| Revision as of 20:47, 23 August 2007 view sourceAngelOfSadness (talk | contribs)21,509 editsm Reverted 1 edit by 69.119.252.59 identified as vandalism to last revision by Sammmttt. using TW← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:48, 23 August 2007 view source 69.119.252.59 (talk)No edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| '''Acne Vulgaris''' is an ] disease of the ], caused by changes in the pilosebaceous units (skin structures consisting of a ] and its associated ]). Acne lesions are commonly referred to as ], spots, or zits. | '''Acne Vulgaris''' is an ] disease of the ], caused by changes in the pilosebaceous units (skin structures consisting of a ] and its associated ]). Acne lesions are commonly referred to as ], spots, or zits. | ||
| Acne develops because of impairments of the functioning of skin glands (] and ]), notably blocked follicles. When the immune and circulatory functions of the dermis are impaired, infections occur. | |||
| ] and formation of a plug of ] and ] (a microcomedo) leads to the enlargement of sebaceous glands, especially during the maturation of skin following puberty. Increase in ] production occur with increased ] (]) production at ]. | |||
| A buildup of sebum becomes prone to infection. The immune system attacks the bacteria and filters the ] into segregated pockets that can be from 0.2mm up to 10mm underneath the intact skin surface ]. Surface infections are called zits whereas the deeper ones are called pustules. The repartition of the inflammations is very variable across individuals. Stress and unhealthy lifestyles increase the causes of acne, while improper treatment increases the symptoms. | |||
| Sufferers experience itching and discomfort due to swelling and bacterial overgrowth inside infected glands and adjacent cells, and try and relieve the swelling by crushing acne with their fingers rather than clinically with a sharp sterilised needle. Damage to underlying layers of flesh destroys the integrity of the dermis and creates a weak zone to be attacked by bacteria, and an immune response resulting in more acne draining into the surrounding sebaceous glands. Bruising can also scar and deform the fine structures of the ] so that its function is impaired and can create longer term havens for bacteria. | |||
| The fine structure of the dermis is very intricate, with dozens of specialized cells, sweat glands, oil glands, nerves and capillaries. it is subject to malformation, damage, and infection. Some sebaceous glands grow deformed without a drainage channel through the skin. Others swell by up to 20 times their original size. when these are drained, the walls of the enlarged gland are still intact under the skin and free to accumulate sebum and may or may not become infected. sometimes a pustule forms around a hair strand that has not reached the surface and that has grown more than a centimetre curled inside the sebaceous gland. | |||
| Acne is a highly complicated and variable form of skin infection. It is most common during ], affecting more than 85% of teenagers, but frequently continues into adulthood.<!-- | Acne is a highly complicated and variable form of skin infection. It is most common during ], affecting more than 85% of teenagers, but frequently continues into adulthood.<!-- | ||
Revision as of 20:48, 23 August 2007
This article is about a skin disease commonly found during adolescence. For other acneform skin diseases, see Acne (disambiguation). Medical condition| Acne | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Dermatology, family medicine |
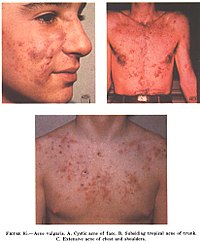
Acne Vulgaris is an inflammatory disease of the skin, caused by changes in the pilosebaceous units (skin structures consisting of a hair follicle and its associated sebaceous gland). Acne lesions are commonly referred to as pimples, spots, or zits.
Acne is a highly complicated and variable form of skin infection. It is most common during adolescence, affecting more than 85% of teenagers, but frequently continues into adulthood. For most people, acne diminishes over time and tends to disappear, or at least decrease, after one reaches his or her early twenties. There is, however, no way to predict how long it will take for it to disappear entirely, and some individuals will continue to suffer from acne decades later, into their thirties and forties and even beyond.
The term acne comes from a corruption of the Greek άκμή (acme in the sense of a skin eruption) in the writings of Aëtius Amidenus. The vernacular term bacne or backne is often used to indicate acne found specifically on one's back.
Symptoms
The most common form of acne is known as "acne vulgaris", meaning "common acne." Many teenagers get this type of acne. Excessive secretion of oils from the sebaceous glands accompanies the plugging of the pores with naturally occurring dead skin cells (corneocytes) blocking hair follicles. The accumulation of these corneocytes in the duct appears to be due to a failure of the normal keratinization process in the skin which usually leads to shedding of skin cells lining the pores. Oil secretions are said to build up beneath the blocked pore, providing a perfect environment for the skin bacteria Propionibacterium acnes and the lipophilic (oil/lipid-loving) yeast Malassezia to multiply uncontrollably. Under the microscope, however, there is no evidence of pooled trapped sebum. Indeed the oil percolates through the plugged duct onto the surface. In response to the bacterial and yeast populations, the skin inflames, producing the visible lesion.
The face and upper neck are the most commonly affected, but the chest, back and shoulders may have acne as well. The upper arms can also have acne, but lesions found there are often keratosis pilaris, not acne. The typical acne lesions are: comedones, papules, pustules, nodules and inflammatory cysts known as cystic acne, one of the more severe forms. These are more inflamed and pus-filled or reddish bumps, that can easily lead to scarring or serious infections. Non-inflamed 'sebaceous cysts', more properly called epidermoid cysts, occur either in association with acne or alone but are not a constant feature. After resolution of acne lesions, prominent unsightly scars may remain.
Aside from scarring, its main effects are psychological, such as reduced self-esteem and, according to at least one study, depression or suicide. Acne usually appears during adolescence, when people already tend to be most socially insecure. Early and aggressive treatment is therefore advocated to lessen the overall impact to individuals.
Causes of acne
There are many misconceptions and rumours about acne. Exactly why some people get acne and some do not is not fully known. It is known to be partly hereditary. Several factors are known to be linked to acne:
- Family history
- Hormonal activity, such as menstrual cycles and puberty
- Stress, through increased output of hormones from the adrenal (stress) glands.
- Hyperactive sebaceous glands, secondary to the three hormone sources above.
- Accumulation of dead skin cells.
- Bacteria in the pores, to which the body becomes 'allergic'.
- Skin irritation or scratching of any sort will activate inflammation.
- Use of anabolic steroids.
- Any medication containing halogens (iodides, chlorides, bromides), lithium, barbiturates, or androgens.
- Exposure to high levels of chlorine compounds, particularly chlorinated dioxins, can cause severe, long-lasting acne, known as Chloracne.
Traditionally, attention has focused mostly on hormone-driven over-production of sebum as the main contributing factor of acne. More recently, more attention has been given to narrowing of the follicle channel as a second main contributing factor. Abnormal shedding of the cells lining the follicle, abnormal cell binding ("hyperkeratinization") within the follicle, and water retention in the skin (swelling the skin and so pressing the follicles shut) have all been put forward as important mechanisms. Several hormones have been linked to acne: the male hormones testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), as well as insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-I). In addition, acne-prone skin has been shown to be insulin resistant .
Development of acne vulgaris in later years is uncommon, although this is the age group for Rosacea which may have similar appearances. True acne vulgaris in adults may be a feature of an underlying condition such as pregnancy and disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome or the rare Cushing's syndrome. Dermatologists are seeing more cases of menopause-associated acne as fewer women replace the natural anti-acne ovarian hormone estradiol whose production fails as women arrive at menopause. The lack of estradiol also causes thinning hair, hot flashes, thin skin, wrinkles, vaginal dryness, and predisposes to osteopenia and osteoporosis as well as triggering acne (known as acne climacterica in this situation).
Diet
There is no widely agreed-upon proof that diet has any effect on most people's acne. Eating greasy foods may get grease on a person's hands: subsequent contact of the hands to the face may exacerbate acne.
Milk
A recent study, based on a survey of 47,335 women, did find a positive epidemiological association between acne and consumption of partially skimmed milk, instant breakfast drink, sherbet, cottage cheese and cream cheese. The researchers hypothesize that the association may be caused by hormones (such as several sex hormones and bovine IGF-I) present in cow milk. Although the association between milk and acne has been definitively shown, the ingredient in the milk responsible for the acne is still unclear. Most dermatologists are awaiting confirmatory research linking diet and acne but some support the idea that acne sufferers should experiment with their diets, and refrain from consuming such fare if they find such food affects the severity of their acne.
Seafood
Seafood often contains relatively high levels of iodine. Iodine is known to make existing acne worse but there is probably not enough to cause an acne outbreak. Still, people who are prone to acne may want to avoid excessive consumption of foods high in iodine.
High carbohydrates/High GI
It has also been suggested that there is a link between a diet high in refined sugars and other processed foods and acne. The theory is that rapidly digested carbohydrate food such as white bread and refined sugars produces an overload in metabolic glucose that is rapidly converted into the types of fat that can build up in sebaceous glands. According to this hypothesis, the startling absence of acne in non-westernized societies could be explained by the low glycemic index of these cultures' diets. Others have cited possible genetic reasons for there being no acne in these populations, but similar populations shifting to these diets do develop acne. Note also that the populations studied consumed no milk or other dairy products. Further research is necessary to establish whether a reduced consumption of high-glycemic foods (such as soft drinks, sweets, white bread) can significantly alleviate acne, though consumption of high-glycemic foods should in any case be kept to a minimum, for general health reasons. Avoidance of 'junk food' with its high fat and sugar content is also recommended. On the other hand there is no evidence that fat alone makes skin oilier or acne worse.
One study suggested that chocolate, french fries, potato chips and sugar, among others, affect acne. A high GI (glycemic index) diet that causes sharp rises in blood sugar worsens acne. If this study's conclusions are verified then a low GI diet may help acne also, but a 2005 review of somewhat dated scientific literature cannot affirm either way. A study in November 2006 in Australia gave a 50% reduction in 12 weeks in mild-moderate facial acne by introducing its subjects to a high protein, low GI diet.
Hygiene
Acne is not caused by dirt. This misconception probably comes from the fact that blackheads look like dirt stuck in the openings of pores. The black color is simply not dirt but compact keratin. In fact, the blockages of keratin that cause acne occur deep within the narrow follicle channel, where it is impossible to wash them away. These plugs are formed by the failure of the cells lining the duct to separate and flow to the surface in the sebum created there by the body.
Sex
Common myths state that masturbation causes acne and, conversely, that celibacy or sexual intercourse can cure it. Sexual activity can lead to hormonal surges and can also serve to relieve stress caused by inactivity or lack of self-confidence, more common in acne sufferers. Healthy sexual activity may improve the psychosomatic metabolism and mental maturity of an individual, but has not been scientifically correlated with changes in acne. Serious levels of inactivity combined with any serious levels of sexual stress worsen an individual's metabolism.
Treatments
Overview of treatment
Acne can be divided into causes and symptoms.
The causes are mostly metabolic pressures from hormonal change and increased stress on the immune system due to lifestyle stress and artificial levels of toxins in the body. These can sometimes be improved through healthy lifestyle, low toxin low sugar natural diets, proper levels of exercise, situational organisation and improvements in stress levels, decent hygiene, gentle skincare, and in more serious cases there is a wide array of clinical methods such as drugs.
The symptoms results from an overactive or poorly drained stressed lymphatic system coping with toxins, sugars and bacteria, in the form of zits and pustules. To clinically treat acne if there is a buildup of pus that remains trapped with no way out after a week of the inflammation, it is far preferable to evacuate it with a sharp sterilised needle, penetrating into the skin and thus creating a channel, than by a sufferer bruising the area and damaging the tissues of the dermis. also antibacterial creams such as Savlon are able to lessen the state of an inflammation from the surface.
Timeline of acne treatment
The history of acne reaches back to the dawn of recorded history. In Ancient Egypt, it is recorded that several pharaohs were acne sufferers. From Ancient Greece comes the English word 'acne' (meaning 'point' or 'peak'). Acne treatments are also of considerable antiquity:
- Ancient Rome: bathing in hot, and often sulfurous, mineral water was one of the few available acne treatments. One of the earliest texts to mention skin problems is De Medicina by the Roman writer Celsus.
- 1800s: Nineteenth century dermatologists used sulphur in the treatment of acne. It was believed to dry the skin.
- 1920s: Benzoyl Peroxide is used
- 1930s: Laxatives were used as a cure for what were known as 'chastity pimples'. Radiation also was used.
- 1950s: When antibiotics became available, it was discovered that they had beneficial effects on acne. They were taken orally to begin with. Much of the benefit was not from killing bacteria but from the anti-inflammatory effects of tetracycline and its relatives. Topical antibiotics became available later.
- 1960s: Tretinoin (original Trade Name Retin A) was found effective for acne. This preceded the development of oral isotretinoin (sold as Accutane and Roaccutane) since the early 1980s.
- 1980s: Accutane is introduced in America
- 1990s: Laser treatment introduced
- 2000s: Blue/red light therapy
Some old treatments, like laxatives, have fallen into disuse but others, like spas, are recovering their popularity.
Available treatments
There are many products sold for the treatment of acne, many of them without any scientifically-proven effects. Generally speaking successful treatments give little improvement within the first week or two; and then the acne decreases over approximately 3 months, after which the improvement starts to flatten out. Treatments that promise improvements within 2 weeks are likely to be largely disappointing. Short bursts of cortisone, quick bursts of antibiotics and many of the laser therapies offer a quick reduction in the redness, swelling and inflammation when used correctly, but none of these empty the pore of all the materials that trigger the inflammation. Emptying the pores takes months.
