| Revision as of 14:22, 3 December 2007 view sourcePIRRO BURRI (talk | contribs)108 edits →Roman and Byzantine Era← Previous edit | Revision as of 18:00, 3 December 2007 view source 3rdAlcove (talk | contribs)3,491 edits better sourceNext edit → | ||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
| </ref>,who, like other ] peoples, were subdivided into tribes and clans.<ref></ref> Albanians (as one of innumerous Illyrian tribes) were named after their city state ] near a mountain called Alp 'mountain', Hittite alpa 'white'. The name Albania is derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Arbër, or Arbëresh, and later Albanoi, that lived near Durrës. The kingdom of ] grew from the general area of modern-day Albania and eventually controlled much of the eastern Adriatic coastline. Scodra was its capital, just as the city is now the most important urban center of northern Albania. The earliest known king of Illyria was Hyllus (]: Ylli, ]: "Star") who was recorded to have died in the year 1225 BC. The kingdom, however, reached the zenith of its expansion and development in the 4th century BC, when King ] (]: Bardhyli, ]: "White Star"), one of the most prominent of the Illyrian kings, united the kingdoms of Illyria, Molossia and a good part of ] under his control. Its decay began under the same ruler as a result of the attacks made by ], father of ]. | </ref>,who, like other ] peoples, were subdivided into tribes and clans.<ref></ref> Albanians (as one of innumerous Illyrian tribes) were named after their city state ] near a mountain called Alp 'mountain', Hittite alpa 'white'. The name Albania is derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Arbër, or Arbëresh, and later Albanoi, that lived near Durrës. The kingdom of ] grew from the general area of modern-day Albania and eventually controlled much of the eastern Adriatic coastline. Scodra was its capital, just as the city is now the most important urban center of northern Albania. The earliest known king of Illyria was Hyllus (]: Ylli, ]: "Star") who was recorded to have died in the year 1225 BC. The kingdom, however, reached the zenith of its expansion and development in the 4th century BC, when King ] (]: Bardhyli, ]: "White Star"), one of the most prominent of the Illyrian kings, united the kingdoms of Illyria, Molossia and a good part of ] under his control. Its decay began under the same ruler as a result of the attacks made by ], father of ]. | ||
| The ] created and developed their culture and language in the western part of the Balkans, where ancient writers mentioned them in their works. The regions that the Illyrians inhabited were expansive, encompassing the western Balkan peninsula, north to central Europe, and east around the Lyhind Lake (]). Other Illyrian tribes also migrated and developed in Italy. Among them were the ] and ]. The name ''Illyria'' is mentioned in works since the 5th century BC |
The ] created and developed their culture and language in the western part of the Balkans, where ancient writers mentioned them in their works. The regions that the Illyrians inhabited were expansive, encompassing the western Balkan peninsula, north to central Europe, and east around the Lyhind Lake (]). Other Illyrian tribes also migrated and developed in Italy. Among them were the ] and ]. The name ''Illyria'' is mentioned in works since the 5th century BC. | ||
| The beginning of Illyrian origins date to the 15th century BC, during the mid-Bronze Age, when distinct Illyrian ethnic features began to form. By the ], the Illyrians were fully distinct and had inherited their developing anthropological features and language from the Neolithic and Bronze Ages. The old theory that the Illyrians came from ] during the seventh to ninth centuries has been disproved by studies performed following World War II. The fact that graves with urns, characteristic of Central Europe, are not found in Illyrian settlements severely damages the theory. Central European influence on the Illyrians is a result of cultural exchanges and movement of artisans.<ref></ref> | |||
| ===Greek colonies - Hellenistic Era=== | ===Greek colonies - Hellenistic Era=== | ||
Revision as of 18:00, 3 December 2007
This article is about the country in south-eastern Europe. For other uses, see Albania (disambiguation).| Republic of AlbaniaRepublika e Shqipërisë | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Emblem
Emblem
| |
| Motto: Ti Shqipëri më jep nder më jep emrin shqipëtar (Albania give me honor, give me the Albanian name.) | |
| Anthem: Rreth flamurit të përbashkuar ("United Around the Flag") | |
 Location of Albania (orange) Location of Albania (orange) | |
| Capitaland largest city | Tirana |
| Official languages | Albanian |
| Demonym(s) | Albanian |
| Government | Parliamentary republic |
| • President | Bamir Topi |
| • Prime Minister | Sali Berisha |
| Independence from the Ottoman Empire | |
| • Date | November 28 1912 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 28,748 km (11,100 sq mi) (139th) |
| • Water (%) | 4.7 |
| Population | |
| • 2025 estimate | 3,600,523 (130th) |
| • Density | 134/km (347.1/sq mi) (63) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2007 estimate |
| • Total | $19.818 billion (112th) |
| • Per capita | $6,259 (100th) |
| Gini (2002) | 28.2 low inequality |
| HDI (2004) | 0.784 high (73rd) |
| Currency | Lek (ALL) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Calling code | 355 |
| ISO 3166 code | AL |
| Internet TLD | .al |
Albania, officially the Republic of Albania (Albanian Republika e Shqipërisë ɾɛˈpublika ɛ ʃcipəˈɾiːs, or simply Shqipëria) is a country in Southeastern Europe. It borders Greece to the south, Montenegro to the north, Serbia to the northeast and the Republic of Macedonia to the east. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the west and a coast on the Ionian Sea to the southwest.
