| Revision as of 02:43, 21 March 2008 editBlindelement99 (talk | contribs)1 edit rosemary nesbitt is not the oldest resident← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 17:17, 3 January 2025 edit undoHushpuckena (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers84,043 edits →Climate: copy edit | ||
| (698 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|City in Oswego County, New York, US}} | |||
| {{wiktionarypar|Oswego}} | |||
| {{distinguish|Owego (disambiguation){{!}}Owego}} | |||
| {{Infobox Settlement | |||
| {{Use American English|date=December 2022}} | |||
| |official_name = City of Oswego | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=December 2022}} | |||
| |settlement_type = ] | |||
| {{Infobox settlement | |||
| |nickname = The Port City | |||
| | |
| name = Oswego | ||
| | |
| official_name = City of Oswego | ||
| | settlement_type = ] | |||
| |imagesize = | |||
| | |
| nickname = The Port City | ||
| | |
| motto = "Where the Water Never Ends"<br/>"Cool by Nature" | ||
| | |
| image_skyline = Market House Oswego NY Nov 08.jpg | ||
| | |
| imagesize = | ||
| | image_caption = Market House, Oswego, NY | |||
| |pushpin_label_position = <!-- the position of the pushpin label: left, right, top, bottom, none --> | |||
| | image_flag = | |||
| |pushpin_map_caption =Location within the state of New York | |||
| | |
| image_seal = | ||
| |image_map |
| image_map = Oswego County New York incorporated and unincorporated areas Oswego highlighted.svg | ||
| |mapsize |
| mapsize = 260px | ||
| |map_caption |
| map_caption = Location in ] and the state of ]. | ||
| | subdivision_type = ] | |||
| |image_map1 = | |||
| | subdivision_name = {{Flag|United States}} | |||
| |mapsize1 = | |||
| | subdivision_type1 = ] | |||
| |map_caption1 = | |||
| | subdivision_name1 = ] | |||
| |subdivision_type = ] | |||
| | subdivision_type2 = ] | |||
| |subdivision_name = ] | |||
| | subdivision_name2 = ] | |||
| |subdivision_type1 = ] | |||
| | government_type = ] | |||
| |subdivision_name1 = ] | |||
| | leader_title = ] | |||
| |subdivision_type2 = ] | |||
| | |
| leader_name = Robert A. Corradino (]) | ||
| | leader_title1 = ] | |||
| |government_type = | |||
| | leader_name1 = {{Collapsible list | |||
| |leader_title = Mayor | |||
| | |
|title = Member List | ||
| |frame_style = border:none; padding: 0; | |||
| |established_title = | |||
| |title_style = <!-- (optional) --> | |||
| |established_date = 1796 | |||
| |list_style = text-align:left;display:none; | |||
| |area_magnitude = | |||
| |1 = • W1: Kyle Walton (]) | |||
| |area_total_km2 = 29.1 | |||
| |2 = • W2: Shawn Burridge (]) | |||
| |area_total_sq_mi = 11.2 | |||
| |3 = • W3: Jessie Vanucchi (]) | |||
| |area_land_km2 = 7.7 | |||
| |4 = • W4: Shawn P. Walker (]) | |||
| |area_land_sq_mi = 7.7 | |||
| |5 = • W5: John B. Gosek (]) | |||
| |area_water_km2 = 3.6 | |||
| |6 = • W6: Tim Plunkett (]) | |||
| |area_water_sq_mi = 3.6 | |||
| |7 = • W7: Peter Allen (]) | |||
| |area_water_percent = 31 | |||
| |area_urban_km2 = | |||
| |area_urban_sq_mi = | |||
| |area_metro_km2 = | |||
| |area_metro_sq_mi = | |||
| |latd = 43 |latm = 27 |lats = 17 |latNS = N | |||
| |longd = 76 |longm = 30 |longs = 24 |longEW = W | |||
| |population_as_of = 2000 | |||
| |population_note = | |||
| |population_total = 17954 | |||
| |population_density_km2 = 905.0 | |||
| |population_density_sq_mi = 2343.4 | |||
| |population_metro = | |||
| |population_density_metro_km2 = | |||
| |population_density_metro_sq_mi = | |||
| |population_urban = 18,096 (2000 census) | |||
| |timezone = ] | |||
| |utc_offset = -5 | |||
| |timezone_DST = EDT | |||
| |Zip code = 13126 | |||
| |utc_offset_DST = -4 | |||
| |elevation_m = 87 | |||
| |elevation_ft = 285 | |||
| |website = http://oswegony.org | |||
| |postal_code_type = ] | |||
| |postal_code = 13126 | |||
| |area_code = ] | |||
| |blank_name = ] | |||
| |blank_info = 36-55574 | |||
| |blank1_name = ] feature ID | |||
| |blank1_info = 0959525 | |||
| |footnotes = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| | established_title = As a Fort | |||
| '''Oswego''' is a ] in ], ], ]. The population was 18,096 at the ]. The ] population estimate for the city of Oswego is 17,705. Oswego is located on ] in north-central ] and promotes itself as "The Port City of Central New York". It is the county seat of ]. | |||
| | established_date = {{start date and age|1796}} | |||
| | established_title2 = Incorporated (city) | |||
| | established_date2 = {{start date and age|1848}} | |||
| | area_magnitude = | |||
| | area_total_km2 = 29.08 | |||
| | area_total_sq_mi = 11.23 | |||
| | area_land_km2 = 19.72 | |||
| | area_land_sq_mi = 7.61 | |||
| | area_water_km2 = 9.36 | |||
| | area_water_sq_mi = 3.61 | |||
| | area_water_percent = 31 | |||
| | area_urban_km2 = | |||
| | area_urban_sq_mi = | |||
| | area_metro_km2 = | |||
| | area_metro_sq_mi = | |||
| | coordinates = {{coord|43|27|17|N|76|30|24|W|region:US-NY|display=inline,title}} | |||
| | population_as_of = ] | |||
| | population_footnotes = | |||
| | population_note = | |||
| | population_total = 16921 | |||
| | population_density_km2 = 858.06 | |||
| | population_density_sq_mi = 2222.35 | |||
| | population_metro = | |||
| | population_density_metro_km2 = | |||
| | population_density_metro_sq_mi = | |||
| | population_demonym = Oswegonian | |||
| | utc_offset = −5 | |||
| | timezone_DST = ] | |||
| | utc_offset_DST = −4 | |||
| | elevation_m = 87 | |||
| | elevation_ft = 285 | |||
| | website = | |||
| | postal_code_type = ] | |||
| | postal_code = 13126 | |||
| | area_code = ] | |||
| | blank_name = ] | |||
| | blank_info = 36-55574 | |||
| | blank1_name = ] feature ID | |||
| | blank1_info = 0959525 | |||
| | footnotes = | |||
| | unit_pref = Imperial | |||
| | area_footnotes = <ref name="TigerWebMapServer">{{cite web|title=ArcGIS REST Services Directory|url=https://tigerweb.geo.census.gov/arcgis/rest/services/TIGERweb/Places_CouSub_ConCity_SubMCD/MapServer|publisher=United States Census Bureau|accessdate=September 20, 2022}}</ref> | |||
| | established_title1 = Incorporated (village) | |||
| | established_date1 = {{start date and age|1828}} | |||
| | timezone1 = ] | |||
| | pop_est_as_of = | |||
| | pop_est_footnotes = | |||
| | population_est = | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Oswego''' ({{IPAc-en|ɒ|s|ˈ|w|iː|g|oʊ}}) is a ] in ], United States. The population was 16,921 at the ].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Explore Census Data |url=https://data.census.gov/cedsci/all?q=Oswego%20city,%20New%20York |access-date=August 31, 2022 |website=data.census.gov}}</ref> Oswego is situated at the mouth of the ] on the southeastern shore of ] in ], about 40 miles (64 km) northwest of ] and 74 miles (119 km) east-northeast of ] by road. The city promotes itself as "The Port City of Central New York." It is the county seat of Oswego County. | |||
| The first European settlement at Oswego was a British trading post established in 1722, and it was first incorporated as a village in 1828 before becoming a city in 1848. British forces briefly captured the city during the ], but were defeated nearby later that same month. The canalization of the Oswego River was a major boon to Oswego, attracting settlement and investment; this was later bolstered by its status as a rail hub for much of the 19th and 20th centuries, though this status had begun to decline by the 1940s. During ], ] was the site of the only Jewish refugee camp in the United States. Today, the city's economy is primarily based around manufacturing and services. | |||
| The city of Oswego is a governmental entity. It is bordered by the Towns of ], ], and ] to the west, south, and east, respectively, and by ] to the north. | |||
| Oswego lies within the Syracuse Metropolitan Statistical Area | |||
| Oswego is governed by a mayor, currently Republican Rob Corradino, and a city council. The city is located within the ], and is also inside Syracuse's broader media market. It is bordered by the towns of ], ], and ] to the west, south, and east, respectively; and by ] to the north. ] is a nationally known automobile racing facility. The ] is located just outside the city in the town of Oswego, on the shores of Lake Ontario, and is a major force in the area. | |||
| The ] is located just outside the city on the lake. | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| The site was first visited in ] by the ] explorer ]. The ] established a trading post in the area in ] and fortified it with a log palisade later called ]. In ] they added ] on the northeast side of the river. | |||
| ===Early history=== | |||
| In August ], French forces defeated the British in the ], capturing the fort during the ]. | |||
| The ] established a trading post in the area in 1722 and fortified it with a log palisade later called ], named after the native ] ] "os-we-go" meaning "pouring out place."<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.oswegony.org/explore/history|title=History | Oswego New York}}</ref> The first fortification on the site of the current ] was built by the British in 1755 and called the "Fort of the Six Nations." | |||
| ===Military base=== | |||
| Permanent settlement began in the early ], and the ], a branch of the ], reached the area in ]. The city was incorporated in ]. When the city incorporated its area and population were removed from the figures reported for the towns. | |||
| ] | |||
| Fort Ontario was destroyed by the French upon capturing it in the ], during the ]. Construction of a second British fort began on the same site in 1759, but Fort Ontario was only used as a cannon emplacement. During the American Revolution, the British abandoned the Fort, and in 1778, American troops destroyed it. In 1782, the British reoccupied Fort Ontario, and didn't forfeit it to the U.S. until 1796, thirteen years after the cessation of hostilities in the Revolution. | |||
| ] | |||
| During the ], a weaker American garrison at Fort Ontario was ] by superior British forces<ref>{{Cite magazine|date=1864|title=SCENES IN THE WAR OF 1812: CLOSING OPERATIONS OF THE ARMY OF THE NORTH.|magazine=Harper's Magazine|volume=28|pages=149|via=Archive.org}}</ref> in order to stem the flow of supplies from the interior of New York state, but were later ] near Oswego later that month. Throughout the 19th Century, the U.S. military maintained a presence at Fort Ontario. | |||
