| Revision as of 08:42, 22 January 2006 editLoxley~enwiki (talk | contribs)888 edits This has new content that Alienus has not addressed dont vandalise← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:58, 22 May 2024 edit undoAutisticeditor 20 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users23,209 edits tweaked #article-section-source-editorTags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit iOS app edit | ||
| (256 intermediate revisions by 63 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Concept in the philosophy of mind}} | |||
| In ], '''Cartesian materialism''' is the idea that, somewhere in the ], there is a preferred set of data that corresponds to our view of the world. | |||
| ]).]] | |||
| In ], '''Cartesian materialism''' is the idea that at some place (or places) in the brain, there is some set of information that directly corresponds to our conscious experience. Contrary to its name, Cartesian materialism is not a view that was held by or formulated by ], who subscribed rather to a form of substance ]. | |||
| In its simplest version, Cartesian materialism might predict, for example, that there is a specific place in the brain which would be a coherent representation of everything we are consciously experiencing in a given moment: what we're seeing, what we're hearing, what we're smelling, and indeed, everything of which we are consciously aware. In essence, Cartesian materialism claims that, somewhere in our brain, there is a ] where a hypothetical observer could somehow "find" the content of conscious experience moment by moment. In contrast, anything occurring outside of this "privileged neural media" is nonconscious. | |||
| Originally Cartesian materialism was defined in the context of ], being the Cartesian concept of the mind without the non-physical soul, Marx and Engels (1845) consider the early history of Cartesian materialism: | |||
| ==History== | |||
| :"Mechanical French materialism adopted Descartes’ physics in opposition to his metaphysics. His followers were by profession anti-metaphysicians, i.e., physicists. | |||
| ===Multiple meanings=== | |||
| ] developed from the ] of Descartes and the ] of Locke, Hobbes, Bacon and ultimately Duns Scotus who asked "Whether matter could not think?" Natural science, in their view, owes to the former its great success as a "Cartesian materialism", bereft of the metaphysics of ] by philosophers and physicians such as ], ], and ], who maintained the viability of Descartes' biological ] without recourse to immaterial cognition. <!-- see http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-43341 for a good overview Cartesian mechanism--> | |||
| However, philosopher ] uses the term to emphasize what he considers the pervasive Cartesian notion of a centralized repository of conscious experience in the brain. Dennett says that "Cartesian materialism is the view that there is a crucial finish line or boundary somewhere in the brain, marking a place where the order of arrival equals the order of 'presentation' in experience because what happens there is what you are conscious of."<ref>{{Cite web |last=Chappell |first=Richard Y. |title=The Cartesian Theatre |url=https://www.philosophyetc.net/2004/11/cartesian-theatre.html |access-date=2023-07-16}}</ref> | |||
| :This school begins with the physician Le Roy, reaches its zenith with the physician Cabanis, and the physician La Mettrie is its centre. Descartes was still living when Le Roy, like La Mettrie in the eighteenth century, transposed the Cartesian structure of the animal to the human soul and declared that the soul is a modus of the body and ideas are mechanical motions. Le Roy even thought Descartes had kept his real opinion secret. Descartes protested. At the end of the eighteenth century Cabanis perfected Cartesian materialism in his treatise: Rapport du physique et du moral de 1'homme." | |||
| Other modern philosophers have generally used less specific definitions. For example, O'Brien and Opie define it as the idea that consciousness is "realized in the physical materials of the brain",<ref>O'Brien & Opie 1999</ref> and W. Teed Rockwell defines Cartesian materialism in the following way: "The basic dogma of Cartesian materialism is that only neural activity in the cranium is functionally essential for the emergence of mind."<ref>Rockwell 2005</ref> However, although Rockwell's concept of Cartesian materialism is less specific in a sense, it is a detailed reply to Dennett's version, not an undeveloped predecessor. The main theme of Rockwell's book ''Neither Brain nor Ghost'' is that the arguments Dennett uses to refute his version of Cartesian materialism actually support the view that the mind is an emergent property of the entire Brain/Body/World Nexus. For Rockwell, claiming the entire brain is identical to the mind has no better justification than claiming that part of the brain is identical to the mind. | |||
| Cartesian materialism can apply to the idea that only a limited area of the brain is the conscious mind or to the general idea that the mind is "realized in the physical materials of the brain" (O'Brien and Opie (1999), see also W. Teed Rockwell (2005), Dennett (1993)). | |||
| Dennett's version of the term is the most popular.{{cn|date=March 2013}} | |||
