| Revision as of 16:54, 23 February 2015 editRationalobserver (talk | contribs)11,997 edits →Rose-Baley Party massacre: ce← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 19:34, 15 November 2024 edit undoMarcocapelle (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers557,979 edits →External links: Removed grandparent of Category:Native American people of the Indian WarsTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Leader of the Mohave Nation (c. 1814 – 1874)}} | |||
| {{good article}} | |||
| {{featured article}} | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=January 2015}} | {{Use mdy dates|date=January 2015}} | ||
| {{Infobox |
{{Infobox Native American leader | ||
| |name = Irataba | |name = Irataba | ||
| |native_name = Yara tav | |||
| |image = ] | |||
| |native_name_lang = ] | |||
| |caption = February 1864 | |||
| |image = ] | |||
| |caption = Irataba, {{circa|1864}} | |||
| |alt = A black and white picture of a long-haired man dressed in a military uniform | |||
| |tribe = ] | |tribe = ] | ||
| |mother_tongue = ] | |||
| |birth_date = {{circa|1814}} | |birth_date = {{circa|1814}} | ||
| |birth_place = ] | |birth_place = ] | ||
| |death_date = May 1874 | |death_date = May 3 or 4, {{death year and age|1874|1814}} | ||
| |death_place = ] | |death_place = ], ], United States | ||
| | |
|known_for = | ||
| |known_for = Irataba was the last independent head chief of the Mohave. | |||
| |death_cause = Uncertain | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Irataba''' (also known as |
'''Irataba''' (]: ''eecheeyara tav'' {{IPA|}}, also known as ''Yara tav'', ''Yarate:va'', ''Arateve''; {{circa|1814}} – 1874) was a leader of the ], known as a mediator between the Mohave and the United States. He was born near the ] in present-day ]. Irataba was a renowned ] and one of the first Mohave to speak English, a skill he used to develop relations with the United States. | ||
| Irataba first encountered ]s in 1851, when he assisted the ]. In 1854, he met ], then leading an expedition crossing the Colorado. Several Mohave aided the group, and Irataba agreed to escort them through the territory of the ] to the ], which would take them to southern California. Noted for his large physical size and gentle demeanor, he later helped and protected other expeditions, earning him a reputation among whites as the most important native leader in the region. | |||
| Against Irataba's advice, in 1858 Mohave warriors attacked the first emigrant ] to use ] through Mohave country. As a result, the ] sent a detachment under ] to pacify the tribe. Following a series of confrontations known as the ], Hoffman succeeded in dominating the natives, and demanded that they allow the passage of settlers through their territory. To ensure compliance, ] was constructed near the site of the battle in April 1859. Hoffman also imprisoned several Mohave leaders. Having been an advocate for friendly relations with the whites, Irataba became the nation's ''Aha macave yaltanack'', an elected, as opposed to hereditary, leader. | |||
| As a result of his many interactions with U.S. officials and settlers, Irataba was invited to ], in 1864, for an official meeting with members of the U.S. military and its government, including President ]. In doing so, he became the first Native American from the Southwest to meet an American president. He received considerable attention during his tours of the U.S. capital, and of New York City and Philadelphia, where he was given gifts, including a silver-headed cane from Lincoln. Upon his return he negotiated the creation of the ], which caused a split in the Mohave Nation when he led several hundred of his supporters to the Colorado River valley. The majority of the Mohave preferred to remain in their ancestral homelands near Fort Mohave and under the leadership of their hereditary leader, ], who was less enthusiastic about direct collaboration with whites. As leader of the Colorado River band of Mohave, Irataba encouraged peaceful relations with whites, served as a mediator between the warring tribes in the area, and during his later years continued to lead the Mohave in their ongoing conflicts with the ] and ]. | |||
| As noted by ethnographer ], "to some he is an heroic figure, to others he was a white collaborator who did not stand up for Mojave rights."{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=30–31}} The Irataba Society, a non-profit charity run by the ], was established in 1970 in ], where a sports venue, ], is also named after him. In 2002, the US ] designated {{convert|32745|acre|km2}} in the ] as ]. In March 2015, Mohave Tribal chairman ] credited Irataba with ensuring that "the Mohaves stayed on land they had lived on since time immemorial."{{sfn|Gutekunst|2015}} | |||
| ==Early life== | |||
| ] in the ]|thumb|left]] | |||
| ==Background== | |||
| Irataba or ''Yara tav'', from the Mohave ''eecheeyara tav'' (meaning "beautiful bird") also rendered as Irateba, Arateve, and Yiratewa, was born into the ''Neolge'', or Sun Fire clan of the ] Nation of Native Americans {{circa|1814}}.<ref>{{harvnb|Ricky|1999|p=100}}: born {{circa|1814}} to the Sun Fire clan; {{harvnb|Sherer|1966|p=6}}: Irataba's Mohave name was Yara tav, a shortened form of the Mohave ''eecheeyara tav'', but it has also been rendered as Irateba, Arateve, and Yiratewa.</ref> He lived in present-day Arizona, near the Nevada and California border, on the east bank of the ] in the ] near a group of sharply pointed rocks known as the ], located south of where the ] empties into the Mohave Canyon.{{sfn|Kroeber|1925|pp=725–7}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Irataba's name, also rendered as Ireteba, Yara tav, Arateve, Yarate:va, and Yiratewa, derives from the ] phrase ''eecheeyara tav'', which means "beautiful bird".<ref>{{harvnb|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=x}}: Yarate:va, {{harvnb|Sherer|1966|p=6}}: origin and variations of Irataba's name.</ref> He was born into the ''Neolge'', or Sun Fire clan of the ] {{circa|1814}}.{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=100}}{{efn|Both the spelling "Mohave" and "Mojave" are correct variants of the English word corresponding to the Mohave word ''pipa aha macave'' "People who live by the side of the water". According to some sources (e.g. {{cite web|title=The Colorado River Indian Tribes (C.R.I.T.) Reservation and Extension Programs|year=2008|url=http://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1461.pdf|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150416135400/http://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1461.pdf|archive-date=April 16, 2015|df=mdy-all}}) the spelling "Mohave" is preferred by the Colorado River tribe of Mohave which Irataba founded.}} He lived near a rock formation that gave its name to ], south of where the ] empties into the ] in present-day Arizona, near the Nevada and California border.{{sfn|Kroeber|1925|pp=725–727}} The Mohave lived in houses along the riverbank in the ], during winter in half-buried dwellings built with ] logs and ] covered in earth, and in the summer in open-air flat-roofed houses called '']s''.{{sfn|Moratto|2014|p=347}} | |||
| Mohave caught fish in the Colorado River and hunted game, such as rabbits and beaver, using a bow and arrow or traps.{{sfn|Johansen|Pritzker|2007|p=1019}} In the spring, when the Colorado River flooded the bottomlands, they cultivated corn, watermelons, beans, gourds, tobacco, and pumpkins.{{sfn|Wilson|2000|p=218}} The Mohave lived in groups of houses along the riverbank, but eschewed centralized villages. During the winter, they lived in semi-subterranean dwellings built with Cottonwood logs and arrow-weed covered in earth. In the summer they lived in open-air flat-roofed houses known as '']'', which provided sufficient shade.{{sfn|Moratto|2014|p=347}} Mohave who enjoyed higher status would cover their body in "goose grease" to help alleviate the summer heat.{{sfn|NYT|May 1864|p=1}} | |||
| In the mid-19th century, the Mohave were composed of three geographical groups; Irataba was the hereditary leader of the ''Huttoh Pah'' group, who lived near the east bank of the ] and occupied the central portion of the ].{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=6, 29–30}} Mohave government consisted of a loose system of hereditary clan leaders with a head of the entire nation.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=29–30}} They were often involved in conflicts with the ], ], and ]s.{{sfn|Stewart|1971|pp=431–434}} Irataba was a member of the Mohave warrior society called ''kwanami'', who led groups of warriors in battle and were dedicated to defending their lands and people.{{sfn|Kroeber|1965|pp=177–178}}<ref>{{harvnb|Johansen|Pritzker|2007|p=1019}}: the kwanami were a Mohave warrior society; {{harvnb|Sherer|1966|p=30}}: Irataba was a kwanami, which means brave or fearless; {{harvnb|Fathauer|1954}}: the role of kwanami in Mohave warfare.</ref> | |||
| ==Adulthood== | |||
| {{quote box|quote= is a big Indian, literally as well as figuratively ... granitic in appearance as one of the Lower Coast mountains, with a head only less in size to a buffalo's and a lower jar massive enough to crush nuts or crush quartz. |source= —''Daily Evening Bulletin'', December 2, 1863 |width=33%|align=right|style=padding:10px;}} | |||
| Little is known of Irataba's family relations, except for the name of his son Tekse thume, and his nephews Qolho qorau (Irataba's sister's son who succeeded him as leader) and Aspamekelyeho.{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=25}} ], who lived with the Mohave for five years, later stated that Irataba was the brother of the former chief, presumably Cairook, with whom Irataba clearly had a close relationship.{{sfn|McGinty|2005|p=176}} One anecdotal description states that Irataba had several wives, among them a ] woman who had been taken as a captive and who is also described as having a young son.{{sfn|The Daily Democrat|1891}} He also had at least one daughter, the mother of his granddaughter Tcatc who was interviewed in the 1950s. She stated that Irataba had wanted to leave his land deeds and medals to his brother's sons, but that they were eventually lost.{{sfn|Devereux|1951}} | |||
| According to cultural anthropologist ], Mohave men were extraordinarily tall; Chief Cairook reached a barefoot height of nearly six and a half feet.<ref>{{harvnb|Kroeber|1925|p=728}}: Mohave men were extraordinarily tall; {{harvnb|United States Army|1861|p=69}}: Chief Cairook was nearly six and a half feet tall.</ref> By adulthood, Irataba had grown almost as tall as Cairook, becoming one of the tribe's sub-chiefs.<ref>{{harvnb|Harte|1886|p=492}}: Irataba's height was approximately 6'4"; {{harvnb|United States Army|1861|p=69}}: Irataba was one of Cairook's sub-chiefs.</ref> | |||
| In contemporary accounts Irataba was described as an eloquent speaker, and linguist ] suggests that he was among the first Mohave people to become fluent in English, which he learned through his many interactions with Anglo-Americans.{{sfn|Hinton|1984|p=281}} Like many Mohave men, Irataba was very tall, particularly by 19th-century standards; the United States Army estimated his height at {{convert|6|ft|4|in|cm}} in 1861.{{sfn|Ives|1861|p=69}} American author ], writing in '']'', referred to him as "the old desert giant".{{sfn|Evans|1869|p=143}} Edward Carlson, a soldier based at ] who knew Irataba well in the 1860s, described him as having a powerful frame, but also a "very gentle" and "kind ... demeanor".{{sfn|Mifflin|2009|p=178}} | |||
| In the opinion of author Kenneth M. Stewart, the Mohave were fierce warriors who were frequently the aggressor, and although they did not plunder their enemy's possessions, they took prisoners and ]. Mohave war parties, which regularly battled against the ], ], and ]s, utilized bowmen tasked with inflicting damage on an approaching group and keeping them distracted in preparation for ] attacks by warriors brandishing war clubs capable of crushing their opponent's skulls.{{sfn|Stewart|1971|pp=431–444}} According to anthropologist Lorraine M. Sherer, Irataba was what the Mohave called, ''kwanami'', which means brave or fearless.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|p=30}} | |||
| Irataba lived through a tumultuous period of Mohave history where the people went from being a politically independent nation to coming under the political control of the United States, and the events surrounding his role in these encounters are well documented. Most historical sources for the life of Irataba come from descriptions by white explorers or government agents with whom he interacted, or from contemporary newspapers that reported on his visits to the East Coast and California, and on the conflicts in Arizona territory. Some Mohave versions of the events also exist: in the early 20th century anthropologist ] interviewed Jo Nelson (Mohave: Chooksa homar), a Mohave man who participated in many of the events and knew Irataba personally;{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973}} another version was told to ] ] by Irataba's granddaughter Tcatc,{{sfn|Devereux|1951}} and versions recounted by members of the Fort Mohave band of Mohave, the descendants of Homoseh quahote, were recorded by ethnographer ] during the 1950s and 1960s.{{sfn|Sherer|1966}} | |||
| ==Contact with European Americans== | |||
| ] | |||
| ==Contact with emigrants and explorers== | |||
| According to author Arthur Woodward, in 1849, Irataba, Cairook, and the Mohave people encountered a large group of ]s, including Captain ] and Lieutenant ], who were leading an exploratory expedition up the Colorado River.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=54}} Whipple and his men counted six hundred Mohave gathered near the explorer's camp, eagerly trading corn, beans, squash, and wheat for beads and ]. By the end of their commerce, the party had purchased six bushels of corn and two hundred pounds of flour. The Mohave taught the European Americans a traditional game played with a hoop and pole, and the two groups entertained themselves with target practice, the Mohave using bows and arrows and the whites shooting pistols and rifles.{{sfn|Whipple|1856|pp=112–9}} | |||
| {{Multiple image| align = right| direction = vertical| width = 200| header = | image1 = Amiel Weeks Whipple.jpg| alt1 = A black and white picture of a man with a moustache| caption1 = Amiel Weeks Whipple|image2 = Whipple with the Mohave.jpg | alt2 = A drawing of some people trading goods near a river | caption2 = A drawing from the Whipple Expedition (1856) by ]}} | |||
| Irataba assisted Captain ] during his 1851 ].{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=100}} On March 19, 1851, a family of ] settlers, the Oatmans, who were traveling by wagon train in what is now Arizona, were ] by a band of Western ], probably the ].{{sfn|Braatz|2003|pp=253–254}} They captured two survivors of the attack: the 14-year-old ] and her 7-year-old sister, Mary Ann. After a year with the Yavapai, the girls were sold to the Mohave, and adopted into the Oach clan where they lived with the family of a Mohave man called Tokwatha (Musk Melon) a friend of Irataba. Olive remained with the Mohave until February 22, 1856, when Tokwatha, having been warned that having a white girl among them might be seen as an offense by whites, brought her to ] carpenter ], releasing her in return for two horses and some blankets and beads.<ref>{{harvnb|Mifflin|2009|pp=104–107}}: Olive was released to Henry Grinnell; {{harvnb|Putzi|2004|p=177}}: Olive and Mary Ann taken captive.</ref> Irataba may have learned about Anglo-Americans and their society from Oatman, and knowing her may have contributed to his generally favourable disposition towards Whites. | |||
| Whipple notes that, when the expedition experienced difficulties crossing the Colorado River on February 27, several Mohave jumped into the water and helped salvage the supplies. They saved many sheep that had fallen into the river using rafts they had constructed in preparation for the crossing.{{sfn|Whipple|1856|pp=112–9}} Whipple then asked the Mohave to guide them across the desert, and Cairook and Irataba agreed. They escorted the group across the hostile territory of the Paiute to the ] that would take them to southern California.{{sfn|Whipple|1856|pp=119–28}}{{refn|group=nb|Irataba assisted Captain Lorenzo Sitgreaves during his 1851 ].{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=100}}}} | |||
| ===Whipple Expedition=== | |||
| ] | |||
| On February 23, 1854, Irataba, ], and other Mohave people encountered ] led by military officers ] and ], as the group approached the Colorado en route to California.{{sfn|Whipple|Ives|1856|p=112}}{{efn|Woodward and Ricky state that this encounter was several years earlier in 1849,{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=54}}{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=100}} but this appears to be a result of confusion over the date of the expedition along the Colorado River led by Whipple and Ives. Whipple himself gives the date of the encounter as February 23, 1854, and there is no question that the Whipple Expedition was in 1853 to 1854,{{sfn|Conrad|1969|p=147}}{{sfn|Whipple|Ives|1856|pp=112–128}} not 1849.}} Whipple and his men counted six hundred Mohave gathered near their camp, trading corn, beans, ], and wheat for beads and ].{{sfn|Whipple|Ives|1856|pp=113–114}} By the end of their commerce, the party had purchased six bushels of corn and two hundred pounds of flour.{{sfn|Whipple|Ives|1856|p=114}} The Mohave played a traditional game played with a hoop and pole, and the two groups entertained themselves with target practice, the Mohave using bows and arrows and the whites firing pistols and rifles.{{sfn|Whipple|Ives|1856|p=114}} When the expedition had difficulty crossing the Colorado on February 27, several Mohave jumped into the water and helped salvage the supplies.{{sfn|Whipple|Ives|1856|p=116}} | |||
| Irataba and Cairook agreed to escort the group across the territory of the Paiute to the ] that would take them to southern California.{{sfn|Whipple|Ives|1856|pp=119–128}} German artist ] accompanied the Whipple expedition, and made drawings of several Mohave, including Irataba. Möllhausen's drawings were featured in Ives' 1861 congressional report, making Irataba "among the first ''named'' likenesses of California Indians ever published".{{sfn|Elsasser|1977|p=62}} | |||
| In October 1857, an expedition led by ] was tasked with establishing a trade route along the ] from ], Arkansas to ], California.{{sfn|Thrapp|1991|p=76}} His journey began at Fort Smith and continued through ] before crossing the Colorado River near Needles, California.{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=100}} This route became known as Beale's Wagon Road and the location where Beale crossed the river, Beale's Crossing.{{sfn|Utley|1981|p=164}} | |||
| ===Ives Expedition=== | |||
| According to Woodward, in February 1858, Irataba and Cairook noticed a ] heading up the Mohave Canyon.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=54}} When the boat stopped and its crew revealed themselves, Irataba quickly realized that their leader was his old friend, Lieutenant Ives.{{sfn|United States Army|1861|p=69}} Ives was leading an expedition to the Grand Canyon in a steamship named the ''Explorer'', and he asked Irataba to guide them into the canyon. Cairook agreed to the arrangement, and he and a Mohave boy named Nahvahroopa joined them.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=54–5}}{{refn|group=nb|After two days, Cairook departed and returned home.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=55}}}} | |||
