| Revision as of 11:51, 21 January 2013 edit93.34.1.67 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 11:59, 21 January 2013 edit undoJingiby (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers, Rollbackers62,608 edits Undo POV - pusher. As per sources.Next edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Synthesis|date=May 2010}} | {{Synthesis|date=May 2010}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Further|Genetic history of Europe|Archaeogenetics of the Near East}} | ||
| In ] the question has been debated whether the modern ] is significantly related to other ], or whether they are rather derived from indigenous populations of ] which were ] during the Middle Ages. The contribution of the Central Asian genetics to the modern Turkish people has been debated and become the subject of several studies. As a result, several studies have concluded that the historical (pre-Islamic) and indigenous Anatolian groups are the primary source of the present-day Turkish population,<ref name=antigens57></ref><ref name=Yardumian_et_al>Yardumian, A., & Schurr, T. G. (2011). Who Are the Anatolian Turks?. Anthropology & Archeology Of Eurasia, 50(1), 6-42. doi:10.2753/AAE1061-1959500101</ref><ref name="Hodoglugil_et_al2">Hodoğlugil, U., & Mahley, R. W. (2012). Turkish Population Structure and Genetic Ancestry Reveal Relatedness among Eurasian Populations. Annals Of Human Genetics, 76(2), 128-141. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2011.00701.x </ref><ref name=eurostudy></ref><ref name=humangenetics112></ref><ref name=stanford></ref><ref name=euroasia></ref> in addition to in addition to neighboring peoples,<ref name="Hodoglugil_et_al2"/> such as ],<ref></ref> and central Asian ].<ref name=Hodoglugil_et_al2/> | |||
| In ] the question has been debated whether the modern ] is significantly related to other ], ] and ] peoples and ], or whether they are rather derived from indigenous populations pre-islamic of ] origin which were ] after the Middle Ages. The contribution of the Central Asian genetics to the modern Turkish people has been debated and become the subject of several studies. As a result, the studies of genetics on the people of Turkey have indicated that the modern Anatolian people are genetically influenced by ] and ] populations<ref></ref> as well as the contribution of their Central Asian and Middle East roots. | |||
| ==DNA studies on modern Anatolia== | |||
| A genetic study based on modern male Anatolian Y-chromosome DNA has revealed gene flow from multiple geographic origins, which may correspond to various migrations over time. The predominant male lineages of ] males are shared with people of ] and neighbouring ] and ] populations (47.8%). Lineages related to ], ] and ] were far less prevalent among the males sampled (25.3%). Furthermore research using HLA profiles stemming from Modern Anatolian population groups suggests a lineages of ethnic ] origin groups related to local (pre-islamic) ] and ] who lived in Anatolia since the ] (26.9%). No genetic signals for intrusions during the ] at around 1200 BC or later ] invasions could be detected. Y-chromosome ] G-M201 was implied to have a possible association with the ].<ref>{{Cite journal |first=C. |last=Cinnioğlu |first2=Roy |last2=King |first3=Toomas |last3=Kivisild |last4=''et al.'' |year=2004 |title=Excavating Y-chromosome haplotype strata in Anatolia |journal=Human Genetics |volume=114 |issue=2 |pages=127–148 |doi=10.1007/s00439-003-1031-4 |pmid=14586639 |first4=E |last5=Atasoy |first5=S |last6=Cavalleri |first6=GL |last7=Lillie |first7=AS |last8=Roseman |first8=CC |last9=Lin |first9=AA |postscript=<!--None--> }}</ref>. It was concluded that subsequent invasions, if they occurred, had few invaders in comparison to populations already settled by 2000 BC, i.e. Anatolian ], ], ], ] and ]-] groups, and to a lesser degree ], ]. The populations present in Anatolia from 2000 BC to 1200 BC may have given rise to the genetic make-up of the present-day Greek, Kurdish, Armenian, Arabic, Indian, Ethiopian and Turkish populations.<ref>http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/118967462/abstract</ref> | |||
| ==Central Asian and Uralic connection== | ==Central Asian and Uralic connection== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The question to what extent a gene flow from ] to ] has contributed to the current gene pool of the Turkish people, and what the role is in this of the 11th century invasion by ], has been the subject of several studies. A factor that makes it difficult to give reliable |
The question to what extent a gene flow from ] to ] has contributed to the current gene pool of the Turkish people, and what the role is in this of the 11th century invasion by ], has been the subject of several studies. A factor that makes it difficult to give reliable estimates, is the problem of distinguishing between the effects of different migratory episodes. Several studies have concluded that the historical and indigenous Anatolian groups are the primary source of the present-day Turkish population.<ref name=antigens57/><ref name=Yardumian_et_al/><ref name="Hodoglugil_et_al2"/><ref name=eurostudy/><ref name=humangenetics112/><ref name=stanford/><ref name=euroasia/> Thus, although the Turks carried out an invasion with ] significance, including the introduction of the ] and ], the genetic significance from ] might have been slight.<ref name=eurostudy/><ref name=med_pops></ref> | ||
| Some of the ] originated from Central Asia and therefore are possibly related with ].<ref name=Keyser-Tracqui_et_al>Christine Keyser-Tracqui, Eric Crubézy, Bertrand Ludes, Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Analysis of a 2,000-Year-Old Necropolis in the Egyin Gol Valley of Mongolia, The American Journal of Human Genetics, Volume 73, Issue 2, August 2003, Pages 247-260, ISSN 0002-9297, 10.1086/377005</ref> A majority (89%) of the Xiongnu sequences can be classified as belonging to an ] ] and nearly 11% belong to ] ].<ref name=Keyser-Tracqui_et_al/> This finding indicates that the contacts between European and Asian populations were anterior to the Xiongnu culture,<ref name=Keyser-Tracqui_et_al/> and it confirms results reported for two samples from an early 3rd century B.C. ]-] population.<ref name=Clisson2002>{{cite journal | |||
| | author = Clisson, I.; Keyser, C.; Francfort, H. P.; Crubezy, E.; Samashev, Z.; Ludes, B. | | author = Clisson, I.; Keyser, C.; Francfort, H. P.; Crubezy, E.; Samashev, Z.; Ludes, B. | ||
| | year = 2002 | | year = 2002 | ||
| Line 18: | Line 17: | ||
| | title = Genetic analysis of human remains from a double inhumation in a frozen kurgan in Kazakhstan | | title = Genetic analysis of human remains from a double inhumation in a frozen kurgan in Kazakhstan | ||
| | pmid = 12376844 | | pmid = 12376844 | ||
| }}</ref> | |||
| }}</ref> and the result of the report by Carol G. Thomas about ] and ] origins ascribable to local anatolic population. <ref name="Thomas1988">{{cite book|author=Carol G. Thomas|title=Paths from ancient Greece|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=NAwVAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA27|accessdate=12 June 2011|year=1988|publisher=BRILL|isbn=978-90-04-08846-7|pages=27–50}}</ref> <ref>{{harvnb|Heffner|1927|pp=123–124}}.</ref>{{r|group=Note|b}} | |||
