| Revision as of 04:58, 25 October 2004 edit67.117.150.92 (talk) sp. today's; cap. German← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 16:08, 16 January 2025 edit undoFILWISE (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users4,158 editsNo edit summaryTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| (491 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|West Germanic language family}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{about|the family of regional language varieties|the Standard High German language|Standard German}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{pp-pc}} | |||
| '''High German''' (in ], ''Hochdeutsch''; please note that Hochdeutsch is also used to refered to today's standard German) is any of several ] ]s spoken in ], ], ], ], and ] (as well as in neighbouring portions of ], ] ('']''), ], ], and ] ('']'') and in some areas of former colonial settlement, i.e. in ]). | |||
| {{Infobox language family | |||
| | name = High German | |||
| | region = ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] | |||
| *] and ] ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] in ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] and ] | |||
| | familycolor = Indo-European | |||
| | fam2 = ] | |||
| | fam3 = ] | |||
| | fam4 = ] | |||
| | child1 = ] | |||
| | child2 = ] | |||
| | glotto = high1289 | |||
| | glottorefname = High German | |||
| }} | |||
| The '''High German languages''' ({{langx|de|hochdeutsche Mundarten}}, i.e. ''High German dialects''), or simply '''High German''' ({{lang|de|Hochdeutsch}} {{IPA|de|ˈhoːxˌdɔɪ̯t͡ʃ||audio=De-Hochdeutsch.ogg}}) – not to be confused with ] which is commonly also called "High German" – comprise the ] of ] spoken south of the ] and ] ]es in central and southern ], ], ], ], ], and eastern ], as well as in neighbouring portions of ] (] and northern ]), ] (]), the ] (]), and ] (]). They are also spoken in ]s in ], ], ], the ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| Alternatively, and especially in Switzerland and Luxembourg, the term "High German" may refer to one High German dialect to the exclusion of all others, ]. | |||
| In the first context, the "high" refers to the ]ous areas of southern Germany and the ]s; in the second context, the "high" means "official". | |||
| The term also sometimes includes ]. | |||
| High German is marked by the ], separating it from ] (Low Saxon) and ] (including ]) within the continental ] ]. "Low" and "high" refer to the lowland and highland geographies typically found in the two areas. | |||
| The use of High German to refer only to the official German language is not ] use, and tends to lead to confusion when discussing the German language: many High German dialects are called ], a term properly used for a different (but related) language family. See below. | |||
| ==Classification== | |||
| High German (and Yiddish) are distinguished from other Western Germanic dialects in that they took part in the second (High German) sound shifting of the ] and ]. | |||
| ], defined as all ] varieties using ] as their literary language:<ref>W. Heeringa: ''Measuring Dialect Pronunciation Differences using Levenshtein Distance.'' University of Groningen, 2009, pp. 232–234.</ref><ref>Peter Wiesinger: ''Die Einteilung der deutschen Dialekte.'' In: Werner Besch, Ulrich Knoop, Wolfgang Putschke, Herbert Ernst Wiegand (Hrsg.): ''Dialektologie. Ein Handbuch zur deutschen und allgemeinen Dialektforschung,'' 2. Halbband. de Gruyter, Berlin / New York 1983, ISBN 3-11-009571-8, pp. 807–900.</ref><ref>Werner König: ''dtv-Atlas Deutsche Sprache.'' 19. Auflage. dtv, München 2019, ISBN 978-3-423-03025-0, pp. 230.</ref><ref>C. Giesbers: ''Dialecten op de grens van twee talen.'' Radboud Universiteit Nijmegen, 2008, pp. 233.</ref> | |||
| To see this, compare German "Pfanne" with ] "pan" (/pf/ to /p/), German "zwei" with English "two" (/ts/ to /t/), German "machen" with English "make" (/x/ to /k/). | |||
| In the ] of ], there is a further shift; "Kaffee" (like English "coffee") becomes "Kchafi" (/k/ to /kx/). | |||
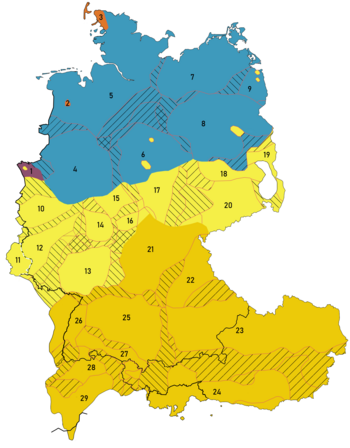
| {{legend|#df772a|]}} | |||
| The name "High German" contrasts with "Low German", a term variously used to refer to the ]s originating from around the ] city of ]; these dialects together with the ]s (], ], and ]); or all of the Western Germanic languages other than High German (including ] and ]). | |||
| {{legend|#8c506e|]}} | |||
| {{legend|#3e9abc|] or ]}} | |||
| {{legend|#f5ef47|]}} | |||
| {{legend|#ecca09|]}}]] | |||