Modes of improvement are not necessarily fully understood but in general treatments are believed to work in at least 4 different ways (with many of the best treatments providing multiple simultaneous effects):
- normalising shedding into the pore to prevent blockage
- killing P. acnes
- antinflammatory effects
- hormonal manipulation
A combination of treatments can greatly reduce the amount and severity of acne in many cases. Those treatments that are most effective tend to have greater potential for side effects and need a greater degree of monitoring, so a step-wise approach is often taken. Many people consult with doctors when deciding which treatments to use, especially when considering using any treatments in combination. There are a number of treatments that have been proven effective:

Exfoliating the skin

This can be done either mechanically, using an abrasive cloth or a liquid scrub, or chemically. Common chemical exfoliating agents include salicylic acid and glycolic acid, which encourage the peeling of the top layer of skin to prevent a build-up of dead skin cells which combine with skin oil to block pores. It also helps to unblock already clogged pores. Note that the word "peeling" is not meant in the visible sense of shedding, but rather as the destruction of the top layer of skin cells at the microscopic level. Depending on the type of exfoliation used, some visible flaking is possible. Moisturizers and anti-acne topicals containing chemical exfoliating agents are commonly available over-the-counter. Mechanical exfoliation is less commonly used as many benefits derived from the exfoliation are negated by the act of mechanically rubbing and irritating the skin.
Topical bactericidals
Widely available OTC bactericidal products containing benzoyl peroxide may be used in mild to moderate acne. The gel or cream containing benzoyl peroxide is rubbed, twice daily, into the pores over the affected region. Bar soaps or washes may also be used and vary from 2 to 10% in strength. In addition to its therapeutic effect as a keratolytic (a chemical that dissolves the keratin plugging the pores) benzoyl peroxide also prevents new lesions by killing P.acnes. Unlike antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide has the advantage of being a strong oxidizer (essentially a mild bleach) and thus does not appear to generate bacterial resistance. However, it routinely causes dryness, local irritation and redness. A sensible regimen may include the daily use of low-concentration (2.5%) benzoyl peroxide preparations, combined with suitable non-comedogenic moisturisers to help avoid overdrying the skin.
Care must be taken when using benzoyl peroxide, as it can very easily bleach any fabric or hair it comes in contact with.
Other antibacterials that have been used include triclosan, or chlorhexidine gluconate but these are often less effective.
Topical antibiotics
Externally applied antibiotics such as erythromycin, clindamycin, Stiemycin or tetracycline aim to kill the bacteria that are harbored in the blocked follicles. Whilst topical use of antibiotics is equally as effective as oral, this method avoids possible side effects of stomach upset or drug interactions (e.g. it will not affect the oral contraceptive pill), but may prove awkward to apply over larger areas than just the face alone.
Oral antibiotics
Oral antibiotics used to treat acne include erythromycin or one of the tetracycline antibiotics (tetracycline, the better absorbed oxytetracycline, or one of the once daily doxycycline, minocycline or lymecycline). Trimethoprim is also sometimes used (off-label use in UK). However, reducing the P. acnes bacteria will not, in itself, do anything to reduce the oil secretion and abnormal cell behaviour that is the initial cause of the blocked follicles. Additionally the antibiotics are becoming less and less useful as resistant P. acnes are becoming more common. Acne will generally reappear quite soon after the end of treatment—days later in the case of topical applications, and weeks later in the case of oral antibiotics.
It has been found that sub-antimicrobial doses of antibiotics such as minocycline also improve acne. It is believed that minocycline's anti-inflammatory effect also prevents acne. These low doses do not kill bacteria and hence cannot induce resistance.
Hormonal treatments
In females, acne can be improved with hormonal treatments. The common combined oestrogen/progestogen methods of hormonal contraception have some effect, but the anti-testosterone, Cyproterone, in combination with an oestrogen (Diane 35) is particularly effective at reducing androgenic hormone levels. Diane-35 is not available in the USA, but a newer oral contraceptive containing the progestin drospirenone is now available with fewer side effects than Diane 35 / Dianette. Both can be used where blood tests show abnormally high levels of androgens, but are effective even when this is not the case. Along with this, treatment with low dose spironolactone can have anti-androgenetic properties, especially in patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome.
If a pimple is large and/or does not seem to be affected by other treatments, a dermatologist may administer an injection of cortisone directly into it, which will usually reduce redness and inflammation almost immediately. This has the effect of flattening the pimple, thereby making it easier to cover up with makeup, and can also aid in the healing process. Side effects are minimal, but may include a temporary whitening of the skin around the injection point. This method also carries a much smaller risk of scarring than surgical removal.