| According to another archeological and genetic study in 2010, the paternal Y-chromosome R1a, which is considered as an Indo-European marker, was found in three skeletons in 2000-year-old elite ] cemetery in Northeast Asia, which supports Kurgan expansion hypothesis for the Indo-European expansion from the Volga steppe region.<ref>Kim et al. A western Eurasian male is found in 2000-year-old elite Xiongnu cemetery in Northeast Mongolia, Am J Phys Anthropol. 2010 Jul;142(3):429-40, quoted pg.2 "The Kurgan expansion hypothesis explains the IndoEuropean expansion from the Volga steppe region (Gimbutas, 1973; Mallory, 1989).The paternal Y-chromosome single nucleotide polymorphisms (Y-SNP) R1a1 is considered as an Indo-European marker, supporting Kurgan expansion hypothesis (Zerjal et al., 1999; Kharkov et al., 2004; Haak et al., 2008). Recent finding of R1a1 in the Krasnoyarsk area east of Siberia marks the eastward expansion of the early Indo-Europeans (Keyser-Tracqui et al., 2009). R1a1 was not found in Scytho-Siberian skeletons from the Seby¨stei site of Altai Republic or in Xiongnu skeletons from Egyin Gol of Mongolia (KeyserTracqui et al., 2009)." quoted p.10: ", paternal, maternal, and biparental genetic analyses were done on three Xiongnu tombs of Northeast Mongolia 2,000 years ago. We showed for the first time that an Indo-European with paternal R1a1 and maternal U2e1 was present in the Xiongnu Empire of ancient Mongolia"</ref> As the R1a was found in Xiongnu people<ref>Kim et al. A western Eurasian male is found in 2000-year-old elite Xiongnu cemetery in Northeast Mongolia, Am J Phys Anthropol. 2010 Jul;142(3):429-40</ref> and the present-day people of Central Asia<ref>Xue et al. Male Demography in East Asia: A North–South Contrast in Human Population Expansion Times, Genetics. 2006April; 172(4): 2431–2439. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.054270</ref> Analysis of skeletal remains from sites attributed to the Xiongnu provides an identification of dolichocephalic Mongoloid, ethnically distinct from neighboring populations in present-day Mongolia.<ref>Fu ren da xue (Beijing, China), S.V.D. Research Institute, Society of the Divine Word - 2003 </ref> | |||
| According to the study, Modern Turkish Anatolian peoples may have some ancestors who originated in an area north of Mongolia at the end of the Xiongnu period (3rd century BCE to the 2nd century CE), since modern Anatolian Turks appear to have some common genetic markers with the remains found at the Xiongnu period graves in Mongolia.<ref name=Henke2001>{{cite journal | |||
| | author = Henke, J.; Henke, L.; Chatthopadhyay, P.; Kayser, Manfred; Dülmer, M.; Cleef, S.; Pöche, H.; Felske-Zech, H. | |||
| | title = Application of Y-chromosomal STR haplotypes to forensic genetics | |||
| | year = 2001 | |||
| | journal = Croatian Medical Journal | |||
| | volume = 42 | |||
| | issue = 3 | |||
| | pages = 292–297 | |||
| | url = http://www.cmj.hr/2001/42/3/11387642.pdf | |||
| | pmid = 11387642 | |||
| }}</ref> Moreover, the ] (female linkeage) sequence shared by four of these paternal relatives were also found in Turkish individuals,<ref name=Comas1996>{{Cite journal | |||
| | author = Comas, M.C.; Sánchez-Gómez, M.; Cornen, G.; de Kaenel, E | |||
| | year = 1996 | |||
| | title = Serpentinized peridotite breccia and olistostrome on basement highs of the Iberia Abyssal Plain: implications for tectonic margin evolution | |||
| | booktitle = Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program | |||
| | volume = 149 | |||
| | doi = 10.2973/odp.proc.sr.149.228.1996 | |||
| | url = http://www-odp.tamu.edu/publications/149_SR/VOLUME/CHAPTERS/SR149_36.PDF | |||
| }}</ref> suggesting a possible Turkic origin of these ancient specimens.<ref name=touchette/><ref name=Richards2000>{{cite journal | |||
| | author = Martin Richards, Vincent Macaulay, Eileen Hickey, Emilce Vega, Bryan Sykes, Valentina Guida, Chiara Rengo, Daniele Sellitto, Fulvio Cruciani, Toomas Kivisild, Richard Villems, Mark Thomas, Serge Rychkov, Oksana Rychkov, Yuri Rychkov, Mukaddes Gölge, Dimitar Dimitrov, Emmeline Hill11, Dan Bradley, Valentino Romano, Francesco Calì, Giuseppe Vona, Andrew Demaine, Surinder Papiha, Costas Triantaphyllidis, Gheorghe Stefanescu, Jiři Hatina, Michele Belledi, Anna Di Rienzo, Andrea Novelletto, Ariella Oppenheim, Søren Nørby, Nadia Al-Zaheri, Silvana Santachiara-Benerecetti, Rosaria Scozzari, Antonio Torroni, and Hans-Jürgen Bandelt | |||
| | title = Tracing European founder lineages in the Near Eastern mtDNA pool | |||
| | journal = American Journal of Human Genetics | |||
| | year = 2000 | |||
| | month = November | |||
| | volume = 67 | |||
| | issue = 5 | |||
| | pages = 1251–1276 | |||
| | url = http://www.stats.gla.ac.uk/~vincent/founder2000/ | |||
| | doi = 10.1016/S0002-9297(07)62954-1 | |||
| | pmid = 11032788 | |||
| | pmc = 1288566 | |||
| }}</ref> According to another archeological and genetic study in 2010, the paternal Y-chromosome R1a, which is considered as an Indo-European marker, was seldom found in three skeletons in 2000-year-old elite ] cemetery in Northeast Asia, which supports Kurgan expansion hypothesis for the Indo-European expansion from the Volga steppe region.<ref>Kim et al. A western Eurasian male is found in 2000-year-old elite Xiongnu cemetery in Northeast Mongolia, Am J Phys Anthropol. 2010 Jul;142(3):429-40, quoted pg.2 "The Kurgan expansion hypothesis explains the IndoEuropean expansion from the Volga steppe region (Gimbutas, 1973; Mallory, 1989). The paternal Y-chromosome single nucleotide polymorphisms (Y-SNP) R1a1 is considered as an Indo-European marker, supporting Kurgan expansion hypothesis (Zerjal et al., 1999; Kharkov et al., 2004; Haak et al., 2008). Recent finding of R1a1 in the Krasnoyarsk area east of Siberia marks the eastward expansion of the early Indo-Europeans (Keyser-Tracqui et al., 2009). R1a1 was not found in Scytho-Siberian skeletons from the Seby¨stei site of Altai Republic or in Xiongnu skeletons from Egyin Gol of Mongolia (KeyserTracqui et al., 2009)." quoted p.10: ", paternal, maternal, and biparental genetic analyses were done on three Xiongnu tombs of Northeast Mongolia 2,000 years ago. We showed for the first time that an Indo-European with paternal R1a1 and maternal U2e1 was slightly present in the Xiongnu Empire of ancient Mongolia"</ref> As the R1a was found in Xiongnu people<ref>Kim et al. A western Eurasian male is found in 2000-year-old elite Xiongnu cemetery in Northeast Mongolia, Am J Phys Anthropol. 2010 Jul;142(3):429-40</ref> and the present-day people of Central Asia<ref>Xue et al. Male Demography in East Asia: A North–South Contrast in Human Population Expansion Times, Genetics. 2006April; 172(4): 2431–2439. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.054270</ref> A majority (89%) of the Xiongnu mtDNA sequences can be classified as belonging to ] ]s, and nearly 11% belong to ] ]s. This finding indicates that the contacts between ] and ] and ] populations were anterior to the Xiongnu culture Well-preserved bodies in Xiongnu and pre-Xiongnu tombs in the Mongolian Republic and southern Siberia show both 'Mongoloid' and 'Caucasian' features<ref> The Great Empires of the Ancient World - Thomas Harrison - 2009 - 288 page</ref> but are predominantly Mongoloid with some admixture of European physical stock, nonetheless the Xiongnu shared many cultural traits with their Indo-European neighbors, such as horse racing, sword worship.