| Revision as of 19:40, 12 July 2024 editUpamedhika (talk | contribs)182 edits →Language comparison chartTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 23:58, 21 August 2024 edit undoMsasag (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,816 edits →LanguagesTags: Mobile edit Mobile web editNext edit → | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | ! ] | ||
| | {{lang| |
| {{lang|bpy|বিষ্ণুপ্রিয়া মণিপুরী}} <br>''Bișnupriya Monipuri'' | ||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| | ]<ref>{{cite book |last1=Kim |first1=Amy |last2=Kim |first2=Seung |title=Bishnupriya (Manipuri) speakers in Bangladesh: a sociolinguistic survey | publisher=SIL INTERNATIONAL |page=11 |url=https://www.sil.org/system/files/reapdata/74/05/96/74059695388257055076108658933060858639/silesr2008_003.pdf |access-date=4 October 2020}}</ref> | | ]<ref>{{cite book |last1=Kim |first1=Amy |last2=Kim |first2=Seung |title=Bishnupriya (Manipuri) speakers in Bangladesh: a sociolinguistic survey | publisher=SIL INTERNATIONAL |page=11 |url=https://www.sil.org/system/files/reapdata/74/05/96/74059695388257055076108658933060858639/silesr2008_003.pdf |access-date=4 October 2020}}</ref> | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | ! ] | ||
| | {{lang| |
| {{lang|rkt|রংপুরী}} <br> {{lang|rkt|কামতাপুৰী}} <br> {{lang|rkt|ৰাজবংশী}} <br> {{lang|de|राजबंशी}} <br>''Rongpuri'' <br>''Kamatapuri'' <br>''Rajbanshi'' | ||
| | ], ]<ref>{{cite book |last1=Minahan |first1=James B. |title=Ethnic Groups of South Asia and the Pacific: An Encyclopedia: An Encyclopedia |date=30 August 2012 |publisher=ABC-CLIO |location=Santa Barbara, Calif. |isbn=978-1-59884-660-7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fOQkpcVcd9AC&pg=PT342 |language=en |quote=Generally, the Rajbongshi language is known as Rangpuri in Bangladesh and Kamta or Rajbangshi in India. The language is usually written in Bengali script in Bangladesh, while the Kamtapura script is favored in India. In Nepal, the language is Devanagari script which is also sometimes used by the Indian Rajbongshis.}}</ref> | | ], ]<ref>{{cite book |last1=Minahan |first1=James B. |title=Ethnic Groups of South Asia and the Pacific: An Encyclopedia: An Encyclopedia |date=30 August 2012 |publisher=ABC-CLIO |location=Santa Barbara, Calif. |isbn=978-1-59884-660-7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fOQkpcVcd9AC&pg=PT342 |language=en |quote=Generally, the Rajbongshi language is known as Rangpuri in Bangladesh and Kamta or Rajbangshi in India. The language is usually written in Bengali script in Bangladesh, while the Kamtapura script is favored in India. In Nepal, the language is Devanagari script which is also sometimes used by the Indian Rajbongshis.}}</ref> | ||
| | ],<ref name="rkt" /> <br/>]<ref>"As a ritual of purgation they are discarding the Bengali /r/ with a dot and the same is replaced with the original /r/ with a diagonal slash, as used in Assamese script despite the fact that the Rajbanshis in Bengal have been conditioned to use the Bengali /r/ owing to the long processes of forceful imposition of Bengali language upon them." {{harvcol|Pradhani|2012|p=52}}</ref> | | ],<ref name="rkt" /> <br/>]<ref>"As a ritual of purgation they are discarding the Bengali /r/ with a dot and the same is replaced with the original /r/ with a diagonal slash, as used in Assamese script despite the fact that the Rajbanshis in Bengal have been conditioned to use the Bengali /r/ owing to the long processes of forceful imposition of Bengali language upon them." {{harvcol|Pradhani|2012|p=52}}</ref> | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | ! ] | ||