| ===Growth=== | |||
| Oswego is home to the ] and once was a major ] hub for the ], ]/], and ] railways. Three stations remain: two passenger (] and ]) and one freight (NYC) as does a rather large trestle over the Oswego River. The tunnel on a local hiking trail in the city was the north end of the ]. | |||
| Oswego was incorporated as a village on March 14, 1828,<ref> by Joshua Victor Hopkins Clark and spouse Jenna Arcese (Syracuse, 1849; page 391)</ref> and the ], a branch of the ], reached the area in 1829. The city was incorporated in 1848. When the city incorporated, its area and population were removed from the figures reported for the towns. | |||
| In the 1850s, at the height of a popular ] movement occurring in the United States, in turn stimulating growth, Oswego was the home of the ''Oswego Water Cure'' establishment, which ] reportedly visited in August 1850.<ref name="SamaritanMedCenter">{{cite book|chapter=Stonewall Jackson and the Henderson Hydropath|title=in Samaritan Medical Center Newsletter|volume=42|chapter-url=http://library.samaritanhealth.com/library/Newsletter/SMCNewsletter42.pdf|author=Samaritan Medical Center|date=September 2008|access-date=December 13, 2009|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/5tFoHOA1J?url=http://library.samaritanhealth.com/library/Newsletter/SMCNewsletter42.pdf|archive-date=October 5, 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Oswego was home to almost 1,000 ]ish refugees during ]. ] was the first and only attempt by the ] to shelter Jewish refugees during the war. Oswego also has the Safe Haven Museum to commemorate the stories of the refugees. | |||
| ===Railroads' role in growth=== | |||
| {{wide image|Oswego NY c1909 LOC pan 6a14162.jpg|2000px|<center>''1909 panorama''</center>}} | |||
| Oswego is home to the ] and once was a hub for several major ]: the ] (NYC), the ] (DL&W) and the ] (O&W). Railways operated a ] for fueling steamships at the Port of Oswego. Into the mid-1940s, the DL&W had daily passenger service from ], through ], to ] ending in Oswego.<ref>Lackawanna Railroad timetable, June 8, 1946, Table 7</ref> The New York Central last had passenger service between Oswego, ] and Syracuse in 1951.<ref>New York Central timetable, June 1951, Table 48 http://streamlinermemories.info/NYC/NYC51-6TT.pdf</ref> Former NYC and DL&W passenger stations remain, as does a NYC freight station. Nothing remains of the O&W, which was abandoned in its entirety on March 30, 1957. The tunnel from the former O&W is used as a ]. | |||
| {{wide image|Oswego NY c1909 LOC pan 6a14162.jpg|2000px|align-cap=center|''1909 panorama''}} | |||
| ==Geography== | |||
| According to the ], the city has a total area of 11.2 ]s (29.1 ]), of which, 7.7 square miles (19.8 km²) of it is land and 3.6 square miles (9.2 km²) of it (31.76%) is water. | |||
| ===Fort Ontario=== | |||
| Oswego is located on the southeastern shore of ] at the mouth of the ], about 35 miles north of ] and 68 miles east of ]. | |||
| ] was built between 1839 and 1844. Major masonry improvements to the forts outer wall were undertaken, but left incomplete when Congress canceled its funding in 1872. By 1901, the old fort was abandoned. | |||
| ] | |||
| The ] of the ] called Fort Ontario home until the brigade was deactivated on June 1, 1940. During ] it was used for interning ] from Europe (see section below). | |||
| In 1946, the fort was transferred to the ]. At that time, it was used to house veterans and their families during the post-war period. Development of the fort as a historic site began in 1949, which included the "Safe Haven Museum." | |||
| ] (from ]) runs north/south to Oswego from ] and ]. ] runs east/west from ] to Oswego. The nearest city is ], located south of Oswego and north of Syracuse. | |||
| Today, Fort Ontario is being restored to its 1867–1872 appearance. Costumed interpreters recreate the lives of the officers, men, and civilians who garrisoned the fort in 1868–1869. | |||
| As Oswego is located on the eastern shore of ], in the center of the ], the region often sees prodigious ] accumulations. Oswego is one of the snowiest towns in America, with some winters totaling over 300 inches. Recently, there was a massive snow storm in the winter of 2007 causing the school to be closed for the week, causing them to lose their winter vacation. | |||
| ===World War II refugee camp=== | |||
| ==Demographics== | |||
| As of the ] of 2000, there were 17,954 ], 7,338 ], and 3,977 ] residing in the city. The ] was 2,343.4 people per square mile (905.0/km²). There were 8,080 ] at an average ] of 407.3 persons/km² (1,054.6 persons/sq mi). The racial makeup of the city was 95.32% ], 1.04% ], 0.33% ], 0.82% ], 1.07% from other races, and 1.42% from two or more races. ] or ] of any race were 2.80% of the population. | |||
| In 1944 amidst ], ] established a camp at the fort for survivors of ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.ushmm.org/collections/bibliography/fort-ontario-emergency-refugee-shelter|title=Fort Ontario Emergency Refugee Shelter — United States Holocaust Memorial Museum|website=www.ushmm.org|access-date=March 19, 2019}}</ref> | |||
| There were 7,338 households out of which 27.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 38.3% were ] living together, and 45.8% were non-families. 34.2% of all households were made up of individuals and 14.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.33 and the average family size was 3.00. | |||
| The fort was used as ] also known as "Safe Haven," home to approximately 982 Jewish refugees, survivors of the ], from August 1944 to February 1946. This was the only attempt by the ] to shelter ] during the war.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Contributor|title=Efforts Under Way to Elevate Fort Ontario to National, International Status|url=http://oswegocountytoday.com/efforts-under-way-to-elevate-fort-ontario-to-national-international-status/|access-date=April 4, 2017|agency=Oswego County Today|publisher=Dot Publishing|date=December 28, 2015}}</ref> | |||
| In the city the population was spread out with 22.2% under the age of 18, 16.5% from 18 to 24, 25.4% from 25 to 44, 18.7% from 45 to 64, and 17.2% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 35 years. For every 100 females there were 87.8 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 83.2 males. | |||
| Approximately 1,000 refugees were transferred to the fort from the ], a concentration camp in ], Calabria, Italy.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.edwardvictor.com/Holocaust/italy_main.htm|title=Italy|website=www.edwardvictor.com|access-date=March 19, 2019}}</ref> The refugees came from 18 different European countries. | |||
| The median income for a household in the city was ]28,248, and the median income for a family was $41,613. Males had a median income of $33,220 versus $21,729 for females. The ] for the city was $16,558. 23.0% of the population and 13.0% of families were below the poverty line. Out of the total people living in poverty, 24.2% are under the age of 18 and 12.5% are 65 or older. | |||
| The refugees were placed behind barbed wire, and given no official status, having been required to sign papers accepting their eventual return to their home countries in Europe at the end of the war. Due to political pressure, President ] allowed them to apply for citizenship.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.atlasobscura.com/articles/fort-ontario-oswego-refugees|title=The New York Community That Welcomed 1,000 WWII Refugees|last=Thompson|first=Alicia|date=March 22, 2017|website=Atlas Obscura|language=en|access-date=March 19, 2019}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2003/07/21/nyregion/59-years-ago-they-fled-to-an-internment-camp.html|title=59 Years Ago, They Fled To an Internment Camp|last=Rowe|first=Claudia|date=July 21, 2003|work=The New York Times|access-date=March 19, 2019|language=en-US|issn=0362-4331}}</ref> | |||
| Locations and communities near Oswego: | |||
| * ] - the town of Oswego | |||
| * ] - the town of Minetto south of the city | |||
| * ] - the town of Scriba east of the city | |||
| * ] - a hamlet located west of the city | |||
| * ] - a hamlet located west of the city | |||
| * ] - a community located on the west side of the city | |||
| The camp comprised 200 buildings of converted army barracks.<ref>{{Cite news|last=Blankfeld|first=Keren|date=September 11, 2020|title=The Secret History of America's Only WWII Refugee Camp|language=en-US|work=The New York Times|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2020/09/11/nyregion/oswego-jewish-refugees-world-war-two.html|access-date=September 14, 2020|issn=0362-4331}}</ref> The site is now the ]. | |||
| ==Politics == | |||
| The city is governed by a ] and ] of ] who are ] from the city's seven ]s. | |||
| ==Geography== | |||
| ==Notable Current or Former Residents== | |||
| ] | |||
| According to the ], the city has a total area of 11.2 square miles (29.1 km<sup>2</sup>), of which 7.7 square miles (19.8 km<sup>2</sup>) is land and 3.6 square miles (9.2 km<sup>2</sup>) (31.76%) is water. | |||
| Oswego is located on the southeastern shore of ] at the mouth of the ], approximately 35 miles north of ] and 69 miles east of ]. The elevation is 298 feet above sea level.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.city-data.com/city/Oswego-New-York.html|title = Oswego, New York (NY 13126) profile: Population, maps, real estate, averages, homes, statistics, relocation, travel, jobs, hospitals, schools, crime, moving, houses, news, sex offenders}}</ref> The nearest city is ], located south of Oswego and north of Syracuse. | |||
| See | |||
| As Oswego is located on the eastern shore of ], in the center of the ], the region often sees prodigious ] accumulations. Oswego is one of the snowiest towns in America, with some winters totaling over 300 inches. In 2007, Oswego gained national attention when approximately 130" (slightly less than 11 feet) of snow fell in a two-week timespan. This broke the record of the ], which blanketed the city with 102" of snow. As a result of this storm, the school district closed all facilities for a week, effectively shifting the planned winter holiday. | |||
| *] Disability Advocate and World record holder | |||
| *], only female ] ], and only woman to receive the ] | |||
| *], Doctor and ] | |||
| *], ] | |||
| *], ] golfer | |||
| *], ] hockey player | |||
| *], American Actor | |||
| *], Famous singer (former singer of metal band Anthrax) | |||
| == |
===Locations and communities near Oswego=== | ||
| * ]: the town of Oswego | |||
| *] - ] for ] ]. | |||
| * ]: the town of Minetto south of the city | |||
| *] - ] Sportscaster. | |||
| * ]: the town of Scriba east of the city | |||
| *] - ] Sportscaster. | |||
| * Southwest Oswego: a hamlet located west of the city | |||
| *] - ] for ]. | |||
| * ]: a hamlet located west of the city | |||
| *] - Former ] ] | |||
| *] - Contestant of ]. | |||
| *] - Current ] to the ] for ]. | |||
| *] - Former Senior Vice President of ]. | |||
| *] - ] and winner of the 1998 ]. | |||
| *] also attended SUNY Oswego through his sophomore year before transferring to and graduating from ]. | |||
| *Fred Festa - President and CEO of ]. Graduated from SUNY Oswego in Spring 1981 from the School of Business. | |||
| ===Climate=== | |||
| == Culture and recreation == | |||
| Oswego has a warm-summer ] (] ''Dfb'') bordering on a hot-summer climate (] ''Dfa'') characterized by cold, snowy winters and warm, often humid summers, typical of the Interior Northeast; it experiences four distinct seasons, and is located in USDA ] 6a (average extreme annual minimum temperature of -10 to -5°F/-23.3 to -20.6°C). The city is known for typically experiencing exceptionally snowy winters, with an average seasonal snowfall of 140.1 inches (356 cm); this is owed primarily to its prolific lake-effect snowfall. Lake-effect precipitation, which begins as rain when the season kicks off in September or October, also contributes to Oswego's autumn precipitation maximum, unusual in this part of ] and typically experienced on the west coast of continents. Occasionally, ] also contribute to the city's snowfall, as do ] systems. | |||
| Lake Ontario also provides significant temperature moderation, allowing for slightly warmer winters and cooler summers than locations a few miles inland; during the transitional seasons, these differences can occasionally be dramatic. As a consequence of this moderation, 90°F (32°C) days are quite rare in Oswego, and the city has never recorded a temperature reaching 100°F (38°C). The lake's cooler temperatures also inhibit thunderstorm development into midsummer, though storm activity increases into August and even through early fall as the lake warms, as do precipitation and relative humidity.<ref>{{Cite web |date=November 17, 2024 |title=U.S. Coast Pilot 6, Chapter 3 |url=https://nauticalcharts.noaa.gov/publications/coast-pilot/files/cp6/CPB6_C03_WEB.pdf}}</ref> During the fall, lake moderation often extends the growing season by days or sometimes even weeks compared to more starkly continental inland locales. {{Weather box | |||
| | location = Oswego, New York (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1926–present) | |||
| | single line = Y | |||
| | Jan record high F = 69 | |||
| | Feb record high F = 69 | |||
| | Mar record high F = 83 | |||
| | Apr record high F = 90 | |||
| | May record high F = 91 | |||
| | Jun record high F = 96 | |||
| | Jul record high F = 95 | |||
| | Aug record high F = 97 | |||
| | Sep record high F = 96 | |||
| | Oct record high F = 86 | |||
| | Nov record high F = 79 | |||
| | Dec record high F = 69 | |||
| | year record high F = 97 | |||
| | Jan avg record high F = 53.2 | |||
| | Feb avg record high F = 51.6 | |||
| | Mar avg record high F = 63.0 | |||
| | Apr avg record high F = 77.8 | |||
| | May avg record high F = 83.8 | |||
| | Jun avg record high F = 88.4 | |||
| | Jul avg record high F = 89.8 | |||
| | Aug avg record high F = 89.6 | |||
| | Sep avg record high F = 86.0 | |||
| | Oct avg record high F = 77.4 | |||
| | Nov avg record high F = 66.4 | |||
| | Dec avg record high F = 54.9 | |||
| | year avg record high F = 91.4 | |||
| | Jan high F = 31.1 | |||
| | Feb high F = 33.2 | |||
| | Mar high F = 40.9 | |||
| | Apr high F = 53.2 | |||
| | May high F = 65.7 | |||
| | Jun high F = 74.8 | |||
| | Jul high F = 79.6 | |||
| | Aug high F = 78.5 | |||
| | Sep high F = 71.6 | |||
| | Oct high F = 59.2 | |||
| | Nov high F = 47.3 | |||
| | Dec high F = 36.7 | |||
| | year high F = 56.0 | |||
| | Jan mean F = 25.0 | |||
| | Feb mean F = 26.7 | |||
| | Mar mean F = 34.2 | |||
| | Apr mean F = 45.3 | |||
| | May mean F = 56.8 | |||
| | Jun mean F = 66.1 | |||
| | Jul mean F = 71.5 | |||
| | Aug mean F = 70.4 | |||
| | Sep mean F = 63.4 | |||
| | Oct mean F = 52.1 | |||
| | Nov mean F = 41.4 | |||
| | Dec mean F = 31.3 | |||
| | year mean F = 48.7 | |||
| | Jan low F = 18.9 | |||
| | Feb low F = 20.2 | |||
| | Mar low F = 27.4 | |||
| | Apr low F = 37.3 | |||
| | May low F = 47.9 | |||
| | Jun low F = 57.4 | |||
| | Jul low F = 63.4 | |||
| | Aug low F = 62.3 | |||
| | Sep low F = 55.2 | |||
| | Oct low F = 45.1 | |||
| | Nov low F = 35.4 | |||
| | Dec low F = 26.0 | |||
| | year low F = 41.4 | |||
| | Jan avg record low F = -0.9 | |||
| | Feb avg record low F = 3.1 | |||
| | Mar avg record low F = 9.3 | |||
| | Apr avg record low F = 25.2 | |||
| | May avg record low F = 35.6 | |||
| | Jun avg record low F = 44.7 | |||
| | Jul avg record low F = 53.1 | |||
| | Aug avg record low F = 51.3 | |||
| | Sep avg record low F = 40.5 | |||
| | Oct avg record low F = 31.5 | |||
| | Nov avg record low F = 20.9 | |||
| | Dec avg record low F = 7.8 | |||
| | year avg record low F = -4.0 | |||
| | Jan record low F = −21 | |||
| | Feb record low F = −21 | |||
| | Mar record low F = −9 | |||
| | Apr record low F = 13 | |||
| | May record low F = 28 | |||
| | Jun record low F = 36 | |||
| | Jul record low F = 44 | |||
| | Aug record low F = 42 | |||
| | Sep record low F = 30 | |||
| | Oct record low F = 21 | |||
| | Nov record low F = 4 | |||
| | Dec record low F = −23 | |||
| | year record low F = −23 | |||
| | precipitation colour = green | |||
| | Jan precipitation inch = 3.76 | |||
| | Feb precipitation inch = 2.85 | |||
| | Mar precipitation inch = 3.03 | |||
| | Apr precipitation inch = 3.48 | |||
| | May precipitation inch = 3.29 | |||
| | Jun precipitation inch = 3.38 | |||
| | Jul precipitation inch = 3.37 | |||
| | Aug precipitation inch = 3.45 | |||
| | Sep precipitation inch = 3.92 | |||
| | Oct precipitation inch = 4.59 | |||
| | Nov precipitation inch = 4.12 | |||
| | Dec precipitation inch = 3.89 | |||
| | year precipitation inch = 43.13 | |||
| | Jan snow inch = 44.7 | |||
| | Feb snow inch = 35.3 | |||
| | Mar snow inch = 17.1 | |||
| | Apr snow inch = 2.8 | |||
| | May snow inch = 0.0 | |||
| | Jun snow inch = 0.0 | |||
| | Jul snow inch = 0.0 | |||
| | Aug snow inch = 0.0 | |||
| | Sep snow inch = 0.0 | |||
| | Oct snow inch = 0.2 | |||
| | Nov snow inch = 9.4 | |||
| | Dec snow inch = 30.6 | |||
| | year snow inch = 140.1 | |||
| | Jan snow depth inch = 20.0 | |||
| | Feb snow depth inch = 20.8 | |||
| | Mar snow depth inch = 12.8 | |||
| | Apr snow depth inch = 1.3 | |||
| | May snow depth inch = 0.0 | |||
| | Jun snow depth inch = 0.0 | |||
| | Jul snow depth inch = 0.0 | |||
| | Aug snow depth inch = 0.0 | |||
| | Sep snow depth inch = 0.0 | |||
| | Oct snow depth inch = 0.1 | |||
| | Nov snow depth inch = 4.0 | |||
| | Dec snow depth inch = 11.0 | |||
| | year snow depth inch = 26.3 | |||
| | unit precipitation days = 0.01 in | |||
| | Jan precipitation days = 20.1 | |||
| | Feb precipitation days = 16.4 | |||
| | Mar precipitation days = 14.6 | |||
| | Apr precipitation days = 13.8 | |||
| | May precipitation days = 12.6 | |||
| | Jun precipitation days = 11.8 | |||
| | Jul precipitation days = 11.0 | |||
| | Aug precipitation days = 10.9 | |||
| | Sep precipitation days = 11.0 | |||
| | Oct precipitation days = 15.1 | |||
| | Nov precipitation days = 16.3 | |||
| | Dec precipitation days = 18.8 | |||
| | year precipitation days = 172.4 | |||
| | unit snow days = 0.1 in | |||
| | Jan snow days = 18.2 | |||
| | Feb snow days = 14.5 | |||
| | Mar snow days = 8.5 | |||
| | Apr snow days = 2.2 | |||
| | May snow days = 0.0 | |||
| | Jun snow days = 0.0 | |||
| | Jul snow days = 0.0 | |||
| | Aug snow days = 0.0 | |||
| | Sep snow days = 0.0 | |||
| | Oct snow days = 0.3 | |||
| | Nov snow days = 5.6 | |||
| | Dec snow days = 13.0 | |||
| | year snow days = 62.3 | |||
| | source 1 = ]<ref> | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| | url = https://www.weather.gov/wrh/climate?wfo=buf | |||
| | title = NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data | |||
| | publisher = National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration | |||
| | access-date = May 16, 2021}}</ref><ref> | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| | url = https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/services/data/v1?dataset=normals-monthly-1991-2020&startDate=0001-01-01&endDate=9996-12-31&stations=USC00306314&format=pdf | |||
| | publisher = National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration | |||
| | title = Station: Oswego, NY | |||
| | work = U.S. Climate Normals 2020: U.S. Monthly Climate Normals (1991–2020) | |||
| | access-date = May 16, 2021}}</ref> | |||
| | date = July 2013 | |||
| | source = | |||
| }} | |||
| ==Transportation== | |||
| Oswego has a long history stretching back to the 15th century. Visitors can learn about the city's history by visiting museums such as the H. Lee White Marine Museum, The Richardson-Bates House, and Fort Ontario. Throughout the city and public parks, many historical monuments can be found honoring historical figures, and other forts that stood in what is now the historical district. The currently most notable historian is Rosemary Nesbitt who is immortalized by a monument in the city's signature public park; Breitbeck Park. Yearly, Rosemary Nesbitt let's down her long silver hair, dresses in a ghostly gown, and tells ghostly haunted tales spanning across the entire history of the city. | |||
| ] (from ]) runs north/south to Oswego from ] and ]. ] runs east/west from ] to Oswego. | |||
| ] provides service within Oswego and connections to ] and ]. Oswego County Public Transit provides service between Oswego and smaller communities in Oswego County.<ref>{{Cite web| title = Transportation {{!}} Oswego County Opportunities| access-date = October 20, 2018| url = https://www.oco.org/transportation}}</ref> | |||
| Dining is becoming widely recognized in Oswego with many classic restaurants, cafes, and more modern family restaurants as the city continues it's expansion eastward. | |||
| ==Demographics== | |||
| Boating, fishing, and hiking are also activities that are enjoyed by all residents and visitors. Oswego also has two ice-skating rinks, a large public pool located on the Fort Ontario grounds, bowling, and a movie theater. | |||
| {{US Census population | |||
| |1850= 12205 | |||
| |1860= 16816 | |||
| |1870= 20910 | |||
| |1880= 21116 | |||
| |1890= 21842 | |||
| |1900= 22199 | |||
| |1910= 23368 | |||
| |1920= 23626 | |||
| |1930= 22652 | |||
| |1940= 22062 | |||
| |1950= 22647 | |||
| |1960= 22155 | |||
| |1970= 20913 | |||
| |1980= 19793 | |||
| |1990= 19195 | |||
| |2000= 17954 | |||
| |2010= 18142 | |||
| |2020= 16921 | |||
| |footnote=U.S. Decennial Census<ref name="DecennialCensus">{{cite web|url=https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennial-census.html|title=Census of Population and Housing|publisher=Census.gov|access-date=June 4, 2015}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| As of the ] of 2010,<ref name="GR8">{{cite web|url=https://www.census.gov|publisher=]|access-date=May 14, 2011|title=U.S. Census website}}</ref> there were 18,142 ], 7,486 ], and 3,896 ] residing in the 8,258 ] in the city. The population density was {{convert|2,343.4|PD/sqmi|PD/km2|sp=us|adj=off}}. The racial makeup of the city was 94.1% ], 2.3% ], 0.1% ], 1.5% ], .6% from other races, and 1.5% from two or more races. ] or ] of any race were 5.1% of the population. | |||
| The median income for a household in the city was ]39,867, and the median income for a family was $57,324. Males employed full-time, year-round, had a median income of $50,074 versus $33,211 for similarly situated females. The ] for the city was $21,139. 24.2% of the population and 14.4% of families were below the poverty line. | |||
| Every year the city hosts the , a four-day festival of music, culture and food, centered around the Oswego Harbor, culminating in a fireworks display on the Saturday evening of the festival. The event is sponsored by local businesses, and the entertainment is mostly admission-free. | |||
| ==Politics== | |||
| Many native citizens of Oswego have reported to local news sources such as , , , etc. that they are becoming weary of this annual festival, as it is frequently associated with excessive drunkards, vandalism of public and private property, city-wide pollution, high food prices, debilitating traffic conditions, and lack of high-profile mainstream entertainment. | |||
| The city is governed by a ], currently Republican Rob Corradino,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Moriarty |first=Rick |date=2023-11-07 |title=Oswego to get new mayor as Billy Barlow moves on |url=https://www.syracuse.com/politics/cny/2023/11/oswego-to-get-new-mayor-as-billy-barlow-moves-on.html |access-date=2024-02-10 |website=syracuse |language=en}}</ref> and a ] of seven ] who are ] from the city's seven ]. Recent previous mayors include Republican Billy Barlow, Democrats Tom Gillen and Randy Bateman, and Republican John Gosek. | |||
| ===Political controversy=== | |||
| Despite these alleged issues, the festival continues to draw approximately 150,000+ attendants every year. | |||
| In September 2005, Oswego Mayor John Gosek was arrested by the FBI and state police in a sting operation outside of a motel near Syracuse after allegedly giving a woman $250 to arrange a sexual encounter with two 14-year-old girls. The arrest came after a three-year investigation that led to charges of the mayor using his city-issued cell phone to “persuade, induce, entice and coerce an individual under the age of 18 years to engage in sexual activity.” The charge alleged that Gosek used his phone as interstate commerce for the purposes of illegal sex and falls under a federal law that is commonly known as the ]. Gosek's term wasn't due to expire until 2007, but he resigned from office five days after his arrest. | |||
| ==Notable people==<!--consensus reached to standardize this heading per WP:WikiProject Cities/US Guideline --> | |||
| == Media == | |||
| {{More citations needed section|date=October 2012}} | |||
| *], U.S. Army soldier in the ] | |||
| *], Civil War photographer and portrait photography pioneer | |||
| *], singer of heavy metal band ]<ref>{{cite web|url= https://www.imdb.com/name/nm0068644/bio|title= Joseph Anthony Bellardini | |||
| |publisher=IMDb|access-date= October 30, 2012}}</ref> | |||
| *], formerly Smith, actor and comedian | |||
| *], ] golfer<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.pgatour.com/golfers/021646/david-branshaw/|title= David Branshaw|publisher= PGA Tour|access-date= October 30, 2012|url-status= dead|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20121026021658/http://www.pgatour.com/golfers/021646/david-branshaw/|archive-date= October 26, 2012}}</ref> | |||
| *], former New York State Senator | |||
| *], national weather anchor on NBC's TODAY | |||
| *], sixth ]<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.nga.org/cms/home/governors/past-governors-bios/page_wyoming/col2-content/main-content-list/title_chatterton_fenimore.html|title= Wyoming Governor Fenimore Chatterton|publisher=National Governors Association|access-date= October 30, 2012}}</ref> | |||
| *], ] hockey player, Olympian<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.hockeydb.com/ihdb/stats/pdisplay.php?pid=35409|title= Erik Cole|publisher=hockeydb.com|access-date= October 30, 2012}}</ref> | |||
| *], former US Congressman | |||
| *], former ] | |||
| *] (1859–1929), suffragist and peace activist | |||
| *], former US Congressman | |||
| *], racing driver | |||
| *], doctor and ] | |||
| *], ] general | |||
| *], disability advocate, poet and world record holder | |||
| *], Vice admiral, USN and ] recipient | |||
| *], former professional baseball player | |||
| *], a ] at ], specialist of ] and ]s who made significant contributions to ] | |||
| *] (1872-1938), businesswoman and clubwoman | |||
| *], founder of California Perfume Company which became Avon Cosmetics | |||
| *], businessman | |||
| *] (1863—?), business woman, author, magazine editor | |||
| *], former US Congressman | |||
| *], strongman<ref name=oswego1>{{cite web|title=He keeps his chin up, sets a Guinness Record; for Bob Natoli, of Oswego, it's about health and fitness lifestyle he's live for 30 years|url=http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G1-151726433.html|archive-url=https://archive.today/20130111074327/http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G1-151726433.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=January 11, 2013|work=Neighbors Oswego|publisher=The Post-Standard|access-date=December 24, 2012}}{{subscription required}}</ref> | |||
| * ] (1838–1900), composer and bandleader, called “the father of band music in America”<ref>{{cite web |title=Reeves, David Wallis |url=https://www.encyclopedia.com/arts/dictionaries-thesauruses-pictures-and-press-releases/reeves-david-wallis |website=Encyclopedia dot com |access-date=July 12, 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *], Nationally published cartoonist, author, and greeting card artist with American Greetings born and raised in Oswego, NY.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.prgreetings.com/rpg/btc-detail/ovrdedge-cartoons-by-dan-reynolds#.VOvGD8ZYXzI|title= PRG B2B}}</ref> | |||
| *], ] recipient | |||
| *], race car driver, author<ref>Oswego Palladium Times, Monday, April 4, 1932,</ref> | |||
| *], Wisconsin State Assemblyman<ref>'Wisconsin Blue Book 1923,' Biographical Sketch of Newcomb Spoor, pg. 624</ref> | |||
| *], member North Carolina House of Representatives, 2013 to present | |||
| *], actor | |||
| *], banker, diplomat, co-founder of '']'' magazine | |||
| *], former US Congressman | |||
| *], only female ] ], and only woman to receive the ] | |||
| *], author | |||
| *] (1840–1903), writer | |||
| *] (1828 – 1894), educator and philanthropist | |||
| ==Culture and recreation== | |||
| The city is served by and is the home to the radio stations ], ], ] (TK105), ] and ]. Oswego is served by the ] TV market. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| Oswego has a long history stretching back to the 15th century. Visitors can learn about the city's history by visiting museums such as the ], The ], and ]. Throughout the city and public parks, many historical monuments can be found honoring historical figures, and other forts that stood in what is now the historical district. The city includes a number of sites on the ] including the ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name="nris">{{NRISref|2009a}}</ref><ref name="nps1">{{cite web|url=http://www.nps.gov/history/nr/listings/20150116.htm|title=National Register of Historic Places|date=January 16, 2015|work=Weekly List of Actions Taken on Properties: 1/05/15 through 1/09/15 |publisher=National Park Service}}</ref> In September 2024, the ] was designated in the waters of southeastern ] off Oswego to protect historic ]s and areas of cultural, historical, and spiritual significance to ] of the ] and to preserve them as educational and recreational resources.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Lake Ontario National Marine Sanctuary |url=https://sanctuaries.noaa.gov/lake-ontario/ |access-date=October 14, 2024 |website=sanctuaries.noaa.gov}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://sanctuaries.noaa.gov/lake-ontario/celebrate.html |title=Lake Ontario National Marine Sanctuary Designation Ceremony |author=<!--Not stated--> |date=<!--Not stated--> |website=sanctuaries.noaa.gov |publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |access-date=October 14, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| The most notable historian was Rosemary Nesbitt, who is immortalized by a monument in the city's signature public park, Breitbeck Park. Every ], she would traditionally let down her long silver hair, dress in a ghostly gown, and tell ghostly haunted tales spanning across the entire history of the city. Nesbitt, who also founded the Marine Museum and wrote various books about the city's history, died on August 2, 2009, at the age of 84.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.palltimes.com/articles/2009/08/03/news/doc4a7622ccac56e444003853.txt |title=Historian leaves a legacy of her own - The Palladium-Times : News |publisher=Palltimes.com |access-date=August 10, 2013}}</ref> | |||
