxiij instead of XXIII or xxiii for the Roman numeral twenty-three. A distinctive usage emerged in ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://germazope.uni-trier.de/Projects/WBB/woerterbuecher/lexer/selectarticle?lemid=LJ00001|title=Wörterbuchnetz|access-date=22 December 2016|archive-date=4 March 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304204600/http://germazope.uni-trier.de/Projects/WBB/woerterbuecher/lexer/selectarticle?lemid=LJ00001|url-status=dead}}</ref> ] (1478–1550) was the first to explicitly distinguish I and J as representing separate sounds, in his ''Ɛpistola del Trissino de le lettere nuωvamente aggiunte ne la lingua italiana'' ("Trissino's ] about the letters recently added in the ]") of 1524.<ref>'']'' in Italian ].</ref> Originally, 'I' and 'J' were different shapes for the same letter, both equally representing {{IPA|/i/}}, {{IPA|/iː/}}, and {{IPA|/j/}}; however, ] developed new sounds (from former {{IPA|/j/}} and {{IPA|/ɡ/}}) that came to be represented as 'I' and 'J'; therefore, ] J, acquired from the ] J, has a sound value quite different from {{IPA|/j/}} (which represents the initial sound in the English language word "''y''et"). | ||
| == |
== Use in writing systems == | ||
| {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" | ||
| |+ Pronunciation of {{angbr|j}} by language | |||
| |+List of pronunciations | |||
| ! Orthography | |||
| ! colspan="5" |Most common pronunciation: {{IPAslink|j}} ''Languages in italics do not use the ]'' | |||
| ! Phonemes | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| !Language | |||
| | {{IPAslink|j}} | |||
| !Dialect(s) | |||
| !Pronunciation | |||
| (]) | |||
| !Environment | |||
| !Notes | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! rowspan="4" |'']'' | |||
| | {{IPAslink|j}} | |||
| !]; most dialects | |||
| |{{IPAslink|dʒ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |Latinization | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| !] | ! ] | ||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|dʒ}} or {{IPAslink|ʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| |Latinization | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| !], ], ] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|ʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| |Latinization | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| !], ] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|dʒ}}, {{IPAslink|j}}, {{IPAslink|ɟ}}, {{IPAslink|ʃ}}, {{IPAslink|x}}, {{IPAslink|ʒ}} | |||
| |{{IPAslink|ʒ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |Latinization | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] (]) | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|t͡s}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] (]) | |||
| ! rowspan="6" |]<ref>{{Cite book|last=Trask, R. L. (Robert Lawrence), 1944-2004.|url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/34514667|title=The history of Basque|date=1997|publisher=Routledge|isbn=0-415-13116-2|location=London|oclc=34514667}}</ref> | |||
| | {{IPAslink|j}} | |||
| !] | |||
| |{{IPAslink|dʒ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| !] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|ʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| |also used in southwest Bizkaian | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! {{nwr|]}} (]) | |||
| !] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|tɕ}} | ||
| | | |||
| |also used in south Lapurdian | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! {{nwr|]}} (]) | |||
| !] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|ʐ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| !] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| |also used in east Bizkaian | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| !] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! |
! ] | ||
| |{{IPAslink|dʒ}} | | {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} or {{IPAslink|i̯}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |'']'' | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" |'']'' | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|dʒ}}, {{IPAslink|h}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| |{{IPAslink|z}}~{{IPAslink|ʑ}} | |||
| | {{IPAslink|j}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|ʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| |{{IPAslink|ʑ}} and {{IPAslink|dʑ}} distinct in some dialects, see '']'' | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] (]) | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] (], ]) | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|dz}} ~ {{IPAslink|dʑ}}, {{IPAslink|z}} ~ {{IPAslink|ʑ}} | |||
| |{{IPAslink|ɟ}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! rowspan="4" |] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|j}} | |||
| ! rowspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink|ts}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| |{{IPAslink|dz}} | |||
| | {{IPAslink|j}} | |||
| |after vowels | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! rowspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| |{{IPAslink|dʑ}} | |||
| | {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | |||
| |after vowels | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}}, {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] (]) | |||
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|ʑ}}, {{IPAslink|dʑ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] (]) | |||
| |{{IPAslink|ʒ}} | |||
| | {{IPAslink|c}} | |||
| | | |||
| |Some words | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! |
! ] | ||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|t}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] (Roman) | |||
| ! rowspan="2" |] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|ɟ}} | |||
| ! rowspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink|tɕ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |] latinization | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] (]) | |||
| |{{IPAslink|ʐ}} | |||
| |{{IPAslink|ts}} ~ {{IPAslink|tɕ}}, {{IPAslink|dz}} ~ {{IPAslink|dʑ}} | |||
| | | |||
| |] latinization | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|ʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}}, {{IPAslink|ʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |'']'' | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink|dʒ}} | | {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! |
! ] | ||
| | {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | |||
| !] | |||
| |{{IPAslink|x}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] romanization | |||
| !Some dialects | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|j}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|ʒ}} | ||
| | | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPAslink|ʒ}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|j}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|j}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|j}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|x}} ~ {{IPAslink|h}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|ɟ}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] | |||
| | {{IPAslink|j}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! ] romanization | |||
| | {{IPAslink|dʑ}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! |
! ] | ||
| |{{IPAslink|ʐ}} | | {{IPAslink|ʐ}} | ||
| | | |- | ||
| ! ] romanization | |||
| | | |||
| | {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|ʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink| |
| {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] (]) | |||
| ! colspan="2" |] | |||
| |{{IPAslink|dʒ}} | | {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! |
! ] | ||
| |{{IPAslink|ɟ}} | | {{IPAslink|ɟ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! |
! ] | ||
| |{{IPAslink|dʒ}} | | {{IPAslink|dʒ}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| === English === | === English === | ||
| In English, {{angbr|j}} most commonly represents the ] {{IPAlink|dʒ|/dʒ/}}. In ], |
In English, {{angbr|j}} most commonly represents the ] {{IPAlink|dʒ|/dʒ/}}. In ], {{IPA|/dʒ/}} was represented orthographically with {{angbr|cᵹ}}<ref name="hogg">{{cite book | ||
| |title=The Cambridge History of the English Language | |title=The Cambridge History of the English Language | ||
| |first=Richard M. | |first=Richard M. | ||
| Line 315: | Line 290: | ||
| |publisher=] | |publisher=] | ||
| |year=1992 | |year=1992 | ||
| |volume=3 | |||
| |isbn=0-521-26476-6 | |isbn=0-521-26476-6 | ||
| |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CCvMbntWth8C | |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CCvMbntWth8C&pg=PA39 | ||
| |pages=39 | |pages=39 | ||
| }}</ref> |
}}</ref> (equivalent to {{angbr|cg}}, as {{angbr|ᵹ}} in Old English was simply the regular form of the letter G, called ]). Middle English scribes began to use {{angbr|i}} (later {{angbr|j}}) to represent word-initial {{IPA|/dʒ/}} under the influence of ], which had a similarly pronounced phoneme deriving from Latin {{IPA|/j/}} (for example, '''''i'''est'' and later '''''j'''est''), while the same sound in other positions could be spelled as {{angbr|dg}} (for example, ''he'''dg'''e'').<ref name="hogg" /> The first ] books to make a clear distinction in writing between {{angbr|i}} and {{angbr|j}} were the ] 1st Revision Cambridge 1629 and an English grammar book published in 1633.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Butler |first=Charles |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SnySAt0gM8IC |title=The English Grammar |date=1633 |publisher=William Turner}}</ref> | ||
| Later, many other uses of {{angbr|i}} (later {{angbr|j}}) were added in ]s from French and other languages (e.g. ''ad'''j'''oin'', '''''j'''unta''). In loanwords such as ''bijou'' or '']'', {{angbr|j}} may represent {{IPA|/ʒ/}}, as in modern French. In some loanwords, including '']'', '']'', '']'' and '']'', the regular pronunciation {{IPA|/dʒ/}} is actually closer to the native pronunciation, making the use of {{IPA|/ʒ/}} an instance of ], a type of ].<ref>{{cite book | |||
| |title=Accents of English 1: An Introduction | |title=Accents of English 1: An Introduction | ||
| |first=John | |first=John | ||
| Line 328: | Line 306: | ||
| |pages=108 | |pages=108 | ||
| |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Ty5RoXyTKQsC | |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Ty5RoXyTKQsC | ||
| }}</ref> Occasionally, {{angbr|j}} represents |
}}</ref> Occasionally, {{angbr|j}} represents its original {{IPA|/j/}} sound, as in '']'' and '']''. In words of Spanish origin, such as ''jalapeño'', English speakers usually pronounce {{angbr|j}} as the ] {{IPAc-en|h}}, an approximation of the Spanish pronunciation of {{angbr|j}} (usually transcribed as a ] {{IPAblink|x}}, although some ] use glottal {{IPAblink|h}}). | ||
| In English, {{angbr|j}} is the ] in words, being more frequent only than {{angbr|]}}, {{angbr|]}}, and {{angbr|]}}. It is, however, quite common in proper nouns, especially personal names. | In English, {{angbr|j}} is the ] in words, being more frequent only than {{angbr|]}}, {{angbr|]}}, and {{angbr|]}}. It is, however, quite common in ], especially personal names. | ||
| === Other languages === | |||
| === Romance languages === | |||
| In the ], {{angbr|j}} has generally developed from its original palatal approximant value in ] to some kind of ]. In ], ], ] (except ]), and ] it has been fronted to the ] {{IPAslink|ʒ}} (like {{angbr|s}} in English ''mea'''s'''ure''). In Valencian and ], it has the same sound as in English, {{IPAslink|dʒ}}. In ], by contrast, it has been both ] and backed from an earlier {{IPAslink|ʝ}} to a present-day {{IPAslink|x}} or {{IPAslink|h}},<ref>{{cite book | |||
