| Revision as of 06:30, 20 March 2004 editWhisperToMe (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users663,056 edits +SW Asia← Previous edit | Revision as of 08:08, 20 March 2004 edit undoWhisperToMe (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users663,056 edits +SW AsiaNext edit → | ||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
| {{msg:OPEC}} | {{msg:OPEC}} | ||
| {{msg:Southwest_Asia}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 08:08, 20 March 2004
- This article is about the country of Kuwait. For the capital city with the same name, see Kuwait City
The State of Kuwait is a small oil-rich monarchy on the coast of the Persian Gulf, enclosed by Saudi Arabia in the south and Iraq in the north. Kuwait is in Southwest Asia.
| ||||
| National motto: None | ||||
 | ||||
| Official language | Arabic | |||
| Capital | Kuwait | |||
| Emir | Jabir Al Sabah | |||
| Crown Prince | Saad Al Sabah | |||
| Prime minister | Sabah al-Ahmad al-Jabir al-Sabah | |||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 152nd 17,820 km² Negligible | |||
| Population
- Density | Ranked 141st
115/km² | |||
| Independence | June 19, 1961 | |||
| Currency | Dinar | |||
| Time zone | UTC +3 | |||
| National anthem | Al-Nasheed Al-Watani | |||
| Internet TLD | .KW | |||
| Calling Code | 965 | |||
History
Main article: History of Kuwait
Kuwait has been a part of the Abbasid empire from the 8th century, and was later incorporated in the Ottoman Empire (16th century), where it was eventually granted some degree of autonomy as a principality; the current ruling family are descendants from these princes.
In 1899, growing British influence led to Kuwait becoming a British protectorate. This status ended with independence in 1961, by which time the discovery of oil had made the nation a wealthy one, attracting many immigrant laborers (which are not granted citizenship).
After being allied with Iraq during the Iran-Iraq War, it was occupied and annexed by Iraq in August 1990. An American-led alliance repelled the Iraqi forces and reinstated the emir.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Kuwait
Chief of state is the Emir, a semi-heriditary title. The emir appoints the prime minister, whom until recently was also the crown prince. A council of ministers aids the prime minister in his task as head of government. The parliament, or Majlis al-Umma, consists of 50 members, who are chosen in elections held every four years. As Kuwaiti citizenship is very restricted, only 10% of the population is eligible to vote.
See also: al-Sabah Royal Family
Governorates
Main article: Governorates of Kuwait
Kuwait is divided into 5 governorates (muhafazat):
Geography
Main article: Geography of Kuwait
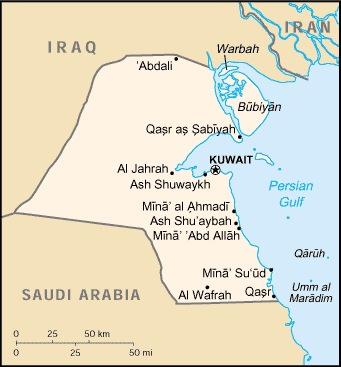
Kuwait consists mostly of desert, with little altitude difference. The climate is dry and hot. On the north coast of the Persian Gulf, an number of islands is situated, largest of which is Bubiyan. It is considered to be one of the fifteen states that comprise the so-called "Cradle of Humanity"
The major cities are the capital Kuwait, Salmiya (most inhabitants) and Hawalli.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Kuwait
Kuwait is a small, rich, relatively open economy with proved crude oil reserves of 94 billion barrels (15 km³) - 10% of world reserves. Petroleum accounts for nearly half of GDP, 90% of export revenues, and 75% of government income. Kuwait's climate limits agricultural development. Consequently, with the exception of fish, it depends almost wholly on food imports. About 75% of potable water must be distilled or imported. Higher oil prices put the FY99/00 budget into a $2 billion surplus. The FY00/01 budget covers only nine months because of a change in the fiscal year. The budget for FY01/02 envisioned higher expenditures for salaries, construction, and other general categories. Kuwait continues its discussions with foreign oil companies to develop fields in the northern part of the country.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Kuwait
About 80% of the Kuwaiti population is Arab; the non-Kuwaiti Arabs contain a large group of Egyptians and also stateless Arabs, locally known as Bidoon (an Arabic word meaning without and different from Bedouin). Other large groups of immigrants include Indians, Bangladeshis, Pakistanis, and Filipinos. Kuwait formerly had a large Palestinian population, though most of them were forced out of the country after PLO leader Yassir Arafat's support of Iraq during the Iraqi occupation of Kuwait.
The official language is Arabic, although English is generally understood. Some immigrants also speak their own local languages. About 85% of the Kuwait are Muslims, mostly Sunni.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Kuwait
Miscellaneous topics
External Links
| Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) | |
|---|---|