| == Education == | |||
| ], a writer best known for his popular ']' stories, was stationed at Fort Ontario, Oswego, N.Y. from 1917. From this experience he wrote the book "My war with the United States" published in 1937. | |||
| The city is part of the ]. The Oswego City School district has one ] (grades 9 - 12), one middle school (grades 7 & 8) and five elementary schools (grades K - 6). The ] (SUNY Oswego) is located just west of the city in the town of Oswego. Trinity Catholic School (formerly St. Paul's Academy) provides classes for K - 6. Oswego Community Christian School provides classes for K - 8. | |||
| Boating, fishing, and hiking are also activities that are enjoyed by residents and visitors. Oswego also has three ice-skating rinks, a large public pool located on the Fort Ontario grounds, bowling, and the historic ]. | |||
| == Trivia == | |||
| Every year the city hosts the Oswego Harborfest, a four-day festival of music, culture and food, centered around the Oswego Harbor, culminating in a fireworks display on the Saturday evening of the festival. The event is sponsored by local businesses, and the entertainment is admission-free. The festival continues to draw approximately 150,000 to 300,000 attendees every year. | |||
| An e-mail answered by ] on ] is from a resident of Oswego, and Strong Bad reads the address "Oswego, New York" as "Os' we go to New York." | |||
| In 2007, SUNY Oswego Lakers men's hockey team won the NCAA Division III Ice Hockey Championship. Garren Reisweber's goal 12:55 into overtime gave Oswego State a 4-3 win over Middlebury on March 18, 2007. The Lakers captured the school's first ever national championship in a team sport. The 2006-07 season marked the first season Oswego played in the newly built, state-of-the-art Marano Campus Center, located on Lake Ontario. The Campus Center replaced Romney Field House Ice Rink which opened in 1962,<ref name="oswego.edu">{{Cite web|url=https://www.oswego.edu/facilities-services/buildings/romney-field-house|title = Romney Field House | Facilities Services}}</ref> and is believed to be the first ice rink built within the State University of New York system. The old ice rink was transformed into a multi-use indoor facility for track, lacrosse and other intramural sports.<ref name="oswego.edu"/> | |||
| From 2005 to 2006 the ] of the ] played in the old ice rink. | |||
| ==Media== | |||
| The city is served by ''The Palladium Times'' newspaper, ''Oswego County Today'', the student-run newspaper ''The Oswegonian'', as well as ''OswegoNYlion'' and is the home to the radio stations ], ], ] and ]. Oswego also has its own television station, WTOP, which is completely student-run at the State University of New York at Oswego, and is served by the Oswego High School television station, WBUC. Oswego is served by the ] TV market. Previous media included the ''Oswego Daily News''. | |||
| ==Education== | |||
| The city is part of the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/PL20/st36_ny/schooldistrict_maps/c36075_oswego/DC20SD_C36075.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Oswego County, NY|publisher=]|access-date=2024-10-18}} - </ref> The Oswego City School district has one ] (grades 9–12), one middle school (grades 7 and 8) and five elementary schools (grades K–6). | |||
| Trinity Catholic School (formerly St. Paul's Academy) provides classes for PreK–6. Oswego Community Christian School provides classes for PreK–8. | |||
| The ] (SUNY Oswego) has portions of its property in Oswego City,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/DC20BLK/st36_ny/place/p3655574_oswego/DC20BLK_P3655574.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Oswego city, NY|publisher=]|access-date=2024-10-18|quote=State University of New York College at Oswego}}</ref> with the rest just west of the city in the Town of Oswego.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/DC20BLK/st36_ny/cousub/cs3607555585_oswego/DC20BLK_CS3607555585.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Oswego town, NY|publisher=]|access-date=2024-10-18|quote=State University of New York College at Oswego}}<br>See also: {{cite web|url=https://www2.census.gov/geo/maps/DC2020/DC20BLK/st36_ny/place/p3672327_suny_oswego/DC20BLK_P3672327.pdf|title=2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: SUNY Oswego CDP, NY|publisher=]|access-date=2024-10-18|quote=State University of New York College at Oswego}}</ref> | |||
| ==Electric power facilities== | |||
| ===Oswego generating station=== | |||
| Pursuant to Section 70 of the ], NRG Energy, Inc. (now operating as NRG Power Marketing LLC) officially received ownership of the Oswego generating station from previous owners Niagara Mohawk Power Corporation and Rochester Gas and Electric in 1999. NRG was the lowest bidder in an auction arranged by Niagara Mohawk. The facility is a 1,803-] (MW) (nameplate) plant with two ]s powered by steam heated in ] from ] (although one of the units has natural gas listed as a backup fuel). The facility went into service in 1976 (for unit 5) and 1980 (for unit 6). In 2017, it injected 39.7 ] of electric energy into the electric transmission system. This is equivalent to operating at full capacity for approximately 0.3% of the year. For comparison, the central region consumed 15,819 GWh of electric energy in 2017. Its power is sold into the electric wholesale market administered by the ]. Since the plant does not produce much electric energy on an annual basis, it is fair to assume that most of its revenue comes from the NYISO's capacity market. For example, at 1.0 ($/kW - Month), the plant would receive annual revenue of $21.6 million from the capacity market without accounting for actual energy production.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://documents.dps.ny.gov/public/Common/ViewDoc.aspx?DocRefId={7175623D-E38B-4D5E-8FE3-86A4E5129E1D}|title=ORDER PROVIDING FOR LIGHTENED REGULATION (case no. 99-E-0974)|page=1,2,6|date=October 21, 1999|access-date=November 19, 2018}}</ref><ref name="2018 GB">{{cite web|url=https://www.nyiso.com/documents/20142/2226333/2018-Load-Capacity-Data-Report-Gold-Book.pdf/7014d670-2896-e729-0992-be44eb935cc2|title=NYISO 2018 Gold Book (pdf)|work=www.nyiso.com|pages=13, 63|access-date=November 26, 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.syracuse.com/news/index.ssf/2016/02/cuomo_targets_power_plant_that_closed_after_110m_subsidy_by_national_grid_custom.html|title=Cuomo targets power plant that closed after $110M subsidy by National Grid customers|publisher=Syracuse.com|author=Tim Knauss|date=February 13, 2018|access-date=November 19, 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://icap.nyiso.com/ucap/public/auc_view_monthly_selection.do|title=NYISO ICAP Monthly Auction price website|access-date=November 19, 2018}}</ref> | |||
| According to the ]'s database management system, DMM, there was a whistle blower complaint filed against the facility (case no. 92-E-0306) in 1992, however, the DMM website for that case number says its contents were moved to the DMM website for case number 92-M-0016. As of November 2018, there are 5 orders on the DMM case number 92-M-0016 website, none of which have to do with a whistle blower complaint against Oswego generating station. | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| <references/> | |||
| ==External links |
==External links== | ||
| {{Commons and category|Oswego, New York}} | |||
| {{External links}} | |||
| {{ |
{{Wikivoyage|Oswego}} | ||
| * | {{Wiktionary|Oswego}} | ||
| * | |||
| * | * {{Dead link|date=February 2022 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Geolinks-US-cityscale|43.458333|-76.503056}} | |||
| {{Oswego County, New York}} | {{Oswego County, New York}} | ||
| {{Central New York colleges}} | |||
| {{New York}} | {{New York}} | ||
| {{New York county seats}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:17, 3 January 2025
City in Oswego County, New York, US Not to be confused with Owego.City in New York, United States
| Oswego | |
|---|---|
| City | |
| City of Oswego | |
 Market House, Oswego, NY Market House, Oswego, NY | |
| Nickname: The Port City | |
| Motto(s): "Where the Water Never Ends" "Cool by Nature" | |
 Location in Oswego County and the state of New York. Location in Oswego County and the state of New York. | |
| Coordinates: 43°27′17″N 76°30′24″W / 43.45472°N 76.50667°W / 43.45472; -76.50667 | |
| Country | |
| State | New York |
| County | Oswego |
| As a Fort | 1796; 229 years ago (1796) |
| Incorporated (village) | 1828; 197 years ago (1828) |
| Incorporated (city) | 1848; 177 years ago (1848) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor-Council |
| • Mayor | Robert A. Corradino (R) |
| • Common Council | Member List |
| Area | |
| • Total | 11.23 sq mi (29.08 km) |
| • Land | 7.61 sq mi (19.72 km) |
| • Water | 3.61 sq mi (9.36 km) 31% |
| Elevation | 285 ft (87 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 16,921 |
| • Density | 2,222.35/sq mi (858.06/km) |
| Demonym | Oswegonian |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| ZIP Code | 13126 |
| Area code | 315 |
| FIPS code | 36-55574 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0959525 |
| Website | www.oswegony.org |
Oswego (/ɒsˈwiːɡoʊ/) is a city in Oswego County, New York, United States. The population was 16,921 at the 2020 census. Oswego is situated at the mouth of the Oswego River on the southeastern shore of Lake Ontario in Upstate New York, about 40 miles (64 km) northwest of Syracuse and 74 miles (119 km) east-northeast of Rochester by road. The city promotes itself as "The Port City of Central New York." It is the county seat of Oswego County.