| In February 1858, Ives returned to the area in a ] named ''Explorer''. He was leading an expedition up the Colorado from the south, and he wanted Irataba to guide them.{{sfn|Mifflin|2009|p=174}} The Mohave gave permission to navigate the river, and Cairook, Irataba, and a 16-year-old Mohave boy named Nahvahroopa joined them.{{sfn|Ives|1861|pp=69–71, 76}} Möllhausen again accompanied the expedition, and was impressed with the Mohave guides, later noting Irataba's enthusiastic handshake and lamenting that their only form of communication was sign language. He also noted that Irataba and the Mohave readily began wearing European clothes given to them by members of the expedition, and showed great interest in ].{{sfn|Miller|1972|pp=178–179, 182}} Aside from the friendship shown to him by Irataba and Cairook, Ives noted that the Mohave appeared less friendly than on earlier occasions, a change that he attributed to their contact with ]s, who were in conflict with the US and had succeeded in converting some Mohave.{{sfn|Mifflin|2009|p=175}}{{sfn|Stewart|1969|p=230}}{{efn|Tensions between Mormons and American emigrants reached their peak during 1857–58, with several hostile encounters collectively known as the ].{{sfn|Baley|2002|pp=4, 14, 28, 131–132}}}} | |||
| Irataba guided the party into the Mohave Canyon, indicating the location of rapids and advising the ''Explorer''{{'s}} pilot of convenient places to anchor while camping for the night.{{sfn|Ives|1861|pp=77, 85, 92}} When they reached the entrance to the ], the ship crashed against a submerged rock, throwing several men overboard, dislodging the ], and damaging the ]. Using their ], the crew towed the ''Explorer'' to the shore, where they camped for three days while repairing the vessel.{{sfn|Ives|1861|pp=81–84}} The expedition had relied on beans and corn provided by the Mohave during the previous weeks; as their supplies dwindled they grew increasingly anxious about the arrival of a resupply pack train from Fort Yuma. Irataba volunteered to hike towards the Mohave Valley to try to locate the supplies that had been requested several days earlier. He also warned that the expedition was being watched by Paiutes.{{sfn|Ives|1861|pp=79–83}} | |||
| ==Exploring the Grand Canyon== | |||
| ] flowing through the ]|alt=A color photo of the Grand Canyon]] | |||
| When Irataba returned he informed Ives that he would not venture any deeper into the territory of the ]s, but agreed to help them locate friendly guides in the region before parting company.{{sfn|Ives|1861|pp=94–97}} Irataba was reluctant to venture into the canyon because he feared the party would be ambushed by Paiutes aligned with Mormons.{{sfn|Zappia|2014|pp=121, 138}} After enlisting three Hualapai guides, Irataba prepared to take his leave from the expedition and return to the Mohave community.{{sfn|Ives|1861|pp=94–97, 102}} On April 4, the Mohave received payment for their services; Möllhausen described the exchange: "Lieutenant Ives informed Irataba that he had been authorized by the 'Great Grandfather in Washington' to give him two mules ... for his loyalty and his trustworthiness so that he could take his possessions and those of his companions more conveniently to his home valley."{{sfn|Miller|1972|p=188}} The next morning, as they were preparing to leave: "Irataba was visibly moved ... and in his sincere eyes expressed so much honesty and loyalty as can only be found in an unspoiled nature ... I maintain that there was not one in our expedition who did not feel a certain sadness to see this huge man with ... a harmless soul leave."{{sfn|Miller|1972|p=188}} | |||
| According to Ives's 1861 report, Irataba guided the party into the Mohave Canyon, indicating the location of sandbars and rapids and advising the ''Explorer''{{'s}} pilot regarding convenient places to anchor while camping for a night. As the expedition progressed, the rapids grew in strength and intensity, and the rock walls increasingly towered above them.{{sfn|United States Army|1861|pp=95–120}} When they reached the entrance to the ], the ship crashed against a submerged rock, throwing several men overboard, dislodging the ], and severely damaging the ].{{sfn|United States Army|1861|pp=81–2}} | |||
| ==Mohave War and aftermath== | |||
| Ives explained how, using their ], they towed the ''Explorer'' to shore, where they camped for three days while making repairs to the badly damaged vessel.{{sfn|United States Army|1861|pp=81–4}} The expedition had relied on beans and corn provided by the Mohave during the last several weeks; however, as their supplies dwindled they increasingly anticipated the arrival of the pack train from Fort Yuma. Irataba volunteered to hike towards the Mohave Valley in an attempt to locate the supplies that had been requested several days earlier. He also warned that the expedition was being watched by Paiutes.{{sfn|United States Army|1861|pp=79–83}} When he returned he informed Ives that he would not venture any deeper into the territory of the Hualapais, but agreed to help them locate friendly guides in the region before departing company.{{sfn|United States Army|1861|pp=94–7}} According to the author Natale A. Zappia, Irataba was reluctant to venture into the canyon because he feared the party would get ambushed by Paiutes aligned with ]s.{{sfn|Zappia|2014|pp=121, 138}}{{refn|group=nb|Tensions between Mormons and European American emigrants reached their zenith during 1857–58, with several hostile encounters collectively known as the ].{{sfn|Baley|2002|p=4, 14, 28, 131–2}}}} Ives noted that, after enlisting three Hualapais guides, Irataba took his leave from the expedition and returned to the Mohave Villages.{{sfn|United States Army|1861|pp=94–7, 102}} | |||
| {{Main|Mohave War}} | |||
| Following their experiences with the Sitgreaves and Whipple expeditions, and encounters with Mormons and the soldiers at Fort Yuma, the Mohave were aware that whites were immigrating to the region in increasing numbers. It was difficult for the Mohave to predict the behavior of the arriving whites, some of whom, like Whipple, were amiably disposed towards them, whereas others such as the Mormons were hostile. The kwanami were divided on how the situation should be approached; some advocated an aggressive posture, denying whites all passage through their territory, but others, including Irataba, preferred a peaceful approach, or even an alliance with them that could put the Mohave in a stronger position relative to their traditional enemies the Paiute, Chemehuevi, and Walapai.{{sfn|Kroeber|1965|pp=177–178}} | |||
| On September 1, 1857, a joint force of Mohave and Quechan warriors launched a major attack with hundreds of warriors on a Maricopa village close to ], on the ]. The ] was described by a group of white mail carriers who witnessed it. They stated that the battle was fought mostly with clubs, as well as bows and arrows, and that probably more than 100 warriors died, most of them from the attacking party. It is unknown whether Irataba participated in the attack, but given his status as kwanami, it is likely that he did. The battle has been described as the last major battle involving only Native American nations.{{sfn|Kroeber|Fontana|1986}} This defeat put the Mohave on the defensive, wary of the possibility that whites would take this moment of weakness as an opportunity to begin settling on tribal lands.{{sfn|Kroeber|1965|p=175}}{{sfn|Stewart|1969|p=230}} | |||
| ==Rose-Baley Party massacre== | |||
| {{main|Rose-Baley Party}} | |||
| ], {{circa|1866}}]] | |||
| ===Rose–Baley Party attack=== | |||
| According to Charles W. Baley, author of ''Disaster at the Colorado: Beale's Wagon Road and the First Emigrant Party'', in 1858 a wealthy farmer from Iowa, Leonard John Rose, formed a large emigrant ] after having sold most of his property in Iowa, amassing what was then a small fortune of $30,000, which enabled him to purchase an animal stock that included two dozen horses and two hundred head of red Durham cattle. The Rose party left Iowa in early April and were joined by the Baley family while traveling through Kansas in May.{{sfn|Baley|2002|pp=2–3, 5, 15}}{{refn|group=nb|The combined Rose-Baley Party traveled with twenty wagons and numbered forty men, fifty to sixty women and children, and five hundred head of cattle.{{sfn|Baley|2002|p=15}}}} They reached ] on June 23, where several more families and their livestock joined them before traveling to the Colorado River by way of ], where they would become the first emigrant train to venture onto Beale's Wagon Road.{{sfn|Baley|2002|pp=24, 28–37, 39–40}} | |||
| In October 1857, an expedition led by ] was tasked with establishing a trade route along the ] from ], Arkansas, to ], California.{{sfn|Thrapp|1991|p=76}}{{sfn|Hunter|1979|p=139}} From Fort Smith, his journey continued through ], before crossing the Colorado near Needles, California.{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=100}} This route became known as ], and the location where Beale crossed the river as Beale's Crossing.{{sfn|Utley|1981|p=164}} Beale's journal and subsequent report to the ] did not mention any problems with Irataba and the Mohave, but an assistant named Humphrey Stacy recorded that the Mohave had prevented Beale from traveling downriver.{{sfn|Sherer|1994|p=69}} | |||
| In 1858, the ] comprising at least a hundred settlers with wagons and a large herd of cattle, was the first emigrant train to venture onto Beale's Wagon Road.{{sfn|Hunter|1979|p=138}}{{efn|Hunter estimates there were two hundred settlers and four hundred head of cattle, while Baley puts the number at about 100 settlers and 500 head of cattle, as reported by party member John Udell.<ref>{{harvnb|Hunter|1979}}; {{harvnb|Baley|2002|p=15}}.</ref>}} Upon entering Mohave territory the settlers started cutting down cottonwood trees, which were an important resource for the Mohave. The most warlike of the kwanamis organized an attack on the party, and drove away and slaughtered many of the party's cattle.{{sfn|Kroeber|1965|pp=174–175}} On August 30, three hundred Mohave warriors attacked the emigrants but were repelled, with one member of the party killed in battle and eleven wounded. Another family who were not with the main party during the attack were killed in an event that has often been blamed on the Mohave, but which in ]'s opinion was more likely carried out by a band of Walapai, along with seven renegade Mohave.{{sfn|Sherer|1994|pp=82–86, 95}} The emigrants killed seventeen Mohave warriors.{{sfn|Hunter|1979|p=139}}<ref>{{harvnb|Baley|2002|pp=2–3, 5, 15, 24, 28–40, 61–62, 67–72}}: emigrant train and attack; {{harvnb|Zappia|2014|p=129}}: seventeen Mohave warriors.</ref> The incident was widely publicized in the media and labeled "a massacre",{{sfn|Sherer|1994|p=82}} scaring many white Californians who feared being cut off from the eastern US by hostile natives, and it motivated the War Department to quickly subjugate the tribe.{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|pp=53–54}}{{sfn|Kroeber|1965|p=175}} | |||
| Baley notes that on August 27, the emigrants reached the ] and made their crossing at Sitgreaves Pass, elevation 3,652 feet.{{sfn|Baley|2002|p=56}}{{refn|group=nb|The pass was named after Lieutenant Lorenzo Sitgreaves, who led an expedition party to the region in 1851.{{sfn|Baley|2002|p=56}}}} From the crest they could see the Colorado River in the distance, but having worked continuously during the morning and afternoon, they stopped to prepare their first meal of the day. While they were cooking, a small group of Mohave approached and asked, in a combination of broken English and Spanish, how many people the wagon train included and whether they intended to settle near the Colorado River. They told the Mohave that they were traveling through the region on their way to California, which seemed to appease them, many of whom helped the party during their decent to the Colorado.{{sfn|Baley|2002|p=59}} | |||
| Irataba was away at Fort Yuma during the attack on the settlers, and upon hearing of it he scolded the Mohave. Chooksa homar participated in the events and reported that Irataba told the warriors, "I hear you fought, though I told you not to. And you will have war again: I know it. You used to fight the Maricopa. I want to go to see the Maricopa and tell them: 'The Mohave will not come any more to attack you'."{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=14}} Irataba, weary of the constant fighting and worried that further conflicts with neighboring tribes would draw more attention from the US soldiers, organized a peace expedition to the Maricopa, settling the ancient disputes between the two peoples.{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|pp=54–54}} | |||
| ], with golden grass, blue sky, and dark foothills| ], a prominent landmark in the western foothills of the Black Mountains, viewed from Mohave Valley]] | |||
| ===Conflict with the US army=== | |||
| According to Baley, while others to stop and make a mountain camp, the Rose company continued to the Colorado, where they planned to water the train's combined stock and build a raft in preparation for the impending river crossing. There the emigrants encountered more Mohave, but unlike the friendly ones that greeted them at Sitgreaves Pass, these were decidedly unwelcoming.{{sfn|Baley|2002|p=61}} Several people were physically harassed, and many of the party's cattle were driven away and slaughtered. The group settled-in for the night at a spot two hundred yards from the river and {{convert|10|mi}} from the Baley company's mountain camp.{{sfn|Baley|2002|pp=61–2}} The following morning they moved closer to the river bank, where they could more easily water their stock. They were visited soon afterward by many Mohave warriors asking about their intentions in the region, including a sub-chief who heard their complaints and assured them that no further depravations would occur.{{sfn|Baley|2002|pp=63–4}} Around noon, they moved closer to where they planned to cross, near a patch of cottonwood trees that were suitable for building rafts.{{sfn|Baley|2002|pp=63–4}} | |||
| ] | |||
| When news of the attack reached California, the ] decided to establish a military fort at Beale's Crossing to keep the Mohave under control and secure white travelers safe passage through Mohave lands. On December 26, 1858, Hoffman and fifty ]s from ] were dispatched to cross the desert and confront the Mohave.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=58}} Irataba attempted to arrange a peaceful meeting, but Hoffman ordered his troops to fire on the warriors, who counterattacked and repelled the force.<ref>{{harvnb|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=63}}: Irataba attempted to arrange a peaceful meeting; {{harvnb|Woodward|1953|p=58}}: the Mohave attacked and repelled the force.</ref> He returned in April 1859, by way of Fort Yuma, with four ] of the ].{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=58}} When they arrived at Beale's Crossing, the Mohave decided against attacking the army of five hundred soldiers.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=58}} On April 23, at Hoffman's request, he and his officers met with several hundred Mohave warriors and their leaders. The indigenous leaders included Cairook, Irataba, ] (also called Seck-a-hoot and Asika hota), and Pascual, leader of the Quechan.<ref>{{harvnb|Sherer|1966|p=3}}: Homoseh quahote attended the meeting; {{harvnb|Woodward|1953|p=59}}: Irataba and Cairook.</ref> During the meeting the Mohave were surrounded by armed soldiers who prevented them from leaving.{{sfn|Hunter|1979|p=150}} | |||
| Hoffman gave the Mohave a choice between war and peace, and he demanded that they agree to never again harm white settlers along the wagon trail. He also declared that, as punishment, the Mohave were required to surrender as hostages a member of each clan and three warriors who had taken part in the attack.{{sfn|Hunter|1979|p=150}} Hoffman demanded that the chief who had ordered the attack on the settlers offer himself up as a hostage. According to Chooksa homar, the chief who had ordered the attack was Homoseh quahote, who was reluctant to give himself up. Cairook offered himself in his place, along with eight others, including Tokwatha, Irataba's son Tekse thume, and Irataba's nephews Qolho qorau, and Aspamekelyeho. Other hostages were named Itsere-'itse, Ilyhanapau, and Tinyam-isalye.{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|pp=25, 66}} They were transported in the river steamer ''General Jessup'' to Fort Yuma.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=59}} Many soldiers remained to begin construction on the Beale's Crossing fort, which was named Fort Mohave.<ref>{{harvnb|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=24}}: soldiers remained to build a fort; {{harvnb|Sherer|1965|p=73}}: the fort was initially called Fort Colorado.</ref> Although Irataba visited the garrison several times and argued for their release, the hostages were held for more than a year.{{sfn|Mifflin|2009|p=177}} On June 21, 1859, Cairook and one other captive were killed by soldiers while attempting to escape their incarceration.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=59–60}} Most of the other Mohave captives escaped.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=59–60}}{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=27}} | |||
| Around 2 p.m. on August 30, the emigrants working near the river were attacked by approximately three hundred Mohave warriors, who according to Baley let out terrifying "war whoops" as they sent arrows flying into the camp.{{sfn|Baley|2002|pp=67–9}} Woodward described how the men quickly armed themselves as women frantically hurried their children to the protection offered by their covered wagons.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=69}} The onslaught continued for several hours, but Rose and others held off the assailants, who eventually retreated.{{sfn|Baley|2002|pp=70–2}} In all, eight members of the ] had been killed, including five children, and twelve wounded; of the train's livestock, only seventeen cattle and ten mules and horses remained.{{sfn|Baley|2002|pp=68, 71}} The emigrants managed to kill seventeen Mohave warriors.{{sfn|Zappia|2014|p=129}} With the wounded in one wagon, the children in another, and the healthy adults on foot, the party began the difficult journey back to Albuquerque, {{convert|500|mi}} away.{{sfn|Baley|2002|p=72}}{{refn|group=nb|According to the author Arthur Woodward, while traveling back to Albuquerque the Rose-Baley Party observed a fiery comet that further upset the already frightened children.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=58}}}} According to cultural anthropologist A.L. Kroeber, "the event sealed the fate of the Mohave as an independent people."{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=53}} | |||
| In July 1861, the commander of Fort Mohave, Major ], ordered soldiers to fire into a group of Mohave who he suspected of having attacked a mail carrier and slaughtered his mule. The Mohave did not respond violently to the attack, but Armistead decided to punish them for harassing the mail party. He arrived at Irataba's ranch where a group of Mohave boys were planting beans, and from a hidden position he shot one of the planters, killing him. This attack prompted an assault on Armistead's detachment, who from an advantageous position on the high ground were able to repel the Mohave, killing many of them in a battle that lasted most of the day. Armistead's report of the assault of Irataba's ranch reported 23 dead Mohave warriors, but the Mohave remember a much higher number of casualties, including women and children killed by the soldiers. Sherer speculated that, given that 50 soldiers fired around 10 shots each, the casualty count could have been much higher than reported. The attack on Irataba's ranch is remembered by the Mohave as "the first and last battle with the Federal Troops."{{sfn|Sherer|1994|pp=103–105}} | |||