| | सुरजापुरी <br> {{lang| |
| सुरजापुरी <br> {{lang|rjs|সুরজাপুরী}}<br>''Surjapuri'' | ||
| | ] <br> ] | | ] <br> ] | ||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! ] | ! ] | ||
| | <span style="font-family: 'Surma';">'''ꠍꠤꠟꠐꠤ'''</span> <br> {{lang| |
| <span style="font-family: 'Surma';">'''ꠍꠤꠟꠐꠤ'''</span> <br> {{lang|syl|ছিলটি}} <br> ''Siloŧi'' | ||
| | ] <br> ] | | ] <br> ] | ||
| | ]<ref name="syl" /> | | ]<ref name="syl" /> | ||
Revision as of 23:58, 21 August 2024
Sub group of the Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Bengali–Assamese languages" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Assamese-Bengali | |
|---|---|
| Gauda–Kamarupa | |
| Geographic distribution | Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Nepal |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European |
| Early form | Magadhi Prakrit |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | gaud1237 (Gauda–Kamrupa) |
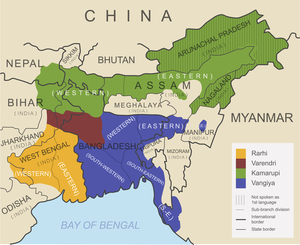 A map showing geographical distribution of the sub-branches of Assamese-Bengali languages according to the classification of Suniti Kumar Chatterji. A map showing geographical distribution of the sub-branches of Assamese-Bengali languages according to the classification of Suniti Kumar Chatterji. | |
The Assamese-Bengali languages (also Gauda–Kamarupa languages) is a grouping of several languages in the eastern Indian subcontinent. This group belongs to the Eastern zone of Indo-Aryan languages. The languages in this group according to Glottolog includes Assamese, Bengali, Bishnupriya, Chakma, Chittagonian, Hajong, Kharia Thar, Kurmukar, Lodhi (also categorised as a Munda language), Mal Paharia, Noakhailla, Rajbangshi, Rohingya, Sylheti, Tangchangya and Surjapuri.
Languages
Language comparison chart
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (April 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
* = borrowed terms (including tatsamas, ardhatatsamas and other borrowings)
| English | Assamese | Bengali | Chakma | Chittagonian | Hajong | Kamata | Rohingya | Sylheti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| beautiful | dhunia, xundor | shundor | dol | dishar,šundor | cúndor*, hásin* | šundor*, kubsurot*, mayasurot | ||
| big | daṅor/daṅar, bor | boṛo, ḍagor, ḍaṅor | đôñr | boro, daṅar | boro, ákbor*, kobira* | boṛo | ||
| blood | tez, rokto* | rôkto*, khun*, lohu | lo | lou, rôktô | lou, hún*, kún* | lou, roxto*, kun* | ||
| bread | ruti (flat), pau*ruti, luf*, bred* | pão*ruṭi, ruṭi (flat) | fõruţi | fiçá, luthi | ruṭi (flat), luf* | |||
| brother | bhai (younger), kokai/kaka (elder), dada (elder)* | bhai, dada, bhaiya | bái, bôdda | bhai | bái | bái | ||
| cat | mekuri, birali, biral | biṛal, beṛal, billi, bilai, biṛali | bilai,bilei | bilai | mekur, bilai | |||
| dark | andhar, endhar | ãdhar, andhar, ondhokar* | ãdár | añdár, miyonda | andáir | |||