<ref>Ancient bronzes, ceramics, and seals: the Nasli M. Heeramaneck Collection of ancient Near Eastern, central Asiatic, and European art, gift of the Ahmanson Foundation</ref> Analysis of skeletal remains from sites attributed to the Xiongnu provides an identification of dolichocephalic Mongoloid, ethnically distinct from neighboring populations in present-day Mongolia.<ref>Fu ren da xue (Beijing, China), S.V.D. Research Institute, Society of the Divine Word - 2003</ref> Russian and Chinese anthropological and craniofacial studies show that the Xiongnu were physically very heterogenous, with six different population clusters showing different degrees of Mongoloid and Caucasoid physical traits. These clusters point to significant cross-regional migrations (both east to west and west to east) that likely started in the Neolithic period and continued to the medieval/Mongolian period.<ref>Tumen D., "Anthropology of Archaeological Populations from Northeast Asia</ref> | |||
| According to a different genetic research on 75 individuals from various parts of ], Mergen et al revealed that genetic structure of the mtDNAs in the ] population bears similarities to |
According to a different genetic research on 75 individuals from various parts of ], Mergen et al revealed that genetic structure of the mtDNAs in the ] population bears similarities to Turkic Central Asian populations. The neighbour-joining tree built from segment I sequences for Turkish and the other populations (French, Bulgarian, British, Finland, Greek, German, Kazakhs, Uighurs and Kirghiz) indicated two poles. Turkic Central Asian populations, Turkish population and British population formed one pole, and European populations formed the other, which revealed Turkish population bears more similarities to ] population and ].<ref>Hatice Mergen et al. Mitochondrial DNA sequence variation in the Anatolian Peninsula (Turkey), Journal of Genetics, Vol. 83, No.1, April 2004, article p.46 and fig.4 or http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15240908</ref> | ||
| Nevertheless, today's Turkish people are more closely related with the Balkan populations than to the ] populations,<ref name=METU></ref><ref></ref> and a study looking into allele frequencies suggested that there was a lack of genetic relationship between the Mongols and the Turks, despite the historical relationship of their languages (The Turks and Germans were equally distant to all three Mongolian populations).<ref></ref> In addition, another study looking into HLA genes allele distributions indicated that Anatolians did not significantly differ from other Mediterranean populations.<ref name=med_pops></ref> Multiple studies suggested an ] ] dominance-driven ] model to explain the adoption of ] by ] indigenous inhabitants.<ref name=Yardumian_et_al/><ref name=euroasia/> | |||
| ==Haplogroup distributions in Turkish people== | ==Haplogroup distributions in Turkish people== | ||
| According to Cinnioglu et al., (2004)<ref name="cinnioglu 2004"></ref> there are many Y-DNA haplogroups present in Turkey. The majority haplogroups are primarily shared with Middle Eastern, |
According to Cinnioglu et al., (2004)<ref name="cinnioglu 2004"></ref> there are many Y-DNA haplogroups present in Turkey. The majority haplogroups are primarily shared with Middle Eastern, Caucasian, and European populations such as haplogroups E3b, G, J, I, R1a, R1b, K and T which form 78.5% from the Turkish ] (without R1b, K, and which notably occur elsewhere, it is 59.3%) and contrast with a smaller share of haplogroups related to Central Asia (N and Q)- 5.7% (but it rises to 36% if K, R1a, R1b and L- which infrequently occur in Central Asia, but are notable in many other Western Turkic groups), India H, R2 - 1.5% and Africa A, E3*, E3a - 1%. Some of the percentages identified were: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| *]=24% - J2 (M172) Typical of populations of Caucasus, the Near East, Southeast Europe, Southwest Asia with a moderate distribution through much of ], South Asia, and North Africa. | |||
| *]=24% - J2 (M172) Typical of populations of Arabic Peninsula<ref name = "AbuAmero2009">{{cite journal | last1 = Abu-Amero | first1 = Khaled K. | last2 = Hellani | first2 = Ali | last3 = Gonzalez | first3 = Ana M. | author-separator =, | last4 = Larruga | author-name-separator= | first4 = Jose M| year = 2009 | last5 = Cabrera | first5 = Vicente M | last6 = Underhill | first6 = Peter A| title = Saudi Arabian Y-Chromosome diversity and its relationship with nearby regions | url = | journal = BMC Genetics | volume = 10 | issue = | page = 59 | doi = 10.1186/1471-2156-10-59 | pmc = 2759955 | pmid=19772609}}</ref> , the Near East, North Africa, Southwest Asia, ] <ref name="yunusbaev2006"/><ref name="cinnioglu2004"/> <ref name="Varzari2006">Alexander Varzari, "" (2006)</ref> with a moderate distribution through much of ], South Asia, and South East Europe. | |||
| *]=14.7% -Typical of Western Europeans, Eurasian People, and typical of ] in the Central Asia <ref>Klyosov A.A. ''"The principal mystery in the relationship of Indo-European and Türkic linguistic families, and an attempt to solve it with the help of DNA genealogy: reflections of a non-linguist"''//Proceedings of Russian Academy of DNA Genealogy (ISSN 1942-7484), Vol. 3, No 1, pp. 3 - 58</ref><ref>Y Haplogroups of the World </ref> | *]=14.7% -Typical of Western Europeans, Eurasian People, and typical of ] in the Central Asia <ref>Klyosov A.A. ''"The principal mystery in the relationship of Indo-European and Türkic linguistic families, and an attempt to solve it with the help of DNA genealogy: reflections of a non-linguist"''//Proceedings of Russian Academy of DNA Genealogy (ISSN 1942-7484), Vol. 3, No 1, pp. 3 - 58</ref><ref>Y Haplogroups of the World </ref> | ||
| *]=10.9% - Typical of people from the ] and to a lesser extent the Middle East. | *]=10.9% - Typical of people from the ] and to a lesser extent the Middle East. | ||
| *]=10.7% - Typical of people from |
*]=10.7% - Typical of people from the ] | ||
| *]=9% - Typical amongst people from the |
*]=9% - Typical amongst people from the Arabian Peninsula and ] (ranging from 3% from Turks around ] to 12% in ]). | ||
| *]=6.9% - Typical of |
*]=6.9% - Typical of Central Asian, Caucasus, ] people, Eastern Europeans and Indo-Aryan people. | ||
| *]=5.3% - Typical of Central Europeans, Western Caucasian and Balkan populations. | *]=5.3% - Typical of Central Europeans, Western Caucasian and Balkan populations. | ||
| *]=4.5% - Typical of Asian populations and |
*]=4.5% - Typical of Asian populations and Caucasian populations. | ||
| *]=4.2% - Typical of Indian Subcontinent and ] populations. | *]=4.2% - Typical of Indian Subcontinent and ] populations. | ||
| *]=3.8% - Typical of Uralic, Siberian and Altaic populations. | *]=3.8% - Typical of Uralic, Siberian and Altaic populations. | ||
| *]=2.5% - Typical of |
*]=2.5% - Typical of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, Northeast African and South Asian populations | ||
| *]=1.9% - Typical of Northern Altaic |