| ==Fort Mohave== | |||
| {{main|Fort Mohave}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ==As ''Aha macave yaltanack''== | |||
| According to Woodward, when news of the massacre reached the west, the ] established a military fort at Beale's Crossing to protect white travelers, and on December 26, 1858, ] and fifty ]s were dispatched from ] to cross the desert and confront the Mohave.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=58}} Kroeber notes that Irataba had attempted to arrange a peaceful meeting, but Hoffman ordered his troops to fire on the warriors, who attacked and repelled the force.<ref>{{harvnb|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=63}}: Irataba attempted to arrange a peaceful meeting; {{harvnb|Woodward|1953|p=58}}: the Mohave attacked and repelled the force.</ref> Hoffman returned in April 1859, by way of ], with four ] of the ].{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=58}} When they arrived at Beale's Crossing, the Mohave decided against attacking the army of five hundred soldiers.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=58}} Hoffman immediately arranged for a meeting between he and his officers and Cairook and his sub-chiefs, with Pascual, chief of the ], translating from English to Spanish to Yuman and Mohave and vice versa.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=59}} | |||
| ] | |||
| After Cairook's death, whites living near the Colorado River began to view Irataba as the main leader of the Mohave.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=60}} He had become ''Aha macave yaltanack'' (leader of the Mohave Nation) or ''hochoch'' (leader elected by the people); "''yaltanack''" is Mohave for "leader", and "''hochach''" means "head of a group".<ref>{{harvnb|Scrivner|1970|p=134}}: becoming leader; {{harvnb|Sherer|1966|pp=2, 5–6}}: attaining ''Aha macave yaltanack''.</ref> Homoseh quahote was a hereditary leader of the ''Malika'' clan ("the understanding people"), and the position of head of the Mohave was traditionally inherited only by someone from that clan. Because Irataba was of the ''Huttoh pah'', in order for him to become the leader of the Mohave Nation, Homoseh quahote had to step down so Irataba, as an elected leader, could take his place.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=3–4}} | |||
| Despite the accepted English translations, the words ''yaltanack'' and ''huchach'' do not mean a "ruler" or "boss".{{sfn|Sherer|1966|p=2}} Devereux describes Mohave government as "one of the least understood segments of Mohave culture", and notes that while white officials "tended to act on the assumption that Indian chiefs exercised absolute authority", as an elected leader Irataba was "primarily a servant of the tribe".{{sfn|Devereux|1951|pp=35–36}} | |||
| According to Woodward, Hoffman demanded that the Mohave agree to never again harm white settlers along the wagon trail, and he ordered that a fort be built at Beale's Crossing to enforce the decree. When he asked which chief was responsible for the Rose-Baley Party massacre, Cairook proudly admitted that he had ordered the attack. Hoffman declared that, as punishment, the Mohave were required to surrender six prominent leaders and three warriors who had taken part in the massacre. Cairook offered himself as a hostage, and he and the others were transported in the river steamer, ''General Jessup'', to Fort Yuma.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=59}} Many soldiers remained to begin construction on ].{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=24}} After its completion, Irataba and five to eight hundred of his most ardent supporters moved to the Colorado River Valley, where in 1865 the ] was established.<ref>{{harvnb|Griffin-Pierce|2000|p=246}}: Irataba moved to the Colorado River Valley, where in 1865 the Colorado River Indian Reservation was established; {{harvnb|Sherer|1966|p=8}}: Irataba relocated with five to eight hundred of his most ardent supporters.</ref> In Sherer's opinion, this marked the beginning of a rift between two rival factions of Mohave, the other led by a respected sub-chief named ''Homoseh quahote'', known by the whites as Seck-a-hoot.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=8–9}} | |||
| By the mid-1860s a deep rift had developed between Irataba, who was proactive in cooperating with white settlers, and Homoseh quahote, who passively tolerated but did not approve of white encroachment on Mohave lands.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=9, 30}} Irataba was ''Aha macave yaltanack'' of the Mohave from 1861 to 1866, but from 1867 to 1869 opinions differ, and by 1870 US government correspondence suggests that Homoseh quahote had succeeded him as leader of the Fort Mohave group.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=1–14}} | |||
| ==Death of Cairook== | |||
| ], {{circa|1902}}]] | |||
| ==Mining ventures== | |||
| Woodward reports that on June 21 1859, Cairook and several others were killed by soldiers while attempting to escape their incarceration at Fort Yuma, which had exposed them to the desert's harsh elements.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=59–60}} According to Sherer, in this way Irataba became the Mohave's head chief, known as an ''Aha macave yaltanack'' or ''hochoch'', which designated him as the leader ''made'', or elected, by the people.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=5–6}} | |||
| Probably first to bring national attention to the potential gold in the region was F. X. Aubry, who in 1853 reported finding gold at a crossing of the Colorado and that he traded for legendary gold bullets further east with Tonto Apache. Newspapers across the country copied the gold strike story.<ref>{{cite news|title=Santa Fe Weekly Gazette|url=http://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn84022165/1853-09-17/ed-1/seq-2/#date1=1850&index=0&date2=1860&searchType=advanced&language=&sequence=0&words=Aubry&proxdistance=5&state=&rows=20&ortext=aubry&proxtext=&phrasetext=&andtext=&dateFilterType=yearRange&page=1|date=September 17, 1853}}</ref> Over the next decade mining discoveries up and down the lower Colorado River valley brought miners into newly formed mining districts.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Paher|first1=Stanley|title=Colorado River Ghost Towns|date=1979|publisher=Nevada Publications|location=Las Vegas, Nevada}}</ref> In the spring of 1861, Mohave, possibly including Irataba, aided a group of prospectors discover gold in Eldorado Canyon north east of Ft. Mohave, site of first mining rush to the immediate area.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Casebier|first1=Dennis|title=Camp El Dorado, Arizona Territory|date=1970|publisher=Arizona Historical Foundation|location=Tempe, Arizona|page=19}}</ref> This was followed by the discovery of the San Francisco district (now Oatman district), where Irataba led John Moss to the rich Moss lode.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Webb|first1=George|title=The Mines in Northwestern Arizona in 1864, a Report by Benjamin Silliman, Jr.|journal=Arizona and the West|date=1974|volume=16|issue=3|page=249 fn 4}}</ref> Earlier, concern for protecting incoming miners brought together tribal leaders to Ft. Yuma in April 1863, including Irataba, where they pledged to allow prospectors into their country. On his return home, the Mohave joined a prospecting party led by mountain man ] who had prospected among them on the river in 1860.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Spude|first1=Robert|title=Who were the First Hassayampers|journal=Territorial Times|date=2009|volume=II|issue=2|page=3}}</ref> In 1863, Irataba acted as a guide for the ], gold prospectors led by Walker and including ], who later founded ]. Irataba brought them to a river that he called ''Hasyamp'', later named the ], where they found plentiful gold. Central Arizona's first mining district was established there the following year, which led to the founding of ] soon afterward.{{sfn|Hanchett|1998|p=9}} Relations between settlers and the Mohave were positive during this period, but as emigration increased, gold seekers founded towns, largest on the river being named ], stirring fear among settlers of a native uprising against further encroachment on Mohave land.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=60–61}} The following year a group of soldiers from Fort Mohave discovered an area between Needles, Fort Mohave, and the Colorado River that was abundant in copper ore. The parcel was named Irataba Mining District, and within the year a mining company had been formed to work it. A small mining town named Irataba City was established on a bluff two miles below Fort Mohave.{{sfn|Shumway|Vredenburgh|Hartill|1980|page=76}}{{sfn|Webb|Silliman|1974|p=270}} High copper market prices during the Civil War brought into operation the Bill Williams Fork copper mines as well, which shipped copper ore from the new Colorado River landing of Aubry. Though there would be down turns, mining in the Mohave lands was now well established. | |||
| ==Travels== | |||
| In Woodward's opinion, European Americans living near the Colorado River viewed Irataba as the most important Native leader in the region.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=60}} With a large army of Mohave warriors in his command, he quickly earned a reputation for just leadership.{{sfn|NYT|February 1864|p=}} In 1862, he acted as a guide for the Walker Party Exploration, led by ] and including ], who would later found ]. They came in search of gold and were brought to a river that Irataba called ''Hasyamp'', later officially named ], where they found plentiful amounts of the precious metal. Arizona's first mining district was established there the following year, which led to the founding of ] soon afterward.{{sfn|Hanchett|1998|p=9}} Relations between the Mohave and European Americans were positive during this period; however, as white emigration increased, gold seekers founded a town nearby named ], stirring tensions among the Mohave and building fear of an uprising against further encroachment on their land.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=60–1}} John Moss, an experienced guide and prospector, suggested they bring Irataba to Washington so that he could see firsthand the United States' military might.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=63–4}} | |||
| ==Trip to Washington D.C.== | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| As related above, during the early 1860s, Irataba befriended prospectors as a guide. One of them was John Moss, whom Irataba had shown the location of a gold mine in the Mojave desert, which Moss later sold.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Webb|first1=George|title="The Mines in Northwestern Arizona 1864, the Report by Benjamin Silliman, Jr.|journal=Arizona and the West|date=1974|volume=16|issue=3|pages=248–250}}</ref>{{sfn|The Daily Democrat|1891}} Moss suggested Irataba be invited to Washington so that he could see firsthand the United States' military might.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=63}}{{efn|Prior to his trip to Washington in 1863, Irataba had visited Los Angeles, first in 1860, and again in 1861.{{sfn|Scrivner|1970|p=134}}}} In November 1863, Irataba traveled with Moss to ], where they boarded the steamship ''Senator'', bound for San Francisco. In San Francisco, he stayed at the ] and created a storm as he walked down ], dressed in clothing typical of European Americans, which Irataba soon preferred to traditional Mohave clothing.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=61–62}} The press documented his every movement and wrote extensively about his physical size and strong features.{{sfn|Mifflin|2009|p=178}} On December 2, 1863, the ''Daily Evening Bulletin'' described Irataba as a large man, "granitic in appearance as one of the Lower Coast mountains, with ... a lower jaw massive enough to crush nuts or crush quartz."{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=61–62}} | |||
| ] | |||
| In January 1864 they sailed for the ] on board the ''Orizaba'', then traveled onwards to ].{{sfn|O'Brien|2006|p=249}} Upon Irataba's arrival in New York, '']'' described him as "the finest specimen of unadulterated aboriginal on this continent".{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=53}} Here Irataba exchanged his suit and sombrero for the uniform and regalia of a ], including a bright yellow sash, a gold badge encrusted with precious stones, and a medal with the inscription, "Irataba, Chief of the Mohaves, Arizona Territory".{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=62–63}} In February, when '']'' asked him to explain the nature of his visit, he replied: "to see where so many pale faces come from".{{sfn|''The New York Times''|1864}} In New York he met with the former Mohave resident ], and the two conversed in Mohave. Irataba told Oatman that her Mohave adoptive sister Topeka, to whom she had grown very close, still missed her and hoped she would return.{{sfn|Mifflin|2009|p=180}} Oatman described the encounter as a meeting between friends.{{sfn|Mifflin|2009|p=180}} | |||
| Irataba moved on to Philadelphia and Washington, D.C., where he earned great acclaim; government officials and military officers lavished him with gifts of medals, swords, and photographs.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=62}} In Washington he met with President ], who gave him a silver-headed cane.{{sfn|Ricky|1999|pp=101–102}} He was the first Native American from the Southwest to meet an American president.{{sfn|Carlson|1886|p=492}} The tour ended in April, when he and Moss sailed to California, again by way of Panama, and made their way back to Beale's Crossing from Los Angeles by wagon.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=62–63}} | |||
| In November 1863, Irataba traveled with Moss to ], where they boarded a steamship named the ''Senator'', bound for San Francisco. The Mohave Chief had been dressed in what Woodward's described as, "the full civilized costume" typical of European Americans, which Irataba soon preferred to traditional Mohave clothing.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=61–2}} | |||
| Upon Irataba's return from Washington D.C., he met with the Mohave while dressed in his major general's uniform, with medals. He wore a European-style hat and carried a long Japanese sword, and he told the Mohave about all the things he had seen.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=63–64}} He tried to convince them that peace with the United States was in their best interests, and that war against them was futile, stressing their dominant military capabilities.{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=102}} Many Mohave were skeptical of his reports, and reacted with disbelief.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=66}} | |||
| In January 1864, they sailed for ], by way of the ], on the ''Orizaba''.<ref>{{harvnb|O'Brien|2006|p=249}}: sailed by way of the Isthmus of Panama; {{harvnb|Woodward|1953|p=62}}: Moss and Irataba sailed on the ''Orizaba''.</ref> Here Irataba traded his suit and sombrero for the uniform and regalia of a ], including a bright yellow sash and gold badge encrusted with precious stones. From it hung a medal that bore the inscription, "Irataba, Chief of the Mohaves, Arizona Territory".{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=62–3}} In February, when '']'' asked him to explain the nature of his visit, he replied: "to see where so many pale faces come from".{{sfn|NYT|February 1864}} That same month, '']'' described him as "the finest specimen of unadulterated aboriginal on this continent".{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=53}} When journalist John Penn Curry asked him what he thought of Americans, he replied: "Mericanos too much talk, too much eat, too much drink; no work, no raise pumpkins, corn, watermelons – all time walk, talk, drink – no good."{{sfn|Curry|1865|page=360}} Irataba toured New York, Philadelphia, and Washington, D.C., and earned great acclaim at each stop; government officials and military officers lavished him with gifts of medals, swords, and photographs.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=62}} While in Washington, he met with President ], who gave him a silver-headed cane "as a symbol of his chieftainship".{{sfn|Ricky|1999|pp=101–02}} He was the first Native American from the Southwestern United States to meet a US president.{{sfn|Harte|1886|p=492}} The tour ended in April, when he and Moss sailed to California, again by way of the Isthmus of Panama, and made their way back to Beale's Crossing, from Los Angeles, in a wagon.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=62–3}} | |||
| ==Colorado River Indian Reservation== | |||
| ==Disgrace and death== | |||
| {{main|Colorado River Indian Reservation}} | |||
| According to Woodward, having recently returned from Washington Irataba met with the Mohave dressed in his major general's uniform, which was covered in medals. He wore a European-style hat and carried a long Japanese sword, and he told the Mohave about all the things he had seen.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=63–4}} He tried to convince the them that peace with European Americans was in their best interests, and that war against them was futile, stressing their dominant military capabilities.{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=102}} Nevertheless, Woodward notes that the Mohave accused him of telling "tall tales", and Irataba was largely discredited.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=66}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The completion of Fort Mohave began the process of military subjugation of the Mohave, and the next step was the establishment of ]. In 1863, ], the first Superintendent of Indian Affairs of the ], called a conference between the Chemehuevi and Irataba's faction of the Mohave, in which he convinced them to form an alliance with the US against the Apache. The treaty was never ratified by the US Congress but formed an important step in establishing friendly relations between the Mohave and the US government following the military campaigns and the establishment of Fort Mohave.{{sfn|Knack|2004|p=97}} | |||
| Poston promoted the idea of establishing a reservation in the southern portion of Mohave country. Many Mohave opposed the proposed location and instead argued for a smaller parcel further north in the Mohave Valley, which had more fertile land.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=6–7}} With Irataba and an engineer, Poston traveled down the Colorado River to survey a location.{{sfn|Caylor|2000|p=196}} In August 1864 the post commander at Fort Mohave, Captain Charles Atchisson, stated that Irataba was against the proposed location. In September 1864, Poston gave the impression that Irataba was in favor of it.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=7–8}} In a letter to General Richard C. Drum, Atchisson reported that Irataba and four Mohave leaders were unhappy with how Poston was handling the situation: | |||
| {{quote box|quote= The old man is here now with his tribe, but he looks feeble, wan, and grief stricken. Age has come to Irataba, but it has brought to him no bright and peaceful twilight. Dark and cheerless appear the skies of his declining years.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=67}}|source= —''The Arizona Weekly Miner'', February 5, 1870|width=25%|align=left|style=padding:10px;}} | |||
