| Revision as of 19:28, 25 April 2014 edit132.3.53.81 (talk) →Limitations on CCW Permits← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 22:43, 28 November 2024 edit undoNonstopdrivel (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users6,158 edits →HistoryTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Laws concerning the carry of weapons in a concealed manner}} | |||
| {{USgunlegalbox}} | {{USgunlegalbox}} | ||
| '''Concealed carry''', or '''carrying a concealed weapon''' ('''CCW'''), is the practice of carrying a weapon (such as a ]) in ] in ], either on one's person or in close proximity. CCW is often practiced as a means of ]. Following the Supreme Court's ] decision, all states in the United States were required to allow for concealed carry of a handgun either permitlessly or with a permit, although the difficulty in obtaining a permit varies per jurisdiction. | |||
| {{See also|Open carry in the United States}} | |||
| ] | |||
| '''Concealed carry''' or '''carrying a concealed weapon''' ('''CCW'''), is the practice of carrying a weapon (such as a ]) in ] in a concealed manner, either on one's person or in close proximity. Not all weapons that fall under CCW controls are lethal. For example, in Florida, carrying pepper spray in more than a specified volume (2 oz.) of chemical requires a CCW permit, whereas anyone may legally carry a smaller, so-called, “self-defense chemical spray” device hidden on their person without a CCW permit.<ref name=790.01>{{cite web | title= 2012 Florida Statutes, TITLE XLVI CRIMES, Chapter 790 WEAPONS AND FIREARMS, 790.01 Carrying concealed weapons | url= http://www.leg.state.fl.us/statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&Search_String=&URL=0700-0799/0790/Sections/0790.01.html |year= 2012 | |||
| | quote=790.01 Carrying concealed weapons.— | |||
| (1) Except as provided in subsection (4), a person who carries a concealed weapon or electric weapon or device on or about his or her person commits a misdemeanor of the first degree, punishable as provided in s. 775.082 or s. 775.083. | |||
| (2) A person who carries a concealed firearm on or about his or her person commits a felony of the third degree, punishable as provided in s. 775.082, s. 775.083, or s. 775.084. | |||
| (3) This section does not apply to a person licensed to carry a concealed weapon or a concealed firearm pursuant to the provisions of s. 790.06. | |||
| (4) It is not a violation of this section for a person to carry for purposes of lawful self-defense, in a concealed manner: | |||
| (a) A self-defense chemical spray. | |||
| (b) A nonlethal stun gun or dart-firing stun gun or other nonlethal electric weapon or device that is designed solely for defensive purposes. | |||
| (5) This section does not preclude any prosecution for the use of an electric weapon or device, a dart-firing stun gun, or a self-defense chemical spray during the commission of any criminal offense under s. 790.07, s. 790.10, s. 790.23, or s. 790.235, or for any other criminal offense.}}</ref><ref name=790.001>{{cite web | title= 2012 Florida Statutes, TITLE XLVI CRIMES, Chapter 790 WEAPONS AND FIREARMS, 790.001 Definitions | url= http://www.leg.state.fl.us/statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&Search_String=&URL=0700-0799/0790/Sections/0790.001.html |year= 2012 | | |||
| quote=(3)(a) “Concealed weapon” means any dirk, metallic knuckles, slungshot, billie, tear gas gun, chemical weapon or device, or other deadly weapon carried on or about a person in such a manner as to conceal the weapon from the ordinary sight of another person. | |||
| (b) “Tear gas gun” or “chemical weapon or device” means any weapon of such nature, except a device known as a “self-defense chemical spray.” “Self-defense chemical spray” means a device carried solely for purposes of lawful self-defense that is compact in size, designed to be carried on or about the person, and contains not more than two ounces of chemical.}}</ref> | |||
| There is conflicting evidence regarding the effect that concealed carry has on crime rates. A 2020 review by the ] concluded there is supportive evidence that shall-issue concealed carry laws, which require states to issue permits to applicants once certain requirements are met, are associated with increased firearm homicides and total homicides.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book |last1=Smart |first1=Rosanna |last2=Morral |first2=Andrew |last3=Smucker |first3=Sierra |last4=Cherney |first4=Samantha |last5=Schell |first5=Terry |last6=Peterson |first6=Samuel |last7=Ahluwalia |first7=Sangeeta |last8=Cefalu |first8=Matthew |last9=Xenakis |first9=Lea |last10=Ramchand |first10=Rajeev |last11=Gresenz |first11=Carole |date=2020 |title=The Science of Gun Policy: A Critical Synthesis of Research Evidence on the Effects of Gun Policies in the United States, Second Edition |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.7249/rr2088-1 |doi=10.7249/rr2088-1|isbn=9781977404312 |s2cid=51928649 }}</ref> Earlier studies by RAND found that shall-issue concealed carry laws may increase violent crime overall, while there was inconclusive evidence for the effect of shall-issue laws on all individual types of violent crime.<ref>{{cite web |title=Effects of Concealed-Carry Laws on Violent Crime |url=https://www.rand.org/research/gun-policy/analysis/concealed-carry/violent-crime.html |publisher=RAND Corporation}}</ref> A 2004 literature review by the ] concluded that there is no link between the existence of laws that allow concealed carry and crime rates.<ref name=":3" /> | |||
| While there is no federal law specifically addressing the issuance of concealed-carry permits, all 50 ] have passed laws allowing citizens to carry certain concealed firearms in public, either without a permit or after obtaining a permit from local government and/or law enforcement.<ref name=nra-rtc-2007>{{cite web |url= http://www.nraila.org/Issues/FactSheets/Read.aspx?ID=18 |title= Right-to-Carry 2008 |date= 2008-08-19 |publisher= National Rifle Association of America, Institute for Legislative Action}}{{dead link|date=March 2013}}</ref> | |||
| Illinois had been the last state without such a provision – but its long-standing ban on concealed weapons was overturned in a federal ], on ] grounds. Illinois was required by the court to draft a concealed carry law by July 9, 2013 (including a 30-day extension) at which time the Illinois legislature, over-riding the amendatory veto of the governor who had sought to impose many restrictions, approved concealed carry to begin January 2014, at the latest. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| The states give different terms for licenses or permits to carry a concealed firearm, such as a Concealed Handgun License/Permit (CHL/CHP), Concealed Carry Weapons (CCW), Concealed (Defensive/Deadly) Weapon Permit/License (CDWL/CWP/CWL), Concealed Carry Permit/License (CCP/CCL), License To Carry (Firearms) (LTC/LTCF), Carry of Concealed Deadly Weapon license (CCDW), Concealed Pistol License (CPL), etc. Thirteen states use a single permit to regulate the practices of both concealed and ] of a handgun. | |||
| {{Main|History of concealed carry in the United States}} | |||
| ]'')]] | |||
| The ] guarantees the right to "keep and bear arms". Concealed weapons bans were passed in Kentucky and Louisiana in 1813. (In those days open carry of weapons for self-defense was considered acceptable; concealed carry was denounced as the practice of criminals.) By 1859, Indiana, Tennessee, Virginia, Alabama, and Ohio had followed suit.<ref name=Winkler2011p162>{{cite book |last=Winkler |first=Adam |date=September 2011 |title=Gunfight: The Battle Over the Right to Bear Arms in America |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oq39ykAGVYQC&pg=PT162|publisher=] |page=162 |isbn=978-0-393-08229-6}}</ref> By the end of the nineteenth century, similar laws were passed in places such as Texas, Florida, and Oklahoma, which protected some gun rights in their state constitutions.<ref name=Winkler2011p165>{{cite book |last=Winkler |first=Adam |date=September 2011 |title=Gunfight: The Battle Over the Right to Bear Arms in America |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oq39ykAGVYQC&pg=PT165|publisher=] |page=165 |isbn=978-0-393-08229-6}}</ref> Before the mid-1900s, most U.S. states had passed concealed carry laws rather than banning weapons completely.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |last=Wilson |first=Harry L.|editor-last=Carter |editor-first=Gregg Lee|encyclopedia=Guns in American Society: An Encyclopedia of History, Politics, Culture, and the Law |title=Concealed Weapons Laws |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QeGJH48PT0kC&pg=PT320|edition=Second |date=May 2012|publisher=ABC-CLIO|location=Santa Barbara, California|isbn=978-0-313-38671-8|page=320}}</ref> Until the late 1990s, many ] were either "No-Issue" or "Restrictive May-Issue". Since then, these states have largely enacted "Shall-Issue" licensing laws, with more than half of the states legalizing "]" (unrestricted concealed carry) and the remaining "May-issue" licensing laws being abolished in 2022 by the U.S. Supreme Court. | |||
| ==State laws== | |||
| Some states publish statistics indicating how many residents hold permits to carry concealed weapons, and their demographics. For example, Florida has issued 2,031,106 licenses since adopting its law in 1987, and had 843,463 licensed permit holders as of July 31, 2011.<ref name="licgweb.doacs.state.fl.us">''{{dead link|date=March 2013}}'', Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services – Division of Licensing. Retrieved October 2011.</ref> Reported permit holders are predominantly male.<ref>''{{dead link|date=March 2013}}'', Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services – Division of Licensing. Retrieved August 2007.</ref> Some states have reported the number of permit holders increasing over time.<ref>'''', Michigan State Police</ref> "With hard numbers or estimates from all but three of the 49 states that have laws allowing for issuance of carry permits, the GAO reports that there were about 8 million active permits in the United States as of December 31, 2011. That's about a million more than previous estimates by scholars."<ref>'''', NRA Institute for Legislative Affairs</ref> | |||
| ===Permitting policies=== | |||
| {{further|Gun laws in the United States by state}} | |||
| * '''Unrestricted jurisdiction''': one in which a permit is not required to carry a concealed handgun. All states in this category allow any non-prohibited person to carry regardless of the state of residency. | |||
| * '''Permit requirement jurisdiction''': one in which a permit is required to carry a concealed handgun. | |||
| Historically, some states were considered "may-issue" jurisdictions where an applicant was required to provide a proper cause or need to be issued a permit to carry a concealed weapon. However, on June 23, 2022, these laws were found unconstitutional by the ] in '']''. | |||
| The number of permits revocations is typically small.<ref name="licgweb.doacs.state.fl.us"/><ref>'''', North Carolina State Bureau of Investigation</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://licgweb.doacs.state.fl.us/stats/cw_monthly.html |title=Concealed Weapon / Firearm Summary Report – October 1, 1987 – September 30, 2010 |accessdate=October 30, 2010}}{{dead link|date=March 2013}}</ref> The grounds for revocation in most states, other than expiration of a time-limited permit without renewal, is typically the commission of a gross misdemeanor or felony by the permit holder. While these crimes are often firearm-related (including unlawful carry), a 3-year study of Texas crime statistics immediately following passage of CHL legislation found that the most common crime committed by CHL holders that would be grounds for revocation was actually ], followed by unlawful carry and then aggravated assault. The same study concluded that Texas CHL holders were always less likely to commit any particular type of crime than the general population, and overall were 13 times less likely to commit any crime.<ref>An Analysis Of The Arrest Rate Of Texas Concealed Handgun License Holders As Compared To The Arrest Rate Of The Entire Texas Population (1996–1998), Revised to include 1999 data and </ref> | |||
| Regulations differ widely by state, with twenty-seven of the fifty states either currently maintaining a ] policy or implementing it in the near future. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| Laws banning the carrying of concealed weapons were passed in Kentucky and Louisiana in 1813, and other states soon followed: Indiana (1820), Tennessee and Virginia (1838), Alabama (1839), and Ohio (1859). Similar laws were passed in Texas, Florida, and Oklahoma.<ref>Adam Winkler, ''Gunfight: The Battle Over the Right to Bear Arms in America'', 2012, cited in , ''The New Yorker'', Jill Lepore, April 23, 2012</ref> Until the early 2000s, many states in the ] were either ''No-Issue'' or ''Restrictive May-Issue,'' which were a vestige of the ]. In the past decade, these states have largely enacted ''Shall-Issue'' licensing laws, with ] and ] (for certain situations) legalizing ''Unrestricted'' concealed carry. | |||
| The ] limits where an unlicensed person may carry; carry of a weapon, openly or concealed, within {{convert|1000|feet}} of a school zone is prohibited, with exceptions granted in the federal law to holders of valid state-issued weapons permits (state laws may reassert the illegality of school zone carry by license holders), and under ] to current and honorably retired law enforcement officers (regardless of permit, usually overriding state law). | |||
| ==State laws== | |||
| ] | |||
| <!--]--> | |||
| When in contact with an officer, some states require individuals to inform that officer that they are carrying a handgun.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://concealednation.org/2015/07/do-you-have-a-duty-to-inform-when-carrying-concealed-we-look-at-all-50-states-for-the-answers/|title=Do You Have A Duty To Inform When Carrying Concealed? We Look At All 50 States For The Answers|work=Concealed Nation|access-date=2017-07-04|language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://reason.com/assets/db/14987220297616.jpg|title=CCW Disclosure|accessdate=24 July 2023}}</ref> | |||
| Regulations differ widely by state, with most states currently maintaining a "]" policy. As recently as the mid-'90s most states were ] or ], but over the past 30 years states have consistently migrated to less restrictive alternatives. For detailed information on individual states' permitting policies, see ]. | |||
| ] | |||
| Not all weapons that fall under ] are lethal. For example, in Florida, carrying ] in more than a specified volume (2 oz.) of chemical requires a CCW permit, whereas everyone may legally carry a smaller, “self-defense chemical spray” device hidden on their person without a CCW permit.<ref name="790.01">{{cite web | title= 2012 Florida Statutes, Title XLVI Crimes, Chapter 790 Weapons and Firearms, 790.01 Carrying concealed weapons | url= http://www.leg.state.fl.us/statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&Search_String=&URL=0700-0799/0790/Sections/0790.01.html |year= 2012 | |||
| | quote=790.01 Carrying concealed weapons. – (1) Except as provided in subsection (4), a person who carries a concealed weapon or electric weapon or device on or about his or her person commits a misdemeanor of the first degree, punishable as provided in s. 775.082 or s. 775.083. (2) A person who carries a concealed firearm on or about his or her person commits a felony of the third degree, punishable as provided in s. 775.082, s. 775.083, or s. 775.084. (3) This section does not apply to a person licensed to carry a concealed weapon or a concealed firearm pursuant to the provisions of s. 790.06. (4) It is not a violation of this section for a person to carry for purposes of lawful self-defense, in a concealed manner: (a) A self-defense chemical spray. (b) A nonlethal stun gun dart-firing stun gun or other nonlethal electric weapon or device that is designed solely for defensive purposes. (5) This section does not preclude any prosecution for the use of an electric weapon or device, a dart-firing stun gun, or a self-defense chemical spray during the commission of any criminal offense under s. 790.07, s. 790.10, s. 790.23, or s. 790.235, or for any other criminal offense.}}</ref><ref name="790.001">{{cite web | title= 2012 Florida Statutes, Title XLVI Crimes, Chapter 790 Weapons and Firearms, 790.001 Definitions | url= http://www.leg.state.fl.us/statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&Search_String=&URL=0700-0799/0790/Sections/0790.001.html |year= 2012 | | |||
| quote=(3)(a) “Concealed weapon” means any dirk, metallic knuckles, slungshot, billie, tear gas gun, chemical weapon or device, or other deadly weapon carried on or about a person in such a manner as to conceal the weapon from the ordinary sight of another person. (b) “Tear gas gun” or “chemical weapon or device” means any weapon of such nature, except a device known as a “self-defense chemical spray.” “Self-defense chemical spray” means a device carried solely for purposes of lawful self-defense that is compact in size, designed to be carried on or about the person, and contains not more than two ounces of chemical.}}</ref> {{As of|2021||df=}} there have been 21.52 million concealed weapon permits issued in the United States.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Lott|first=John R.|date=2021-10-11|title=Concealed Carry Permit Holders Across the United States: 2021|ssrn=3937627|language=en|location=Rochester, NY|doi=10.2139/ssrn.3937627|journal=SSRN }}</ref> | |||
| {| role="presentation" class="wikitable mw-collapsible innercollapse plainrowheaders sortable" style="text-align:center;font-size:90%;" | |||
| |+ class="wikitable nowrap" | Status of concealed carry, by jurisdiction | |||
| ===Permitting policies=== | |||
| <div class="tright"> | |||
| {| class="wikitable plainrowheaders" style="text-align:center;font-size:90%;" | |||
| |- | |||
| |+Status of concealed carry, by state or other jurisdiction | |||
| ! scope="col"| Jurisdiction<ref name="Steven W. Kranz 2006">{{cite journal |first= Steven W. |last=Kranz |title= A Survey of State Conceal And Carry Statutes: Can Small Changes Help Reduce the Controversy? |volume= 29 |journal= Hamline Law Review |issue= 638 |year=2006 }}</ref> | ! scope="col"| Jurisdiction<ref name="Steven W. Kranz 2006">{{cite journal |first= Steven W. |last=Kranz |title= A Survey of State Conceal And Carry Statutes: Can Small Changes Help Reduce the Controversy? |volume= 29 |journal= Hamline Law Review |issue= 638 |year=2006 }}</ref> | ||
| ! scope="col"| Shall-issue | |||
| ! scope="col"| May-issue | |||
| ! scope="col"| Unrestricted | ! scope="col"| Unrestricted | ||
| ! scope="col"| |
! scope="col"| Permit Required | ||
| ! scope="col"| |
! scope="col"| Illegal | ||
| ! scope="col"| Non-Resident <br /> Permits Available | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="col"| Permit Recognition<ref name="handgunlaw.us">{{cite web |date=<!-- this page is updated frequently --> |url=http://www.handgunlaw.us/states/USStatesMyStateHonors.pdf |title=Permits / Licenses That Each State Honors |website=Handgunlaw.us |access-date=April 22, 2018}}</ref> | |||
| ! scope="row" | Alabama | |||
| ! scpe = "col" | Age | |||
| | {{X mark}}<ref></ref> | |||
| | |
|- | ||
| ! scope="row" | ] | |||
| | | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 18 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | ] | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| 21+ only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| |{{Tick}} | |||
| | ] | |||
| | No | |||
| | N/A | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | ] | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Yes | |||
| 21+ only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | ] | |||
| ! scope="row" | American Samoa<ref>http://handgunlaw.us/states/americansamoa.pdf</ref> | |||
| | {{Tick}}<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.handgunlaw.us/states/arkansas.pdf|title=Gun laws in Arkansas|accessdate=24 July 2023}}</ref> | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes<ref name="A.C.A. § 5-73-321">{{cite web | title= A.C.A. § 5-73-321. Recognition of other states' licenses. | url= https://advance.lexis.com/container?config=00JAA3ZTU0NTIzYy0zZDEyLTRhYmQtYmRmMS1iMWIxNDgxYWMxZTQKAFBvZENhdGFsb2cubRW4ifTiwi5vLw6cI1uX&crid=41d7bf2b-03e7-40a9-b25b-b7c7afcb9176 |year= 2013}}</ref> | |||
| | 18 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| |{{Green check}}<ref>{{Cite web |title=CA attorney General Legal Alert |url=https://oag.ca.gov/system/files/media/legal-alert-oag-2022-02.pdf}}</ref> | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | | |||
| | No | |||
| |21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | On Journey | |||
| | | | | ||
| | |
| ] | ||
| | Partial (33 states) | |||
| Resident permits only | |||
| 21+ only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | |||
| | Some counties in practice | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | Colorado | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | No | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | ] | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} (Rarely issued) | |||
| | Partial (21 states) | |||
| | 18 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | Briefly from July 26, 2014 – July 29, 2014; see below for details | |||
| | In practice | |||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}}<ref>Dejean, Ashley (October 3, 2017) – ''Mother Jones''. Retrieved October 7, 2017.</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| | No | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | In practice | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Yes | |||
| Resident permits only | |||
| 21+ only; 18+ if military | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 21 (18 with out of state carry permit) | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}}<ref>Matanane, Sabrina Salas (May 28, 2014) – ''Kuam News''. Retrieved February 2, 2015.</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | Georgia | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | No | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | |
| | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | |||
| | in practice | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | No | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | For concealed carry by non-military permanent resident aliens | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | | Yes | ||
| | 18 | |||
| | In practice | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | Unloaded and enclosed in a case, firearm carrying box, shipping box, or other container<ref>{{cite web|url=https://law.justia.com/cases/illinois/court-of-appeals-fourth-appellate-district/1996/4951016.html |title=People v. Bruner – 1996 – Illinois Appellate Court, Fourth District Decisions |website=Justia |access-date=April 22, 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|date=October 8, 2009 |url=http://www.illinoiscourts.gov/Opinions/SupremeCourt/2009/October/106367.pdf |title=Docket No. 106367 – People v. Diggins |website=Illinois Courts |access-date=April 22, 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |first=Michael |last=Higgins |date=November 28, 2000 |url=https://www.chicagotribune.com/2000/11/28/owners-say-law-lets-them-tote-guns-in-fanny-packs/ |title=Owners Say Law Lets Them Tote Guns in Fanny Packs |website=Chicago Tribune |access-date=April 22, 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |first=Ted |last=Gregory |date=June 3, 2004 |url=https://www.chicagotribune.com/2004/06/03/dupage-pays-for-handgun-arrest/ |title=Dupage Pays for Handgun Arrest |website=Chicago Tribune |access-date=April 22, 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=May 18, 2004 |url=https://thecrimereport.org/2004/05/18/gun-rights-advocates-win-victory-in-chicago-court/ |title=Gun-Rights Advocates Win Victory in Chicago Court |website=The Crime Report |access-date=April 22, 2018}}</ref> | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | {{Tick}}<ref>McCune, Greg (July 9, 2013). , ''Reuters''. Retrieved July 20, 2013.</ref><ref>Jones, Ashby (July 9, 2013). , ''Wall Street Journal''. Retrieved July 20, 2013.</ref><ref>McDermott, Kevin, and Hampel, Paul (July 11, 2013). , ''St. Louis Post-Dispatch''. Retrieved July 20, 2013.</ref><ref>DeFiglio, Pam (July 9, 2013). , ''Patch Media''. Retrieved July 20, 2013.</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| | Rural Areas | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | Only for residents of Arkansas, Idaho, Mississippi, Nevada, Texas and Virginia.<ref>{{cite web |date=March 3, 2018 |url=http://www.handgunlaw.us/states/illinois.pdf |title=Illinois |website=Handgunlaw.us |access-date=April 22, 2018}}</ref> | |||
| | Vehicle carry only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| |{{X mark}}<ref>McCune, Greg (July 9, 2013). , ''Reuters''. Retrieved July 20, 2013.</ref><ref>Jones, Ashby (July 9, 2013). , ''Wall Street Journal''. Retrieved July 20, 2013.</ref><ref>McDermott, Kevin, and Hampel, Paul (July 11, 2013). , ''St. Louis Post-Dispatch''. Retrieved July 20, 2013.</ref><ref>DeFiglio, Pam (July 9, 2013). , ''Patch Media''. Retrieved July 20, 2013.</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Yes | |||
| Includes foreign countries | |||
| | 18 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} (Rarely issued) | |||
| | Yes<ref name="§724.11A">{{cite web | title= §724.11A. Recognitions. | url= https://www.legis.iowa.gov/docs/code/2021/724.11A.pdf|year= 2017}}</ref> | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | For concealed carry between ages 18–20 | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 18 with permit | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}}{{efn|Permit not required as of July 4, 2024.}} | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | ] | |||
| | Partial (36 states) | |||
| 21+ only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}} Duty to inform if carrying concealed without a permit | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | For carrying in state/national parks, regular archery hunting during deer season, employees' vehicles on work premises and concealed carry between ages 18–20 | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Partial (27 states) | |||
| Resident permits only 18+ | |||
| Can carry permitless if 21+; 18+ if military | |||
| | 18 with permit | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}}<ref name="NRA-ILA">{{Cite web |last=NRA-ILA |title=NRA-ILA {{!}} Maryland Gun Laws |url=https://www.nraila.org/gun-laws/state-gun-laws/maryland/ |access-date=2017-10-07 |website=NRA-ILA |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| | No | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | |
| | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | |
| | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | In practice | |||
| | No | |||
| | {{X mark}}<ref name="mdlaw"></ref> | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | |
| | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| Resident permits only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Partial (17 states) | |||
| | 18 by court order | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}}Only if carried in a belt/shoulder holster, sheath, purse, handbag, satchel, other similar bag or briefcase or fully enclosed case when concealed | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | For concealed carry without a belt/shoulder holster, sheath, purse, handbag, satchel, other similar bag or briefcase or fully enclosed. For carrying concealed at any polling place, meeting place of the state legislature or other governing body, school, college, professional athletic event, establishment licensed to serve alcoholic beverages, passenger terminal of an airport, federal buildings (under state law), permitted parade/demonstration or courthouse for those with an enhanced firearms permit. | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 18 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | For open carry in localities where restricted | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 18 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Partial (43 states) | |||
| Can carry permitless | |||
| | 18 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | |
| | ||
| | Outside of city limits | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| |Partial (35 states + DC) | |||
| 21+ only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Partial (24 states) | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| |Partial (28 states) | |||
| Resident permits only | |||
| Can carry permitless | |||
| | 18* | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | New |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}}<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://apnews.com/article/us-supreme-court-gun-politics-new-york-violence-kathy-hochul-ebe58ea297c154a25a62650dec935529|title=States with strict gun-permitting laws consider next steps|website=AP News|date=23 June 2022|access-date=2022-06-23}}</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| |{{Tick}} | |||
| | No | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | New |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | Unloaded | |||
| | | |||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | |||
| | In practice | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Partial (23 states) | |||
| 21+ only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | New |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | |||
| | In vehicle/Unloaded | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}}<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.scotusblog.com/2022/06/in-6-3-ruling-court-strikes-down-new-yorks-concealed-carry-law/|title=In 6-3 ruling, court strikes down New York's concealed-carry law|last=Howe|first=Amy|website=SCOTUSblog|date=23 June 2022|access-date=2022-06-23}}</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| | ] | |||
| | No | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | New York | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | |
| | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | |
| | ||
| | ] | |||
| | {{X mark}}<ref name="NYS Assembly Bill S01863">. Assembly.state.ny.us (2011-01-13). Retrieved on 2011-10-16.</ref><ref name="Kachalsky vs. Cacase">. www.saf.org</ref> | |||
| | Does not recognize any other jurisdictions' permits. Permits may be approved by the city's police commissioner on an individual basis. | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | North Carolina | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{X mark}}<ref name="NC_SI_law">{{cite web|url=http://www.jus.state.nc.us/NCJA/ncfirearmslaws.pdf |title=North Carolina ''shall-issue'' laws |publisher=Jus.state.nc.us |date= |accessdate=2010-11-08}}</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}}<ref name="NC_SI_law">{{cite web |url=http://www.jus.state.nc.us/NCJA/ncfirearmslaws.pdf |title=North Carolina ''shall-issue'' laws |publisher=Jus.state.nc.us|access-date=2010-11-08 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090326132237/http://www.jus.state.nc.us/NCJA/ncfirearmslaws.pdf |archive-date=2009-03-26}}</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 21 (18 with out of state carry permit) | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | North Dakota | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}} Duty to inform if carrying concealed without a permit | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | For open-carry | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Partial (39 states) | |||