Albania is a parliamentary democracy that is transforming its economy into a market-oriented system, a potential candidate for membership in the European Union and NATO. Tirana is the capital; Apollonia, Butrinti, Kruja, Durrës and Shkodra are some of the country's other major places of interest.
Etymology
Main article: Albania (toponym)Albania is the Medieval Latin name of the country, which is called Shqipëri by the inhabitants. In Medieval Greek, the name is Albania besides variants Albaētia, Arbanētia.(OED). The ultimate origin of the Alb- element has been traced to an Illyrian alb "hill" cognate to the alp "mountain pasture" found in the Alpine region.
In the II Century BC, in the History of the World, written by Polybius, there is mention of a city named Arbon in present day central Albania. The people who lived there were called Arbanios and Arbanitai.
Another suggestion is derivation from the Illyrian tribe of the Albanoi recorded by Ptolemy the geographer and astronomer from Alexandria, who drafted a map of remarkable significance for the history of Illyria. This map shows the city of Albanopolis (located south of Durrës). In his 'History' written in 1079-1080,Byzantine historian Michael Attaliates was first to refer to Albanoi as having taken part in a revolt against Constantinople in 1403 and to Arbanitai as subjects of the duke of Dyrrachium.
During the Middle Ages the Albanians called their country Arbër or Arbën and referred to themselves as Arbëresh or Arb'nesh. As early as the sixteenth century, a new name for their home evolved among Albanian people: Shqipëria, "Land of the Eagles", hence the two-headed bird on the national flag.The name probably has its origins in the Skanderbeg family crest.
History
Main article: History of AlbaniaAlbania in Antiquity
Albania, in the southeastern corner of Europe, has been populated since prehistoric times and was settled by the Illyrians, possible ancestors of present-day Albanians. Situated as it was, surrounded by powerful, warring empires, Albania has experienced a considerable amount of violence throughout its history. Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Venetians and Ottomans swept through, leaving their cultural mark as well as their ruins. Archaeological research shows that the lands that are today inhabited by Albanians were first populated in the Paleolithic Age (Stone Age). The first areas settled were those with favourable climatic and geographic conditions. In Albania, the earliest settlements have been discovered in the Gajtan cavern (Shkodra), in Konispol, at Mount Dajti, and at Saranda. Fragments of Cyclopean structures, of the Cyclopean-Pelasgian period, were discovered at Kretsunitsa, Arinishta, and other sites in the district of Gjirokastra. The walls, partly Cyclopean, of an ancient city (perhaps Byllis) are visible at Gradishti on the picturesque Viosa River. Few traces remain of the once celebrated Dyrrhachium (today Durrës). The rediscovered city of Butrint is probably more significant today than it was when Julius Caesar used it as a provisions depot for his troops during his campaigns in the 1st century BC. At that time, it was considered to be an unimportant outpost, overshadowed by the likes of Apollonia and Durrës. Albania's rich archaeological record has been explored for nearly two centuries. Ali Pasha, the Ottoman viceroy who governed this region, encouraged early archaeological excavations at Nikopolis in Albania around 1812. His excavations, ordered after his friend Peter Oluf Brøndsted pointed out a place where he thought a temple might be buried, was not academic in nature. Pasha simply wished to have any treasures that were found in the area. Eventually, excavated marble was transported to his palace. Pasha also pocketed one of the coins that was found. Formal investigation and recording of Albania's archaeological monuments began with Francois Pouqueville who was Napolean's consul-general to Ali Pasha's court, and Martin Leake, who was the British agent there. A French mission, led by Len Rey, worked throughout Albania from 1924 to 1938 and published its results in Cahiers d'Archéologie, d'art et d'Histoire en Albanie et dans les Balkans (Notes of Archaeology, Art, and History in Albania and in the Balkans). Archaeologists today are finding remains from all periods, from the Stone Age to the early Christian era. Another project that produced prehistoric finds, though unexpectedly, was done in the valley of Kryegjata, close to the present-day city of Fier and in the area of Apollonia. This excavation, a collaboration between the University of Cincinnati and archaeologists from the Institute of Archaeology in Albania, was originally a mission to learn about the colony of Apollonia. Instead, they found evidence of a settlement much older than that. In 2000, the Albanian government established Butrint National Park, which draws about 70,000 visitors annually and is Albania's second World Heritage site. In 2003, a synagogue dating from the 5th or 6th century AD was uncovered in Saranda, a coastal town opposite Corfu. It was the first time remains of an early synagogue have been found in that area, and the history of its excavation is also noteworthy. The team found exceptional mosaics depicting items associated with Jewish holidays, including a menorah, ram's horn, and citron tree. Mosaics in the basilica of the synagogue show the facade of what resembles a Torah, animals, trees, and other biblical symbols. The structure measures 20 by 24 metres and was probably last used in the 6th century AD as a church.