| As a technical term, the "high" in High German is a geographical reference to the group of dialects that forms "High German" (i.e. "Highland" German), out of which developed ], ] and ]. It refers to the ] ('']'') and ] areas of central and southern Germany; it also includes Luxembourg, Austria, Liechtenstein, and most of Switzerland. This is opposed to ], which is spoken in the lowlands and along the flat sea coasts of the ].<ref>Compare the definition of "high" in the Oxford English Dictionary (Concise Edition): "... situated far above ground, sealevel, etc; upper, inland, as ... High German".</ref> | |||
| == Family tree == | |||
| High German can be subdivided into ] (''Oberdeutsch'') and ] (''Mitteldeutsch'', this includes ], which itself is now a ]).<ref>E.g. | |||
| Note that divisions between subfamilies of Germanic are rarely precisely defined; most form continuous clines, with adjacent ]s being mutually intelligible and more separated ones not. In particular, there never has been an original "]". | |||
| * Hermann Niebaum, Jürgen Macha, ''Einführung in die Dialektologie des Deutschen'' (series: ''Germanistische Arbeitshefte''), 2nd ed., Max Niemeyer Verlag, Tübingen, 2006, p. 220 <!-- : „In den ''niederdeutschen'' (und ''niederfränkischen'') Mundarten , während in den ''hochdeutschen'' Mundarten (unter diesem Terminus werden die ''mitteldeutschen'' und ''oberdeutschen'' Mundarten zusammengefasst) “ --> | |||
| * Gabriele Graefen, Martina Liedke-Göbel, ''Germanistische Sprachwissenschaft: Deutsch als Erst-, Zweit- oder Fremdsprache'', 3rd ed., 2020, p. 31. | |||
| For the Middle High German time e.g.: | |||
| * Howard Jones & Martin H. Jones, ''The Oxford Guide to Middle High German'', Oxford University Press, 2019, p. 7 | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * M. O'C. Walshe, ''A Middle High German reader with grammar, notes, and glossary'', Oxford University Press, 1974, p. 3 | |||
| *** ] | |||
| </ref> | |||
| *** ] (mostly in ] and ]) | |||
| *** ] (mostly in ], ] and ] | |||
| *** ] (in Saxony and Brandenburg) | |||
| *** ] (mostly in ], in ]) | |||
| ** ] (in ]) | |||
| ** ] | |||
| *** ''Middle Franconian'' | |||
| **** ]'' | |||
| **** ] | |||
| *** ''Rhine Franconian'' | |||
| **** ] | |||
| **** ] (France) | |||
| **** ] | |||
| **** ] | |||
| **** ] | |||
| *** ] (Hesse) | |||
| ** Transition area between ''Middle German'' and ''Upper German'' | |||
| *** ] | |||
| **** ], colloquially miscalled '']'' because dialects of this sub-family are spoken all over '']'' | |||
| *** ] | |||
| ** ] (in the ] and ]) | |||
| * ] | |||
| ** ] | |||
| *** ] (mostly in ]) | |||
| *** ] (in ], in ]) | |||
| *** ] (mostly in ], in Germany) | |||
| *** ] (in ]) | |||
| *** ] (originally in the ] of Switzerland) | |||
| ** ] | |||
| *** ] (mostly in ], in Germany) | |||
| *** ] (in ]) | |||
| *** ] (northeastern ]) | |||
| *** ] (], in Italy) | |||
| *** ] (in ] and the ]) | |||
| * ] (extinct in the ]) | |||
| High German varieties are distinguished from other West Germanic varieties in that they took part in the ] ({{circa|AD 500}}) to various degrees. To see this, compare the following:<ref>]. Old English and its Closest Relatives. Routledge, 1994.</ref>{{page needed|date=August 2023}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| * (in German) | |||
| * | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| ] | |||
| ! ] !! ] !! Standard High German !! Consonant shift | |||
| |- | |||
| | pan || Pann || Pfanne || {{IPA|}} to {{IPA|}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | two || twee || zwei || {{IPA|}} to {{IPA|}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | make || maken || machen || {{IPA|}} to {{IPA|}} | |||
| |} | |||
| In the southernmost ] dialects, there is a further shift: ''Sack'' (like English/Low German "sack/Sack") is pronounced {{IPA|}} ({{IPA|}} to {{IPA|}}). | |||
| ==History== | |||
| {{see also|Theodiscus}} | |||
| ] evolved from about 500 AD. Around 1200 the ] and ] varieties of ] became dominant as a court and poetry language ('']'') under the rule of the House of ]. | |||
| The term "High German" as spoken in central and southern Germany (], ], ], ]) and ] was first documented in the 15th century.{{citation needed|date=August 2023}} | |||
| Gradually driving back Low German variants since the ], the ] varieties, especially the ] of the ], formed an important basis for the development of Standard German.<ref>Russ, Charles V.J. ''The German Language Today: A Linguistic Introduction.'' Routledge, 1994, p. 15f.</ref> | |||
| ==Family== | |||
| {{Unreferenced section|date=February 2024}} | |||