| daughter | zi, mai, zhia | meye, konna*, jhi | zee, maifuā | beti | futúni, zíi | zi, fuṛi | ||
| day | din, rüz*, bela | din, bêla, roz*, dibôš* | din | din | din | din, ruz* | ||
| dog | kukur | kukur, kutta | kutto | kuñr | atu, kutta | |||
| door | duar*, dorza*, dar | dôrza*, duar*, doja*, dôroza*, dôrwaza* | duōr, kebar | duar* | duar* | xeir, dorza*, duar* | ||
| earth | bhũi, p(r)ithiwi/p(r)ithibi*, dunia* | duniya*, prithibi*, dhora, jahan* | duniye,fithibi, | duniyai* | duniai*, dunia*, zahan* | |||
| egg | koni, dima | ḍim, anḍa, boida* | boda* | đim,anḍa | ḍima | andha, dhim | enḍa, ḍim, boida* | |
| elephant | hati | hati | áti | hati | áñti, háñtih | átti | ||
| eye | soku, sokhu, noyon* | chokh, chokkhu*, ãkhi, noyon* | sóg | suk | soku, uki, souk | |||
| father | deuta*, bap, büpai/bapa, baba*, aba/abba/abu/abbu* | bap, abba, baba, waled*, abbu*, babaji, pita* | baf, ba,abba | abbá* | baf, bazi | |||
| fear | bhoy, dor | bhôy*, ḍor | đôr | ḍor | ḍor | |||
| finger | aṅuli | aṅgul, onguli* | ôuñl | ouñl | aṅguil | |||
| fire | zui, aguni*, ogni* | agun, ogni*, nar*, atosh*, anol*, pabok*, dahon* | ôin* | ooin* | aguin*, nar*, atosh* | |||
| fish | mas | machh | mas | mas | mas | mas, mai* | ||
| food | khüabostu*, ahar*, khayddo*, khana* | khabar, khaon, khana*, khani*, khaddo*, ahar* | hána | hána, háñna | xani | |||
| god | bhogowan*, issôr*, deu, khüda* | Khoda*, isshôr*, bhagôban*,allah* ,shrishtikarta*, Ishôr | khúda*,rôb, ūôr ôla | ila*, rob*, ixor* | mobud*, mola*, rob*, xoda*, bhogòban* | |||
| good | bhal | bhalo | bála, gôm | bhala | bhal | gom | bála | |
| grass | ghah, kher (hay) | ghaš, khôṛ (hay) | kér | ghaṣ | kérr | ga, gaš | ||
| hand | hat | hat | át | hat | árt | át | ||
| hand fan | bisoni | hat-pakha, biuni, bijoni | bisôin, bisein | bisoin, fanka | ||||
| head | mur, matha, math | matha, shir*, kolla* | mata, hôlla | matá | sir*, xolla*, mata | |||
| heart (emotion) | hia, ontor*, koliza/koilza, hidoy* | hridôy*, ôntor*, hiya, dil*, kolob*, kolija | dil*, hôilze, ridôy, ôntôr | dil* | dil*, hia | |||
| heart (organ) | dil, amothu | hritpindo*,dil*, kolija | dil* | gurda | ||||
| horse | ghüra | ghoṛa | gúṛa | gúñra, gúra | gúṛa | |||
| house | ghor | ghôr, baṛi, basha, khana* | gór | gor, bari | gór, bari, xan* | |||
| hunger | bhük | khudha*, khida*, khide*, bhuk | búk | búk | buk, feto(r) buk | |||
| language | bhaxa*, mat (call), kotha*, raw | bhaša*, buli, joban* | hodá* | basha,zúban,buli | raw, bhaṣa* | zoban*, hodá* | mat, bul, rau, zoban*, basha* | |
| laughter | hahi | haši | aši | haṣi | aši | |||
| life | ziwon/zibon, ziu (soul), zindegi*, hayat* | jiu, jibôn*, zindegi*, hayat* | zibon,zindegi*,hayat* | zibon | zindegi*, hayat* | |||
| moon | zün, san(d), sond(r)o* | chád, chôndro*,bôdôr*, shashôdhor*, chand | sãn | san | san | san(d), sondoni | ||
| mother | ma, ai, mai, ammi/amma* | ma, amma*, ammu, waleda*, mata*, ai, mamoni | ma | maö, ai | mai, ai, maizi | |||
| mouth | mukh* | mukh* | mukh* | muk* | muk* | |||
| name | nam, naü | nam | nam | nam | nam | |||
| night | rati, nixa*, ratri* | rat, ratri*, shob* | rait | rati | rait | rait, rati, nii, shob*, lailot* | ||
| peace | xanti*, xokah | shanti*, aman*, salamôt* | šanti* | ṣanti* | niraii, shanti*, salamôt* | |||
| place | thai, zega/zaga*, than | jayga*, ṭhai, sthan*, jaga* | ṭai, zāga* | zega*, tan | ||||
| queen | rani | rani, shahbanu* | rani | rani | rani | rani, razbibi, sha(h)banu* | ||
| rest | zironi, aram* | aram*, bisram*, jirano*, jiron* | dom*,zirôn,aram gôrôn | zirani, aram* | ||||
| river | noi, gaṅ, nodi* | nôdi*, doriya*, ɡaṅg | dôijja*,dôirge | hál | ɡaṅg, nodi* | |||
| road | bat, ali, rasta*, poth* | rasta*, shoṛok, pôth* | sorox, rah*, rasta*, ail, fot* | |||||
| salt | nimokh*, lün, nun | lôbôn*, nun, nomok* | nun, lôbôn* | nimox*, nun, lobon* | ||||
| sister | bhoni (younger), ba/bai (elder) | apa, bon, didi, apu, api, didimoni, bubu, boin | bóin,afa/bôbbu/dî/afu (elder) | bóin, buai | ||||
| small | xoru | chhoṭo, pati | guro | huru, nii, kuṭimuti, gura, titkina, geda, suṭu | ||||
| son | put, pü, putro/putto* | chhele, putro*, put, poa, bêṭa | (morod) fuā, fut | beṭa | fut | fut, fua | ||
| soul | ziu, atma* | attã*, pran*, pôran*, ruh*,jiu | foran*, rû* | ru*, atma*, zaan* | ||||
| sun | beli, xuruz*, xuydzo* | shurjo*, shuruj* | beil, šuroz* | beil | suruz*, shurzo* | |||
| ten | doh, dos* | dosh | doš | doṣ | dosh, do | |||
| three | tini | tin | tín | tin | tin | |||
| village | gaü | gram*, gã, gão | geram | gau | ||||
| waist | kokal, kakal | komor*, maja | keĩl | keñil | xomor*, xaxal | |||
| water | pani | pani, jôl* | fani | pani | pani, zol* | faní | fani, ab*, tam | |
| when | ketia, ketiyake | kôkhon, kobe, kon shomoy*, kon bêla | hótte | könbela | kunbala(n->m), kunomoy | |||
| wind | botah/batah, hawa* | batash*, hawa*, ba, bayu*, bao, bat*, anil* | ába*, bataš* | boyar, batash*, hawa* | ||||
| wolf | kukurnesia bagh, xial (jackal, fox) | nekṛe-bagh, sheyal/shiyal (jackal, fox) | neṛi kutta | atubag, hial (jackal, fox) | ||||
| woman | maiki manuh, tiri*, tirüta, mohila* | mohila*, nari*, beṭi manush, ccheri | maiye fua,maifuā (soft) | beṭi saöa | beṭi, moíla* | |||
| year | bosor, son* | bochhor, shal*, borsho* | bosor | bosor | fira, bosor, son*, shal* | |||
| yes | hoy, o, ü̃, mm | hễ, ji*, agge, hã | ô, ôy | ô, ôy | óe, i, zi* óe | |||
| no | nohoy, nai, ühü, na | na, nai, nay, noy, nei, non | nô, nôy | nô, nôy | na, nai, nay | |||
| yesterday | kali, züa-kali | (goto*-)kal(-ke), (gelo-)kal(-ke),kal(-ke) | goto* hail, goto* halia | (gese-)xail(-ku), xail(-ku) | ||||
| English | Assamese | Bengali | Chakma | Chittagonian | Hajong | Kamata | Rohingya | Sylheti |
* = borrowed terms (including tatsamas, ardhatatsamas and other borrowings)
Verbs
| English | Assamese | Sylheti | Bengali | Chakma | Chittagonian | Kamata | Rohingya | Hajong |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ask | xudh-, xudhpus kor- (investigate) | zika-, fus-, zar- | jiggaśa kor-, puchh-, puch kor-, jiggesh kor-, jiga- | pũsar ɡor- | ||||
| bite | kamur-, kamür mar- | xamṛa-, xamor mar- | kamoṛ mar-, kamṛa- | hõr- | ||||
| blow | phu de-, phuk-, phu kor- | fu de-, hu de- | phu de- | |||||
| breathe | uxah lo- | dom lo- | šãš ne-, šãš lo-, dôm ne-, dôm lo- | |||||
| bring | an- | an- | an- | an- | ||||
| can | par- | far- | par- | |||||
| catch | dhor- | dór- | dhôr- | |||||
| come | ah- | a- | aś- | a- | a- | ah- | ||
| count | gon-, hisap kor-, gonti kor- | gon-, isab xor- | gon-, hišab kôr- | |||||
| cry | kand-, kan- | xand-, xan- | kãd- | hãd- | ||||
| cut | kat- | xaṭ- | kaṭ- | |||||