| {{quote|Mr. Poston had marked out a reservation for the Mojave Indians in the upper part of the La Paz valley on the East side of the Colorado River ... Iratabu says this reservation is covered with sand and unfit for cultivation and the Indians are opposed to giving up their good lands in the Mojave Valley and moving to it ... Iratabu says if he can have the valley below the Fort Mojave reserved for the home of the Indians, he is willing to give up all claims to lands on other parts of the river, and bring his Indians from La Paz and other points to this valley ... I have full confidence in the friendship of Iratabu towards white men, but not in his tribe, if troubles with any other Indians should occur, while he has more influence over them than any other chief, his control over them is not complete, and they are as likely to lead him (as he is them).{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=7–8}}}} | |||
| According to Woodward, Irataba continued to lead the Mohave in their ongoing conflicts with neighboring tribes. In March 1865, he helped defeat the Chemehuevi in response to their allies, the Paiutes, having killed two Mohave women in retaliation for the Mohave's killing of a Paiute medicine man after he failed to heal nine Mohave people inflicted with small pox.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=64–5}} Irataba attacked the Chemehuevi first because they had disrespected the Mohave, and to avoid "a fire in the rear" when he turned their attention to the Paiutes, who were planning an attack on the Mohave farm and granary on Cottonwood Island.{{sfn|Daily Alta California|1865}} During a subsequent battle with the Paiutes, Irataba was taken prisoner while wearing his major general's uniform. They feared that killing him would invite repercussions from the soldiers stationed at Fort Mohave, so they instead stripped him naked and sent him home badly beaten.{{sfn|Daily Alta California|1865}}{{refn|group=nb|The Paiutes gave Irataba's major general's uniform to Irataba's Mohave rival, Seck-a-hoot.{{sfn|Daily Alta California|1865}}}} This defeat further eroded Irataba's influence over the Mohave people.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=66}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Faced with Irataba's disagreement, Poston promised that the US government would assist the Mohave with installing an irrigation system at the Colorado that would make most of the reservation arable.{{sfn|Caylor|2000}} This apparently convinced Irataba, who traveled to the Colorado River Valley with about 800 people, almost a fifth of the entire Mohave Nation.<ref>{{harvnb|Griffin-Pierce|2000|p=246}}: relocating to the Colorado River Valley; {{harvnb|Caylor|2000|p=196}}: a fifth of the entire Mohave Nation; {{harvnb|Sherer|1966|pp=6–8}}: 800 Mohave.</ref> General ] thought a reservation was unnecessary, and engineer ] disagreed with Poston's proposed location on the basis that the soil was too alkaline for farming, the need for irrigation too great, and the task of raising the river too insurmountable. Nonetheless, on March 3, 1865,{{sfn|Kappler|1904}} Congress established the ] at Poston's proposed location.<ref>{{harvnb|Caylor|2000|p=197}}: soil was too alkaline</ref> Ehrenberg's concerns proved valid, and neither Poston nor any subsequent US authority was willing to dedicate the considerable resources required to make the location suitable for farming.{{sfn|Caylor|2000}} The reservation was established without a treaty having been established between the Mohave and the US government.{{sfn|Swanton|1952|p=357}} The boundaries were expanded and clarified by ]s issued by ] in 1873, 1874 and 1867.{{sfn|Swanton|1952|p=357}}{{sfn|Kappler|1904}} | |||
| Most of the Mohave refused to leave their ancestral homelands for the reservation, but Irataba's conviction that the reservation was their best option marked the beginning of a rift between his group and those who stayed behind to follow Homoseh quahote, the nation's hereditary leader.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=4–5, 8–9}} According to an eyewitness account by Chooksa homar, Irataba explained his decision to move: | |||
| Sherer notes that by the late 1860s a strong rift had developed between Irataba, who was sympathetic to white settlement, and the militant Mohave sub-chief, Homoseh Quahote, also known as Seck-a-hoot, who vehemently opposed white encroachment on Mohave lands.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=9, 30}} At one time, Seck-a-hoot briefly imprisoned Irataba in an effort to supplant him as head chief.{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=102}} Ashamed and disgraced, Irataba scorned Native and European Americans alike, and retired in near isolation to a small hut where he lived out his final days. As time went on the people softened in their disdain for him. The Mohave never replaced Irataba; he was their last independent head chief, and when he died at the Colorado River Indian Reservation in May 1874, they burned his body, hut, and belongings according to tradition.<ref>{{harvnb|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=8}}: Irataba died at the Colorado River Indian Reservation; {{harvnb|Devereux|1951|p=34}}: Irataba was the last independent Mohave head chief; {{harvnb|Woodward|1953|p=67}}: Arizona press reported that Irataba died on May 3 or 4, 1874.</ref>{{refn|group=nb|Irataba's cause of death is unknown, but old age and ] are both cited as possible causes.{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=102}} The Mohave were so committed to Irataba's cremation ritual they burned their entire village.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=68}}}} | |||
| {{quote|"You get angry sometimes; I know you are brave men and think you can beat anybody. You thought you could beat the whites: you said so. I told you you could not; the whites have beaten all tribes; all are friends to them now. You did not listen to what I said when I told you that. You did what you thought, and many have got killed. If the soldiers come, you cannot resist them. You did not know that, but now you know it. The country down river from here, which we took away from another tribe , I will live there. Those of you who want to go on fighting can stay here. I do not want to and will leave you."{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=31}}}} | |||
| As the promised irrigation assistance was not immediately forthcoming, the first year at the reservation brought a drought that made it necessary for the Mohave to request food assistance. In 1867, Irataba and the Mohave began to build an irrigation canal, digging by hand a ditch that ran for {{convert|9|mile}}.{{sfn|Caylor|2000}}{{efn|The canal was completed a few months after Irataba's death in 1874.{{sfn|Caylor|2000}}}} A report by a US official visiting the reservation in 1870 recorded that attempts by the Mohave at agricultural cultivation on the site were restricted to an area of not more than {{convert|40|acres}}.{{sfn|Andrews|1870|p=647}} | |||
| ==Later years== | |||
| ] photograph collection){{sfn|Gentile|1870}}]] | |||
| Irataba continued to lead the Colorado River band of Mohave during the 1860s. He pursued peaceful relations with the surrounding tribes and cooperated actively with US authorities. He also helped the Yavapai and Walapai in ongoing conflicts with Paiutes and Chemehuevi.{{sfn|Kroeber|1965|pp=176–178}} | |||
| In March 1865, Irataba and the Mohave defeated the Chemehuevi after their allies, the Paiutes, killed two Mohave women.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|pp=64–65}} The Mohave pushed the Chemehuevi off their traditional territory and into the California desert, but they soon returned.{{sfn|Knack|2004|pp=97–98}} To avoid fighting a two-front war, Irataba attacked the Chemehuevi first, then turned his attention to the Paiutes, who were planning an attack on the Mohave farm and granary on the Colorado's Cottonwood Island.{{sfn|''Daily Alta California''|1865|p=1}} During a subsequent battle with the Chemehuevi in October 1865, Irataba was taken prisoner while wearing his major general's uniform.{{sfn|McNichols|1944|pp=120–121}} According to a contemporary news report based on second hand accounts from white travelers, the captors feared that killing him would invite repercussions from the soldiers stationed at Fort Mohave, so they instead stripped him naked and sent him home badly beaten.{{sfn|''Daily Alta California''|1865|p=1}} In the Mohave account of the events as told by Chooksa homar, Irataba surrendered in an effort to make peace with the Chemehuevi, and offered his uniform to their chief as a gesture of peace.{{sfn|Kroeber|Kroeber|1973|p=40}} In 1867, a treaty signed by Irataba and the Chemehuevi leader Pan Coyer restored peaceful relations between the two nations.{{sfn|Kroeber|1965|p=179}} | |||
| {{quote box|quote= The old man is here now with his tribe, but he looks feeble, wan, and grief stricken. Age has come to Irataba, but it has brought to him no bright and peaceful twilight. Dark and cheerless appear the skies of his declining years.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=67}}{{efn|An 1867 description indicates that Irataba's hair had remained dark, but due to an old injury he walked with a cane.{{sfn|Evans|1870|p=41}}}}|source= —''The ]'', February 5, 1870|width=25%|align=left|style=padding:10px;}} | |||
| Irataba also welcomed bands of Yavapai onto the reservation after they had been subject to massacres by US troops, or suffered starvation due to having been driven from their lands. The meager resources of the reservation proved unable to sustain the additional population and eventually the Yavapai had to leave. Irataba frequently served as a mediator between Yavapai and Walapai who had become embroiled in conflicts with the US army, and participated in peace parlays. In 1871–72, General ] came to the Mohave reservation looking for a group of Yavapai thought to be responsible for the ], and Irataba had no choice but to turn the war party over to the army.{{sfn|Kroeber|1965|p=179}} He traveled to the trial proceedings at ], where he was instructed to hand tobacco to the Yavapai he believed to be responsible, as a way for him to testify against them without their realizing it. As soldiers attempted to arrest the men that Irataba identified, fighting broke out and one of the Yavapai leaders, ], and his brother were shot.{{sfn|Farish|1918}} Despite having been shot twice and stabbed with a bayonet, Ohatchecama survived and escaped to organize the Tolkepaya Yavapai in resistance against the US army.{{sfn|Braatz|2003|pp=112, 135}} The Yavapai felt betrayed by Irataba, and plotted to kill him in revenge, but were eventually persuaded that he was not the one who had turned them over to Crook.{{sfn|Wilson|2007|p=130}}{{sfn|Braatz|2003|p=135}} | |||
| The Colorado River band of Mohave never replaced Irataba; he was their leader when he died at their reservation on May 3 or 4, 1874.{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=67}} His cause of death is unknown, but ] and natural causes are both cited.{{sfn|Ricky|1999|p=102}} The Mohave grieved deeply; Irataba's cremation and the rituals of mourning were reported in newspapers as far away as Omaha, Nebraska.{{sfn|''The Omaha Daily Bee''|1874|p=2}}{{efn|Several contemporary newspapers including ''The Omaha Daily Bee'' and ''The Prescott Miner'' claim that the Mohave were so committed to Irataba's cremation ritual that they burned their entire village, slaughtered the horses, and fasted for a prolonged period.{{sfn|''Arizona Weekly Miner''|1874|p=1}}{{sfn|''The Omaha Daily Bee''|1874|p=2}}{{sfn|Woodward|1953|p=68}}}} Irataba was succeeded as leader on the Colorado Reservation by his nephew, Qolho qorau of the ''Vemacka'' clan, who upheld his uncle's policies.{{sfn|Sherer|1966|p=13}} | |||
| ==Legacy and influence== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| In 1966, Sherer commented regarding Irataba's legacy amongst the Mohave: "Estimation of his position in Mojave history from the Mojave viewpoint differs. To some he is an heroic figure, to others he was a white collaborator who did not stand up for Mojave rights. From the standpoint of white men who were conquering a wilderness, he was indeed the Mojave who worked unswervingly for peace."{{sfn|Sherer|1966|pp=30–31}} | |||
| Irataba's influence as a leader may even have left its mark on the ]. A list of Mohave words that he dictated to an anthropologist during his visit in Washington shows that he was among the first Mohave speakers to shift the sounds and {{IPA|}} (similar to sh as in "shack") to {{IPA|}} (th as in "thick") and , respectively. By the late 19th century all Mohave speakers had adopted this change. Linguist Leanne Hinton has suggested that this may be due in part to Irataba's influence, both because he was a prestigious leader whose ways of speaking may have been emulated by other Mohave, and also because when he led the Mohave onto the reservation the old distinctions between dialect groups were erased through ], making new changes spread quickly through the community.{{sfn|Hinton|1979}} | |||
| The Irataba Society, a non-profit charity run by the ], was established in ], in 1970.{{sfn|Kulp|1974|p=3}} The charity holds an annual ] or National Indian Days celebration.{{sfn|Cook|1985|p=B-2}} Irataba Hall, a sports venue in Parker, is also named after him.{{sfn|''The Yuma Daily Sun''|1975|p=3}} In 2002, the US ] designated {{convert|32745|acre}} of the ], contained largely within the ], as Ireteba Peaks Wilderness.{{sfn|Bureau of Land Management}} | |||
| In March 2015, the Colorado River Indian Tribes celebrated the sesquicentennial history of their reservation with a weekend-long event that included cultural activities and a parade. Speakers at the event stressed the important role that Irataba's strong leadership played in establishing and preserving the reservation, and the continuing need for Native leaders to protect native language and culture. Tribal chairman Dennis Patch commented: "Some people would think we're lucky, as we have this river and 220,000 acre feet of water ... But we have had great leaders, like Chief Irataba. He made sure the Mohaves stayed on land they had lived on since time immemorial."{{sfn|Gutekunst|2015}} Former CRIT Museum Director Dr. Michael Tsosie stated, "Irataba understood the Mohave people would need to keep fighting to keep what they had." He noted that the Colorado River Indian Reservation "is unique in American history in that they have not lost any land".{{sfn|Gutekunst|2015}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist|30em}} | |||
| ==Notes== | ===Notes=== | ||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| {{reflist|group=nb}} | |||
| == |
===Citations=== | ||
| {{ |
{{reflist}} | ||
| * {{cite book|last=Baley|first=Charles W.|title=Disaster at the Colorado: Beale's Wagon Road and the First Emigrant Party|year=2002|publisher=Utah State University Press|isbn=978-0874214376|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Curry|first=John Penn|title=Gazlay's Pacific Monthly, Volume 1|work=The New York Public Library|publisher=D. M. Gazlay|year=1865|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=j_QRAAAAYAAJ&vq |ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite newspaper|title=Latest from Irataba's Land|work=Daily Alta California|volume=17|issue=5707|date=October 22, 1865|url=http://cdnc.ucr.edu/cgi-bin/cdnc?a=d&d=DAC18651022.2.3&srpos=&dliv=none&e=-------en--20--1--txt-txIN-------|publisher=California Digital Newspaper Collection (CDNC)|accessdate=January 8, 2015|ref={{sfnref|Daily Alta California|1865}}}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Devereux|first=George|authorlink=George Devereux|title=Mohave Chieftainship in Action: A Narrative of the First Contacts of the Mohave Indians with the United States|year=1951|work=Plateau|publisher=Northern Arizona Society of Science and Art; Museum of Northern Arizona|volume=23|issue=3|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Griffin-Pierce|first=Trudy|title=Native Peoples of the Southwest|year=2000|publisher=University of New Mexico Press|isbn=9780826319081|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=t2MszsCnZbQC&dq |ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Hanchett|first=Leland J.|title=Catch the Stage to Phoenix|year=1998|publisher=Pine Rim Publishing LLC|isbn=9780963778567|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|editor-last=Harte|year=1886|editor-first=Brett|title=Overland Monthly and Out West Magazine|publisher=A. Roman|work=''Making of America Project: Cornell University''|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|editor1-last=Johansen |editor1-first=Bruce E.|editor2-last=Pritzker|editor2-first=Barry M. |title=Encyclopedia of American Indian History|year=2007|edition=illustrated|publisher=ABC-CLIO|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last1=Kroeber|first1=A.L.|last2=Kroeber|first2=C.B.|title=A Mohave War Reminiscence, 1854-1880 |year=1973|publisher=Dover Publications|isbn=978-0486281636|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=2E-pQjaZNbYC&dq |ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Kroeber|first=Alfred Louis|authorlink=Alfred L. Kroeber|title=Handbook of the Indians of California|year=1925|publisher=Courier Corporation|isbn=9780486233680|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YDdn0WNMQMYC&printsec=frontcover&dq|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Moratto|first=Michael J.|title=California Archaeology|year=2014|publisher=Academic Press|isbn=9781483277356|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite news|title=Arrival of the Indian Warrior, Irataba|work=]|date=February 7, 1864|url=http://www.nytimes.com/1864/02/07/news/arrival-of-the-indian-warrior-irataba.html|accessdate=January 8, 2015|ref={{sfnref|NYT|February 1864}}}} | |||
| * {{cite news|title= Return of Irataba: What he Thinks of New-York |work=]|date=May 4, 1864|url= http://www.nytimes.com/1864/06/04/news/california-gossip-return-irataba-what-he-thinks-new-york-his-style-prepared.html?pagewanted=1 |accessdate=January 8, 2015|ref={{sfnref|NYT|May 1864}}}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=O'Brien|first=Anne Hughes|title=Traveling Indian Arizona|year=2006|publisher=Big Earth Publishing|isbn=9781565795181|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Ricky|first=Donald B.|title=Indians of Arizona: Past and Present|publisher=North American Book Distributors|year=1999|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QP6Gyee4TgIC&source=gbs_navlinks_s|isbn=9780403098637|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Sherer|first=Lorraine M.|title=Great Chieftains of the Mojave Indians|work=Southern California Quarterly|volume=48|issue=1|date=March 1966|publisher=University of California Press|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Stewart|first=Kenneth M.|year=1971|chapter=Mohave Warfare|title=The California Indians: A Source Book|editor1-last=Heizer|editor1-first=Robert Fleming|editor2-last=Whipple|editor2-first=Mary Anne|publisher=University of California Press|isbn=9780520020313|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Thrapp|first=Dan L.|title=Encyclopedia of Frontier Biography: A-F|year=1991|publisher=University of Nebraska Press|isbn= 9780803294189|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite work|author=United States Army|title=Report upon the Colorado River of the West: explored in 1857 and 1858 by Joseph C. Ives|publisher=University of Michigan Library|year=1861|url=http://name.umdl.umich.edu/ADU2374.0001.001|accessdate=February 16, 2015|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Utley|first=Robert Marshall|title=Frontiersmen in Blue: The United States Army and the Indian, 1848-1865|year=1981|publisher=University of Nebraska Press|isbn=9780803295506|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite work|last=Whipple|first=Amiel|title=Reports of Explorations and Surveys to Ascertain the Most Practicable and Economical Route for a Railroad from the Mississippi River to the Pacific Ocean|year=1856|publisher=Beverley Tucker|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IUH15BsafDYC&dq|ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Wilson|first=James|title=The Earth Shall Weep: A History of Native America|year=2000|publisher=Grove Press|isbn=978-0802136800|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=wLiz-YM2xhgC&dq |ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Woodward|first=Arthur|title=Irataba: Chief of the Mohave|volume=25|issue=3|date=January 1953|work=Plateau|publisher=Northern Arizona Society of Science and Art; Museum of Northern Arizona |ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Zappia|first=Natale A.|title=Traders and Raiders: The Indigenous World of the Colorado Basin, 1540-1859|year=2014|publisher=University of North Carolina Press|isbn=9781469615851|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jENhBAAAQBAJ&dq|ref=harv}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == |
===Bibliography=== | ||
| {{refbegin}} | {{refbegin}} | ||
| *{{cite news |url=http://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn82014898/1874-06-05/ed-1/seq-1/ |title=Irataba |newspaper=] |date=June 5, 1874 |page=1 |via=] |volume=XI |issue=23 |ref={{harvid|''Arizona Weekly Miner''|1874}}}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Brown|first=Dee|authorlink=Dee Brown (writer)|title=Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee: An Indian History of the American West|year=2007|origyear=1970|publisher=Holt McDougal|isbn= 978-0805086843|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=XIg9L1HZuJ0C&dq }} | |||
| * |
*{{cite book |last=Andrews |first=George L. |chapter=Accompanying Papers, No. 38 |pages=646–648 |editor=United States Department of the Interior |title=Executive Documents Printed by Order of the House of Representatives During the Second Session of the Forty-First Congress, 1869–'70 |volume=3 |publisher=Government Printing Office |year=1870 |oclc=30751534 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=knRBAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA647}} | ||
| * |
*{{cite book |last=Baley |first=Charles W. |title=Disaster at the Colorado: Beale's Wagon Road and the First Emigrant Party |page=115 |date=2002 |publisher=] |location=] |isbn=978-0-87421-437-6 |url=https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/usupress_pubs/105/ |quote=Free Download Full Text}} | ||
| * |
*{{cite book |last=Braatz |first=Timothy |year=2003 |title=Surviving Conquest |publisher=University of Nebraska Press |isbn=978-0-8032-2242-7}} | ||
| *{{cite web |url=http://www.blm.gov/nv/st/en/fo/lvfo/blm_programs/blm_special_areas/blm_special_areas/ireteba_peaks_wilderness.html |title=Ireteba Peaks Wilderness |author=] |publisher=United States Government |access-date=March 24, 2015 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150410161420/http://www.blm.gov/nv/st/en/fo/lvfo/blm_programs/blm_special_areas/blm_special_areas/ireteba_peaks_wilderness.html |archive-date=April 10, 2015}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Carlson |first=Edward |title=The Martial Experiences of the California Volunteers |pages=480–496 |journal=The Overland Monthly |volume=7 |series=Second series |issue=41 |year=1886 |url=https://archive.org/stream/overlandmonthly2737742sanfrich#page/492/mode/1up}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |title=A Promise Long Deferred: Federal Reclamation on the Colorado River Indian Reservation |last=Caylor |first=Ann |journal=Pacific Historical Review |volume=69 |issue=2 |year=2000 |pages=193–215 |doi=10.2307/3641438 |jstor=3641438}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Conrad |first=David E. |title=The Whipple Expedition in Arizona 1853–1854 |date=1969 |journal=Arizona and the West |volume=11 |issue=2 |pages=147–178}} | |||
| *{{cite news |url=https://www.newspapers.com/image/64825579/?terms=Irataba |title=Celebration planned by Indian tribes for re-opening of museum |last=Cook |first=Fred |newspaper=The San Bernardino County Sun |page=B-2 |date=September 25, 1985 |via=]}}{{subscription required}} | |||
| *{{cite news |title=Latest from Irataba's Land |newspaper=Daily Alta California |volume=17 |issue=5707 |page=1 |date=October 22, 1865 |url=http://cdnc.ucr.edu/cgi-bin/cdnc?a=d&d=DAC18651022.2.3&e=-------en--20--1--txt-txIN-------# |ref={{harvid|Daily Alta California|1865}}}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Devereux |first=George |author-link=George Devereux |title=Mohave Chieftainship in Action: A Narrative of the First Contacts of the Mohave Indians with the United States |pages=33–43 |year=1951 |journal=Plateau |volume=23 |issue=3}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Elsasser |first=Albert B. |title=Mohave Indian Images and the Artist Maynard Dixon |journal=The Journal of California Anthropology |volume=4 |issue=1 |year=1977 |pages=60–79 |url=https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7pb3t575}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Evans |first=Albert S. |title=A Cloud-Burst on the Desert |journal=The Overland Monthly |volume=3 |issue=2 |year=1869 |pages=138–143 |url=https://archive.org/stream/overlandmonthly3136sanfrich#page/142/mode/1up}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Evans |first=Albert S. |date=July 1870 |title=Lo-land Adventure |journal=The Galaxy |volume=10 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xxxBAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA41}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |first=George H. |last=Fathauer |year=1954 |title=The Structure and Causation of Mohave Warfare |journal=Southwestern Journal of Anthropology |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=97–118 |doi=10.1086/soutjanth.10.1.3629078 |s2cid=155976554}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Farish |first=T. E. |year=1918 |title=History of Arizona (Vol. VIII) |chapter=XVI |publisher=Filmer brothers electrotype Company |chapter-url=http://southwest.library.arizona.edu/hav8/body.1_div.16.html}} | |||
| *{{cite web |last1=Gentile |first1=Carlo |title=Ah-oochy Kah-mah & his friend Irateba Two Tonto Apache girls, civilized & christians, good girls; Coyotero Apache woman, sold by her lord & master for 40 yards Manta at Camp Grant; Joséa, Pimo Fat Boy, front view. |url=http://loc.gov/pictures/resource/ds.03970/ |website=Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Division |access-date=19 May 2015 |year=1870}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Griffin-Pierce |first=Trudy |title=Native Peoples of the Southwest |year=2000 |publisher=University of New Mexico Press |isbn=978-0-8263-1908-1 |author-link=Trudy Griffin-Pierce |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=t2MszsCnZbQC}} | |||
| *{{cite web |last=Gutekunst |first=John |title=CRIT celebrates 150th anniversary of reservation |date=March 3, 2015 |website=Parker Pioneer |url=http://www.parkerpioneer.net/news/article_f877204e-c223-11e4-a0cd-b712b391fdd9.html |access-date=March 30, 2015}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Hanchett |first=Leland J. |title=Catch the Stage to Phoenix |year=1998 |publisher=Pine Rim Publishing |isbn=978-0-9637785-6-7}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Hinton |first=Leanne |year=1979 |title=Irataba's gift: a closer look at the ṣ > s > θ sound shift in Mohave and Northern Pai |journal=Journal of California and Great Basin Anthropology Papers in Linguistics |volume=1 |issue=1 |pages=3–39}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Hinton |first=Leanne |title=Spirit Mountain: An Anthology of Yuman Story and Song |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=45FkAAAAMAAJ |year=1984 |publisher=Sun Tracks and University of Arizona Press |isbn=978-0-8165-0843-3}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Hunter |first=L. G. |year=1979 |title=The Mojave Expedition of 1858–59 |journal=Arizona and the West |volume=21 |issue=2 |pages=137–156}} | |||
| *{{cite news |title=Indian Marriages |newspaper=The Daily Democrat |date=June 3, 1891 |page=2 |url=https://www.newspapers.com/clip/13125908/indian_marriages/ |ref={{harvid|The Daily Democrat|1891}} |via=]}} {{Open access}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Ives |first=Joseph C. |chapter=Part I: General Report |editor=United States Army Corps of Topographical Engineers |title=Report upon the Colorado River of the West : Explored in 1857 and 1858 by Joseph C. Ives |publisher=Government Printing Office |year=1861 |id=36th Congress, 1st Session Senate executive document, unnumbered |oclc=3095199 |chapter-url=https://archive.org/stream/reportuponcolor00bairgoog#page/n90/mode/2up}} | |||
| *{{cite book |editor1-last=Johansen |editor1-first=Bruce E. |editor2-last=Pritzker |editor2-first=Barry M. |title=Encyclopedia of American Indian History |year=2007 |edition=illustrated |publisher=ABC-CLIO |isbn=978-1-85109-818-7}} | |||
| *{{cite book |title=Boundaries Between: The Southern Paiutes, 1775–1995 |first=Martha C. |last=Knack |publisher=University of Nebraska Press |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-8032-7818-9}} | |||
| *{{cite web |url=http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/vol1/html_files/ARI0801.html |title=PART III.—Executive Orders Relating to Indian Reserves |last=Kappler |first=Charles J. |location=Washington |publisher=Government Printing Office |year=1904 |access-date=August 6, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111209232734/http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol1/HTML_files/ARI0801.html |archive-date=December 9, 2011 |url-status=dead}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Kroeber |first=Alfred Louis |author-link=Alfred L. Kroeber |title=Handbook of the Indians of California |year=1925 |publisher=Courier |isbn=978-0-486-23368-0 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YDdn0WNMQMYC}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Kroeber |first1=Alfred Louis |last2=Kroeber |first2=Clifton B. |title=A Mohave War Reminiscence, 1854–1880 |year=1973 |publisher=Dover Publications |isbn=978-0-486-28163-6 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2E-pQjaZNbYC}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Kroeber |first=Clifton B. |date=June 15, 1965 |title=The Mohave as Nationalist, 1859–1874 |volume=109 |issue=3 |journal=Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society |pages=173–180}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Kroeber |first1=C. B. |last2=Fontana |first2=B. L. |year=1986 |title=Massacre on the Gila. An account of the last major battle between American Indians, with reflections on the origin of war |publisher=University of Arizona Press |isbn=978-0-8165-0969-0 |url=https://archive.org/details/massacreongilaac0000kroe}} | |||
| *{{cite news |url=https://www.newspapers.com/image/47174731/?terms=Irataba |title=Parker's Irataba receives $5000 plus bonus of meeting Franco Harris |last=Kulp |first=Neil |newspaper=The Yuma Daily Sun |page=3 |date=April 3, 1974 |via=]}}{{subscription required}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=McGinty |first=B. |year=2005 |title=The Oatman Massacre: A Tale of Desert Captivity and Survival |publisher=University of Oklahoma Press |isbn=978-0-8061-8024-3}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=McNichols |first=Charles Longstreth |title=Crazy Weather |url=https://archive.org/details/crazyweathe00mcni |url-access=registration |year=1944 |publisher=Macmillan |oclc=1267884}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Mifflin |first=Margot |title=The Blue Tattoo: The Life of Olive Oatman |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=c_w0DxpwKbgC&pg=PA178 |year=2009 |publisher=University of Nebraska Press |isbn=978-0-8032-1148-3}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Miller |first=David H. |title=The Ives Expedition Revisited: Overland into Grand Canyon |journal=The Journal of Arizona History |volume=13 |issue=3 |year=1972 |pages=177–196}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Moratto |first=Michael J. |title=California Archaeology |year=2014 |publisher=Academic Press |isbn=978-1-4832-7735-6}} | |||
| *{{cite news |title=Arrival of the Indian Warrior, Irataba |work=] |date=February 7, 1864 |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1864/02/07/news/arrival-of-the-indian-warrior-irataba.html |access-date=January 8, 2015 |ref={{harvid|''The New York Times''|1864}}}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=O'Brien |first=Anne Hughes |title=Traveling Indian Arizona |year=2006 |publisher=Big Earth Publishing |isbn=978-1-56579-518-1}} | |||
| *{{cite news |title=Aboriginalities |newspaper=The Omaha Daily Bee |volume=4 |issue=12 |date=July 2, 1874 |page=2 |via=] |url=http://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn99021999/1874-07-02/ed-1/seq-2.pdf |ref={{harvid|''The Omaha Daily Bee''|1874}}}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Putzi |first=Jennifer |title=Capturing Identity in Ink: The Captivities of Olive Oatman |pages=176–199 |volume=39 |issue=2 |year=2004 |journal=Western American Literature |doi=10.1353/wal.2004.0002 |s2cid=165937685}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Ricky |first=Donald B. |title=Indians of Arizona: Past and Present |publisher=Native American Books Distributor |year=1999 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QP6Gyee4TgIC |isbn=978-0-403-09863-7}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Scrivner |first=Fulsom Charles |title=Mohave People |year=1970 |publisher=The Naylor Company |isbn=978-0-8111-0335-0}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Sherer |first=Lorraine M. |title=The Clan System of the Fort Mojave Indians |publisher=Historical Society of Southern California |year=1965 |oclc=3512671}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Sherer |first=Lorraine M. |title=Great Chieftains of the Mojave Indians |journal=Southern California Quarterly |pages=1–35 |volume=48 |issue=1 |date=March 1966 |doi=10.2307/41169985 |jstor=41169985}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Sherer |first=Lorraine M. |editor1-last=Vane |editor1-first=Sylvia Brakke |editor2-last=Bean |editor2-first=Lowell John |title=Bitterness Road: The Mojave: 1604 to 1860 |year=1994 |publisher=Ballena Press |isbn=978-0-87919-128-3}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Shumway |first1=G. L. |last2=Vredenburgh |first2=L. M. |last3=Hartill |first3=R. D. |year=1980 |title=Desert Fever: An Overview of Mining in the California Desert Conservation Area |publisher=] |url=http://www.blm.gov/style/medialib/blm/ca/pdf/cdd/aml.Par.54155.File.dat/Desert%20Fever%20-%20History%20of%20Mining%20in%20the%20CDCA.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150526192114/http://www.blm.gov/style/medialib/blm/ca/pdf/cdd/aml.Par.54155.File.dat/Desert%20Fever%20-%20History%20of%20Mining%20in%20the%20CDCA.pdf |archive-date=May 26, 2015 |df=mdy-all}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Stewart |first=Kenneth M. |year=1971 |chapter=Mohave Warfare |pages= |title=The California Indians: A Source Book |url=https://archive.org/details/californiaindian00heiz |url-access=registration |editor1-last=Heizer |editor1-first=Robert Fleming |editor2-last=Whipple |editor2-first=Mary Anne |publisher=University of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-02031-3}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |title=A Brief History of the Mohave Indians since 1850 |first=Kenneth M. |last=Stewart |journal=Kiva |volume=34 |issue=4 |year=1969 |pages=219–236 |doi=10.1080/00231940.1969.11760552}} | |||
| *{{cite book |title=The Indian Tribes of North America |first=John Reed |last=Swanton |publisher=Genealogical Publishing Company |year=1952 |isbn=978-0-8063-1730-4}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Thrapp |first=Dan L. |title=Encyclopedia of Frontier Biography: A-F |year=1991 |publisher=University of Nebraska Press |isbn=978-0-8032-9418-9}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Utley |first=Robert Marshall |title=Frontiersmen in Blue: The United States Army and the Indian, 1848–1865 |year=1981 |publisher=University of Nebraska Press |isbn=978-0-8032-9550-6 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780026212403}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Webb |first1=G. E. |last2=Silliman |first2=B. |year=1974 |title=The Mines in Northwestern Arizona in 1864: A Report by Benjamin Silliman, Jr. |journal=Arizona and the West |volume=16 |issue=3 |pages=247–270}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Whipple |first1=Amiel Weeks |last2=Ives |first2=Joseph C. |chapter=Part I: Itinerary |editor=United States Department of War |title=Reports of Explorations and Surveys to Ascertain the Most Practicable and Economical Route for a Railroad from the Mississippi River to the Pacific Ocean |volume=3 |publisher=A.O.P. Nicholson |year=1856 |id=33rd Congress, 2nd Session House executive document number 91 |chapter-url=https://archive.org/stream/reportsofexplora03unit_0#page/n187/mode/1up}} | |||
| *{{cite book |title=Massacre at Wickenburg: Arizona's Greatest Mystery |first=R. Michael |last=Wilson |publisher=Globe Pequot |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-7627-4453-4}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last=Woodward |first=Arthur |title=Irataba: Chief of the Mohave |pages=53–68 |volume=25 |issue=3 |date=January 1953 |journal=Plateau}} | |||
| *{{cite news |url=https://www.newspapers.com/image/47139760/?terms=Irataba |title=Parker Troth |page=3 |newspaper=The Yuma Daily Sun |date=January 21, 1975 |via=] |ref={{harvid|The Yuma Daily Sun|1975}}}}{{subscription required}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Zappia |first=Natale A. |title=Traders and Raiders: The Indigenous World of the Colorado Basin, 1540–1859 |year=2014 |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |isbn=978-1-4696-1585-1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jENhBAAAQBAJ}} | |||
| {{refend}} | {{refend}} | ||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Curry|first=John Penn|year=1865|title=An Indian Chief's Opinion of Americans |journal=Gazlay's Pacific Monthly |page=360|volume=1 |issue=1 |url=https://archive.org/stream/gazlayspacificmo01gazl#page/360/mode/1up}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Kroeber |first=Alfred Louis|author-link=Alfred L. Kroeber|title=Preliminary Sketch of the Mohave Indians|journal=American Anthropologist |series=New Series|volume=4|issue=2|pages=276–285|date=1902|jstor=659222|doi=10.1525/aa.1902.4.2.02a00060|doi-access=}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Wilson|first=James|title=The Earth Shall Weep: A History of Native America|year=2000|publisher=Grove Press|isbn=978-0-8021-3680-0|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=wLiz-YM2xhgC }} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{commons category|Irataba}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * , InterTribal Council of Arizona | * | ||
| * | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Irataba}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:34, 15 November 2024
Leader of the Mohave Nation (c. 1814 – 1874)
| Irataba | |
|---|---|
| Yara tav | |
 | |
| Mohave leader | |
| Personal details | |
| Born | c. 1814 Arizona |
| Died | May 3 or 4, 1874 (aged 59–60) Colorado River Indian Reservation, Arizona Territory, United States |
| Mother tongue | Mohave |
Irataba (Mohave: eecheeyara tav , also known as Yara tav, Yarate:va, Arateve; c. 1814 – 1874) was a leader of the Mohave Nation, known as a mediator between the Mohave and the United States. He was born near the Colorado River in present-day Arizona. Irataba was a renowned orator and one of the first Mohave to speak English, a skill he used to develop relations with the United States.