| Divisions between subfamilies within Germanic are rarely precisely defined, because most form continuous clines, with adjacent ]s being mutually intelligible and more separated ones not. In particular, there has never been an original "]". For this and other reasons, the idea of representing the relationships between ] language forms in a tree diagram at all is controversial among linguists. What follows should be used with care in the light of this caveat. | |||
| {{tree list}} | |||
| * High German | |||
| ** ''']''' (German: {{lang|de|Mitteldeutsch}}) | |||
| *** '']'' | |||
| **** ] | |||
| **** ], including ] | |||
| **** ] | |||
| **** ] | |||
| **** ] (now mostly spoken by the ] in ]) | |||
| **** ] (nearly extinct) | |||
| *** '']'' | |||
| **** ] | |||
| ***** ] | |||
| ***** ], including ] | |||
| ****** ] (from the ]) | |||
| **** ] | |||
| ***** ], including ] (France) | |||
| ****** ] (in the ] and ]) | |||
| ***** ] | |||
| ** ''']''', in the transitional area between Central and Upper German | |||
| *** '']'' | |||
| *** '']'' | |||
| ** ''']''' (German: {{lang|de|Oberdeutsch}}) | |||
| *** '']'' in the broad sense or West Upper German (German: ''Westoberdeutsch''), including ] dialects | |||
| **** ] | |||
| **** ] in the strict sense | |||
| ***** ], including ] and ] | |||
| ***** ] | |||
| ***** ] | |||
| *** '']'' or East Upper German (German: ''Ostoberdeutsch''), including ] dialects | |||
| **** ] | |||
| **** ], including ] | |||
| **** ], including ] in ], Italy | |||
| ***** ] | |||
| **** ], nearly extinct | |||
| **** ] (in ] and the ]) | |||
| *** '']'', extinct | |||
| ** ''']''', evolved from Middle High German | |||
| {{tree list/end}} | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Portal|Germany}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| * ] (1942), ''Nordgermanen und Alemannen: Studien zur germanischen und frühdeutschen Sprachgeschichte, Stammes- und Volkskunde'', Strasbourg: Hünenburg, ]''']. | |||
| {{Germanic languages}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:High German Languages}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:08, 16 January 2025
West Germanic language family This article is about the family of regional language varieties. For the Standard High German language, see Standard German.
| High German | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | German-speaking Europe, United States, Canada, Brazil, Chile, Argentina, Paraguay, Colonia Tovar |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European
|
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | high1289 |
The High German languages (German: hochdeutsche Mundarten, i.e. High German dialects), or simply High German (Hochdeutsch [ˈhoːxˌdɔɪ̯t͡ʃ] ) – not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called "High German" – comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and Uerdingen isoglosses in central and southern Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, Luxembourg, and eastern Belgium, as well as in neighbouring portions of France (Alsace and northern Lorraine), Italy (South Tyrol), the Czech Republic (Bohemia), and Poland (Upper Silesia). They are also spoken in diasporas in Romania, Russia, Canada, the United States, Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, Chile, and Namibia.
High German is marked by the High German consonant shift, separating it from Low German (Low Saxon) and Low Franconian (including Dutch) within the continental West Germanic dialect continuum. "Low" and "high" refer to the lowland and highland geographies typically found in the two areas.
Classification
As a technical term, the "high" in High German is a geographical reference to the group of dialects that forms "High German" (i.e. "Highland" German), out of which developed Standard German, Yiddish and Luxembourgish. It refers to the Central Uplands (Mittelgebirge) and Alpine areas of central and southern Germany; it also includes Luxembourg, Austria, Liechtenstein, and most of Switzerland. This is opposed to Low German, which is spoken in the lowlands and along the flat sea coasts of the North German Plain.
High German can be subdivided into Upper German (Oberdeutsch) and Central or Middle German (Mitteldeutsch, this includes Luxembourgish, which itself is now a standard language).
High German varieties are distinguished from other West Germanic varieties in that they took part in the High German consonant shift (c. AD 500) to various degrees. To see this, compare the following:
| English | Low German | Standard High German | Consonant shift |
|---|---|---|---|
| pan | Pann | Pfanne | to |
| two | twee | zwei | to |
| make | maken | machen | to |
In the southernmost High Alemannic dialects, there is a further shift: Sack (like English/Low German "sack/Sack") is pronounced ( to ).