| Cartesian materialism is associated with ] and is generally attacked by ], although it should be noted that ] and other proposals that consciousness arises from reflexes in the brain might be encompassed by Cartesian materialism. | |||
| === Cartesian dualism === | |||
| Many ] such as ] and ] are opposed to Cartesian materialism. In '']'' (1991), Dennett concentrates on the timing of mental events and offers this definition: | |||
| {{main|Cartesian dualism}} | |||
| Descartes believed that a human being was composed of both a material body and an immaterial soul (or "mind"). According to Descartes, the mind and the body could interact. The body can affect the mind; for example, when you place your hand in a fire, the body relays sensory information from your hand to your mind, which results in your having the experience of pain. Similarly, the mind can affect the body; for example, you can decide to move your hand and your muscles obey, moving your hand as you desired. | |||
| :Cartesian materialism is the view that there is a crucial finish line or boundary somewhere in the brain, marking a place where the order of arrival equals the order of "presentation" in experience because what happens there is what you are conscious of. (p.107) | |||
| Descartes noted that, although our two eyes independently see an object, our conscious experience is not of two separate fields of vision each possessing an image of the object. Rather, we seem to experience one continuous, oval-shaped field of vision that possesses information from both eyes which seems to have somehow been 'merged' into a single image. (Consider in a movie, when a character looks through binoculars and the audience is shown what he is looking at, from the character's point of view. The image shown is never made up of two completely separate circular images-- rather the director shows us a single figure-eight shaped region made up of information from each eyepiece.) | |||
| In his ] model of ], Dennett argues against this version of Cartesian materialism using his metaphor of the "]". Cartesian materialists such as O'Brien and Opie (1999) argue that Dennett's characterisation of the concept is incorrect and that his analysis of the ] can be accommodated in the Cartesian materialist paradigm. | |||
| <!-- If you don't understand what i'm getting at-- see for example http://www.artnet.com/artwork/424038366/markus-raetz-binocular-view.html in case you want to include the 'looking through binoculars analogy' but don't like my description--> | |||
| Descartes noted that information from both eyes seems to have been merged somehow before "entering" conscious perception. He also noted similar effects for the other senses. Based on this, Descartes hypothesized that there must be some single place in the brain where all the sensory information is assembled, before finally being relayed to the immaterial mind. | |||
| Intriguingly Dennett (1991b) agrees with Rosenthal's Direct Realist idea that our intuitions reflect how things "really are". An insight into Dennett's idea of the mind is to be found on pages 407-408 of ''Consciousness Explained'': | |||
| His best candidate for this location was the pineal gland, since he thought it was the only part of the brain that is a single structure, rather than one duplicated on both the left and right halves of the brain. Descartes therefore believed that the pineal gland was the "seat of the soul" and that any information that was to "enter" consciousness had to pass through the pineal gland before it could enter the mind. In his perspective, the pineal gland is the place where all information "comes together." | |||
| :"It seemed to him, according to the text, as if his mind - his visual field - were filled with intricate details of gold-green buds and wiggling branches, but although this is how it seemed this was an illusion. No such "plenum" ever came into his mind; the plenum remained out in the world where it it didn't have to be ''represented'', but could just ''be''. When we marvel, in those moments of heightened self-consciousness, at the glorious richness of our conscious experience, the richness we marvel at is actually the richness of the world outside, in all its ravishing detail. It does not "enter" our conscious minds, but is simply available" | |||
| ===Dennett's account of Cartesian materialism=== | |||
| So Dennett defines "mind" as a thing that does not contain the direct objects of perception. He is a Direct Realist. For Dennett "mind" is solely the processes in conscious experience. Dennett's objection is to a particular sort of Cartesian materialism that he himself has defined. Dennett objects to a form of ], especially indirect realism where the contents of conscious perceptual experience are held to be in the brain as some form of virtual reality that is instantaneously apprehended. | |||
| At the present time, the consensus of scientists and philosophers is to reject dualism and its immaterial mind, for a variety of reasons. (See ]). Similarly, many other aspects of Descartes' theories have been rejected; for example, the pineal gland turned out to be endocrinological, rather than having a large role in information processing. | |||
