| Revision as of 11:36, 6 July 2008 view sourceVanished User 4517 (talk | contribs)11,419 editsm →External links: rm linkspam per WP:EL← Previous edit | Revision as of 05:16, 8 July 2008 view source CameronPG (talk | contribs)1,067 edits →EvolutionNext edit → | ||
| Line 277: | Line 277: | ||
| In the past, there was a much wider variety of elephant genera, including the ]s, ]s and ]. There was also a much wider variety of species.<ref>Todd, N. E. (2001). (pdf). In: Cavarretta, G., P. Gioia, M. Mussi, and M. R. Palombo. The World of Elephants, Proceedings of the 1st International Congress. Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche. Rome, Italy.</ref><ref>Todd, N. E. (2005). Reanalysis of African Elephas recki: implications for time, space and taxonomy. Quaternary International 126-128:65-72.</ref> | In the past, there was a much wider variety of elephant genera, including the ]s, ]s and ]. There was also a much wider variety of species.<ref>Todd, N. E. (2001). (pdf). In: Cavarretta, G., P. Gioia, M. Mussi, and M. R. Palombo. The World of Elephants, Proceedings of the 1st International Congress. Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche. Rome, Italy.</ref><ref>Todd, N. E. (2005). Reanalysis of African Elephas recki: implications for time, space and taxonomy. Quaternary International 126-128:65-72.</ref> | ||
| The ] was entitled ''The "Micro" Evolution of Elephants'' which includes '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']''. | |||
| ===Diet=== | ===Diet=== | ||
Revision as of 05:16, 8 July 2008
| This article may be too long to read and navigate comfortably. Consider splitting content into sub-articles, condensing it, or adding subheadings. Please discuss this issue on the article's talk page. |
For other uses, see Elephant (disambiguation).
| Elephant | |
|---|---|

| |
| An African Bush Elephant near the border of the Serengeti and Ngorongoro Conservation Area in Tanzania. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Vertebrata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Proboscidea |
| Superfamily: | Elephantoidea |
| Family: | Elephantidae Gray, 1821 |
| Subfamilia | |
| |
Elephants (Elephantidae) are a family in the order Proboscidea in the class Mammalia. They were once classified along with other thick skinned animals in a now invalid order, Pachydermata. There are three living species: the African Bush Elephant, the African Forest Elephant (until recently known collectively as the African Elephant), and the Asian Elephant (also known as the Indian Elephant). Other species have become extinct since the last ice age, which ended about 10,000 years ago, the Mammoths being the most well-known of these.
Elephants are mammals, and the largest land animals alive today. The elephant's gestation period is 22 months, the longest of any land animal. At birth it is common for an elephant calf to weigh 120 kilograms (265 lb). An elephant may live as long as 70 years, sometimes longer. The largest elephant ever recorded was shot in Angola in 1956. This male weighed about 12,000 kg (26,400 lb), with a shoulder height of 4.2 m (13.8 ft), a metre (3 ft 4 in) taller than the average male African elephant. The smallest elephants, about the size of a calf or a large pig, were a prehistoric species that lived on the island of Crete during the Pleistocene epoch.
Elephants are symbols of wisdom in Asian cultures and are famed for their memory and high intelligence, where they are thought to be on par with cetaceans and hominids. Aristotle once said the elephant was "the beast which passeth all others in wit and mind."
Elephants are increasingly threatened by human intrusion and poaching. Once numbering in the millions, the African elephant population has dwindled to between 470,000 and 690,000 individuals. The elephant is now a protected species worldwide, with restrictions in place on capture, domestic use, and trade in products such as ivory. Elephants generally have no natural predators, although lions may take calves and occasionally adults. In some areas, lions may regularly take to preying on elephants.
The word "elephant" has its origins in the Greek ἐλέφας, meaning "ivory" or "elephant".
Zoology
Species
The African Elephant genus contains two (or, arguably, three) living species; whereas, the Asian Elephant species is the only surviving member of the Asian Elephant genus, but can be divided into four subspecies.
African elephants, at up to 3.9 m (13 ft) tall and weighing 7500 kg (8.25 short tons), are usually larger than the Asian species and they have bigger ears. Both male and female African elephants have long tusks, while their Asian counterparts have shorter ones, with those of females vanishingly small. African elephants have a dipped back, smooth forehead and two "fingers" at the tip of their trunks, whereas the Asian have an arched back, two humps on the forehead and only one "finger" at the tip of their trunks.
African elephants are further subdivided into two populations, the Savanna and Forest, and recent genetic studies have led to a reclassification of these as separate species, the forest population now being called Loxodonta cyclotis, and the Savanna (or Bush) population termed Loxodonta africana. This reclassification has important implications for conservation, because it means that where previously it was assumed that a single and endangered species comprised two small populations, if in reality these are two separate species, then as a consequence, both could be more gravely endangered than a more numerous and wide-ranging single species might have been. There is also a potential danger in that, if the forest elephant is not explicitly listed as an endangered species, poachers and smugglers might be able to evade the law forbidding trade in endangered animals and their body parts.
The Forest elephant and the Savanna elephant can hybridise – that is, breed together – successfully, though their preferences for different terrains reduce such opportunities. As the African elephant has only recently been recognized to comprise two separate species, groups of captive elephants have not been comprehensively classified and some could well be hybrids.
Successful hybridisation between African and Asian Elephant species is much more unlikely, as is animal hybridization across different genera in general. In 1978, however, at Chester Zoo, an Asian elephant cow gave birth to a hybrid calf sired by an African elephant bull (the old terms are used here as these events pre-date the current classifications). "Motty", the resulting hybrid male calf, had an African elephant's cheeks, their ears (large with pointed lobes) and legs (longer and slimmer), but the toenail numbers, (5 for each front foot, 4 hind) and the single trunk finger of an Asian elephant. His wrinkled trunk was like that of an African elephant. His forehead was sloping with one dome and two smaller domes behind it. The body was African in type, but had an Asian-type centre hump and an African-type rear hump. The calf died of infection 12 days later. It is preserved as a mounted specimen at the British Natural History Museum, London. There are unconfirmed rumours of three other hybrid elephants born in zoos or circuses; all are said to have been deformed and none survived.
African Elephant
Main articles: African Elephant, African Bush Elephant, and African Forest Elephant


The Elephants of the genus Loxodonta, known collectively as African elephants, are currently found in 37 countries in Africa.
African elephants are distinguished from Asian elephants in several ways, the most noticeable being their ears. Africans' ears are much larger. The African is typically larger than the Asian and has a concave back. Both African males and females have external tusks and are usually less hairy than their Asian cousins.
African elephants have traditionally been classified as a single species comprising two distinct subspecies, namely the savanna elephant (Loxodonta africana africana) and the forest elephant (Loxodonta africana cyclotis), but recent DNA analysis suggests that these may actually constitute distinct species. While this split is not universally accepted by experts a third species of African elephant has also been proposed.
Under the new two species classification, Loxodonta africana refers specifically to the Savanna Elephant, the largest of all elephants. In fact, it is the largest land animal in the world, standing up to 4 m (13 ft) at the shoulder and weighing approximately 7,000 kg (7.7 tons). The average male stands about 3 m (10 ft) tall at the shoulder and weighs about 5500–6000 kg (6.1–6.6 tons), the female being much smaller. Most often, Savanna Elephants are found in open grasslands, marshes, and lakeshores. They range over much of the savanna zone south of the Sahara.