History
See also: TheodiscusOld High German evolved from about 500 AD. Around 1200 the Swabian and East Franconian varieties of Middle High German became dominant as a court and poetry language (Minnesang) under the rule of the House of Hohenstaufen.
The term "High German" as spoken in central and southern Germany (Upper Saxony, Franconia, Swabia, Bavaria) and Austria was first documented in the 15th century.
Gradually driving back Low German variants since the Early modern period, the Early New High German varieties, especially the East Central German of the Luther Bible, formed an important basis for the development of Standard German.
Family
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (February 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Divisions between subfamilies within Germanic are rarely precisely defined, because most form continuous clines, with adjacent dialects being mutually intelligible and more separated ones not. In particular, there has never been an original "Proto-High German". For this and other reasons, the idea of representing the relationships between West Germanic language forms in a tree diagram at all is controversial among linguists. What follows should be used with care in the light of this caveat.
- High German
- Central German (German: Mitteldeutsch)
- East Central German
- Thuringian
- Upper Saxon, including Erzgebirgisch
- South Marchian
- Lusatian
- Silesian (now mostly spoken by the German minority in Upper Silesia)
- High Prussian (nearly extinct)
- West Central German
- Central Franconian
- Ripuarian
- Moselle Franconian dialects, including Luxembourgish
- Hunsrik language (from the Hunsrückisch dialect)
- Rhine Franconian
- Palatine, including Lorraine Franconian (France)
- Pennsylvania Dutch (in the United States and Canada)
- Hessian
- Palatine, including Lorraine Franconian (France)
- Central Franconian
- East Central German
- High Franconian, in the transitional area between Central and Upper German
- Upper German (German: Oberdeutsch)
- Alemannic in the broad sense or West Upper German (German: Westoberdeutsch), including Swiss German dialects
- Swabian
- Alemannic in the strict sense
- Low Alemannic, including Alsatian and Basel German
- High Alemannic
- Highest Alemannic
- Bavarian or East Upper German (German: Ostoberdeutsch), including Austrian German dialects
- Northern Bavarian
- Central Bavarian, including Viennese
- Southern Bavarian, including Mócheno in Trentino, Italy
- Cimbrian, nearly extinct
- Hutterite German (in Canada and the United States)
- Lombardic, extinct
- Alemannic in the broad sense or West Upper German (German: Westoberdeutsch), including Swiss German dialects
- Yiddish, evolved from Middle High German
- Central German (German: Mitteldeutsch)
See also
References
- W. Heeringa: Measuring Dialect Pronunciation Differences using Levenshtein Distance. University of Groningen, 2009, pp. 232–234.
- Peter Wiesinger: Die Einteilung der deutschen Dialekte. In: Werner Besch, Ulrich Knoop, Wolfgang Putschke, Herbert Ernst Wiegand (Hrsg.): Dialektologie. Ein Handbuch zur deutschen und allgemeinen Dialektforschung, 2. Halbband. de Gruyter, Berlin / New York 1983, ISBN 3-11-009571-8, pp. 807–900.
- Werner König: dtv-Atlas Deutsche Sprache. 19. Auflage. dtv, München 2019, ISBN 978-3-423-03025-0, pp. 230.
- C. Giesbers: Dialecten op de grens van twee talen. Radboud Universiteit Nijmegen, 2008, pp. 233.
- Compare the definition of "high" in the Oxford English Dictionary (Concise Edition): "... situated far above ground, sealevel, etc; upper, inland, as ... High German".
- E.g.
- Hermann Niebaum, Jürgen Macha, Einführung in die Dialektologie des Deutschen (series: Germanistische Arbeitshefte), 2nd ed., Max Niemeyer Verlag, Tübingen, 2006, p. 220
- Gabriele Graefen, Martina Liedke-Göbel, Germanistische Sprachwissenschaft: Deutsch als Erst-, Zweit- oder Fremdsprache, 3rd ed., 2020, p. 31.
- Howard Jones & Martin H. Jones, The Oxford Guide to Middle High German, Oxford University Press, 2019, p. 7
- M. O'C. Walshe, A Middle High German reader with grammar, notes, and glossary, Oxford University Press, 1974, p. 3
- Robinson, Orrin. Old English and its Closest Relatives. Routledge, 1994.
- Russ, Charles V.J. The German Language Today: A Linguistic Introduction. Routledge, 1994, p. 15f.
Further reading
- Friedrich Maurer (1942), Nordgermanen und Alemannen: Studien zur germanischen und frühdeutschen Sprachgeschichte, Stammes- und Volkskunde, Strasbourg: Hünenburg, .