| Can carry permitless | |||
| | 18 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Northern Mariana Islands |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | |
| | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| |{{Tick}} | |||
| | ] | |||
| | No | |||
| | N/A | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Ohio | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 21 (18 with out of state carry permit) | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Oklahoma | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Oregon | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}}<ref name="OR_SI_law">{{Cite web |url=http://www.oregonlaws.org/ors/166.291 |title=166.291: Issuance of concealed handgun license |quote= The sheriff of a county, upon a persons application for an Oregon concealed handgun license, upon receipt of the appropriate fees and after compliance with the procedures set out in this section, '''shall issue''' the person a concealed handgun license}}</ref> | |||
| | {{Tick}}<ref name="OR_SI_law">{{cite web |url=http://www.oregonlaws.org/ors/166.291 |title=166.291: Issuance of concealed handgun license |quote= The sheriff of a county, upon a person's application for an Oregon concealed handgun license, upon receipt of the appropriate fees and after compliance with the procedures set out in this section, '''shall issue''' the person a concealed handgun license}}</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} Only for residents of California, Idaho, Nevada, and Washington. | |||
| | No | |||
| |21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Pennsylvania | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| |Partial (29 states) | |||
| Resident permits only | |||
| 21+ only | |||
| All permits recognized for vehicle carry | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Puerto Rico | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | From June 20, 2015, to October 31, 2016. | |||
| | | |||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | |||
| | In practice | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Has reciprocity law, but does not recognize any other state permits | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Rhode Island | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | | |||
| | Local permits | |||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | |
| | ||
| | {{Tick}} Both the local authorities and the Attorney General issue. | |||
| | In practice | |||
| | Vehicle carry only | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | South Carolina | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Partial (29 states) | |||
| Resident permits only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | South Dakota | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 18 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Tennessee | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | {{X mark}}<ref name="TN_SI_law">{{cite web|url=http://www.tennessee.gov/safety/handgunmain.htm |title=Tennessee ''shall-issue'' laws |publisher=Tennessee.gov |date= |accessdate=2010-11-08}}</ref> | |||
| | For carrying in buildings posted with "concealed firearms by permit only" signs, state/national parks, campgrounds, greenways, and nature trails | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 18 by court order | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Texas | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | {{X mark}}<ref name="TX_CHL" /><ref name="TX_SI_law" /> | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Partial (43 states) | |||
| Can carry permitless | |||
| | 18 by court order | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | United States Virgin Islands |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | | | ||
| |{{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | ] | |||
| | Has reciprocity law, but does not recognize any other state permits<ref name="V.I.C Title 23 Chpt. 5 § 460">{{cite web | title= V.I.C Title 23 Chpt. 5 § 460. Reciprocal recognition of out-of-state licenses.| url= https://advance.lexis.com/container?config=024453JABiMWFjOTk0OS1hNTVlLTQ1MDctYmZkOS1mNGRkY2I0ZTg2YzQKAFBvZENhdGFsb2fNaUTUAugmXPqNctTcuqLy&crid=af62b105-2add-4f86-b81a-9ab37de79993 |year= 1968}}</ref> | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Utah | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | {{X mark}}<ref name="UT_SI_law">{{cite web|url=http://publicsafety.utah.gov/bci/concealedfirearms.html |title=Utah ''shall-issue'' laws |publisher=Publicsafety.utah.gov |date=2010-10-05 |accessdate=2010-11-08}}</ref> | |||
| | For carrying between ages 18–20 | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Yes | |||
| | 18 with permit | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Vermont | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | | |||
| | ] | |||
| | N/A | |||
| | 16 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Virginia | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{X mark}}<ref>. Concealed-carry.net. Retrieved on 2011-10-16.</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}}<ref>. vaguntraining.com. Retrieved on 2014-04-15.</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Yes | |||
| 21+ only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Washington | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | Any person engaging in a lawful outdoor recreational activity such as hunting, fishing, camping, hiking, or horseback riding, so long as it is reasonable to assume that they are performing that activity or traveling to or from the activity.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.atg.wa.gov/firearms-faq|title=Firearms FAQ {{!}} Washington State|website=www.atg.wa.gov|access-date=September 16, 2021}}</ref> | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Partial (9 states) | |||
| 21+ only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | West Virginia | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | For concealed carry between ages 18–20 | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | Partial (35 states) | |||
| Can carry permitless | |||
| 21+ only; 18+ if military for both | |||
| | 18 with permit | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | Wisconsin | ! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Partial (44 states + DC, PR & VI) | |||
| 21+ only | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | ] | ||
| | {{ |
| {{Tick}} | ||
| | | | | ||
| |{{X mark}} WY Residents Only | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | ] | |||
| | Partial (35 states) | |||
| Can carry permitless | |||
| | 21 (18 with out of state carry permit) | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope="row" | |
! scope="row" | U.S. Military installations | ||
| | | |||
| | {{X mark}} | |||
| | | |||
| | | |||
| | | | | ||
| | {{Tick}}<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.militarytimes.com/articles/troops-concealed-handguns-armed-military-recruiters|title=Acknowledging domestic terror threat, Pentagon says troops, recruiters can carry concealed guns|website=Military Times|date=21 November 2016|access-date=2016-11-23}}</ref> | |||
| | | |||
| | ] | |||
| | No | |||
| | 21 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope="row" | Native American reservations | |||
| | | |||
| | {{Tick}} | |||
| | | |||
| | Varies | |||
| | Varies | |||
| | Varies | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| </div> | |||
| <nowiki>*</nowiki> Jurisdiction gives no minimum age to conceal carry in law. The age is set at 18 by federal law. | |||
| State regulations relating to the issuance of concealed carry permits generally fall into four categories described as Unrestricted, Shall Issue, May issue and No Issue. | |||
| ====Unrestricted==== | ====Unrestricted jurisdictions==== | ||
| {{Main|Constitutional carry}} | |||
| An Unrestricted jurisdiction is one in which a ] is not required to carry a concealed handgun. This is sometimes called ]. | |||
| An '''unrestricted''' jurisdiction is one in which a ] is not required to carry a concealed handgun. This is sometimes called ]. Within the unrestricted category, there exist states that are ''fully unrestricted,'' where no permit is required for lawful open or concealed carry, and ''partially unrestricted,'' where certain forms of concealed carry may be legal without a permit, while other forms of carry may require a permit. | |||
| Among ] states, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, Vermont and Wyoming allow residents to carry a concealed firearm without a permit.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dps.state.ak.us/statewide/permitslicensing/concealedhandguns.aspx |title=Alaska Concealed Handgun Permits – Permits and Licensing Unit |publisher=Dps.state.ak.us |date= |accessdate=2010-11-08}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.leg.state.vt.us/statutes/fullchapter.cfm?Title=13&Chapter=085 |title=The Vermont Statutes Online |publisher=Leg.state.vt.us |date= |accessdate=2010-11-08}}</ref><ref name="thewyonews.net">{{cite web|url=http://thewyonews.net/2011/03/02/gov-mead-signs-bill-allowing-concealed-carry-without-a-permit/ |title=Governor Mead Signs Bill Allowed Concealed-Carry Without a Permit |publisher=thewyonews.net |date = |accessdate=2011-03-03}}{{dead link|date=March 2013}}</ref> These states also allow the ] of a handgun without a permit. | |||
| Some states have a limited form of permitless carry, restricted based on one or more of the following: a person's location, the loaded/unloaded state of the firearm, or the specific persons who may carry without a permit. {{As of|2021|02|18|df=US}}, these states are ], ], and ]. Some states that allow permitless concealed carry and still issue concealed carry permits may impose restrictions on concealed carry for certain places and/or at certain times (e.g., special events, large public gatherings, etc.). In some such situations, those holding a valid concealed carry permit may be exempt from such restrictions. | |||
| Vermont does not have any provision for issue of concealed-carry licenses, as none has ever been necessary. As such, Vermont residents wishing to carry handguns in other states must acquire a license from a state which is valid in their destination. A popular choice is Florida's concealed handgun permit, which is valid for nonresident holders in 28 other states. Alaska, Arizona, and Wyoming all previously had concealed-carry license requirements prior to adoption of unrestricted carry laws, and continue to issue licenses on a "shall-issue" basis for the purposes of inter-state reciprocity (allowing residents of the state to travel to other states with a concealed weapon, abiding by that state's law). | |||
| ====Permit requirement jurisdictions==== | |||
| In ], ], ], and ], bills are being discussed that would allow unrestricted carry.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.deseretnews.com/article/700100439/Utah-lawmaker-Guns-should-be-legal-without-permit.html|title=Utah lawmaker: Guns should be legal without permit|publisher=Deseret News|accessdate=16 January 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.thestate.com/2011/02/25/1711532/sc-political-briefs.html|title=S.C. Political Briefs|publisher=thestate.com |accessdate=February 25, 2011}}{{dead link|date=March 2013}}</ref><ref>{{dead link|date=March 2013}}. Nraila.org (March 16, 2011). Retrieved on October 16, 2011.</ref><ref>{{dead link|date=October 2011}}</ref> Montana and Idaho both currently allow concealed carry without a permit in places outside of any incorporated municipality. ] and ] laws allow an individual to conceal carry an unloaded handgun without a permit. New Mexico further allows one to carry a loaded hangun either openly or concealed while traveling in a vehicle, including motorcycles, bicycles or while riding a horse. | |||
| A permit requirement jurisdiction is one in which a government-issued permit is required to carry a concealed handgun in public. Before the U.S. Supreme Court ruling in ''New York State Rifle & Pistol Association, Inc. v. Bruen'', these jurisdictions were further split between "shall-issue", which is the current national licensing standard where the granting of licenses is subject only to meeting determinate criteria laid out in the law, and "may-issue" where the granting of such licenses was at the discretion of local authorities. Since the abolishment of "may-issue" permitting the U.S. Supreme Court has stated it is still legal for U.S. jurisdictions subject to the Constitution to require a permit to carry a concealed handgun, and that background checks, training, and proper fees can be required without violating the ] which guarantees a right of the people to carry a concealed firearm outside of the home. | |||
| ==== Concealed carry on U.S. military installations ==== | |||
| ] limits where an unlicensed person may carry; carry of a weapon, openly or concealed, within 1000 feet of a school zone is prohibited, with exceptions granted in the Federal law to holders of valid State-issued weapons permits (State laws may reassert the illegality of school zone carry by license holders), and under LEOSA to current and honorably retired law enforcement officers (regardless of permit, usually trumping State law). | |||
| While members of the Armed Services may receive extensive small arms training, ] installations have some of the most restrictive rules for the possession, transport, and carrying of personally-owned firearms in the country. | |||
| Overall authority for carrying a personally-owned firearm on a military installation rests with the installation commander, although the authority to permit individuals to carry firearms on an installation is usually delegated to the ]. Military installations do not recognize state-issued concealed carry permits, and state firearms laws generally do not apply to military bases, regardless of the state in which the installation is located. Federal law (18 USC, Section 930) generally forbids the possession, transport, and carrying of firearms on military installations without approval from the installation commander. Federal law gives installation commanders wide discretion in establishing firearms policies for their respective installations. In practice, local discretion is often constrained by policies and directives from the headquarters of each military branch and major commands. | |||
| ====Shall-Issue==== | |||
| A Shall-Issue jurisdiction is one that requires a ] to carry a concealed handgun, but where the granting of such licenses is subject only to meeting determinate criteria laid out in the law; the granting authority has no discretion in the awarding of the licenses, and there is no requirement of the applicant to demonstrate "good cause". The laws in a Shall-Issue jurisdiction typically state that a granting authority ''shall issue'' a license if the criteria are met, as opposed to laws in which the authority ''may issue'' a license at their discretion. | |||
| Installation policies can vary from no-issue for most bases to shall-issue in rare circumstances. Installations that do allow the carrying of firearms typically restrict carrying to designated areas and for specific purposes (i.e., hunting or officially sanctioned shooting competitions in approved locations on the installation). Installation commanders may require the applicant to complete extensive firearms safety training, undergo a mental health evaluation, and obtain a letter of recommendation from their unit commander (or employer) before such authorization is granted. Personnel that reside on a military installation are typically required to store their personally-owned firearms in the installation armory, although the installation commander or provost marshal may permit a service member to store their personal firearms in their on-base dwelling if they have a ] or similarly designed cabinet where the firearms can be secured. | |||
| Typical license requirements include residency, minimum age, submitting fingerprints, passing a computerized instant background check (or a more comprehensive manual background check), attending a certified handgun/firearm safety class, passing a practical qualification demonstrating handgun proficiency, and paying a required fee. These requirements vary widely by jurisdiction, with some having few or none of these and others having most or all. | |||
| Prior to 2011, military commanders could impose firearms restrictions to servicemembers residing off-base, such as mandatory registration of firearms with the base provost marshal, restricting or banning the carrying of firearms by servicemembers either on or off the installation regardless of whether the member had a state permit to carry, and requiring servicemembers to have a gun safe or similar container to secure firearms when not in use. A provision was included in the ] that limited commanders' authority to impose restrictions on the possession and use of personally-owned firearms by service members who reside off-base. | |||
| The following are Shall-Issue states: Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Carolina,<ref name="NC_SI_law"/> North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon,<ref name="OR_SI_law"/> Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee,<ref name="TN_SI_law"/> Texas,<ref name="TX_CHL">{{cite web |url=http://www.txdps.state.tx.us/RSD/CHL/index.htm |title=Concealed Handgun Licensing Program |publisher=]}}</ref><ref name="TX_SI_law">{{cite web |url=http://www.statutes.legis.state.tx.us/Docs/GV/htm/GV.411.htm#411.172 |title=Texas Government Code, Chapter 411, Subchapter H. License to carry a concealed handgun, Section 411.172. Eligibility}}</ref> Utah,<ref name="UT_SI_law"/> Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and Wyoming.<ref name="Steven W. Kranz 2006"/> | |||
| ==== Concealed carry on Native American reservations ==== | |||
| Certain states and jurisdictions, while "may-issue" by law, direct their issuing authorities to issue licenses to all or nearly all qualified applicants, and as such they are considered "shall-issue" in practice. ], and certain cities and counties in ] are examples. | |||
| Concealed carry policies on Native American reservations are covered by the tribal laws for each reservation, which vary widely from "No-Issue" to "Shall-Issue" and "Unrestricted" either in law or in practice. Some Native American tribes recognize concealed carry permits for the state(s) in which the reservation is located, while others do not. For reservations that do not recognize state-issued concealed carry permits, some completely ban concealed carry, while others offer a tribal permit for concealed carry issued by the tribal police or tribal council. Tribal concealed carry permits may be available to the general populace or limited to tribal members, depending on tribal policies. Tribal law typically pre-empts state law on the reservation. The only exception is while traversing the reservation on a state-owned highway (including interstate, U.S. routes, and in some instances county roads), in which case state law and the federal Firearm Owners' Protection Act (FOPA) apply. | |||
| ====Limitations on concealed carry==== | |||
| Connecticut law specifies that CCW licenses be granted on a ''May-Issue'' basis, but the state's courts have established that issuing authorities must grant CCW licenses on a ''Shall-Issue'' basis for applicants who meet all statutory qualifications, as unlike other ''May-Issue'' states Connecticut law does not contain a requirement for the applicant to show "necessary and proper reason" for obtaining a license. Connecticut has a two-tiered system of Temporary (60-day) and Regular (5-year) licenses, the permanent licensing process considered to be shall-issue in practice. In Connecticut, issuance of the temporary license from local authorities is not a prerequisite to obtain the regular license; however one must apply for the temporary license and wait for a decision from local authorities before applying for the regular license. Normally, the regular license is generally granted for applicants that meet statutory criteria regardless of whether the temporary license is issued or denied. | |||
| Prohibitions of the concealed carry of firearms and other weapons by local governments predate the establishment of the United States. In 1686, New Jersey law stated "no person or persons … shall presume privately to wear any pocket pistol … or other unusual or unlawful weapons within this Province." After the federal government was established, states and localities continued to restrict people from carrying hidden weapons. Tennessee law prohibited this as early as 1821. By 1837, Georgia passed into effect “An Act to guard and protect the citizens of this State, against the unwarrantable and too prevalent use of deadly weapons." Two years later, Alabama followed suit with “An Act to Suppress the Evil Practice of Carrying Weapons Secretly." Delaware prohibited the practice in 1852.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Robert J.|first1=Spitzer|title=Even in the Wild West, there were rules about carrying concealed weapons|url=https://www.latimes.com/opinion/op-ed/la-oe-spitzer-peruta-concealed-carry-20160619-snap-story.html|access-date=21 June 2016|work=Los Angeles Times|date=19 June 2016}}</ref> Ohio did the same in 1859, a policy that remained in effect until 1974.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Joe|first1=Eaton|last2=Chad D.|first2=Baus|title=Ohio Gun Rights Timeline|url=http://www.buckeyefirearms.org/ohio-gun-rights-timeline-journey-towards-freedom|website=Buckeye Firearms Association|access-date=21 June 2016}}</ref> Cities also regulated weapons within their boundaries. In 1881, ], enacted Ordinance No. 9 "To Provide against Carrying of Deadly Weapons", a regulation that sparked the ] later that year. | |||
| Some permit requirement jurisdictions allow issuing authorities to impose limitations on CCW permits, such as the type and caliber of handguns that may be carried (], ]), restrictions on places where the permit is valid (], ], ]), restricting concealed carry to purposes or activities specified on the approved permit application (], Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York), limitations on magazine size (], Massachusetts, New York), or limitations on the number of firearms that may be carried concealed by a permit-holder at any given time (some states). Permits issued by all but two states (New York and Hawaii) are valid statewide. New York State pistol licenses, which are generally issued by counties, are valid statewide with one exception. A permit not issued by New York City is invalid in that city unless validated by its police commissioner.<ref name="New York State License Validity">{{Cite web|url=https://ypdcrime.com/penal.law/article400.php|title=Article 400 | NYS Penal Law | Licensing Provisions Firearms|website=ypdcrime.com|accessdate=24 July 2023}}</ref><ref name="New York State firearm law table, 'Carry Permit' row">]</ref> Permits issued by Hawaii are valid only in the county of issuance. | |||
| ====May-Issue==== | |||
| A ''May-Issue'' jurisdiction is one that requires a ] to carry a concealed handgun, and where the granting of such permits is partially at the discretion of local authorities (frequently the ] or ]), with a few states consolidating this discretionary power under state-level law enforcement. The law typically states that a granting authority "may issue" a permit if various criteria are met, or that the permit applicant must have "good cause" (or similar) to carry a concealed weapon. In most such situations, self-defense in and of itself often does not satisfy the "good cause" requirement, and issuing authorities in some ''May-Issue'' jurisdictions have been known to arbitrarily deny applications for CCW permits without providing the applicant with any substantive reason for the denial. | |||
| ''May-Issue'' can be compared to ''Shall-Issue'' where in a ''May-Issue'' jurisdiction, the burden of proof for justifying the need for a permit rests with the applicant, whereas in a ''Shall-Issue'' jurisdiction the burden of proof to justify denying a permit rests with the issuing authority. | |||
| The following are "may-issue" states: ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| A state that is '']'' a ''May-Issue'' jurisdiction may range anywhere from ''Shall-Issue'' to ''No-Issue'' in practice,<ref name=i2i-shall-issue>{{cite web |url= http://www.i2i.org/main/article.php?article_id=643&print=1 |title=  'Shall Issue': The New Wave of Concealed Handgun Permit Laws |accessdate= 2008-04-13 |author= Clayton E. Cramer and David B. Kopel | |||
| |date= 1994-10-17 |publisher= ] }}</ref><ref>Clayton E. Cramer & David B. Kopel, " 'Shall Issue': The New Wave of Concealed Handgun Permit Laws", Tennessee Law Review, July 1995. </ref> i.e., ''Permissive May-Issue'' to ''Restrictive May-Issue'', based on each licensing authority's willingness to issue permits to applicants: | |||
| * ] and ] are regarded as ''Permissive May-Issue'' states, where either governmental policy or court precedence direct issuing authorities to approve applications that meet all non-discretionary criteria. | |||
| * ], ], ], ] and ] (for statewide CCW permits) are considered ''Restrictive May-Issue'' states, where issuing authorities are directed to deny most or all applications, either based on hard-to-meet "good cause" requirements or agency policies specifically prohibiting issue. Additionally, ] (for state permits), Maryland and New Jersey require the applicant provide substantive evidence of a clear and immediate threat on their lives that exists outside of their home at the time the permit application is filed. Rhode Island further requires applicants for the statewide permit to submit to a mental health records check at the applicant's expense. | |||
| * ], ], and ] vary within state; Inland California, rural portions of Massachusetts, and ] are Permissive, while the ], ], ], ], and ] metropolitan areas are Restrictive. California's "May Issue" status has been thrown into question with the 9th District Court's ruling in ''Peruta v County of San Diego'', where the state's mostly restrictive concealed carry requirements & qualifications were deemed unconstitutional.<ref></ref> | |||
| * ] state law is two-tier; local authorities are directed by state law and court precedent (''Archer v McGarry'') to practice shall-issue permitting policy, but the Attorney General's office has discretionary authority over state-issued permits (required for open carry in general and for concealed carry outside the resident's home jurisdiction), and some local jurisdictions, at the recommendation of the AG, still refer all applicants to the AG's office and the "may-issue" state-level system in violation of ''Archer''.<ref></ref> | |||
| In some ''May-Issue'' jurisdictions, permits are only issued to individuals with celebrity status, have political connections, or have a high degree of wealth.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.cato.org/pubs/pas/pa-284.html | title=Fighting Back: Crime, Self-Defense, and the Right to Carry a Handgun | publisher=Cato Institute | accessdate=January 3, 2012 | author=Snyder, Jeffrey}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.nypost.com/p/news/local/madoff_son_of_gun_LDcUvEw9PXY0rS1oNFfl1J | title=Madoff son of a gun Bernie kid on pistol-permit list | publisher=NY Post | accessdate=January 3, 2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite news | url=http://www.nytimes.com/2011/02/20/nyregion/20guns.html | title=The Rich, the Famous, the Armed | work=] |date=February 18, 2011 |author=Jo Craven McGinty | accessdate=January 3, 2012}}</ref> In some such cases, issuing authorities charge arbitrarily-defined fees that go well beyond the basic processing fee for a CCW permit, thereby making the CCW permit unaffordable to most applicants. | |||
| May-issue permitting policies are currently under legal challenge in California, Hawaii, Maryland, New Jersey and New York; most thus far have survived challenge though the "May Issue" status for California and Hawaii have recently been thrown into question by the ruling of the 9th District Federal Appeals court in ''Peruta v County of San Diego''. In recent cases challenging restrictive discretionary issue laws, federal district and appeals courts have generally applied ] to these and other Second Amendment related cases, where the courts recognize that restrictive concealed carry laws "infringe on an individual's right to keep and bear arms," but also recognizes that such infringement is permitted to further "an important government interest in public safety." In Maryland, '']'', the ] decided in favor of a Maryland resident who was denied a permit renewal due to lack of "good cause" in accordance with Maryland law.<ref>{{cite court |litigants=Woollard v. Sheridan |vol=863 |reporter=F.Supp 2d |opinion=462 |pinpoint= |court=D. Md.|date=2012|url= |accessdate= |quote=}}, ''rev'd sub nom'' ''Woollard v. Gallagher'', 712 F.3d 865 (4th Cir. 2013).</ref> The ] reversed, holding the "good cause" requirement met the standard of ] applicable to restrictions on the right to carry arms outside the home, and reinstated the "good cause" requirement on March 21, 2013.<ref>{{cite court |litigants=Woollard v. Gallagher |vol=712 |reporter=F.3d |opinion=865 |pinpoint= |court=4th Cir. |date=2013 |url=http://www.ca4.uscourts.gov/Opinions/Published/121437.P.pdf |accessdate= 17 November 2013 |quote=}}</ref> The plaintiffs in the case filed a petition for ] in the ]; the court denied certiorari without comment on October 15.<ref>{{cite court |litigants=Woollard v. Gallagher |vol=--- |reporter=S.Ct.|opinion=---- <!-----This should be filled in once the Supreme Court Reporter gets around to adding this term's denials of cert.---->|pinpoint= |court=|date=2013 |url=http://www.supremecourt.gov/Search.aspx?FileName=/docketfiles/13-42.htm|accessdate= 17 November 2013 |quote=}}</ref> New York's similar "good cause" requirement was also under challenge in '']. ''However, '']'' before SCOTUS was denied on April 15, 2013. Additionally, the case ''Peruta v. County of San Diego'' that is being heard by the Ninth Circuit U.S. Court of Appeals is challenging discretionary issue laws in California. Drake v. Filko, involving several plaintiffs (including one kidnap victim) denied permits under New Jersey's permitting system; the suit challenged New Jersey's "justifiable need" requirement for obtaining a carry permit. The ] affirmed the lower court's judgment holding the requirement constitutional, holding (much like the 4th Circuit in ''Woollard'' and the 2nd Circuit in ''Kachalsky'') that the New Jersey statute survived ].<ref>{{cite court |litigants=Drake v. Filko |vol=724 |reporter=F.3d |opinion=426 |pinpoint= |court=3d Cir. |date=2013 |url=http://vls.law.villanova.edu/locator/3d/July2013/121150p.pdf |accessdate= 17 November 2013 |quote=}}</ref> The common theme from Courts of Appeals rulings upholding ''May-Issue'' laws is that state or local policies in limiting who is granted permits to carry firearms in public "furthers an important government interest in public safety." The courts have opined that these laws survive intermediate scrutiny on that basis. | |||