| ] | |||
| The great majority of ], such as ], ], ], ], ] and ], use {{angbr|j}} for the ] {{IPAslink|j}}, which is usually represented by the letter {{angbr|y}} in English. Notable exceptions are ], ] and (to a lesser degree) ]. {{angbr|j}} also represents {{IPAslink|j}} in ], and those ], ] and ] that use the Latin alphabet, such as ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. Some related languages, such as Serbo-Croatian and ], also adopted {{angbr|j}} into the ] for the same purpose. Because of this standard, the ] letter was chosen to be used in the ] as the phonetic symbol for the sound. | |||
| ==== Romance languages ==== | |||
| In the ], {{angbr|j}} has generally developed from its original palatal approximant value in ] to some kind of ]. In ], ], ], and ] it has been fronted to the ] {{IPAslink|ʒ}} (like {{angbr|s}} in English ''mea'''s'''ure''). In ], by contrast, it has been both ] and backed from an earlier {{IPAslink|ʝ}} to a present-day {{IPAslink|x}} ~ {{IPAslink|h}},<ref>{{cite book | |||
| |title=A History of the Spanish Language | |title=A History of the Spanish Language | ||
| |url=https://archive.org/details/historyofspanish0000penn | |url=https://archive.org/details/historyofspanish0000penn | ||
| Line 351: | Line 323: | ||
| }}</ref> with the actual phonetic realization depending on the speaker's dialect. | }}</ref> with the actual phonetic realization depending on the speaker's dialect. | ||
| ⟨j⟩ is not commonly used in modern standard ] spelling. Only proper nouns (such as ] and ]), ] words (]), or words borrowed from foreign languages have {{angbr|j}}. The proper nouns and Latin words are pronounced with the ] {{IPAslink|j}}, while words borrowed from foreign languages tend to follow that language's pronunciation of {{angbr|j}}. Until the 19th century, {{angbr|j}} was used instead of non-syllabic {{angbr|i}} in word-initial and intervocalic positions (as in ''Savoja'') and as a replacement for final ''-ii''; this rule was quite strict in official writing. {{angbr|j}} is also used to render {{IPAslink|j}} in dialectal spelling, ''e.g.'' ] {{angbr|ajo}} {{IPA|it-IT-RM|ˈajjo]|}} (garlic; {{Cf.}}Italian ''aglio'' {{IPA|it|ˈaʎʎo|}}). The Italian novelist ] used {{angbr|j}} in vowel groups in his works written in Italian; he also wrote in his native ], which still uses the letter {{angbr|j}} to represent {{IPAslink|j}} (and sometimes also or , depending on its environment).<ref>{{cite book |last=Cipolla |first=Gaetano |title=The Sounds of Sicilian: A Pronunciation Guide |year=2007 |publisher=Legas |location=Mineola, NY |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pZy-gVVN64kC&pg=PA11 |pages=11–12 |isbn=9781881901518 |author-link=Gaetano Cipolla |access-date=2013-03-31}}</ref> | |||
| === Other European languages === | |||
| The great majority of ], such as ], ], ], ], ] and ], use {{angbr|j}} for the ] {{IPAslink|j}}, which is usually represented by the letter {{angbr|y}} in English. Other than English, notable exceptions are ], where it represents {{IPAslink|dʒ}}, and ], where it represents both {{IPAslink|j}} and {{IPAslink|ʒ}}. | |||
| The letter also represents {{IPAslink|j}} in ], the ] languages spoken in Europe, and those ] and ] that use the Latin alphabet, such as ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. Some related languages, such as Serbo-Croatian and ], also adopted {{angbr|j}} into the ] for the same purpose. | |||
| The ], though a ], has been deeply influenced by the Romance languages (especially Sicilian), and also uses {{angbr|j}} for {{IPAslink|j}}. | |||
| ==== Basque ==== | |||
| In ], the ] represented by {{angbr|j}} has a variety of realizations according to the regional dialect: {{IPA|}} (the last one is typical of ]). | In ], the ] represented by {{angbr|j}} has a variety of realizations according to the regional dialect: {{IPA|}} (the last one is typical of ]). | ||
| === Other languages === | |||
| Among non-European languages that have adopted the ], {{angbr|j}} stands for {{IPAslink|ʒ}} in ] and ], for {{IPAslink|ʐ}} in ] |
Among non-European languages that have adopted the ], {{angbr|j}} stands for {{IPAslink|ʒ}} in ] and ], for {{IPAslink|ʐ}} in ], and for {{IPAslink|dʒ}} in ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. It represents a ] {{IPAslink|ɟ}} in ], ] and ]. In ], {{angbr|j}} stands for a voiceless alveolar plosive, {{IPAslink|t}}. | ||
| {{angbr|j}} stands for {{IPAslink|dʒ}} in the romanization systems of most of the ] such as ] and ] and stands for {{IPAslink|dʑ}} in the |
{{angbr|j}} stands for {{IPAslink|dʒ}} in the romanization systems of most of the ], such as ] and ], and stands for {{IPAslink|dʑ}} in the romanization of ] and ]. | ||
| For ]s, {{angbr|j}} stands for {{IPAslink|t͡ɕ}} in ] ] system, the unaspirated equivalent of {{angbr|q}} ({{IPAslink|t͡ɕʰ}}). In ], {{angbr|j}} stands for Mandarin Chinese {{IPAslink|ʐ}}. ] of ] and ] for ], {{angbr|j}} stands for {{IPAslink|z}} and {{IPAslink|ʑ}}, or {{IPAslink|d͡z}} and {{IPAslink|d͡ʑ}}, depending on accents. In |
For ]s, {{angbr|j}} stands for {{IPAslink|t͡ɕ}} in the ] ] system, the unaspirated equivalent of {{angbr|q}} ({{IPAslink|t͡ɕʰ}}). In ], {{angbr|j}} stands for Mandarin Chinese {{IPAslink|ʐ}}. ] of ] and ] for ], {{angbr|j}} stands for {{IPAslink|z}} and {{IPAslink|ʑ}}, or {{IPAslink|d͡z}} and {{IPAslink|d͡ʑ}}, depending on accents. In ], {{angbr|j}} stands for {{IPAslink|j}} in ] and {{IPAslink|t͡s}} in ]. | ||
| The ] does not use the letter {{angbr|j}}, although it is used in some proper names and non-standard transcriptions to represent either {{lang|th|จ}} {{IPA|}} or {{lang|th|ช}} {{IPA|}} (the latter following Pali/Sanskrit root equivalents). | The ] does not use the letter {{angbr|j}}, although it is used in some proper names and non-standard transcriptions to represent either {{lang|th|จ}} {{IPA|}} or {{lang|th|ช}} {{IPA|}} (the latter following ]/] root equivalents). | ||
| In romanized ], {{angbr|j}} represents ځ, pronounced {{IPA|}}. | In romanized ], {{angbr|j}} represents ځ, pronounced {{IPA|}}. | ||
| In the ''Qaniujaaqpait'' spelling of the ] language, {{angbr|j}} is used to transcribe {{IPAslink|j}}. | In ] and in the '']'' spelling of the ] language, {{angbr|j}} is used to transcribe {{IPAslink|j}}. | ||
| Following Spanish usage, {{angbr|j}} represents {{IPA|}} or similar sounds in many Latin-alphabet-based writing systems for ], such as {{IPA|}} in ] (] alphabet) and a glottal fricative in some spelling systems used for ]. | |||
| === Other writing systems === | |||
| In the ], {{angbr IPA|j}} is used for the ], and a superscript ⟨ʲ⟩ is used to represent ]. | |||
| == Other uses == | |||
| {{main article|J (disambiguation)}} | |||
| * In ], J stands for ]. | |||
| * In ], ''j'' is one of the three imaginary units of ]s. | |||
| * Also in ], ''j'' is one of the three unit vectors. | |||
| * In the ], J is the symbol for the ], the ] for ]. | |||
| * In some areas of ], ] and related fields, ''j'' is the symbol for the ] (the square root of −1) (in other fields, the letter ] is used, but this would be ambiguous as it is also the symbol for ]). | |||
| * A '''J''' can be a ] term for a ] (] cigarette) | |||
| == Related characters == | == Related characters == | ||
| <!-- Please only list characters (symbols in a writing system, but not just convenience code points in Unicode) that are actually related in terms of origin to the letter that is the topic of this article. Characters that merely look subjectively similar need not apply. See ] and ] before adding more. --> | <!-- Please only list characters (symbols in a writing system, but not just convenience code points in Unicode) that are actually related in terms of origin to the letter that is the topic of this article. Characters that merely look subjectively similar need not apply. See ] and ] before adding more. --> | ||
| * 𐤉 : ] letter ], from which the following symbols originally derive | * 𐤉 : ] letter ], from which the following symbols originally derive: | ||
| * I i : Latin letter ], from which J derives | * I i : Latin letter ], from which J derives | ||
| * ȷ : ] | * ȷ : ] | ||
| * ᶡ : Modifier letter small dotless j with stroke<ref name="L204132">{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2004/04132-n2740-phonetic.pdf|title=L2/04-132 Proposal to add additional phonetic characters to the UCS|date=2004-04-19|first=Peter|last=Constable}}</ref> | * ᶡ : Modifier letter small dotless j with stroke<ref name="L204132">{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2004/04132-n2740-phonetic.pdf|title=L2/04-132 Proposal to add additional phonetic characters to the UCS|date=2004-04-19|first=Peter|last=Constable}}</ref> | ||
| * ᶨ : Modifier letter small j with crossed-tail<ref name="L204132"/> | * ᶨ : Modifier letter small j with crossed-tail<ref name="L204132"/> | ||
| * ]-specific symbols related to J: {{IPA link|ʝ}} {{IPA link|ɟ}} {{IPA link| |
* ]-specific symbols related to J: {{IPA link|ʝ}} {{IPA link|ɟ}} {{IPA link|ʲ}} {{IPA link|ʄ}} {{nounderlines|]}}<ref name="L220252">{{Cite web|title=L2/20-252R: Unicode request for IPA modifier-letters (a), pulmonic|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2020/20252r-mod-ipa-a.pdf|date=2020-11-08|first1=Kirk|last1=Miller|first2=Michael|last2=Ashby}}</ref> | ||
| * ]-specific symbols related to J: | * ]-specific symbols related to J: | ||
| **{{Unichar|1D0A|LATIN LETTER SMALL CAPITAL J}}<ref name="L202141" /> | **{{Unichar|1D0A|LATIN LETTER SMALL CAPITAL J}}<ref name="L202141" /> | ||
| **{{Unichar|1D36|MODIFIER LETTER CAPITAL J}}<ref name="L202141">{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2002/02141-n2419-uralic-phonetic.pdf|title=L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS|date=2002-03-20|first1=Michael|last1=Everson|author-link1=Michael Everson|display-authors=etal}}</ref> | **{{Unichar|1D36|MODIFIER LETTER CAPITAL J}}<ref name="L202141">{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2002/02141-n2419-uralic-phonetic.pdf|title=L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS|date=2002-03-20|first1=Michael|last1=Everson|author-link1=Michael Everson|display-authors=etal}}</ref> | ||
| **{{Unichar|2C7C|LATIN SUBSCRIPT SMALL LETTER J}}<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2006/06215-n3070.pdf|title=L2/06-215: Proposal for Encoding 3 Additional Characters of the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet|date=2006-04-07|first1=Klaas|last1=Ruppel|first2=Jack|last2=Rueter|first3=Erkki I.|last3=Kolehmainen}}</ref> | **{{Unichar|2C7C|LATIN SUBSCRIPT SMALL LETTER J}}<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2006/06215-n3070.pdf|title=L2/06-215: Proposal for Encoding 3 Additional Characters of the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet|date=2006-04-07|first1=Klaas|last1=Ruppel|first2=Jack|last2=Rueter|first3=Erkki I.|last3=Kolehmainen}}</ref> | ||
| * J with ]s: ] ] ] ] | * J with ]s: ] ] ] ] ] | ||
| == |
== Other representations == | ||
| === Computing <span class="anchor" id="Computing codes"></span> === | |||
| {{charmap | {{charmap | ||
| | 004a | 006a | 0237 | name1 = Latin Capital Letter J | name2 = Latin Small Letter J | name3 = Latin Small Letter dotless J | | 004a | 006a | 0237 | FF2A | FF4A | name1 = Latin Capital Letter J | name2 = Latin Small Letter J | name3 = Latin Small Letter dotless J | ||
| | name4 = FULLWIDTH LATIN CAPITAL LETTER J | |||
| | name5 = FULLWIDTH LATIN SMALL LETTER J | |||