*]=1.9% - Typical of Northern Altaic populations. | ||
| ==Further research on Turkish Y-DNA groups== | |||
| ]ern, ]n and ]n populations<ref name="Varzari et al. (2007)">Varzari et al. (2007) Population history of the Dniester-Carpathians: evidence from Alu markers. J Hum Genet. 2007;52(4):308-16. </ref>]] | |||
| ===Further research on Turkish Y-DNA groups=== | |||
| A study from Turkey by Gokcumen (2008)<ref></ref><ref></ref> took into account oral histories and historical records. They went to four settlements in Central Anatolia and did not do a random selection from a group of university students like many other studies. Accordingly here are the results: | A study from Turkey by Gokcumen (2008)<ref></ref><ref></ref> took into account oral histories and historical records. They went to four settlements in Central Anatolia and did not do a random selection from a group of university students like many other studies. Accordingly here are the results: | ||
| Line 81: | Line 49: | ||
| '''2)''' An older Turkish village center that did not receive much migration was about 25% N and 25% J2a with 3% G and close to 30% of some sort of R1 but mostly R1b. | '''2)''' An older Turkish village center that did not receive much migration was about 25% N and 25% J2a with 3% G and close to 30% of some sort of R1 but mostly R1b. | ||
| ==Other Studies== | |||
| In 2001, Benedetto et al revealed that Central Asian genetic contribution to the current Anatolian ] gene pool was estimated as roughly 30%, by comparing the populations of ], ], and Turkic-speaking people of ]. <ref></ref> In 2003, Cinnioğlu et al. made a research of ] including the samples from eight regions of Turkey, without classifying the ethnicity of the people, which indicated that high resolution ] analysis totally provides evidence of a detectable weak signal (<9%) of gene flow from Central Asia.<ref>"Excavating Y-chromosome haplotype strata in Anatolia." Human Genetics 114:2 (January 2004): pages 127-148. First published electronically on October 29, 2003. 523</ref> In 2006, Berkman concluded that the true Central Asian contribution to Anatolia for both males and females were assumed to be 22%, with respect to the Balkans.<ref>Ceren Berkman, Comparative Analyses for the Central Asian Contribution to Anatolian Gene Pool with Reference to Balkans, p.98, METU, Sep. 2006 quoted "Lower male than female contribution from Central Asia to Anatolia was obtained. The situation was explained by invoking the idea of homogenization between the males of the Balkans and Anatolia. Since females could not migrate alone, the true Central Asian contribution for both males and females were assumed to be 22%."</ref> In 2011 ] and ] published their study "Who Are the Anatolian Turks? A Reappraisal of the Anthropological Genetic Evidence." They revealed the impossibility of long-term, and continuing genetic contacts between Anatolia and Siberia, and confirmed the presence of significant mitochondrial DNA and Y-chromosome divergence between this regions, with minimal admixture. The research confirms also the lack of mass migration and suggested that it was irregular punctuated migration events that engendered large-scale shifts in language and culture among Anatolia's diverse autochthonous inhabitants.<ref>Yardumian A, Schurr TG. 2011. Who are the Anatolian Turks? A reappraisal of the anthropological genetic evidence. Archeol Anthropol Eurasia 50(1): 6-43 (Summer).</ref> According to a 2012 study on ethnic Turks of Turkey, Hodoğlugil revealed that there is a significant overlap between Turks and Middle Easterners and a relationship with Europeans and South and Central Asians when Kyrgyz samples are genotyped and analysed. It displays a genetic ancestry for the Turks of 65% Middle Eastern, 20% European and 15% Central Asian. However, the Turkish ] is unique, and there is an admixture of Turkish people reflecting the population migration patterns.<ref>Uğur Hodoğlugil and Robert W. Mahley - Turkish Population Structure and Genetic Ancestry Reveal Relatedness among Eurasian Populations, Annals of Human Genetics, March 2012, Volume 76, Issue 2, pg. 128-141. Abstract "Turkey has experienced major population movements. Population structure and genetic relatedness of samples from three regions of Turkey, using over 500,000 SNP genotypes, were compared together with Human Genome Diversity Panel (HGDP) data. To obtain a more representative sampling from Central Asia, Kyrgyz samples (Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan) were genotyped and analysed. Principal component (PC) analysis reveals a significant overlap between Turks and Middle Easterners, North Africans, Eastern African and marginally a relationship with Europeans and South Asians; however, the Turkish genetic structure is unique. FRAPPE, STRUCTURE, and phylogenetic analyses support the PC analysis depending upon the number of parental ancestry components chosen. For example, supervised STRUCTURE (K=3) illustrates a genetic ancestry for the Turks of 65% Middle Eastern (95% CI, 42-49), 20% European (95% CI, 36-44) and 15% Central Asian (95% CI, 13-16), whereas at K=4 the genetic ancestry of the Turks was 18% European (95% CI, 35-42), 65% Middle Eastern (95% CI, 33-38), 18% South Asian (95% CI, 16-19) and 9% Central Asian (95% CI, 7-11). PC analysis and FRAPPE/STRUCTURE results from three regions in Turkey (Aydin, Istanbul and Kayseri) were superimposed, without clear subpopulation structure, suggesting sample homogeneity. Thus, this study demonstrates admixture of Turkish people reflecting the population migration patterns."</ref> | |||
| </ref>]] | |||
| In 2001, Benedetto et al revealed that Central Asian genetic contribution to the current Anatolian ] gene pool was estimated as roughly 30%, by comparing the populations of ], and Turkic-speaking people of ].<ref></ref> In 2003, Cinnioğlu et al. made a research of ] including the samples from eight regions of Turkey, without classifying the ethnicity of the people, which indicated that high resolution ] analysis totally provides evidence of a detectable weak signal (<9%) of gene flow from Central Asia.<ref>"Excavating Y-chromosome haplotype strata in Anatolia." Human Genetics 114:2 (January 2004): pages 127-148. First published electronically on October 29, 2003. 523</ref> In 2006, Berkman concluded that the true Central Asian contribution to Anatolia for both males and females were assumed to be 22%, with respect to the Balkans.<ref>Ceren Berkman, Comparative Analyses for the Central Asian Contribution to Anatolian Gene Pool with Reference to Balkans, p.98, METU, Sep. 2006 quoted "Lower male than female contribution from Central Asia to Anatolia was obtained. The situation was explained by invoking the idea of homogenization between the males of the Balkans and Anatolia. Since females could not migrate alone, the true Central Asian contribution for both males and females were assumed to be 22%."</ref> In 2011 ] and ] published their study "Who Are the Anatolian Turks? A Reappraisal of the Anthropological Genetic Evidence." They revealed the impossibility of long-term, and continuing genetic contacts between Anatolia and Siberia, and confirmed the presence of significant mitochondrial DNA and Y-chromosome divergence between this regions, with minimal admixture. The research confirms also the lack of mass migration and suggested that it was irregular punctuated migration events that engendered large-scale shifts in language and culture among Anatolia's diverse autochthonous inhabitants.