Topical retinoids
Normalizing the follicle cell lifecycle. A group of medications for this are topical retinoids such as tretinoin (brand name Retin-A), adapalene (brand name Differin) and tazarotene (brand name Tazorac). Like isotretinoin, they are related to vitamin A, but they are administered as topicals and generally have much milder side effects. They can, however, cause significant irritation of the skin. The retinoids appear to influence the cell creation and death lifecycle of cells in the follicle lining. This helps prevent the hyperkeratinization of these cells that can create a blockage. Retinol, a form of vitamin A, has similar but milder effects and is used in many over-the-counter moisturizers and other topical products. Effective topical retinoids have been in use over 30 years but are available only on prescription so are not as widely used as the other topical treatments. Topical retinoids often cause an initial flare up of acne and facial flushing (physiology).
Oral retinoids
Reducing the secretion of oils from the glands. This is done by a daily oral intake of vitamin A derivatives like isotretinoin (marketed as Accutane, Sotret, Claravis) over a period of 4-6 months. It is believed that isotretinoin works primarily by reducing the secretion of oils from the glands, however some studies suggest that it affects other acne-related factors as well. Isotretinoin has been shown to be very effective in treating severe acne and can either improve or clear well over 80% of patients. The drug has a much longer effect than anti-bacterial treatments and will often cure acne for good. The treatment requires close medical supervision by a dermatologist because the drug has many known side effects (many of which can be severe). About 25% of patients may relapse after one treatment. In those cases, a second treatment for another 4-6 months may be indicated to obtain desired results. It is often recommended that one lets a few months pass between the two treatments, because the condition can actually improve somewhat in the time after stopping the treatment and waiting a few months also gives the body a chance to recover. Occasionally a third or even a fourth course is used, but the benefits are often less substantial. The most common side effects are dry skin and occasional nosebleeds (secondary to dry nasal mucosa). Oral retinoids also often cause an initial flare up of acne within a month or so, which can be severe. There are reports that the drug has damaged the liver of patients. For this reason, it is recommended that patients have blood samples taken and examined before and during treatment. In some cases, treatment is terminated due to elevated liver enzymes in the blood, which might be related to liver damage. Others claim that the reports of permanent damage to the liver are unsubstantiated, and routine testing is considered unnecessary by some dermatologists. Blood triglycerides also need to be monitored. However, routine testing are part of the official guidelines for the use of the drug in many countries. Some press reports suggest that isotretinoin may cause depression but as of September 2005 there is no agreement in the medical literature as to the risk. The drug also causes birth defects if women become pregnant while taking it or take it while pregnant. For this reason, female patients are required to use two separate forms of birth control or vow abstinence while on the drug. Because of this, the drug is supposed to be given to females as a last resort after milder treatments have proven insufficient. Restrictive rules (see iPledge Program) for use were put into force in the USA beginning in March 2006 to prevent misuse. This has occasioned widespread editorial comment.
Phototherapy
'Blue' and red light
It has long been known that short term improvement can be achieved with sunlight. However, studies have shown that sunlight worsens acne long-term, as the skin's natural reaction is to produce more oils. More recently, visible light has been successfully employed to treat acne (Phototherapy) - in particular intense violet light (405-420nm) generated by purpose-built fluorescent lighting, dichroic bulbs, LEDs or lasers. Used twice weekly, this has been shown to reduce the number of acne lesions by about 64%; and is even more effective when applied daily. The mechanism appears to be that a porphyrin (Coproporphyrin III) produced within P. acnes generates free radicals when irradiated by 420nm and lower wavelengths of light. Particularly when applied over several days, these free radicals ultimately kill the bacteria. Since porphyrins are not otherwise present in skin, and no UV light is employed, it appears to be safe, and has been licensed by the U.S. FDA. The treatment apparently works even better if used with red visible light (660 nanometer) resulting in a 76% reduction of lesions after 3 months of daily treatment for 80% of the patients; and overall clearance was similar or better than benzoyl peroxide. Unlike most of the other treatments few if any negative side effects are typically experienced, and the development of bacterial resistance to the treatment seems very unlikely. After treatment, clearance can be longer lived than is typical with topical or oral antibiotic treatments; several months is not uncommon. The equipment or treatment, however, is relatively new and reasonably expensive. The equipment can be found in dermatologist offices but is moving towards personal portable devices. There are currently a number of brands coming out with hand held devices that are more affordable but not as powerful.
Photodynamic therapy
In addition, basic science and clinical work by dermatologists Yoram Harth and Alan Shalita and others has produced evidence that intense blue/violet light (405-425 nanometer) can decrease the number of inflammatory acne lesion by 60-70% in 4 weeks of therapy, particularly when the P.acnes is pretreated with delta-aminolevulinic acid (ALA), which increases the production of porphyrins. However this photodynamic therapy is controversial and apparently not published in a peer reviewed journal.
Less widely used treatments
- Azelaic acid (brand names Azelex, Finevin, Skinoren) is suitable for mild, comedonal acne.
- Zinc: Orally administered zinc gluconate has been shown to be effective in the treatment of inflammatory acne, although less so than tetracyclines.
- Tea Tree Oil (Melaleuca Oil) has been used with some success, and has been shown to be an effective anti-inflammatory in skin infections.
- Nicotinamide, (Vitamin B3) used topically in the form of a gel, has been shown in a 1995 study to be more effective than a topical antibiotic used for comparison, as well as having fewer side effects. Topical nicotinamide is available both on prescription and over-the-counter. The property of topical nicotinamide's benefit in treating acne seems to be its anti-inflammatory nature. It is also purported to result in increased synthesis of collagen, keratin, involucrin and flaggrin.
- There are also certain treatments for acne mentioned in Ayurveda using herbs such as Aloe vera, Aruna, Haldi (Turmeric),and Papaya. There is limited evidence from conventional medical studies on these products. Products from Rubia cordifolia, Curcuma longa (commonly known as Turmeric), Hemidesmus indicus (known as ananthamoola or anantmula), and Azadirachta indica (Neem) have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, but not aloe vera.
- Rofecoxib was shown to improve premenstrual acne vulgaris in a placebo controlled study.
Laser treatment
Laser surgery has been in use for some time to reduce the scars left behind by acne, but research has been done on lasers for prevention of acne formation itself. The laser is used to produce one of the following effects:
- to burn away the follicle sac from which the hair grows
- to burn away the sebaceous gland which produces the oil
- to induce formation of oxygen in the bacteria, killing them
Since lasers and intense pulsed light sources cause thermal damage to the skin there are concerns that laser or intense pulsed light treatments for acne will induce hyperpigmented macules (spots) or cause long term dryness of the skin.
The FDA has approved several companies, such as Candela Corp. to use a cosmetic laser for the treatment of acne. Laser treatments such as this have shown to have exceeded 98% reduction in lesion count; and have show to be effective in 4 treatments and with most seeing results in as little as 1. However, laser treatment being relatively new, can be quite expensive.
Future treatments
Because acne appears to have a significant hereditary link, there is some expectation that cheap whole-genome DNA sequencing may help isolate the body mechanisms involved in acne more precisely, possibly leading to a more satisfactory treatment. (Crudely put, take the DNA of large samples of people with significant acne and of people without, and let a computer search for statistically strong differences in genes between the two groups). However, as of 2007, DNA sequencing is not yet affordable for most, and all this may still be decades off. It is also possible that gene therapy could be used to alter the skin's DNA.
Phage therapy has been proposed to kill P. acnes, and has seen some use, particularly in Georgia.
Preferred treatments by types of acne vulgaris
- Comedonal (non-inflammatory) acne: local treatment with azelaic acid, salicylic acid, topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide.
- Mild papulo-pustular (inflammatory) acne: benzoyl peroxide or topical retinoids, topical antibiotics (such as erythromycin).
- Moderate inflammatory acne: benzoyl peroxide or topical retinoids combined with oral antibiotics (tetracyclines). Isotretinoin is an option.
- Severe inflammatory acne, nodular acne, acne resistant to the above treatments: isotretinoin, or contraceptive pills with cyproterone for females with virilization or drospirenone.
Acne scars
Severe acne often leaves small scars where the skin gets a "volcanic" shape. Acne scars are difficult and expensive to treat, and it is unusual for the scars to be successfully removed completely.
Physical acne scars are often referred to as "Icepick" scars. This is because the scars tend to cause an indentation in the skin's surface.
Acne scars are unsightly, and it is for this reason they can be psychologically and emotionally distressing. However, there is a range of treatments available. If acne scars are causing severe psychological distress, social withdrawal and/or emotional ill-health, a physician should be contacted.
Those who suffered from acne before, and have developed scars are generally relieved that the acne has gone, and emotional effects of acne scars tend to be less distressing.
Although quite rare, the medical condition Atrophia Maculosa Varioliformis Cutis results in "acne like" depressed scars on the face.
Ice pick scars - Deep pits, that are the most common and a classic sign of acne scarring.
Box car scars - Angular scars that usually occur on the temple and cheeks, and can be either superficial or deep, these are similar to chickenpox scars.
Rolling scars - Scars that give the skin a wave-like appearance.
Hypertrophic scars - Thickened, or keloid scars.
Pigmentation
Pigmented scars is a slightly misleading term, suggesting a change in the skin's pigmentation, and that they are true scars. Neither is true. Pigmented scars are usually the result of nodular or cystic acne (the painful 'bumps' lying under the skin). They often leave behind an inflamed red mark. Often, the pigmentation scars can be avoided simply by avoiding aggravation of the nodule or cyst. When sufferers try to 'pop' cysts or nodules, pigmentation scarring becomes significantly worse, and may even bruise the affected area. Pigmentation scars nearly always fade with time taking between 3 months to two years to do so, although rarely can persist.
On the other hand, some people, particularly people with naturally tanned skin do develop brown hyperpigmentation scars which is caused by a local increased production of the pigment melanin. These too typically fade over time.
Grading scale
There are multiple grading scales for grading the severity of acne vulgaris, three of these being: Leeds acne grading technique: Counts and categorises lesions into inflammatory and non-inflammatory (ranges from 0-10.0). 'Cook's acne grading scale: Uses photographs to grade severity from 0 to 8 (0 being the least severe and 8 being the most severe). Pillsbury scale: Simply classifies the severity of the acne from 1 (least severe) to 4 (most severe).
See also
References
- James W (2005). "Clinical practice. Acne". N Engl J Med. 352 (14): 1463–72. PMID 15814882.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Webster G (2002). "Acne vulgaris". BMJ. 325 (7362): 475–9. PMID 12202330.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
Footnotes
- James WD (2005). "Clincal practice. Acne". N Engl J Med. 352 (14): 1463–72. PMID 15814882.
- Anderson, Laurence. 2006. Looking Good, the Australian guide to skin care, cosmetic medicine and cosmetic surgery. AMPCo. Sydney. ISBN 0 85557 044 X.
- ^ Goodman G (2006). "Acne and acne scarring - the case for active and early intervention" (PDF). Aust Fam Physician. 35 (7): 503–4. PMID 16820822.
- Purvis D, Robinson E, Merry S, Watson P (2006). "Acne, anxiety, depression and suicide in teenagers: a cross-sectional survey of New Zealand secondary school students". J Paediatr Child Health. 42 (12): 793–6. PMID 17096715.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
One study has estimated the incidence of suicidal ideation in patients with acne as 7.1% :
* Picardi A, Mazzotti E, Pasquini P (2006). "Prevalence and correlates of suicidal ideation among patients with skin disease". J Am Acad Dermatol. 54 (3): 420–6. PMID 16488292.{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Adebamowo CA, Spiegelman D, Danby FW, Frazier AL, Willett WC, Holmes MD (2005). "High school dietary dairy intake and teenage acne". J Am Acad Dermatol. 52 (2): 207–14. PMID 15692464.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Fries JH (1978). "Chocolate: a review of published reports of allergic and other deleterious effects, real or presumed". Ann Allergy. 41 (4): 195–207. PMID 152075.
- Danby FW (2007). "Acne and iodine: Reply". J Am Acad Dermatol. 56 (1): 164–5. PMID 17190637.
- Loren Cordain, et al. "Acne Vulgaris - A Disease of Western Civilization" Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1584-1590. Observation
- Smith R, Mann N, Makelainen H, Braue A, Varigos G (2004). "The effect of short-term altered macronutrient status on acne vulgaris and biochemical markers of insulin sensitivity". Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 13 (Suppl): S67. PMID 15294556.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Anderson, Laurence. 2006. Looking Good, the Australian guide to skin care, cosmetic medicine and cosmetic surgery. AMPCo. Sydney. ISBN 0-85557-044-X.
- CHOICE - Citizens for Healthy Options In Children's Education (2003). "Acne Has Nothing to Do with Diet - Wrong!".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Magin P, Pond D, Smith W, Watson A (2005). "A systematic review of the evidence for 'myths and misconceptions' in acne management: diet, face-washing and sunlight". Fam Pract. 22 (1): 62–70. PMID 15644386.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - RMIT acne study
- Endocrine effects of masturbation in men.
- Kern, Daniel W. "Clear skin regimen: A free, step by step program." Acne.org. Instructions
- "The iPLEDGE Program - Guide to Best Practices for Isotretinoin - "The resource to help the prescriber prepare, plan treatments, and prevent pregnancies during the course of isotretinoin therapy"" (PDF). 2005.
- Bernadine Healy (2005-05-09). "Pledging for Accutane". US News Best Health.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Kawada A, Aragane Y, Kameyama H, Sangen Y, Tezuka T (2002). "Acne phototherapy with a high-intensity, enhanced, narrow-band, blue light source: an open study and in vitro investigation". J Dermatol Sci. 30 (2): 129–35. PMID 12413768.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Kjeldstad B (1984). "Photoinactivation of Propionibacterium acnes by near-ultraviolet light". Z Naturforsch . 39 (3–4): 300–2. PMID 6730638.
- Ashkenazi H, Malik Z, Harth Y, Nitzan Y (2003). "Eradication of Propionibacterium acnes by its endogenic porphyrins after illumination with high intensity blue light". FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 35 (1): 17–24. PMID 12589953.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "New Light Therapy for Acne" U.S. Food and Drug Administration, FDA Consumer magazine, November-December 2002 Notice
- Papageorgiou P, Katsambas A, Chu A (2000). "Phototherapy with blue (415 nm) and red (660 nm) light in the treatment of acne vulgaris" (PDF). Br J Dermatol. 142 (5): 973–8. PMID 10809858.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - MedlinePlus (2001-07-24). "Azelaic Acid (Topical)".
- Dreno B, Amblard P, Agache P, Sirot S, Litoux P (1989). "Low doses of zinc gluconate for inflammatory acne". Acta Derm Venereol. 69 (6): 541–3. PMID 2575335.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Dreno B, Moyse D, Alirezai M, Amblard P, Auffret N, Beylot C, Bodokh I, Chivot M, Daniel F, Humbert P, Meynadier J, Poli F (2001). "Multicenter randomized comparative double-blind controlled clinical trial of the safety and efficacy of zinc gluconate versus minocycline hydrochloride in the treatment of inflammatory acne vulgaris". Dermatology. 203 (2): 135–40. PMID 11586012.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mantle D, Gok MA, Lennard TW (2001). "Adverse and beneficial effects of plant extracts on skin and skin disorders". Adverse drug reactions and toxicological reviews. 20 (2): 89–103. PMID 11482001.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Koh KJ, Pearce AL, Marshman G, Finlay-Jones JJ, Hart PH (2002). "Tea tree oil reduces histamine-induced skin inflammation". Br. J. Dermatol. 147 (6): 1212–7. PMID 12452873.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Khalil Z, Pearce AL, Satkunanathan N, Storer E, Finlay-Jones JJ, Hart PH (2004). "Regulation of wheal and flare by tea tree oil: complementary human and rodent studies". J. Invest. Dermatol. 123 (4): 683–90. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.23407.x. PMID 15373773.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Shalita A, Smith J, Parish L, Sofman M, Chalker D (1995). "Topical nicotinamide compared with clindamycin gel in the treatment of inflammatory acne vulgaris". Int J Dermatol. 34 (6): 434–7. PMID 7657446.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Greenleaf Aloe Vera Gel". Brihans.
- Ayurveda Encyclopedia, "Acne Treatment"
- Jain A, Basal E (2003). "Inhibition of Propionibacterium acnes-induced mediators of inflammation by Indian herbs". Phytomedicine. 10 (1): 34–8. PMID 12622461.
- Tehrani R, Dharmalingam M (2004). "Management of premenstrual acne with Cox-2 inhibitors: A placebo controlled study". Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol . 70: 345–348. Retrieved 2007-06-23.
- http://www.reflectionscenter.com/sb_acne_press_trade.pdf
- The star ledger- Germs that fight germs
- Types of Acne Scars
- Leeds, Cook's and Pillsbury scales obtained from here
External links
- Acne vulgaris: more than skin deep (on the psychological effects of acne)
- Story on Acne from the Better Health Channel (Quality assured by the Victorian government, Australia)
- "AcneNet". American Academy of Dermatology. - Dermatologist-reviewed information about acne.
- "Acne Questions and Answers". From the National Institute of Health.
- Acne Home Remedies (Several home remedies for Acne)
| Acne-treating agents (D10) | |
|---|---|
| Antibacterial | |
| Keratolytic | |
| Anti-inflammatory | |
| Antibiotics | |
| Hormonal | |
| Retinoids | |
| Other | |
| Combinations | |
| |
| Dermatitis and eczema | |
|---|---|
| Atopic dermatitis | |
| Seborrheic dermatitis | |
| Contact dermatitis (allergic, irritant) | |
| Eczema | |
| Pruritus/Itch/ Prurigo |
|
| Other |
|