| do | kor- | xor- | kôr- | gor- | ɡor- | |||
| die | mor-, dhuka- | mor- | môr- | mor- | ||||
| dig | khand- | kur-, kus- | khõṛ-, khõc- | |||||
| drink | kha-, pi kha-, pi- | xa-, fia xa-, fi- | kha-, pan kor-, pi- | |||||
| eat | kha- | xa- | kha- | há- | ||||
| fall | por- | foṛ- | poṛ- | |||||
| fear | bhoy kha-, dora- | ḍora- | bhoy pa-, ḍora- | |||||
| fight | zũz-, maramari/moramori kor- | mair xor-, xaijja xor- | maramari kor-, jhogṛa kôr- | |||||
| float | üpoṅ-, bhah- | bai-, bo- | bhaš- | |||||
| flow | bo- | bo- | bo- | |||||
| fly | ur- | uṛ- | uṛ- | ur- | ur- | |||
| give | de-, di- | de-, di- | de- | |||||
| go | za-, ɡo-/ge- | za-, ɡo-, ɡe- | ja-, ɡe- | za-, zo- | za-, zo- | |||
| happen | ho- | ó- | ho- | ó- | ||||
| hear | xun- | hun- | śun- | un- | ||||
| hit | mar-, pit-, kila- | mar-, fiț-, kila- | mar-, kela- | |||||
| kill | mar-, mari pela- | mar-, mari de- | mar-, mere fel-, mariya fal- | |||||
| know | zan- | zan- | jan- | |||||
| laugh | hah- | aś- | haś- | aś- | ||||
| learn | xik-, xikh- | hik- | śekh-, śikh- | hik- | ||||
| lie (in bed) | baɡor-, kati ho-, bisonat/bisnat por- | xait o-, hut- | shuye por- | |||||
| live | thak-, zi(ai) thak-, tik-, basi thak- | tax-, zia-, basi tax- | thak-, jibito thak-, jinda thak-, bece thak-, bãchiya thak- | thah- | ||||
| look | sa- | sa- | dekh-, ca-, taka- | sa- | ||||
| open | khul- | kúa- | khol-, khul- | uid-, khúl- | ||||
| play | khel- | xél- | khel- | |||||
| pull | tan- | ṭan- | ṭan- | |||||
| push | thel- | ṭel-, dekka- | ṭhel- | |||||
| read | porh/poh/por- | foṛ- | poṛ- | foṛ- | ||||
| run | dour-, daur- | douṛ- | douṛa-, choṭ-, chuṭ- | dũr- | ||||
| say | ko-, mat-, bul- | xo-, mat- | bol-, ko- | ho- | ho- | |||
| scratch | ãsür- | xawza-, xamsa- | ãcoṛ de-, ãcṛa-, khamca- | |||||
| see | dekh- | dex- | dekh- | sa- | ||||
| sew | xi-, sila-, bo- (weave) | sia- | śela-, śila | |||||
| sing | ɡa-, gan ga- | ɡa- | ɡa-, gan ga- | |||||
| sit | boh- | bo- | boś- | bo- | ||||
| sleep | xu-, ɡhuma-, tüponi za/mar- | hut-, ɡúma- | ɡhuma-, śo-, śu- | ɡhum za- | ||||
| smell | xuṅ- | huṅ(ɡ)- | śũk-, śõk- | ũ- | ||||
| spit | thu pela-, pik-, pik pela- | sef fal-, fik fal- (betel nut/leaf) | thu phel-, thu phal- | |||||
| split | phal- | atra- | bhag kor-, bhang- | |||||
| squeeze | sep-, hẽs- | sif- | cap-, pesh-, cip- | |||||
| stand | thio ho-, thia- | uba- | dãṛa-, khaṛa- | thio- | tía- | |||
| stab | khũs-, han- | kus-, gauua- | ||||||
| suck | suh-, sup-, xüh- | sua- | chosh-, chush- | |||||
| swell | ful-, fit- | phuler | ||||||
| swim | xatũr- | hatra- | śatar kor-, shatra- | |||||
| think | bhab-, sinta kor-, sint- | bab-, sinta xor- | bhab-, cinta kôr-, mone kôr- | |||||
| throw | dolia- | ița-, iṭa mar- | chõṛ-, ḍhêla mar-, dol- | |||||
| tie | bandh- | ban(d)- | bãdh- | |||||
| vomit | bomi kor- | bait xor- | bomi kor- | |||||
| walk | khüz karh-, bul- | aṭ- | hãṭ- | ãd- | ||||
| want | lag-, bisar- | maɡ-, sa- | ca- | sa- | ||||
| wash | dhu- | dó- | dho- | dú- | ||||
| wipe | mos-, müs- | fus-, mus- | moch-, much-, poch-, puch- | |||||
| English | Assamese | Sylheti | Bengali | Chakma | Chittagonian | Kamata | Rohingya | Hajong |
See also
References
- Toulmin, Mathew W S (2006). Reconstructing linguistic history in a dialect continuum: The Kamta, Rajbanshi, and Northern Deshi Bangla subgroup of Indo-Aryan (PhD). The Australian National University. p. 305.
- Suniti Kumar Chaterjee (1926). The origin and development of Bengali language. p. 140.
- "Assamese". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- "Bengali". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- Kim, Amy; Kim, Seung. Bishnupriya (Manipuri) speakers in Bangladesh: a sociolinguistic survey (PDF). SIL INTERNATIONAL. p. 11. Retrieved 4 October 2020.
- ^ "Chakma". Ethnologue. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- "Chakma". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- "Chittagonian". Ethnologue. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- "Chittagonian". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- Hajong, Phillips & Phillips (2008, p. 1)
- "Hajong".
- ^ "Hajong". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- Minahan, James B. (30 August 2012). Ethnic Groups of South Asia and the Pacific: An Encyclopedia: An Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, Calif.: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-59884-660-7.
Generally, the Rajbongshi language is known as Rangpuri in Bangladesh and Kamta or Rajbangshi in India. The language is usually written in Bengali script in Bangladesh, while the Kamtapura script is favored in India. In Nepal, the language is Devanagari script which is also sometimes used by the Indian Rajbongshis.
- ^ "Rangpuri". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- "As a ritual of purgation they are discarding the Bengali /r/ with a dot and the same is replaced with the original /r/ with a diagonal slash, as used in Assamese script despite the fact that the Rajbanshis in Bengal have been conditioned to use the Bengali /r/ owing to the long processes of forceful imposition of Bengali language upon them." (Pradhani 2012:52)
- "Rohingya". Ethnologue. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- "Rohingya". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- "Surjapuri". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- ^ "Sylheti". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- "Tangchangya". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
Bibliography
- Hajong, Abonis; Phillips, D; Phillips, V (2008), Hajong–English Phrase Book (PDF), SIL International
- Pradhani, Jyotirmoy (2012). "Resonance of Identity in Rajbanshi Poetry" (PDF). The NEHU Journal. X (1).
| Indo-Aryan languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dardic |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Northern |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Northwestern |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Western |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Central |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eastern |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Southern |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Old | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Middle |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proto- languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unclassified |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pidgins and creoles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||