| Revision as of 00:59, 6 April 2012 editRezabot (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users48,194 editsm r2.7.1) (Robot: Adding fa:بیبنزیل← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 22:48, 26 April 2023 edit undoTrappist the monk (talk | contribs)Administrators480,308 editsm →Occurrences: cite repair;Tag: AWB | ||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 20 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Chembox | {{Chembox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 486407303 | |||
| | ImageFile = Bibenzyl.svg | | ImageFile = Bibenzyl.svg | ||
| | ImageSize = 200px | | ImageSize = 200px | ||
| | |
| PIN = 1,1′-(Ethane-1,2-diyl)dibenzene | ||
| | OtherNames = |
| OtherNames = 1,2-Diphenylethane<br />Dibenzil<br />Dibenzyl<br />Dihydrostilbene<br />''sym''-Diphenylethane | ||
| | |
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | |
| CASNo = 103-29-7 | ||
| | |
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | ||
| | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | |
| ChEMBL = 440895 | ||
| | ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | ChEBI = 34047 | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|changed|FDA}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | UNII = 007C07V77Z | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | PubChem = 7647 | ||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| | ChemSpiderID = 7364 | |||
| ⚫ | | SMILES = c1ccc(cc1)CCc2ccccc2 | ||
| ⚫ | | InChI = 1/C14H14/c1-3-7-13(8-4-1)11-12-14-9-5-2-6-10-14/h1-10H,11-12H2 | ||
| ⚫ | | InChIKey = QWUWMCYKGHVNAV-UHFFFAOYAL | ||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ⚫ | | StdInChI = 1S/C14H14/c1-3-7-13(8-4-1)11-12-14-9-5-2-6-10-14/h1-10H,11-12H2 | ||
| | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ⚫ | | StdInChIKey = QWUWMCYKGHVNAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| | |
|Section2={{Chembox Properties | ||
| | |
| C=14|H=14 | ||
| | |
| Appearance = Crystalline solid<ref name=Merck>'']'', 11th Edition, '''1219'''</ref> | ||
| | |
| Density = 0.9782 g/cm<sup>3</sup><ref name=Merck/> | ||
| | |
| MeltingPtC = 52.0 to 52.5 | ||
| ⚫ | | MeltingPt_ref = <ref name=Merck/> | ||
| | MeltingPtCL = 52.5 | |||
| ⚫ | | BoilingPtC = 284 | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | BoilingPt_ref = <ref name=Merck/> | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | Solubility = Insoluble | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | MagSus = -126.8·10<sup>−6</sup> cm<sup>3</sup>/mol }} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | |Section3={{Chembox Hazards | ||
| }} | |||
| | MainHazards = | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | |
| FlashPtC = | ||
| | |
| AutoignitionPt = | ||
| | Autoignition = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Bibenzyl''' |
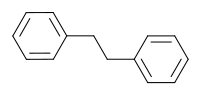
'''Bibenzyl''' is the ] with the formula (C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>2</sub>. It can be viewed as a derivative of ] in which one ] is bonded to each carbon atom. It is a colorless solid. | ||
| ==Occurrences == | |||
| ⚫ | Bibenzyl forms the central core of some ] ]s<ref>{{cite book | title = The biochemistry of the stilbenoids | |
||
| The compound is the product from the coupling of a pair of ] radicals.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Divalent lanthanide derivatives in organic synthesis. 1. Mild preparation of samarium iodide and ytterbium iodide and their use as reducing or coupling agents|author1=Girard, P. |author2=Namy, J. L. |author3=], H. B. |journal=Journal of the American Chemical Society|year=1980|volume=102|issue=8|pages=2693–8|doi=10.1021/ja00528a029}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | Bibenzyl forms the central core of some ]s like ]s<ref>{{cite book | title = The biochemistry of the stilbenoids |author1=John Gorham |author2=Motoo Tori |author3=Yoshinori Asakawa | publisher = Springer | year = 1995 | isbn = 0-412-55070-9 }}</ref> and ] ]s. Marchantins are a family of bis(bibenzyl)-containing macrocycles.<ref>{{cite journal|title=The chemistry of macrocyclic bis(bibenzyls)|journal=Natural Product Reports|year=1995|volume=12|pages=69–75|doi=10.1039/NP9951200069|last1=Keserű|first1=G. M.|last2=Nógrádi|first2=M.}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | ==See also== | ||
| ⚫ | == See also == | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| ==References== | == References == | ||
| {{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| {{hydrocarbon-stub}} | {{hydrocarbon-stub}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:48, 26 April 2023
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1,1′-(Ethane-1,2-diyl)dibenzene | |
| Other names
1,2-Diphenylethane Dibenzil Dibenzyl Dihydrostilbene sym-Diphenylethane | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.816 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C14H14 |
| Molar mass | 182.266 g·mol |
| Appearance | Crystalline solid |
| Density | 0.9782 g/cm |
| Melting point | 52.0 to 52.5 °C (125.6 to 126.5 °F; 325.1 to 325.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 284 °C (543 °F; 557 K) |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -126.8·10 cm/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Bibenzyl is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5CH2)2. It can be viewed as a derivative of ethane in which one phenyl group is bonded to each carbon atom. It is a colorless solid.
Occurrences
The compound is the product from the coupling of a pair of benzyl radicals.
Bibenzyl forms the central core of some natural products like dihydrostilbenoids and isoquinoline alkaloids. Marchantins are a family of bis(bibenzyl)-containing macrocycles.
See also
References
- ^ The Merck Index, 11th Edition, 1219
- Girard, P.; Namy, J. L.; Kagan, H. B. (1980). "Divalent lanthanide derivatives in organic synthesis. 1. Mild preparation of samarium iodide and ytterbium iodide and their use as reducing or coupling agents". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 102 (8): 2693–8. doi:10.1021/ja00528a029.
- John Gorham; Motoo Tori; Yoshinori Asakawa (1995). The biochemistry of the stilbenoids. Springer. ISBN 0-412-55070-9.
- Keserű, G. M.; Nógrádi, M. (1995). "The chemistry of macrocyclic bis(bibenzyls)". Natural Product Reports. 12: 69–75. doi:10.1039/NP9951200069.
This article about a hydrocarbon is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |