| Revision as of 03:45, 4 August 2007 editSengkang (talk | contribs)38,820 edits →See also: +← Previous edit | Revision as of 03:46, 4 August 2007 edit undoSengkang (talk | contribs)38,820 editsm →See alsoNext edit → | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| ⚫ | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| ⚫ | *] | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Revision as of 03:46, 4 August 2007
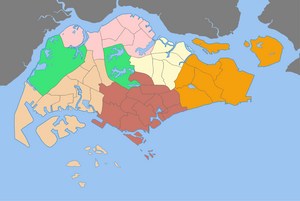
A Development Guide Plan (DGP) is a detailed urban land use plan for each of the 55 areas in Singapore designated by the Urban Redevelopment Authority (URA), Singapore's national planning and conservation authority.
History
In 1991, URA released the revised Concept Plan, which maps out the vision for Singapore's long term physical development for a population of 4 million. With the completion of the Concept Plan, URA proceeded to prepare detailed plans called DGPs for gazetting as the new Master Plan.
For the purpose of preparing the detailed plans, Singapore was divided into 55 planning areas. For each of these areas, a DGP was prepared where the broad vision of the Concept Plan was detailed into specific proposals.
Each DGP covers a planning area with a population of around 150,000 served by a town centre. The planning areas are further divided into sub-zones, each served by a commercial centre. The size of each planning area and its sub-zone varies depending on the land uses, proximity to the Central Area, and existing physical separators such as expressways, rivers, major open spaces and other demarcators.
All the 55 DGPs were completed in December 1998 and were gazetted as the new statutory Master Plan, known as Master Plan 1998. The Master Plan provides a clear guide to landowners on what their land can be used for, and is reviewed every five years.