The first European settlement at Oswego was a British trading post established in 1722, and it was first incorporated as a village in 1828 before becoming a city in 1848. British forces briefly captured the city during the War of 1812, but were defeated nearby later that same month. The canalization of the Oswego River was a major boon to Oswego, attracting settlement and investment; this was later bolstered by its status as a rail hub for much of the 19th and 20th centuries, though this status had begun to decline by the 1940s. During World War II, Fort Ontario was the site of the only Jewish refugee camp in the United States. Today, the city's economy is primarily based around manufacturing and services.
Oswego is governed by a mayor, currently Republican Rob Corradino, and a city council. The city is located within the Syracuse metropolitan area, and is also inside Syracuse's broader media market. It is bordered by the towns of Oswego, Minetto, and Scriba to the west, south, and east, respectively; and by Lake Ontario to the north. Oswego Speedway is a nationally known automobile racing facility. The State University of New York at Oswego (SUNY Oswego) is located just outside the city in the town of Oswego, on the shores of Lake Ontario, and is a major force in the area.
History
Early history
The British established a trading post in the area in 1722 and fortified it with a log palisade later called Fort Oswego, named after the native Iroquois place name "os-we-go" meaning "pouring out place." The first fortification on the site of the current Fort Ontario was built by the British in 1755 and called the "Fort of the Six Nations."
Military base
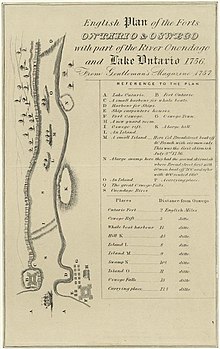
Fort Ontario was destroyed by the French upon capturing it in the Battle of Fort Ontario, during the French and Indian War. Construction of a second British fort began on the same site in 1759, but Fort Ontario was only used as a cannon emplacement. During the American Revolution, the British abandoned the Fort, and in 1778, American troops destroyed it. In 1782, the British reoccupied Fort Ontario, and didn't forfeit it to the U.S. until 1796, thirteen years after the cessation of hostilities in the Revolution.

During the War of 1812, a weaker American garrison at Fort Ontario was overwhelmed by superior British forces in order to stem the flow of supplies from the interior of New York state, but were later defeated near Oswego later that month. Throughout the 19th Century, the U.S. military maintained a presence at Fort Ontario.
Growth
Oswego was incorporated as a village on March 14, 1828, and the Oswego Canal, a branch of the Erie Canal, reached the area in 1829. The city was incorporated in 1848. When the city incorporated, its area and population were removed from the figures reported for the towns.
In the 1850s, at the height of a popular water-cure movement occurring in the United States, in turn stimulating growth, Oswego was the home of the Oswego Water Cure establishment, which Stonewall Jackson reportedly visited in August 1850.
Railroads' role in growth
Oswego is home to the Port of Oswego and once was a hub for several major railroads: the New York Central Railroad (NYC), the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (DL&W) and the New York, Ontario and Western Railway (O&W). Railways operated a coal trestle for fueling steamships at the Port of Oswego. Into the mid-1940s, the DL&W had daily passenger service from Hoboken, through Binghamton, to Syracuse ending in Oswego. The New York Central last had passenger service between Oswego, Fulton and Syracuse in 1951. Former NYC and DL&W passenger stations remain, as does a NYC freight station. Nothing remains of the O&W, which was abandoned in its entirety on March 30, 1957. The tunnel from the former O&W is used as a rail trail.
 1909 panorama
1909 panorama
Fort Ontario
Fort Ontario was built between 1839 and 1844. Major masonry improvements to the forts outer wall were undertaken, but left incomplete when Congress canceled its funding in 1872. By 1901, the old fort was abandoned.

The 2nd Brigade of the U.S. 1st Infantry Division called Fort Ontario home until the brigade was deactivated on June 1, 1940. During World War II it was used for interning Jewish refugees from Europe (see section below).
In 1946, the fort was transferred to the state of New York. At that time, it was used to house veterans and their families during the post-war period. Development of the fort as a historic site began in 1949, which included the "Safe Haven Museum."
Today, Fort Ontario is being restored to its 1867–1872 appearance. Costumed interpreters recreate the lives of the officers, men, and civilians who garrisoned the fort in 1868–1869.
World War II refugee camp
In 1944 amidst World War II, President Franklin D. Roosevelt established a camp at the fort for survivors of the Holocaust.
The fort was used as Fort Ontario Emergency Refugee Shelter also known as "Safe Haven," home to approximately 982 Jewish refugees, survivors of the Nazi Holocaust, from August 1944 to February 1946. This was the only attempt by the United States government to shelter Jewish refugees during the war.
Approximately 1,000 refugees were transferred to the fort from the Ferramonti di Tarsia, a concentration camp in Cosenza, Calabria, Italy. The refugees came from 18 different European countries.
The refugees were placed behind barbed wire, and given no official status, having been required to sign papers accepting their eventual return to their home countries in Europe at the end of the war. Due to political pressure, President Harry S. Truman allowed them to apply for citizenship.
The camp comprised 200 buildings of converted army barracks. The site is now the Safe Haven Museum.
Geography

According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 11.2 square miles (29.1 km), of which 7.7 square miles (19.8 km) is land and 3.6 square miles (9.2 km) (31.76%) is water.
Oswego is located on the southeastern shore of Lake Ontario at the mouth of the Oswego River, approximately 35 miles north of Syracuse and 69 miles east of Rochester. The elevation is 298 feet above sea level. The nearest city is Fulton, located south of Oswego and north of Syracuse.
As Oswego is located on the eastern shore of Lake Ontario, in the center of the Snowbelt, the region often sees prodigious lake effect snow accumulations. Oswego is one of the snowiest towns in America, with some winters totaling over 300 inches. In 2007, Oswego gained national attention when approximately 130" (slightly less than 11 feet) of snow fell in a two-week timespan. This broke the record of the Blizzard of 1966, which blanketed the city with 102" of snow. As a result of this storm, the school district closed all facilities for a week, effectively shifting the planned winter holiday.
Locations and communities near Oswego
- Oswego: the town of Oswego
- Minetto: the town of Minetto south of the city
- Scriba: the town of Scriba east of the city
- Southwest Oswego: a hamlet located west of the city
- Fruit Valley: a hamlet located west of the city
Climate
Oswego has a warm-summer humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb) bordering on a hot-summer climate (Köppen Dfa) characterized by cold, snowy winters and warm, often humid summers, typical of the Interior Northeast; it experiences four distinct seasons, and is located in USDA hardiness zone 6a (average extreme annual minimum temperature of -10 to -5°F/-23.3 to -20.6°C). The city is known for typically experiencing exceptionally snowy winters, with an average seasonal snowfall of 140.1 inches (356 cm); this is owed primarily to its prolific lake-effect snowfall. Lake-effect precipitation, which begins as rain when the season kicks off in September or October, also contributes to Oswego's autumn precipitation maximum, unusual in this part of North America and typically experienced on the west coast of continents. Occasionally, nor'easters also contribute to the city's snowfall, as do Alberta clipper systems.
Lake Ontario also provides significant temperature moderation, allowing for slightly warmer winters and cooler summers than locations a few miles inland; during the transitional seasons, these differences can occasionally be dramatic. As a consequence of this moderation, 90°F (32°C) days are quite rare in Oswego, and the city has never recorded a temperature reaching 100°F (38°C). The lake's cooler temperatures also inhibit thunderstorm development into midsummer, though storm activity increases into August and even through early fall as the lake warms, as do precipitation and relative humidity. During the fall, lake moderation often extends the growing season by days or sometimes even weeks compared to more starkly continental inland locales.
| Climate data for Oswego, New York (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1926–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 69 (21) |
69 (21) |
83 (28) |
90 (32) |
91 (33) |
96 (36) |
95 (35) |
97 (36) |
96 (36) |
86 (30) |
79 (26) |
69 (21) |
97 (36) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 53.2 (11.8) |
51.6 (10.9) |
63.0 (17.2) |
77.8 (25.4) |
83.8 (28.8) |
88.4 (31.3) |
89.8 (32.1) |
89.6 (32.0) |
86.0 (30.0) |
77.4 (25.2) |
66.4 (19.1) |
54.9 (12.7) |
91.4 (33.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 31.1 (−0.5) |
33.2 (0.7) |
40.9 (4.9) |
53.2 (11.8) |
65.7 (18.7) |
74.8 (23.8) |
79.6 (26.4) |
78.5 (25.8) |
71.6 (22.0) |
59.2 (15.1) |
47.3 (8.5) |
36.7 (2.6) |
56.0 (13.3) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 25.0 (−3.9) |
26.7 (−2.9) |
34.2 (1.2) |
45.3 (7.4) |
56.8 (13.8) |
66.1 (18.9) |
71.5 (21.9) |
70.4 (21.3) |
63.4 (17.4) |
52.1 (11.2) |
41.4 (5.2) |
31.3 (−0.4) |
48.7 (9.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 18.9 (−7.3) |
20.2 (−6.6) |
27.4 (−2.6) |
37.3 (2.9) |
47.9 (8.8) |
57.4 (14.1) |
63.4 (17.4) |
62.3 (16.8) |
55.2 (12.9) |
45.1 (7.3) |
35.4 (1.9) |
26.0 (−3.3) |
41.4 (5.2) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −0.9 (−18.3) |
3.1 (−16.1) |
9.3 (−12.6) |
25.2 (−3.8) |
35.6 (2.0) |
44.7 (7.1) |
53.1 (11.7) |
51.3 (10.7) |
40.5 (4.7) |
31.5 (−0.3) |
20.9 (−6.2) |
7.8 (−13.4) |
−4.0 (−20.0) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −21 (−29) |
−21 (−29) |
−9 (−23) |
13 (−11) |
28 (−2) |
36 (2) |
44 (7) |
42 (6) |
30 (−1) |
21 (−6) |
4 (−16) |
−23 (−31) |
−23 (−31) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.76 (96) |
2.85 (72) |
3.03 (77) |
3.48 (88) |
3.29 (84) |
3.38 (86) |
3.37 (86) |
3.45 (88) |
3.92 (100) |
4.59 (117) |
4.12 (105) |
3.89 (99) |
43.13 (1,096) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 44.7 (114) |
35.3 (90) |
17.1 (43) |
2.8 (7.1) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
9.4 (24) |
30.6 (78) |
140.1 (356) |
| Average extreme snow depth inches (cm) | 20.0 (51) |
20.8 (53) |
12.8 (33) |
1.3 (3.3) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.1 (0.25) |
4.0 (10) |
11.0 (28) |
26.3 (67) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 20.1 | 16.4 | 14.6 | 13.8 | 12.6 | 11.8 | 11.0 | 10.9 | 11.0 | 15.1 | 16.3 | 18.8 | 172.4 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 18.2 | 14.5 | 8.5 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 5.6 | 13.0 | 62.3 |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
Transportation
New York State Route 481 (from Interstate 81) runs north/south to Oswego from Syracuse and Fulton. New York State Route 104 runs east/west from Rochester to Oswego.
Central New York Regional Transportation Authority provides service within Oswego and connections to Fulton and Syracuse. Oswego County Public Transit provides service between Oswego and smaller communities in Oswego County.
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1850 | 12,205 | — | |
| 1860 | 16,816 | 37.8% | |
| 1870 | 20,910 | 24.3% | |
| 1880 | 21,116 | 1.0% | |
| 1890 | 21,842 | 3.4% | |
| 1900 | 22,199 | 1.6% | |
| 1910 | 23,368 | 5.3% | |
| 1920 | 23,626 | 1.1% | |
| 1930 | 22,652 | −4.1% | |
| 1940 | 22,062 | −2.6% | |
| 1950 | 22,647 | 2.7% | |
| 1960 | 22,155 | −2.2% | |
| 1970 | 20,913 | −5.6% | |
| 1980 | 19,793 | −5.4% | |
| 1990 | 19,195 | −3.0% | |
| 2000 | 17,954 | −6.5% | |
| 2010 | 18,142 | 1.0% | |
| 2020 | 16,921 | −6.7% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
As of the census of 2010, there were 18,142 people, 7,486 households, and 3,896 families residing in the 8,258 housing units in the city. The population density was 2,343.4 inhabitants per square mile (904.8/km). The racial makeup of the city was 94.1% White, 2.3% African American, 0.1% Native American, 1.5% Asian, .6% from other races, and 1.5% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 5.1% of the population.
The median income for a household in the city was $39,867, and the median income for a family was $57,324. Males employed full-time, year-round, had a median income of $50,074 versus $33,211 for similarly situated females. The per capita income for the city was $21,139. 24.2% of the population and 14.4% of families were below the poverty line.
Politics
The city is governed by a mayor, currently Republican Rob Corradino, and a board of seven aldermen who are elected from the city's seven wards. Recent previous mayors include Republican Billy Barlow, Democrats Tom Gillen and Randy Bateman, and Republican John Gosek.
Political controversy
In September 2005, Oswego Mayor John Gosek was arrested by the FBI and state police in a sting operation outside of a motel near Syracuse after allegedly giving a woman $250 to arrange a sexual encounter with two 14-year-old girls. The arrest came after a three-year investigation that led to charges of the mayor using his city-issued cell phone to “persuade, induce, entice and coerce an individual under the age of 18 years to engage in sexual activity.” The charge alleged that Gosek used his phone as interstate commerce for the purposes of illegal sex and falls under a federal law that is commonly known as the Mann Act. Gosek's term wasn't due to expire until 2007, but he resigned from office five days after his arrest.
Notable people
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (October 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
- Neil Bancroft, U.S. Army soldier in the Black Hills War
- George Barnard, Civil War photographer and portrait photography pioneer
- Joey Belladonna, singer of heavy metal band Anthrax
- Owen Benjamin, formerly Smith, actor and comedian
- David Branshaw, PGA Tour golfer
- Latham A. Burrows, former New York State Senator
- Al Roker, national weather anchor on NBC's TODAY
- Fenimore Chatterton, sixth Governor of Wyoming
- Erik Cole, NHL hockey player, Olympian
- Francis D. Culkin, former US Congressman
- Noel Francisco, former Solicitor General of the United States
- Rose Morgan French (1859–1929), suffragist and peace activist
- Robert H. Gittins, former US Congressman
- Joe Gosek, racing driver
- George Grant, doctor and inventor
- John Porter Hatch, Union army general
- Robert M. Hensel, disability advocate, poet and world record holder
- Willard A. Kitts, Vice admiral, USN and Navy Cross recipient
- Greg LaRocca, former professional baseball player
- Doug Lea, a computer scientist at SUNY Oswego, specialist of concurrent programming and concurrent data structures who made significant contributions to Java
- Gladys H. Lent-Barndollar (1872-1938), businesswoman and clubwoman
- David H. McConnell, founder of California Perfume Company which became Avon Cosmetics
- Edward Nathaniel McDonald, businessman
- Nettie Leila Michel (1863—?), business woman, author, magazine editor
- Luther W. Mott, former US Congressman
- Robert Natoli, strongman
- D. W. Reeves (1838–1900), composer and bandleader, called “the father of band music in America”
- Dan Reynolds, Nationally published cartoonist, author, and greeting card artist with American Greetings born and raised in Oswego, NY.
- Curtis F. Shoup, Medal of Honor recipient
- Carroll Smith, race car driver, author
- Newcomb Spoor, Wisconsin State Assemblyman
- Bob Steinburg, member North Carolina House of Representatives, 2013 to present
- Peter Stickles, actor
- Willard Dickerman Straight, banker, diplomat, co-founder of The New Republic magazine
- Charles A. Talcott, former US Congressman
- Mary E. Walker, only female Civil War doctor, and only woman to receive the Medal of Honor
- Leigh Allison Wilson, author
- Julia McNair Wright (1840–1903), writer
- Lois E. Trott (1828 – 1894), educator and philanthropist
Culture and recreation


Oswego has a long history stretching back to the 15th century. Visitors can learn about the city's history by visiting museums such as the H. Lee White Marine Museum, The Richardson-Bates House, and Fort Ontario. Throughout the city and public parks, many historical monuments can be found honoring historical figures, and other forts that stood in what is now the historical district. The city includes a number of sites on the National Register of Historic Places including the Derrick Boat No. 8, Kingsford Historic District, Market House, Oswego Armory, Oswego City Hall, Oswego City Library, Oswego County Courthouse, Oswego Yacht Club, Tanner Block, and U.S. Customhouse. In September 2024, the Lake Ontario National Marine Sanctuary was designated in the waters of southeastern Lake Ontario off Oswego to protect historic shipwrecks and areas of cultural, historical, and spiritual significance to Native Americans of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy and to preserve them as educational and recreational resources.