The other postulated species is the Forest Elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis). Compared with the Savanna Elephant, its ears are usually smaller and rounder, and its tusks thinner and straighter and not directed outwards as much. The Forest Elephant can weigh up to 4,500 kg (10,000 lb) and stand about 3 m (10 ft) tall. Much less is known about these animals than their savanna cousins because environmental and political obstacles make them difficult to study. Normally, they inhabit the dense African rain forests of central and western Africa, though occasionally they roam the edges of forests and so overlap the territories of the Savanna elephants and breed with them. In 1979, Iain Douglas-Hamilton estimated the continental population of African elephants at around 1.3 million animals. This estimate is controversial and is believed to be a gross overestimate, but it is very widely cited and has become a de facto baseline that continues to be incorrectly used to quantify downward population trends in the species. Through the 1980s, Loxodonta received worldwide attention due to the dwindling numbers of major populations in East Africa, largely as a result of poaching. Today, according to IUCN’s African Elephant Status Report 2007 there are approximately between 470,000 and 690,000 African elephants in the wild. Although this estimate only covers about half of the total elephant range, experts do not believe the true figure to be much higher, as it is unlikely that large populations remain to be discovered. By far the largest populations are now found in Southern and Eastern Africa, which together account for the majority of the continental population. According to a recent analysis by IUCN experts, most major populations in Eastern and Southern Africa are stable or have been steadily increasing since the mid-1990s, at an average rate of 4.5% per annum.
Elephant populations in West Africa, on the other hand, are generally small and fragmented, and only account for a small proportion of the continental total. Much uncertainty remains as to the size of the elephant population in Central Africa, where the prevalence of forest makes population surveys difficult, but poaching for ivory and bushmeat is believed to be intense through much of the region. South Africa elephant population more than doubled, rising from from 8,000 to over 20,000, in the thirteen years after a 1995 ban on killing the animals. The ban was lifted in February 2008, sparking controversy among environmental groups.
Asian Elephant
Main article: Asian Elephant
The Asian elephant is smaller than the African. It has smaller ears, and typically, only the males have large external tusks.

The world population of Asian elephants – also called Indian Elephants or Elephas maximus – is estimated to be around 60,000, about a tenth of the number of African elephants. More precisely, it is estimated that there are between 38,000 and 53,000 wild elephants and between 14,500 and 15,300 domesticated elephants in Asia with perhaps another 1,000 scattered around zoos in the rest of the world. The Asian elephants' decline has possibly been more gradual with the causes primarily being poaching and habitat destruction by human encroachment.
There are several subspecies of Elephas maximus and some have been identified only using molecular markers. The first found subspecies is the Sri Lankan Elephant (Elephas maximus maximus). Found only on the island of Sri Lanka, it is the largest of the Asians. There are only an estimated 3,000–4,500 members of this subspecies left today in the wild, although no accurate census has been carried out in the recent past. Large males can weigh upward to 5,400 kg (12,000 lb) and stand over 3.4 m (11 ft) tall. Sri Lankan males have very large cranial bulges, and both sexes have more areas of depigmentation than are found in the other Asians. Typically, their ears, face, trunk, and belly have large concentrations of pink-speckled skin. There is an orphanage for elephants in Pinnawala Sri Lanka, which gives shelter to disabled, injured elephants. This program plays a large role in protecting the Sri Lankan Elephant from extinction.
Another subspecies, the Indian Elephant (Elephas maximus indicus) makes up the bulk of the Asian elephant population. Numbering approximately 36,000, these elephants are lighter grey in colour, with depigmentation only on the ears and trunk. Large males will ordinarily weigh only about 5,000 kg (11,000 lb) but are as tall as the Sri Lankan. The mainland Asian can be found in 11 Asian countries, from India to Indonesia. They prefer forested areas and transitional zones, between forests and grasslands, where greater food variety is available.
The smallest of all the elephants is the Sumatran Elephant (Elephas maximus sumatranus). Population estimates for this group range from 2,100 to 3,000 individuals. It is very light grey and has less depigmentation than the other Asians, with pink spots only on the ears. Mature Sumatrans will usually only measure 1.7–2.6 m (5.6–8.5 ft) at the shoulder and weigh less than 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). An enormous animal nonetheless, it is considerably smaller than its other Asian (and African) cousins and exists only on the island of Sumatra, usually in forested regions and partially wooded habitats.