Irataba first encountered European Americans in 1851, when he assisted the Sitgreaves Expedition. In 1854, he met Amiel Whipple, then leading an expedition crossing the Colorado. Several Mohave aided the group, and Irataba agreed to escort them through the territory of the Paiute to the Old Spanish Trail, which would take them to southern California. Noted for his large physical size and gentle demeanor, he later helped and protected other expeditions, earning him a reputation among whites as the most important native leader in the region.
Against Irataba's advice, in 1858 Mohave warriors attacked the first emigrant wagon train to use Beale's Wagon Road through Mohave country. As a result, the U.S. War Department sent a detachment under Colonel William Hoffman to pacify the tribe. Following a series of confrontations known as the Mohave War, Hoffman succeeded in dominating the natives, and demanded that they allow the passage of settlers through their territory. To ensure compliance, Fort Mohave was constructed near the site of the battle in April 1859. Hoffman also imprisoned several Mohave leaders. Having been an advocate for friendly relations with the whites, Irataba became the nation's Aha macave yaltanack, an elected, as opposed to hereditary, leader.
As a result of his many interactions with U.S. officials and settlers, Irataba was invited to Washington, D.C., in 1864, for an official meeting with members of the U.S. military and its government, including President Abraham Lincoln. In doing so, he became the first Native American from the Southwest to meet an American president. He received considerable attention during his tours of the U.S. capital, and of New York City and Philadelphia, where he was given gifts, including a silver-headed cane from Lincoln. Upon his return he negotiated the creation of the Colorado River Indian Reservation, which caused a split in the Mohave Nation when he led several hundred of his supporters to the Colorado River valley. The majority of the Mohave preferred to remain in their ancestral homelands near Fort Mohave and under the leadership of their hereditary leader, Homoseh quahote, who was less enthusiastic about direct collaboration with whites. As leader of the Colorado River band of Mohave, Irataba encouraged peaceful relations with whites, served as a mediator between the warring tribes in the area, and during his later years continued to lead the Mohave in their ongoing conflicts with the Paiute and Chemehuevi.
As noted by ethnographer Lorraine Sherer, "to some he is an heroic figure, to others he was a white collaborator who did not stand up for Mojave rights." The Irataba Society, a non-profit charity run by the Colorado River Indian Tribes, was established in 1970 in Parker, Arizona, where a sports venue, Irataba Hall, is also named after him. In 2002, the US Bureau of Land Management designated 32,745 acres (132.51 km) in the Eldorado Mountains as Ireteba Peaks Wilderness. In March 2015, Mohave Tribal chairman Dennis Patch credited Irataba with ensuring that "the Mohaves stayed on land they had lived on since time immemorial."
Background

Irataba's name, also rendered as Ireteba, Yara tav, Arateve, Yarate:va, and Yiratewa, derives from the Mohave language phrase eecheeyara tav, which means "beautiful bird". He was born into the Neolge, or Sun Fire clan of the Mohave Nation c. 1814. He lived near a rock formation that gave its name to Needles, south of where the Grand Canyon empties into the Mohave Canyon in present-day Arizona, near the Nevada and California border. The Mohave lived in houses along the riverbank in the Mohave Valley, during winter in half-buried dwellings built with cottonwood logs and arrowweed covered in earth, and in the summer in open-air flat-roofed houses called ramadas.
In the mid-19th century, the Mohave were composed of three geographical groups; Irataba was the hereditary leader of the Huttoh Pah group, who lived near the east bank of the Colorado River and occupied the central portion of the Mohave Valley. Mohave government consisted of a loose system of hereditary clan leaders with a head of the entire nation. They were often involved in conflicts with the Chemehuevi, Paiute, and Maricopa peoples. Irataba was a member of the Mohave warrior society called kwanami, who led groups of warriors in battle and were dedicated to defending their lands and people.
Little is known of Irataba's family relations, except for the name of his son Tekse thume, and his nephews Qolho qorau (Irataba's sister's son who succeeded him as leader) and Aspamekelyeho. Olive Oatman, who lived with the Mohave for five years, later stated that Irataba was the brother of the former chief, presumably Cairook, with whom Irataba clearly had a close relationship. One anecdotal description states that Irataba had several wives, among them a Hualapai woman who had been taken as a captive and who is also described as having a young son. He also had at least one daughter, the mother of his granddaughter Tcatc who was interviewed in the 1950s. She stated that Irataba had wanted to leave his land deeds and medals to his brother's sons, but that they were eventually lost.
In contemporary accounts Irataba was described as an eloquent speaker, and linguist Leanne Hinton suggests that he was among the first Mohave people to become fluent in English, which he learned through his many interactions with Anglo-Americans. Like many Mohave men, Irataba was very tall, particularly by 19th-century standards; the United States Army estimated his height at 6 feet 4 inches (193 cm) in 1861. American author Albert S. Evans, writing in The Overland Monthly, referred to him as "the old desert giant". Edward Carlson, a soldier based at Fort Mohave who knew Irataba well in the 1860s, described him as having a powerful frame, but also a "very gentle" and "kind ... demeanor".
Irataba lived through a tumultuous period of Mohave history where the people went from being a politically independent nation to coming under the political control of the United States, and the events surrounding his role in these encounters are well documented. Most historical sources for the life of Irataba come from descriptions by white explorers or government agents with whom he interacted, or from contemporary newspapers that reported on his visits to the East Coast and California, and on the conflicts in Arizona territory. Some Mohave versions of the events also exist: in the early 20th century anthropologist A. L. Kroeber interviewed Jo Nelson (Mohave: Chooksa homar), a Mohave man who participated in many of the events and knew Irataba personally; another version was told to ethnographer George Devereux by Irataba's granddaughter Tcatc, and versions recounted by members of the Fort Mohave band of Mohave, the descendants of Homoseh quahote, were recorded by ethnographer Lorraine Sherer during the 1950s and 1960s.
Contact with emigrants and explorers
 Amiel Weeks Whipple
Amiel Weeks Whipple A drawing from the Whipple Expedition (1856) by H. Balduin Möllhausen
A drawing from the Whipple Expedition (1856) by H. Balduin Möllhausen
Irataba assisted Captain Lorenzo Sitgreaves during his 1851 exploration of the Colorado. On March 19, 1851, a family of Brewsterite settlers, the Oatmans, who were traveling by wagon train in what is now Arizona, were attacked by a band of Western Yavapai, probably the Tolkepaya. They captured two survivors of the attack: the 14-year-old Olive Oatman and her 7-year-old sister, Mary Ann. After a year with the Yavapai, the girls were sold to the Mohave, and adopted into the Oach clan where they lived with the family of a Mohave man called Tokwatha (Musk Melon) a friend of Irataba. Olive remained with the Mohave until February 22, 1856, when Tokwatha, having been warned that having a white girl among them might be seen as an offense by whites, brought her to Fort Yuma carpenter Henry Grinnell, releasing her in return for two horses and some blankets and beads. Irataba may have learned about Anglo-Americans and their society from Oatman, and knowing her may have contributed to his generally favourable disposition towards Whites.
Whipple Expedition
On February 23, 1854, Irataba, Cairook, and other Mohave people encountered an expedition led by military officers Amiel Whipple and J.C. Ives, as the group approached the Colorado en route to California. Whipple and his men counted six hundred Mohave gathered near their camp, trading corn, beans, squash (plant), and wheat for beads and calico. By the end of their commerce, the party had purchased six bushels of corn and two hundred pounds of flour. The Mohave played a traditional game played with a hoop and pole, and the two groups entertained themselves with target practice, the Mohave using bows and arrows and the whites firing pistols and rifles. When the expedition had difficulty crossing the Colorado on February 27, several Mohave jumped into the water and helped salvage the supplies.
Irataba and Cairook agreed to escort the group across the territory of the Paiute to the Old Spanish Trail that would take them to southern California. German artist Balduin Möllhausen accompanied the Whipple expedition, and made drawings of several Mohave, including Irataba. Möllhausen's drawings were featured in Ives' 1861 congressional report, making Irataba "among the first named likenesses of California Indians ever published".
Ives Expedition
In February 1858, Ives returned to the area in a paddle steamer named Explorer. He was leading an expedition up the Colorado from the south, and he wanted Irataba to guide them. The Mohave gave permission to navigate the river, and Cairook, Irataba, and a 16-year-old Mohave boy named Nahvahroopa joined them. Möllhausen again accompanied the expedition, and was impressed with the Mohave guides, later noting Irataba's enthusiastic handshake and lamenting that their only form of communication was sign language. He also noted that Irataba and the Mohave readily began wearing European clothes given to them by members of the expedition, and showed great interest in smoking tobacco. Aside from the friendship shown to him by Irataba and Cairook, Ives noted that the Mohave appeared less friendly than on earlier occasions, a change that he attributed to their contact with Mormons, who were in conflict with the US and had succeeded in converting some Mohave.
Irataba guided the party into the Mohave Canyon, indicating the location of rapids and advising the Explorer's pilot of convenient places to anchor while camping for the night. When they reached the entrance to the Black Canyon of the Colorado, the ship crashed against a submerged rock, throwing several men overboard, dislodging the boiler, and damaging the wheelhouse. Using their skiff, the crew towed the Explorer to the shore, where they camped for three days while repairing the vessel. The expedition had relied on beans and corn provided by the Mohave during the previous weeks; as their supplies dwindled they grew increasingly anxious about the arrival of a resupply pack train from Fort Yuma. Irataba volunteered to hike towards the Mohave Valley to try to locate the supplies that had been requested several days earlier. He also warned that the expedition was being watched by Paiutes.
When Irataba returned he informed Ives that he would not venture any deeper into the territory of the Hualapais, but agreed to help them locate friendly guides in the region before parting company. Irataba was reluctant to venture into the canyon because he feared the party would be ambushed by Paiutes aligned with Mormons. After enlisting three Hualapai guides, Irataba prepared to take his leave from the expedition and return to the Mohave community. On April 4, the Mohave received payment for their services; Möllhausen described the exchange: "Lieutenant Ives informed Irataba that he had been authorized by the 'Great Grandfather in Washington' to give him two mules ... for his loyalty and his trustworthiness so that he could take his possessions and those of his companions more conveniently to his home valley." The next morning, as they were preparing to leave: "Irataba was visibly moved ... and in his sincere eyes expressed so much honesty and loyalty as can only be found in an unspoiled nature ... I maintain that there was not one in our expedition who did not feel a certain sadness to see this huge man with ... a harmless soul leave."
Mohave War and aftermath
Main article: Mohave WarFollowing their experiences with the Sitgreaves and Whipple expeditions, and encounters with Mormons and the soldiers at Fort Yuma, the Mohave were aware that whites were immigrating to the region in increasing numbers. It was difficult for the Mohave to predict the behavior of the arriving whites, some of whom, like Whipple, were amiably disposed towards them, whereas others such as the Mormons were hostile. The kwanami were divided on how the situation should be approached; some advocated an aggressive posture, denying whites all passage through their territory, but others, including Irataba, preferred a peaceful approach, or even an alliance with them that could put the Mohave in a stronger position relative to their traditional enemies the Paiute, Chemehuevi, and Walapai.
On September 1, 1857, a joint force of Mohave and Quechan warriors launched a major attack with hundreds of warriors on a Maricopa village close to Maricopa Wells, Arizona, on the Gila river. The Battle of Pima Butte was described by a group of white mail carriers who witnessed it. They stated that the battle was fought mostly with clubs, as well as bows and arrows, and that probably more than 100 warriors died, most of them from the attacking party. It is unknown whether Irataba participated in the attack, but given his status as kwanami, it is likely that he did. The battle has been described as the last major battle involving only Native American nations. This defeat put the Mohave on the defensive, wary of the possibility that whites would take this moment of weakness as an opportunity to begin settling on tribal lands.
Rose–Baley Party attack
In October 1857, an expedition led by Edward Fitzgerald Beale was tasked with establishing a trade route along the 35th parallel from Fort Smith, Arkansas, to Los Angeles, California. From Fort Smith, his journey continued through Fort Defiance, Arizona, before crossing the Colorado near Needles, California. This route became known as Beale's Wagon Road, and the location where Beale crossed the river as Beale's Crossing. Beale's journal and subsequent report to the United States Secretary of War did not mention any problems with Irataba and the Mohave, but an assistant named Humphrey Stacy recorded that the Mohave had prevented Beale from traveling downriver.
In 1858, the Rose–Baley Party comprising at least a hundred settlers with wagons and a large herd of cattle, was the first emigrant train to venture onto Beale's Wagon Road. Upon entering Mohave territory the settlers started cutting down cottonwood trees, which were an important resource for the Mohave. The most warlike of the kwanamis organized an attack on the party, and drove away and slaughtered many of the party's cattle. On August 30, three hundred Mohave warriors attacked the emigrants but were repelled, with one member of the party killed in battle and eleven wounded. Another family who were not with the main party during the attack were killed in an event that has often been blamed on the Mohave, but which in Colonel William Hoffman's opinion was more likely carried out by a band of Walapai, along with seven renegade Mohave. The emigrants killed seventeen Mohave warriors. The incident was widely publicized in the media and labeled "a massacre", scaring many white Californians who feared being cut off from the eastern US by hostile natives, and it motivated the War Department to quickly subjugate the tribe.
Irataba was away at Fort Yuma during the attack on the settlers, and upon hearing of it he scolded the Mohave. Chooksa homar participated in the events and reported that Irataba told the warriors, "I hear you fought, though I told you not to. And you will have war again: I know it. You used to fight the Maricopa. I want to go to see the Maricopa and tell them: 'The Mohave will not come any more to attack you'." Irataba, weary of the constant fighting and worried that further conflicts with neighboring tribes would draw more attention from the US soldiers, organized a peace expedition to the Maricopa, settling the ancient disputes between the two peoples.
Conflict with the US army

When news of the attack reached California, the US War Department decided to establish a military fort at Beale's Crossing to keep the Mohave under control and secure white travelers safe passage through Mohave lands. On December 26, 1858, Hoffman and fifty dragoons from Fort Tejon were dispatched to cross the desert and confront the Mohave. Irataba attempted to arrange a peaceful meeting, but Hoffman ordered his troops to fire on the warriors, who counterattacked and repelled the force. He returned in April 1859, by way of Fort Yuma, with four companies of the 6th Infantry Regiment. When they arrived at Beale's Crossing, the Mohave decided against attacking the army of five hundred soldiers. On April 23, at Hoffman's request, he and his officers met with several hundred Mohave warriors and their leaders. The indigenous leaders included Cairook, Irataba, Homoseh quahote (also called Seck-a-hoot and Asika hota), and Pascual, leader of the Quechan. During the meeting the Mohave were surrounded by armed soldiers who prevented them from leaving.
Hoffman gave the Mohave a choice between war and peace, and he demanded that they agree to never again harm white settlers along the wagon trail. He also declared that, as punishment, the Mohave were required to surrender as hostages a member of each clan and three warriors who had taken part in the attack. Hoffman demanded that the chief who had ordered the attack on the settlers offer himself up as a hostage. According to Chooksa homar, the chief who had ordered the attack was Homoseh quahote, who was reluctant to give himself up. Cairook offered himself in his place, along with eight others, including Tokwatha, Irataba's son Tekse thume, and Irataba's nephews Qolho qorau, and Aspamekelyeho. Other hostages were named Itsere-'itse, Ilyhanapau, and Tinyam-isalye. They were transported in the river steamer General Jessup to Fort Yuma. Many soldiers remained to begin construction on the Beale's Crossing fort, which was named Fort Mohave. Although Irataba visited the garrison several times and argued for their release, the hostages were held for more than a year. On June 21, 1859, Cairook and one other captive were killed by soldiers while attempting to escape their incarceration. Most of the other Mohave captives escaped.