| While members of the Armed Services receive extensive small arms training, ] installations have some of the most restrictive rules for the possession, transport, and carrying of personally-owned firearms in the country. Overall authority for carrying a personally-owned firearm on a military installation rests with the installation commander, although the authority to permit individuals to carry firearms on an installation is usually delegated to the ]. Military installations do not recognize state-issued concealed carry permits, and state firearms laws generally do not apply to military bases, regardless of the state in which the installation is located. Federal law (18 USC, Section 930) generally forbids the possession, transport, and carrying of firearms on military installations without approval from the installation commander. While federal law gives installation commanders wide discretion in establishing firearms policies for their respective installations, local discretion is often constrained by policies and directives from the headquarters of each military branch and major commands. Installation policies can vary from ''No-Issue'' for most bases to ''Shall-Issue'' in rare circumstances. Installations that do allow the carrying of firearms typically restrict carrying to designated areas and for specific purposes (i.e., hunting or officially-sanctioned shooting competitions in approved locations on the installation). Installation commanders may require the applicant complete extensive firearms safety training, undergo a mental health evaluation, and obtain a letter of recommendation from his or her unit commander (or employer) before such authorization is granted. Personnel that reside on a military installation are typically required to store their personally-owned firearms in the installation armory, although the installation commander or provost marshal may permit a servicemember to store his or her personal firearms in their on-base dwelling if he or she has a ] or similarly-designed cabinet where the firearms can be secured. Prior to 2011, military commanders could impose firearms restrictions to servicemenbers residing off-base, such as mandatory registration of firearms with the base Provost Marshal, restricting or banning the carrying of firearms by servicemembers either on or off the installation regardless of whether the member had a state permit to carry, and requiring servicemembers to have a gun safe or similar container to secure firearms when not in use. A provision was included in the ] that limited commanders' authority to impose restrictions on the possession and use of personally-owned firearms by servicemembers who reside off-base. | |||
| ====No-Issue==== | |||
| A ''No-Issue'' jurisdiction is one that – with very limited exceptions – does not allow any private citizen to carry a concealed handgun in public. The term refers to the fact that no concealed carry permits will be issued (or recognized). Since July 2013, with the legalization of concealed carry in Illinois, there are no patently no-issue states. | |||
| The ] is a ''No-Issue'' jurisdiction by law, and forbids both open and concealed carry except under a very limited set of circumstances. The District of Columbia recently lost a Supreme Court case relating to restrictions on ownership and possession of firearms ('']''), however, the case did not specifically address the question of public carry, either open or concealed. While technically ''May-Issue'' under state law, ], ], ], ] (for statewide permits issued by the Attorney General's Office) and certain cities and counties within California and New York are ''No-Issue'' jurisdictions in practice, with governmental policy directing officials with discretionary power to rarely or never issue licenses. Additionally, all of the United States' insular territories (Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, etc.) are ''No-Issue'' jurisdictions either by law or in practice. Most ''No-Issue'' jurisdictions have exceptions to their laws that permit open or concealed carry by active and retired law enforcement officials, armed security personnel while on duty and in uniform, and for members of the Armed Forces.{{citation needed|date=August 2013}} | |||
| ====Limitations on CCW Permits==== | |||
| Most ''May-Issue'' jurisdictions, and some ''Shall-Issue'' jurisdictions allow issuing authorities to impose limitations on CCW permits, such as the type and caliber of handguns that may be carried (], ], ]), restrictions on places where the permit is valid (], ]), restricting concealed carry to purposes or activities specified on the approved permit application (New York, ]), limitations on magazine size (], ], New York), or limitations on the number of firearms that may be carried concealed by a permit-holder at any given time. | |||
| ===Training requirements=== | ===Training requirements=== | ||
| Some states require concealed carry applicants to certify their proficiency with a firearm through some type of training or instruction. |
Some states require concealed carry applicants to certify their proficiency with a firearm through some type of training or instruction. Certain training courses developed by the ] that combine classroom and live-fire instruction typically meet most state training requirements. Some states recognize prior military or police service as meeting training requirements.<ref name="vsp.state.va.us">. Vsp.state.va.us. Retrieved on 2011-10-16.</ref> | ||
| Classroom instruction would typically include ] mechanics and terminology, cleaning and maintenance of a firearm, concealed carry legislation and limitations, liability issues, carry methods and safety, home defense, methods for managing and defusing confrontational situations, and practice of gun handling techniques without firing the weapon. Most required CCW training courses devote a considerable amount of time to liability issues. | Classroom instruction would typically include ] mechanics and terminology, cleaning and maintenance of a firearm, concealed carry legislation and limitations, liability issues, carry methods and safety, home defense, methods for managing and defusing confrontational situations, and practice of gun handling techniques without firing the weapon. Most required CCW training courses devote a considerable amount of time to liability issues. | ||
| Depending on the state, a practical component during which the attendee shoots the weapon for the purpose of demonstrating safety and proficiency, may be required. During range instruction, applicants would typically learn and demonstrate safe handling and operation of a firearm and accurate shooting from common self-defense distances. Some states require a certain proficiency to receive a passing grade, whereas other states (e.g., Florida) technically require only a single |
Depending on the state, a practical component during which the attendee shoots the weapon for the purpose of demonstrating safety and proficiency, may be required. During range instruction, applicants would typically learn and demonstrate safe handling and operation of a firearm and accurate shooting from common self-defense distances. Some states require a certain proficiency to receive a passing grade, whereas other states (e.g., Florida) technically require only a single shot to be fired to demonstrate handgun handling proficiency. | ||
| CCW training courses are typically completed in a single day and are good for a set period, the exact duration varying by state. Some states require re-training, sometimes in a shorter, simpler format, for each renewal |
CCW training courses are typically completed in a single day and are good for a set period, the exact duration varying by state. Some states require re-training, sometimes in a shorter, simpler format, for each renewal. | ||
| A few states, e.g., South Carolina, recognize the safety and use-of-force training given to military personnel as acceptable in lieu of formal civilian training certification. Such states will ask for a ] (South Carolina) for active persons or ] for honorably discharged persons. These few states will commonly request a copy of the applicant's BTR (Basic Training Record) proving an up-to-date pistol qualification. Active and retired law enforcement officers are generally exempt from qualification requirements, due to a federal statute permitting retired law enforcement officers to carry concealed weapons in the United States.<ref>{{ |
A few states, e.g., South Carolina, recognize the safety and use-of-force training given to military personnel as acceptable in lieu of formal civilian training certification. Such states will ask for a ] (South Carolina) for active persons or ] for honorably discharged persons. These few states will commonly request a copy of the applicant's BTR (Basic Training Record) proving an up-to-date pistol qualification. Active and retired law enforcement officers are generally exempt from qualification requirements, due to a ] permitting qualified active and retired law enforcement officers to carry concealed weapons in the United States.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.flsenate.gov/statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&URL=Ch0790/ch0790.htm|title=Florida Statute 790|accessdate=24 July 2023}}</ref> | ||
| Virginia recognizes eight specific training options to prove competency in handgun handling, ranging from DD214 for honorably discharged military veterans, to certification from law enforcement training, to firearms training conducted by a state or NRA |
Virginia recognizes eight specific training options to prove competency in handgun handling, ranging from DD214 for honorably discharged military veterans, to certification from law enforcement training, to firearms training conducted by a state or NRA-certified firearms instructor including electronic, video, or online courses. While any one of the eight listed options will be considered adequate proof, individual circuit courts may recognize other training options.<ref name="vsp.state.va.us"/> A small number of states, such as Alabama and Georgia, have no training requirements to obtain a permit—only a requirement that the applicant successfully pass the required background check before issuance. | ||
| ===Reciprocity=== | ===Reciprocity=== | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| Many jurisdictions recognize (honor) a permit or license issued by other jurisdictions. Recognition may be granted to all jurisdictions or some subset that meets a set of permit-issuing criteria, such as training comparable to the honoring jurisdiction or certain background checks. Several states have entered into formal agreements to mutually recognize permits. This arrangement is commonly called reciprocity or mutual recognition. A few states do not recognize permits issued by any other jurisdiction but offer non-resident permits for out-of-state individuals (who possess a valid concealed carry permit from their home state) who wish to carry while visiting such states. There are also states that neither recognize out-of-state concealed carry permits nor issue permits to non-residents, resulting in a complete ban on concealed carry by non-residents in such states. There are also states (Illinois and Rhode Island) that do not recognize out-of-state permits for carry-on-foot but do permit individuals with out-of-state concealed carry permits to carry while traveling in their vehicle (normally in accordance with the rules of the state of issuance). | |||
| Many jurisdictions have established arrangements where they recognize or honor permits or licenses issued by other jurisdictions with comparable standards, for instance in regard to marriage or driver's licenses. This is known as Reciprocity and is based on U.S. Constitution "full faith and credit" provision.<ref>Article IV, Section 1, "Full faith and credit shall be given in each state to the public acts, records, and judicial proceedings of every other state."</ref> Due to the nature of ], reciprocity in regard to weapons carry permits or licenses has been controversial. | |||
| Reciprocal recognition of concealed carry privileges and rights vary state-to-state, are negotiated between individual states, and sometimes additionally depend on the residency status of the license holder.<ref name="usacarry.com">{{cite web|author=08:27 PM |url=http://www.usacarry.com/concealed_carry_permit_information.html |title=''Concealed Carry (CCW) Laws by State'' on |publisher=Usacarry.com |date= |accessdate=2010-11-08}}</ref> While 37 states have reciprocity agreements with at least one other state and several states honor all out-of-state concealed carry permits, some states have special requirements like training courses or safety exams, and therefore do not honor permits from states that do not have such requirements for issue. Some states make exceptions for persons under the minimum age (usually 21) if they are active or honorably-discharged members of the military or a police force (the second of these two is allowed under Federal law). States that do not have this exemption generally do not recognize any license from states that do. An example of this is the State of Washington's refusal to honor any Texas CHL as Texas has the military exception to age.<ref>. Atg.wa.gov. Retrieved on 2011-10-16.</ref> | |||
| Recognition and reciprocity of concealed carry privileges vary. Some states (e.g. Indiana, Virginia, Ohio) unilaterally recognize all permits. Others such as Michigan, limit such universal recognition to residents of the permit-issuing state.<ref name="usacarry.com">{{cite web|url=http://www.usacarry.com/concealed_carry_permit_information.html |title=''Concealed Carry (CCW) Laws by State'' on |publisher=Usacarry.com|access-date=2010-11-08}}</ref> While 37 states have reciprocity agreements with at least one other state and several states honor all out-of-state concealed carry permits, some states have special requirements like training courses or safety exams, and therefore do not honor permits from states that do not have such requirements for issue. Some states make exceptions for persons under the minimum age (usually 21) if they are active or honorably discharged members of the military or a police force (the second of these two is subject additionally to ]). States that do not have this exemption generally do not recognize any license from states that do. An example of this is the state of Washington's refusal to honor any Texas LTC as Texas has the military exception to age.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110606120455/http://www.atg.wa.gov/page.aspx?id=7772 |date=2011-06-06 }}. Atg.wa.gov. Retrieved on 2011-10-16.</ref> Idaho, Mississippi, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Tennessee have standard and enhanced permits that have different requirements to obtain and also have unique reciprocity with different states; Utah and West Virginia have provisional permits for 18-20-year-olds with more limited recognition by other states.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.concealedcarry.com/dynamic-ccw-permit-reciprocity-map-builder |title=Idaho Enhanced Concealed Carry Permit Recognition|website=ConcealedCarry.com|date=23 March 2015|access-date=2016-03-10}}</ref> | |||
| Florida (Resident), Michigan and Missouri hold the widest reciprocity of all the states in the U.S. with the number of other states honoring their permits at 37,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://ago.mo.gov/Concealed-Weapons/ |title=Missouri Attorney General's Office – Concealed Carry Reciprocity}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.michigan.gov/ag/0,1607,7-164-17334_17362_22672-60639--,00.html |title=Michigan Attorney General's Office – Concealed Carry Reciprocity}}</ref> followed by Oklahoma at 36, Alaska at 35<ref></ref> then Florida (Non-Resident) and Utah at 33;<ref>{{cite web |url=http://licgweb.doacs.state.fl.us/news/concealed_carry.html |title=Florida Division of Licensing, DOACS – Concealed Carry Reciprocity}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://publicsafety.utah.gov/bci/FAQother.html |title=Utah Department of Public Safety – Reciprocity with Other States}}</ref> Both Michigan and Missouri, however, do not issue permits to non-residents, and some states that honor Utah permits do ''not'' extend that to include Utah's non-resident permits. Also, effective May 10, 2011, Utah requires that non-resident applicants, who reside in states that have reciprocity with Utah, must first obtain the CCW permit from their state of residence before applying for the Utah permit.<ref></ref> | |||
| Permits from Idaho (enhanced), Kansas, Michigan, North Dakota (class 1), and North Carolina have the highest number of recognition by other states (39 states). One can obtain multiple state permits in an effort to increase the number of states where that user can carry a legally concealed weapon. It is common practice to use a CCW Reciprocity Map<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.concealedcarry.com/dynamic-ccw-permit-reciprocity-map-builder |title=Concealed Carry Reciprocity and Recognition Map|website=ConcealedCarry.com|date=23 March 2015|access-date=2016-03-10}}</ref> to gain clarity on which states will honor the person's combination of resident and non-resident permits given the variety of standards and legal policies from state to state. There are also various mobile applications<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.concealedcarry.com/helpful-websites-and-apps/ |title=Concealed Carry Mobile Applications|website=ConcealedCarry.com|date=31 October 2014|access-date=2016-03-10}}</ref> that guide users in researching state concealed carry permit reciprocity. | |||
| Although carry may be legal under State law in accordance with reciprocity agreements, the ] subjects an out-of-state permit holder to federal felony prosecution if they carry a firearm within 1000 feet of any K-12 school's property line. | |||
| Although carry may be legal under State law in accordance with reciprocity agreements, the ] subjects an out-of-state permit holder to federal felony prosecution if they carry a firearm within 1000 feet of any K–12 school's property line; however, the enforcement of this statute is rare given several states' nullification statutes prohibiting state law enforcement officers from enforcing federal firearms laws. However, states may have their own similar statutes that such officers will enforce, and potentially expose the carrier to later prosecution under the Act. | |||
| ===Restricted Premises=== | |||
| While generally a concealed carry permit allows the permit holder to carry a concealed weapon in public, a state may restrict carry of a firearm including a permitted concealed weapon while in or on certain properties, facilities or types of businesses that are otherwise open to the public. These areas vary by state (except for the first item below; Federal offices are subject to superseding Federal law) and can include: | |||
| ===Restricted premises=== | |||
| * '''Federal government facilities''', including post offices, IRS offices, federal court buildings, military/VA facilities and/or correctional facilities, Amtrak trains and facilities, and Corps of Engineers-controlled property (carry in these places is prohibited by Federal law and preempts any existing State law). Carry on land controlled by the Bureau of Land Management (federal parks and wildlife preserves) is allowed by Federal law as of the 2009 CARD Act, but is still subject to State law. However, carry into restrooms or any other buildings or structures located within federal parks is illegal in the United States, despite concealed carry being otherwise legal in federal parks with a permit recognized by the state in which the federal park is located. Similarly, concealed carry into caves located within federal parks is illegal. | |||
| While generally a concealed carry permit allows the permit holder to carry a concealed weapon in public, a state may restrict carry of a firearm including a permitted concealed weapon while in or on certain properties, facilities or types of businesses that are otherwise open to the public. These areas vary by state (except for the first item below; federal offices are subject to superseding federal law) and can include: | |||
| * '''State government facilities''', including courthouses, DMV/DoT offices, police stations, correctional facilities, and/or meeting places of government entities (exceptions may be made for certain persons working in these facilities such as judges, lawyers, and certain government officials both elected and appointed) | |||
| * '''Federal government facilities''', including post offices, IRS offices, federal court buildings, military/VA facilities and/or correctional facilities, Amtrak trains and facilities, and Corps of Engineers-controlled property (carry in these places is prohibited by federal law and preempts any existing state law). Carry on land controlled by the Bureau of Land Management (federal parks and wildlife preserves) is allowed by federal law as of the 2009 CARD Act, but is still subject to state law. However, carry into restrooms or any other buildings or structures located within federal parks is illegal in the United States, despite concealed carry being otherwise legal in federal parks with a permit recognized by the state in which the federal park is located. Similarly, concealed carry into caves located within federal parks is illegal. | |||
| * '''State and local government facilities''', including courthouses, DMV/DoT offices, police stations, correctional facilities, and/or meeting places of government entities (exceptions may be made for certain persons working in these facilities such as judges, lawyers, and certain government officials both elected and appointed) | |||
| * '''Venues for political events''', including rallies, parades, debates, and/or polling places | * '''Venues for political events''', including rallies, parades, debates, and/or polling places | ||
| * '''Educational institutions''' including elementary/secondary schools and colleges. Some states have "drop-off exceptions" which only prohibit carry inside school buildings, or permit carry while inside a personal vehicle on school property. ] |
* '''Educational institutions''' including elementary/secondary schools and colleges. Some states have "drop-off exceptions" which only prohibit carry inside school buildings, or permit carry while inside a personal vehicle on school property. ] laws vary by state. | ||
| * '''Public interscholastic{{citation needed|date=August 2013}} and/or professional sporting events''' and/or venues (sometimes only during a time window surrounding such an event) | * '''Public interscholastic{{citation needed|date=August 2013}} and/or professional sporting events''' and/or venues (sometimes only during a time window surrounding such an event) | ||
| * '''Amusement parks, fairs, parades and/or carnivals'''{{citation needed|date=August 2013}} | * '''Amusement parks, fairs, parades and/or carnivals'''{{citation needed|date=August 2013}} | ||
| * '''Businesses that sell alcohol''' (sometimes only "by-the-drink" sellers like restaurants, sometimes only establishments defined as a "bar" or "nightclub", or establishments where the percentage of total sales from alcoholic beverages exceeds a specified threshold) | * '''Businesses that sell alcohol''' (sometimes only "by-the-drink" sellers like restaurants, sometimes only establishments defined as a "bar" or "nightclub", or establishments where the percentage of total sales from alcoholic beverages exceeds a specified threshold) | ||
| * '''Hospitals''' (even if hospitals themselves are not restricted, "teaching hospitals" partnered with a medical school are sometimes considered "educational institutions"; exceptions are sometimes made for medical professionals working in these facilities) | * '''Hospitals''' (even if hospitals themselves are not restricted, "teaching hospitals" partnered with a medical school are sometimes considered "educational institutions"; exceptions are sometimes made for medical professionals working in these facilities) | ||
| * '''Churches''', mosques and other "Houses of worship |
* '''Churches''', mosques and other "Houses of worship", usually at the discretion of the church clergy (Ohio allows with specific permission of house of worship)<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.gunstocarry.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/Concealed-Carry-Laws-Manual.pdf|title=Ohio's Concealed Carry Laws and License Application|page=12|access-date=2014-05-30}}</ref> | ||
| * '''Municipal mass transit vehicles or facilities''' | * '''Municipal mass transit vehicles or facilities''' | ||
| * '''Sterile areas of airports''' (sections of the airport located beyond security screening checkpoints) | * '''Sterile areas of airports''' (sections of the airport located beyond security screening checkpoints, unless explicitly authorized) | ||
| * '''Non-government facilities with heightened security measures''' (Nuclear facilities, power plants, dams, oil and gas production facilities, banks, factories, unless explicitly authorized) | |||
| * '''Aboard aircraft or ships''' unless specifically authorized by the pilot in command or ship captain | |||
| * '''Private property''' where the lawful owner or lessee has posted a sign or verbally stated that firearms are not permitted. Some states have enacted laws prohibiting the carrying of firearms on private property, unless the property owner or lawful occupant has explicitly granted permission for the carrying of weapons on the premises. | |||
| * '''Any public place, while under the influence of alcohol or drugs''' (including certain prescription or over-the-counter medications, depending on jurisdiction) | |||
| ==="Opt-out" statutes ("gun-free zones")=== | ==="Opt-out" statutes ("gun-free zones")=== | ||
| Some states allow private businesses to post a specific sign prohibiting concealed carry within their premises. The exact language and format of such a sign varies by state. By posting the signs, businesses create areas where it is illegal to carry a concealed handgun—similar to regulations concerning schools, hospitals, and public gatherings. | |||
| Arizona, Arkansas, Connecticut, Illinois, Kansas, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska,<ref>{{cite web|title=Nebraska Revised Statute 69-2441|url=http://nebraskalegislature.gov/laws/statutes.php?statute=69-2441|work=Nebraska Statutes|publisher=Nebraska Legislature|accessdate=12 February 2013}}</ref> Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and Wisconsin all allow private businesses to post a specific sign (language and format vary by state) prohibiting concealed carry, violation of which, in some of these states, is grounds for revocation of the offender's concealed carry permit and criminal prosecution. Other states, such as Virginia, enforce only trespassing laws when a person violates a "Gun Free Zone" sign. By posting the signs, businesses create areas where it is illegal to carry a concealed handgun similar to regulations concerning schools, hospitals, and public gatherings. In addition to signage, virtually all jurisdictions allow some form of oral communication by the lawful owner or controller of the property that a person is not welcome and should leave. This notice can be given to anyone for any reason (except for statuses that are protected by the Federal ] and other CRAs, such as race), including due to the carrying of firearms by that person, and refusal to heed such a request to leave may constitute trespassing. In some jurisdictions trespass by a person carrying a firearm may have more severe penalties than "simple" trespass, while in other jurisdictions, penalties are lower than for trespass.<ref>{{cite web|title=Chapter 624, Section 714, Subdivision 17|url=https://www.revisor.mn.gov/statutes/?id=624.714#stat.624.714.17|work=Minnesota Statutes|publisher=Minnesota Revisor of Statutes|accessdate=13 October 2011}}</ref> | |||
| Violation of such a sign, in some of these states, is grounds for revocation of the offender's concealed carry permit and criminal prosecution. Other states, such as Virginia, enforce only trespassing laws when a person violates a "Gun Free Zone" sign. In some jurisdictions, trespass by a person carrying a firearm may have more severe penalties than "simple" trespass, while in other jurisdictions, penalties are lower than for trespass.<ref>{{cite web|title=Chapter 624, Section 714, Subdivision 17|url=https://www.revisor.mn.gov/statutes/?id=624.714#stat.624.714.17|website=Minnesota Statutes|publisher=Minnesota Revisor of Statutes|access-date=13 October 2011}}</ref> | |||
| There is considerable dispute over the effectiveness of such "]s". Opponents of such measures, such as ], state that, much like other '']'' laws banning gun-related practices, only law-abiding individuals will heed the signage and disarm.{{Citation needed|date=September 2013}} Individuals or groups intent on committing far more serious crimes, such as armed robbery or murder, will not be deterred by signage prohibiting weapons. Further, the reasoning follows that those wishing to commit mass murder might ''intentionally'' choose gun-free venues like shopping malls, schools and churches (where weapons carry is generally prohibited by statute or signage) because the population inside is disarmed and thus less able to stop them.<ref name=Deakins-JAPS>{{cite journal|last=Deakins|first=Jacob|title=Guns, Truth, Medicine, and the Constitution|journal=Journal of American Physicians and Surgeons|date=Summer 2008|volume=13|issue=2|url=http://www.jpands.org/vol13no2/deakins.pdf|accessdate=September 7, 2013}}</ref><ref name=Hetzner-MLR>{{cite journal|last=Hetzner|first=Amy|title=Where Angels Tread: Gun-Free School Zone Laws and an Individual Right to Bear Arms|journal=Marquette Law Review|year=2011–2012|volume=95|pages=359–398|url=http://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?collection=journals&handle=hein.journals/marqlr95&div=13&id=&page=}}</ref> | |||
| Such states include Arizona, Arkansas, Connecticut, Illinois, Kansas, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska,<ref>{{cite web|title=Nebraska Revised Statute 69-2441|url=http://nebraskalegislature.gov/laws/statutes.php?statute=69-2441|website=Nebraska Statutes|publisher=Nebraska Legislature|access-date=12 February 2013}}</ref> Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and Wisconsin. | |||
| In some states, business owners have been documented posting signs that appear to prohibit guns, but legally do not because the signs do not meet local or state laws defining required appearance, placement, or wording of signage. Such signage can be posted out of ignorance to the law, or intent to pacify gun control advocates while not actually prohibiting the practice. The force of law behind a non-compliant sign varies based on state statutes and case law. Some states interpret their statutes' high level of specification of signage as evidence that the signage must meet the specification exactly, and any quantifiable deviation from the statute makes the sign non-binding. Other states have decided in case law that if efforts were made in good faith to conform to the statutes, the sign carries the force of law even if it fails to meet current specification. Still others have such lax descriptions of what is a valid sign that virtually any sign that can be interpreted as "no guns allowed" is binding on the license holder.{{Citation needed|date=September 2013}} | |||
| There is considerable dispute over the effectiveness of such "]s". Opponents of such measures, such as ], state that, much like other '']'' laws banning gun-related practices, only law-abiding individuals will heed the signage and disarm. Individuals or groups intent on committing far more serious crimes, such as armed robbery or murder, will not be deterred by signage prohibiting weapons. Further, the reasoning follows that those wishing to commit mass murder might ''intentionally'' choose gun-free venues like shopping malls, schools, and churches (where weapons carry is generally prohibited by statute or signage) because the population inside is disarmed and thus less able to stop them.<ref name="Hetzner-MLR">{{cite journal|last=Hetzner|first=Amy|title=Where Angels Tread: Gun-Free School Zone Laws and an Individual Right to Bear Arms|journal=Marquette Law Review|year=2011–2012|volume=95|pages=359–98|url=http://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?collection=journals&handle=hein.journals/marqlr95&div=13&id=&page=}}</ref> | |||
| In some states, business owners have been documented posting signs that appear to prohibit guns, but legally do not because the signs do not meet local or state laws defining the required appearance, placement, or wording of signage. Such signage can be posted out of ignorance of the law, or intent to pacify gun control advocates while not actually prohibiting the practice. The force of law behind a non-compliant sign varies based on state statutes and case law. Some states interpret their statutes' high level of specification of signage as evidence that the signage must meet the specification exactly, and any quantifiable deviation from the statute makes the sign non-binding. Other states have decided in case law that if efforts were made in good faith to conform to the statutes, the sign carries the force of law even if it fails to meet current specifications. Still, others have such lax descriptions of what is a valid sign that virtually any sign that can be interpreted as "no guns allowed" is binding on the license holder. {{Citation needed|date=September 2013}} | |||
| Note that virtually all jurisdictions allow some form of oral communication by the lawful owner or controller of the property that a person is not welcome and should leave. This notice can be given to anyone for any reason (except for statuses that are protected by the Federal ] and other CRAs, such as race),{{Citation needed|date=June 2016}} including due to the carrying of firearms by that person, and refusal to heed such a request to leave may constitute trespassing. | |||
| ===Brandishing and printing=== | ===Brandishing and printing=== | ||
| Printing refers to a circumstance where the shape or outline of a firearm is visible through a garment while the gun is still fully covered, and is generally not desired when carrying a concealed weapon. Brandishing can refer to different actions depending on jurisdiction. These actions can include printing through a garment, pulling back clothing to expose a gun, or unholstering a gun and exhibiting it in the hand. The intent to intimidate or threaten someone may or may not be required legally for it to be considered brandishing. | Printing refers to a circumstance where the shape or outline of a firearm is visible through a garment while the gun is still fully covered, and is generally not desired when carrying a concealed weapon. Brandishing can refer to different actions depending on jurisdiction. These actions can include printing through a garment, pulling back clothing to expose a gun, or unholstering a gun and exhibiting it in the hand. The intent to intimidate or threaten someone may or may not be required legally for it to be considered brandishing. | ||
| Brandishing is a crime in most jurisdictions, but the definition of brandishing varies widely. | |||
| Under California law, the following conditions have to be present to prove brandishing: | Under California law, the following conditions have to be present to prove brandishing: | ||
| {{blockquote| A person, in the presence of another person, drew or exhibited a ; That person did so in a rude, angry, or threatening manner That person, in any manner, unlawfully used the in a fight or quarrel The person was not acting in lawful self-defense.]<ref name="shouselaw">{{cite web|title=Brandishing a Weapon, Gun or Firearm |url=http://www.shouselaw.com/brandishing-weapon-pc417.html|access-date=2014-02-19}}</ref>}} | |||
| In Virginia law: | In Virginia law: | ||
| {{blockquote|It shall be unlawful for any person to point, hold or brandish any firearm or any air or gas operated weapon or any object similar in appearance, whether capable of being fired or not, in such manner as to reasonably induce fear in the mind of another or hold a firearm or any air or gas operated weapon in a public place in such a manner as to reasonably induce fear in the mind of another of being shot or injured. However, this section shall not apply to any person engaged in excusable or justifiable self-defense.|Code of Virginia 18.2-282<ref name="virginialaw">{{cite web |title=Code of Virginia 18.2-282 |url=https://law.lis.virginia.gov/vacode/18.2-282/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20000413152019/http://leg1.state.va.us/cgi-bin/legp504.exe?000+cod+18.2-282 |url-status=dead |archive-date=2000-04-13 |access-date=2014-02-19}}</ref>}} | |||
| ==Federal law== | ==Federal law== | ||
| ===Gun Control Act of 1968=== | ===Gun Control Act of 1968=== | ||
| The ] passed by Congress in 1968 lists felons, illegal aliens, and other codified persons as prohibited from purchasing or possessing firearms. During the application process for concealed carry states carry out thorough background checks to prevent these individuals from obtaining permits. |
The ] passed by Congress in 1968 lists felons, illegal aliens, and other codified persons as prohibited from purchasing or possessing firearms. During the application process for concealed carry, states carry out thorough background checks to prevent these individuals from obtaining permits. Additionally, the ] created an FBI-maintained system in 1994 for instantly checking the backgrounds of potential firearms buyers in an effort to prevent these individuals from obtaining weapons. | ||
| === Firearm Owners Protection Act === | === Firearm Owners Protection Act === | ||
| The ] (FOPA) of 1986 allows a ] to travel through ] in which their firearm possession is illegal as long as it is ] of origination and destination, the owner is in transit and does not remain in the state in which firearm possession is illegal, and the firearm is transported unloaded and in a locked container. The FOPA addresses the issue of transport of private firearms from origin to destination for purposes lawful in state of origin and destination; FOPA does not authorize concealed carry as a weapon of defense during transit. ] arrested those carrying firearms in violation of state law, and then required them to use FOPA as an ] to the charges of illegal possession.{{citation needed|date=October 2018}} | |||
| {{Main|Firearm Owners Protection Act}} | |||
| The Firearm Owners Protection Act (FOPA) of 1986 allows a ] to travel through ] in which their firearm possession is illegal as long as it is ] of origination and destination, the owner is in transit and does not remain in the state in which firearm possession is illegal, and the firearm is transported unloaded and in a locked container. The FOPA addresses the issue of transport of private firearms from origin to destination for purposes lawful in state of origin and destination; FOPA does not authorize concealed carry as a weapon of defense during transit. ] do not recognize this law. If caught you will be arrested and then required to use FOPA as an ] to the charges of illegal possession. | |||
| ===Law Enforcement |
===Law Enforcement Officers Safety Act=== | ||
| In 2004, the ] enacted the ], 18 U.S. Code 926B and 926C. This federal law allows two classes of persons |
In 2004, the ] enacted the ], 18 U.S. Code 926B and 926C. This federal law allows two classes of persons – the "qualified law enforcement officer" and the "qualified retired law enforcement officer" – to carry a concealed firearm in any jurisdiction in the United States, regardless of any state or local law to the contrary, with the exception of areas where all firearms are prohibited without permission, and certain ]. | ||
| ===Federal Gun Free School Zones Act=== | ===Federal Gun Free School Zones Act=== | ||
| ] limits where a person may legally carry a firearm. It does this by making it generally unlawful for an armed citizen to be within |
] limits where a person may legally carry a firearm. It does this by making it generally unlawful for an armed citizen to be within 1,000 feet (extending out from the property lines) of a place that the individual knows, or has reasonable cause to believe, is a K–12 school. Although a state-issued carry permit may exempt a person from this restriction in the state that physically issued their permit, it does not exempt them in other states which recognize their permit under reciprocity agreements made with the issuing state. | ||
| ===Federal property=== | ===Federal property=== | ||
| Some federal statutes restrict the carrying of firearms on the premises of certain |
Some federal statutes restrict the carrying of firearms on the premises of certain federal properties such as military installations or land controlled by the ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://ecfr.gpoaccess.gov/cgi/t/text/text-idx?c=ecfr&sid=631dea6d364fc8790efb67d9478168ee&rgn=div8&view=text&node=36:3.0.1.1.3.0.1.14&idno=36 |title=Title 36 CFR §327.13 |publisher=Ecfr.gpoaccess.gov|access-date=2010-11-08 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110612174340/http://ecfr.gpoaccess.gov/cgi/t/text/text-idx?c=ecfr&sid=631dea6d364fc8790efb67d9478168ee&rgn=div8&view=text&node=36%3A3.0.1.1.3.0.1.14&idno=36 |archive-date=2011-06-12}}</ref> | ||
| ===National park carry=== | ===National park carry=== | ||
| On May 22, 2009, President ] signed H.R. 627, the "Credit Card Accountability Responsibility and Disclosure Act of 2009 |
On May 22, 2009, President ] signed H.R. 627, the "Credit Card Accountability Responsibility and Disclosure Act of 2009", into law. The bill contained a ] introduced by Senator ] (R-OK) that prohibits the ] from enacting or enforcing any regulations that restrict possession of firearms in National Parks or Wildlife Refuges, as long as the person complies with laws of the state in which the unit is found.<ref> Washington Post, May 22, 2009.</ref> This provision was supported by the National Rifle Association and opposed by the Brady Campaign to Prevent Gun Violence, the National Parks Conservation Association, and the Coalition of National Park Service Retirees, among other organizations.<ref> Washington Post, March 20, 2009.</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nraila.org/media/PDFs/nationalparks_MemoOpiniononintervention.PDF |title=Copy of Injunction |access-date=2010-11-08 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090407054553/http://www.nraila.org/media/PDFs/nationalparks_MemoOpiniononintervention.PDF |archive-date=2009-04-07 |url-status=dead }}</ref> As of February 2010 concealed handguns are for the first time legal in all but 3 of the nation's 391 national parks and wildlife refuges so long as all applicable federal, state, and local regulations are adhered to.<ref>{{cite news| url=http://latimesblogs.latimes.com/greenspace/2009/05/new-law-allows-guns-in-parks.html | work=The Los Angeles Times | title=Greenspace | date=May 20, 2009}}</ref> Hawaii is a notable exception. Concealed and open carry are both illegal in Hawaii for all except retired military or law enforcement personnel. Previously firearms were allowed into parks if cased and unloaded. | ||
| ===Full faith and credit (CCW permits)=== | ===Full faith and credit (CCW permits)=== | ||
| Attempts were made in the 110th Congress, ] (H.R. 226) and the ] (S. 388), to enact legislation to compel complete reciprocity for concealed carry licenses. Opponents of national reciprocity have pointed out that this legislation would effectively require states with more restrictive standards of permit issuance (e.g., training courses, safety exams, "good cause" requirements, |
Attempts were made in the 110th Congress, ] (H.R. 226) and the ] (S. 388), to enact legislation to compel complete reciprocity for concealed carry licenses. Opponents of national reciprocity have pointed out that this legislation would effectively require states with more restrictive standards of permit issuance (e.g., training courses, safety exams, "good cause" requirements, etc.) to honor permits from states with more liberal issuance policies. Supporters have pointed out that the same situation already occurs with marriage certificates, adoption decrees, and other state documents under the ].<ref>Constitution for the United States of America, Article IV, Section 1: "Full faith and credit shall be given in each state to the public acts, records, and judicial proceedings of every other state. And the Congress may by general laws prescribe the manner in which such acts, records, and proceedings shall be proved, and the effect thereof."</ref> Some states have already adopted a "full faith and credit" policy treating out-of-state carry permits the same as out-of-state driver's license or marriage certificates without federal legislation mandating such a policy.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160412221416/http://www.tn.gov/safety/article/hgreciprocity |date=2016-04-12 }} "Tennessee now recognizes a facially valid handgun permit, firearms permit, weapons permit, or a license issued by another state according to its terms..."</ref> In the 115th Congress, another universal reciprocity bill, the ], was introduced by ]. The bill passed the House but did not get a vote in the Senate.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.congress.gov/bill/115th-congress/house-bill/38/ |title=House Bill 38 |website=congress.gov|year=2017 }}</ref> | ||
| ==Legal issues== | ==Legal issues== | ||
| ===Court rulings=== | ===Court rulings=== | ||
| Prior to the 1897 |
Prior to the 1897 Supreme Court case ''Robertson v. Baldwin'',<ref>{{cite web|url=http://supreme.justia.com/us/165/275/case.html|title=Robertson v. Baldwin:: 165 U.S. 275 (1897)|website=Justia U.S. Supreme Court Center}}</ref> the federal courts had been silent on the issue of concealed carry. In the {{lang|la|]}} from a maritime law case, the Supreme Court commented that state laws restricting concealed weapons do not infringe upon the right to bear arms protected by the federal ].<ref name="isbn1-57607-268-1">{{cite book |author=Carter, Gregg Lee |title=Guns in American society: an encyclopedia of history, politics, culture, and the law |publisher=ABC-CLIO |location=Santa Barbara, Calif |year=2002 |page=506 |isbn=978-1-57607-268-4 |quote= Justice Brown spotlighted his belief that the guarantee of the right to keep and bear arms was not infringed by laws prohibiting the carrying of concealed weapons|url = https://books.google.com/books?id=H_RrLyV9rDUC&pg=RA1-PA506}}</ref> However, in the context of such rulings, ] of firearms was generally unrestricted in the jurisdictions in question, which provided an alternative means of "bearing" arms. | ||
| In the majority decision in the 2008 Supreme Court case of '']'', Justice Antonin Scalia wrote; | In the majority decision in the 2008 Supreme Court case of '']'', Justice ] wrote; | ||
| {{blockquote|Like most rights, the Second Amendment right is not unlimited. It is not a right to keep and carry any weapon whatsoever in any manner whatsoever and for whatever purpose: For example, concealed weapons prohibitions have been upheld under the Amendment or state analogues ... The majority of the 19th-century courts to consider the question held that prohibitions on carrying concealed weapons were lawful under the Second Amendment or state analogs.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.scotusblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2008/06/07-290.pdf |title=District of Columbia v. Heller, 554 U.S. 570 |date=2008 |access-date=30 October 2010}}</ref>}} | |||
| ''Heller'' was a landmark case because for the first time in United States history a Supreme Court decision defined the right to bear arms as constitutionally guaranteed to private citizens rather than a right restricted to "well |
''Heller'' was a landmark case because, for the first time in United States history, a Supreme Court decision defined the right to bear arms as constitutionally guaranteed to private citizens rather than a right restricted to "well-regulated militia". The Justices asserted that sensible restrictions on the right to bear arms are constitutional, however, an outright ban on a specific type of firearm, in this case handguns, was in fact unconstitutional. The Heller decision is limited because it only applies to federal enclaves such as the ]. In 2010, the SCOTUS expanded Heller in '']'' incorporating the 2nd Amendment through the 14th Amendment as applying to local and state laws. Various Circuit Courts have upheld their local and state laws using intermediate scrutiny. The correct standard is a strict scrutiny review for all "fundamental" and "individual" rights.<ref>Leonard W. Levy, ''Encyclopedia of the American Constitution'', Macmillan (1991), article "Strict Scrutiny" by ]. "The term 'strict scrutiny' appears to have been used first by Justice William O. Douglas in his opinion for the Supreme Court in Skinner v. Oklahoma (1942), in a context suggesting special judicial solicitude both for certain rights that were 'basic' and for certain persons who seemed the likely victims of legislative prejudice." After a right is identified as a fundamental or basic individual right protected by the Constitution, restrictions on that right are subject to strict scrutiny.</ref><ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Gunther | first1 = Gerald | year = 1972 | title = The Supreme Court, 1971 Term, Foreword: In Search of Evolving Doctrine on a Changing Court: A Model for a Newer Equal Protection| journal = Harvard Law Review | volume = 86 | issue = 1| pages = 1–48 | doi=10.2307/1339852| jstor = 1339852 }}</ref> On June 28, 2010, the U.S. Supreme Court struck down the handgun ban enacted by the city of Chicago, Illinois, in '']'', effectively extending the Heller decision to states and local governments nationwide.<ref>{{cite news| url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2009/09/30/AR2009093001723.html | newspaper=The Washington Post | title=Justices to Decide if State Gun Laws Violate Rights | first=Robert | last=Barnes | date=October 1, 2009}}</ref> Banning handguns in any jurisdiction has the effect of rendering invalid any licensed individual's right to carry concealed in that area except for federally exempted retired and current law enforcement officers and other government employees acting in the discharge of their official duties. | ||
| In 2022, the Supreme Court ruled in '']'', that the Second Amendment does protect "an individual's right to carry a handgun for self-defense outside the home." The case struck down New York's strict law requiring people to show "proper cause" in order to get a concealed weapons permit, and could affect similar laws in other states such as California, Hawaii, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Rhode Island.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://abc7ny.com/supreme-court-gun-case-guns-rights-concealed-carry/11990123/ |title=Supreme Court Strikes Down New York Conceal Carry Gun Law |date=June 23, 2022 |work=] |access-date=June 23, 2022 |quote=California, Hawaii, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey and Rhode Island all have similar laws likely to be challenged as a result of the ruling.}}</ref> Shortly after the Supreme Court ruling, the attorney generals of each of California,<ref>{{cite web | title= California Attorney General Legal Alert OAG-2022-02 | url=https://oag.ca.gov/system/files/media/legal-alert-oag-2022-02.pdf}}</ref> Hawaii (concealed-carry licenses only),<ref>{{cite web | title= Hawaii Attorney General Op. No. 22-02 | url=https://ag.hawaii.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/Attorney-General-Opinion-22-02.pdf }}</ref> Maryland,<ref>{{cite web | title= Maryland Attorney General Letter to Maryland Department of State Police Licensing Division | url=https://reason.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/MarylandAGBruen.pdf}}</ref> Massachusetts,<ref>{{cite web | title= Joint Advisory Regarding the Massachusetts Firearms Licensing System After the Supreme Court's Decision in New York State Rifle & Pistol Association v. Bruen | url=https://www.mass.gov/doc/ago-eopss-ltc-guidance/download}}</ref> New Jersey,<ref>{{cite web | title= New Jersey Attorney General Law Enforcement Directive No. 2022-07 | url=https://www.nj.gov/oag/dcj/agguide/directives/ag-Directive-2022-07_Directive-Clarifying-Requirements-For-Carrying-Of-Firearms-In-Public.pdf}}</ref> and Rhode Island (permits issued by municipalities only)<ref>{{cite web | url=https://riag.ri.gov/press-releases/attorney-general-neronha-issues-guidance-concealed-carry-permits-following-scotus | title=Attorney General Neronha issues guidance on concealed-carry permits following SCOTUS decision | Rhode Island Attorney General's Office }}</ref> issued guidance that their "proper cause" or similar requirements would no longer be enforced. | |||
| On June 28, 2010, the ] struck down the handgun ban enacted by the city of ], in '']'', effectively extending the Heller decision to states and local governments nationwide.<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2009/09/30/AR2009093001723.html | work=The Washington Post | title=Justices to Decide if State Gun Laws Violate Rights | first=Robert | last=Barnes | date=October 1, 2009}}</ref> Banning handguns in any jurisdiction has the effect of rendering invalid any licensed individual's right to carry concealed in that area except for federally exempted retired and current law enforcement officers and other government employees acting in the discharge of their official duties. | |||
| ===Legal liability=== | ===Legal liability=== | ||
| Even when self-defense is justified, there can be serious civil or criminal liabilities related to self-defense when a concealed carry permit holder brandishes or fires |
Even when self-defense is justified, there can be serious civil or criminal liabilities related to self-defense when a concealed carry permit holder brandishes or fires their weapon. For example, if innocent bystanders are hurt or killed, there could be both civil and criminal liabilities even if the use of deadly force was completely justified.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.freep.com/article/20100604/NEWS01/6040313/Charges-in-stray-bullet-death |title=Charges in stray-bullet death: Carjacking victim faces manslaughter rap |date= June 4, 2010 |first=Joe |last=Swickard |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100609231801/http://www.freep.com/article/20100604/NEWS01/6040313/Charges-in-stray-bullet-death |archive-date=2010-06-09 |work=] <!-- http://www.freep.com/article/20100604/NEWS01/6040313/Charges-in-stray-bullet-death valid URL but article text hidden behind archive paywall -->}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.chicagotribune.com/news/nationworld/ct-maryland-shootings-20160509-story.html |title=Wayne County judge lessens bond for man accused of killing bystander |newspaper=The Detroit News |date=June 28, 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170823160727/http://www.chicagotribune.com/news/nationworld/ct-maryland-shootings-20160509-story.html |archive-date=August 23, 2017}}<!-- no copy on Archive.org --></ref> Some states technically allow an assailant who is shot by a gun owner to bring a civil action. In some states, liability is present when a resident brandishes the weapon, threatens use, or exacerbates a volatile situation, or when the resident is carrying it while intoxicated. It is important to note that simply pointing a firearm at any person constitutes felony assault with a deadly weapon unless circumstances validate a demonstration of force. A majority of states that allow concealed carry, however, forbid suits being brought in such cases, either by barring lawsuits for damages resulting from a criminal act on the part of the plaintiff, or by granting the gun owner immunity from such a civil suit if it is found that they were justified in shooting. | ||
| Simultaneously, increased passage of "]" laws allow persons who own firearms and/or carry them concealed to use them without first attempting to retreat. The " |
Simultaneously, increased passage of "]" laws allow persons who own firearms and/or carry them concealed to use them without first attempting to retreat. The "Castle Doctrine" typically applies to situations within the confines of one's own home.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cga.ct.gov/2007/rpt/2007-R-0052.htm|title=Castle Doctrine and Self-Defense |website=ct.gov}}</ref> Nevertheless, many states have adopted escalation of force laws along with provisions for concealed carry. These include the necessity to first verbally warn a trespasser or lay hands on a trespasser before a shooting is justified (unless the trespasser is armed or assumed to be so). This escalation of force does not apply if the shooter reasonably believes a violent felony has been or is about to be committed on the property by the trespasser. Additionally, some states have a ] provision which requires a permit holder, especially in public places, to vacate themself from a potentially dangerous situation before resorting to deadly force. The duty to retreat does not restrictively apply in a person's home or business though escalation of force may be required. In 1895 the Supreme Court ruled in '']'' that if an individual does not provoke an assault and is residing in a place they have a right to be, then they may use considerable force against someone they reasonably believe may do them serious harm without being charged with murder or manslaughter should that person be killed.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://supreme.justia.com/us/158/550/case.html |title=Beard v. United States, 158 U.S. 550 (1897) | ||
| | |
|access-date=30 October 2010}}</ref> Further, in Texas<ref>{{Cite news |url=http://www.news-leader.com/article/20100608/NEWS01/6080342/Case-highlights-concealed-carry-weapons-issues |title=Case highlights concealed carry weapons issues |date=June 8, 2010 |first=Kary |last=Booher |newspaper=Springfield News-Leader |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100610040807/http://www.news-leader.com/article/20100608/NEWS01/6080342/Case-highlights-concealed-carry-weapons-issues |archive-date=2010-06-10 |quote="Missouri is like 48 other states, except the state of Texas, that does not allow deadly force in defense of property," said Randy Gibson, a captain in the Greene County Sheriff's Department.|url-access=subscription }}<!-- URL is not dead but article text is now hidden behind an archive paywall --></ref> and California<ref>CALCRIM No. 3476</ref><ref>Cal. Penal Code §197 (West 2013.) </ref> homicide is justifiable solely in defense of property. In other states, lethal force is authorized only when serious harm is presumed to be imminent. | ||
| Even given these relaxed restrictions on use of force, using a handgun must still be a last resort in some jurisdictions; meaning the user must reasonably believe that nothing short of deadly force will protect the life or property at stake in a situation. Additionally, civil liabilities for errors that cause harm to others still exist, although civil immunity is provided in the Castle Doctrine laws of some states (e.g., Texas).<ref>{{ |
Even given these relaxed restrictions on the use of force, using a handgun must still be a last resort in some jurisdictions; meaning the user must reasonably believe that nothing short of deadly force will protect the life or property at stake in a situation. Additionally, civil liabilities for errors that cause harm to others still exist, although civil immunity is provided in the Castle Doctrine laws of some states (e.g., Texas).<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://capitol.texas.gov/tlodocs/80R/billtext/html/SB00378F.HTM|title=80(R) SB 378 - Enrolled version - Bill Text|website=capitol.texas.gov|accessdate=24 July 2023}}</ref> | ||
| ===Penalties for carrying illegally=== | ===Penalties for carrying illegally=== | ||
| {{Main| |
{{Main|Criminal possession of a weapon}} | ||
| Criminal possession of a weapon is the unlawful ] of a weapon by a citizen. Many societies both past and present have placed restrictions on what forms of weaponry private citizens (and to a lesser extent police) are allowed to purchase, own, and carry in public. Such crimes are ]s and are considered '']'', in that the possession of a weapon in and of itself is not evil. Rather, the ''potential'' for use in acts of unlawful violence creates a possible need to control them. Some restrictions are ], whereas others require some element of ] to use the weapon for an illegal purpose. Some regulations allow a citizen to obtain a permit or other authorization to possess the weapon under certain circumstances. Lawful uses of weapons by civilians commonly include hunting, sport, collection and ]. | |||
| Based on state law, the penalty for illegally carrying a firearm varies widely throughout the United States, ranging from a simple infraction punishable by a fine, to a felony conviction and mandatory ], depending on the state. Similarly, actual enforcement of laws restricting or prohibiting open or concealed carry also varies greatly between localities. Authorities in jurisdictions that favor strong gun control policies will typically prosecute people for the mere fact they were carrying a firearm in an unlawful manner, regardless of actual intent. In jurisdictions that favor individual gun rights, authorities will typically not prosecute someone for illegally carrying a firearm, unless the individual clearly demonstrates some form of malicious intent. Typical policies that are used to determine who can legally carry concealed weapons are a prohibition of concealed carry, discretionary licensing, non-discretionary licensing, minimum age requirements (e.g., 18 or 21 years), successful completion of an instructor-led course, and marksmanship/handling qualification on a firing range. Less common is unregulated, legal concealed carry such as in Vermont, Alaska, Arizona, Wyoming, and unincorporated rural areas of Montana. | |||
| The penalties for carrying a firearm in an unlawful manner vary widely from state-to-state, and may range from a simple infraction punishable by a fine to a felony conviction and mandatory incarceration. An individual may also be charged and convicted of criminal charges other than unlawful possession of a firearm, such as ], ], ], or ]. In the case of an individual with no prior criminal convictions, the state of ] classifies the unlawful concealed carry of a loaded handgun as a Class C misdemeanor punishable by a maximum of 30 days imprisonment and/or a $500 fine.<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://law.justia.com/codes/tennessee/2010/title-39/chapter-17/part-13/39-17-1307/ | title=2010 Tennessee Code :: Title 39 – Criminal Offenses :: Chapter 17 – Offenses Against Public Health, Safety and Welfare :: Part 13 – Weapons :: 39-17-1307 – Unlawful carrying or possession of a weapon}}</ref> While in ], a similar crime committed by an individual with no criminal convictions is classified as a Class D felony, punishable by a mandatory minimum of 3.5 years imprisonment, to a maximum of 7 years.<ref>{{Cite web | url=http://ypdcrime.com/penal.law/article265.htm#p265.02 | title=Article 265 Penal Law Firearms | Dangerous Weapons | NY Law}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web | url=https://www.criminaldefense.sullivangalleshaw.com/sentencing-guidelines-for-criminal-possession-of-a-weapon-in-new-york/ | title=Sentencing Guidelines for Possession of Weapon in NY| date=21 January 2016}}</ref> As New York State does not recognize any pistol permits issued in other states, the statute would apply to any individual who does not have a valid New York State issued concealed carry permit, even if such individual has a valid permit issued in another jurisdiction.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.handgunlaw.us/states/newyork.pdf|title=New York | |||
| In the United States no convicted felon may purchase, transfer, or otherwise be in the possession of any firearm.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://codes.lp.findlaw.com/uscode/18/I/44/922 |title=18 U.S.C. § 922 : US Code – Section 922: Unlawful acts |accessdate=January 6, 2012}}</ref> Illegally concealing a handgun is a felony in many states therefore conviction of such a crime would automatically result in the forfeiture of a citizen's gun rights for life nationwide.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://codes.lp.findlaw.com/uscode/18/I/44/922 |title=18 U.S.C. § 922 : US Code – Section 922: Unlawful acts, Subsections g and n |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.sanduskyregister.com/sandusky/2010/jun/17/sandusky-police-arrest-accused-7-eleven-shooter |title=Sandusky police arrest accused 7-Eleven shooter |author=Melissa Topey |date=June 16, 2010 |newspaper=Sandusky Register |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> Additional state penalties for unlawful carry of a concealed firearm can be severe with punishments including expensive fines, extended jail time, loss of voting rights, and even passport cancellation.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.criminaldefenselawyer.com/crime-penalties/federal/Carrying-Concealed-Weapon.htm |title=Carrying a Concealed Weapon |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> A federal penalty of ten years in prison has been enacted for those found to be in possession of either firearms or ammunition while subject to a protection or restraining order.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.atf.gov/publications/download/i/atf-i-3310-2.pdf |title=PROTECTION ORDERS AND FEDERAL FIREARMS PROHIBITIONS |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> Such an order is grounds for the revocation of any concealed carry permit and the outright denial of any person's new application while the order is active. Weapon possession, in the context of concealed weapons, is a ] of that circumstance in which a person who is not legally authorized to carry a concealed weapon is found in possession of such a weapon. In the United States this can be interpreted as the possession of a firearm by a person ] from doing so under the ]. These prohibited individuals include those who have been ], those who have been convicted of misdemeanor ], ], and individuals who have ]. None of these individuals are eligible for concealed weapons permits and may be punished not only for unlawful concealed carry of a handgun but for unlawful possession of a firearm.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.leagle.com/unsecure/page.htm?shortname=inlaco20100611330 |title=STATE v. HOLIFIELD 39 So.3d 853 (2010) |publisher=Court of Appeal of Louisiana, First Circuit |date=June 11, 2010 |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.kmov.com/news/local/Metro-East-man-arrested-for-gun-possesion-by-a-felon-swung-bat-at-family-members-96618604.html |title=Cottage Hills: Man arrested on weapons charges, swinging bat at family |author=Jeff Mason |date=June 18, 2010 |accessdate=30 October 2010 |newspaper=kmov.com}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.stamfordadvocate.com/news/article/Stamford-psychotherapist-arraigned-on-firearms-525834.php |title=Psychotherapist arraigned on firearms |author=Jeff Morganteen |date=16 June 2010|accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |url=http://www.correctionsone.com/arrests-and-sentencing/articles/2083794-25-arrested-230-guns-seized-in-NM-thrift-store-sting/ |title=25 arrested, 230 guns seized in NM thrift store sting |author=Mike Gallagher |journal=Albuquerque Journal |date=June 17, 2010 |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> Depending on state law, it can apply to concealed carry of otherwise illegal knives such as ], ]s or ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://pweb.netcom.com/~brlevine/nc.txt |title=North Carolina |date=Updated July 2004, August 2005 |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://pw1.netcom.com/~brlevine/sta-law.htm |title=STATE KNIFE LAWS |date=Compiled in September 1996 for BLADE Magazine |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.google.com/hostednews/ap/article/ALeqM5g3ZKrHXH2INEaWpIKXIVhQtz16xgD9GDB4JO0 |title=? |agency=Associated Press |accessdate=30 October 2010}}{{dead link|date=October 2010}}</ref> | |||
| |website=handgunlaw.us|access-date=24 July 2023}}</ref> In addition, the New York State statutory definition of a "loaded firearm" differs significantly from what may be commonly understood, as simply possessing any ammunition along with a weapon capable of firing such ammunition satisfies the legal definition of a loaded firearm in New York.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.atf.gov/resource-center/docs/guide/state-laws-and-published-ordinances-2010-2011-new-york/download |title=State Laws and Published Ordinances – New York|website=atf.gov|access-date=24 July 2023}}</ref> The large variability of state carry laws has resulted in confusing circumstances where a person in ] (which requires no license of any kind to carry a concealed weapon by anyone who is not prohibited by law), could unwittingly travel into the adjacent state of New York, where such individual, despite acting entirely within the law of Vermont, would then face a mandatory 3.5-year prison sentence simply for accidentally crossing the state's border into New York. These circumstances are aggravated by the fact that many NYS police departments as well as the ] do not recognize the protections granted federally under the ], which was intended to prevent such prosecutions.<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://www.gunstocarry.com/gun-laws-state/new-york-gun-laws/ | title=New York Gun Laws}}</ref> | |||
| ==Effect on crime and deaths== | |||
| Citizens holding concealed carry permits may be prosecuted for failing to adhere to state and federal rules and regulations concerning the lawful exercise of carrying a concealed weapon. Some states do not allow the carrying of more than one concealed firearm by permit holders. Concealing two handguns, for example, might constitute a violation of law resulting in permit revocation or criminal charges. Carrying a handgun in the glove box of a vehicle, though commonly regarded as safe and legal, is considered illegal concealment in some states and could be punishable as a felony offense among non-permit holders.<ref name="ncrpa.org">{{cite web |url=http://www.ncrpa.org/ccwfaq.htm |title=Frequently Asked Questions About Concealed Carry in North Carolina |publisher=North Carolina Rifle & Pistol Association |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.vsp.state.va.us/Firearms_ResidentConcealed.shtm |title=Resident Concealed Handgun Permits |publisher=Virginia State Police |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> When arrested for any firearms offense the weapon(s) in question will be confiscated and could be destroyed upon conviction.<ref name="ncrpa.org"/> While legally carrying concealed outside of one's particular state of residence, such as in a state which grants reciprocity to the bearer's permit, he or she must comply with all regulations in the state in which they are currently carrying even if those rules and regulations differ from those of the individual's permit issuing state. Some states require that a person carrying a concealed weapon immediately declare this fact to any law enforcement officer they may encounter in the line of their official duties.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://codes.ohio.gov/orc/2923.12 |title=2923.12 Carrying concealed weapons |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> This provision most commonly applies to traffic stops and police questioning but is required upon approach of an officer by the person who is carrying concealed.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.philly.com/dailynews/local/20100617_Cops_stop_ex-NFL_receiver_Marvin_Harrison__take_gun.html#axzz0rACAKlrJ |title=Cops stop ex-NFL receiver Marvin Harrison, take gun |author=David Gambacorta |date=June 17, 2010 |newspaper=Philadelphia Daily News |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> Failure to comply with this provision is an arrestable misdemeanor and additionally may require the mandatory revocation of the licensee's permit. However simply passing an officer on the street, even at close distance, does not generally require the declaration of a concealed weapon. Carry of a concealed weapon by a licensed individual where prohibited is generally referred to as illegal weapon possession. In some states, no person may be in the public possession of a firearm while under the intoxicating effects of narcotics (whether prescribed or otherwise) or alcohol (usually defined as .01% BAC but up to .05% BAC in some areas).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.lsp.org/handguns.html |title=Concealed Handgun Permit Unit |publisher=Louisiana State Police |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.vsp.state.va.us/Firearms_ResidentConcealed.shtm#RevocationSuspensionorSurrenderofPermit |title=Revocation, Suspension, or Surrender of Permit |publisher=Virginia State Police |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Research has had mixed results, indicating variously that right-to-carry laws have no impact on violent crime, that they increase violent crime, and that they decrease violent crime. | |||
| A 2020 study by the ] of over 200 combinations of gun policies and outcomes found "supportive evidence that shall-issue concealed carry laws are associated with increased firearm homicides and total homicides". They also found supportive evidence that child access prevention laws reduce firearm homicides and self-injuries among youth, and further evidence supporting the conclusion that stand-your-ground laws are associated with increased levels of firearm homicides.<ref name=":0" /> The researchers credit a much greater investment in gun safety research over the past few years with providing this and other more recent studies with stronger and more reliable evidence. | |||
| Even in localities where concealed carrying is permitted, there may be legal restrictions on where a person may carry a concealed weapon unless state law overrides a business posting that no firearms are allowed. | |||
| A 2004 review of the existing literature by the ] found that the results of existing studies were sensitive to the specification and time period examined, and concluded that a causal link between right-to-carry laws and crime rates cannot be shown.<ref name=":3">{{Cite book|url=https://www.nap.edu/read/10881/chapter/8|title=6 Right-to-Carry Laws {{!}} Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review {{!}} The National Academies Press|language=en|doi=10.17226/10881|year=2004|isbn=978-0-309-09124-4}}</ref> Quinnipiac University economist Mark Gius summarized literature published between 1993 and 2005, and found that ten papers suggested that permissive CCW laws reduce crime, one paper suggested they increase crime, and nine papers showed no definitive results.<ref name="Gius2016">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kaCKDQAAQBAJ&pg=SA5-PA23|title=Guns and Crime: The Data Don't Lie|last=Gius|first=Mark|date=2016-11-03|publisher=CRC Press|isbn=9781315450872|access-date=3 December 2017}}</ref> A 2017 review of the existing literature concluded, "Given the most recent evidence, we conclude with considerable confidence that deregulation of gun carrying over the last four decades has undermined public safety—which is to say that restricting concealed carry is one gun regulation that appears to be effective."<ref name=":4">{{Cite journal|last1=Philip J. Cook|last2=Harold A. Pollack|date=2017|title=Reducing Access to Guns by Violent Offenders|journal=RSF: The Russell Sage Foundation Journal of the Social Sciences|volume=3|issue=5|pages=2|doi=10.7758/rsf.2017.3.5.01|jstor=10.7758/rsf.2017.3.5.01|doi-access=free}}</ref> A 2016 study in the '']'' which examined the conflicting claims in the existing literature concluded that the evidence CCW either increases or decreases crime on average "seems weak"; the study's model found "some support to the law having a negative (but with a positive trend) effect on property crimes, and a small but positive (and increasing) effect on violent crimes".<ref name=":5">{{Cite journal|last1=Durlauf|first1=Steven N.|last2=Navarro|first2=Salvador|last3=Rivers|first3=David A.|date=2016-01-01|title=Model uncertainty and the effect of shall-issue right-to-carry laws on crime|journal=European Economic Review|series=Model Uncertainty in Economics|volume=81|issue=Supplement C|pages=32–67|doi=10.1016/j.euroecorev.2015.07.020|citeseerx=10.1.1.696.3159|s2cid=1575410}}</ref> The ''Washington Post'' fact-checker concluded that it could not state that CCW laws reduced crime, as the evidence was murky and in dispute.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/fact-checker/post/do-concealed-weapon-laws-result-in-less-crime/2012/12/16/e80a5d7e-47c9-11e2-ad54-580638ede391_blog.html|title=Do concealed weapon laws result in less crime?|last=Kessler|first=Glenn|date=2012-12-17|newspaper=Washington Post|language=en-US|access-date=2017-12-03}}</ref> In a 2017 article in the journal ''],'' Stanford University law professor John Donohue and Duke University economist Philip J. Cook write that "there is an emerging consensus that, on balance, the causal effect of deregulating concealed carry (by replacing a restrictive law with an RTC law) has been to increase violent crime".<ref name=":2">{{cite journal |last1=Cook |first1=Philip J. |last2=Donohue |first2=John J. |title=Saving lives by regulating guns: Evidence for policy |journal=Science |date=7 December 2017 |volume=358 |issue=6368 |pages=1259–1261 |doi=10.1126/science.aar3067 |pmid=29217559 |bibcode=2017Sci...358.1259C |s2cid=206665567 }}</ref> Donohue and Cook argue that the ] made it difficult to determine the causal effects of CCW laws and that this made earlier results inconclusive; recent research does not suffer the same challenges with causality.<ref name=":2" /> A 2018 RAND review of the literature concluded that concealed carry either has no impact on crime or that it may increase violent crime. The review said, "We found no qualifying studies showing that concealed-carry laws decreased ."<ref name=":7">{{Cite web|url=https://www.rand.org/research/gun-policy/analysis/concealed-carry.html|title=The Effects of Concealed-Carry Laws|website=rand.org|language=en|access-date=2019-12-25}}</ref> | |||
| The city of Chicago, Illinois as well as the District of Columbia had previously banned handguns completely within their respective jurisdictions. However, two recent Supreme Court cases have effectively deemed those statutes to be illegal (see above).<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=124210232 |title=Supreme Court To Hear Chicago Gun Rights Case|author=Nina totenberg |date=March 2, 2010 |publisher=NPR |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Lastly, some states regulate which firearms may be concealed by a particular permit holder. Texas, for example, differentiates between ] and non-semi-automatic firearms, and an "NSA"-class permit holder cannot carry an autoloading handgun (restricting them largely to revolvers).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.txdps.state.tx.us/InternetForms/Forms/CHL-16.pdf |title=TEXAS CONCEALED HANDGUN LAWS AND SELECTED STATUTES |publisher=Texas Department of Public Safety |date=October 2009 |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> Texans who qualify with a revolver are only allowed to carry a revolver; if they qualify with a semi-automatic, they can carry either a semi-automatic or a revolver.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.texasconcealedhandgunlicense.us/ |title=Steps To Getting Your Texas Concealed Handgun License |publisher=texasconcealedhandgundlicense.us |accessdate=30 October 2010}}</ref> Other restrictions seen in certain states include restricting the user to a gun no more powerful than they used when qualifying, or to one or more specific guns specified by the permit holder when applying. New York prohibits certain specific makes and models of pistols (mostly ]) and will not issue a permit for those specific weapons{{Citation needed|date=April 2011}}. Other states ban the carrying of handguns with large-capacity magazines. In most states, though, a CCW permit holder is limited only by what they can conceal while wearing particular clothing. | |||
| A 2020 study in '']'' found that right-to-carry laws were associated with higher firearm deaths.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Anderson|first1=D. Mark|last2=Sabia|first2=Joseph|last3=Tekin|first3=Erdal|date=2018|title=Child Access Prevention Laws and Juvenile Firearm-Related Homicides|location=Cambridge, MA|doi=10.3386/w25209|s2cid=158944952|doi-access=free|journal=National Bureau of Economic Research Working Papers}}</ref> A 2019 ] published in the '']'' by medical researchers including ] of the ] and ] of the ] found that “shall issue" concealed carry laws were associated with a 9% increase in homicides.<ref>{{cite journal |title=The Impact of State Firearm Laws on Homicide and Suicide Deaths in the USA, 1991–2016: a Panel Study |first1=Michael |last1=Siegel |author-link1=Michael Siegel |first2=Molly |last2=Pahn |first3=Ziming |last3=Xuan |first4=Eric |last4=Fleegler |first5=David |last5=Hemenway |author-link5=David Hemenway |journal=] |volume=34 |issue=10 |pages=2021–2028 |date=March 28, 2019 |pmid=30924089 |pmc=6816623 |doi=10.1007/s11606-019-04922-x }}</ref> A 2019 study in the '']'' found that greater restrictions on concealed carry laws were associated with decreases in workplace homicide rates.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Sabbath |first1=Erika L. |last2=Hawkins |first2=Summer Sherburne |last3=Baum |first3=Christopher F. |title=State-Level Changes in Firearm Laws and Workplace Homicide Rates: United States, 2011 to 2017 |journal=American Journal of Public Health |date=February 2020 |volume=110 |issue=2 |pages=230–236 |doi=10.2105/AJPH.2019.305405 |pmid=31855477 |pmc=6951380 }}</ref> Another 2019 study in the ''American Journal of Public Health'' found that states with right-to-carry laws were associated with a 29% higher rate of firearm workplace homicides.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Doucette |first1=Mitchell L. |last2=Crifasi |first2=Cassandra K. |last3=Frattaroli |first3=Shannon |title=Right-to-Carry Laws and Firearm Workplace Homicides: A Longitudinal Analysis (1992–2017) |journal=American Journal of Public Health |date=December 2019 |volume=109 |issue=12 |pages=1747–1753 |doi=10.2105/AJPH.2019.305307 |pmid=31622144 |pmc=6836804 }}</ref> A 2019 study in the '']'' found that right-to-carry laws led to an increase in overall violent crime.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Donohue |first1=John J. |last2=Aneja |first2=Abhay |last3=Weber |first3=Kyle D. |title=Right-to-Carry Laws and Violent Crime: A Comprehensive Assessment Using Panel Data and a State-Level Synthetic Control Analysis |journal=Journal of Empirical Legal Studies |date=15 May 2019 |volume=16 |issue=2 |pages=198–247 |doi=10.1111/jels.12219 |s2cid=181734017 }}</ref> A 2017 study in the '']'' found that "shall-issue laws" (where concealed carry permits must be given if criteria are met) "are associated with significantly higher rates of total, firearm-related, and handgun-related homicide" than "may-issue laws" (where local law enforcement have discretion over who can get a concealed carry permit).<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Siegel |first1=Michael |last2=Xuan |first2=Ziming |last3=Ross |first3=Craig S. |last4=Galea |first4=Sandro |last5=Kalesan |first5=Bindu |last6=Fleegler |first6=Eric |last7=Goss |first7=Kristin A. |title=Easiness of Legal Access to Concealed Firearm Permits and Homicide Rates in the United States |journal=American Journal of Public Health |date=December 2017 |volume=107 |issue=12 |pages=1923–1929 |doi=10.2105/AJPH.2017.304057 |pmid=29048964 |pmc=5678379 }}</ref> A 2011 study found that aggravated assaults increase when concealed carry laws are adopted.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Aneja |first1=A. |last2=Donohue |first2=J. J. |last3=Zhang |first3=A. |title=The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws and the NRC Report: Lessons for the Empirical Evaluation of Law and Policy |journal=American Law and Economics Review |date=29 October 2011 |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=565–631 |doi=10.1093/aler/ahr009 }}</ref> | |||
| A 2019 study in '']'' found "no statistically significant association between the liberalization of state level firearm carry legislation over the last 30 years and the rates of homicides or other violent crime."<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Hamill |first1=Mark E. |last2=Hernandez |first2=Matthew C. |last3=Bailey |first3=Kent R. |last4=Zielinski |first4=Martin D. |last5=Matos |first5=Miguel A. |last6=Schiller |first6=Henry J. |title=State Level Firearm Concealed-Carry Legislation and Rates of Homicide and Other Violent Crime |journal=Journal of the American College of Surgeons |date=January 2019 |volume=228 |issue=1 |pages=1–8 |doi=10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2018.08.694 |pmid=30359832 |doi-access=free }}</ref> This is also in line with a 1997 study researching county-level data from 1977 to 1992 concluding that allowing citizens to carry concealed weapons deters violent crimes and it appears to produce no increase in accidental deaths.<ref>{{cite journal|ssrn=10129|title=Crime, Deterrence, and Right-to-Carry Concealed Handguns|date=1998-04-17|journal=Journal of Legal Studies|last1=Mustard|first1=David B.|last2=Lott|first2=John R.}}</ref> A 2018 study in '']'' found that the impact of right-to-carry laws was mixed and changed over time. RTC laws increased some crimes over some periods while decreasing other crimes over other periods. The study suggested that conclusions drawn in other studies are highly dependent on the time periods that are studied, the types of models that are adopted and the assumptions that are made.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Manski |first1=Charles F. |last2=Pepper |first2=John V. |title=How Do Right-to-Carry Laws Affect Crime Rates? Coping with Ambiguity Using Bounded-Variation Assumptions |journal=The Review of Economics and Statistics |date=May 2018 |volume=100 |issue=2 |pages=232–244 |doi=10.1162/rest_a_00689 |s2cid=43138806 |url=http://www.nber.org/papers/w21701.pdf }}</ref> A 2015 study that looked at issuance rates of concealed-carry permits and changes in violent crime by county-level in four shall-issue states found no increases or decreases in violent crime rates with changes in permit issuances.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Phillips |first1=Charles D. |last2=Nwaiwu |first2=Obioma |last3=Lin |first3=Szu-hsuan |last4=Edwards |first4=Rachel |last5=Imanpour |first5=Sara |last6=Ohsfeldt |first6=Robert |title=Concealed Handgun Licensing and Crime in Four States |journal=Journal of Criminology |date=2015 |volume=2015 |pages=1–8 |doi=10.1155/2015/803742 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web | url=http://research.tamu.edu/2015/09/28/increasing-permits-to-conceal-guns-has-zero-effect-on-crime-data-say/ | title=Increasing permits to conceal guns has zero effect on crime, data say| date=2015-09-28}}</ref> A 2019 study in the '']'' found that with one method, right-to-carry laws had no impact on violent crime, but with another method led to an increase in violent crime; neither method showed that right-to-carry laws led to a reduction in crime.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Gius |first1=Mark |title=Using the synthetic control method to determine the effects of concealed carry laws on state-level murder rates |journal=International Review of Law and Economics |date=March 2019 |volume=57 |pages=1–11 |doi=10.1016/j.irle.2018.10.005 |s2cid=158186157 }}</ref> A 2003 study found no significant changes in violent crime rates amongst 58 Florida counties with increases of concealed-carry permits.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Kovandzic|first1=Tomislav V.|last2=Marvell|first2=Thomas B.|year=2003|title=Right-To-Carry Concealed Handguns and Violent Crime: Crime Control Through Gun Decontrol?|journal=Criminology & Public Policy|volume=2|issue=3|pages=363–396|doi=10.1111/j.1745-9133.2003.tb00002.x}}</ref> A 2004 study found no significant association between homicide rates and shall-issue concealed carry laws.<ref>{{cite journal |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/8577749 |doi=10.1097/01.TA.0000068996.01096.39|title=The Effect of Nondiscretionary Concealed Weapon Carrying Laws on Homicide |year=2004 |last1=Hepburn |first1=Lisa |last2=Miller |first2=Matthew |last3=Azrael |first3=Deborah |last4=Hemenway |first4=David |journal=The Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection, and Critical Care |volume=56 |issue=3 |pages=676–681 |pmid=15128143 }}</ref> | |||
| ==Research on the efficacy of concealed carry== | |||
| {{main|Defensive gun use}} | |||
| According to attorney Frank Espohl, between 1987, when Florida adopted a concealed carry law, and 1993, its homicide rate dropped from 11.4 to 8.7 persons per 100,000.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.saf.org/LawReviews/Espohl1.htm |title=The right to carry concealed weapons for self-defense |last=Espohl |first=Frank |year=1997 |website=saf.org |publisher=Board of Trustees of Southern Illinois University |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20000816064235/http://www.saf.org/LawReviews/Espohl1.htm |archivedate=August 16, 2000 |accessdate= }}</ref> However, in 2003, economists and law professors ] and ] wrote that shall-issue laws do not reduce crime.<ref name=AyresDonohue2003>{{cite journal |last=Ayres |first=Ian |last2=Donohue |first2=John J. III |date=April 16, 2003 |title=Shooting Down the 'More Guns, Less Crime' Hypothesis |url=http://islandia.law.yale.edu/ayers/Ayres_Donohue_article.pdf |journal=Stanford Law Review |publisher= |volume=55 |issue= |pages=1193–1312 |doi= |accessdate=March 13, 2014}}</ref>{{rp|1296}} | |||
| A 2013 study of eight years of Texas data found that concealed handgun licensees were much less likely to be convicted of crimes than were nonlicensees. The same study found that licensees' convictions were more likely to be for less common crimes, "such as sexual offenses, gun offenses, or offenses involving a death."<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Phillips|first1=Charles D.|last2=Nwaiwu|first2=Obioma|last3=McMaughan Moudouni|first3=Darcy K.|last4=Edwards|first4=Rachel|last5=Lin|first5=Szu-hsuan|date=January 2013|title=When Concealed Handgun Licensees Break Bad: Criminal Convictions of Concealed Handgun Licensees in Texas, 2001–2009|journal=American Journal of Public Health|volume=103|issue=1|pages=86–91|doi=10.2105/AJPH.2012.300807|pmc=3518334|pmid=23153139}}</ref> A 2020 study in '']'' examining concealed-carry permits per capita by state found a significant negative effect on violent crime rates.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Gius|first1=Mark|year=2019|title=The relationship between concealed carry permits and state-level crime rates|journal=Applied Economics Letters|volume=27|issue=11|pages=937–939|doi=10.1080/13504851.2019.1646866|s2cid=199829764}}</ref> A 2016 study found a significant negative effect on violent crime rates with passage of shall-issue laws.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Barati |first1=Mehdi |title=New evidence on the impact of concealed carry weapon laws on crime |journal=International Review of Law and Economics |date=August 2016 |volume=47 |pages=76–83 |doi=10.1016/j.irle.2016.05.011 }}</ref> A 2017 study in '']'' found that property crime decreased in Chicago after the implementation of the shall issue concealed carry law.<ref>{{Cite journal|title=An examination of the effects of 2014 concealed weapons law in Illinois on property crimes in Chicago|journal=Applied Economics Letters|volume=25|issue=16|pages=1125–1129|doi=10.1080/13504851.2017.1400645|year = 2018|last1 = Devaraj|first1 = Srikant|last2=Patel|first2=Pankaj C.|s2cid=158932191}}</ref> A 2014 '']'' study found states with more permissive conceal carry laws had lower murder rates than states with restrictive laws.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Gius |first1=Mark |title=An examination of the effects of concealed weapons laws and assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates |journal=Applied Economics Letters |date=26 November 2013 |volume=21 |issue=4 |pages=265–267 |doi=10.1080/13504851.2013.854294 |s2cid=154746184 }}</ref> Another 2014 study found that RTC laws by state significantly reduce homicide rates.<ref>{{Cite journal|url=https://ideas.repec.org/a/bap/journl/140103.html|title=The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws on Crime: An Exercise in Replication|journal=Review of Economics & Finance|year=2014|volume=4|pages=33–43|last1=Moody|first1=Carlisle E.|last2=Marvell|first2=Thomas B.|last3=Zimmerman|first3=Paul R.|last4=Alemante|first4=Fasil}}</ref> | |||
| Economist ] studied FBI crime statistics from 1977 to 1993. In his 1998 book, '']'', Lott said that the passage of concealed carry laws resulted in a murder rate decrease of 8.5%, rape rate decrease of 5%, and aggravated assault reduction of 7%. He said that his analysis of crime report data showed a statistically significant effect of concealed carry laws on crime.<ref name=Hinyub100612>{{cite web |url=http://caivn.org/article/2010/06/12/more-guns-less-crime |title=More guns, less crime |last=Hinyub |first=Chris |date=June 12, 2010 |website=ivn.us |publisher=Foundation for Independent Voter Education (FIVE) |accessdate=October 30, 2010}}</ref> | |||
| In 1996 economists ] and ] analyzed crime data in all 3,054 counties in the United States from 1977 to 1992, finding counties that had shall-issue licensing laws overall saw murders decrease by 7.65 percent, rapes decrease by 5.2 percent, aggravated assaults decrease by 7 percent and robberies decrease by 2.2 percent.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://object.cato.org/sites/cato.org/files/pubs/pdf/pa284.pdf|title=Cato Institute Policy Analysis No. 284: Fighting Back: Crime, Self-Defense, and the Right to Carry a Handgun|author=Jeffrey R. Snyder|date=October 22, 1997|website=Cato Institute}}</ref> The study was widely disputed by numerous economists. The 2004 ] panel reviewing the research on the subject concluded, with one dissenting panelist, that the Lott and Mustard study was unreliable.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Philip J. Cook|last2=Harold A. Pollack|date=2017|title=Reducing Access to Guns by Violent Offenders|journal=RSF: The Russell Sage Foundation Journal of the Social Sciences|volume=3|issue=5|page=9|doi=10.7758/rsf.2017.3.5.01|jstor=10.7758/rsf.2017.3.5.01|doi-access=free}}</ref> ] Professor ], ] of ] and ] of the ] in ''The Journal of Legal Studies'', said of the Lott-Mustard study, "once Florida is removed from the sample, there is no longer any detectable impact of right-to-carry laws on the rates of murder and rape".<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.vpc.org/studies/uninapb.htm|title=Do Right-to-Carry Laws Deter Violent Crime?|author1=Black, Dan A.|author2=Nagin, Daniel S|date=January 1998}}</ref> | |||
| In their 2003 article, Ayres and Donohue said that Lott's conclusions were the result of a limited data set and that re-running his tests with more complete data, subjected to less-constrained specifications and tweaked in plausible ways, yielded none of Lott's results.<ref name=AyresDonohue2003/> In 2010, Lott updated his findings with new data. According to the FBI, during the first year of the Obama administration the national murder rate declined by 7.4% along with other categories of crime which fell by significant percentages.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.fbi.gov/ucr/prelimsem2009/table_1.html |title=About Crime in the U.S. (CIUS) |publisher=] |accessdate=October 30, 2010}}</ref> During that same time national gun sales increased dramatically. According to Lott, 450,000 more people bought guns in November 2008 than in November 2007, representing a 40% increase in sales, a trend that continued throughout 2009.<ref name=Hinyub100612/> The drop in the murder rate was the biggest one-year drop since 1999, another year when gun sales soared in the wake of increased calls for gun control as a result of the ].<ref name=Hinyub100612/> | |||
| A 2022 study examining the ] found that the law had no impact on overall homicide rates, reduced overall suicide rates, and caused large and sustained decrease in gun-related suicide rates.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Depew|first1=Briggs|last2=Swensen|first2=Isaac|date=2022|title=The Effect of Concealed-Carry and Handgun Restrictions on Gun-Related Deaths: Evidence from the Sullivan Act of 1911|url=https://doi.org/10.1093/ej/ueac004|journal=The Economic Journal|volume=132 |issue=646 |pages=2118–2140 |doi=10.1093/ej/ueac004|issn=0013-0133}}</ref> | |||
| In a '']'' interview, Ayres and Donohue said, "There are many factors that people might weigh in deciding whether to pass these laws or not, but this idea that there is a statistical basis for thinking that these laws will reduce crime simply is not true." When asked about Lott's response to their work, Donohue said: "There's really nothing they can say. It's sort of like we caught them failing to carry the 1." He later went on to acknowledge that, "Mr. Lott's research has convinced his peers of at least one point: No scholars now claim that legalizing concealed weapons causes a major ''increase'' in crime."<ref name="CHE">{{cite journal |last=Glenn |first=David |date=May 9, 2003 |title='More Guns, Less Crime' Thesis Rests on a Flawed Statistical Design, Scholars Argue |journal=The Chronicle of Higher Education |volume=49 |issue=35 |page=A18 |url= http://chronicle.com/weekly/v49/i35/35a01801.htm |accessdate=May 27, 2007}}</ref> | |||
| === Firearms permit holders in active shooter incidents === | |||
| A committee of the ] (NRC), the working arm of the ] (NAS), wrote that it found "no credible evidence" either supporting or disproving Lott's thesis.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://books.nap.edu/openbook.php?isbn=0309091241&page=2 |title=Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review (2004) |page=2}}</ref> However, economist and committee member ] wrote a dissent in which he said that "some of results survive virtually every reanalysis done by the committee."<ref name="wilson">"" Appendix A Dissent by James Q. Wilson, retrieved January 11, 2006</ref> On the Ayres and Donohue hybrid model showing more guns-more crime, the NAS panel stated: "The committee takes no position on whether the hybrid model provides a correct description of crime levels or the effects of right-to-carry laws."<ref>National Research Council (National Academy of Sciences), ''Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review,'' The National Academies Press, 2005. Chapter 6.</ref> In an article for '']'' (ALER), Donohue said the NRC results published from the hybrid model "could not be replicated on its data set."<ref>, Am Law Econ Rev (Fall 2011) 13(2): 565–631.</ref> Lott replicated the NRC's results using its copy of the Ayres and Donohue model and data set, pointing out that the model used for the ''ALER'' article was different and introduced a truncation bias.<ref>, SSRN Working Paper Series, January 25, 2012.</ref> | |||
| In 2016 FBI analyzed 40 "active shooter incidents" in 2014 and 2015 where bystanders were put in peril in ongoing incidents that could be affected by police or citizen response. Six incidents were successfully ended when citizens intervened. In two stops citizens restrained the shooters, one unarmed, one with pepper spray. In two stops at schools, the shooters were confronted by teachers: one shooter disarmed, and one committed suicide. In two stops citizens with firearms permits exchanged gunfire with the shooter. In a failed stop attempt, a citizen with a firearms permit was killed by the shooter.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.fbi.gov/file-repository/activeshooterincidentsus_2014-2015.pdf|title=Schweit, Katherine W., "Active Shooter Incidents in the United States in 2014 and 2015", Federal Bureau of Investigation, 2016.|accessdate=24 July 2023}}</ref> In 2018 the FBI analyzed 50 active shooter incidents in 2016 and 2017. This report focused on policies to neutralize active shooters to save lives. In 10 incidents citizens confronted an active shooter. In eight incidents the citizens stopped the shooter. Four stops involved unarmed citizens who confronted and restrained or blocked the shooter or talked the shooter into surrendering. Four stops involved citizens with firearms permits: two exchanged gunfire with a shooter and two detained the shooter at gunpoint for arrest by responding police. Of the two failed stops, one involved a permit holder who exchanged gunfire with the shooter but the shooter fled and continued shooting and the other involved a permit holder who was wounded by the shooter. "Armed and unarmed citizens engaged the shooter in 10 incidents. They safely and successfully ended the shootings in eight of those incidents. Their selfless actions likely saved many lives."<ref> "The FBI defines an active shooter as one or more individuals actively engaged in killing or attempting to kill people in a populated area. ... The active aspect of the definition inherently implies that both law enforcement personnel and citizens have the potential to affect the outcome of the event based upon their responses to the situation."</ref> | |||
| A 2008 article by Carlisle E. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell uses a more extensive data set and projects effects of the Ayres and Donohue hybrid model beyond a five-year span. Though their data set renders an apparent reduction in the cost of crime, Ayres and Donohue point out that the cost of crime increased in 23 of the 24 jurisdictions under scrutiny. Florida was the only jurisdiction showing positive effects from shall-issue laws. Ayres and Donohue question the special case of Florida as well.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Ayres, Ian, and John J. Donohue III|year= 2009|url=http://econjwatch.org/articles/yet-another-refutation-of-the-more-guns-less-crime-hypothesis-with-some-help-from-moody-and-marvell |title=Yet Another Refutation of the More Guns, Less Crime Hypothesis – With Some Help From Moody and Marvell|journal=Econ Journal Watch|volume= 6|issue=1|pages=35–59}}</ref> | |||
| Using publicly available media reports, the ] (VPC) said that from May 2007 through the end of 2009, concealed carry permit holders in the U.S. killed at least 117 individuals, including nine law enforcement officers (excluding cases where individuals were acquitted, but including pending cases). There were about 25,000 murders by firearm during that period.<ref> {{dead link|date=October 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fbi.gov/ucr/prelimsem2009/table_3.html |title=FBI's Crime in the United States 2009 |publisher=Fbi.gov |date= |accessdate=2010-11-08}}</ref> Furthermore, a large number of the victims were killed in extended suicides, most of which took place in the home of the shooter, where arms can be possessed without special permits. VPC also includes in its numbers several homicides using only ] and several instances of ].<ref>, Violence Policy Center</ref> | |||
| According to FBI Uniform Crime Reports (UCR), in 2011 there were 12,664 murders and 653 justifiable homicides (of which 393 were performed by law enforcement) in the United States. Over previous years this reflects a decline in criminal homicide and an increase in homicides reported as justifiable (for 2008 UCR listed 14,180 murders, 616 justifiable homicides (of which 371 were by law enforcement). The UCR states that the justifiable homicide statistic does not represent eventual adjudication by medical examiner, coroner, district attorney, grand jury, trial jury or appellate court.<ref>, Federal Bureau of Investigation. "In the UCR Program, justifiable homicide is defined as and limited to: ■ The killing of a felon by a peace officer in the line of duty. ■ The killing of a felon, during the commission of a felony, by a private citizen."</ref> Few U.S. jurisdictions allow a police crime report to adjudicate a homicide as justifiable and in any given year fifteen to twenty states do not report such statistics to FBI UCR, resulting in an undercount in the UCR table. The majority of defensive gun uses (DGUs) do not involve killing or wounding an attacker. Government surveys indicate 108,000 to 23 million DGUs per year,<ref> NIJ Research in Brief, May 1997</ref> while private surveys indicate 764,000 to 3.6 million DGUs per year.<ref>, 86 Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology 1, 1995.</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| == |
== Notes == | ||
| {{ |
{{notelist}} | ||
| == |
== References == | ||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| * 1997 John Lott and David Mustard, "Crime, Deterrence, and Right-to-Carry Concealed Handguns," ''Journal of Legal Studies''. | |||
| * 1998 Dan Black and Daniel Nagin, "Do Right-to-Carry Laws Deter Violent Crime?" ''Journal of Legal Studies''. | |||
| * 1998 John Lott, "The Concealed-Handgun Debate." ''Journal of Legal Studies''. | |||
| * 1998 John Lott, ''More Guns, Less Crime'' (U Chicago Press). | |||
| * 2000 John Lott, ''More Guns, Less Crime'', Second Edition (U Chicago Press). | |||
| * 2003 Ian Ayres and John Donohue, "Shooting Down the ‘More Guns, Less Crime’ Hypothesis, ''Stanford Law Review''. | |||
| * 2003 Florenz Plassmann and John Whitley, "Confirming ‘More Guns, Less Crime," ''Stanford Law Review''. | |||
| * 2003 Ian Ayres and John Donohue, "The Latest Misfires in Support of the ‘More Guns, Less Crime’ Hypothesis," ''Stanford Law Review''. | |||
| * 2003 John Lott, ''The Bias against Guns'' (AEI). | |||
| * 2004 John Donohue. "Guns, Crime, and the Impact of State Right-to-Carry Laws" ''Fordham Law Review'' 73 (2004): 623. | |||
| * 2005 Robert Martin Jr., & Richard Legault, "Systematic Measurement Error with State-Level Crime Data: Evidence From the "More Guns, Less Crime" Debate," J. RESEARCH IN CRIME & DELINQUENCY | |||
| * 2008 Carlisle E. Moody and Thomas B. Marvell. "The Debate on Shall-Issue Laws," ''Econ Journal Watch'' 5.3: 269–293. | |||
| * 2009 John Donohue and Ian Ayres. "More Guns, Less Crime Fails Again: The Latest Evidence from 1977–2006" ''Econ Journal Watch'' 6.2: 218–238. | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| <! |
<!--WP is not a link farm. Common practice is to first discuss adding an external link after reading the external link guidelines (see: WP:EL) and policy is to not add a link to a site you are affiliated with in some way (see: Misplaced Pages:WikiProject Spam). Please consider helping us improve the content of the article instead. However, there are MANY notations (i.e., requests) for citations in this article, for statements which would be considered common knowledge in many other articles --> | ||
| * |
* | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| {{Gun laws in the United States (by state)}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Concealed carry In The United States}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Concealed carry In The United States}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:43, 28 November 2024
Laws concerning the carry of weapons in a concealed mannerConcealed carry, or carrying a concealed weapon (CCW), is the practice of carrying a weapon (such as a handgun) in public in a concealed manner, either on one's person or in close proximity. CCW is often practiced as a means of self-defense. Following the Supreme Court's NYSRPA v. Bruen (2022) decision, all states in the United States were required to allow for concealed carry of a handgun either permitlessly or with a permit, although the difficulty in obtaining a permit varies per jurisdiction.
There is conflicting evidence regarding the effect that concealed carry has on crime rates. A 2020 review by the RAND Corporation concluded there is supportive evidence that shall-issue concealed carry laws, which require states to issue permits to applicants once certain requirements are met, are associated with increased firearm homicides and total homicides. Earlier studies by RAND found that shall-issue concealed carry laws may increase violent crime overall, while there was inconclusive evidence for the effect of shall-issue laws on all individual types of violent crime. A 2004 literature review by the National Academy of Sciences concluded that there is no link between the existence of laws that allow concealed carry and crime rates.
History
Main article: History of concealed carry in the United States
The Second Amendment to the United States Constitution guarantees the right to "keep and bear arms". Concealed weapons bans were passed in Kentucky and Louisiana in 1813. (In those days open carry of weapons for self-defense was considered acceptable; concealed carry was denounced as the practice of criminals.) By 1859, Indiana, Tennessee, Virginia, Alabama, and Ohio had followed suit. By the end of the nineteenth century, similar laws were passed in places such as Texas, Florida, and Oklahoma, which protected some gun rights in their state constitutions. Before the mid-1900s, most U.S. states had passed concealed carry laws rather than banning weapons completely. Until the late 1990s, many Southern states were either "No-Issue" or "Restrictive May-Issue". Since then, these states have largely enacted "Shall-Issue" licensing laws, with more than half of the states legalizing "constitutional carry" (unrestricted concealed carry) and the remaining "May-issue" licensing laws being abolished in 2022 by the U.S. Supreme Court.
State laws
Permitting policies
Further information: Gun laws in the United States by state- Unrestricted jurisdiction: one in which a permit is not required to carry a concealed handgun. All states in this category allow any non-prohibited person to carry regardless of the state of residency.
- Permit requirement jurisdiction: one in which a permit is required to carry a concealed handgun.
Historically, some states were considered "may-issue" jurisdictions where an applicant was required to provide a proper cause or need to be issued a permit to carry a concealed weapon. However, on June 23, 2022, these laws were found unconstitutional by the U.S. Supreme Court in New York State Rifle & Pistol Association, Inc. v. Bruen.
Regulations differ widely by state, with twenty-seven of the fifty states either currently maintaining a constitutional carry policy or implementing it in the near future.
The Federal Gun-Free School Zones Act limits where an unlicensed person may carry; carry of a weapon, openly or concealed, within 1,000 feet (300 m) of a school zone is prohibited, with exceptions granted in the federal law to holders of valid state-issued weapons permits (state laws may reassert the illegality of school zone carry by license holders), and under LEOSA to current and honorably retired law enforcement officers (regardless of permit, usually overriding state law).
When in contact with an officer, some states require individuals to inform that officer that they are carrying a handgun.

Not all weapons that fall under CCW laws are lethal. For example, in Florida, carrying pepper spray in more than a specified volume (2 oz.) of chemical requires a CCW permit, whereas everyone may legally carry a smaller, “self-defense chemical spray” device hidden on their person without a CCW permit. As of 2021 there have been 21.52 million concealed weapon permits issued in the United States.
| Jurisdiction | Unrestricted | Permit Required | Illegal | Non-Resident Permits Available |
Permit Recognition | Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | Yes | 18 | ||||
| Alaska | Yes
21+ only |
21 | ||||
| American Samoa | No | N/A | ||||
| Arizona | Yes
21+ only |
21 | ||||
| Arkansas | Yes | 18 | ||||
| California | No | 21 | ||||
| Colorado | Partial (33 states)
Resident permits only 21+ only |
21 | ||||
| Connecticut | No | 21 | ||||
| Delaware | Partial (21 states) | 18 | ||||
| District of Columbia | Briefly from July 26, 2014 – July 29, 2014; see below for details | No | 21 | |||
| Florida | Yes
Resident permits only 21+ only; 18+ if military |
21 | ||||
| Georgia | Yes | 21 (18 with out of state carry permit) | ||||
| Guam | No | 21 | ||||
| Hawaii | No | 21 | ||||
| Idaho | For concealed carry by non-military permanent resident aliens | Yes | 18 | |||
| Illinois | Unloaded and enclosed in a case, firearm carrying box, shipping box, or other container | Only for residents of Arkansas, Idaho, Mississippi, Nevada, Texas and Virginia. | Vehicle carry only | 21 | ||
| Indiana | Yes
Includes foreign countries |
18 | ||||
| Iowa | Yes | 21 | ||||
| Kansas | For concealed carry between ages 18–20 | Yes | 18 with permit | |||
| Kentucky | Yes | 21 | ||||
| Louisiana | Partial (36 states)
21+ only |
21 | ||||
| Maine | For carrying in state/national parks, regular archery hunting during deer season, employees' vehicles on work premises and concealed carry between ages 18–20 | Partial (27 states)
Resident permits only 18+ Can carry permitless if 21+; 18+ if military |
18 with permit | |||
| Maryland | No | 21 | ||||
| Massachusetts | No | 21 | ||||
| Michigan | Yes
Resident permits only |
21 | ||||
| Minnesota | Partial (17 states) | 18 by court order | ||||
| Mississippi | For concealed carry without a belt/shoulder holster, sheath, purse, handbag, satchel, other similar bag or briefcase or fully enclosed. For carrying concealed at any polling place, meeting place of the state legislature or other governing body, school, college, professional athletic event, establishment licensed to serve alcoholic beverages, passenger terminal of an airport, federal buildings (under state law), permitted parade/demonstration or courthouse for those with an enhanced firearms permit. | Yes | 18 | |||
| Missouri | For open carry in localities where restricted | Yes | 18 | |||
| Montana | Partial (43 states)
Can carry permitless |
18 | ||||
| Nebraska | Partial (35 states + DC)
21+ only |
21 | ||||
| Nevada | Partial (24 states) | 21 | ||||
| New Hampshire | Partial (28 states)
Resident permits only Can carry permitless |
18* | ||||
| New Jersey | No | 21 | ||||
| New Mexico | Unloaded | Partial (23 states)
21+ only |
21 | |||
| New York | No | 21 | ||||
| New York City | Does not recognize any other jurisdictions' permits. Permits may be approved by the city's police commissioner on an individual basis. | 21 | ||||
| North Carolina | Yes | 21 (18 with out of state carry permit) | ||||
| North Dakota | For open-carry | Partial (39 states)
Can carry permitless |
18 | |||
| Northern Mariana Islands | No | N/A | ||||
| Ohio | Yes | 21 (18 with out of state carry permit) | ||||
| Oklahoma | Yes | 21 | ||||
| Oregon | No | 21 | ||||
| Pennsylvania | Partial (29 states)
Resident permits only 21+ only All permits recognized for vehicle carry |
21 | ||||
| Puerto Rico | From June 20, 2015, to October 31, 2016. | Has reciprocity law, but does not recognize any other state permits | 21 | |||
| Rhode Island | Vehicle carry only | 21 | ||||
| South Carolina | Partial (29 states)
Resident permits only |
21 | ||||
| South Dakota | Yes | 18 | ||||
| Tennessee | For carrying in buildings posted with "concealed firearms by permit only" signs, state/national parks, campgrounds, greenways, and nature trails | Yes | 18 by court order | |||
| Texas | Partial (43 states)
Can carry permitless |
18 by court order | ||||
| United States Virgin Islands | Has reciprocity law, but does not recognize any other state permits | 21 | ||||
| Utah | For carrying between ages 18–20 | Yes | 18 with permit | |||
| Vermont | N/A | 16 | ||||
| Virginia | Yes
21+ only |
21 | ||||
| Washington | Any person engaging in a lawful outdoor recreational activity such as hunting, fishing, camping, hiking, or horseback riding, so long as it is reasonable to assume that they are performing that activity or traveling to or from the activity. | Partial (9 states)
21+ only |
21 | |||
| West Virginia | For concealed carry between ages 18–20 | Partial (35 states)
Can carry permitless 21+ only; 18+ if military for both |
18 with permit | |||
| Wisconsin | Partial (44 states + DC, PR & VI)
21+ only |
21 | ||||
| Wyoming | Partial (35 states)
Can carry permitless |
21 (18 with out of state carry permit) | ||||
| U.S. Military installations | No | 21 | ||||
| Native American reservations | Varies | Varies | Varies |
* Jurisdiction gives no minimum age to conceal carry in law. The age is set at 18 by federal law.
Unrestricted jurisdictions
Main article: Constitutional carryAn unrestricted jurisdiction is one in which a permit is not required to carry a concealed handgun. This is sometimes called constitutional carry. Within the unrestricted category, there exist states that are fully unrestricted, where no permit is required for lawful open or concealed carry, and partially unrestricted, where certain forms of concealed carry may be legal without a permit, while other forms of carry may require a permit.
Some states have a limited form of permitless carry, restricted based on one or more of the following: a person's location, the loaded/unloaded state of the firearm, or the specific persons who may carry without a permit. As of February 18, 2021, these states are Illinois, New Mexico, and Washington. Some states that allow permitless concealed carry and still issue concealed carry permits may impose restrictions on concealed carry for certain places and/or at certain times (e.g., special events, large public gatherings, etc.). In some such situations, those holding a valid concealed carry permit may be exempt from such restrictions.
Permit requirement jurisdictions
A permit requirement jurisdiction is one in which a government-issued permit is required to carry a concealed handgun in public. Before the U.S. Supreme Court ruling in New York State Rifle & Pistol Association, Inc. v. Bruen, these jurisdictions were further split between "shall-issue", which is the current national licensing standard where the granting of licenses is subject only to meeting determinate criteria laid out in the law, and "may-issue" where the granting of such licenses was at the discretion of local authorities. Since the abolishment of "may-issue" permitting the U.S. Supreme Court has stated it is still legal for U.S. jurisdictions subject to the Constitution to require a permit to carry a concealed handgun, and that background checks, training, and proper fees can be required without violating the Second Amendment to the United States Constitution which guarantees a right of the people to carry a concealed firearm outside of the home.
Concealed carry on U.S. military installations
While members of the Armed Services may receive extensive small arms training, United States Military installations have some of the most restrictive rules for the possession, transport, and carrying of personally-owned firearms in the country.
Overall authority for carrying a personally-owned firearm on a military installation rests with the installation commander, although the authority to permit individuals to carry firearms on an installation is usually delegated to the Provost Marshal. Military installations do not recognize state-issued concealed carry permits, and state firearms laws generally do not apply to military bases, regardless of the state in which the installation is located. Federal law (18 USC, Section 930) generally forbids the possession, transport, and carrying of firearms on military installations without approval from the installation commander. Federal law gives installation commanders wide discretion in establishing firearms policies for their respective installations. In practice, local discretion is often constrained by policies and directives from the headquarters of each military branch and major commands.
Installation policies can vary from no-issue for most bases to shall-issue in rare circumstances. Installations that do allow the carrying of firearms typically restrict carrying to designated areas and for specific purposes (i.e., hunting or officially sanctioned shooting competitions in approved locations on the installation). Installation commanders may require the applicant to complete extensive firearms safety training, undergo a mental health evaluation, and obtain a letter of recommendation from their unit commander (or employer) before such authorization is granted. Personnel that reside on a military installation are typically required to store their personally-owned firearms in the installation armory, although the installation commander or provost marshal may permit a service member to store their personal firearms in their on-base dwelling if they have a gun safe or similarly designed cabinet where the firearms can be secured.
Prior to 2011, military commanders could impose firearms restrictions to servicemembers residing off-base, such as mandatory registration of firearms with the base provost marshal, restricting or banning the carrying of firearms by servicemembers either on or off the installation regardless of whether the member had a state permit to carry, and requiring servicemembers to have a gun safe or similar container to secure firearms when not in use. A provision was included in the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2011 that limited commanders' authority to impose restrictions on the possession and use of personally-owned firearms by service members who reside off-base.
Concealed carry on Native American reservations
Concealed carry policies on Native American reservations are covered by the tribal laws for each reservation, which vary widely from "No-Issue" to "Shall-Issue" and "Unrestricted" either in law or in practice. Some Native American tribes recognize concealed carry permits for the state(s) in which the reservation is located, while others do not. For reservations that do not recognize state-issued concealed carry permits, some completely ban concealed carry, while others offer a tribal permit for concealed carry issued by the tribal police or tribal council. Tribal concealed carry permits may be available to the general populace or limited to tribal members, depending on tribal policies. Tribal law typically pre-empts state law on the reservation. The only exception is while traversing the reservation on a state-owned highway (including interstate, U.S. routes, and in some instances county roads), in which case state law and the federal Firearm Owners' Protection Act (FOPA) apply.
Limitations on concealed carry
Prohibitions of the concealed carry of firearms and other weapons by local governments predate the establishment of the United States. In 1686, New Jersey law stated "no person or persons … shall presume privately to wear any pocket pistol … or other unusual or unlawful weapons within this Province." After the federal government was established, states and localities continued to restrict people from carrying hidden weapons. Tennessee law prohibited this as early as 1821. By 1837, Georgia passed into effect “An Act to guard and protect the citizens of this State, against the unwarrantable and too prevalent use of deadly weapons." Two years later, Alabama followed suit with “An Act to Suppress the Evil Practice of Carrying Weapons Secretly." Delaware prohibited the practice in 1852. Ohio did the same in 1859, a policy that remained in effect until 1974. Cities also regulated weapons within their boundaries. In 1881, Tombstone, Arizona, enacted Ordinance No. 9 "To Provide against Carrying of Deadly Weapons", a regulation that sparked the Gunfight at the O.K. Corral later that year.
Some permit requirement jurisdictions allow issuing authorities to impose limitations on CCW permits, such as the type and caliber of handguns that may be carried (Rhode Island, New Mexico), restrictions on places where the permit is valid (New York, Massachusetts, Illinois), restricting concealed carry to purposes or activities specified on the approved permit application (California, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York), limitations on magazine size (Connecticut, Massachusetts, New York), or limitations on the number of firearms that may be carried concealed by a permit-holder at any given time (some states). Permits issued by all but two states (New York and Hawaii) are valid statewide. New York State pistol licenses, which are generally issued by counties, are valid statewide with one exception. A permit not issued by New York City is invalid in that city unless validated by its police commissioner. Permits issued by Hawaii are valid only in the county of issuance.
Training requirements
Some states require concealed carry applicants to certify their proficiency with a firearm through some type of training or instruction. Certain training courses developed by the National Rifle Association that combine classroom and live-fire instruction typically meet most state training requirements. Some states recognize prior military or police service as meeting training requirements.
Classroom instruction would typically include firearm mechanics and terminology, cleaning and maintenance of a firearm, concealed carry legislation and limitations, liability issues, carry methods and safety, home defense, methods for managing and defusing confrontational situations, and practice of gun handling techniques without firing the weapon. Most required CCW training courses devote a considerable amount of time to liability issues.
Depending on the state, a practical component during which the attendee shoots the weapon for the purpose of demonstrating safety and proficiency, may be required. During range instruction, applicants would typically learn and demonstrate safe handling and operation of a firearm and accurate shooting from common self-defense distances. Some states require a certain proficiency to receive a passing grade, whereas other states (e.g., Florida) technically require only a single shot to be fired to demonstrate handgun handling proficiency.
CCW training courses are typically completed in a single day and are good for a set period, the exact duration varying by state. Some states require re-training, sometimes in a shorter, simpler format, for each renewal.
A few states, e.g., South Carolina, recognize the safety and use-of-force training given to military personnel as acceptable in lieu of formal civilian training certification. Such states will ask for a military ID (South Carolina) for active persons or DD214 for honorably discharged persons. These few states will commonly request a copy of the applicant's BTR (Basic Training Record) proving an up-to-date pistol qualification. Active and retired law enforcement officers are generally exempt from qualification requirements, due to a federal statute permitting qualified active and retired law enforcement officers to carry concealed weapons in the United States.
Virginia recognizes eight specific training options to prove competency in handgun handling, ranging from DD214 for honorably discharged military veterans, to certification from law enforcement training, to firearms training conducted by a state or NRA-certified firearms instructor including electronic, video, or online courses. While any one of the eight listed options will be considered adequate proof, individual circuit courts may recognize other training options. A small number of states, such as Alabama and Georgia, have no training requirements to obtain a permit—only a requirement that the applicant successfully pass the required background check before issuance.
Reciprocity
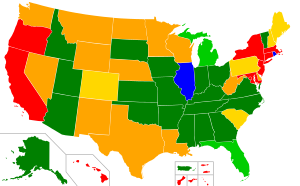
Level of permit reciprocity (recognition of out-of-state permits):
Full reciprocity Full reciprocity for resident permits only Full reciprocity for vehicle carry only Partial reciprocity Partial reciprocity for resident permits only No reciprocityMany jurisdictions recognize (honor) a permit or license issued by other jurisdictions. Recognition may be granted to all jurisdictions or some subset that meets a set of permit-issuing criteria, such as training comparable to the honoring jurisdiction or certain background checks. Several states have entered into formal agreements to mutually recognize permits. This arrangement is commonly called reciprocity or mutual recognition. A few states do not recognize permits issued by any other jurisdiction but offer non-resident permits for out-of-state individuals (who possess a valid concealed carry permit from their home state) who wish to carry while visiting such states. There are also states that neither recognize out-of-state concealed carry permits nor issue permits to non-residents, resulting in a complete ban on concealed carry by non-residents in such states. There are also states (Illinois and Rhode Island) that do not recognize out-of-state permits for carry-on-foot but do permit individuals with out-of-state concealed carry permits to carry while traveling in their vehicle (normally in accordance with the rules of the state of issuance).
Recognition and reciprocity of concealed carry privileges vary. Some states (e.g. Indiana, Virginia, Ohio) unilaterally recognize all permits. Others such as Michigan, limit such universal recognition to residents of the permit-issuing state. While 37 states have reciprocity agreements with at least one other state and several states honor all out-of-state concealed carry permits, some states have special requirements like training courses or safety exams, and therefore do not honor permits from states that do not have such requirements for issue. Some states make exceptions for persons under the minimum age (usually 21) if they are active or honorably discharged members of the military or a police force (the second of these two is subject additionally to federal law). States that do not have this exemption generally do not recognize any license from states that do. An example of this is the state of Washington's refusal to honor any Texas LTC as Texas has the military exception to age. Idaho, Mississippi, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Tennessee have standard and enhanced permits that have different requirements to obtain and also have unique reciprocity with different states; Utah and West Virginia have provisional permits for 18-20-year-olds with more limited recognition by other states.
Permits from Idaho (enhanced), Kansas, Michigan, North Dakota (class 1), and North Carolina have the highest number of recognition by other states (39 states). One can obtain multiple state permits in an effort to increase the number of states where that user can carry a legally concealed weapon. It is common practice to use a CCW Reciprocity Map to gain clarity on which states will honor the person's combination of resident and non-resident permits given the variety of standards and legal policies from state to state. There are also various mobile applications that guide users in researching state concealed carry permit reciprocity.
Although carry may be legal under State law in accordance with reciprocity agreements, the Federal Gun Free School Zones Act subjects an out-of-state permit holder to federal felony prosecution if they carry a firearm within 1000 feet of any K–12 school's property line; however, the enforcement of this statute is rare given several states' nullification statutes prohibiting state law enforcement officers from enforcing federal firearms laws. However, states may have their own similar statutes that such officers will enforce, and potentially expose the carrier to later prosecution under the Act.
Restricted premises
While generally a concealed carry permit allows the permit holder to carry a concealed weapon in public, a state may restrict carry of a firearm including a permitted concealed weapon while in or on certain properties, facilities or types of businesses that are otherwise open to the public. These areas vary by state (except for the first item below; federal offices are subject to superseding federal law) and can include:
- Federal government facilities, including post offices, IRS offices, federal court buildings, military/VA facilities and/or correctional facilities, Amtrak trains and facilities, and Corps of Engineers-controlled property (carry in these places is prohibited by federal law and preempts any existing state law). Carry on land controlled by the Bureau of Land Management (federal parks and wildlife preserves) is allowed by federal law as of the 2009 CARD Act, but is still subject to state law. However, carry into restrooms or any other buildings or structures located within federal parks is illegal in the United States, despite concealed carry being otherwise legal in federal parks with a permit recognized by the state in which the federal park is located. Similarly, concealed carry into caves located within federal parks is illegal.
- State and local government facilities, including courthouses, DMV/DoT offices, police stations, correctional facilities, and/or meeting places of government entities (exceptions may be made for certain persons working in these facilities such as judges, lawyers, and certain government officials both elected and appointed)
- Venues for political events, including rallies, parades, debates, and/or polling places
- Educational institutions including elementary/secondary schools and colleges. Some states have "drop-off exceptions" which only prohibit carry inside school buildings, or permit carry while inside a personal vehicle on school property. Campus carry laws vary by state.
- Public interscholastic and/or professional sporting events and/or venues (sometimes only during a time window surrounding such an event)
- Amusement parks, fairs, parades and/or carnivals
- Businesses that sell alcohol (sometimes only "by-the-drink" sellers like restaurants, sometimes only establishments defined as a "bar" or "nightclub", or establishments where the percentage of total sales from alcoholic beverages exceeds a specified threshold)
- Hospitals (even if hospitals themselves are not restricted, "teaching hospitals" partnered with a medical school are sometimes considered "educational institutions"; exceptions are sometimes made for medical professionals working in these facilities)
- Churches, mosques and other "Houses of worship", usually at the discretion of the church clergy (Ohio allows with specific permission of house of worship)
- Municipal mass transit vehicles or facilities
- Sterile areas of airports (sections of the airport located beyond security screening checkpoints, unless explicitly authorized)
- Non-government facilities with heightened security measures (Nuclear facilities, power plants, dams, oil and gas production facilities, banks, factories, unless explicitly authorized)
- Aboard aircraft or ships unless specifically authorized by the pilot in command or ship captain
- Private property where the lawful owner or lessee has posted a sign or verbally stated that firearms are not permitted. Some states have enacted laws prohibiting the carrying of firearms on private property, unless the property owner or lawful occupant has explicitly granted permission for the carrying of weapons on the premises.
- Any public place, while under the influence of alcohol or drugs (including certain prescription or over-the-counter medications, depending on jurisdiction)
"Opt-out" statutes ("gun-free zones")
Some states allow private businesses to post a specific sign prohibiting concealed carry within their premises. The exact language and format of such a sign varies by state. By posting the signs, businesses create areas where it is illegal to carry a concealed handgun—similar to regulations concerning schools, hospitals, and public gatherings.
Violation of such a sign, in some of these states, is grounds for revocation of the offender's concealed carry permit and criminal prosecution. Other states, such as Virginia, enforce only trespassing laws when a person violates a "Gun Free Zone" sign. In some jurisdictions, trespass by a person carrying a firearm may have more severe penalties than "simple" trespass, while in other jurisdictions, penalties are lower than for trespass.
Such states include Arizona, Arkansas, Connecticut, Illinois, Kansas, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and Wisconsin.
There is considerable dispute over the effectiveness of such "gun-free zones". Opponents of such measures, such as OpenCarry.org, state that, much like other malum prohibitum laws banning gun-related practices, only law-abiding individuals will heed the signage and disarm. Individuals or groups intent on committing far more serious crimes, such as armed robbery or murder, will not be deterred by signage prohibiting weapons. Further, the reasoning follows that those wishing to commit mass murder might intentionally choose gun-free venues like shopping malls, schools, and churches (where weapons carry is generally prohibited by statute or signage) because the population inside is disarmed and thus less able to stop them.
In some states, business owners have been documented posting signs that appear to prohibit guns, but legally do not because the signs do not meet local or state laws defining the required appearance, placement, or wording of signage. Such signage can be posted out of ignorance of the law, or intent to pacify gun control advocates while not actually prohibiting the practice. The force of law behind a non-compliant sign varies based on state statutes and case law. Some states interpret their statutes' high level of specification of signage as evidence that the signage must meet the specification exactly, and any quantifiable deviation from the statute makes the sign non-binding. Other states have decided in case law that if efforts were made in good faith to conform to the statutes, the sign carries the force of law even if it fails to meet current specifications. Still, others have such lax descriptions of what is a valid sign that virtually any sign that can be interpreted as "no guns allowed" is binding on the license holder.
Note that virtually all jurisdictions allow some form of oral communication by the lawful owner or controller of the property that a person is not welcome and should leave. This notice can be given to anyone for any reason (except for statuses that are protected by the Federal Civil Rights Act of 1964 and other CRAs, such as race), including due to the carrying of firearms by that person, and refusal to heed such a request to leave may constitute trespassing.
Brandishing and printing
Printing refers to a circumstance where the shape or outline of a firearm is visible through a garment while the gun is still fully covered, and is generally not desired when carrying a concealed weapon. Brandishing can refer to different actions depending on jurisdiction. These actions can include printing through a garment, pulling back clothing to expose a gun, or unholstering a gun and exhibiting it in the hand. The intent to intimidate or threaten someone may or may not be required legally for it to be considered brandishing.
Brandishing is a crime in most jurisdictions, but the definition of brandishing varies widely.
Under California law, the following conditions have to be present to prove brandishing:
A person, in the presence of another person, drew or exhibited a ; That person did so in a rude, angry, or threatening manner That person, in any manner, unlawfully used the in a fight or quarrel The person was not acting in lawful self-defense.]
In Virginia law:
It shall be unlawful for any person to point, hold or brandish any firearm or any air or gas operated weapon or any object similar in appearance, whether capable of being fired or not, in such manner as to reasonably induce fear in the mind of another or hold a firearm or any air or gas operated weapon in a public place in such a manner as to reasonably induce fear in the mind of another of being shot or injured. However, this section shall not apply to any person engaged in excusable or justifiable self-defense.
— Code of Virginia 18.2-282
Federal law
Gun Control Act of 1968
The Gun Control Act passed by Congress in 1968 lists felons, illegal aliens, and other codified persons as prohibited from purchasing or possessing firearms. During the application process for concealed carry, states carry out thorough background checks to prevent these individuals from obtaining permits. Additionally, the Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act created an FBI-maintained system in 1994 for instantly checking the backgrounds of potential firearms buyers in an effort to prevent these individuals from obtaining weapons.
Firearm Owners Protection Act
The Firearm Owners Protection Act (FOPA) of 1986 allows a gun owner to travel through states in which their firearm possession is illegal as long as it is legal in the states of origination and destination, the owner is in transit and does not remain in the state in which firearm possession is illegal, and the firearm is transported unloaded and in a locked container. The FOPA addresses the issue of transport of private firearms from origin to destination for purposes lawful in state of origin and destination; FOPA does not authorize concealed carry as a weapon of defense during transit. New York State Police arrested those carrying firearms in violation of state law, and then required them to use FOPA as an affirmative defense to the charges of illegal possession.
Law Enforcement Officers Safety Act
In 2004, the United States Congress enacted the Law Enforcement Officers Safety Act, 18 U.S. Code 926B and 926C. This federal law allows two classes of persons – the "qualified law enforcement officer" and the "qualified retired law enforcement officer" – to carry a concealed firearm in any jurisdiction in the United States, regardless of any state or local law to the contrary, with the exception of areas where all firearms are prohibited without permission, and certain Title II weapons.
Federal Gun Free School Zones Act
The Federal Gun Free School Zone Act limits where a person may legally carry a firearm. It does this by making it generally unlawful for an armed citizen to be within 1,000 feet (extending out from the property lines) of a place that the individual knows, or has reasonable cause to believe, is a K–12 school. Although a state-issued carry permit may exempt a person from this restriction in the state that physically issued their permit, it does not exempt them in other states which recognize their permit under reciprocity agreements made with the issuing state.
Federal property
Some federal statutes restrict the carrying of firearms on the premises of certain federal properties such as military installations or land controlled by the USACE.
National park carry
On May 22, 2009, President Barack Obama signed H.R. 627, the "Credit Card Accountability Responsibility and Disclosure Act of 2009", into law. The bill contained a rider introduced by Senator Tom Coburn (R-OK) that prohibits the Secretary of the Interior from enacting or enforcing any regulations that restrict possession of firearms in National Parks or Wildlife Refuges, as long as the person complies with laws of the state in which the unit is found. This provision was supported by the National Rifle Association and opposed by the Brady Campaign to Prevent Gun Violence, the National Parks Conservation Association, and the Coalition of National Park Service Retirees, among other organizations. As of February 2010 concealed handguns are for the first time legal in all but 3 of the nation's 391 national parks and wildlife refuges so long as all applicable federal, state, and local regulations are adhered to. Hawaii is a notable exception. Concealed and open carry are both illegal in Hawaii for all except retired military or law enforcement personnel. Previously firearms were allowed into parks if cased and unloaded.
Full faith and credit (CCW permits)
Attempts were made in the 110th Congress, United States House of Representatives (H.R. 226) and the United States Senate (S. 388), to enact legislation to compel complete reciprocity for concealed carry licenses. Opponents of national reciprocity have pointed out that this legislation would effectively require states with more restrictive standards of permit issuance (e.g., training courses, safety exams, "good cause" requirements, etc.) to honor permits from states with more liberal issuance policies. Supporters have pointed out that the same situation already occurs with marriage certificates, adoption decrees, and other state documents under the "full faith and credit" clause of the U.S. Constitution. Some states have already adopted a "full faith and credit" policy treating out-of-state carry permits the same as out-of-state driver's license or marriage certificates without federal legislation mandating such a policy. In the 115th Congress, another universal reciprocity bill, the Concealed Carry Reciprocity Act of 2017, was introduced by Richard Hudson. The bill passed the House but did not get a vote in the Senate.
Legal issues
Court rulings
Prior to the 1897 Supreme Court case Robertson v. Baldwin, the federal courts had been silent on the issue of concealed carry. In the dicta from a maritime law case, the Supreme Court commented that state laws restricting concealed weapons do not infringe upon the right to bear arms protected by the federal Second Amendment. However, in the context of such rulings, open carry of firearms was generally unrestricted in the jurisdictions in question, which provided an alternative means of "bearing" arms.
In the majority decision in the 2008 Supreme Court case of District of Columbia v. Heller, Justice Antonin Scalia wrote;
Like most rights, the Second Amendment right is not unlimited. It is not a right to keep and carry any weapon whatsoever in any manner whatsoever and for whatever purpose: For example, concealed weapons prohibitions have been upheld under the Amendment or state analogues ... The majority of the 19th-century courts to consider the question held that prohibitions on carrying concealed weapons were lawful under the Second Amendment or state analogs.
Heller was a landmark case because, for the first time in United States history, a Supreme Court decision defined the right to bear arms as constitutionally guaranteed to private citizens rather than a right restricted to "well-regulated militia". The Justices asserted that sensible restrictions on the right to bear arms are constitutional, however, an outright ban on a specific type of firearm, in this case handguns, was in fact unconstitutional. The Heller decision is limited because it only applies to federal enclaves such as the District of Columbia. In 2010, the SCOTUS expanded Heller in McDonald v. Chicago incorporating the 2nd Amendment through the 14th Amendment as applying to local and state laws. Various Circuit Courts have upheld their local and state laws using intermediate scrutiny. The correct standard is a strict scrutiny review for all "fundamental" and "individual" rights. On June 28, 2010, the U.S. Supreme Court struck down the handgun ban enacted by the city of Chicago, Illinois, in McDonald v. Chicago, effectively extending the Heller decision to states and local governments nationwide. Banning handguns in any jurisdiction has the effect of rendering invalid any licensed individual's right to carry concealed in that area except for federally exempted retired and current law enforcement officers and other government employees acting in the discharge of their official duties.
In 2022, the Supreme Court ruled in New York State Rifle & Pistol Association, Inc. v. Bruen, that the Second Amendment does protect "an individual's right to carry a handgun for self-defense outside the home." The case struck down New York's strict law requiring people to show "proper cause" in order to get a concealed weapons permit, and could affect similar laws in other states such as California, Hawaii, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Rhode Island. Shortly after the Supreme Court ruling, the attorney generals of each of California, Hawaii (concealed-carry licenses only), Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Rhode Island (permits issued by municipalities only) issued guidance that their "proper cause" or similar requirements would no longer be enforced.
Legal liability
Even when self-defense is justified, there can be serious civil or criminal liabilities related to self-defense when a concealed carry permit holder brandishes or fires their weapon. For example, if innocent bystanders are hurt or killed, there could be both civil and criminal liabilities even if the use of deadly force was completely justified. Some states technically allow an assailant who is shot by a gun owner to bring a civil action. In some states, liability is present when a resident brandishes the weapon, threatens use, or exacerbates a volatile situation, or when the resident is carrying it while intoxicated. It is important to note that simply pointing a firearm at any person constitutes felony assault with a deadly weapon unless circumstances validate a demonstration of force. A majority of states that allow concealed carry, however, forbid suits being brought in such cases, either by barring lawsuits for damages resulting from a criminal act on the part of the plaintiff, or by granting the gun owner immunity from such a civil suit if it is found that they were justified in shooting.
Simultaneously, increased passage of "Castle Doctrine" laws allow persons who own firearms and/or carry them concealed to use them without first attempting to retreat. The "Castle Doctrine" typically applies to situations within the confines of one's own home. Nevertheless, many states have adopted escalation of force laws along with provisions for concealed carry. These include the necessity to first verbally warn a trespasser or lay hands on a trespasser before a shooting is justified (unless the trespasser is armed or assumed to be so). This escalation of force does not apply if the shooter reasonably believes a violent felony has been or is about to be committed on the property by the trespasser. Additionally, some states have a duty to retreat provision which requires a permit holder, especially in public places, to vacate themself from a potentially dangerous situation before resorting to deadly force. The duty to retreat does not restrictively apply in a person's home or business though escalation of force may be required. In 1895 the Supreme Court ruled in Beard v. United States that if an individual does not provoke an assault and is residing in a place they have a right to be, then they may use considerable force against someone they reasonably believe may do them serious harm without being charged with murder or manslaughter should that person be killed. Further, in Texas and California homicide is justifiable solely in defense of property. In other states, lethal force is authorized only when serious harm is presumed to be imminent.
Even given these relaxed restrictions on the use of force, using a handgun must still be a last resort in some jurisdictions; meaning the user must reasonably believe that nothing short of deadly force will protect the life or property at stake in a situation. Additionally, civil liabilities for errors that cause harm to others still exist, although civil immunity is provided in the Castle Doctrine laws of some states (e.g., Texas).
Penalties for carrying illegally
Main article: Criminal possession of a weaponCriminal possession of a weapon is the unlawful possession of a weapon by a citizen. Many societies both past and present have placed restrictions on what forms of weaponry private citizens (and to a lesser extent police) are allowed to purchase, own, and carry in public. Such crimes are public order crimes and are considered mala prohibita, in that the possession of a weapon in and of itself is not evil. Rather, the potential for use in acts of unlawful violence creates a possible need to control them. Some restrictions are strict liability, whereas others require some element of intent to use the weapon for an illegal purpose. Some regulations allow a citizen to obtain a permit or other authorization to possess the weapon under certain circumstances. Lawful uses of weapons by civilians commonly include hunting, sport, collection and self-preservation.
The penalties for carrying a firearm in an unlawful manner vary widely from state-to-state, and may range from a simple infraction punishable by a fine to a felony conviction and mandatory incarceration. An individual may also be charged and convicted of criminal charges other than unlawful possession of a firearm, such as assault, disorderly conduct, disturbing the peace, or trespassing. In the case of an individual with no prior criminal convictions, the state of Tennessee classifies the unlawful concealed carry of a loaded handgun as a Class C misdemeanor punishable by a maximum of 30 days imprisonment and/or a $500 fine. While in New York State, a similar crime committed by an individual with no criminal convictions is classified as a Class D felony, punishable by a mandatory minimum of 3.5 years imprisonment, to a maximum of 7 years. As New York State does not recognize any pistol permits issued in other states, the statute would apply to any individual who does not have a valid New York State issued concealed carry permit, even if such individual has a valid permit issued in another jurisdiction. In addition, the New York State statutory definition of a "loaded firearm" differs significantly from what may be commonly understood, as simply possessing any ammunition along with a weapon capable of firing such ammunition satisfies the legal definition of a loaded firearm in New York. The large variability of state carry laws has resulted in confusing circumstances where a person in Vermont (which requires no license of any kind to carry a concealed weapon by anyone who is not prohibited by law), could unwittingly travel into the adjacent state of New York, where such individual, despite acting entirely within the law of Vermont, would then face a mandatory 3.5-year prison sentence simply for accidentally crossing the state's border into New York. These circumstances are aggravated by the fact that many NYS police departments as well as the New York State Police do not recognize the protections granted federally under the Firearm Owners Protection Act, which was intended to prevent such prosecutions.
Effect on crime and deaths
Research has had mixed results, indicating variously that right-to-carry laws have no impact on violent crime, that they increase violent crime, and that they decrease violent crime.
A 2020 study by the RAND Corporation of over 200 combinations of gun policies and outcomes found "supportive evidence that shall-issue concealed carry laws are associated with increased firearm homicides and total homicides". They also found supportive evidence that child access prevention laws reduce firearm homicides and self-injuries among youth, and further evidence supporting the conclusion that stand-your-ground laws are associated with increased levels of firearm homicides. The researchers credit a much greater investment in gun safety research over the past few years with providing this and other more recent studies with stronger and more reliable evidence.
A 2004 review of the existing literature by the National Academy of Sciences found that the results of existing studies were sensitive to the specification and time period examined, and concluded that a causal link between right-to-carry laws and crime rates cannot be shown. Quinnipiac University economist Mark Gius summarized literature published between 1993 and 2005, and found that ten papers suggested that permissive CCW laws reduce crime, one paper suggested they increase crime, and nine papers showed no definitive results. A 2017 review of the existing literature concluded, "Given the most recent evidence, we conclude with considerable confidence that deregulation of gun carrying over the last four decades has undermined public safety—which is to say that restricting concealed carry is one gun regulation that appears to be effective." A 2016 study in the European Economic Review which examined the conflicting claims in the existing literature concluded that the evidence CCW either increases or decreases crime on average "seems weak"; the study's model found "some support to the law having a negative (but with a positive trend) effect on property crimes, and a small but positive (and increasing) effect on violent crimes". The Washington Post fact-checker concluded that it could not state that CCW laws reduced crime, as the evidence was murky and in dispute. In a 2017 article in the journal Science, Stanford University law professor John Donohue and Duke University economist Philip J. Cook write that "there is an emerging consensus that, on balance, the causal effect of deregulating concealed carry (by replacing a restrictive law with an RTC law) has been to increase violent crime". Donohue and Cook argue that the crack epidemic made it difficult to determine the causal effects of CCW laws and that this made earlier results inconclusive; recent research does not suffer the same challenges with causality. A 2018 RAND review of the literature concluded that concealed carry either has no impact on crime or that it may increase violent crime. The review said, "We found no qualifying studies showing that concealed-carry laws decreased ."
A 2020 study in PNAS found that right-to-carry laws were associated with higher firearm deaths. A 2019 panel study published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine by medical researchers including Michael Siegel of the Boston University School of Public Health and David Hemenway of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health found that “shall issue" concealed carry laws were associated with a 9% increase in homicides. A 2019 study in the American Journal of Public Health found that greater restrictions on concealed carry laws were associated with decreases in workplace homicide rates. Another 2019 study in the American Journal of Public Health found that states with right-to-carry laws were associated with a 29% higher rate of firearm workplace homicides. A 2019 study in the Journal of Empirical Legal Studies found that right-to-carry laws led to an increase in overall violent crime. A 2017 study in the American Journal of Public Health found that "shall-issue laws" (where concealed carry permits must be given if criteria are met) "are associated with significantly higher rates of total, firearm-related, and handgun-related homicide" than "may-issue laws" (where local law enforcement have discretion over who can get a concealed carry permit). A 2011 study found that aggravated assaults increase when concealed carry laws are adopted.
