|
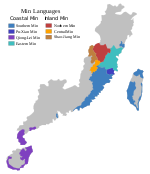
'''Pontianak Teochew''' ({{zh|t=坤甸潮州話|s=坤甸潮州话}}; ]: ''kung¹ diêng⁶ dio⁵ ziu¹ uê'') is a dialect of ] primarily spoken by the ] in ], ], ]. Pontianak Teochew was originally spoken by the ] who migrated from ] in ], ]. Today, however, it serves as the ] for the entire Chinese community in Pontianak.<ref>{{Citation |last=Chiang |first=Bien |title=Ethnic Chinese Enterprises in Indonesia: A Case Study of West Kalimantan |date=2017 |work=Chinese Capitalism in Southeast Asia: Cultures and Practices |pages=131–153 |editor-last=Santasombat |editor-first=Yos |url=https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-10-4696-4_6 |access-date=2025-01-04 |place=Singapore |publisher=Springer |language=en |doi=10.1007/978-981-10-4696-4_6 |isbn=978-981-10-4696-4 |last2=Cheng |first2=Jean Chih-yin}}</ref> The Teochew language has also become a common trade or marketplace language in Pontianak and its surrounding areas.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Thamrin |first=Lily |last2=Suhardi |last3=Veronica |first3=Tjen |last4=Lusi |date=2022 |title=Pergeseran Bahasa Teochew Pada Remaja Tionghoa Teochew di Pontianak |url=https://ejournal.upi.edu/index.php/lokabasa/issue/view/1423 |journal=LOKABASA: Jurnal Kajian Bahasa, Sastra, dan Budaya Daerah serta Pengajarannya |language=en-US |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=91-99 |doi=10.17509/jlb.v10i1 |issn=2338-6193 |eissn=2528-5904}}</ref> |
|
'''Pontianak Teochew''' ({{zh|t=坤甸潮州話|s=坤甸潮州话}}; ]: ''kung¹ diêng⁶ dio⁵ ziu¹ uê'') is a dialect of ] primarily spoken by the ] in ], ], ]. Pontianak Teochew was originally spoken by the ] who migrated from ] in ], ]. Today, however, it serves as the ] for the entire Chinese community in Pontianak.<ref>{{Citation |last=Chiang |first=Bien |title=Ethnic Chinese Enterprises in Indonesia: A Case Study of West Kalimantan |date=2017 |work=Chinese Capitalism in Southeast Asia: Cultures and Practices |pages=131–153 |editor-last=Santasombat |editor-first=Yos |url=https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-10-4696-4_6 |access-date=2025-01-04 |place=Singapore |publisher=Springer |language=en |doi=10.1007/978-981-10-4696-4_6 |isbn=978-981-10-4696-4 |last2=Cheng |first2=Jean Chih-yin}}</ref> Pontianak Teochew has also become a common trade or marketplace language in Pontianak and its surrounding areas.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Thamrin |first=Lily |last2=Suhardi |last3=Veronica |first3=Tjen |last4=Lusi |date=2022 |title=Pergeseran Bahasa Teochew Pada Remaja Tionghoa Teochew di Pontianak |url=https://ejournal.upi.edu/index.php/lokabasa/issue/view/1423 |journal=LOKABASA: Jurnal Kajian Bahasa, Sastra, dan Budaya Daerah serta Pengajarannya |language=en-US |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=91-99 |doi=10.17509/jlb.v10i1 |issn=2338-6193 |eissn=2528-5904}}</ref> |