In 2003 a further subspecies was identified on Borneo. Named the Borneo pygmy elephant, it is smaller and tamer than other Asian elephants. It also has relatively larger ears, longer tail and straighter tusks.
Body characteristics
Trunk
The proboscis, or trunk, is a fusion of the nose and upper lip, elongated and specialized to become the elephant's most important and versatile appendage. African elephants are equipped with two fingerlike projections at the tip of their trunk, while Asians have only one. According to biologists, the elephant's trunk may have over forty thousand individual muscles in it, making it sensitive enough to pick up a single blade of grass, yet strong enough to rip the branches off a tree. Some sources indicate that the correct number of muscles in an elephant's trunk is closer to one hundred thousand.
Most herbivores (plant eaters, like the elephant) possess teeth adapted for cutting and tearing off plant materials. However, except for the very young or infirm, elephants always use their trunks to tear up their food and then place it in their mouth. They will graze on grass or reach up into trees to grasp leaves, fruit, or entire branches. If the desired food item is too high up, the elephant will wrap its trunk around the tree or branch and shake its food loose or sometimes simply knock the tree down altogether.
The trunk is also used for drinking. Elephants suck water up into the trunk (up to fifteen quarts or fourteen litres at a time) and then blow it into their mouth. Elephants also inhale water to spray on their body during bathing. On top of this watery coating, the animal will then spray dirt and mud, which act as a protective sunscreen. When swimming, the trunk makes an excellent snorkel.
This appendage also plays a key role in many social interactions. Familiar elephants will greet each other by entwining their trunks, much like a handshake. They also use them while play-wrestling, caressing during courtship and mother / child interactions, and for dominance displays – a raised trunk can be a warning or threat, while a lowered trunk can be a sign of submission. Elephants can defend themselves very well by flailing their trunk at unwanted intruders or by grasping and flinging them.

An elephant also relies on its trunk for its highly developed sense of smell. Raising the trunk up in the air and swivelling it from side to side, like a periscope, it can determine the location of friends, enemies, and food sources.
Tusks
The tusks of an elephant are its second upper incisors. Tusks grow continuously; an adult male's tusks will grow about 18 cm (7 in) a year. Tusks are used to dig for water, salt, and roots; to debark trees, to eat the bark; to dig into baobab trees to get at the pulp inside; and to move trees and branches when clearing a path. In addition, they are used for marking trees to establish territory and occasionally as weapons.
Like humans who are typically right- or left-handed, elephants are usually right- or left-tusked. The dominant tusk, called the master tusk, is generally shorter and more rounded at the tip from wear. Both male and female African elephants have large tusks that can reach over 3 m (10 ft) in length and weigh over 90 kg (200 lb). In the Asian species, only the males have large tusks. Female Asians have tusks which are very small or absent altogether. Asian males can have tusks as long as the much larger Africans, but they are usually much slimmer and lighter; the heaviest recorded is 39 kg (86 lb). The tusk of both species is mostly made of calcium phosphate in the form of apatite. As a piece of living tissue, it is relatively soft (compared with other minerals such as rock), and the tusk, also known as ivory, is strongly favoured by artists for its carvability. The desire for elephant ivory has been one of the major factors in the reduction of the world's elephant population.
Some extinct relatives of elephants had tusks in their lower jaws in addition to their upper jaws, such as Gomphotherium, or only in their lower jaws, such as Deinotherium.
Teeth
Elephants' teeth are very different from those of most other mammals. Over their lives they usually have 28 teeth. These are:
- The two upper second incisors: these are the tusks.
- The milk precursors of the tusks.
- 12 premolars, 3 in each side of each jaw.
- 12 molars, 3 in each side of each jaw.

This gives elephants a dental formula of:
| Dentition |
|---|
| 1.0.3.3 |
| 0.0.3.3 |
Unlike most mammals, which grow baby teeth and then replace them with a permanent set of adult teeth, elephants have cycles of tooth rotation throughout their entire life. After one year the tusks are permanent, but the molars are replaced six times in an average elephant's lifetime. The teeth do not emerge from the jaws vertically like with human teeth. Instead, they have a horizontal progression, like a conveyor belt. New teeth grow in at the back of the mouth, pushing older teeth toward the front, where they wear down with use and the remains fall out. When an elephant becomes very old, the last set of teeth is worn to stumps, and it must rely on softer foods to chew. Very elderly elephants often spend their last years exclusively in marshy areas where they can feed on soft wet grasses. Eventually, when the last teeth fall out, the elephant will be unable to eat and will die of starvation. Were it not for tooth wearout, their metabolism would allow them to live much longer. Rupert Sheldrake has proposed this as an explanation for the elephant graveyards. However, as more habitat is destroyed, the elephants' living space becomes smaller and smaller; the elderly no longer have the opportunity to roam in search of more appropriate food and will, consequently, die of starvation at an earlier age.
Tusks in the lower jaw are also second incisors. These grew out large in Deinotherium and some mastodons, but in modern elephants they disappear early without erupting.
Skin

Elephants are called pachyderms, which means thick-skinned animals. An elephant's skin is extremely tough around most parts of its body and measures about 2.5 centimetres (1 in) thick. However, the skin around the mouth and inside of the ear is paper thin. Normally, the skin of an Asian is covered with more hair than its African counterpart. This is most noticeable in the young. Asian calves are usually covered with a thick coat of brownish red fuzz. As they get older, this hair darkens and becomes more sparse, but it will always remain on their heads and tails.
The species of elephants are typically greyish in colour, but the Africans very often appear brown or reddish from wallowing in mud holes of coloured soil. Wallowing is an important behaviour in elephant society. Not only is it important for socialization, but the mud acts as a sunscreen, protecting their skin from harsh ultraviolet radiation. Though tough, an elephant's skin is very sensitive. Without regular mud baths to protect it from burning, as well as from insect bites and moisture loss, an elephant's skin would suffer serious damage. After bathing, the elephant will usually use its trunk to blow dirt on its body to help dry and bake on its new protective coat. As elephants are limited to smaller and smaller areas, there is less water available, and local herds will often come too close over the right to use these limited resources.
Wallowing also aids the skin in regulating body temperatures. Elephants have difficulty in releasing heat through the skin because, in proportion to their body size, they have very little of it. The ratio of an elephant's mass to the surface area of its skin is many times that of a human. Elephants have even been observed lifting up their legs to expose the soles of their feet, presumably in an effort to expose more skin to the air. Since wild elephants live in very hot climates, they must have other means of getting rid of excess heat.
Legs and feet

An elephant's legs are great straight pillars, as they must be to support its bulk. The elephant needs less muscular power to stand because of its straight legs and large pad-like feet. For this reason an elephant can stand for very long periods of time without tiring. In fact, African elephants rarely lie down unless they are sick or wounded. Indian elephants, in contrast, lie down frequently.
The feet of an elephant are nearly round. African elephants have three nails on each hind foot, and four on each front foot. Indian elephants have four nails on each hind foot and five on each front foot. Beneath the bones of the foot is a tough, gelatinous material that acts as a cushion or shock absorber. Under the elephant's weight the foot swells, but it gets smaller when the weight is removed. An elephant can sink deep into mud, but can pull its legs out readily because its feet become smaller when they are lifted.
An elephant is a good swimmer, but it can neither trot, jump, nor gallop. It does have two gaits: a walk, and a faster gait that is similar to running. In walking the legs act as pendulums, with the hips and shoulders rising and falling while the foot is planted on the ground. With no "aerial phase," the faster gait does not meet all the criteria of running, as elephants always have at least one foot on the ground. However an elephant moving fast uses its legs like a running animal does, with the hips and shoulders falling and then rising while the feet are on the ground. In this gait an elephant will have three feet off the ground at one time. As both of the hind feet and both of the front feet are off the ground at the same time, this gait has been likened to the hind legs and the front legs taking turns running. Although they start this "run" at only 8 km/h, elephants may reach 25 km/h, all the while using the same gait. At this speed most other four-legged creatures are well into a gallop, even with leg length accounted for. Spring-like kinetics may explain the difference between the motion of these and other animals.