<ref>Yardumian A, Schurr TG. 2011. Who are the Anatolian Turks? A reappraisal of the anthropological genetic evidence. Archeol Anthropol Eurasia 50(1): 6-43 (Summer).</ref> According to a 2012 study on ethnic Turks of Turkey, Hodoğlugil revealed that there is a significant overlap between Turks and Middle Easterners and a relationship with Europeans and South and Central Asians when Kyrgyz samples are genotyped and analysed. It displays a genetic ancestry for the Turks of 45% Middle Eastern, 40% European and 15% Central Asian. However, the Turkish ] is unique, and there is an admixture of Turkish people reflecting the population migration patterns.<ref>Uğur Hodoğlugil and Robert W. Mahley - Turkish Population Structure and Genetic Ancestry Reveal Relatedness among Eurasian Populations, Annals of Human Genetics, March 2012, Volume 76, Issue 2, pg. 128-141. Abstract "Turkey has experienced major population movements. Population structure and genetic relatedness of samples from three regions of Turkey, using over 500,000 SNP genotypes, were compared together with Human Genome Diversity Panel (HGDP) data. To obtain a more representative sampling from Central Asia, Kyrgyz samples (Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan) were genotyped and analysed. Principal component (PC) analysis reveals a significant overlap between Turks and Middle Easterners and a relationship with Europeans and South and Central Asians; however, the Turkish genetic structure is unique. FRAPPE, STRUCTURE, and phylogenetic analyses support the PC analysis depending upon the number of parental ancestry components chosen. For example, supervised STRUCTURE (K=3) illustrates a genetic ancestry for the Turks of 45% Middle Eastern (95% CI, 42-49), 40% European (95% CI, 36-44) and 15% Central Asian (95% CI, 13-16), whereas at K=4 the genetic ancestry of the Turks was 38% European (95% CI, 35-42), 35% Middle Eastern (95% CI, 33-38), 18% South Asian (95% CI, 16-19) and 9% Central Asian (95% CI, 7-11). PC analysis and FRAPPE/STRUCTURE results from three regions in Turkey (Aydin, Istanbul and Kayseri) were superimposed, without clear subpopulation structure, suggesting sample homogeneity. Thus, this study demonstrates admixture of Turkish people reflecting the population migration patterns."</ref> | |||
| Furthermore, and maybe more so, in a study called 'The Genetics of Modern Assyrians and their Relationship to Other People of the Middle East' Dr. Joel J. Elias, a Professor at University of California School of Medicine at San Francisco conducted a genetic test about Turkish people. The aim was to discover the origins of the peoples of the Middle East presently, and over time. He found that "In spite of the complex history of the Middle East and the great number of internal group migrations revealed by history, as well as the mosaic of cultures and languages, the region is relatively homogeneous" in relation to the people that speak different languages throughout the region including Iranian and Kurdish (Indo-European), Turkish (Turkic), African (Ethiopian) and Arabic, Assyrian and Aramaic (Semitic)<ref>The Genetics of Modern Assyrians and their Relationship to Other People of the Middle East></ref>. A group of Armenian scientists conducted a study about the origins of the Turkish people in relation to Armenians. Savak Avagian; director of Armenia's bone marrow bank found that “Turks and Armenians were the two societies throughout the world that were genetically close to each other. Arabic people and Jews are also in same genetic pool as well Kurds are also in same genetic pool”<ref>ref name= Turks, Armenians share similar genes, say scientists (Hürriyet Daily News) ></ref>. | |||
| Furthermore, and maybe more so, in a study called 'The Genetics of Modern Assyrians and their Relationship to Other People of the Middle East' Dr. Joel J. Elias, a Professor at University of California School of Medicine at San Francisco conducted a genetic test about Turkish people. The aim was to discover the origins of the peoples of the Middle East presently, and over time. He found that "In spite of the complex history of the Middle East and the great number of internal group migrations revealed by history, as well as the mosaic of cultures and languages, the region is relatively homogeneous" in relation to the people that speak different languages throughout the region including Iranian and Kurdish (Indo-European), Turkish (Turkic) and Arabic, Assyrian and Aramaic (Semitic).<ref>The Genetics of Modern Assyrians and their Relationship to Other People of the Middle East></ref> A group of Armenian scientists conducted a study about the origins of the Turkish people in relation to Armenians. Savak Avagian; director of Armenia's bone marrow bank found that “Turks and Armenians were the two societies throughout the world that were genetically close to each other. Kurds are also in same genetic pool”.<ref>ref name= Turks, Armenians share similar genes, say scientists (Hürriyet Daily News) ></ref> | |||
| Further genetic studies conducted by ] have revealed that Turkish have strong correlation with Near Eastern groups and Indian and Indo-Europeans speaking populations.<ref name="Genes"> — University of Chicago, American Journal of Human Genetics . Retrieved 4 June 2006. {{dead link|date=June 2010| bot=DASHBot}}</ref> | |||
| This study is partially supported by another one, based on Y-Chromosome haplogroups.<ref> – Regueiro M, Cadenas AM, Gayden T, Underhill PA, Herrera RJ, Department of Biological Sciences, Florida International University, University Park, OE 304, Miami, FL 33199, USA, ]</ref> | |||
| The findings of this study reveal many common genetic markers found among the Turkish people from the ] river of ] to the ] of ]. This correlates with the ] spoken from the ] to Kurdish areas in the ] region and eastwards to western Pakistan and Tajikistan and parts of Uzbekistan in ]. The extensive gene flow is perhaps an indication of the spread of Turkish-speaking people, whose languages are now spoken mainly on the Anatolian plateau and adjacent regions. | |||
| Another recent study of the genetic landscape of Turkey, Iranian Palteau and Near East Area was done by a team of ] geneticists led by Dr. Maziar Ashrafian Bonab.<ref name="Dr. Bonab page">{{dead link|date=July 2010}} — ''Department of Genetics, University of Cambridge'' . Retrieved 9 June 2006. {{Wayback|url=http://www.gen.cam.ac.uk/Research/balloux.htm|date =20060618211320|bot=DASHBot}}{{dead link|date=July 2010}}</ref> Bonab remarked that his group had done extensive ] testing on different language groups, including ], ] and non Indo-European speakers.<ref name="Iran Cambridge Genetic Study"/> The study found that the Kurdish of Turkey do not have a similar FSt and other genetic markers found in Anatolians and Europeans. However, the genetic Fst and other genetic traits like MRca and mtDNA of Kurdish were identical to ]. Zazaki of Turkey also show very close genetic ties to Kurds.<ref>{{Cite journal|author=S. Farjadian1, A. Ghaderi |title=HLA class II similarities in Iranian Kurds and Azeris |journal=International Journal of Immunogenetics |volume=34 |issue=6 |pages=457–463 |year=2007 |month=December|pmid= 18001303|doi=10.1111/j.1744-313X.2007.00723.x}}</ref>. Another result of the study using the ] of modern Turkish males found relatively high frequencies of ], similar results were found with males of surrounding ]ern countries, namely North East African haplogroups are predominant in ] and ] populations.<ref name="lucotte">{{cite journal|title=Brief communication: Y-chromosome haplotypes in Egypt |year=2001|last=Lucotte|doi=10.1002/ajpa.10190|url=http://wysinger.homestead.com/haplotypes_in_egypt.pdf|first1=G.|last2=Mercier|first2=G.|journal=American Journal of Physical Anthropology|volume=121|pages=63–6|pmid=12687584|issue=1}}</ref> | |||
| == See also == | == See also == | ||
| {{Col-begin}} | |||
| {{Col-3}} | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| {{Col-3}} | |||
| {{Portal box|Molecular Anthropology|Evolutionary biology}} | |||
| {{Col-end}} | |||
| == References and notes == | == References and notes == | ||
| {{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
| http://en.wikipedia.org/Haplogroup_J2_%28Y-DNA%29 | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Genetic Origins Of The Turkish People}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Genetic Origins Of The Turkish People}} | ||
| Line 145: | Line 74: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| http://en.wikipedia.org/Haplogroup_J2_%28Y-DNA%29 | |||
Revision as of 11:59, 21 January 2013
| This article or section possibly contains synthesis of material that does not verifiably mention or relate to the main topic. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. (May 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In population genetics the question has been debated whether the modern Turkish population is significantly related to other Turkic peoples, or whether they are rather derived from indigenous populations of Anatolia which were culturally assimilated during the Middle Ages. The contribution of the Central Asian genetics to the modern Turkish people has been debated and become the subject of several studies. As a result, several studies have concluded that the historical (pre-Islamic) and indigenous Anatolian groups are the primary source of the present-day Turkish population, in addition to in addition to neighboring peoples, such as Balkan peoples, and central Asian Turkic people.
Central Asian and Uralic connection

The question to what extent a gene flow from Central Asia to Anatolia has contributed to the current gene pool of the Turkish people, and what the role is in this of the 11th century invasion by Oghuz Turks, has been the subject of several studies. A factor that makes it difficult to give reliable estimates, is the problem of distinguishing between the effects of different migratory episodes. Several studies have concluded that the historical and indigenous Anatolian groups are the primary source of the present-day Turkish population. Thus, although the Turks carried out an invasion with cultural significance, including the introduction of the Turkish language and Islam, the genetic significance from Central Asia might have been slight.
Some of the Turkic peoples originated from Central Asia and therefore are possibly related with Xiongnu. A majority (89%) of the Xiongnu sequences can be classified as belonging to an Asian haplogroups and nearly 11% belong to European haplogroups. This finding indicates that the contacts between European and Asian populations were anterior to the Xiongnu culture, and it confirms results reported for two samples from an early 3rd century B.C. Scytho-Siberian population.
According to another archeological and genetic study in 2010, the paternal Y-chromosome R1a, which is considered as an Indo-European marker, was found in three skeletons in 2000-year-old elite Xiongnu cemetery in Northeast Asia, which supports Kurgan expansion hypothesis for the Indo-European expansion from the Volga steppe region. As the R1a was found in Xiongnu people and the present-day people of Central Asia Analysis of skeletal remains from sites attributed to the Xiongnu provides an identification of dolichocephalic Mongoloid, ethnically distinct from neighboring populations in present-day Mongolia.
According to a different genetic research on 75 individuals from various parts of Turkey, Mergen et al revealed that genetic structure of the mtDNAs in the Turkish population bears similarities to Turkic Central Asian populations. The neighbour-joining tree built from segment I sequences for Turkish and the other populations (French, Bulgarian, British, Finland, Greek, German, Kazakhs, Uighurs and Kirghiz) indicated two poles. Turkic Central Asian populations, Turkish population and British population formed one pole, and European populations formed the other, which revealed Turkish population bears more similarities to Turkic Central Asian population and British people.
Nevertheless, today's Turkish people are more closely related with the Balkan populations than to the Central Asian populations, and a study looking into allele frequencies suggested that there was a lack of genetic relationship between the Mongols and the Turks, despite the historical relationship of their languages (The Turks and Germans were equally distant to all three Mongolian populations). In addition, another study looking into HLA genes allele distributions indicated that Anatolians did not significantly differ from other Mediterranean populations. Multiple studies suggested an elite cultural dominance-driven linguistic replacement model to explain the adoption of Turkish language by Anatolian indigenous inhabitants.
Haplogroup distributions in Turkish people
According to Cinnioglu et al., (2004) there are many Y-DNA haplogroups present in Turkey. The majority haplogroups are primarily shared with Middle Eastern, Caucasian, and European populations such as haplogroups E3b, G, J, I, R1a, R1b, K and T which form 78.5% from the Turkish Gene pool (without R1b, K, and which notably occur elsewhere, it is 59.3%) and contrast with a smaller share of haplogroups related to Central Asia (N and Q)- 5.7% (but it rises to 36% if K, R1a, R1b and L- which infrequently occur in Central Asia, but are notable in many other Western Turkic groups), India H, R2 - 1.5% and Africa A, E3*, E3a - 1%. Some of the percentages identified were:
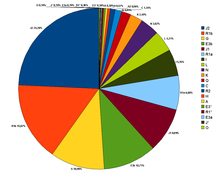
- J2=24% - J2 (M172) Typical of populations of Caucasus, the Near East, Southeast Europe, Southwest Asia with a moderate distribution through much of Central Asia, South Asia, and North Africa.
- R1b=14.7% -Typical of Western Europeans, Eurasian People, and typical of Uyghurs in the Central Asia
- G=10.9% - Typical of people from the Caucasus and to a lesser extent the Middle East.
- E1b1b1=10.7% - Typical of people from the Mediterranean
- J1=9% - Typical amongst people from the Arabian Peninsula and Dagestan (ranging from 3% from Turks around Konya to 12% in Kurds).
- R1a=6.9% - Typical of Central Asian, Caucasus, Altaic people, Eastern Europeans and Indo-Aryan people.
- I=5.3% - Typical of Central Europeans, Western Caucasian and Balkan populations.
- K=4.5% - Typical of Asian populations and Caucasian populations.
- L=4.2% - Typical of Indian Subcontinent and Khorasan populations.
- N=3.8% - Typical of Uralic, Siberian and Altaic populations.
- T=2.5% - Typical of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, Northeast African and South Asian populations
- Q=1.9% - Typical of Northern Altaic populations.
Further research on Turkish Y-DNA groups
A study from Turkey by Gokcumen (2008) took into account oral histories and historical records. They went to four settlements in Central Anatolia and did not do a random selection from a group of university students like many other studies. Accordingly here are the results:
1) At an Afshar village whose oral stories tell they come from Central Asia they found that 57% come from haplogroup L, 13% from haplogroup Q, 3% from haplogroup N thus indicating that the L haplogroups in Turkey are of Central Asian heritage rather than Indian, although these Central Asians would have gotten the L markers from the Indians from the beginning. These Asian groups add up to 73% in this village. Furthermore 10% of these Afshars were E3a and E3b. Only 13% were J2a, the most common haplogroup in Turkey.
2) An older Turkish village center that did not receive much migration was about 25% N and 25% J2a with 3% G and close to 30% of some sort of R1 but mostly R1b.
Other Studies

In 2001, Benedetto et al revealed that Central Asian genetic contribution to the current Anatolian mtDNA gene pool was estimated as roughly 30%, by comparing the populations of Mediterranean Europe, and Turkic-speaking people of Central Asia. In 2003, Cinnioğlu et al. made a research of Y-DNA including the samples from eight regions of Turkey, without classifying the ethnicity of the people, which indicated that high resolution SNP analysis totally provides evidence of a detectable weak signal (<9%) of gene flow from Central Asia. In 2006, Berkman concluded that the true Central Asian contribution to Anatolia for both males and females were assumed to be 22%, with respect to the Balkans. In 2011 Aram Yardumian and Theodore G. Schurr published their study "Who Are the Anatolian Turks? A Reappraisal of the Anthropological Genetic Evidence." They revealed the impossibility of long-term, and continuing genetic contacts between Anatolia and Siberia, and confirmed the presence of significant mitochondrial DNA and Y-chromosome divergence between this regions, with minimal admixture. The research confirms also the lack of mass migration and suggested that it was irregular punctuated migration events that engendered large-scale shifts in language and culture among Anatolia's diverse autochthonous inhabitants. According to a 2012 study on ethnic Turks of Turkey, Hodoğlugil revealed that there is a significant overlap between Turks and Middle Easterners and a relationship with Europeans and South and Central Asians when Kyrgyz samples are genotyped and analysed. It displays a genetic ancestry for the Turks of 45% Middle Eastern, 40% European and 15% Central Asian. However, the Turkish genetic structure is unique, and there is an admixture of Turkish people reflecting the population migration patterns.
Furthermore, and maybe more so, in a study called 'The Genetics of Modern Assyrians and their Relationship to Other People of the Middle East' Dr. Joel J. Elias, a Professor at University of California School of Medicine at San Francisco conducted a genetic test about Turkish people. The aim was to discover the origins of the peoples of the Middle East presently, and over time. He found that "In spite of the complex history of the Middle East and the great number of internal group migrations revealed by history, as well as the mosaic of cultures and languages, the region is relatively homogeneous" in relation to the people that speak different languages throughout the region including Iranian and Kurdish (Indo-European), Turkish (Turkic) and Arabic, Assyrian and Aramaic (Semitic). A group of Armenian scientists conducted a study about the origins of the Turkish people in relation to Armenians. Savak Avagian; director of Armenia's bone marrow bank found that “Turks and Armenians were the two societies throughout the world that were genetically close to each other. Kurds are also in same genetic pool”.
See also
- Demographics of Turkey
- History of the Turkish people
- Archaeogenetics of the Near East
- Genetic history of Europe
References and notes
- ^ (2001) HLA alleles and haplotypes in the Turkish population: relatedness to Kurds, Armenians and other Mediterraneans Tissue Antigens 57 (4), 308–317
- ^ Yardumian, A., & Schurr, T. G. (2011). Who Are the Anatolian Turks?. Anthropology & Archeology Of Eurasia, 50(1), 6-42. doi:10.2753/AAE1061-1959500101
- ^ Hodoğlugil, U., & Mahley, R. W. (2012). Turkish Population Structure and Genetic Ancestry Reveal Relatedness among Eurasian Populations. Annals Of Human Genetics, 76(2), 128-141. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2011.00701.x
- ^ Y-chromosomal diversity in Europe is clinal and influenced primarily by geography, rather than by language.
- ^ Testing hypotheses of language replacement in the neighbouring Caucasus: evidence from the Y-chromosome. Human genetics. 2003, vol. 112, no3, pp. 255–261. ISSN 0340-6717
- ^ Excavating Y-chromosome haplotype strata in Anatolia. Department of Genetics, Stanford University School of Medicine, 300 Pasteur Drive, Stanford, CA 94305-5120, USA.
- ^ The Eurasian Heartland: A continental perspective on Y-chromosome diversity.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, Vol. 98, No. 18 (Aug. 28, 2001), pp. 10244–10249.
- Alu insertion polymorphisms in the Balkans and the origins of the Aromuns. Annals of Human Genetics.Volume 68 Issue 2 Page 120-127, March 2004.
- Mergen et al. Mitochondrial DNA sequence variation in the Anatolian Peninsula (Turkey), Journal of Genetics, Vol. 83, No.1, April 2004, P.46, Figure 4. http://www.ias.ac.in/jgenet/Vol83No1/39.pdf & http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15240908
- ^ Tissue Antigens Volume 60 Issue 2 Page 111-121, August(2002) Population genetic relationships between Mediterranean populations determined by HLA allele distribution and a historic perspective. Tissue Antigens 60 (2), 111–121
- ^ Christine Keyser-Tracqui, Eric Crubézy, Bertrand Ludes, Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Analysis of a 2,000-Year-Old Necropolis in the Egyin Gol Valley of Mongolia, The American Journal of Human Genetics, Volume 73, Issue 2, August 2003, Pages 247-260, ISSN 0002-9297, 10.1086/377005
- Clisson, I.; Keyser, C.; Francfort, H. P.; Crubezy, E.; Samashev, Z.; Ludes, B. (2002). "Genetic analysis of human remains from a double inhumation in a frozen kurgan in Kazakhstan". International Journal of Legal Medicine. 116 (5): 304–308. doi:10.1007/s00414-002-0295-x. PMID 12376844.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Kim et al. A western Eurasian male is found in 2000-year-old elite Xiongnu cemetery in Northeast Mongolia, Am J Phys Anthropol. 2010 Jul;142(3):429-40, quoted pg.2 "The Kurgan expansion hypothesis explains the IndoEuropean expansion from the Volga steppe region (Gimbutas, 1973; Mallory, 1989).The paternal Y-chromosome single nucleotide polymorphisms (Y-SNP) R1a1 is considered as an Indo-European marker, supporting Kurgan expansion hypothesis (Zerjal et al., 1999; Kharkov et al., 2004; Haak et al., 2008). Recent finding of R1a1 in the Krasnoyarsk area east of Siberia marks the eastward expansion of the early Indo-Europeans (Keyser-Tracqui et al., 2009). R1a1 was not found in Scytho-Siberian skeletons from the Seby¨stei site of Altai Republic or in Xiongnu skeletons from Egyin Gol of Mongolia (KeyserTracqui et al., 2009)." quoted p.10: ", paternal, maternal, and biparental genetic analyses were done on three Xiongnu tombs of Northeast Mongolia 2,000 years ago. We showed for the first time that an Indo-European with paternal R1a1 and maternal U2e1 was present in the Xiongnu Empire of ancient Mongolia"
- Kim et al. A western Eurasian male is found in 2000-year-old elite Xiongnu cemetery in Northeast Mongolia, Am J Phys Anthropol. 2010 Jul;142(3):429-40
- Xue et al. Male Demography in East Asia: A North–South Contrast in Human Population Expansion Times, Genetics. 2006April; 172(4): 2431–2439. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.054270
- Fu ren da xue (Beijing, China), S.V.D. Research Institute, Society of the Divine Word - 2003
- Hatice Mergen et al. Mitochondrial DNA sequence variation in the Anatolian Peninsula (Turkey), Journal of Genetics, Vol. 83, No.1, April 2004, article p.46 and fig.4 Online Read or http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15240908
- Alu insertion polymorphisms and an assessment of the genetic contribution of Central Asia to Anatolia with respect to the Balkans. Department of Biological Sciences, Middle East Technical University, 06531 Ankara, Turkey. American Journal of Physical Anthropoly 2008 May;136(1):11-8.
- Alu insertion polymorphisms in the Balkans and the origins of the Aromuns. Annals of Human Genetics.Volume 68 Issue 2 Page 120-127, March 2004.
- Tissue Antigens. Volume 61 Issue 4 Page 292–299, April 2003. Genetic affinities among Mongol ethnic groups and their relationship to Turks
- ^ Excavating Y-chromosome haplotype strata in Anatolia. Hum Genet (2004) 114 : 127–148, Springer-Verlag 2003
- Klyosov A.A. "The principal mystery in the relationship of Indo-European and Türkic linguistic families, and an attempt to solve it with the help of DNA genealogy: reflections of a non-linguist"//Proceedings of Russian Academy of DNA Genealogy (ISSN 1942-7484), Vol. 3, No 1, pp. 3 - 58
- Y Haplogroups of the World Online Edition
- Gokcumen O. et al (2008), Ethnohistorical and genetic survey of four Central Anatolian settlements, a dissertation/thesis
- Gokcumen O. Ethnohistorical and genetic survey of four central Anatolian settlements, dissertation, Univ. of Pennsylvania, 2008.
- Varzari et al. (2007) Population history of the Dniester-Carpathians: evidence from Alu markers. J Hum Genet. 2007;52(4):308-16.
- Online Reference Di Benedetto G, Ergüven A, Stenico M, Castrì L, Bertorelle G, Togan I, Barbujani G., DNA diversity and population admixture in Anatolia, Am J Phys Anthropol. 115(2):144-56, 2001. quoted: "The Turkic language was introduced in Anatolia at the start of this millennium, by nomadic Turkmen groups from Central Asia. Whether that cultural transition also had significant population-genetics consequences is not fully understood. Three nuclear microsatellite loci, the hypervariable region I of the mitochondrial genome, six microsatellite loci of the Y chromosome, and one Alu insertion (YAP) were amplified and typed in 118 individuals from four populations of Anatolia. For each locus, the number of chromosomes considered varied between 51-200. Genetic variation was large within samples, and much less so between them. The contribution of Central Asian genes to the current Anatolian gene pool was quantified using three different methods, considering for comparison populations of Mediterranean Europe, and Turkic-speaking populations of Central Asia. The most reliable estimates suggest roughly 30% Central Asian admixture for both mitochondrial and Y-chromosome loci. That (admittedly approximate) figure is compatible both with a substantial immigration accompanying the arrival of the Turkmen armies (which is not historically documented), and with continuous gene flow from Asia into Anatolia, at a rate of 1% for 40 generations. Because a military invasion is expected to more deeply affect the male gene pool, similar estimates of admixture for female- and male-transmitted traits are easier to reconcile with continuous migratory contacts between Anatolia and its Asian neighbors, perhaps facilitated by the disappearance of a linguistic barrier between them." [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11385601 Online Reference
- "Excavating Y-chromosome haplotype strata in Anatolia." Human Genetics 114:2 (January 2004): pages 127-148. First published electronically on October 29, 2003. 523
- Ceren Berkman, Comparative Analyses for the Central Asian Contribution to Anatolian Gene Pool with Reference to Balkans, p.98, METU, Sep. 2006 quoted "Lower male than female contribution from Central Asia to Anatolia was obtained. The situation was explained by invoking the idea of homogenization between the males of the Balkans and Anatolia. Since females could not migrate alone, the true Central Asian contribution for both males and females were assumed to be 22%."
- Yardumian A, Schurr TG. 2011. Who are the Anatolian Turks? A reappraisal of the anthropological genetic evidence. Archeol Anthropol Eurasia 50(1): 6-43 (Summer).
- Uğur Hodoğlugil and Robert W. Mahley - Turkish Population Structure and Genetic Ancestry Reveal Relatedness among Eurasian Populations, Annals of Human Genetics, March 2012, Volume 76, Issue 2, pg. 128-141. Abstract "Turkey has experienced major population movements. Population structure and genetic relatedness of samples from three regions of Turkey, using over 500,000 SNP genotypes, were compared together with Human Genome Diversity Panel (HGDP) data. To obtain a more representative sampling from Central Asia, Kyrgyz samples (Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan) were genotyped and analysed. Principal component (PC) analysis reveals a significant overlap between Turks and Middle Easterners and a relationship with Europeans and South and Central Asians; however, the Turkish genetic structure is unique. FRAPPE, STRUCTURE, and phylogenetic analyses support the PC analysis depending upon the number of parental ancestry components chosen. For example, supervised STRUCTURE (K=3) illustrates a genetic ancestry for the Turks of 45% Middle Eastern (95% CI, 42-49), 40% European (95% CI, 36-44) and 15% Central Asian (95% CI, 13-16), whereas at K=4 the genetic ancestry of the Turks was 38% European (95% CI, 35-42), 35% Middle Eastern (95% CI, 33-38), 18% South Asian (95% CI, 16-19) and 9% Central Asian (95% CI, 7-11). PC analysis and FRAPPE/STRUCTURE results from three regions in Turkey (Aydin, Istanbul and Kayseri) were superimposed, without clear subpopulation structure, suggesting sample homogeneity. Thus, this study demonstrates admixture of Turkish people reflecting the population migration patterns."
- The Genetics of Modern Assyrians and their Relationship to Other People of the Middle East>
- ref name= Turks, Armenians share similar genes, say scientists (Hürriyet Daily News) >
http://en.wikipedia.org/Haplogroup_J2_%28Y-DNA%29
Categories: