| Revision as of 16:29, 13 August 2024 editJc3s5h (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers32,958 editsm Reverted 1 edit by 176.29.171.113 (talk) to last revision by Kovcszaln6Tags: Twinkle Undo← Previous edit | Revision as of 05:27, 7 September 2024 edit undoVery different name (talk | contribs)497 edits Redirected a source link and re-targeted linksTags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web editNext edit → | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| {{M1 year in topic}} | {{M1 year in topic}} | ||
| __NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| '''AD 1''' (''']''') or '''1 CE''' was a ] or ],<ref group="note">Sources disagree regarding the starting day of Julian year Anno Domino I (see ] for further information).</ref> a ] by the ], and a ] by the ]. It is the ] for the ] (AD) Christian ], and the 1st year of the ] and ] of the Christian or ] (CE). | '''AD 1''' (''']''') or '''1 CE''' was a ] or ],<ref group="note">Sources disagree regarding the starting day of Julian year Anno Domino I (see ] for further information).</ref> a ] by the ], and a ] by the ]. It is the ] year for the ] (AD) Christian ], and the 1st year of the ] and ] of the Christian or ] (CE). | ||
| In the ], AD 1 was known as the "Year of the consulship of ] and ]",<ref> |
In the ], AD 1 was known as the "Year of the consulship of ] and ]",<ref>{{Cite web |title=Fasti Capitolini (2) - translation |url=http://www.attalus.org/translate/fasti3.html |access-date=2024-09-07 |website=www.attalus.org}}</ref> and less frequently, as the year {{auc|1|CE|disp=alone|alinks=off}} (see '']''). The denomination "AD 1" for this year has been in consistent use since the mid-] when the Anno Domini (AD) calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. It was the beginning of the ]/]. The preceding year is ]; there is no ] in this numbering scheme. The ''Anno Domini'' dating system was devised in ] by ]. | ||
| The ], a ] reform of the ], was the calendar used by Rome in AD 1. | The ], a ] reform of the ], was the calendar used by Rome in AD 1. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
| == Births == | == Births == | ||
| * ], Roman ] (d. ]) | * ], Roman ] (d. ]) | ||
| * ], King of ] (d. |
* ], King of ] (d. ]) | ||
| * ], Roman stoic philosopher was born in ] (d. ])<ref>{{cite web | series=Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy | first=Katja | last=Vogt | title=Seneca | url=https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/seneca/ | access-date=February 23, 2024 | date=February 13, 2024}}</ref> | * ], Roman stoic philosopher was born in ] (d. ])<ref>{{cite web | series=Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy | first=Katja | last=Vogt | title=Seneca | url=https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/seneca/ | access-date=February 23, 2024 | date=February 13, 2024}}</ref> | ||
| == Deaths == | == Deaths == | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
| {{Legend|Lime|New settlements after 100 AD}} | {{Legend|Lime|New settlements after 100 AD}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| {{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
Revision as of 05:27, 7 September 2024
For other uses, see AD 1 (disambiguation). "1 AD" redirects here. For other uses, see 1 AD (disambiguation).Calendar year
| Millennium: | 1st millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Decades: | |
| Years: |
| AD 1 by topic |
|---|
| Leaders |
| Categories |
| Gregorian calendar | AD 1 I |
| Ab urbe condita | 754 |
| Assyrian calendar | 4751 |
| Balinese saka calendar | N/A |
| Bengali calendar | −593 – −592 |
| Berber calendar | 951 |
| Buddhist calendar | 545 |
| Burmese calendar | −637 |
| Byzantine calendar | 5509–5510 |
| Chinese calendar | 庚申年 (Metal Monkey) 2698 or 2491 — to — 辛酉年 (Metal Rooster) 2699 or 2492 |
| Coptic calendar | −283 – −282 |
| Discordian calendar | 1167 |
| Ethiopian calendar | −7 – −6 |
| Hebrew calendar | 3761–3762 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | 57–58 |
| - Shaka Samvat | N/A |
| - Kali Yuga | 3101–3102 |
| Holocene calendar | 10001 |
| Iranian calendar | 621 BP – 620 BP |
| Islamic calendar | 640 BH – 639 BH |
| Javanese calendar | N/A |
| Julian calendar | AD 1 I |
| Korean calendar | 2334 |
| Minguo calendar | 1911 before ROC 民前1911年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −1467 |
| Seleucid era | 312/313 AG |
| Thai solar calendar | 543–544 |
| Tibetan calendar | 阳金猴年 (male Iron-Monkey) 127 or −254 or −1026 — to — 阴金鸡年 (female Iron-Rooster) 128 or −253 or −1025 |
AD 1 (I) or 1 CE was a common year starting on Saturday or Sunday, a common year starting on Saturday by the proleptic Julian calendar, and a common year starting on Monday by the proleptic Gregorian calendar. It is the epoch year for the Anno Domini (AD) Christian calendar era, and the 1st year of the 1st century and 1st millennium of the Christian or Common Era (CE).
In the Roman Empire, AD 1 was known as the "Year of the consulship of Gaius Caesar and Lucius Paullus", and less frequently, as the year AUC 754 (see ab urbe condita). The denomination "AD 1" for this year has been in consistent use since the mid-medieval period when the Anno Domini (AD) calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. It was the beginning of the Christian era/common era. The preceding year is 1 BC; there is no year 0 in this numbering scheme. The Anno Domini dating system was devised in AD 525 by Dionysius Exiguus.
The Julian calendar, a 45 BC reform of the Roman calendar, was the calendar used by Rome in AD 1.
Events
By place
Roman Empire
Asia
- Confucius is given his first royal title (posthumous name) of Baocheng Xuan Ni Gong.
By topic
Religion
- Birth of Jesus, as assigned by Dionysius Exiguus in his anno Domini era according to at least one scholar. However, most scholars think that Dionysius placed the birth of Jesus in the previous year, 1 BC. Furthermore, most modern scholars do not consider Dionysius' calculations authoritative, placing the event several years earlier (see Chronology of Jesus).
Births
- Sextus Afranius Burrus, Roman praetorian prefect (d. AD 62)
- Izates II, King of Adiabene (d. AD 54)
- Seneca the Younger, Roman stoic philosopher was born in Cordoba (d. AD 65)
Deaths
- Amanishakheto, queen of Kush (Nubia)
Gallery
-
 Map of the world in AD 1.
Map of the world in AD 1.
-
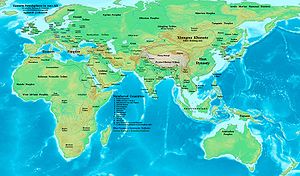 Map of the Eastern Hemisphere in AD 1.
Map of the Eastern Hemisphere in AD 1.
-
 Germanic tribes in Europe in AD 1: Settlements before 750 BC New settlements after 750 BC until 1 AD New settlements until 100 AD New settlements after 100 AD
Germanic tribes in Europe in AD 1: Settlements before 750 BC New settlements after 750 BC until 1 AD New settlements until 100 AD New settlements after 100 AD
References
- "Fasti Capitolini (2) - translation". www.attalus.org. Retrieved September 7, 2024.
- Velleius Paterculus, The Roman History, Book II. p 271.
- Thomas A. Wilson (2003), in Xinzhong Yao (Ed.), RoutledgeCurzon Encyclopedia of Confucianism, "Baocheng Xuan Ni Gong", p. 26.
- Book of Han, 12.351
- ^ Declercq 2000.
- ^ Declercq 2002.
- Dunn 2003.
- Vogt, Katja (February 13, 2024). "Seneca". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Retrieved February 23, 2024.
Sources
- Declercq, Georges (2000). Anno Domini: The origins of the Christian Era. Turnhout, Belgium: Brepols. pp. 143–147. ISBN 978-2503510507.
- Declercq, Georges (2002). "Dionysius Exiguus and the introduction of the Christian Era". Sacris Erudiri. 41. Brussels: Brepols: 165–246. doi:10.1484/J.SE.2.300491. ISSN 0771-7776.
Annotated version of a portion of Anno Domini
- Dunn, James D. G. (2003). Jesus Remembered. Christianity in the Making. Vol. 1. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 324. ISBN 978-0802839312.
Footnotes
- Sources disagree regarding the starting day of Julian year Anno Domino I (see leap year error for further information).