A 2019 study in Journal of American College of Surgeons found "no statistically significant association between the liberalization of state level firearm carry legislation over the last 30 years and the rates of homicides or other violent crime." This is also in line with a 1997 study researching county-level data from 1977 to 1992 concluding that allowing citizens to carry concealed weapons deters violent crimes and it appears to produce no increase in accidental deaths. A 2018 study in The Review of Economics and Statistics found that the impact of right-to-carry laws was mixed and changed over time. RTC laws increased some crimes over some periods while decreasing other crimes over other periods. The study suggested that conclusions drawn in other studies are highly dependent on the time periods that are studied, the types of models that are adopted and the assumptions that are made. A 2015 study that looked at issuance rates of concealed-carry permits and changes in violent crime by county-level in four shall-issue states found no increases or decreases in violent crime rates with changes in permit issuances. A 2019 study in the International Review of Law and Economics found that with one method, right-to-carry laws had no impact on violent crime, but with another method led to an increase in violent crime; neither method showed that right-to-carry laws led to a reduction in crime. A 2003 study found no significant changes in violent crime rates amongst 58 Florida counties with increases of concealed-carry permits. A 2004 study found no significant association between homicide rates and shall-issue concealed carry laws.
A 2013 study of eight years of Texas data found that concealed handgun licensees were much less likely to be convicted of crimes than were nonlicensees. The same study found that licensees' convictions were more likely to be for less common crimes, "such as sexual offenses, gun offenses, or offenses involving a death." A 2020 study in Applied Economics Letters examining concealed-carry permits per capita by state found a significant negative effect on violent crime rates. A 2016 study found a significant negative effect on violent crime rates with passage of shall-issue laws. A 2017 study in Applied Economics Letters found that property crime decreased in Chicago after the implementation of the shall issue concealed carry law. A 2014 Applied Economics Letters study found states with more permissive conceal carry laws had lower murder rates than states with restrictive laws. Another 2014 study found that RTC laws by state significantly reduce homicide rates.
In 1996 economists John R. Lott, Jr. and David B. Mustard analyzed crime data in all 3,054 counties in the United States from 1977 to 1992, finding counties that had shall-issue licensing laws overall saw murders decrease by 7.65 percent, rapes decrease by 5.2 percent, aggravated assaults decrease by 7 percent and robberies decrease by 2.2 percent. The study was widely disputed by numerous economists. The 2004 National Academy of Sciences panel reviewing the research on the subject concluded, with one dissenting panelist, that the Lott and Mustard study was unreliable. Georgetown University Professor Jens Ludwig, Daniel Nagin of Carnegie Mellon University and Dan A. Black of the University of Chicago in The Journal of Legal Studies, said of the Lott-Mustard study, "once Florida is removed from the sample, there is no longer any detectable impact of right-to-carry laws on the rates of murder and rape".
A 2022 study examining the Sullivan Act of 1911 found that the law had no impact on overall homicide rates, reduced overall suicide rates, and caused large and sustained decrease in gun-related suicide rates.
Firearms permit holders in active shooter incidents
In 2016 FBI analyzed 40 "active shooter incidents" in 2014 and 2015 where bystanders were put in peril in ongoing incidents that could be affected by police or citizen response. Six incidents were successfully ended when citizens intervened. In two stops citizens restrained the shooters, one unarmed, one with pepper spray. In two stops at schools, the shooters were confronted by teachers: one shooter disarmed, and one committed suicide. In two stops citizens with firearms permits exchanged gunfire with the shooter. In a failed stop attempt, a citizen with a firearms permit was killed by the shooter. In 2018 the FBI analyzed 50 active shooter incidents in 2016 and 2017. This report focused on policies to neutralize active shooters to save lives. In 10 incidents citizens confronted an active shooter. In eight incidents the citizens stopped the shooter. Four stops involved unarmed citizens who confronted and restrained or blocked the shooter or talked the shooter into surrendering. Four stops involved citizens with firearms permits: two exchanged gunfire with a shooter and two detained the shooter at gunpoint for arrest by responding police. Of the two failed stops, one involved a permit holder who exchanged gunfire with the shooter but the shooter fled and continued shooting and the other involved a permit holder who was wounded by the shooter. "Armed and unarmed citizens engaged the shooter in 10 incidents. They safely and successfully ended the shootings in eight of those incidents. Their selfless actions likely saved many lives."
See also
- American gun ownership
- Concealed carry
- Defensive gun use
- Gun control
- Gun politics in the United States
- Overview of gun laws by nation
- Self-defense
Notes
- Permit not required as of July 4, 2024.
References
- ^ Smart, Rosanna; Morral, Andrew; Smucker, Sierra; Cherney, Samantha; Schell, Terry; Peterson, Samuel; Ahluwalia, Sangeeta; Cefalu, Matthew; Xenakis, Lea; Ramchand, Rajeev; Gresenz, Carole (2020). The Science of Gun Policy: A Critical Synthesis of Research Evidence on the Effects of Gun Policies in the United States, Second Edition. doi:10.7249/rr2088-1. ISBN 9781977404312. S2CID 51928649.
- "Effects of Concealed-Carry Laws on Violent Crime". RAND Corporation.
- ^ 6 Right-to-Carry Laws | Firearms and Violence: A Critical Review | The National Academies Press. 2004. doi:10.17226/10881. ISBN 978-0-309-09124-4.
- Winkler, Adam (September 2011). Gunfight: The Battle Over the Right to Bear Arms in America. W. W. Norton. p. 162. ISBN 978-0-393-08229-6.
- Winkler, Adam (September 2011). Gunfight: The Battle Over the Right to Bear Arms in America. W. W. Norton. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-393-08229-6.
- Wilson, Harry L. (May 2012). "Concealed Weapons Laws". In Carter, Gregg Lee (ed.). Guns in American Society: An Encyclopedia of History, Politics, Culture, and the Law (Second ed.). Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 320. ISBN 978-0-313-38671-8.
- "Do You Have A Duty To Inform When Carrying Concealed? We Look At All 50 States For The Answers". Concealed Nation. Retrieved 2017-07-04.
- "CCW Disclosure". Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- "2012 Florida Statutes, Title XLVI Crimes, Chapter 790 Weapons and Firearms, 790.01 Carrying concealed weapons". 2012.
790.01 Carrying concealed weapons. – (1) Except as provided in subsection (4), a person who carries a concealed weapon or electric weapon or device on or about his or her person commits a misdemeanor of the first degree, punishable as provided in s. 775.082 or s. 775.083. (2) A person who carries a concealed firearm on or about his or her person commits a felony of the third degree, punishable as provided in s. 775.082, s. 775.083, or s. 775.084. (3) This section does not apply to a person licensed to carry a concealed weapon or a concealed firearm pursuant to the provisions of s. 790.06. (4) It is not a violation of this section for a person to carry for purposes of lawful self-defense, in a concealed manner: (a) A self-defense chemical spray. (b) A nonlethal stun gun dart-firing stun gun or other nonlethal electric weapon or device that is designed solely for defensive purposes. (5) This section does not preclude any prosecution for the use of an electric weapon or device, a dart-firing stun gun, or a self-defense chemical spray during the commission of any criminal offense under s. 790.07, s. 790.10, s. 790.23, or s. 790.235, or for any other criminal offense.
- "2012 Florida Statutes, Title XLVI Crimes, Chapter 790 Weapons and Firearms, 790.001 Definitions". 2012.
(3)(a) "Concealed weapon" means any dirk, metallic knuckles, slungshot, billie, tear gas gun, chemical weapon or device, or other deadly weapon carried on or about a person in such a manner as to conceal the weapon from the ordinary sight of another person. (b) "Tear gas gun" or "chemical weapon or device" means any weapon of such nature, except a device known as a "self-defense chemical spray." "Self-defense chemical spray" means a device carried solely for purposes of lawful self-defense that is compact in size, designed to be carried on or about the person, and contains not more than two ounces of chemical.
- Lott, John R. (2021-10-11). "Concealed Carry Permit Holders Across the United States: 2021". SSRN. Rochester, NY. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3937627. SSRN 3937627.
- Kranz, Steven W. (2006). "A Survey of State Conceal And Carry Statutes: Can Small Changes Help Reduce the Controversy?". Hamline Law Review. 29 (638).
- ^ "Permits / Licenses That Each State Honors" (PDF). Handgunlaw.us. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- "Gun laws in Arkansas" (PDF). Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- "A.C.A. § 5-73-321. Recognition of other states' licenses". 2013.
- "CA attorney General Legal Alert" (PDF).
- Dejean, Ashley (October 3, 2017) – "Just Days After Las Vegas, Gun Laws in the Nation’s Capitol Are About to Get Weaker" Mother Jones. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
- Matanane, Sabrina Salas (May 28, 2014) – "Governor Signs 12 Bills, Vetoes 2" Kuam News. Retrieved February 2, 2015.
- "People v. Bruner – 1996 – Illinois Appellate Court, Fourth District Decisions". Justia. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- "Docket No. 106367 – People v. Diggins" (PDF). Illinois Courts. October 8, 2009. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- Higgins, Michael (November 28, 2000). "Owners Say Law Lets Them Tote Guns in Fanny Packs". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- Gregory, Ted (June 3, 2004). "Dupage Pays for Handgun Arrest". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- "Gun-Rights Advocates Win Victory in Chicago Court". The Crime Report. May 18, 2004. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- McCune, Greg (July 9, 2013). "Illinois Is Last State to Allow Concealed Carry of Guns", Reuters. Retrieved July 20, 2013.
- Jones, Ashby (July 9, 2013). "Illinois Abolishes Ban on Carrying Concealed Weapons", Wall Street Journal. Retrieved July 20, 2013.
- McDermott, Kevin, and Hampel, Paul (July 11, 2013). "Illinois Concealed Carry Now on the Books – But Not Yet in the Holster", St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Retrieved July 20, 2013.
- DeFiglio, Pam (July 9, 2013). "General Assembly Overrides Veto, Legalizing Concealed Carry in Illinois", Patch Media. Retrieved July 20, 2013.
- "Illinois" (PDF). Handgunlaw.us. March 3, 2018. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- "§724.11A. Recognitions" (PDF). 2017.
- NRA-ILA. "NRA-ILA | Maryland Gun Laws". NRA-ILA. Retrieved 2017-10-07.
- "States with strict gun-permitting laws consider next steps". AP News. 23 June 2022. Retrieved 2022-06-23.
- Howe, Amy (23 June 2022). "In 6-3 ruling, court strikes down New York's concealed-carry law". SCOTUSblog. Retrieved 2022-06-23.
- "North Carolina shall-issue laws" (PDF). Jus.state.nc.us. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-26. Retrieved 2010-11-08.
- "166.291: Issuance of concealed handgun license".
The sheriff of a county, upon a person's application for an Oregon concealed handgun license, upon receipt of the appropriate fees and after compliance with the procedures set out in this section, shall issue the person a concealed handgun license
- "V.I.C Title 23 Chpt. 5 § 460. Reciprocal recognition of out-of-state licenses". 1968.
- Concealed Handgun Permit Firearms Safety Class – Virginia Concealed Handgun Permit. vaguntraining.com. Retrieved on 2014-04-15.
- "Firearms FAQ | Washington State". www.atg.wa.gov. Retrieved September 16, 2021.
- "Acknowledging domestic terror threat, Pentagon says troops, recruiters can carry concealed guns". Military Times. 21 November 2016. Retrieved 2016-11-23.
- Robert J., Spitzer (19 June 2016). "Even in the Wild West, there were rules about carrying concealed weapons". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- Joe, Eaton; Chad D., Baus. "Ohio Gun Rights Timeline". Buckeye Firearms Association. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- "Article 400 | NYS Penal Law | Licensing Provisions Firearms". ypdcrime.com. Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- New York State firearm law table, "Carry Permit" row
- ^ Virginia State Police, application for a concealed handgun permit page. Vsp.state.va.us. Retrieved on 2011-10-16.
- "Florida Statute 790". Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- "Concealed Carry (CCW) Laws by State on". Usacarry.com. Retrieved 2010-11-08.
- State of Washington reciprocity Archived 2011-06-06 at the Wayback Machine. Atg.wa.gov. Retrieved on 2011-10-16.
- "Idaho Enhanced Concealed Carry Permit Recognition". ConcealedCarry.com. 23 March 2015. Retrieved 2016-03-10.
- "Concealed Carry Reciprocity and Recognition Map". ConcealedCarry.com. 23 March 2015. Retrieved 2016-03-10.
- "Concealed Carry Mobile Applications". ConcealedCarry.com. 31 October 2014. Retrieved 2016-03-10.
- "Ohio's Concealed Carry Laws and License Application" (PDF). p. 12. Retrieved 2014-05-30.
- "Chapter 624, Section 714, Subdivision 17". Minnesota Statutes. Minnesota Revisor of Statutes. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- "Nebraska Revised Statute 69-2441". Nebraska Statutes. Nebraska Legislature. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- Hetzner, Amy (2011–2012). "Where Angels Tread: Gun-Free School Zone Laws and an Individual Right to Bear Arms". Marquette Law Review. 95: 359–98.
- "Brandishing a Weapon, Gun or Firearm". Retrieved 2014-02-19.
- "Code of Virginia 18.2-282". Archived from the original on 2000-04-13. Retrieved 2014-02-19.
- "Title 36 CFR §327.13". Ecfr.gpoaccess.gov. Archived from the original on 2011-06-12. Retrieved 2010-11-08.
- National Parks Gun Law Takes Effect in February Washington Post, May 22, 2009.
- Judge Blocks Rule Permitting Concealed Guns In U.S. Parks Washington Post, March 20, 2009.
- "Copy of Injunction" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-04-07. Retrieved 2010-11-08.
- "Greenspace". The Los Angeles Times. May 20, 2009.
- Constitution for the United States of America, Article IV, Section 1: "Full faith and credit shall be given in each state to the public acts, records, and judicial proceedings of every other state. And the Congress may by general laws prescribe the manner in which such acts, records, and proceedings shall be proved, and the effect thereof."
- Tennessee reciprocity policy Archived 2016-04-12 at the Wayback Machine "Tennessee now recognizes a facially valid handgun permit, firearms permit, weapons permit, or a license issued by another state according to its terms..."
- "House Bill 38". congress.gov. 2017.
- "Robertson v. Baldwin:: 165 U.S. 275 (1897)". Justia U.S. Supreme Court Center.
- Carter, Gregg Lee (2002). Guns in American society: an encyclopedia of history, politics, culture, and the law. Santa Barbara, Calif: ABC-CLIO. p. 506. ISBN 978-1-57607-268-4.
Justice Brown spotlighted his belief that the guarantee of the right to keep and bear arms was not infringed by laws prohibiting the carrying of concealed weapons
- "District of Columbia v. Heller, 554 U.S. 570" (PDF). 2008. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- Leonard W. Levy, Encyclopedia of the American Constitution, Macmillan (1991), article "Strict Scrutiny" by Kenneth L. Karst. "The term 'strict scrutiny' appears to have been used first by Justice William O. Douglas in his opinion for the Supreme Court in Skinner v. Oklahoma (1942), in a context suggesting special judicial solicitude both for certain rights that were 'basic' and for certain persons who seemed the likely victims of legislative prejudice." After a right is identified as a fundamental or basic individual right protected by the Constitution, restrictions on that right are subject to strict scrutiny.
- Gunther, Gerald (1972). "The Supreme Court, 1971 Term, Foreword: In Search of Evolving Doctrine on a Changing Court: A Model for a Newer Equal Protection". Harvard Law Review. 86 (1): 1–48. doi:10.2307/1339852. JSTOR 1339852.
- Barnes, Robert (October 1, 2009). "Justices to Decide if State Gun Laws Violate Rights". The Washington Post.
- "Supreme Court Strikes Down New York Conceal Carry Gun Law". WABC-TV. June 23, 2022. Retrieved June 23, 2022.
California, Hawaii, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey and Rhode Island all have similar laws likely to be challenged as a result of the ruling.
- "California Attorney General Legal Alert OAG-2022-02" (PDF).
- "Hawaii Attorney General Op. No. 22-02" (PDF).
- "Maryland Attorney General Letter to Maryland Department of State Police Licensing Division" (PDF).
- "Joint Advisory Regarding the Massachusetts Firearms Licensing System After the Supreme Court's Decision in New York State Rifle & Pistol Association v. Bruen".
- "New Jersey Attorney General Law Enforcement Directive No. 2022-07" (PDF).
- "Attorney General Neronha issues guidance on concealed-carry permits following SCOTUS decision | Rhode Island Attorney General's Office".
- Swickard, Joe (June 4, 2010). "Charges in stray-bullet death: Carjacking victim faces manslaughter rap". Detroit Free Press. Archived from the original on 2010-06-09.
- "Wayne County judge lessens bond for man accused of killing bystander". The Detroit News. June 28, 2010. Archived from the original on August 23, 2017.
- "Castle Doctrine and Self-Defense". ct.gov.
- "Beard v. United States, 158 U.S. 550 (1897)". Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- Booher, Kary (June 8, 2010). "Case highlights concealed carry weapons issues". Springfield News-Leader. Archived from the original on 2010-06-10.
"Missouri is like 48 other states, except the state of Texas, that does not allow deadly force in defense of property," said Randy Gibson, a captain in the Greene County Sheriff's Department.
- CALCRIM No. 3476
- Cal. Penal Code §197 (West 2013.)
- "80(R) SB 378 - Enrolled version - Bill Text". capitol.texas.gov. Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- "2010 Tennessee Code :: Title 39 – Criminal Offenses :: Chapter 17 – Offenses Against Public Health, Safety and Welfare :: Part 13 – Weapons :: 39-17-1307 – Unlawful carrying or possession of a weapon".
- "Article 265 Penal Law Firearms | Dangerous Weapons | NY Law".
- "Sentencing Guidelines for Possession of Weapon in NY". 21 January 2016.
- "New York" (PDF). handgunlaw.us. Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- "State Laws and Published Ordinances – New York". atf.gov. Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- "New York Gun Laws".
- Gius, Mark (2016-11-03). Guns and Crime: The Data Don't Lie. CRC Press. ISBN 9781315450872. Retrieved 3 December 2017.
- Philip J. Cook; Harold A. Pollack (2017). "Reducing Access to Guns by Violent Offenders". RSF: The Russell Sage Foundation Journal of the Social Sciences. 3 (5): 2. doi:10.7758/rsf.2017.3.5.01. JSTOR 10.7758/rsf.2017.3.5.01.
- Durlauf, Steven N.; Navarro, Salvador; Rivers, David A. (2016-01-01). "Model uncertainty and the effect of shall-issue right-to-carry laws on crime". European Economic Review. Model Uncertainty in Economics. 81 (Supplement C): 32–67. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.696.3159. doi:10.1016/j.euroecorev.2015.07.020. S2CID 1575410.
- Kessler, Glenn (2012-12-17). "Do concealed weapon laws result in less crime?". Washington Post. Retrieved 2017-12-03.
- ^ Cook, Philip J.; Donohue, John J. (7 December 2017). "Saving lives by regulating guns: Evidence for policy". Science. 358 (6368): 1259–1261. Bibcode:2017Sci...358.1259C. doi:10.1126/science.aar3067. PMID 29217559. S2CID 206665567.
- "The Effects of Concealed-Carry Laws". rand.org. Retrieved 2019-12-25.
- Buchanan, Larry; Leatherby, Lauren (June 22, 2022). "Who Stops a 'Bad Guy With a Gun'?". The New York Times. Archived from the original on June 22, 2022.
Data source: Advanced Law Enforcement Rapid Response Training Center
- Anderson, D. Mark; Sabia, Joseph; Tekin, Erdal (2018). "Child Access Prevention Laws and Juvenile Firearm-Related Homicides". National Bureau of Economic Research Working Papers. Cambridge, MA. doi:10.3386/w25209. S2CID 158944952.
- Siegel, Michael; Pahn, Molly; Xuan, Ziming; Fleegler, Eric; Hemenway, David (March 28, 2019). "The Impact of State Firearm Laws on Homicide and Suicide Deaths in the USA, 1991–2016: a Panel Study". Journal of General Internal Medicine. 34 (10): 2021–2028. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-04922-x. PMC 6816623. PMID 30924089.
- Sabbath, Erika L.; Hawkins, Summer Sherburne; Baum, Christopher F. (February 2020). "State-Level Changes in Firearm Laws and Workplace Homicide Rates: United States, 2011 to 2017". American Journal of Public Health. 110 (2): 230–236. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2019.305405. PMC 6951380. PMID 31855477.
- Doucette, Mitchell L.; Crifasi, Cassandra K.; Frattaroli, Shannon (December 2019). "Right-to-Carry Laws and Firearm Workplace Homicides: A Longitudinal Analysis (1992–2017)". American Journal of Public Health. 109 (12): 1747–1753. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2019.305307. PMC 6836804. PMID 31622144.
- Donohue, John J.; Aneja, Abhay; Weber, Kyle D. (15 May 2019). "Right-to-Carry Laws and Violent Crime: A Comprehensive Assessment Using Panel Data and a State-Level Synthetic Control Analysis". Journal of Empirical Legal Studies. 16 (2): 198–247. doi:10.1111/jels.12219. S2CID 181734017.
- Siegel, Michael; Xuan, Ziming; Ross, Craig S.; Galea, Sandro; Kalesan, Bindu; Fleegler, Eric; Goss, Kristin A. (December 2017). "Easiness of Legal Access to Concealed Firearm Permits and Homicide Rates in the United States". American Journal of Public Health. 107 (12): 1923–1929. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2017.304057. PMC 5678379. PMID 29048964.
- Aneja, A.; Donohue, J. J.; Zhang, A. (29 October 2011). "The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws and the NRC Report: Lessons for the Empirical Evaluation of Law and Policy". American Law and Economics Review. 13 (2): 565–631. doi:10.1093/aler/ahr009.
- Hamill, Mark E.; Hernandez, Matthew C.; Bailey, Kent R.; Zielinski, Martin D.; Matos, Miguel A.; Schiller, Henry J. (January 2019). "State Level Firearm Concealed-Carry Legislation and Rates of Homicide and Other Violent Crime". Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 228 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2018.08.694. PMID 30359832.
- Mustard, David B.; Lott, John R. (1998-04-17). "Crime, Deterrence, and Right-to-Carry Concealed Handguns". Journal of Legal Studies. SSRN 10129.
- Manski, Charles F.; Pepper, John V. (May 2018). "How Do Right-to-Carry Laws Affect Crime Rates? Coping with Ambiguity Using Bounded-Variation Assumptions" (PDF). The Review of Economics and Statistics. 100 (2): 232–244. doi:10.1162/rest_a_00689. S2CID 43138806.
- Phillips, Charles D.; Nwaiwu, Obioma; Lin, Szu-hsuan; Edwards, Rachel; Imanpour, Sara; Ohsfeldt, Robert (2015). "Concealed Handgun Licensing and Crime in Four States". Journal of Criminology. 2015: 1–8. doi:10.1155/2015/803742.
- "Increasing permits to conceal guns has zero effect on crime, data say". 2015-09-28.
- Gius, Mark (March 2019). "Using the synthetic control method to determine the effects of concealed carry laws on state-level murder rates". International Review of Law and Economics. 57: 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.irle.2018.10.005. S2CID 158186157.
- Kovandzic, Tomislav V.; Marvell, Thomas B. (2003). "Right-To-Carry Concealed Handguns and Violent Crime: Crime Control Through Gun Decontrol?". Criminology & Public Policy. 2 (3): 363–396. doi:10.1111/j.1745-9133.2003.tb00002.x.
- Hepburn, Lisa; Miller, Matthew; Azrael, Deborah; Hemenway, David (2004). "The Effect of Nondiscretionary Concealed Weapon Carrying Laws on Homicide". The Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection, and Critical Care. 56 (3): 676–681. doi:10.1097/01.TA.0000068996.01096.39. PMID 15128143.
- Phillips, Charles D.; Nwaiwu, Obioma; McMaughan Moudouni, Darcy K.; Edwards, Rachel; Lin, Szu-hsuan (January 2013). "When Concealed Handgun Licensees Break Bad: Criminal Convictions of Concealed Handgun Licensees in Texas, 2001–2009". American Journal of Public Health. 103 (1): 86–91. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2012.300807. PMC 3518334. PMID 23153139.
- Gius, Mark (2019). "The relationship between concealed carry permits and state-level crime rates". Applied Economics Letters. 27 (11): 937–939. doi:10.1080/13504851.2019.1646866. S2CID 199829764.
- Barati, Mehdi (August 2016). "New evidence on the impact of concealed carry weapon laws on crime". International Review of Law and Economics. 47: 76–83. doi:10.1016/j.irle.2016.05.011.
- Devaraj, Srikant; Patel, Pankaj C. (2018). "An examination of the effects of 2014 concealed weapons law in Illinois on property crimes in Chicago". Applied Economics Letters. 25 (16): 1125–1129. doi:10.1080/13504851.2017.1400645. S2CID 158932191.
- Gius, Mark (26 November 2013). "An examination of the effects of concealed weapons laws and assault weapons bans on state-level murder rates". Applied Economics Letters. 21 (4): 265–267. doi:10.1080/13504851.2013.854294. S2CID 154746184.
- Moody, Carlisle E.; Marvell, Thomas B.; Zimmerman, Paul R.; Alemante, Fasil (2014). "The Impact of Right-to-Carry Laws on Crime: An Exercise in Replication". Review of Economics & Finance. 4: 33–43.
- Jeffrey R. Snyder (October 22, 1997). "Cato Institute Policy Analysis No. 284: Fighting Back: Crime, Self-Defense, and the Right to Carry a Handgun" (PDF). Cato Institute.
- Philip J. Cook; Harold A. Pollack (2017). "Reducing Access to Guns by Violent Offenders". RSF: The Russell Sage Foundation Journal of the Social Sciences. 3 (5): 9. doi:10.7758/rsf.2017.3.5.01. JSTOR 10.7758/rsf.2017.3.5.01.
- Black, Dan A.; Nagin, Daniel S (January 1998). "Do Right-to-Carry Laws Deter Violent Crime?".
- Depew, Briggs; Swensen, Isaac (2022). "The Effect of Concealed-Carry and Handgun Restrictions on Gun-Related Deaths: Evidence from the Sullivan Act of 1911". The Economic Journal. 132 (646): 2118–2140. doi:10.1093/ej/ueac004. ISSN 0013-0133.
- "Schweit, Katherine W., "Active Shooter Incidents in the United States in 2014 and 2015", Federal Bureau of Investigation, 2016" (PDF). Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- "Active Shooter Incidents in the United States in 2016 and 2017", Federal Bureau of Investigation, April 2018. "The FBI defines an active shooter as one or more individuals actively engaged in killing or attempting to kill people in a populated area. ... The active aspect of the definition inherently implies that both law enforcement personnel and citizens have the potential to affect the outcome of the event based upon their responses to the situation."
External links
- NRA-ILA guide to gun laws
- A guide to gun laws and reciprocity
- Concealed Carry Reciprocity Maps
- U.S. Concealed Carry Association