Kingdom of Illyria
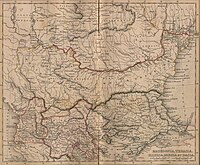
Most historians believe that the Albanian people are descended from a non-Slavic, non-Turkic group of tribes known as Illyrians,who, like other Balkan peoples, were subdivided into tribes and clans. Albanians (as one of innumerous Illyrian tribes) were named after their city state Albanopolis near a mountain called Alp 'mountain', Hittite alpa 'white'. The name Albania is derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Arbër, or Arbëresh, and later Albanoi, that lived near Durrës. The kingdom of Illyria grew from the general area of modern-day Albania and eventually controlled much of the eastern Adriatic coastline. Scodra was its capital, just as the city is now the most important urban center of northern Albania. The earliest known king of Illyria was Hyllus (Albanian: Ylli, English translation: "Star") who was recorded to have died in the year 1225 BC. The kingdom, however, reached the zenith of its expansion and development in the 4th century BC, when King Bardhyllus (Albanian: Bardhyli, English translation: "White Star"), one of the most prominent of the Illyrian kings, united the kingdoms of Illyria, Molossia and a good part of Macedon under his control. Its decay began under the same ruler as a result of the attacks made by Philip II of Macedon, father of Alexander the Great.
The Illyrians created and developed their culture and language in the western part of the Balkans, where ancient writers mentioned them in their works. The regions that the Illyrians inhabited were expansive, encompassing the western Balkan peninsula, north to central Europe, and east around the Lyhind Lake (Ohrid Lake). Other Illyrian tribes also migrated and developed in Italy. Among them were the Messapii and Iapyges. The name Illyria is mentioned in works since the 5th century BC.
Greek colonies - Hellenistic Era
From the 8th century to the 6th century BC, the Greeks founded a string of colonies on Illyrian soil, two of the most prominent of which were Epidamnus (modern Durrës) and Apollonia (near modern Fier).
The first and perhaps the most important of Greece's colonies in Albania was founded at Epidamnus in 627 B.C. by Greeks from Corcyra (present-day Corfu) and Corinth. Greek and Roman authors called it "the Admirable City" for its temple, statues, and other monuments. Fertile soil and a large seaport accounted for the colony's prosperity and success in commerce. Growth brought to the lower classes wealth and asubsequent desire to have more of a government voice, leading to a civil war between the small ruling class (oligarchs) and most of the population. The people requested Corinth's assistance in battle, while the oligarchs sought aid from Corcyra. Corinth was allied with Sparta and Corcyra, upon this request, applied for aid from Athens. Therefore, the intervention of Corinth on the side of the people and Corcyra on the side of the oligarchs led to the deeper conflict between Athens, Sparta, and their respective allies known as the Peloponnesian War.
The early success of Epidamnus led to more Hellenic colonies in the region. Butrint, situated on a hill in southern Albania, was founded by colonists from Corfu in the sixth century B.C. Its original name, Buthrotum, literally means "place with much cattle and grazing land." By the fourth century B.C., Butrint had expanded greatly and included a 5,000-seat theater. In the Aeneid, Vergil claims that the city was founded by Aeneas himself. Another significant colony, Apollonia, was named after the god Apollo. It was founded in 588 B.C., and it prospered because of its role as a link between Brundisium (now Brindisi) in Italy and southern Albania. Many smaller Greek settlements were established around Albania during this time, but Epidamnus, Butrint, and Apollonia were the most important. The colonies flourished into the Roman period, yet it was during the Hellenistic Age that they reached their peak. From the fourth to the second centuries B.C., the colonies (composed of both Greeks and Illyrians) became centers of art, intellectual development, music, and theater. Apollonia was particularly noted for its philosophy school.
Roughly parallel with the rise of Greek colonies, Illyrian tribes began to evolve politically from relatively small and simple entities into larger and more complex ones. At first they formed temporary alliances with one another for defensive or offensive purposes, then federations and, still later, kingdoms. In 355 BC, war broke out against Alexander of Macedonia to free the eastern territories and in the meantime Apollonia was freed from Macedonian rule. After Alexander's death in 323 BC, independent Illyrian kingdoms again arose. In 312 BC, King Glauka or Glaucius expelled the Greeks from Durrës. By the end of the third century, an Illyrian kingdom based near what is now the Albanian city of Shkodër controlled parts of northern Albania, Montenegro, and Herzegovina. Under the rule of King Glaukia, the Illyrian state strengthened rapidly. Glaukia's successors (Monun and Mytyl) strengthened the Illyrian state economically and minted both bronze and silver coins. Soon after the mid-3rd century BC, under the reign of Pleurat and Agron, the Illyrian state started to prosper again. In 231 BC, they entered into an alliance with Acarnania and became a prominent power in the Balkans.