| | map1 = ] family | map1char1 = D1 | map1char2 = 91 | | map1 = ] family | map1char1 = D1 | map1char2 = 91 | ||
| | map2 = ] <sup>1</sup> | map2char1 = 4a | map2char2 = 6a | | map2 = ] <sup>1</sup> | map2char1 = 4a | map2char2 = 6a | ||
| Line 392: | Line 387: | ||
| :<sup>1</sup> Also for encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings. | :<sup>1</sup> Also for encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings. | ||
| Unicode also has a dotless variant, ȷ (U+0237). It is primarily used in ] and in mathematics. It is not intended to be used with diacritics since the normal j is softdotted in Unicode (that is, the dot is removed if a diacritic is to be placed above; Unicode further states that, for example i+ ¨ ≠ ı+¨ and the same holds true for j and ȷ).<ref> (at the very bottom)</ref> | Unicode also has a dotless variant, ȷ (U+0237). It is primarily used in ] and in mathematics. It is not intended to be used with diacritics since the normal j is softdotted in Unicode (that is, the dot is removed if a diacritic is to be placed above; Unicode further states that, for example, i+ ¨ ≠ ı+¨ and the same holds true for j and ȷ).<ref> (at the very bottom)</ref> | ||
| {{anchor|Greek letter Yot}}In Unicode, a duplicate of 'J' for use as a special phonetic character in historical ] linguistics is encoded in the Greek script block as ϳ (Unicode U+03F3). It is used to denote the ] {{IPA|/j/}} in the context of Greek script. It is called "Yot" in the Unicode standard, after the German name of the letter J.<ref>Nick Nicholas, {{ |
{{anchor|Greek letter Yot}}In Unicode, a duplicate of 'J' for use as a special phonetic character in historical ] linguistics is encoded in the Greek script block as ϳ (Unicode U+03F3). It is used to denote the ] {{IPA|/j/}} in the context of Greek script. It is called "Yot" in the Unicode standard, after the German name of the letter J.<ref>Nick Nicholas, {{Webarchive|url=https://archive.today/20120805184433/http://www.tlg.uci.edu/~opoudjis/unicode/yot.html |date=2012-08-05 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fileformat.info/info/unicode/char/03f3/index.htm|title=Unicode Character 'GREEK LETTER YOT' (U+03F3)|access-date=22 December 2016}}</ref> An uppercase version of this letter was added to the Unicode Standard at U+037F with the release of version 7.0 in June 2014.<ref>{{cite web|title=Unicode: Greek and Coptic|url=https://www.unicode.org/charts/PDF/Unicode-7.0/U70-0370.pdf|access-date=2014-06-26}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web | title=Unicode 7.0.0 | url=https://www.unicode.org/versions/Unicode7.0.0/ | publisher=] | access-date=2014-06-26 }}</ref> | ||
| === Wingdings smiley issue === | ==== Wingdings smiley issue ==== | ||
| In the ] font by ], the letter "J" is rendered as a ] ( |
In the ] font by ], the letter "J" is rendered as a ], sometimes creating confusion in emails after formatting is removed and a smiley turns back into an out-of-context "J".<ref>{{cite web |last=Chen |first=Raymond |title=That mysterious J |url=https://devblogs.microsoft.com/oldnewthing/20060523-10/?p=31103 |work=The Old New Thing |publisher=] |date=23 May 2006 |access-date=2023-08-03 }}</ref> (This is distinct from the Unicode code point U+263A, which renders as ☺︎). In Microsoft applications, ":)" is automatically replaced by a smiley rendered in a specific ] when composing rich text documents or ]. This autocorrection feature can be switched off or changed to a Unicode smiley.<ref name="pirillo">{{cite web|url=http://chris.pirillo.com/2010/06/25/j-smiley-outlook-email-problem-and-fix/|title=J Smiley Outlook Email: Problem and Fix!|first=Chris|last=Pirillo|date=26 June 2010|access-date=22 December 2016|archive-date=26 November 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161126164223/http://chris.pirillo.com/2010/06/25/j-smiley-outlook-email-problem-and-fix/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | ||
| <ref>{{cite web |last=Chen |first=Raymond |title=That mysterious J |url=http://blogs.msdn.com/b/oldnewthing/archive/2006/05/23/604741.aspx |work=The Old New Thing |publisher=] |date=23 May 2006 |access-date=2011-04-01 }}</ref> | |||
| ==Other |
=== Other === | ||
| * In ], J stands for ]. | |||
| * In ], ''j'' is one of the three imaginary units of ]s. | |||
| * In the ], J is the symbol for the ], the ] for ]. | |||
| * In some areas of ], ] and related fields, ''j'' is the symbol for the ] (the square root of -1) (in other fields the letter ] is used, but this would be ambiguous as it is also the symbol for ]). | |||
| * A '''J''' can be a ] term for a ] (] cigarette) | |||
| *In the ] under the ] (before 2001), a licence plate that begins with "J" for example "J123 XYZ" would correspond to a vehicle registered between August 1, 1991 and July 31, 1992. Again under the old system, a licence plate that ends with "J" for example "ABC 123J" would correspond to a vehicle that was registered between August 1, 1970 and July 31, 1971.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.platehunter.com/car-registration-years-|title=Car Registration Years {{!}} Suffix Number Plates {{!}} Platehunter|website=www.platehunter.com|access-date=2018-12-20}}</ref> | |||
| == Other representations == | |||
| {{Letter other reps | {{Letter other reps | ||
| |NATO=Juliet | |NATO=Juliet | ||
| Line 416: | Line 402: | ||
| |fingerspelling=J | |fingerspelling=J | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{clear}} | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 14:32, 13 January 2025
10th letter of the Latin alphabet This article is about the tenth letter of the Latin alphabet. For other uses, see J (disambiguation). For technical reasons, "J#" redirects here. For the programming language, see J Sharp. For the Cyrillic letter Ј, see Je (Cyrillic).