In July 1861, the commander of Fort Mohave, Major Lewis Armistead, ordered soldiers to fire into a group of Mohave who he suspected of having attacked a mail carrier and slaughtered his mule. The Mohave did not respond violently to the attack, but Armistead decided to punish them for harassing the mail party. He arrived at Irataba's ranch where a group of Mohave boys were planting beans, and from a hidden position he shot one of the planters, killing him. This attack prompted an assault on Armistead's detachment, who from an advantageous position on the high ground were able to repel the Mohave, killing many of them in a battle that lasted most of the day. Armistead's report of the assault of Irataba's ranch reported 23 dead Mohave warriors, but the Mohave remember a much higher number of casualties, including women and children killed by the soldiers. Sherer speculated that, given that 50 soldiers fired around 10 shots each, the casualty count could have been much higher than reported. The attack on Irataba's ranch is remembered by the Mohave as "the first and last battle with the Federal Troops."
As Aha macave yaltanack

After Cairook's death, whites living near the Colorado River began to view Irataba as the main leader of the Mohave. He had become Aha macave yaltanack (leader of the Mohave Nation) or hochoch (leader elected by the people); "yaltanack" is Mohave for "leader", and "hochach" means "head of a group". Homoseh quahote was a hereditary leader of the Malika clan ("the understanding people"), and the position of head of the Mohave was traditionally inherited only by someone from that clan. Because Irataba was of the Huttoh pah, in order for him to become the leader of the Mohave Nation, Homoseh quahote had to step down so Irataba, as an elected leader, could take his place.
Despite the accepted English translations, the words yaltanack and huchach do not mean a "ruler" or "boss". Devereux describes Mohave government as "one of the least understood segments of Mohave culture", and notes that while white officials "tended to act on the assumption that Indian chiefs exercised absolute authority", as an elected leader Irataba was "primarily a servant of the tribe".
By the mid-1860s a deep rift had developed between Irataba, who was proactive in cooperating with white settlers, and Homoseh quahote, who passively tolerated but did not approve of white encroachment on Mohave lands. Irataba was Aha macave yaltanack of the Mohave from 1861 to 1866, but from 1867 to 1869 opinions differ, and by 1870 US government correspondence suggests that Homoseh quahote had succeeded him as leader of the Fort Mohave group.
Mining ventures
Probably first to bring national attention to the potential gold in the region was F. X. Aubry, who in 1853 reported finding gold at a crossing of the Colorado and that he traded for legendary gold bullets further east with Tonto Apache. Newspapers across the country copied the gold strike story. Over the next decade mining discoveries up and down the lower Colorado River valley brought miners into newly formed mining districts. In the spring of 1861, Mohave, possibly including Irataba, aided a group of prospectors discover gold in Eldorado Canyon north east of Ft. Mohave, site of first mining rush to the immediate area. This was followed by the discovery of the San Francisco district (now Oatman district), where Irataba led John Moss to the rich Moss lode. Earlier, concern for protecting incoming miners brought together tribal leaders to Ft. Yuma in April 1863, including Irataba, where they pledged to allow prospectors into their country. On his return home, the Mohave joined a prospecting party led by mountain man Joseph R. Walker who had prospected among them on the river in 1860. In 1863, Irataba acted as a guide for the Walker Party, gold prospectors led by Walker and including Jack Swilling, who later founded Phoenix, Arizona. Irataba brought them to a river that he called Hasyamp, later named the Hassayampa River, where they found plentiful gold. Central Arizona's first mining district was established there the following year, which led to the founding of Prescott, Arizona soon afterward. Relations between settlers and the Mohave were positive during this period, but as emigration increased, gold seekers founded towns, largest on the river being named La Paz, stirring fear among settlers of a native uprising against further encroachment on Mohave land. The following year a group of soldiers from Fort Mohave discovered an area between Needles, Fort Mohave, and the Colorado River that was abundant in copper ore. The parcel was named Irataba Mining District, and within the year a mining company had been formed to work it. A small mining town named Irataba City was established on a bluff two miles below Fort Mohave. High copper market prices during the Civil War brought into operation the Bill Williams Fork copper mines as well, which shipped copper ore from the new Colorado River landing of Aubry. Though there would be down turns, mining in the Mohave lands was now well established.
Travels

As related above, during the early 1860s, Irataba befriended prospectors as a guide. One of them was John Moss, whom Irataba had shown the location of a gold mine in the Mojave desert, which Moss later sold. Moss suggested Irataba be invited to Washington so that he could see firsthand the United States' military might. In November 1863, Irataba traveled with Moss to San Pedro, Los Angeles, where they boarded the steamship Senator, bound for San Francisco. In San Francisco, he stayed at the Occidental Hotel and created a storm as he walked down Jackson Street, dressed in clothing typical of European Americans, which Irataba soon preferred to traditional Mohave clothing. The press documented his every movement and wrote extensively about his physical size and strong features. On December 2, 1863, the Daily Evening Bulletin described Irataba as a large man, "granitic in appearance as one of the Lower Coast mountains, with ... a lower jaw massive enough to crush nuts or crush quartz."

In January 1864 they sailed for the Isthmus of Panama on board the Orizaba, then traveled onwards to New York City. Upon Irataba's arrival in New York, Harper's Weekly described him as "the finest specimen of unadulterated aboriginal on this continent". Here Irataba exchanged his suit and sombrero for the uniform and regalia of a major general, including a bright yellow sash, a gold badge encrusted with precious stones, and a medal with the inscription, "Irataba, Chief of the Mohaves, Arizona Territory". In February, when The New York Times asked him to explain the nature of his visit, he replied: "to see where so many pale faces come from". In New York he met with the former Mohave resident Olive Oatman, and the two conversed in Mohave. Irataba told Oatman that her Mohave adoptive sister Topeka, to whom she had grown very close, still missed her and hoped she would return. Oatman described the encounter as a meeting between friends.
Irataba moved on to Philadelphia and Washington, D.C., where he earned great acclaim; government officials and military officers lavished him with gifts of medals, swords, and photographs. In Washington he met with President Abraham Lincoln, who gave him a silver-headed cane. He was the first Native American from the Southwest to meet an American president. The tour ended in April, when he and Moss sailed to California, again by way of Panama, and made their way back to Beale's Crossing from Los Angeles by wagon.
Upon Irataba's return from Washington D.C., he met with the Mohave while dressed in his major general's uniform, with medals. He wore a European-style hat and carried a long Japanese sword, and he told the Mohave about all the things he had seen. He tried to convince them that peace with the United States was in their best interests, and that war against them was futile, stressing their dominant military capabilities. Many Mohave were skeptical of his reports, and reacted with disbelief.
Colorado River Indian Reservation
Main article: Colorado River Indian Reservation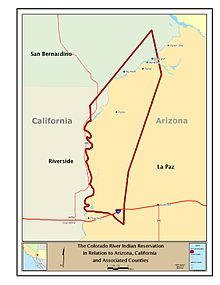
The completion of Fort Mohave began the process of military subjugation of the Mohave, and the next step was the establishment of reservations. In 1863, Charles Debrille Poston, the first Superintendent of Indian Affairs of the Arizona Territory, called a conference between the Chemehuevi and Irataba's faction of the Mohave, in which he convinced them to form an alliance with the US against the Apache. The treaty was never ratified by the US Congress but formed an important step in establishing friendly relations between the Mohave and the US government following the military campaigns and the establishment of Fort Mohave.
Poston promoted the idea of establishing a reservation in the southern portion of Mohave country. Many Mohave opposed the proposed location and instead argued for a smaller parcel further north in the Mohave Valley, which had more fertile land. With Irataba and an engineer, Poston traveled down the Colorado River to survey a location. In August 1864 the post commander at Fort Mohave, Captain Charles Atchisson, stated that Irataba was against the proposed location. In September 1864, Poston gave the impression that Irataba was in favor of it. In a letter to General Richard C. Drum, Atchisson reported that Irataba and four Mohave leaders were unhappy with how Poston was handling the situation:
Mr. Poston had marked out a reservation for the Mojave Indians in the upper part of the La Paz valley on the East side of the Colorado River ... Iratabu says this reservation is covered with sand and unfit for cultivation and the Indians are opposed to giving up their good lands in the Mojave Valley and moving to it ... Iratabu says if he can have the valley below the Fort Mojave reserved for the home of the Indians, he is willing to give up all claims to lands on other parts of the river, and bring his Indians from La Paz and other points to this valley ... I have full confidence in the friendship of Iratabu towards white men, but not in his tribe, if troubles with any other Indians should occur, while he has more influence over them than any other chief, his control over them is not complete, and they are as likely to lead him (as he is them).

Faced with Irataba's disagreement, Poston promised that the US government would assist the Mohave with installing an irrigation system at the Colorado that would make most of the reservation arable. This apparently convinced Irataba, who traveled to the Colorado River Valley with about 800 people, almost a fifth of the entire Mohave Nation. General James Henry Carleton thought a reservation was unnecessary, and engineer Herman Ehrenberg disagreed with Poston's proposed location on the basis that the soil was too alkaline for farming, the need for irrigation too great, and the task of raising the river too insurmountable. Nonetheless, on March 3, 1865, Congress established the Colorado River Indian Reservation at Poston's proposed location. Ehrenberg's concerns proved valid, and neither Poston nor any subsequent US authority was willing to dedicate the considerable resources required to make the location suitable for farming. The reservation was established without a treaty having been established between the Mohave and the US government. The boundaries were expanded and clarified by executive orders issued by President Grant in 1873, 1874 and 1867.
Most of the Mohave refused to leave their ancestral homelands for the reservation, but Irataba's conviction that the reservation was their best option marked the beginning of a rift between his group and those who stayed behind to follow Homoseh quahote, the nation's hereditary leader. According to an eyewitness account by Chooksa homar, Irataba explained his decision to move:
"You get angry sometimes; I know you are brave men and think you can beat anybody. You thought you could beat the whites: you said so. I told you you could not; the whites have beaten all tribes; all are friends to them now. You did not listen to what I said when I told you that. You did what you thought, and many have got killed. If the soldiers come, you cannot resist them. You did not know that, but now you know it. The country down river from here, which we took away from another tribe , I will live there. Those of you who want to go on fighting can stay here. I do not want to and will leave you."
As the promised irrigation assistance was not immediately forthcoming, the first year at the reservation brought a drought that made it necessary for the Mohave to request food assistance. In 1867, Irataba and the Mohave began to build an irrigation canal, digging by hand a ditch that ran for 9 miles (14 km). A report by a US official visiting the reservation in 1870 recorded that attempts by the Mohave at agricultural cultivation on the site were restricted to an area of not more than 40 acres (16 ha).
Later years

Irataba continued to lead the Colorado River band of Mohave during the 1860s. He pursued peaceful relations with the surrounding tribes and cooperated actively with US authorities. He also helped the Yavapai and Walapai in ongoing conflicts with Paiutes and Chemehuevi.
In March 1865, Irataba and the Mohave defeated the Chemehuevi after their allies, the Paiutes, killed two Mohave women. The Mohave pushed the Chemehuevi off their traditional territory and into the California desert, but they soon returned. To avoid fighting a two-front war, Irataba attacked the Chemehuevi first, then turned his attention to the Paiutes, who were planning an attack on the Mohave farm and granary on the Colorado's Cottonwood Island. During a subsequent battle with the Chemehuevi in October 1865, Irataba was taken prisoner while wearing his major general's uniform. According to a contemporary news report based on second hand accounts from white travelers, the captors feared that killing him would invite repercussions from the soldiers stationed at Fort Mohave, so they instead stripped him naked and sent him home badly beaten. In the Mohave account of the events as told by Chooksa homar, Irataba surrendered in an effort to make peace with the Chemehuevi, and offered his uniform to their chief as a gesture of peace. In 1867, a treaty signed by Irataba and the Chemehuevi leader Pan Coyer restored peaceful relations between the two nations.
—The Arizona Weekly Miner, February 5, 1870The old man is here now with his tribe, but he looks feeble, wan, and grief stricken. Age has come to Irataba, but it has brought to him no bright and peaceful twilight. Dark and cheerless appear the skies of his declining years.
Irataba also welcomed bands of Yavapai onto the reservation after they had been subject to massacres by US troops, or suffered starvation due to having been driven from their lands. The meager resources of the reservation proved unable to sustain the additional population and eventually the Yavapai had to leave. Irataba frequently served as a mediator between Yavapai and Walapai who had become embroiled in conflicts with the US army, and participated in peace parlays. In 1871–72, General George Crook came to the Mohave reservation looking for a group of Yavapai thought to be responsible for the Wickenburg Massacre, and Irataba had no choice but to turn the war party over to the army. He traveled to the trial proceedings at Fort Date Creek, where he was instructed to hand tobacco to the Yavapai he believed to be responsible, as a way for him to testify against them without their realizing it. As soldiers attempted to arrest the men that Irataba identified, fighting broke out and one of the Yavapai leaders, Ohatchecama, and his brother were shot. Despite having been shot twice and stabbed with a bayonet, Ohatchecama survived and escaped to organize the Tolkepaya Yavapai in resistance against the US army. The Yavapai felt betrayed by Irataba, and plotted to kill him in revenge, but were eventually persuaded that he was not the one who had turned them over to Crook.
The Colorado River band of Mohave never replaced Irataba; he was their leader when he died at their reservation on May 3 or 4, 1874. His cause of death is unknown, but smallpox and natural causes are both cited. The Mohave grieved deeply; Irataba's cremation and the rituals of mourning were reported in newspapers as far away as Omaha, Nebraska. Irataba was succeeded as leader on the Colorado Reservation by his nephew, Qolho qorau of the Vemacka clan, who upheld his uncle's policies.
Legacy and influence

In 1966, Sherer commented regarding Irataba's legacy amongst the Mohave: "Estimation of his position in Mojave history from the Mojave viewpoint differs. To some he is an heroic figure, to others he was a white collaborator who did not stand up for Mojave rights. From the standpoint of white men who were conquering a wilderness, he was indeed the Mojave who worked unswervingly for peace."
Irataba's influence as a leader may even have left its mark on the Mohave language. A list of Mohave words that he dictated to an anthropologist during his visit in Washington shows that he was among the first Mohave speakers to shift the sounds and (similar to sh as in "shack") to (th as in "thick") and , respectively. By the late 19th century all Mohave speakers had adopted this change. Linguist Leanne Hinton has suggested that this may be due in part to Irataba's influence, both because he was a prestigious leader whose ways of speaking may have been emulated by other Mohave, and also because when he led the Mohave onto the reservation the old distinctions between dialect groups were erased through dialect leveling, making new changes spread quickly through the community.
The Irataba Society, a non-profit charity run by the Colorado River Indian Tribes, was established in Parker, Arizona, in 1970. The charity holds an annual pow wow or National Indian Days celebration. Irataba Hall, a sports venue in Parker, is also named after him. In 2002, the US Bureau of Land Management designated 32,745 acres (13,251 ha) of the Eldorado Mountains, contained largely within the Lake Mead National Recreation Area, as Ireteba Peaks Wilderness.
In March 2015, the Colorado River Indian Tribes celebrated the sesquicentennial history of their reservation with a weekend-long event that included cultural activities and a parade. Speakers at the event stressed the important role that Irataba's strong leadership played in establishing and preserving the reservation, and the continuing need for Native leaders to protect native language and culture. Tribal chairman Dennis Patch commented: "Some people would think we're lucky, as we have this river and 220,000 acre feet of water ... But we have had great leaders, like Chief Irataba. He made sure the Mohaves stayed on land they had lived on since time immemorial." Former CRIT Museum Director Dr. Michael Tsosie stated, "Irataba understood the Mohave people would need to keep fighting to keep what they had." He noted that the Colorado River Indian Reservation "is unique in American history in that they have not lost any land".
References
Notes
- Both the spelling "Mohave" and "Mojave" are correct variants of the English word corresponding to the Mohave word pipa aha macave "People who live by the side of the water". According to some sources (e.g. "The Colorado River Indian Tribes (C.R.I.T.) Reservation and Extension Programs" (PDF). 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 16, 2015.) the spelling "Mohave" is preferred by the Colorado River tribe of Mohave which Irataba founded.
- Woodward and Ricky state that this encounter was several years earlier in 1849, but this appears to be a result of confusion over the date of the expedition along the Colorado River led by Whipple and Ives. Whipple himself gives the date of the encounter as February 23, 1854, and there is no question that the Whipple Expedition was in 1853 to 1854, not 1849.
- Tensions between Mormons and American emigrants reached their peak during 1857–58, with several hostile encounters collectively known as the Mormon War.
- Hunter estimates there were two hundred settlers and four hundred head of cattle, while Baley puts the number at about 100 settlers and 500 head of cattle, as reported by party member John Udell.
- Prior to his trip to Washington in 1863, Irataba had visited Los Angeles, first in 1860, and again in 1861.
- The canal was completed a few months after Irataba's death in 1874.
- An 1867 description indicates that Irataba's hair had remained dark, but due to an old injury he walked with a cane.
- Several contemporary newspapers including The Omaha Daily Bee and The Prescott Miner claim that the Mohave were so committed to Irataba's cremation ritual that they burned their entire village, slaughtered the horses, and fasted for a prolonged period.
Citations
- ^ Sherer 1966, pp. 30–31.
- ^ Gutekunst 2015.
- Digital Collections, The New York Public Library. "(still image), (1857)". The New York Public Library, Astor, Lennox, and Tilden Foundation. Retrieved March 21, 2015.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, p. x: Yarate:va, Sherer 1966, p. 6: origin and variations of Irataba's name.