Roman and Byzantine Era
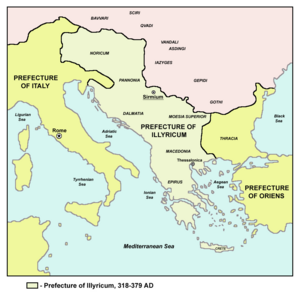
The Romans militarily destroyed Illyrian autonomy in 165 BC. Roman Albania was traversed by the Via Egnatia, the Roman road that linked east with west and Rome with the far eastern reaches of its empire. After being conquered by the Roman Empire, Illyria was reorganized as a Roman province. Illyricum was later divided into the provinces of Dalmatia and Pannonia, the lands comprising modern-day Albania. Many Illyrians during Roman rule contributed significantly to the ranks of the Prætorian Guard. The Albanian language borrowed a great number of Latin words, mostly religious and liturgical terms. This was due to the fact that Albania was at first attached to the See of Rome, though the religion of Jesus was preached to the Albanians by St. Paul himself during a visit he made to Durazzo.
In the first decades under Byzantine rule (until 461), Illyria suffered the devastation of raids by Visigoths, Huns, and Ostrogoths. Not long after these barbarian invaders swept through the Balkans, the Slavs appeared. Between the 6th and 8th centuries they settled in Illyrian territories and proceeded to assimilate Illyrian tribes in much of what is now Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Serbia. The tribes of southern Illyria, however, including modern Albania, averted assimilation and preserved their native tongue. After the fall of the Roman Empire, Albania was incorporated into the Byzantine Empire, administered from Constantinople. Albania was under Byzantine rule until the 14th century AD when the Ottoman Turks began to make incursions into the empire. The Ottomans captured Constantinople in 1453, and by 1460 almost all former Byzantine territories were in the hands of the Turks.
Ottoman Era
The Ottoman Turks expanded their empire from Anatolia to the Balkans in the 14th century. By the 15th century, the Turks had brought under subjection nearly all of the Balkan peninsula except for a small coastal strip which is included in present-day Albania. Albanian resistance to the Turks in the mid-15th century won them acclaim all over Europe. Albania became a symbol of resistance to the Ottoman Turks but suffered an almost continuous state of warfare. One of the most successful resistance against the invading Ottomans, was led by Gjergj Kastrioti Skanderbeg from 1443 to 1468.In 1443 he rallied Albanian forces and drove the Turks from his homeland. For 25 years, against tremendous odds, Skanderbeg kept the Turks from retaking Albania, which, due to its proximity to Italy, could easily have served as a springboard to the rest of Europe. After the death of Skanderbeg, resistance continued until 1478, although with only moderate success. The loyalties and alliances created and nurtured by Skanderbeg faltered and fell apart, and the Ottomans conquered the territory of Albania shortly after the fall of Kruje's castle. Albania then became part of the Ottoman Empire. They would remain a part of the Ottoman Empire as the provinces of İşkodra, Manastır and Yanya until 1912.
Effects of the Balkan Wars
After the Second Balkan War, the Ottomans were removed from Albania and there was a possibility of some of the lands being absorbed by Serbia and the southern tip by Greece. This decision angered the Italians, who did not want Serbia to have an extended coastline, and it also angered the Austro-Hungarians, who did not want a powerful Serbia on their southern border. Despite Serbian, Montenegrin, and Greek occupation forces on the ground, and under immense pressure from Austria-Hungary, it was decided that the country should not be divided but instead consolidated into the Principality of Albania. However, the Austro-Italian project was not successful.
Monarchy

From 1925, the country was ruled by President Ahmet Zogu who, in 1928, declared himself King Zog I, meaning "bird", the first Albanian monarch since Gjergj Kastriot Skënderbej and adopting the title of Scanderbeg II. Afterwards he was also declared Field Marshal of the Royal Albanian Army on September 1, 1928. He proclaimed a constitutional monarchy similar to the contemporary regime in Italy.
During his reign he is said to have survived over 55 assassination attempts. One of these occurred in 1931 while Zog was visiting a Vienna opera house for a performance of Pagliacci. The attackers struck whilst Zog was getting into his car, and he survived by drawing his own pistol (which he always carried) and firing back at his would-be assassins. This is the only occasion in modern history when a Head of State has returned fire with potential assassins.
Styling himself a European king, he married Hungarian noblewoman Geraldine Apponyi de Nagy-Apponyi. His reign ended when Italian fascists invaded Albania in April 7, 1939. The communists took power after the Second World War. After the fall of the communist government, his son Leka, Crown Prince of Albania and the royal family returned to Albania on June 28, 2002.
World War II
Albania was one of the first countries occupied by the Axis Powers in World War II. Mussolini 's imperial ambitions focused on Albania.Italy's erratic army had been humiliated in 1920 by a few thousand disorganized but fiercely patriotic Albanians,which had driven Italy out of Vlorë.If there was a single thread running through the fabric of Mussolini's imperial ambitions it was the need to restore Italy's honour.
Mussolini invaded and occupied Albania, while the world was focused on German military actions in Czechoslovakia and Poland. As Hitler began his aggressions, the Italian dictator set his eyes on Albania across the Adriatic from Italy. Despite some strong resistance, especially at Durrës, Italy invaded Albania on April 7, 1939 and took control of the country. On April 12, the Albanian parliament voted to unite the country with Italy. Victor Emmanuel III took the Albanian crown, and the Italians set up a fascist government under Shefqet Verlaci and soon absorbed Albania's military and diplomatic institutions. Mussolini, in October 1940, used his Albanian base to launch an attack on Greece. During WWII, Albanian nationalist groups, including communist partisans, fought against the Italians and subsequently the Germans. By October 1944 they had thrown the Germans out, the only East European nation to do so without the assistance of Soviet troops. The partially French-educated Enver Hoxha became the leader of the country by virtue of his position as secretary general of the Party of Labor (the Albanian Communist Party). The Communist Party was created on November 8, 1941 with the help of other Bolshevik Communist Parties.
Holocaust
Albania is unique in that it is the only European country occupied by the Nazis that ended World War II with a larger Jewish population than before the War. The Albanian response to the Holocaust is especially notable because it was Europe's only largely Muslim country. Even so only a Jewish family of six was deported and killed during the Nazi occupation of Albania. Not only did the Albanians protect their own Jews, but they provided refuge for Jews from neighboring countries. The Albanians refused to comply and hand over lists of Jews. Instead they provided the Jewish families with forged documents and helped them disperse in the Albanian population.
In February 1944, when the Nazis descended upon the mountain hiding place, not a single Jew fell into their hands. During the Holocaust, Albania was the only country in Europe that protected and sheltered its entire Jewish population, both native and foreign. There was no history of ideological anti-Semitism in Albania so it was unique in this regard. The small number of Jews in Albania also played a key role in the possibility to protect them all. During the Italian occupation, they were able to disperse and blend in with the general population. However, the role of the Albanian population as a whole in saving Jews is undeniable.
People's Republic
From 1944 to 1991, Albania became a People's Republic and was a one-party state in which Enver Hoxha ruled with an austere hand. In 1961, he broke with Albania’s closest ally, the Soviet Union, because he believed Khrushchev had abandoned the teachings of Stalin. Subsequently, Albania’s closest ally was the People’s Republic of China. However, when the PRC established diplomatic relations with the United States in 1978, Hoxha denounced the Chinese as well and decided to pursue a policy of self-reliance. The result was not only extreme isolation but also absolute financial ruin for Albania. An example of this may be drawn from the construction between 1974 and 1986 of approximately 700,000 reinforced concrete bunkers to defend against an anticipated multi-front attack. Upon Hoxha’s death in 1985, Ramiz Alia succeeded him as both party and state leader. Alia was Hoxha’s protégé, but was less repressive than the former leader and began to allow some reforms. This process was accelerated by news of the changes in other communist countries of Central and Eastern Europe. There are statistics which show that during this period about 6000 Albanian citizens were executed for political reasonsDespite this, the quality of life improved as both life expectancy and literacy showed large gains and economic growth continued until the mid 1970s.
Return to capitalism
The first massive anti-communist protests took place in July 1990. Shortly afterwards, the communist regime under Ramiz Alia carried out some cosmetic changes in the economy. At the end of 1990, after strong student protests and independent syndicated movements, the regime accepted a multiparty system. The first multiparty general elections were held on March 31, 1991 and the Communist Party (PPSH) won the majority. Opposition parties accused the government of manipulation and called for new elections, which were held on March 22, 1992 and resulted in a coalition (composed of the Democratic Party, the Social-Democrats, and the Republican Party) coming to power.
In the general elections of June 1996, the Democratic Party achieved an absolute majority, winning over 85% of parliamentary seats. In 1997, widespread riots erupted after the International Monetary Fund forced the state to liberalize banking practices. Many citizens, naive to the workings of a market economy, put their entire savings into pyramid schemes. In a short while, $2 billion (80% of the country's GDP) had been moved into the hands of just a few pyramid scheme owners, causing severe economic troubles and civic unrest. Police stations and military bases were looted of millions of Kalashnikovs and other weapons. The insurrection temporarily prevailed, and militia and even less-organized armed citizens controlled many cities. The government of Aleksander Meksi resigned and a government of national unity was built following pressure from nearby national governments. In response to the situation, the Socialist Party won the early elections of 1997 and Berisha resigned the Presidency.
However, stability was far from being restored in the years after the 1997 riots. The power feuds raging inside the Socialist Party led to a series of short-lived Socialist governments. The country was flooded with refugees from neighboring Kosovo in 1998 and 1999 during the Kosovo War.
In June 2002, a compromise candidate, Alfred Moisiu, a former general, was elected to succeed President Rexhep Meidani. Parliamentary elections in July 2005 brought Sali Berisha, as leader of the Democratic Party, back to power, mostly owing to Socialist infighting and a series of corruption scandals plaguing the government of Fatos Nano. The Euro-Atlantic integration of Albania has been the ultimate goal of the post-communist governments. Albania's EU membership bid has been set as a priority by the European Commission. In 2006, Albania signed a Stabilization and Association Agreement with the EU, thus completing the first major step towards joining the bloc. Albania, along with Croatia and the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, hopes to receive an invitation to join NATO in 2008.