The most notable historian was Rosemary Nesbitt, who is immortalized by a monument in the city's signature public park, Breitbeck Park. Every Halloween, she would traditionally let down her long silver hair, dress in a ghostly gown, and tell ghostly haunted tales spanning across the entire history of the city. Nesbitt, who also founded the Marine Museum and wrote various books about the city's history, died on August 2, 2009, at the age of 84.
Ludwig Bemelmans, a writer best known for his popular 'Madeline' stories, was stationed at Fort Ontario, Oswego, N.Y. from 1917. From this experience he wrote the book "My war with the United States" published in 1937.
Boating, fishing, and hiking are also activities that are enjoyed by residents and visitors. Oswego also has three ice-skating rinks, a large public pool located on the Fort Ontario grounds, bowling, and the historic Oswego Theater.
Every year the city hosts the Oswego Harborfest, a four-day festival of music, culture and food, centered around the Oswego Harbor, culminating in a fireworks display on the Saturday evening of the festival. The event is sponsored by local businesses, and the entertainment is admission-free. The festival continues to draw approximately 150,000 to 300,000 attendees every year.
In 2007, SUNY Oswego Lakers men's hockey team won the NCAA Division III Ice Hockey Championship. Garren Reisweber's goal 12:55 into overtime gave Oswego State a 4-3 win over Middlebury on March 18, 2007. The Lakers captured the school's first ever national championship in a team sport. The 2006-07 season marked the first season Oswego played in the newly built, state-of-the-art Marano Campus Center, located on Lake Ontario. The Campus Center replaced Romney Field House Ice Rink which opened in 1962, and is believed to be the first ice rink built within the State University of New York system. The old ice rink was transformed into a multi-use indoor facility for track, lacrosse and other intramural sports.
From 2005 to 2006 the Oswego Admirals of the Ontario Junior Hockey League played in the old ice rink.
Media
The city is served by The Palladium Times newspaper, Oswego County Today, the student-run newspaper The Oswegonian, as well as OswegoNYlion and is the home to the radio stations WRVO, WSGO, WNYO and WMVN. Oswego also has its own television station, WTOP, which is completely student-run at the State University of New York at Oswego, and is served by the Oswego High School television station, WBUC. Oswego is served by the Syracuse TV market. Previous media included the Oswego Daily News.
Education
The city is part of the Oswego City School District. The Oswego City School district has one high school (grades 9–12), one middle school (grades 7 and 8) and five elementary schools (grades K–6).
Trinity Catholic School (formerly St. Paul's Academy) provides classes for PreK–6. Oswego Community Christian School provides classes for PreK–8.
The State University of New York at Oswego (SUNY Oswego) has portions of its property in Oswego City, with the rest just west of the city in the Town of Oswego.
Electric power facilities
Oswego generating station
Pursuant to Section 70 of the Public Service Law, NRG Energy, Inc. (now operating as NRG Power Marketing LLC) officially received ownership of the Oswego generating station from previous owners Niagara Mohawk Power Corporation and Rochester Gas and Electric in 1999. NRG was the lowest bidder in an auction arranged by Niagara Mohawk. The facility is a 1,803-megawatt (MW) (nameplate) plant with two steam turbines powered by steam heated in boilers from fuel oil (although one of the units has natural gas listed as a backup fuel). The facility went into service in 1976 (for unit 5) and 1980 (for unit 6). In 2017, it injected 39.7 GWh of electric energy into the electric transmission system. This is equivalent to operating at full capacity for approximately 0.3% of the year. For comparison, the central region consumed 15,819 GWh of electric energy in 2017. Its power is sold into the electric wholesale market administered by the NYISO. Since the plant does not produce much electric energy on an annual basis, it is fair to assume that most of its revenue comes from the NYISO's capacity market. For example, at 1.0 ($/kW - Month), the plant would receive annual revenue of $21.6 million from the capacity market without accounting for actual energy production.
According to the New York State Public Service Commission's database management system, DMM, there was a whistle blower complaint filed against the facility (case no. 92-E-0306) in 1992, however, the DMM website for that case number says its contents were moved to the DMM website for case number 92-M-0016. As of November 2018, there are 5 orders on the DMM case number 92-M-0016 website, none of which have to do with a whistle blower complaint against Oswego generating station.
References
- "ArcGIS REST Services Directory". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 20, 2022.
- "Explore Census Data". data.census.gov. Retrieved August 31, 2022.
- "History | Oswego New York".
- "English Plan of the Forts Ontario & Oswego with part of the River Onondago and Lake Ontario 1756. From Gentleman's Magazine 1757 - Barry Lawrence Ruderman Antique Maps Inc". Barry Lawrence Ruderman. Retrieved November 21, 2022.
- "SCENES IN THE WAR OF 1812: CLOSING OPERATIONS OF THE ARMY OF THE NORTH". Harper's Magazine. Vol. 28. 1864. p. 149 – via Archive.org.
- Onondaga, or, Reminiscences of Earlier and Later Times by Joshua Victor Hopkins Clark and spouse Jenna Arcese (Syracuse, 1849; page 391)
- Samaritan Medical Center (September 2008). "Stonewall Jackson and the Henderson Hydropath" (PDF). in Samaritan Medical Center Newsletter. Vol. 42. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 5, 2010. Retrieved December 13, 2009.
- Lackawanna Railroad timetable, June 8, 1946, Table 7
- New York Central timetable, June 1951, Table 48 http://streamlinermemories.info/NYC/NYC51-6TT.pdf
- "Fort Ontario Emergency Refugee Shelter — United States Holocaust Memorial Museum". www.ushmm.org. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- Contributor (December 28, 2015). "Efforts Under Way to Elevate Fort Ontario to National, International Status". Dot Publishing. Oswego County Today. Retrieved April 4, 2017.
{{cite news}}:|last1=has generic name (help) - "Italy". www.edwardvictor.com. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- Thompson, Alicia (March 22, 2017). "The New York Community That Welcomed 1,000 WWII Refugees". Atlas Obscura. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- Rowe, Claudia (July 21, 2003). "59 Years Ago, They Fled To an Internment Camp". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- Blankfeld, Keren (September 11, 2020). "The Secret History of America's Only WWII Refugee Camp". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved September 14, 2020.
- "Oswego, New York (NY 13126) profile: Population, maps, real estate, averages, homes, statistics, relocation, travel, jobs, hospitals, schools, crime, moving, houses, news, sex offenders".
- "U.S. Coast Pilot 6, Chapter 3" (PDF). November 17, 2024.
- "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- "Station: Oswego, NY". U.S. Climate Normals 2020: U.S. Monthly Climate Normals (1991–2020). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- "Transportation | Oswego County Opportunities". Retrieved October 20, 2018.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 14, 2011.
- Moriarty, Rick (November 7, 2023). "Oswego to get new mayor as Billy Barlow moves on". syracuse. Retrieved February 10, 2024.
- "Joseph Anthony Bellardini". IMDb. Retrieved October 30, 2012.
- "David Branshaw". PGA Tour. Archived from the original on October 26, 2012. Retrieved October 30, 2012.
- "Wyoming Governor Fenimore Chatterton". National Governors Association. Retrieved October 30, 2012.
- "Erik Cole". hockeydb.com. Retrieved October 30, 2012.
- "He keeps his chin up, sets a Guinness Record; for Bob Natoli, of Oswego, it's about health and fitness lifestyle he's live for 30 years". Neighbors Oswego. The Post-Standard. Archived from the original on January 11, 2013. Retrieved December 24, 2012.(subscription required)
- "Reeves, David Wallis". Encyclopedia dot com. Retrieved July 12, 2021.
- "PRG B2B".
- Oswego Palladium Times, Monday, April 4, 1932,
- 'Wisconsin Blue Book 1923,' Biographical Sketch of Newcomb Spoor, pg. 624
- "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. March 13, 2009.
- "National Register of Historic Places". Weekly List of Actions Taken on Properties: 1/05/15 through 1/09/15. National Park Service. January 16, 2015.
- "Lake Ontario National Marine Sanctuary". sanctuaries.noaa.gov. Retrieved October 14, 2024.
- "Lake Ontario National Marine Sanctuary Designation Ceremony". sanctuaries.noaa.gov. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved October 14, 2024.
- "Historian leaves a legacy of her own - The Palladium-Times : News". Palltimes.com. Retrieved August 10, 2013.
- ^ "Romney Field House | Facilities Services".
- "2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Oswego County, NY" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved October 18, 2024. - Text list
- "2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Oswego city, NY" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved October 18, 2024.
State University of New York College at Oswego
- "2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Oswego town, NY" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved October 18, 2024.
State University of New York College at Oswego
See also: "2020 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: SUNY Oswego CDP, NY" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved October 18, 2024.State University of New York College at Oswego
- "ORDER PROVIDING FOR LIGHTENED REGULATION (case no. 99-E-0974)". October 21, 1999. p. 1,2,6. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- "NYISO 2018 Gold Book (pdf)". www.nyiso.com. pp. 13, 63. Retrieved November 26, 2018.
- Tim Knauss (February 13, 2018). "Cuomo targets power plant that closed after $110M subsidy by National Grid customers". Syracuse.com. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- "NYISO ICAP Monthly Auction price website". Retrieved November 19, 2018.
External links
- City of Oswego, New York
- History of Oswego, NY
- Oswego Public Library
- Images of Oswego
- List of famous inhabitants
- CBS News - Ms. Harris vs. Oswego re:sidewalk hazards
| Municipalities and communities of Oswego County, New York, United States | ||
|---|---|---|
| County seat: Oswego | ||
| Cities |  | |
| Towns | ||
| Villages | ||
| CDPs | ||
| Other hamlets | ||
| Footnotes | ‡This populated place also has portions in an adjacent county or counties | |