- ^ Ricky 1999, p. 100.
- Kroeber 1925, pp. 725–727.
- Moratto 2014, p. 347.
- Sherer 1966, pp. 6, 29–30.
- Sherer 1966, pp. 29–30.
- Stewart 1971, pp. 431–434.
- ^ Kroeber 1965, pp. 177–178.
- Johansen & Pritzker 2007, p. 1019: the kwanami were a Mohave warrior society; Sherer 1966, p. 30: Irataba was a kwanami, which means brave or fearless; Fathauer 1954: the role of kwanami in Mohave warfare.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, p. 25.
- McGinty 2005, p. 176.
- ^ The Daily Democrat 1891.
- ^ Devereux 1951.
- Hinton 1984, p. 281.
- Ives 1861, p. 69.
- Evans 1869, p. 143.
- ^ Mifflin 2009, p. 178.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973.
- Sherer 1966.
- Braatz 2003, pp. 253–254.
- Mifflin 2009, pp. 104–107: Olive was released to Henry Grinnell; Putzi 2004, p. 177: Olive and Mary Ann taken captive.
- Whipple & Ives 1856, p. 112.
- Woodward 1953, p. 54.
- Conrad 1969, p. 147.
- Whipple & Ives 1856, pp. 112–128.
- Whipple & Ives 1856, pp. 113–114.
- ^ Whipple & Ives 1856, p. 114.
- Whipple & Ives 1856, p. 116.
- Whipple & Ives 1856, pp. 119–128.
- Elsasser 1977, p. 62.
- Mifflin 2009, p. 174.
- Ives 1861, pp. 69–71, 76.
- Miller 1972, pp. 178–179, 182.
- Mifflin 2009, p. 175.
- ^ Stewart 1969, p. 230.
- Baley 2002, pp. 4, 14, 28, 131–132.
- Ives 1861, pp. 77, 85, 92.
- Ives 1861, pp. 81–84.
- Ives 1861, pp. 79–83.
- Ives 1861, pp. 94–97.
- Zappia 2014, pp. 121, 138.
- Ives 1861, pp. 94–97, 102.
- ^ Miller 1972, p. 188.
- Kroeber & Fontana 1986.
- ^ Kroeber 1965, p. 175.
- Thrapp 1991, p. 76.
- ^ Hunter 1979, p. 139.
- Utley 1981, p. 164.
- Sherer 1994, p. 69.
- Hunter 1979, p. 138.
- Hunter 1979; Baley 2002, p. 15.
- Kroeber 1965, pp. 174–175.
- Sherer 1994, pp. 82–86, 95.
- Baley 2002, pp. 2–3, 5, 15, 24, 28–40, 61–62, 67–72: emigrant train and attack; Zappia 2014, p. 129: seventeen Mohave warriors.
- Sherer 1994, p. 82.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, pp. 53–54.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, p. 14.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, pp. 54–54.
- ^ Woodward 1953, p. 58.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, p. 63: Irataba attempted to arrange a peaceful meeting; Woodward 1953, p. 58: the Mohave attacked and repelled the force.
- Sherer 1966, p. 3: Homoseh quahote attended the meeting; Woodward 1953, p. 59: Irataba and Cairook.
- ^ Hunter 1979, p. 150.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, pp. 25, 66.
- Woodward 1953, p. 59.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, p. 24: soldiers remained to build a fort; Sherer 1965, p. 73: the fort was initially called Fort Colorado.
- Mifflin 2009, p. 177.
- ^ Woodward 1953, pp. 59–60.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, p. 27.
- Sherer 1994, pp. 103–105.
- Woodward 1953, p. 60.
- Scrivner 1970, p. 134: becoming leader; Sherer 1966, pp. 2, 5–6: attaining Aha macave yaltanack.
- Sherer 1966, pp. 3–4.
- Sherer 1966, p. 2.
- Devereux 1951, pp. 35–36.
- Sherer 1966, pp. 9, 30.
- Sherer 1966, pp. 1–14.
- "Santa Fe Weekly Gazette". September 17, 1853.
- Paher, Stanley (1979). Colorado River Ghost Towns. Las Vegas, Nevada: Nevada Publications.
- Casebier, Dennis (1970). Camp El Dorado, Arizona Territory. Tempe, Arizona: Arizona Historical Foundation. p. 19.
- Webb, George (1974). "The Mines in Northwestern Arizona in 1864, a Report by Benjamin Silliman, Jr". Arizona and the West. 16 (3): 249 fn 4.
- Spude, Robert (2009). "Who were the First Hassayampers". Territorial Times. II (2): 3.
- Hanchett 1998, p. 9.
- Woodward 1953, pp. 60–61.
- Shumway, Vredenburgh & Hartill 1980, p. 76.
- Webb & Silliman 1974, p. 270.
- Webb, George (1974). ""The Mines in Northwestern Arizona 1864, the Report by Benjamin Silliman, Jr". Arizona and the West. 16 (3): 248–250.
- Woodward 1953, p. 63.
- Scrivner 1970, p. 134.
- ^ Woodward 1953, pp. 61–62.
- O'Brien 2006, p. 249.
- Woodward 1953, p. 53.
- ^ Woodward 1953, pp. 62–63.
- The New York Times 1864.
- ^ Mifflin 2009, p. 180.
- Woodward 1953, p. 62.
- Ricky 1999, pp. 101–102.
- Carlson 1886, p. 492.
- Woodward 1953, pp. 63–64.
- ^ Ricky 1999, p. 102.
- Woodward 1953, p. 66.
- Knack 2004, p. 97.
- Sherer 1966, pp. 6–7.
- Caylor 2000, p. 196.
- ^ Sherer 1966, pp. 7–8.
- ^ Caylor 2000.
- Griffin-Pierce 2000, p. 246: relocating to the Colorado River Valley; Caylor 2000, p. 196: a fifth of the entire Mohave Nation; Sherer 1966, pp. 6–8: 800 Mohave.
- ^ Kappler 1904.
- Caylor 2000, p. 197: soil was too alkaline
- ^ Swanton 1952, p. 357.
- Sherer 1966, pp. 4–5, 8–9.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, p. 31.
- Andrews 1870, p. 647.
- Gentile 1870.
- Kroeber 1965, pp. 176–178.
- Woodward 1953, pp. 64–65.
- Knack 2004, pp. 97–98.
- ^ Daily Alta California 1865, p. 1.
- McNichols 1944, pp. 120–121.
- Kroeber & Kroeber 1973, p. 40.
- ^ Kroeber 1965, p. 179.
- ^ Woodward 1953, p. 67.
- Evans 1870, p. 41.
- Farish 1918.
- Braatz 2003, pp. 112, 135.
- Wilson 2007, p. 130.
- Braatz 2003, p. 135.
- ^ The Omaha Daily Bee 1874, p. 2.
- Arizona Weekly Miner 1874, p. 1.
- Woodward 1953, p. 68.
- Sherer 1966, p. 13.
- Hinton 1979.
- Kulp 1974, p. 3.
- Cook 1985, p. B-2.
- The Yuma Daily Sun 1975, p. 3.
- Bureau of Land Management.
Bibliography
- "Irataba". Arizona Weekly Miner. Vol. XI, no. 23. June 5, 1874. p. 1 – via Chronicling America.
- Andrews, George L. (1870). "Accompanying Papers, No. 38". In United States Department of the Interior (ed.). Executive Documents Printed by Order of the House of Representatives During the Second Session of the Forty-First Congress, 1869–'70. Vol. 3. Government Printing Office. pp. 646–648. OCLC 30751534.
- Baley, Charles W. (2002). Disaster at the Colorado: Beale's Wagon Road and the First Emigrant Party. Logan, UT: Utah State University Press. p. 115. ISBN 978-0-87421-437-6.
Free Download Full Text
- Braatz, Timothy (2003). Surviving Conquest. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-2242-7.
- Bureau of Land Management. "Ireteba Peaks Wilderness". United States Government. Archived from the original on April 10, 2015. Retrieved March 24, 2015.
- Carlson, Edward (1886). "The Martial Experiences of the California Volunteers". The Overland Monthly. Second series. 7 (41): 480–496.
- Caylor, Ann (2000). "A Promise Long Deferred: Federal Reclamation on the Colorado River Indian Reservation". Pacific Historical Review. 69 (2): 193–215. doi:10.2307/3641438. JSTOR 3641438.
- Conrad, David E. (1969). "The Whipple Expedition in Arizona 1853–1854". Arizona and the West. 11 (2): 147–178.
- Cook, Fred (September 25, 1985). "Celebration planned by Indian tribes for re-opening of museum". The San Bernardino County Sun. p. B-2 – via Newspapers.com.(subscription required)
- "Latest from Irataba's Land". Daily Alta California. Vol. 17, no. 5707. October 22, 1865. p. 1.
- Devereux, George (1951). "Mohave Chieftainship in Action: A Narrative of the First Contacts of the Mohave Indians with the United States". Plateau. 23 (3): 33–43.
- Elsasser, Albert B. (1977). "Mohave Indian Images and the Artist Maynard Dixon". The Journal of California Anthropology. 4 (1): 60–79.
- Evans, Albert S. (1869). "A Cloud-Burst on the Desert". The Overland Monthly. 3 (2): 138–143.
- Evans, Albert S. (July 1870). "Lo-land Adventure". The Galaxy. 10.
- Fathauer, George H. (1954). "The Structure and Causation of Mohave Warfare". Southwestern Journal of Anthropology. 10 (1): 97–118. doi:10.1086/soutjanth.10.1.3629078. S2CID 155976554.
- Farish, T. E. (1918). "XVI". History of Arizona (Vol. VIII). Filmer brothers electrotype Company.
- Gentile, Carlo (1870). "Ah-oochy Kah-mah & his friend Irateba Two Tonto Apache girls, civilized & christians, good girls; Coyotero Apache woman, sold by her lord & master for 40 yards Manta at Camp Grant; Joséa, Pimo [i.e., Pima] Fat Boy, front view". Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Division. Retrieved May 19, 2015.
- Griffin-Pierce, Trudy (2000). Native Peoples of the Southwest. University of New Mexico Press. ISBN 978-0-8263-1908-1.
- Gutekunst, John (March 3, 2015). "CRIT celebrates 150th anniversary of reservation". Parker Pioneer. Retrieved March 30, 2015.
- Hanchett, Leland J. (1998). Catch the Stage to Phoenix. Pine Rim Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9637785-6-7.
- Hinton, Leanne (1979). "Irataba's gift: a closer look at the ṣ > s > θ sound shift in Mohave and Northern Pai". Journal of California and Great Basin Anthropology Papers in Linguistics. 1 (1): 3–39.
- Hinton, Leanne (1984). Spirit Mountain: An Anthology of Yuman Story and Song. Sun Tracks and University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-0843-3.
- Hunter, L. G. (1979). "The Mojave Expedition of 1858–59". Arizona and the West. 21 (2): 137–156.
- "Indian Marriages". The Daily Democrat. June 3, 1891. p. 2 – via Newspapers.com. [REDACTED]
- Ives, Joseph C. (1861). "Part I: General Report". In United States Army Corps of Topographical Engineers (ed.). Report upon the Colorado River of the West : Explored in 1857 and 1858 by Joseph C. Ives. Government Printing Office. OCLC 3095199. 36th Congress, 1st Session Senate executive document, unnumbered.
- Johansen, Bruce E.; Pritzker, Barry M., eds. (2007). Encyclopedia of American Indian History (illustrated ed.). ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-85109-818-7.
- Knack, Martha C. (2004). Boundaries Between: The Southern Paiutes, 1775–1995. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-7818-9.
- Kappler, Charles J. (1904). "PART III.—Executive Orders Relating to Indian Reserves". Washington: Government Printing Office. Archived from the original on December 9, 2011. Retrieved August 6, 2015.
- Kroeber, Alfred Louis (1925). Handbook of the Indians of California. Courier. ISBN 978-0-486-23368-0.
- Kroeber, Alfred Louis; Kroeber, Clifton B. (1973). A Mohave War Reminiscence, 1854–1880. Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-28163-6.
- Kroeber, Clifton B. (June 15, 1965). "The Mohave as Nationalist, 1859–1874". Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society. 109 (3): 173–180.
- Kroeber, C. B.; Fontana, B. L. (1986). Massacre on the Gila. An account of the last major battle between American Indians, with reflections on the origin of war. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-0969-0.
- Kulp, Neil (April 3, 1974). "Parker's Irataba receives $5000 plus bonus of meeting Franco Harris". The Yuma Daily Sun. p. 3 – via Newspapers.com.(subscription required)
- McGinty, B. (2005). The Oatman Massacre: A Tale of Desert Captivity and Survival. University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0-8061-8024-3.
- McNichols, Charles Longstreth (1944). Crazy Weather. Macmillan. OCLC 1267884.
- Mifflin, Margot (2009). The Blue Tattoo: The Life of Olive Oatman. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-1148-3.
- Miller, David H. (1972). "The Ives Expedition Revisited: Overland into Grand Canyon". The Journal of Arizona History. 13 (3): 177–196.
- Moratto, Michael J. (2014). California Archaeology. Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-4832-7735-6.
- "Arrival of the Indian Warrior, Irataba". The New York Times. February 7, 1864. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- O'Brien, Anne Hughes (2006). Traveling Indian Arizona. Big Earth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-56579-518-1.
- "Aboriginalities" (PDF). The Omaha Daily Bee. Vol. 4, no. 12. July 2, 1874. p. 2 – via Chronicling America.
- Putzi, Jennifer (2004). "Capturing Identity in Ink: The Captivities of Olive Oatman". Western American Literature. 39 (2): 176–199. doi:10.1353/wal.2004.0002. S2CID 165937685.
- Ricky, Donald B. (1999). Indians of Arizona: Past and Present. Native American Books Distributor. ISBN 978-0-403-09863-7.
- Scrivner, Fulsom Charles (1970). Mohave People. The Naylor Company. ISBN 978-0-8111-0335-0.
- Sherer, Lorraine M. (1965). The Clan System of the Fort Mojave Indians. Historical Society of Southern California. OCLC 3512671.
- Sherer, Lorraine M. (March 1966). "Great Chieftains of the Mojave Indians". Southern California Quarterly. 48 (1): 1–35. doi:10.2307/41169985. JSTOR 41169985.
- Sherer, Lorraine M. (1994). Vane, Sylvia Brakke; Bean, Lowell John (eds.). Bitterness Road: The Mojave: 1604 to 1860. Ballena Press. ISBN 978-0-87919-128-3.
- Shumway, G. L.; Vredenburgh, L. M.; Hartill, R. D. (1980). Desert Fever: An Overview of Mining in the California Desert Conservation Area (PDF). Bureau of Land Management. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 26, 2015.
- Stewart, Kenneth M. (1971). "Mohave Warfare". In Heizer, Robert Fleming; Whipple, Mary Anne (eds.). The California Indians: A Source Book. University of California Press. pp. 431–444. ISBN 978-0-520-02031-3.
- Stewart, Kenneth M. (1969). "A Brief History of the Mohave Indians since 1850". Kiva. 34 (4): 219–236. doi:10.1080/00231940.1969.11760552.
- Swanton, John Reed (1952). The Indian Tribes of North America. Genealogical Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-8063-1730-4.
- Thrapp, Dan L. (1991). Encyclopedia of Frontier Biography: A-F. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-9418-9.
- Utley, Robert Marshall (1981). Frontiersmen in Blue: The United States Army and the Indian, 1848–1865. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-9550-6.
- Webb, G. E.; Silliman, B. (1974). "The Mines in Northwestern Arizona in 1864: A Report by Benjamin Silliman, Jr". Arizona and the West. 16 (3): 247–270.
- Whipple, Amiel Weeks; Ives, Joseph C. (1856). "Part I: Itinerary". In United States Department of War (ed.). Reports of Explorations and Surveys to Ascertain the Most Practicable and Economical Route for a Railroad from the Mississippi River to the Pacific Ocean. Vol. 3. A.O.P. Nicholson. 33rd Congress, 2nd Session House executive document number 91.
- Wilson, R. Michael (2007). Massacre at Wickenburg: Arizona's Greatest Mystery. Globe Pequot. ISBN 978-0-7627-4453-4.
- Woodward, Arthur (January 1953). "Irataba: Chief of the Mohave". Plateau. 25 (3): 53–68.
- "Parker Troth". The Yuma Daily Sun. January 21, 1975. p. 3 – via Newspapers.com.(subscription required)
- Zappia, Natale A. (2014). Traders and Raiders: The Indigenous World of the Colorado Basin, 1540–1859. University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 978-1-4696-1585-1.
Further reading
- Curry, John Penn (1865). "An Indian Chief's Opinion of Americans". Gazlay's Pacific Monthly. 1 (1): 360.
- Kroeber, Alfred Louis (1902). "Preliminary Sketch of the Mohave Indians". American Anthropologist. New Series. 4 (2): 276–285. doi:10.1525/aa.1902.4.2.02a00060. JSTOR 659222.
- Wilson, James (2000). The Earth Shall Weep: A History of Native America. Grove Press. ISBN 978-0-8021-3680-0.
External links
- Pipa Aha Macav – "The People by the River": The Official Website of the Fort Mojave Indian Tribe
- InterTribal Council of Arizona – Colorado River Indian Tribes
- Tribal website – Colorado River Indian Tribes