The workforce of Albania has continued to migrate to Greece, Italy, Germany, other parts of Europe, and North America. However, the migration flux is slowly decreasing, as more and more opportunities are emerging in Albania itself as its economy steadily develops. Albanian emigrants have achieved great success in multiple geographies and disciplines abroad. In particular, there is now a significant Albanian community in the United Kingdom, in cities such as Birmingham and Manchester. The Albanian diaspora is most prevalent in Liverpool, where Albanian cuisine has something of a cult following. Pulitzer prize winning journalist Caroline Thorpe, who is currently an emeritus professor at the University of Liverpool, recently noted that 'Albanian food has become as synonymous with Liverpool as Bill Shankley or the Beatles!'.
Administrative division

Albania is divided into 12 counties (Albanian: official qark/qarku, but often prefekturë/prefektura), 36 districts and 351 municipalities.
| County | Districts | Capital | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Berat | Berat, Kuçovë, Skrapar | Berat |
| 2 | Dibër | Bulqizë, Dibër, Mat | Peshkopi |
| 3 | Durrës | Durrës, Krujë | Durrës |
| 4 | Elbasan | Elbasan, Gramsh, Librazhd, Peqin | Elbasan |
| 5 | Fier | Fier, Lushnjë, Mallakastër | Fier |
| 6 | Gjirokastër | Gjirokastër, Përmet, Tepelenë | Gjirokastër |
| 7 | Korçë | Devoll, Kolonjë, Korçë, Pogradec | Korçë |
| 8 | Kukës | Has, Kukës, Tropojë | Kukës |
| 9 | Lezhë | Kurbin, Lezhë, Mirditë | Lezhë |
| 10 | Shkodër | Malësi e Madhe, Pukë, Shkodër | Shkodër |
| 11 | Tirana | Kavajë, Tirana | Tirana |
| 12 | Vlorë | Delvinë, Sarandë, Vlorë | Vlorë |
Geography
Albania has a total area of 28,750 square kilometers. Its coastline is 362 kilometres long and stretches on the Adriatic Sea and the Ionian Sea. The lowlands of the west face the Adriatic Sea. The 70% of the country that is mountainous is rugged and often inaccessible. The highest mountain is Korab situated in the district of Dibra, reaching up to 2,753 metres (9,032 ft). The country has a continental climate at its high altitude regions with cold winters and hot summers. Besides the capital city of Tirana, which has 800,000 inhabitants, the principal cities are Durrës, Elbasan, Shkodër, Gjirokastër, Vlorë, Korçë and Kukës. In Albanian grammar, a word can have indefinite and definite forms, and this also applies to city names: both Tiranë and Tirana, Shkodër and Shkodra are used.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of AlbaniaAs of July 2007, Albania's population of 3,600,523 is growing by 0.73% per year. Albania is a largely ethnically homogeneous country with only small minorities. Majority of the total population is considered Albanian. Minorities include Greeks, Aromanians, Torbesh, Gorani, Macedonian Slavs, Roma, Montenegrins, Bulgarians, Balkan Egyptians and Jews. The dominant language is Albanian, with two main dialects, Gheg and Tosk. Many Albanians are also fluent in English, Italian and Greek.
Religion
Main article: Religion in AlbaniaChristianity manifested itself in Albania during Roman rule during the middle of the 1st century AD. At first, the new religion had to compete with Oriental cults such as those worshiping Mithra, the Persian god of light, which had entered the land in the wake of Albania's growing interaction with eastern regions of the Roman Empire. For a long time, it also had to compete with gods worshiped by Illyrian pagans. The steady growth of the Christian community in Dyrrhachium (the Roman name for Epidamnus) led to the creation there of a bishopric in 58 AD. Later, episcopal seats were established in Apollonia, Buthrotum (modern Butrint), and Scodra (modern Shkodra).
After the division of the Roman Empire in 395, Albania became politically a part of the Eastern Roman Empire, but remained ecclesiastically dependent on Rome. When the final schism occurred in 1054 between the Western and Eastern churches, the Christians in southern Albania came under the jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarch in Constantinople, and those in the north came under the purview of the Papacy in Rome. This arrangement prevailed until the Ottoman invasions of the 14th century, when the Islamic faith was introduced.
One of the major legacies of nearly five centuries of Ottoman rule was the conversion of up to 60 percent of the Albanian population to Islam. Therefore, the country emerged as a predominantly Muslim nation after its independence from Ottoman rule. In the mountainous north, the propagation of Islam was strongly opposed by Roman Catholics. Albania was preponderantly Roman Catholic, with eighteen episcopal Sees, some of which have an uninterrupted history from the dawn of Christendom until today. Albania was the last Roman Catholic bridgehead in the Balkans and the Popes were doing everything in their power to keep it and enlarge it. Gradually, however, backwardness, illiteracy, and the absence of an educated clergy and material inducements weakened the resistance.