Ears
The large flapping ears of an elephant are also very important for temperature regulation. Elephant ears are made of a very thin layer of skin stretched over cartilage and a rich network of blood vessels. On hot days, elephants will flap their ears constantly, creating a slight breeze. This breeze cools the surface blood vessels, and then the cooler blood gets circulated to the rest of the animal's body. The hot blood entering the ears can be cooled as much as ten degrees Fahrenheit before returning to the body. Differences in the ear sizes of African and Asian elephants can be explained, in part, by their geographical distribution. Africans originated and stayed near the equator, where it is warmer. Therefore, they have bigger ears. Asians live farther north, in slightly cooler climates, and thus have smaller ears.
The ears are also used in certain displays of aggression and during the males' mating period. If an elephant wants to intimidate a predator or rival, it will spread its ears out wide to make itself look more massive and imposing. During the breeding season, males give off an odour from a gland located behind their eyes. Joyce Poole, a well-known elephant researcher, has theorized that the males will fan their ears in an effort to help propel this "elephant cologne" great distances.
Evolution
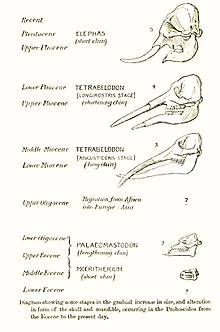
Although the fossil evidence is uncertain, scientists discovered genetic evidence that the elephant family shares distant ancestry with the sirenians (sea cows) and the hyraxes through gene comparisons. In the distant past, members of the hyrax family grew to large sizes, and it seems likely that the common ancestor of all three modern families was some kind of amphibious hyracoid. One theory suggests that these animals spent most of their time under water, using their trunks like snorkels for breathing. Modern elephants have retained this ability and are known to swim in that manner for up to 6 hours and 50 km (30 miles).
In the past, there was a much wider variety of elephant genera, including the mammoths, stegodons and deinotheria. There was also a much wider variety of species.
The poster was entitled The "Micro" Evolution of Elephants which includes Moeritherium, Deinotherium, Palaeomastodon, Mammut, Gomphotherium, Stegodon, Primelephas, Mammuthus, Elephas, and Loxodonta.
Diet
Elephants are herbivores, spending 16 hours a day collecting plant food. Their diet is at least 50% grasses, supplemented with leaves, bamboo, twigs, bark, roots, and small amounts of fruits, seeds and flowers. Because elephants only digest 40% of what they eat, they have to make up for their digestive system's lack of efficiency in volume. An adult elephant can consume 140–270 kg (300–600 lb) of food a day. 60% of that food leaves the elephant's body undigested.
Intelligence
Main article: Elephant intelligenceWith a mass just over 5 kg (11 lb), elephant brains are larger than those of any land animal, and although the largest whales have body masses twentyfold those of a typical elephant, whale brains are barely twice the mass of an elephant's. A wide variety of behaviours, including those associated with grief, making music, art, altruism, allomothering, play, use of tools, compassion and self-awareness evidence a highly intelligent species on par with cetaceans and primates.
The largest areas in elephant brain are those responsible for hearing, smell and movement coordination, and a large portion of the brain has to do with trunk management and sensitivity.
Senses
Elephants have well innervated trunks, and an exceptional sense of hearing and smell. The hearing receptors reside not only in ears, but also in trunks that are sensitive to vibrations, and most significantly feet, which have special receptors for low frequency sound and are exceptionally well innervated. It is believed that sound communication between elephants on large distances, through the ground, is important in their social lives, and elephants are observed listening by putting trunks on the ground and carefully moving their very sensitive feet.