| According to Daniel Dennett, however, many scientists and philosophers still believe, either explicitly or implicitly, in Descartes' idea of some centralized repository where the contents of consciousness are merged and assembled, a place he calls the ]. | |||
| Rockwell also rejects Cartesian materialism, proposing that the mind should be identified not only with the brain but the rest of the body as it acts in its environment. ] also tend to adopt this viewpoint as do proponents of the ] strand of ]. | |||
| In his book '']'' (1991), Dennett writes: | |||
| :Let's call the idea of such a centered locus in the brain ''Cartesian materialism'', since it's the view you arrive at when you discard Descartes' dualism but fail to discard the imagery of a central (but material) Theater where it "all comes together"<ref>Dennett 1991, p.107</ref> | |||
| Although this central repository is often called a "place" or a "location", Dennett is quick to clarify that Cartesian materialism's "centered locus" need not be anatomically defined-- such a locus might consists of a network of diverse regions.<ref>Dennett 1991, p.107</ref> | |||
| ==Dennett's arguments against Cartesian materialism== | |||
| In ''Consciousness Explained'', Dennett offers several lines of evidence to dispute the idea of Cartesian materialism. | |||
| ===Timing anomalies of conscious experience=== | |||
| Another argument against Cartesian materialism is inspired by the results of several scientific experiments in the fields of psychology and neuroscience. In experiments that demonstrate the ] and the metacontrast effect, two stimuli are rapidly flashed on a screen, one after the other. Amazingly, the second stimulus can, in some cases, actually affect the perception of the first stimulus. In other experiments conducted by ], two electrical stimulations are delivered, one after another, to a conscious subject. Under some conditions, subjects report having felt the second stimulation before they felt the first stimulation. | |||
| These experiments call into question the idea that brain states are directly translatable into the contents of consciousness. How can the second stimuli be 'projected backwards in time', such that it can affect the perception of things that occurred before the second stimulus was even administered? | |||
| ===Two attempted explanations=== | |||
| Two different types of explanations have been offered in response to the timing anomalies. One is that perhaps sensory information is assembled into a ] before being passed on to consciousness after a substantial time delay. Since consciousness occurs only after a time lag, the incoming second stimulus would have time to affect the stored information about the first stimulus. In this view, subjects correctly remember their having had inaccurate experiences. Dennett calls this the "Stalinesque Explanation" (after the ] Soviet Union's show trials that presented manufactured evidence to an unwitting jury). | |||
| A second explanation for the timing takes the opposite tack. Perhaps the subjects, contrary to their own reports, initially experienced the first stimulus as being prior to and untainted by the second stimulus. However, when subjects were later asked to recall what their experiences had been, they found that their memories of the first stimulus had been tainted by the second stimulus. Therefore, they inaccurately report experiences that never actually occurred. In this view, subjects have accurate initial experiences, but inaccurately remember them. Dennett calls this view the "Orwellian Explanation", after ]'s novel ], in which a totalitarian government frequently rewrites history to suit its purposes. | |||
| How are we to choose which of these two explanations is the correct one? Both explanations seem to adequately explain the given data, both seem to make the same predictions. Dennett sees no principled basis for choosing either of the explanations, so he rejects their common assumption of a theater. He says: | |||
| {{quotation|We can suppose, both theorists have ''exactly'' the same theory of what happens in your brain; they agree about just where and when in the brain the mistaken content enters the causal pathways; they just disagree about whether that location is to be deemed pre-experiential or post-experiential. <nowiki></nowiki> They even agree about how it ought to "feel" to subjects: Subjects should be unable to tell the difference between misbegotten experiences and immediately misremembered experiences.<ref>Dennett 1991, p.125, original emphasis.</ref>}} | |||
| ===Dennett's conclusions=== | |||
| Dennett's argument has the following basic structure: | |||
| :1. If Cartesian materialism were true and there really was a special brain area (or areas) that stored the contents of conscious experience, then it should be possible to ascertain exactly when something enters conscious experience. | |||
| :2. It is impossible, even in theory, to ever precisely determine when something enters conscious experience. | |||
| :3. Therefore, Cartesian materialism is false. | |||