| J | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| J j | |||
 | |||
| Usage | |||
| Writing system | Latin script | ||
| Type | Alphabetic | ||
| Language of origin | Latin language | ||
| Sound values | |||
| In Unicode | U+004A, U+006A, U+0237 | ||
| Alphabetical position | 10 | ||
| History | |||
| Development |
| ||
| Time period | 14th century to present | ||
| Descendants | • Ɉ • Tittle • J | ||
| Sisters | |||
| Other | |||
| Associated graphs | j(x), ij | ||
| Writing direction | Left-to-right | ||
| This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between , / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters. | |||
| ISO basic Latin alphabet |
|---|
| AaBbCcDdEeFfGgHhIiJjKkLlMmNnOoPpQqRrSsTtUuVvWwXxYyZz |
J or j is the tenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual name in English is jay (pronounced /ˈdʒeɪ/), with a now-uncommon variant jy /ˈdʒaɪ/.
When used in the International Phonetic Alphabet for the voiced palatal approximant (the sound of "y" in "yes") it may be called yod or jod (pronounced /ˈjɒd/ or /ˈjoʊd/).
History
| Egyptian hieroglyph ꜥ | Phoenician Yodh |
Western Greek Iota |
Etruscan I |
Latin I |
Latin J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

The letter J used to be used as the swash letter I, used for the letter I at the end of Roman numerals when following another I, as in XXIIJ or xxiij instead of XXIII or xxiii for the Roman numeral twenty-three. A distinctive usage emerged in Middle High German. Gian Giorgio Trissino (1478–1550) was the first to explicitly distinguish I and J as representing separate sounds, in his Ɛpistola del Trissino de le lettere nuωvamente aggiunte ne la lingua italiana ("Trissino's epistle about the letters recently added in the Italian language") of 1524. Originally, 'I' and 'J' were different shapes for the same letter, both equally representing /i/, /iː/, and /j/; however, Romance languages developed new sounds (from former /j/ and /ɡ/) that came to be represented as 'I' and 'J'; therefore, English J, acquired from the French J, has a sound value quite different from /j/ (which represents the initial sound in the English language word "yet").
Use in writing systems
English
In English, ⟨j⟩ most commonly represents the affricate /dʒ/. In Old English, /dʒ/ was represented orthographically with ⟨cᵹ⟩ (equivalent to ⟨cg⟩, as ⟨ᵹ⟩ in Old English was simply the regular form of the letter G, called Insular G). Middle English scribes began to use ⟨i⟩ (later ⟨j⟩) to represent word-initial /dʒ/ under the influence of Old French, which had a similarly pronounced phoneme deriving from Latin /j/ (for example, iest and later jest), while the same sound in other positions could be spelled as ⟨dg⟩ (for example, hedge). The first English language books to make a clear distinction in writing between ⟨i⟩ and ⟨j⟩ were the King James Bible 1st Revision Cambridge 1629 and an English grammar book published in 1633.
Later, many other uses of ⟨i⟩ (later ⟨j⟩) were added in loanwords from French and other languages (e.g. adjoin, junta). In loanwords such as bijou or Dijon, ⟨j⟩ may represent /ʒ/, as in modern French. In some loanwords, including raj, Azerbaijan, Taj Mahal and Beijing, the regular pronunciation /dʒ/ is actually closer to the native pronunciation, making the use of /ʒ/ an instance of hyperforeignism, a type of hypercorrection. Occasionally, ⟨j⟩ represents its original /j/ sound, as in Hallelujah and fjord. In words of Spanish origin, such as jalapeño, English speakers usually pronounce ⟨j⟩ as the voiceless glottal fricative /h/, an approximation of the Spanish pronunciation of ⟨j⟩ (usually transcribed as a voiceless velar fricative [x], although some varieties of Spanish use glottal [h]).
In English, ⟨j⟩ is the fourth least frequently used letter in words, being more frequent only than ⟨z⟩, ⟨q⟩, and ⟨x⟩. It is, however, quite common in proper nouns, especially personal names.
Romance languages
In the Romance languages, ⟨j⟩ has generally developed from its original palatal approximant value in Latin to some kind of fricative. In French, Portuguese, Catalan (except Valencian), and Romanian it has been fronted to the postalveolar fricative /ʒ/ (like ⟨s⟩ in English measure). In Valencian and Occitan, it has the same sound as in English, /dʒ/. In Spanish, by contrast, it has been both devoiced and backed from an earlier /ʝ/ to a present-day /x/ or /h/, with the actual phonetic realization depending on the speaker's dialect.
