| Revision as of 16:06, 6 February 2011 edit85.157.100.161 (talk) fi← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:38, 7 December 2024 edit undoMithoron (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,491 editsNo edit summary | ||
| (86 intermediate revisions by 46 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{DISPLAYTITLE:''n''-Butylamine}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:''n''-Butylamine}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Chembox | ||
| | |
|Verifiedfields = changed | ||
| |Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 398782308 | |||
| |verifiedrevid = 412364052 | |||
| | Name = ''n''-Butylamine | |||
| | |
|Name = ''n''-Butylamine | ||
| |ImageFile = N-Butylamine.svg | |||
| | ImageSize = 150px | |||
| |ImageFile_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | |||
| | ImageName = ''n''-Butylamine | |||
| |ImageSize = 200 | |||
| | IUPACName = butan-1-amine | |||
| |ImageName = Skeletal formula of ''n''-butylamine | |||
| | OtherNames = NBA; Monobutylamime; 1-Butanamine; 1-Aminobutane | |||
| |ImageFile1 = N-butylamine-from-xtal-1994-3D-balls.png | |||
| | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| | |
|ImageSize1 = 180 | ||
| |ImageAlt1 = Ball-and-stick model of the ''n''-butylamine molecule | |||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| |PIN = Butan-1-amine | |||
| | ChemSpiderID = 7716 | |||
| |OtherNames = {{Unbulleted list|1-Aminobutane|1-Butanamine|Monobutylamine | |||
| | PubChem = 8007 | |||
| | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| | ChEMBL = 13968 | |||
| | InChI = 1/C4H11N/c1-2-3-4-5/h2-5H2,1H3 | |||
| | InChIKey = HQABUPZFAYXKJW-UHFFFAOYAE | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C4H11N/c1-2-3-4-5/h2-5H2,1H3 | |||
| | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChIKey = HQABUPZFAYXKJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| | CASNo = 109-73-9 | |||
| | RTECS = | |||
| | UNNumber = UN 1125 | |||
| }} | |||
| | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | |||
| |C=4|H=11|N=1 | |||
| | Appearance = Colorless liquid | |||
| | Density = 0.74 g/cm<sup>3</sup> | |||
| | Solubility = Miscible | |||
| | MeltingPtC = -49 | |||
| | BoilingPtC = 77 | |||
| | pKa = 10.59<ref>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1021/ja01577a030 | author = Hall, H.K. | journal = J. Am. Chem. Soc. | year = 1957 | volume = 79 | pages = 5441}}</ref> | |||
| | Viscosity = 0.5 ] at 20 °C | |||
| }} | |||
| | Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards | |||
| | ExternalMSDS = | |||
| | MainHazards = Corrosive, if touched an cause smelling and taste problems and Highly flammable | |||
| | FlashPt = -14 °C | |||
| | RPhrases = {{R11}} {{R35}} {{R20}} {{R21}} {{R22}} | |||
| | SPhrases = {{S3}} {{S16}} {{S26}} {{S29}} {{S45}} {{S36}} {{S37}} {{S39}} | |||
| }} | |||
| | Section8 = {{Chembox Related | |||
| | OtherCpds = ]<br />]<br />]<br />]<br />] | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| |Abbreviations = NBA | |||
| |CASNo = 109-73-9 | |||
| |CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| |PubChem = 8007 | |||
| |ChemSpiderID = 7716 | |||
| |ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| |UNII = N2QV60B4WR | |||
| |UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|changed|FDA}} | |||
| |EINECS = 203-699-2 | |||
| |UNNumber = 1125 | |||
| |DrugBank = DB03659 | |||
| |DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|changed|drugbank}} | |||
| |MeSHName = n-butylamine | |||
| |ChEBI = 43799 | |||
| |ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | |||
| |ChEMBL = 13968 | |||
| |ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| |RTECS = EO29750002 | |||
| |Beilstein = 605269 | |||
| |Gmelin = 1784 | |||
| |SMILES = CCCCN | |||
| |StdInChI = 1S/C4H11N/c1-2-3-4-5/h2-5H2,1H3 | |||
| |StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| |StdInChIKey = HQABUPZFAYXKJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| |StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| }} | |||
| |Section2={{Chembox Properties | |||
| |C=4 | H=11 | N=1 | |||
| |Appearance = Colorless liquid | |||
| |Odor = fishy, ammoniacal | |||
| |Density = 740 mg ml<sup>−1</sup> | |||
| |MeltingPtK = 224 | |||
| |BoilingPtK = 350 to 352 | |||
| |Solubility = Miscible | |||
| |LogP = 1.056 | |||
| |VaporPressure = 9.1 kPa (at 20 °C) | |||
| |HenryConstant = 570 μmol Pa<sup>−1</sup> kg<sup>−1</sup> | |||
| |pKb = 3.22 | |||
| |RefractIndex = 1.401 | |||
| |Viscosity = 500 µPa s (at 20 °C) | |||
| |MagSus = -58.9·10<sup>−6</sup> cm<sup>3</sup>/mol | |||
| }} | |||
| |Section3={{Chembox Thermochemistry | |||
| |DeltaHf = −128.9–−126.5 kJ mol<sup>−1</sup> | |||
| |DeltaHc = −3.0196–−3.0174 MJ mol<sup>−1</sup> | |||
| |HeatCapacity = 188 J K<sup>−1</sup> mol<sup>−1</sup> | |||
| }} | |||
| |Section4={{Chembox Hazards | |||
| |ExternalSDS = | |||
| |GHSPictograms = {{GHS flame}} {{GHS corrosion}} {{GHS exclamation mark}} | |||
| |GHSSignalWord = '''DANGER''' | |||
| |HPhrases = {{H-phrases|225|302|312|314|332}} | |||
| |PPhrases = {{P-phrases|210|280|305+351+338|310}} | |||
| |NFPA-F = 3 | |||
| |NFPA-H = 2 | |||
| |NFPA-R = 0 | |||
| |FlashPtC = -7 | |||
| |AutoignitionPtC = 312 | |||
| |ExploLimits = 1.7–9.8% | |||
| |LD50 = {{Unbulleted list|366 mg kg<sup>−1</sup> <small>(oral, rat)</small>|626 mg kg<sup>−1</sup> <small>(dermal, rabbit)</small>|430 mg kg<sup>−1</sup> <small>(oral, mouse)</small>|430 mg kg<sup>−1</sup> <small>(oral, guinea pig)</small>}}<ref name=IDLH>{{IDLH|109739|N-Butylamine}}</ref> | |||
| |PEL = C 5 ppm (15 mg/m<sup>3</sup>) <ref name=NIOSH>{{PGCH|0079}}</ref> | |||
| |IDLH = 300 ppm<ref name=NIOSH/> | |||
| |REL = C 5 ppm (15 mg/m<sup>3</sup>) <ref name=NIOSH/> | |||
| |LCLo = 4000 ppm (rat, 4 hr)<br/>263 ppm (mouse, 2 hr)<ref name=IDLH/> | |||
| }} | |||
| |Section5={{Chembox Related | |||
| |OtherFunction_label = alkanamines | |||
| |OtherFunction = {{Unbulleted list|]|]|]|]|]|]|]|]|]|]}} | |||
| |OtherCompounds = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | |||
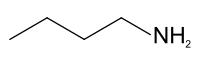
| '''''n''-Butylamine''' is an organic compound (specifically, an ]) with the formula CH<sub>3</sub>(CH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>. This colourless liquid is one of the four ]ic ]s of ], the others being ], ], and ]. It is a liquid having the fishy, ammonia-like odor common to amines. The liquid acquires a yellow color upon storage in air. It is soluble in all organic solvents. Its vapours are heavier than air and it produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion.<ref>{{Cite web|last=PubChem|title=Butylamine|url=https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/8007|access-date=2022-02-15|website=pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ==Synthesis and reactions== | |||
| '''''n''-Butylamine''' is an organic compound (specifically, an ]) with the formula CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>. This colourless liquid is one of the four ]ic ]s of ], the others being ], ] and ]. At standard temperature and pressure, ''n''-butylamine is a liquid having the fishy, ammonia-like odor common to amines. The liquid acquires a yellow color upon storage in air. It is soluble in all organic solvents. | |||
| It is produced by the reaction of ammonia and alcohols over ]: | |||
| :CH<sub>3</sub>(CH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>3</sub>OH + NH<sub>3</sub> → CH<sub>3</sub>(CH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub> + H<sub>2</sub>O | |||
| ''n''-Butylamine is a ]. The pK<sub>a</sub> of <sup>+</sup> is 10.78.<ref>{{cite journal|author=H. K. Hall, Jr.|year=1957|journal=J. Am. Chem. Soc.|volume=79|pages=5441–5444|title=Correlation of the Base Strengths of Amines|issue=20|doi=10.1021/ja01577a030}}</ref> | |||
| ''n''-Butylamine exhibits reactions typical of other simple alkyl amines, i.e., alkylation, acylation, condensation with carbonyls. | |||
| It forms complexes with metal ions, examples being ''cis''- and ''trans''-.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1016/j.ica.2003.10.039|title=Multinuclear NMR Study and Crystal Structures of Complexes of the Types ''cis''- and ''trans''-Pt(amine)''2''I''2''|year=2004|last1=Rochon|first1=Fernande D.|last2=Buculei|first2=Viorel|journal=Inorganica Chimica Acta|volume=357|issue=8|pages=2218–2230}}</ref> | |||
| ==Uses== | ==Uses== | ||
| ].]] | |||
| This compound is used as an ingredient in the manufacture of ]s (such as ]s), ]s, and ]s. It is also a precursor for the manufacture of N,N'-dibutylthio], a rubber ] accelerator, and n-butylbenzenesulfonamide, a ] of ]. | |||
| This compound is used as an ingredient in the manufacture of ]s (such as ]s), ]s, and ]s. It is also a precursor for the manufacture of ], a rubber ] accelerator, and ''n''-butylbenzenesulfonamide, a ] of ]. It is used in the synthesis of ], the fungicide ], and ], and the ] ].<ref name=Ullmann>Karsten Eller, Erhard Henkes, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke, "Amines, Aliphatic" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.{{doi|10.1002/14356007.a02_001}}</ref> | |||
| ==Safety== | |||
| The ] to rats through the oral exposure route is 366 mg/kg.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://us.vwr.com/stibo/hi_res/8235547.pdf |title=''n''-Butylamine MSDS |access-date=2013-11-12 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131112205047/https://us.vwr.com/stibo/hi_res/8235547.pdf |archive-date=2013-11-12 |url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| In regards to occupational exposures to ''n''-butylamine, the ] and ] have set occupational exposure limits at a ceiling of 5 ppm (15 mg/m<sup>3</sup>) for dermal exposure.<ref></ref> | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{ |
{{Reflist}} | ||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Butylamine, n-}} | |||
| *{{Commonscatinline|N-Butylamine}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Butylamine, n-}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:38, 7 December 2024
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Butan-1-amine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | NBA |
| Beilstein Reference | 605269 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.364 |
| EC Number |
|
| Gmelin Reference | 1784 |
| MeSH | n-butylamine |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1125 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4H11N |
| Molar mass | 73.139 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 740 mg ml |
| Melting point | −49 °C; −56 °F; 224 K |
| Boiling point | 77 to 79 °C; 170 to 174 °F; 350 to 352 K |
| Solubility in water | Miscible |
| log P | 1.056 |
| Vapor pressure | 9.1 kPa (at 20 °C) |
| Henry's law constant (kH) |
570 μmol Pa kg |
| Basicity (pKb) | 3.22 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -58.9·10 cm/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.401 |
| Viscosity | 500 µPa s (at 20 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Heat capacity (C) | 188 J K mol |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
−128.9–−126.5 kJ mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH298) |
−3.0196–−3.0174 MJ mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |   
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H225, H302, H312, H314, H332 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | −7 °C (19 °F; 266 K) |
| Autoignition temperature |
312 °C (594 °F; 585 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.7–9.8% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
|
| LCLo (lowest published) | 4000 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 263 ppm (mouse, 2 hr) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
| PEL (Permissible) | C 5 ppm (15 mg/m) |
| REL (Recommended) | C 5 ppm (15 mg/m) |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | 300 ppm |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | hazard.com |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanamines | |
| Related compounds | 2-Methyl-2-nitrosopropane |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
n-Butylamine is an organic compound (specifically, an amine) with the formula CH3(CH2)3NH2. This colourless liquid is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being sec-butylamine, tert-butylamine, and isobutylamine. It is a liquid having the fishy, ammonia-like odor common to amines. The liquid acquires a yellow color upon storage in air. It is soluble in all organic solvents. Its vapours are heavier than air and it produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion.
Synthesis and reactions
It is produced by the reaction of ammonia and alcohols over alumina:
- CH3(CH2)3OH + NH3 → CH3(CH2)3NH2 + H2O
n-Butylamine is a weak base. The pKa of is 10.78.
n-Butylamine exhibits reactions typical of other simple alkyl amines, i.e., alkylation, acylation, condensation with carbonyls. It forms complexes with metal ions, examples being cis- and trans-.
Uses

This compound is used as an ingredient in the manufacture of pesticides (such as thiocarbazides), pharmaceuticals, and emulsifiers. It is also a precursor for the manufacture of N,N′-dibutylthiourea, a rubber vulcanization accelerator, and n-butylbenzenesulfonamide, a plasticizer of nylon. It is used in the synthesis of fengabine, the fungicide benomyl, and butamoxane, and the antidiabetic tolbutamide.
Safety
The LD50 to rats through the oral exposure route is 366 mg/kg.
In regards to occupational exposures to n-butylamine, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration and National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health have set occupational exposure limits at a ceiling of 5 ppm (15 mg/m) for dermal exposure.
References
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0079". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "N-Butylamine". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- PubChem. "Butylamine". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-02-15.
- H. K. Hall, Jr. (1957). "Correlation of the Base Strengths of Amines". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 (20): 5441–5444. doi:10.1021/ja01577a030.
- Rochon, Fernande D.; Buculei, Viorel (2004). "Multinuclear NMR Study and Crystal Structures of Complexes of the Types cis- and trans-Pt(amine)2I2". Inorganica Chimica Acta. 357 (8): 2218–2230. doi:10.1016/j.ica.2003.10.039.
- Karsten Eller, Erhard Henkes, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke, "Amines, Aliphatic" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001
- "n-Butylamine MSDS" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-11-12. Retrieved 2013-11-12.
- CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
External links
- [REDACTED] Media related to N-Butylamine at Wikimedia Commons