| According to Dennett, the debate between Stalinesque and Orwellian explanations is unresolvable — no amount of scientific information could ever answer the question. Dennett therefore argues (in accord with the philosophical doctrine of ]) that, since the differences between the two explanations are unresolvable, the point of disagreement is logically meaningless so both explanations are mistaken. | |||
| Dennett feels that the insistence on a place where 'it all comes together' (the ]) is fundamentally flawed, and therefore that Cartesian materialism is false. Dennett's view is that "there is no single, definitive 'stream of consciousness,' because there is no central Headquarters, no Cartesian theatre where 'it all comes together'". | |||
| To avoid the perceived shortcomings of Cartesian materialism, Dennett instead proposes the ] — a model of consciousness which lacks a central Cartesian theater. | |||
| ==Replies and objections to Dennett and his arguments== | |||
| ===A philosophy without adherents?=== | |||
| Perhaps the primary objection to Dennett's use of the term Cartesian materialism is that | |||
| it is a philosophy without adherents. In this view, Cartesian materialism is essentially a "]" — an argument explicitly constructed just so it can be refuted: | |||
| {{quotation|The now standard response to Dennett’s project is that he has picked a fight with a straw man. Cartesian materialism, it is alleged, is an impossibly naive account of phenomenal consciousness held by no one currently working in cognitive science or the philosophy of mind. Consequently, whatever the effectiveness of Dennett’s demolition job, it is fundamentally misdirected (see, e.g., Block, 1993, 1995; Shoemaker, 1993; and Tye, 1993).<ref>O'Brien and Opie 1999</ref>}} | |||
| It is a point of intense debate as to how many philosophers and scientists even accept Cartesian materialism. On the one hand, some say that this view is "held by no one currently working in cognitive science or the philosophy of mind"<ref>O'Brien and Opie 1999</ref> or insist that they "know of no one who endorses it." (Michael Tye) On the other hand, some say that Cartesian materialism "informs virtually all research on mind and brain, explicitly and implicitly" (Antonio Damasio) or argue that the common "commitment to qualia or 'phenomenal seemings'" entails an implicit commitment to Cartesian materialism that becomes explicit when they "work out a theory of consciousness in sufficient detail".<ref>Dennett 1993</ref> | |||
| Dennett suggests that the Cartesian materialism, though rejected by many philosophers, still colors people's thinking. He writes: | |||
| :"Perhaps no one today explicitly endorses Cartesian materialism. Many theorists would insist that they have explicitly rejected such an obviously bad idea. But as we shall see, the persuasive imagery of a Cartesian theater keeps coming back to haunt us — laypeople and scientists alike — even after its ghostly dualism has been denounced and exorcised." | |||
| ===Replies from dualism=== | |||
| Many philosophers question Dennett's immediate rejection of dualism (dismissing it after only a few pages of argument in ''Consciousness Explained''), pointing to a variety of reasons that people often find dualism to be a compelling view (see ]). | |||
| To proponents of dualism, mental events have a certain subjective quality to them, whereas physical events obviously do not. That is, for example, what a burned finger feels like, what sky blue looks like, what nice music sounds like, and so on. There is something that it is like to feel pain, to see a familiar shade of blue, and so on; These sensations independent of behavior are known as ], and the philosophical problem posed by their alleged existence is called the ] by Chalmers.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://ase.tufts.edu/cogstud/papers/chalmers.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20000303162756/http://ase.tufts.edu/cogstud/papers/chalmers.htm |archive-date=2000-03-03 |title=Commentary on Chalmers}}</ref> | |||
| Dualists argue that Dennett does not explain these phenomena, so much as ignore them. Indeed, the title of Dennett's book ''Consciousness Explained'' is often lampooned by critics, who call the book ''Consciousness Explained Away'' or even ''Consciousness Ignored''. | |||
| ===Replies from Cartesian materialists=== | |||
| Some philosophers have actively accepted the moniker of Cartesian materialists, and are not convinced by Dennett's arguments. | |||
| O'Brien and Opie (1999) embrace Cartesian materialism, arguing against Dennett's claim that the onset of phenomenal experience in the brain cannot in principle be precisely determined, and offering what they consider to be a way to accommodate ] within the Cartesian materialist paradigm. | |||
| Block has described an alternative called "Cartesian Modularism" in which the contents of conscious experience are distributed in the brain.<ref>Block 1995</ref> | |||
| ===Replies from neuroscience=== | |||
| Despite Dennett's insistence that there are no special brain areas that store the contents of consciousness, many neuroscientists reject this assertion. Indeed, what separates conscious information from unconscious information remains a question of interest, and how information from disparate brain regions are assembled into a coherent whole (the ]) remains a question which is actively investigated. Recently ] has argued that perhaps the brain does possess some universally accessible "workspace".<ref>Jay Ingram (2005)''The Theatre of the Mind: Rasising The Curtain on Consciousness''</ref> | |||
| Another criticism comes from investigation into the human visual system. Although both eyes each have a blind spot, conscious visual experience does not subjectively seem to have any holes in it. Some scientists and philosophers had argued, based on subjective reports, that perhaps the brain somehow "fills in" the holes, based upon adjacent visual information. Dennett had powerfully argued that such "filling in" was unnecessary, based on his objections to a Cartesian theater. Ultimately, however, studies have confirmed that the visual cortex does perform a very complex "filling in" process.<ref>Pessoa & De Weerd, 2003</ref> | |||
| The impact of this is itself controversial. Some assume that this is a devastating blow against Dennett, while others have argued that this in no way confirms Cartesian materialism or refutes the multiple drafts model, and that Dennett is fundamentally right even if he's mistaken about this detail.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.bbsonline.org/Preprints/OldArchive/bbs.pessoa.html|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20060214185758/http://www.bbsonline.org/Preprints/OldArchive/bbs.pessoa.html|archive-date = 2006-02-14|title = Behavioral and Brain Sciences}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| * ] | * ] and ] | ||
| * ], ], and ] | |||
| * ] and ] | |||
| * ], ], and ] | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Wikibooks|Consciousness Studies}} | |||
| *Daniel C Dennett. (1991), ''Consciousness Explained'', Little, Brown & Co. USA (ISBN 0316180653) | |||
| * {{cite journal|last1=Block|first1=Ned|authorlink1=Ned Block|title=On a confusion about a function of consciousness|journal=Behavioral and Brain Sciences|date=June 1995|volume=18|issue=2|pages=227–287|doi=10.1017/S0140525X00038188|ref=Block 1995|language=English|issn=0140-525X|oclc=04172559|citeseerx=10.1.1.207.6880|s2cid=146168066 }} | |||
| * Dennett, D.C. (1991b). Lovely and suspect qualities. Commentary on David Rosenthal, "The Independence of Consciousness and Sensory Quality" in E. Villanueva, ed., Consciousness, (SOFIA Conference, Buenos Aires), Atascadero, CA: Ridgeview 1991 | |||
| * Dennett, D.C. (1991), ''Consciousness Explained'', Little, Brown & Co. USA ({{ISBN|0-316-18065-3}}) | |||
| * Dennett, D.C. (1993). The Message is: There is no Medium (reply to Jackson, Rosenthal, Shoemaker & Tye), Philosophy & Phenomenological Research, 53, (4), 889-931, Dec. 1993. | |||
| * |
* Dennett, D.C. (1993). , Philosophy & Phenomenological Research, 53, (4), 889-931, Dec. 1993. | ||
| * Engels, F. and Marx, K. (1845). The Holy Family. http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1845/holy-family/ch06_3_d.htm | |||
| *Rockwell, W. Teed. (2005), ''Neither Brain nor Ghost: A Nondualist Alternative to the Mind-Brain Identity Theory'', MIT Press (ISBN 0262182475) | |||
| * O'Brien, G. & Opie, J. (1999), , ''Philosophy and Phenomenological Research'' 59:939-63. | |||
| * Engels, F and Marx, K. (1845). The Holy Family. http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1845/holy-family/ch06_3_d.htm | |||
| * Pessoa, L. and De Weerd, P. (2003), "Filling-In: From Perceptual Completion to Cortical Reorganization", Oxford University Press, USA ({{ISBN|0-19-514013-3}}) | |||
| ] | |||
| * Rockwell, W. Teed. (2005), ''Neither Brain nor Ghost: A Nondualist Alternative to the Mind-Brain Identity Theory'', MIT Press ({{ISBN|0-262-18247-5}}) | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:58, 22 May 2024
Concept in the philosophy of mind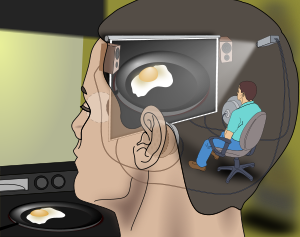
In philosophy of mind, Cartesian materialism is the idea that at some place (or places) in the brain, there is some set of information that directly corresponds to our conscious experience. Contrary to its name, Cartesian materialism is not a view that was held by or formulated by René Descartes, who subscribed rather to a form of substance dualism.
In its simplest version, Cartesian materialism might predict, for example, that there is a specific place in the brain which would be a coherent representation of everything we are consciously experiencing in a given moment: what we're seeing, what we're hearing, what we're smelling, and indeed, everything of which we are consciously aware. In essence, Cartesian materialism claims that, somewhere in our brain, there is a Cartesian theater where a hypothetical observer could somehow "find" the content of conscious experience moment by moment. In contrast, anything occurring outside of this "privileged neural media" is nonconscious.
History
Multiple meanings
French materialism developed from the mechanism of Descartes and the empiricism of Locke, Hobbes, Bacon and ultimately Duns Scotus who asked "Whether matter could not think?" Natural science, in their view, owes to the former its great success as a "Cartesian materialism", bereft of the metaphysics of Cartesian dualism by philosophers and physicians such as Regius, Cabanis, and La Mettrie, who maintained the viability of Descartes' biological automata without recourse to immaterial cognition.
However, philosopher Daniel Dennett uses the term to emphasize what he considers the pervasive Cartesian notion of a centralized repository of conscious experience in the brain. Dennett says that "Cartesian materialism is the view that there is a crucial finish line or boundary somewhere in the brain, marking a place where the order of arrival equals the order of 'presentation' in experience because what happens there is what you are conscious of."
Other modern philosophers have generally used less specific definitions. For example, O'Brien and Opie define it as the idea that consciousness is "realized in the physical materials of the brain", and W. Teed Rockwell defines Cartesian materialism in the following way: "The basic dogma of Cartesian materialism is that only neural activity in the cranium is functionally essential for the emergence of mind." However, although Rockwell's concept of Cartesian materialism is less specific in a sense, it is a detailed reply to Dennett's version, not an undeveloped predecessor. The main theme of Rockwell's book Neither Brain nor Ghost is that the arguments Dennett uses to refute his version of Cartesian materialism actually support the view that the mind is an emergent property of the entire Brain/Body/World Nexus. For Rockwell, claiming the entire brain is identical to the mind has no better justification than claiming that part of the brain is identical to the mind.
Dennett's version of the term is the most popular.
Cartesian dualism
Main article: Cartesian dualismDescartes believed that a human being was composed of both a material body and an immaterial soul (or "mind"). According to Descartes, the mind and the body could interact. The body can affect the mind; for example, when you place your hand in a fire, the body relays sensory information from your hand to your mind, which results in your having the experience of pain. Similarly, the mind can affect the body; for example, you can decide to move your hand and your muscles obey, moving your hand as you desired.
Descartes noted that, although our two eyes independently see an object, our conscious experience is not of two separate fields of vision each possessing an image of the object. Rather, we seem to experience one continuous, oval-shaped field of vision that possesses information from both eyes which seems to have somehow been 'merged' into a single image. (Consider in a movie, when a character looks through binoculars and the audience is shown what he is looking at, from the character's point of view. The image shown is never made up of two completely separate circular images-- rather the director shows us a single figure-eight shaped region made up of information from each eyepiece.)
Descartes noted that information from both eyes seems to have been merged somehow before "entering" conscious perception. He also noted similar effects for the other senses. Based on this, Descartes hypothesized that there must be some single place in the brain where all the sensory information is assembled, before finally being relayed to the immaterial mind.
His best candidate for this location was the pineal gland, since he thought it was the only part of the brain that is a single structure, rather than one duplicated on both the left and right halves of the brain. Descartes therefore believed that the pineal gland was the "seat of the soul" and that any information that was to "enter" consciousness had to pass through the pineal gland before it could enter the mind. In his perspective, the pineal gland is the place where all information "comes together."
Dennett's account of Cartesian materialism
At the present time, the consensus of scientists and philosophers is to reject dualism and its immaterial mind, for a variety of reasons. (See Dualism -- Arguments Against). Similarly, many other aspects of Descartes' theories have been rejected; for example, the pineal gland turned out to be endocrinological, rather than having a large role in information processing.
According to Daniel Dennett, however, many scientists and philosophers still believe, either explicitly or implicitly, in Descartes' idea of some centralized repository where the contents of consciousness are merged and assembled, a place he calls the Cartesian theater.
In his book Consciousness Explained (1991), Dennett writes:
- Let's call the idea of such a centered locus in the brain Cartesian materialism, since it's the view you arrive at when you discard Descartes' dualism but fail to discard the imagery of a central (but material) Theater where it "all comes together"
Although this central repository is often called a "place" or a "location", Dennett is quick to clarify that Cartesian materialism's "centered locus" need not be anatomically defined-- such a locus might consists of a network of diverse regions.
Dennett's arguments against Cartesian materialism
In Consciousness Explained, Dennett offers several lines of evidence to dispute the idea of Cartesian materialism.
Timing anomalies of conscious experience
Another argument against Cartesian materialism is inspired by the results of several scientific experiments in the fields of psychology and neuroscience. In experiments that demonstrate the Color Phi phenomenon and the metacontrast effect, two stimuli are rapidly flashed on a screen, one after the other. Amazingly, the second stimulus can, in some cases, actually affect the perception of the first stimulus. In other experiments conducted by Benjamin Libet, two electrical stimulations are delivered, one after another, to a conscious subject. Under some conditions, subjects report having felt the second stimulation before they felt the first stimulation.