⟨j⟩ is not commonly used in modern standard Italian spelling. Only proper nouns (such as Jesi and Letojanni), Latin words (Juventus), or words borrowed from foreign languages have ⟨j⟩. The proper nouns and Latin words are pronounced with the palatal approximant /j/, while words borrowed from foreign languages tend to follow that language's pronunciation of ⟨j⟩. Until the 19th century, ⟨j⟩ was used instead of non-syllabic ⟨i⟩ in word-initial and intervocalic positions (as in Savoja) and as a replacement for final -ii; this rule was quite strict in official writing. ⟨j⟩ is also used to render /j/ in dialectal spelling, e.g. Romanesco dialect ⟨ajo⟩ [ˈajjo]] (garlic; cf. Italian aglio [ˈaʎʎo]). The Italian novelist Luigi Pirandello used ⟨j⟩ in vowel groups in his works written in Italian; he also wrote in his native Sicilian language, which still uses the letter ⟨j⟩ to represent /j/ (and sometimes also or , depending on its environment).
Other European languages
The great majority of Germanic languages, such as German, Dutch, Icelandic, Swedish, Danish and Norwegian, use ⟨j⟩ for the palatal approximant /j/, which is usually represented by the letter ⟨y⟩ in English. Other than English, notable exceptions are Scots, where it represents /dʒ/, and Luxembourgish, where it represents both /j/ and /ʒ/.
The letter also represents /j/ in Albanian, the Uralic languages spoken in Europe, and those Slavic and Baltic languages that use the Latin alphabet, such as Polish, Czech, Serbo-Croatian, Slovak, Slovenian, Latvian and Lithuanian. Some related languages, such as Serbo-Croatian and Macedonian, also adopted ⟨j⟩ into the Cyrillic alphabet for the same purpose.
The Maltese language, though a Semitic language, has been deeply influenced by the Romance languages (especially Sicilian), and also uses ⟨j⟩ for /j/.
In Basque, the diaphoneme represented by ⟨j⟩ has a variety of realizations according to the regional dialect: (the last one is typical of Gipuzkoa).
Other languages
Among non-European languages that have adopted the Latin script, ⟨j⟩ stands for /ʒ/ in Turkish and Azerbaijani, for /ʐ/ in Tatar, and for /dʒ/ in Indonesian, Somali, Malay, Igbo, Shona, Oromo, Turkmen, and Zulu. It represents a voiced palatal plosive /ɟ/ in Konkani, Yoruba and Swahili. In Kiowa, ⟨j⟩ stands for a voiceless alveolar plosive, /t/.
⟨j⟩ stands for /dʒ/ in the romanization systems of most of the languages of India, such as Hindi and Telugu, and stands for /dʑ/ in the romanization of Japanese and Korean.
For Chinese languages, ⟨j⟩ stands for /t͡ɕ/ in the Mandarin Chinese pinyin system, the unaspirated equivalent of ⟨q⟩ (/t͡ɕʰ/). In Wade–Giles, ⟨j⟩ stands for Mandarin Chinese /ʐ/. Pe̍h-ōe-jī of Hokkien and Tâi-lô for Taiwanese Hokkien, ⟨j⟩ stands for /z/ and /ʑ/, or /d͡z/ and /d͡ʑ/, depending on accents. In Cantonese, ⟨j⟩ stands for /j/ in Jyutping and /t͡s/ in Yale.
The Royal Thai General System of Transcription does not use the letter ⟨j⟩, although it is used in some proper names and non-standard transcriptions to represent either จ or ช (the latter following Pali/Sanskrit root equivalents).
In romanized Pashto, ⟨j⟩ represents ځ, pronounced .
In Greenlandic and in the Qaniujaaqpait spelling of the Inuktitut language, ⟨j⟩ is used to transcribe /j/.
Following Spanish usage, ⟨j⟩ represents or similar sounds in many Latin-alphabet-based writing systems for indigenous languages of the Americas, such as in Mayan languages (ALMG alphabet) and a glottal fricative in some spelling systems used for Aymara.
Other writing systems
In the International Phonetic Alphabet, ⟨j⟩ is used for the voiced palatal approximant, and a superscript ⟨ʲ⟩ is used to represent palatalization.
Other uses
Main article: J (disambiguation)- In international licence plate codes, J stands for Japan.
- In mathematics, j is one of the three imaginary units of quaternions.
- Also in mathematics, j is one of the three unit vectors.
- In the Metric system, J is the symbol for the joule, the SI derived unit for energy.
- In some areas of physics, electrical engineering and related fields, j is the symbol for the imaginary unit (the square root of −1) (in other fields, the letter i is used, but this would be ambiguous as it is also the symbol for current).
- A J can be a slang term for a joint (marijuana cigarette)
Related characters
- 𐤉 : Semitic letter Yodh, from which the following symbols originally derive:
- I i : Latin letter I, from which J derives
- ȷ : Dotless j
- ᶡ : Modifier letter small dotless j with stroke
- ᶨ : Modifier letter small j with crossed-tail
- IPA-specific symbols related to J: ʝ ɟ ʲ ʄ 𐞘
- Uralic Phonetic Alphabet-specific symbols related to J:
- U+1D0A ᴊ LATIN LETTER SMALL CAPITAL J
- U+1D36 ᴶ MODIFIER LETTER CAPITAL J
- U+2C7C ⱼ LATIN SUBSCRIPT SMALL LETTER J
- J with diacritics: J́ j́ Ĵ ĵ J̌ ǰ Ɉ ɉ J̃ j̇̃
Other representations
Computing
| Preview | J | j | ȷ | J | j | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER J | LATIN SMALL LETTER J | LATIN SMALL LETTER DOTLESS J | FULLWIDTH LATIN CAPITAL LETTER J | FULLWIDTH LATIN SMALL LETTER J | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 74 | U+004A | 106 | U+006A | 567 | U+0237 | 65322 | U+FF2A | 65354 | U+FF4A |
| UTF-8 | 74 | 4A | 106 | 6A | 200 183 | C8 B7 | 239 188 170 | EF BC AA | 239 189 138 | EF BD 8A |
| Numeric character reference | J |
J |
j |
j |
ȷ |
ȷ |
J |
J |
j |
j |
| Named character reference | ȷ | |||||||||
| EBCDIC family | 209 | D1 | 145 | 91 | ||||||
| ASCII | 74 | 4A | 106 | 6A | ||||||
- Also for encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
Unicode also has a dotless variant, ȷ (U+0237). It is primarily used in Landsmålsalfabet and in mathematics. It is not intended to be used with diacritics since the normal j is softdotted in Unicode (that is, the dot is removed if a diacritic is to be placed above; Unicode further states that, for example, i+ ¨ ≠ ı+¨ and the same holds true for j and ȷ).
In Unicode, a duplicate of 'J' for use as a special phonetic character in historical Greek linguistics is encoded in the Greek script block as ϳ (Unicode U+03F3). It is used to denote the palatal glide /j/ in the context of Greek script. It is called "Yot" in the Unicode standard, after the German name of the letter J. An uppercase version of this letter was added to the Unicode Standard at U+037F with the release of version 7.0 in June 2014.
Wingdings smiley issue
In the Wingdings font by Microsoft, the letter "J" is rendered as a smiley face, sometimes creating confusion in emails after formatting is removed and a smiley turns back into an out-of-context "J". (This is distinct from the Unicode code point U+263A, which renders as ☺︎). In Microsoft applications, ":)" is automatically replaced by a smiley rendered in a specific font face when composing rich text documents or HTML emails. This autocorrection feature can be switched off or changed to a Unicode smiley.
Other
| NATO phonetic | Morse code |
| Juliet |
▄ ▄▄▄ ▄▄▄ ▄▄▄ |

|
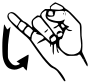
|

|

| |
| Signal flag | Flag semaphore | American manual alphabet (ASL fingerspelling) | British manual alphabet (BSL fingerspelling) | Braille dots-245 Unified English Braille |
References
- "J-letter". Encyclopedia Britannica.
- "J", Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1989)
- "J" and "jay", Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged (1993)
- "yod". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- "Wörterbuchnetz". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 22 December 2016.
- De le lettere nuωvamente aggiunte ne la lingua Italiana in Italian Wikisource.
- ^ Hogg, Richard M.; Norman Francis Blake; Roger Lass; Suzanne Romaine; R. W. Burchfield; John Algeo (1992). The Cambridge History of the English Language. Vol. 3. Cambridge University Press. p. 39. ISBN 0-521-26476-6.
- Butler, Charles (1633). The English Grammar. William Turner.
- Wells, John (1982). Accents of English 1: An Introduction. Cambridge, UN: Cambridge University Press. p. 108. ISBN 0-521-29719-2.
- Penny, Ralph John (2002). A History of the Spanish Language. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-01184-1.
- Cipolla, Gaetano (2007). The Sounds of Sicilian: A Pronunciation Guide. Mineola, NY: Legas. pp. 11–12. ISBN 9781881901518. Retrieved 2013-03-31.
- ^ Constable, Peter (2004-04-19). "L2/04-132 Proposal to add additional phonetic characters to the UCS" (PDF).
- Miller, Kirk; Ashby, Michael (2020-11-08). "L2/20-252R: Unicode request for IPA modifier-letters (a), pulmonic" (PDF).
- ^ Everson, Michael; et al. (2002-03-20). "L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS" (PDF).
- Ruppel, Klaas; Rueter, Jack; Kolehmainen, Erkki I. (2006-04-07). "L2/06-215: Proposal for Encoding 3 Additional Characters of the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet" (PDF).
- The Unicode Standard, Version 8.0, p. 293 (at the very bottom)
- Nick Nicholas, "Yot" Archived 2012-08-05 at archive.today
- "Unicode Character 'GREEK LETTER YOT' (U+03F3)". Retrieved 22 December 2016.
- "Unicode: Greek and Coptic" (PDF). Retrieved 2014-06-26.
- "Unicode 7.0.0". Unicode Consortium. Retrieved 2014-06-26.
- Chen, Raymond (23 May 2006). "That mysterious J". The Old New Thing. MSDN Blogs. Retrieved 2023-08-03.
- Pirillo, Chris (26 June 2010). "J Smiley Outlook Email: Problem and Fix!". Archived from the original on 26 November 2016. Retrieved 22 December 2016.
External links
- [REDACTED] The dictionary definition of J at Wiktionary
- [REDACTED] The dictionary definition of j at Wiktionary
- "J" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 15 (11th ed.). 1911.
| Latin script | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alphabets (list) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Letters (list) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Multigraphs |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Keyboard layouts (list) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical Standards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current Standards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
