| Revision as of 03:28, 10 August 2011 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:WikiProject_C← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 14:18, 18 April 2024 edit undoJJMC89 bot III (talk | contribs)Bots, Administrators3,759,505 editsm Moving Category:Thiosemicarbazone to Category:Thiosemicarbazones per Misplaced Pages:Categories for discussion/Speedy | ||
| (83 intermediate revisions by 38 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Oral antiseptic}} | |||
| {{More medical citations needed|date=October 2013}} | |||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 443989497 | |||
| | UNII = BYK4592A3Q | |||
| | Reference=<ref></ref> | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 437164533 | |||
| | ImageFile=Ambazone.svg | |||
| |Reference=<ref></ref> | |||
| | ImageSize= | |||
| |ImageFile=Ambazone.svg | |||
| | IUPACName=iminothiourea | |||
| |ImageSize= | |||
| | OtherNames= 2--2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene]-Hydrazinecarbothioamide; (4-Oxo-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylideneamino)guanidine thiosemicarbazone; 1,4-Benzoquinone amidinohydrazone thiosemicarbazone; Ambazon; Anginon; Benzoquinone guanylhydrazone thiosemicarbazone; Faringosept; Guanothiazon; Inversal; Inversal; Ivertol; N-Guanidino-N'-thioureido-p-benzoquinonediimide; Primal; p-Benzoquinone amidinohydrazone thiosemicarbazone;Faringosept (TN); Ambazone (INN); OAMBAZONE; Ambazonum ; Ambazona ; Ambazone ; CCRIS 1926; MLS001240207 | |||
| |IUPACName=iminothiourea | |||
| |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| |OtherNames= 2--2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene]-Hydrazinecarbothioamide; (4-Oxo-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylideneamino)guanidine thiosemicarbazone; 1,4-Benzoquinone amidinohydrazone thiosemicarbazone; Ambazon; Anginon; Benzoquinone guanylhydrazone thiosemicarbazone; Faringosept; Guanothiazon; Inversal; Inversal; Ivertol; N-Guanidino-N'-thioureido-p-benzoquinonediimide; Primal; p-Benzoquinone amidinohydrazone thiosemicarbazone;Faringosept (TN); Ambazone (INN); OAMBAZONE; Ambazonum ; Ambazona ; Ambazone ; CCRIS 1926; MLS001240207 | |||
| | InChIKey = MLMFUKWWZIZRHX-UWRPRBHNBF | |||
| |Section1= {{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| | InChIKey = MLMFUKWWZIZRHX-UWRPRBHNBF | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C8H11N7S/c9-7(10)14-12-5-1-3-6(4-2-5)13-15-8(11)16/h1-4H,(H4,9,10,14)(H3,11,15,16)/b12-5-,13-6+ | | StdInChI = 1S/C8H11N7S/c9-7(10)14-12-5-1-3-6(4-2-5)13-15-8(11)16/h1-4H,(H4,9,10,14)(H3,11,15,16)/b12-5-,13-6+ | ||
| | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | StdInChIKey = MLMFUKWWZIZRHX-UWRPRBHNSA-N | | StdInChIKey = MLMFUKWWZIZRHX-UWRPRBHNSA-N | ||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| | CASNo=539-21-9 | | CASNo=539-21-9 | ||
| | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | |||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| | ChEMBL = 2103762 | |||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| | UNII = BYK4592A3Q | |||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| | ChemSpiderID = 12232507 | | ChemSpiderID = 12232507 | ||
| | |
| EINECS = 208-713-0 | ||
| | |
| PubChem= 1549158 | ||
| | |
| SMILES = NC(=S)N\N=C1\C=C/C(=N\NC(N)=N)/C=C1 | ||
| | |
| InChI = 1/C8H11N7S/c9-7(10)14-12-5-1-3-6(4-2-5)13-15-8(11)16/h1-4H,(H4,9,10,14)(H3,11,15,16)/b12-5-,13-6+ | ||
| | ATCvet = ATC | |||
| | ATCCode_prefix = R02 | |||
| | ATCCode_suffix = AA01 | |||
| | KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | | KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | ||
| | KEGG = D07376 | | KEGG = D07376 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section2= |
|Section2={{Chembox Properties | ||
| | |
| Formula=C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>11</sub>N<sub>7</sub>S | ||
| | |
| MolarMass= 237.28 g/mol | ||
| | |
| Appearance= Dark Brown Powder | ||
| | |
| Density= | ||
| | |
| MeltingPt= | ||
| | |
| BoilingPt= | ||
| | |
| Solubility= 0.2 mg/100 ml water | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| | |
|Section6={{Chembox Pharmacology | ||
| | ATCvet = ATC | |||
| | MainHazards= | |||
| | ATCCode_prefix = R02 | |||
| | FlashPt= | |||
| | ATCCode_suffix = AA01 | |||
| | Autoignition= | |||
| }} | |||
| |Section7={{Chembox Hazards | |||
| | MainHazards= | |||
| | FlashPt= | |||
| | AutoignitionPt = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Ambazone''' is an oral ]. | '''Ambazone''' is an oral ]. | ||
| Ambazone was patented in 1957 by ] under the trade name '''Iversal''', and briefly used in Germany. It is still used in Russia, countries of the former Soviet Union, Poland<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://bazalekow.mp.pl/lek/54002,Faringosept-tabletki#effect|title = Faringosept tabletki - działanie, dawkowanie, cena, refundacja | Medycyna Praktyczna}}</ref> and Romania. It has not been approved by the United States ] (FDA).{{citation needed|date=September 2023}} | |||
| ==Synthesis== | |||
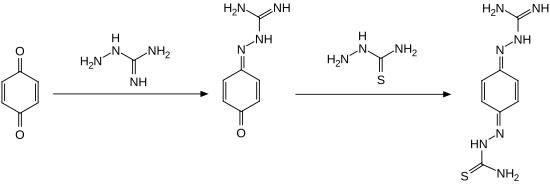
| Ambazone can be obtained in a two step synthetic method, reacting 1,4-benzoquinone with aminoguanidine and thiosemicarbazide.<ref>Patent DE965723: Verfahren zur Herstellung von ondensationsprodukten. Angemeldet am 31. Januar 1953, veröffentlicht am 19. Juni 1957, Anmelder: Bayer AG, Erfinder: Siegfried Petersen, Gerhard Domagk.</ref><ref>A. Kleemann, J. Engel, B. Kutscher, D. Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances - Synthesis, Patents, Applications, 4. Auflage (2001) Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart, {{ISBN|978-1-58890-031-9}}.</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Obtaining a pharmaceutical grade material is difficult due to high amounts of by-products, synthetic intermediates and decomposition products.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detailPdf.jsf?ia=RO2004000016&docIdPdf=id00000001847575%3FparSeparator1=&name=WO2005028431PROCESS+FOR+THE+PURIFICATION+OF+1%2C4-BENZOQUINONE+GUANYLHYDRAZONE+THIOSEMICARBAZONE+%28AMBAZONE%29&parSeparator2=&woNum=WO2005028431&prevRecNum=298&nextRecNum=300&recNum=298&queryString=ABE%2F%22toluene%22&office=&sortOption=&prevFilter=&maxRec=856 |title=Patent WO 2005/028431 |access-date=2014-03-31 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140331130134/http://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detailPdf.jsf?ia=RO2004000016&docIdPdf=id00000001847575%3FparSeparator1=&name=WO2005028431PROCESS+FOR+THE+PURIFICATION+OF+1%2C4-BENZOQUINONE+GUANYLHYDRAZONE+THIOSEMICARBAZONE+%28AMBAZONE%29&parSeparator2=&woNum=WO2005028431&prevRecNum=298&nextRecNum=300&recNum=298&queryString=ABE%2F%22toluene%22&office=&sortOption=&prevFilter=&maxRec=856 |archive-date=2014-03-31 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ==Applications== | ==Applications== | ||
| ] action on ], ] and ]. | ] action on ], '']'' and ]. | ||
| == Physical properties == | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| Through experimental testing ambazone has shown ] properties, along with ]. Ambazone has the following physical characteristics. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Table 1. Physical properties | |||
| |- | |||
| | Dark brown | |||
| |- | |||
| | Odorless | |||
| |- | |||
| | Tasteless | |||
| |- | |||
| | Powder | |||
| |- | |||
| | Melting Point 192–194 °C (decomp.)<ref>Marshall Sittig: Pharmaceutical manufacturing encyclopedia. -- 3rd ed. 2007 p. 215</ref> | |||
| |} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Table 2. Solubility !! per 100 ml | |||
| |- | |||
| | Water || 0.2 mg | |||
| |- | |||
| | Methanol || 0.5 mg | |||
| |- | |||
| | Chloroform || 0.3 mg | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1-butanol || 6.5 mg | |||
| |- | |||
| | Ethyl acetate || 17 mg | |||
| |- | |||
| | Acetone || 50 mg | |||
| |- | |||
| | Ethanol || 85 mg | |||
| |- | |||
| | Dimethyl formamide || 1.7 g | |||
| |- | |||
| | sulfoxide || 2.5 g | |||
| |} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Table 3. Uv-Vis !! nm | |||
| |- | |||
| | Water || 403 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Alcohols || 440-445 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Ethyl acetate || 453 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Dimethyl sulfoxide || 467 | |||
| |} | |||
| Ambazone is prepared by way of solid based crystallization or grinding. | |||
| {{organic-compound-stub}} | |||
| == Mode of action == | |||
| The mode of action for ambazone has been studied extensively and has been shown to react via different methods. Ambazone shows low ] activity and no cardiovascular, CNS, metabolic, or gastrointestinal ] with I.V. doses up to 10-5 mol/kg and oral doses up to 10-3 mol/kg. Ambazone can be administered via oral or I.V. administration, but the problem with oral administration is that one experimental study shows there is only a 35–50% absorption while another study shows 40% in the intestines; these results would tend to lead the reader to think that ambazone would not be the best choice for treatment, because with such a low absorbance, there is going to have to be a greater concentration ingested to gain a positive effect from the drug. The problem with a greater concentration is that ambazone has a half-life of 6–7 hours. It was stated above that ambazone possess no CNS side-effects due to the fact, that it will not cross the blood brain barrier. Although this is the body's way of protecting unwanted substances from attacking the brain, this also limits the treatment of brain tumors with ambazone. | |||
| == Research == | |||
| The therapeutic properties of ambazone were studied in lab rats and the therapeutic dose was determined to be 60–125 mg/kg of body weight. As stated above, ambazone possesses anti-septic properties shown by its increased activity against gram-positive cocci. Along with anti-septic properties, ambazone has also shown its ability to fight forms of leukemia in lab rats. When administered orally the results showed prolongation of life expectancy and curing of ] and ] ] in lab rats. Scientists used different methods to determine the results, such as; mean survival time (MST), percent increase of life span, survival rates, percent change in body weights and number of peritoneal cells. When testing ambazone via AMES with no metabolic activation, it was found there are no mutagenic or carcinogenic properties. When the same test was performed with metabolic activation or when the C-Test was performed, it showed the potential for mutagenicity. The results show two different paths and until further testing has been performed it cannot be determined if the good outweighs the bad when it comes to using ambazone for treatment. | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| {{Throat preparations}} | {{Throat preparations}} | ||
| Line 61: | Line 137: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:18, 18 April 2024
Oral antiseptic| This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. Please review the contents of the article and add the appropriate references if you can. Unsourced or poorly sourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Ambazone" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2013) |  |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name iminothiourea | |
| Other names 2--2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene]-Hydrazinecarbothioamide; (4-Oxo-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylideneamino)guanidine thiosemicarbazone; 1,4-Benzoquinone amidinohydrazone thiosemicarbazone; Ambazon; Anginon; Benzoquinone guanylhydrazone thiosemicarbazone; Faringosept; Guanothiazon; Inversal; Inversal; Ivertol; N-Guanidino-N'-thioureido-p-benzoquinonediimide; Primal; p-Benzoquinone amidinohydrazone thiosemicarbazone;Faringosept (TN); Ambazone (INN); OAMBAZONE; Ambazonum ; Ambazona ; Ambazone ; CCRIS 1926; MLS001240207 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.922 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H11N7S |
| Molar mass | 237.28 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark Brown Powder |
| Solubility in water | 0.2 mg/100 ml water |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | R02AA01 (WHO) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Ambazone is an oral antiseptic.
Ambazone was patented in 1957 by Bayer under the trade name Iversal, and briefly used in Germany. It is still used in Russia, countries of the former Soviet Union, Poland and Romania. It has not been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Synthesis
Ambazone can be obtained in a two step synthetic method, reacting 1,4-benzoquinone with aminoguanidine and thiosemicarbazide.
Obtaining a pharmaceutical grade material is difficult due to high amounts of by-products, synthetic intermediates and decomposition products.
Applications
Bacteriostatic action on hemolytic streptococcus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and viridans streptococci.
Physical properties
Through experimental testing ambazone has shown antiseptic properties, along with anti-tumor properties. Ambazone has the following physical characteristics.
| Table 1. Physical properties |
|---|
| Dark brown |
| Odorless |
| Tasteless |
| Powder |
| Melting Point 192–194 °C (decomp.) |
| Table 2. Solubility | per 100 ml |
|---|---|
| Water | 0.2 mg |
| Methanol | 0.5 mg |
| Chloroform | 0.3 mg |
| 1-butanol | 6.5 mg |
| Ethyl acetate | 17 mg |
| Acetone | 50 mg |
| Ethanol | 85 mg |
| Dimethyl formamide | 1.7 g |
| sulfoxide | 2.5 g |
| Table 3. Uv-Vis | nm |
|---|---|
| Water | 403 |
| Alcohols | 440-445 |
| Ethyl acetate | 453 |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide | 467 |
Ambazone is prepared by way of solid based crystallization or grinding.
Mode of action
The mode of action for ambazone has been studied extensively and has been shown to react via different methods. Ambazone shows low mutagenic activity and no cardiovascular, CNS, metabolic, or gastrointestinal side-effects with I.V. doses up to 10-5 mol/kg and oral doses up to 10-3 mol/kg. Ambazone can be administered via oral or I.V. administration, but the problem with oral administration is that one experimental study shows there is only a 35–50% absorption while another study shows 40% in the intestines; these results would tend to lead the reader to think that ambazone would not be the best choice for treatment, because with such a low absorbance, there is going to have to be a greater concentration ingested to gain a positive effect from the drug. The problem with a greater concentration is that ambazone has a half-life of 6–7 hours. It was stated above that ambazone possess no CNS side-effects due to the fact, that it will not cross the blood brain barrier. Although this is the body's way of protecting unwanted substances from attacking the brain, this also limits the treatment of brain tumors with ambazone.
Research
The therapeutic properties of ambazone were studied in lab rats and the therapeutic dose was determined to be 60–125 mg/kg of body weight. As stated above, ambazone possesses anti-septic properties shown by its increased activity against gram-positive cocci. Along with anti-septic properties, ambazone has also shown its ability to fight forms of leukemia in lab rats. When administered orally the results showed prolongation of life expectancy and curing of L1210 and P388 leukemia in lab rats. Scientists used different methods to determine the results, such as; mean survival time (MST), percent increase of life span, survival rates, percent change in body weights and number of peritoneal cells. When testing ambazone via AMES with no metabolic activation, it was found there are no mutagenic or carcinogenic properties. When the same test was performed with metabolic activation or when the C-Test was performed, it showed the potential for mutagenicity. The results show two different paths and until further testing has been performed it cannot be determined if the good outweighs the bad when it comes to using ambazone for treatment.
References
- Ambazone
- "Faringosept tabletki - działanie, dawkowanie, cena, refundacja | Medycyna Praktyczna".
- Patent DE965723: Verfahren zur Herstellung von ondensationsprodukten. Angemeldet am 31. Januar 1953, veröffentlicht am 19. Juni 1957, Anmelder: Bayer AG, Erfinder: Siegfried Petersen, Gerhard Domagk.
- A. Kleemann, J. Engel, B. Kutscher, D. Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances - Synthesis, Patents, Applications, 4. Auflage (2001) Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart, ISBN 978-1-58890-031-9.
- "Patent WO 2005/028431". Archived from the original on 2014-03-31. Retrieved 2014-03-31.
- Marshall Sittig: Pharmaceutical manufacturing encyclopedia. -- 3rd ed. 2007 p. 215
| Throat preparations (R02) | |
|---|---|
| Antiseptics | |
| Antibiotics | |
| Local anesthetics | |
| Other | |