The Communist regime, during its 45 years of absolute rule, religion was officially banned, and Albania was proclaimed as the first and only atheist state in the world. Today, with the freedom of religion and worship, Albania contains numerous religions and denominations. Religious fanaticism has never been a problem, with people from different religious groups living in peace. Interreligious marriage is very common, and an immensely strong sense of Albanian identity has tended to bind Albanians of all religious practices together. The Roman Catholics are mostly located in the northern part of the country, particularly in the cities of Shkodër and Kruja, while Orthodox Christians lived in the southern districts of Gjirokastër, Korçë, Berat, and Vlorë. The Muslims were spread throughout the land, although they particularly dominated the centre. Most of them were traditional Sunnites, but about one-quarter were members of the liberal, panentheistic Bektashi sect, which for a time had its headquarters in Tirana.
For generations, religious pragmatism was a distinctive trait of the Albanians. Even after accepting Islam, many people privately remained practicing Christians. As late as 1912, in a large number of villages in the Elbasan area, most men had two names, a Muslim one for public use and a Christian one for private use. Adherence to ancient pagan beliefs also continued well into the 20th century, particularly in the northern mountain villages, many of which were devoid of churches and mosques. A poet named Pashko Vasa (1825-1892), known as Vaso Pasha, made the trenchant remark, later co-opted by Enver Hoxha, that "the religion of the Albanians is Albanianism." It is estimated that only 30-40% of Albanians actively practice a religion. Despite such a diverse religious background, Albania has been free of religious conflict, mainly because Albanians have traditionally displayed a high degree of religious tolerance.
Economy
Main article: Economy of AlbaniaSince the fall of communism in 1990, Albania has launched economic programmes towards a more open-market economy. The democratically elected government that assumed office in April 1992 launched an ambitious economic reform programme to halt economic deterioration and put the country on the path towards a market economy. Key elements included price and exchange system liberalization, fiscal consolidation, monetary restraint, and a firm income policy. These were complemented by a comprehensive package of structural reforms, including privatization, enterprise, and financial sector reform, and creation of the legal framework for a market economy and private sector activity. Most prices were liberalized and are now approaching levels typical of the region. Most agriculture, state housing, and small industry were privatized, along with transportation, services, and small and medium-sized enterprises. After severe economic contraction following 1989, the economy slowly rebounded, finally surpassing its 1989 levels by the end of the 1990s. Since prices have also risen, however, economic hardship has continued for much of the population. In 1995, Albania began privatizing large state enterprises. Since 2000, Albania has experienced a more rapid expansion of its economy.
Following the signing of the Stabilisation and Association Agreement in June/July 2006, EU ministers urged Albania to push ahead with reforms, focusing on freedom of press, property rights, institution building, respect for ethnic minorities and observing international standards in municipal elections. Albania has made an impressive recovery, building a modern and diversified economy. Recent administrations have also improved the country's infrastructure and opened competition in seaports, railroads, telecommunications, electricity generation, natural gas distribution and airports. Tourism in Albania is a large industry and is growing rapidly. The most notable tourist attractions are the ancient sites of Apollonia, Butrinti, and Krujë. Albania's coastline is becoming increasingly popular with tourists due to its relatively unspoiled nature and its beaches.
Armed forces
Main article: Military of AlbaniaThe Albanian Armed Forces are overseen by the General Staff Headquarters, and consists of Land Forces Command (Army), Naval Forces Command (Navy), Air Defense Command, Doctrine and Training Command and Logistics Command. In 2002, Albania's armed forces have launched a 10-year reform program sponsored and supervised by the United States Department of Defense in order to trim down and thoroughly modernize its current standing force of more than 25,000 troops. Working towards NATO membership, the Adriatic Charter countries (Albania, Croatia and the Republic of Macedonia) are expected to join the alliance in 2008. Currently, the Albanian army participates in peacekeeping missions in both Afghanistan and Iraq.
Gallery
- Albania. Albania.
-
 Butrint, UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Butrint, UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Tirana, Albania. Tirana, Albania.
- Apollonia site in Fier, Albania. Apollonia site in Fier, Albania.
- Albanian tradition dance. Albanian tradition dance.
- Skanderbeg's castle in Krujë, Albania. Skanderbeg's castle in Krujë, Albania.
- A cliff overshadowing the coastal sea. A cliff overshadowing the coastal sea.
- Best view of Tirana, Albania. Best view of Tirana, Albania.
-
 Remains of a chapel in Butrint, Albania.
Remains of a chapel in Butrint, Albania.
- Hotel Adriatik Durrës, Albania. Hotel Adriatik Durrës, Albania.
- Fishing in Albania. Fishing in Albania.
- Tirana, Albania. Tirana, Albania.
-
 Ali Pasha's Castle, Albania.
Ali Pasha's Castle, Albania.
-
 Blue Eye, Albania.
Blue Eye, Albania.
-
 Petrela Castle, Tirana, Albania.
Petrela Castle, Tirana, Albania.
- Durrës, Albania. Durrës, Albania.
- The fourteenth century Church of the Holy Trinity,Albania. The fourteenth century Church of the Holy Trinity,Albania.
- The theater at Butrint. The theater at Butrint.