These experiments call into question the idea that brain states are directly translatable into the contents of consciousness. How can the second stimuli be 'projected backwards in time', such that it can affect the perception of things that occurred before the second stimulus was even administered?
Two attempted explanations
Two different types of explanations have been offered in response to the timing anomalies. One is that perhaps sensory information is assembled into a buffer before being passed on to consciousness after a substantial time delay. Since consciousness occurs only after a time lag, the incoming second stimulus would have time to affect the stored information about the first stimulus. In this view, subjects correctly remember their having had inaccurate experiences. Dennett calls this the "Stalinesque Explanation" (after the Stalinist Soviet Union's show trials that presented manufactured evidence to an unwitting jury).
A second explanation for the timing takes the opposite tack. Perhaps the subjects, contrary to their own reports, initially experienced the first stimulus as being prior to and untainted by the second stimulus. However, when subjects were later asked to recall what their experiences had been, they found that their memories of the first stimulus had been tainted by the second stimulus. Therefore, they inaccurately report experiences that never actually occurred. In this view, subjects have accurate initial experiences, but inaccurately remember them. Dennett calls this view the "Orwellian Explanation", after George Orwell's novel 1984, in which a totalitarian government frequently rewrites history to suit its purposes.
How are we to choose which of these two explanations is the correct one? Both explanations seem to adequately explain the given data, both seem to make the same predictions. Dennett sees no principled basis for choosing either of the explanations, so he rejects their common assumption of a theater. He says:
We can suppose, both theorists have exactly the same theory of what happens in your brain; they agree about just where and when in the brain the mistaken content enters the causal pathways; they just disagree about whether that location is to be deemed pre-experiential or post-experiential. They even agree about how it ought to "feel" to subjects: Subjects should be unable to tell the difference between misbegotten experiences and immediately misremembered experiences.
Dennett's conclusions
Dennett's argument has the following basic structure:
- 1. If Cartesian materialism were true and there really was a special brain area (or areas) that stored the contents of conscious experience, then it should be possible to ascertain exactly when something enters conscious experience.
- 2. It is impossible, even in theory, to ever precisely determine when something enters conscious experience.
- 3. Therefore, Cartesian materialism is false.
According to Dennett, the debate between Stalinesque and Orwellian explanations is unresolvable — no amount of scientific information could ever answer the question. Dennett therefore argues (in accord with the philosophical doctrine of verificationism) that, since the differences between the two explanations are unresolvable, the point of disagreement is logically meaningless so both explanations are mistaken.
Dennett feels that the insistence on a place where 'it all comes together' (the Cartesian theater) is fundamentally flawed, and therefore that Cartesian materialism is false. Dennett's view is that "there is no single, definitive 'stream of consciousness,' because there is no central Headquarters, no Cartesian theatre where 'it all comes together'".
To avoid the perceived shortcomings of Cartesian materialism, Dennett instead proposes the multiple drafts model — a model of consciousness which lacks a central Cartesian theater.
Replies and objections to Dennett and his arguments
A philosophy without adherents?
Perhaps the primary objection to Dennett's use of the term Cartesian materialism is that it is a philosophy without adherents. In this view, Cartesian materialism is essentially a "Straw Man" — an argument explicitly constructed just so it can be refuted:
The now standard response to Dennett’s project is that he has picked a fight with a straw man. Cartesian materialism, it is alleged, is an impossibly naive account of phenomenal consciousness held by no one currently working in cognitive science or the philosophy of mind. Consequently, whatever the effectiveness of Dennett’s demolition job, it is fundamentally misdirected (see, e.g., Block, 1993, 1995; Shoemaker, 1993; and Tye, 1993).
It is a point of intense debate as to how many philosophers and scientists even accept Cartesian materialism. On the one hand, some say that this view is "held by no one currently working in cognitive science or the philosophy of mind" or insist that they "know of no one who endorses it." (Michael Tye) On the other hand, some say that Cartesian materialism "informs virtually all research on mind and brain, explicitly and implicitly" (Antonio Damasio) or argue that the common "commitment to qualia or 'phenomenal seemings'" entails an implicit commitment to Cartesian materialism that becomes explicit when they "work out a theory of consciousness in sufficient detail".
Dennett suggests that the Cartesian materialism, though rejected by many philosophers, still colors people's thinking. He writes:
- "Perhaps no one today explicitly endorses Cartesian materialism. Many theorists would insist that they have explicitly rejected such an obviously bad idea. But as we shall see, the persuasive imagery of a Cartesian theater keeps coming back to haunt us — laypeople and scientists alike — even after its ghostly dualism has been denounced and exorcised."
Replies from dualism
Many philosophers question Dennett's immediate rejection of dualism (dismissing it after only a few pages of argument in Consciousness Explained), pointing to a variety of reasons that people often find dualism to be a compelling view (see Arguments for dualism).
To proponents of dualism, mental events have a certain subjective quality to them, whereas physical events obviously do not. That is, for example, what a burned finger feels like, what sky blue looks like, what nice music sounds like, and so on. There is something that it is like to feel pain, to see a familiar shade of blue, and so on; These sensations independent of behavior are known as qualia, and the philosophical problem posed by their alleged existence is called the hard problem of consciousness by Chalmers.
Dualists argue that Dennett does not explain these phenomena, so much as ignore them. Indeed, the title of Dennett's book Consciousness Explained is often lampooned by critics, who call the book Consciousness Explained Away or even Consciousness Ignored.
Replies from Cartesian materialists
Some philosophers have actively accepted the moniker of Cartesian materialists, and are not convinced by Dennett's arguments.
O'Brien and Opie (1999) embrace Cartesian materialism, arguing against Dennett's claim that the onset of phenomenal experience in the brain cannot in principle be precisely determined, and offering what they consider to be a way to accommodate Phi phenomenon within the Cartesian materialist paradigm.
Block has described an alternative called "Cartesian Modularism" in which the contents of conscious experience are distributed in the brain.
Replies from neuroscience
Despite Dennett's insistence that there are no special brain areas that store the contents of consciousness, many neuroscientists reject this assertion. Indeed, what separates conscious information from unconscious information remains a question of interest, and how information from disparate brain regions are assembled into a coherent whole (the Binding problem) remains a question which is actively investigated. Recently Global Workspace Theory has argued that perhaps the brain does possess some universally accessible "workspace".
Another criticism comes from investigation into the human visual system. Although both eyes each have a blind spot, conscious visual experience does not subjectively seem to have any holes in it. Some scientists and philosophers had argued, based on subjective reports, that perhaps the brain somehow "fills in" the holes, based upon adjacent visual information. Dennett had powerfully argued that such "filling in" was unnecessary, based on his objections to a Cartesian theater. Ultimately, however, studies have confirmed that the visual cortex does perform a very complex "filling in" process.
The impact of this is itself controversial. Some assume that this is a devastating blow against Dennett, while others have argued that this in no way confirms Cartesian materialism or refutes the multiple drafts model, and that Dennett is fundamentally right even if he's mistaken about this detail.
See also
- Consciousness and mind-body problem
- Dualism, epiphenomenalism, and qualia
- Materialism and eliminative materialism
- Direct realism, indirect realism, and representationalism
Notes
- Chappell, Richard Y. "The Cartesian Theatre". Retrieved 2023-07-16.
- O'Brien & Opie 1999
- Rockwell 2005
- Dennett 1991, p.107
- Dennett 1991, p.107
- Dennett 1991, p.125, original emphasis.
- O'Brien and Opie 1999
- O'Brien and Opie 1999
- Dennett 1993
- "Commentary on Chalmers". Archived from the original on 2000-03-03.
- Block 1995
- Jay Ingram (2005)The Theatre of the Mind: Rasising The Curtain on Consciousness
- Pessoa & De Weerd, 2003
- "Behavioral and Brain Sciences". Archived from the original on 2006-02-14.
References
- Block, Ned (June 1995). "On a confusion about a function of consciousness". Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 18 (2): 227–287. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.207.6880. doi:10.1017/S0140525X00038188. ISSN 0140-525X. OCLC 04172559. S2CID 146168066.
- Dennett, D.C. (1991), Consciousness Explained, Little, Brown & Co. USA (ISBN 0-316-18065-3)
- Dennett, D.C. (1993). The Message is: There is no Medium (reply to Jackson, Rosenthal, Shoemaker & Tye), Philosophy & Phenomenological Research, 53, (4), 889-931, Dec. 1993.
- Engels, F. and Marx, K. (1845). The Holy Family. http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1845/holy-family/ch06_3_d.htm
- O'Brien, G. & Opie, J. (1999), "A Defence of Cartesian Materialism", Philosophy and Phenomenological Research 59:939-63.
- Pessoa, L. and De Weerd, P. (2003), "Filling-In: From Perceptual Completion to Cortical Reorganization", Oxford University Press, USA (ISBN 0-19-514013-3)
- Rockwell, W. Teed. (2005), Neither Brain nor Ghost: A Nondualist Alternative to the Mind-Brain Identity Theory, MIT Press (ISBN 0-262-18247-5)