| Revision as of 21:22, 2 November 2020 editSammi Brie (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Page movers, File movers, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers, Template editors151,509 edits Adding local short description: "Arsenic-based herbicide", overriding Wikidata description "chemical compound" (Shortdesc helper)← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 23:50, 29 December 2023 edit undoGreenC bot (talk | contribs)Bots2,590,068 edits Move 1 url. Wayback Medic 2.5 | ||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
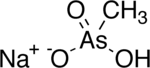
| '''Monosodium methyl arsenate''' (MSMA) is an ]-based ]. It is an organo-arsenate; less toxic than the inorganic form of arsenates. However, the EPA states that all forms of arsenic are a serious risk to human health and the United States' Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry ranked arsenic as number 1 in its 2001 Priority List of Hazardous Substances at Superfund sites.<ref name="EPA1">{{cite web |url=https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncer_abstracts/index.cfm/fuseaction/display.highlight/abstract/6015 |title=Biogeochemistry of Arsenic in Contaminated Soils of Superfund Sites |last1=Dibyendu |first1=Sarkar |last2=Datta |first2=Rupali |date=2007 |website=EPA |publisher=United States Environmental Protection Agency |access-date=25 February 2018 }}</ref> | '''Monosodium methyl arsenate''' (MSMA) is an ]-based ]. It is an organo-arsenate; less toxic than the inorganic form of arsenates. However, the EPA states that all forms of arsenic are a serious risk to human health and the United States' Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry ranked arsenic as number 1 in its 2001 Priority List of Hazardous Substances at Superfund sites.<ref name="EPA1">{{cite web |url=https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncer_abstracts/index.cfm/fuseaction/display.highlight/abstract/6015 |title=Biogeochemistry of Arsenic in Contaminated Soils of Superfund Sites |last1=Dibyendu |first1=Sarkar |last2=Datta |first2=Rupali |date=2007 |website=EPA |publisher=United States Environmental Protection Agency |access-date=25 February 2018 }}</ref> | ||
| It is a herbicide used against weeds in agriculture, combining selectivity{{Citation needed|date=February 2018}}, low weed-resistance, and cost-efficiency.{{Citation needed|date=February 2018}} Target weeds include: grasses and broad-leaf weeds including some weeds that are resistant to the herbicide ].{{Citation needed|date=February 2018}} | |||
| Weed resistance to herbicides is on the rise due to the use of the herbicides in general, as well as in conjunction with the introduction of ]. Resistant crops are endowed with natural resistance to certain herbicides, a resistance which they may impart to non-crops through cross pollination. There are very few, if any, new herbicides capable of economically combating the resistance problem.{{Citation needed|date=February 2018}} With the exception of isolated cases of common ] ], no resistance build-up has occurred with the weeds that MSMA controls.{{Citation needed|date=February 2018}} | |||
| MSMA provides post-emergent selective{{Citation needed|date=February 2018}} annual grass and yellow ] control, in cool season. MSMA can be used to control ] (morning glory) and ] (nutgrass). | |||
| Arsenic is classified as a Group-A ].<ref name="EPA1"/> The EPA states that:<ref>{{cite web |url=https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncer_abstracts/index.cfm/fuseaction/display.highlight/abstract/6015/report/F |title=Final Report: Biogeochemistry of Arsenic in Contaminated Soils of Superfund Sites |last=Carelton |first=James |date=2007 |website=EPA |publisher=United States Environmental Protection Agency |access-date=25 February 2018 }}</ref> | Arsenic is classified as a Group-A ].<ref name="EPA1"/> The EPA states that:<ref>{{cite web |url=https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncer_abstracts/index.cfm/fuseaction/display.highlight/abstract/6015/report/F |title=Final Report: Biogeochemistry of Arsenic in Contaminated Soils of Superfund Sites |last=Carelton |first=James |date=2007 |website=EPA |publisher=United States Environmental Protection Agency |access-date=25 February 2018 }}</ref> | ||
| Line 67: | Line 62: | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| *{{cite web | last=Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry | title=Arsenic Toxicity Case Study | work=Environmental Health and Medicine Education | |
*{{cite web | last=Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry | title=Arsenic Toxicity Case Study | work=Environmental Health and Medicine Education | access-date=25 December 2013 | url=https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/csem/csem.html}} | ||
| *{{cite web | author=MAA Research Task Force | title=Organic Arsenical Products Task Force | url=http://www.maatf.com/index.html}} | *{{cite web | author=MAA Research Task Force | title=Organic Arsenical Products Task Force | url=http://www.maatf.com/index.html}} | ||
| *{{cite web | author=National Library of Medicine | title=Sodium Methanearsonate | work=HSDB Database | url=http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/r?dbs+hsdb:@term+@rn+@rel+2163-80-6}} | *{{cite web | author=National Library of Medicine | title=Sodium Methanearsonate | work=HSDB Database | url=http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/r?dbs+hsdb:@term+@rn+@rel+2163-80-6}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:50, 29 December 2023
Arsenic-based herbicide| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Monosodium methyl arsonate" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Sodium hydrogen methylarsonate | |
| Other names Monosodium methyl arsenate; sodium methylarsonate; monosodium methane arsonate; methyl arsonic acid monosodium salt; EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 013803 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | MSMA |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.815 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | CH4AsNaO3 |
| Molar mass | 161.95 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Monosodium methyl arsenate (MSMA) is an arsenic-based herbicide. It is an organo-arsenate; less toxic than the inorganic form of arsenates. However, the EPA states that all forms of arsenic are a serious risk to human health and the United States' Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry ranked arsenic as number 1 in its 2001 Priority List of Hazardous Substances at Superfund sites.
Arsenic is classified as a Group-A carcinogen. The EPA states that:
Arsenate (AsV) is the oxidized form and occurs in well-aerated soils, whereas in chemically-reduced soil environments, arsenite (AsIII) is the prevalent As form. Although arsenite is more toxic than arsenate, arsenate can also have deleterious effects on humans, plants, and microorganisms. Arsenic-contaminated soils pose serious risk to human health. The EPA also states that, while contaminated soil poses a serious risk to health, arsenic frequently mobilizes from soils and other sources, ending up in water where it is even more of a toxicity issue.
Trade names include:
- Target 6 Plus
- Target 6.6
- MSMA 6 Plus
- MSMA 6.6
References
- Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry. "Arsenic Toxicity Case Study". Environmental Health and Medicine Education. Retrieved 25 December 2013.
- MAA Research Task Force. "Organic Arsenical Products Task Force".
- National Library of Medicine. "Sodium Methanearsonate". HSDB Database.
- Specific
- ^ Dibyendu, Sarkar; Datta, Rupali (2007). "Biogeochemistry of Arsenic in Contaminated Soils of Superfund Sites". EPA. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
- Carelton, James (2007). "Final Report: Biogeochemistry of Arsenic in Contaminated Soils of Superfund Sites". EPA. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved 25 February 2018.