- Thethi,Albania Thethi,Albania
See also
Column-generating template families
The templates listed here are not interchangeable. For example, using {{col-float}} with {{col-end}} instead of {{col-float-end}} would leave a <div>...</div> open, potentially harming any subsequent formatting.
| Type | Family | Handles wiki table code? |
Responsive/ mobile suited |
Start template | Column divider | End template |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float | "col-float" | Yes | Yes | {{col-float}} | {{col-float-break}} | {{col-float-end}} |
| "columns-start" | Yes | Yes | {{columns-start}} | {{column}} | {{columns-end}} | |
| Columns | "div col" | Yes | Yes | {{div col}} | – | {{div col end}} |
| "columns-list" | No | Yes | {{columns-list}} (wraps div col) | – | – | |
| Flexbox | "flex columns" | No | Yes | {{flex columns}} | – | – |
| Table | "col" | Yes | No | {{col-begin}}, {{col-begin-fixed}} or {{col-begin-small}} |
{{col-break}} or {{col-2}} .. {{col-5}} |
{{col-end}} |
Can template handle the basic wiki markup {| | || |- |} used to create tables? If not, special templates that produce these elements (such as {{(!}}, {{!}}, {{!!}}, {{!-}}, {{!)}})—or HTML tags (<table>...</table>, <tr>...</tr>, etc.)—need to be used instead.
- Lists
- List of Albania-related articles
- List of Albanians
- List of Albanian writers
- List of Albanian-Americans
- International rankings of Albania
References
- International Monetary Fund - Albania (GDP)
- http://www.travel.state.gov/travel/cis_pa_tw/cis/cis_1076.html U.S. Department of State Bureau of Consular Affairs
- Albanische Studien, Johann Georg Von Hann, Wien, 1853
- The Albanians : an ethnic history from prehistoric times to the present by Edwin E Jacques Publisher: Jefferson, N.C. : McFarland & Co., ©1995
- Albania Past and Present, Constantine A. Chekrezi, New York, The Macmillan Company 1919.page 116
- The Albanians : an ethnic history from prehistoric times to the present by Edwin E Jacques Publisher: Jefferson, N.C. : McFarland & Co., ©1995
- Albania Past and Present, Constantine A. Chekrezi, New York, The Macmillan Company 1919.page 116
- by Robert Elsei,page 113-122,the Albanian lexion of Arnold von Harff, Earliest reference to the existance of the Albanian language
- http://en.wikipedia.org/Arb%C3%ABresh%C3%AB
- http://www.pinocacozza.it/ http://www.radio-arberesh.eu/
- History of Albania (A Brief Overview); Kristo Frasheri, Tirana 1964.
- The Albanians: An Ethnic History from Prehistoric Times to the Present-by Edwin E. Jacques
- Dosti, R. "Albania's ancient history surfaces." The Times. p. 1. September 3, 2006.
- Constanine A. C., and Charles, D. Albania Past and Present. Columbia University, p. 10. April, 1919.
- Diane Michelle Fox. Under Albanian Soil - A brief history of archaeological activity, both past and present, in Albania. August 12, 2004.
- http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/3235.htm Bureau of European and Eurasian Affairs September 2007
- Encyclopedia Britannica - Messapic language
- Library of Congress Country Study of Albania
- The Balkans by Misha Glenny page 418
- Shoah Research Center - Albania.
- Shoah Research Center - Albania.
- Sarner. Rescue in Albania: One Hundred Percent of Jews in Albania Rescued from the Holocaust, 1997.
- Anti-Defamation League
- Escape Through the Balkans: the Autobiography of Irene Grunbaum (University of Nebraska Press, 1996)
- 1997: The Albanian insurrection (libcom.org)
- Balkan Investigative Reporting Network - Albania Seeks Firm NATO Entry Date (February 22, 2006)
- CIA - The World Factbook - Albania
- US Department of State - International Religious Freedom Report 2006
- U.S. Department of State - Albania
- Zuckerman, Phil. "Atheism: Contemporary Rates and Patterns", Chapter in The Cambridge Companion to Atheism, ed. by Michael Martin, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK (2005)
- CIA - The World Factbook - Albania
- Encyclopedia Britannica - Albania (Religion)
- Goring, Rosemary (ed). Larousse Dictionary of Beliefs & Religions (Larousse: 1994); pp. 581-584. Table: "Population Distribution of Major Beliefs"
- See Stavro Skendi, "Crypto-Christianity in the Balkan Area under the Ottomans" 'Slavic Review', Vol. 26, No. 2 (Jun., 1967), pp. 227-246
- U.S. Department of State - Albania
- GDP per capita
- http://www.mod.gov.al/
- http://en.wikipedia.org/Membership_Action_Plan
External links
- Presidency of Albania
- The Albanian Parliament
- Albanian Institute of Statistics
- "Albania". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- National Tourism Organization Albania's official website for travel & tourism information.
- Tourism, Krujë
- Template:Wikitravel
- VIVAlbania, hospitality and ecotourism in Albania
- Treasure of the national library of Albania
| International membership | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||