Social behaviour

Elephants live in a structured social order. The social lives of male and female elephants are very different. The females spend their entire lives in tightly knit family groups made up of mothers, daughters, sisters, and aunts. These groups are led by the eldest female, or matriarch. Adult males, on the other hand, live mostly solitary lives.
The social circle of the female elephant does not end with the small family unit. In addition to encountering the local males that live on the fringes of one or more groups, the female's life also involves interaction with other families, clans, and subpopulations. Most immediate family groups range from five to fifteen adults, as well as a number of immature males and females. When a group gets too big, a few of the elder daughters will break off and form their own small group. They remain very aware of which local herds are relatives and which are not.
The life of the adult male is very different. As he gets older, he begins to spend more time at the edge of the herd, gradually going off on his own for hours or days at a time. Eventually, days become weeks, and somewhere around the age of fourteen, the mature male, or bull, sets out from his natal group for good. While males do live primarily solitary lives, they will occasionally form loose associations with other males. These groups are called bachelor herds. The males spend much more time than the females fighting for dominance with each other. Only the most dominant males will be permitted to breed with cycling females. The less dominant ones must wait their turn. It is usually the older bulls, forty to fifty years old, that do most of the breeding.
The dominance battles between males can look very fierce, but typically they inflict very little injury. Most of the bouts are in the form of aggressive displays and bluffs. Ordinarily, the smaller, younger, and less confident animal will back off before any real damage can be done. However, during the breeding season, the battles can get extremely aggressive, and the occasional elephant is injured. During this season, known as musth, a bull will fight with almost any other male it encounters, and it will spend most of its time hovering around the female herds, trying to find a receptive mate.
Rogue elephant is a term for a lone, violently aggressive wild elephant, separated from the rest of the herd. It is a calque of the Sinhala term hora aliya. Its introduction to English has been attributed by the Oxford English Dictionary to Sir James Emerson Tennent, but this usage may have been pre-dated by William Sirr.
Self-awareness
Mirror self recognition is a test of self awareness and cognition used in animal studies. A mirror was provided and visible marks were made on the elephant. The elephants investigated these marks, that were visible only via the mirror. The tests also included non-visible marks to rule out the possibility of their using other senses to detect these marks. This shows that elephants recognize the fact that the image in the mirror is their own self and such abilities are considered the basis for empathy, altruism and higher social interactions. This ability had earlier only been demonstrated in humans, apes and dolphins.

Homosexuality
African as well as Asiatic males will engage in same-sex bonding and mounting. Such encounters are often associated with affectionate interactions, such as kissing, trunk intertwining, and placing trunks in each other's mouths. The encounters are analogous to heterosexual bouts, one male often extending his trunk along the other's back and pushing forward with his tusks to signify his intention to mount. Unlike heterosexual relations, which are always of a fleeting nature, those between males result in a "companionship", consisting of an older individual and one or two younger, attendant males. Same-sex relations are common and frequent in both sexes, with Asiatic elephants in captivity devoting roughly 45% of sexual encounters to same-sex activity.
Communication
Elephants communicate over long distances by producing and receiving low-frequency sound (infrasound), a sub-sonic rumbling, which can travel through the ground farther than sound travels through the air. This can be felt by the sensitive skin of an elephant's feet and trunk, which pick up the resonant vibrations much as the flat skin on the head of a drum. To listen attentively, every member of the herd will lift one foreleg from the ground, and face the source of the sound, or often lay its trunk on the ground. The lifting presumably increases the ground contact and sensitivity of the remaining legs. This ability is thought also to aid their navigation by use of external sources of infrasound. Discovery of this new aspect of elephant social communication and perception came with breakthroughs in audio technology, which can pick up frequencies outside the range of the human ear. Pioneering research in elephant infrasound communication was done by Katy Payne, of the Elephant Listening Project, and is detailed in her book Silent Thunder. Though this research is still in its infancy, it is helping to solve many mysteries, such as how elephants can find distant potential mates, and how social groups are able to coordinate their movements over extensive range.
Painting
Some elephants in Thailand have been trained to paint self portraits.
Videos of elephants painting self-portraits have circulated the internet leaving many to wonder if they had been part of a hoax. The myth-busting website De-Fact-o.com has dedicated an article to validating the authenticity of the videos.
Reproduction, calves, and calf rearing
Elephant calves
Elephant social life revolves around breeding and raising of the calves. A female will usually be ready to breed around the age of thirteen, at which time she will seek out the most attractive male to mate with. Females are generally attracted to bigger, stronger, and, most importantly, older males. Such a reproductive strategy tends to increase their offspring's chances of survival.
After a twenty-two-month pregnancy, the mother will give birth to a calf that will weigh about 113 kg (250 lb) and stand over 76 cm (2.5 ft) tall. Elephants have a very long childhood. They are born with fewer survival instincts than many other animals. Instead, they must rely on their elders to teach them the things they need to know. Today, however, the pressures humans have put on the wild elephant populations, from poaching to habitat destruction, mean that the elderly often die at a younger age, leaving fewer teachers for the young.
All members of the tightly knit female group participate in the care and protection of the young. Since everyone in the herd is related, there is never a shortage of baby-sitters. In fact, a new calf is usually the centre of attention for all herd members. All the adults and most of the other young will gather around the newborn, touching and caressing it with their trunks. The baby is born nearly blind and at first relies, almost completely, on its trunk to discover the world around it.
Allomothers
After the initial excitement, the mother will usually select several full-time baby-sitters, or "allomothers", from her group. According to Cynthia Moss, a well known researcher, these allomothers will help in all aspects of raising the calf. They walk with the young as the herd travels, helping the calves along if they fall or get stuck in the mud. The more allomothers a baby has, the more free time its mother has to feed herself. Providing a calf with nutritious milk means the mother has to eat more nutritious food herself. So, the more allomothers, the better the calf's chances of survival. An elephant is considered an allomother when she is not able to have her own baby. A benefit of being an allomother is that she can gain experience or receive assistance when caring for her own calf.
Effect on the environment
Elephants' foraging activities affect the areas in which they live:
- By pulling down trees to eat leaves, breaking branches, and pulling out roots they create clearings in which new young trees and other vegetation grow to provide future nutrition for elephants and other organisms.
- Elephants make pathways through the environment that are used by other animals to access areas normally out of reach. The pathways have been used by several generations of elephants, and today people are converting many of them to paved roads.
- During the dry season elephants use their tusks to dig into dry river beds to reach underground sources of water. These newly dug water holes may become the only source of water in the area.
- Elephants are a species which many other organisms depend on. For example, termites eat elephant feces and often begin building termite mounds under piles of elephant feces.
Threat of extinction
Hunting

The threat to the African elephant presented by the ivory trade is unique to the species. Larger, long-lived, slow-breeding animals, like the elephant, are more susceptible to overhunting than other animals. They cannot hide, and it takes many years for an elephant to grow and reproduce. An elephant needs an average of 140 kg (300 lb) of vegetation a day to survive. As large predators are hunted, the local small grazer populations (the elephant's food competitors) find themselves on the rise. The increased number of herbivores ravage the local trees, shrubs, and grasses. Elephants themselves have few natural predators besides man and, occasionally, lions.
Dehabitation
Another threat to elephant's survival in general is the ongoing cultivation of their habitats with increasing risk of conflicts of interest with human cohabitants. These conflicts kill 150 elephants and up to 100 people per year in Sri Lanka. Lacking the massive tusks of its African cousins, the Asian elephant's demise can be attributed mostly to loss of its habitat.
As larger patches of forest disappear, the ecosystem is affected in profound ways. The trees are responsible for anchoring soil and absorbing water runoff. Floods and massive erosion are common results of deforestation. Elephants need massive tracts of land because, much like the slash-and-burn farmers, they are used to crashing through the forest, tearing down trees and shrubs for food and then cycling back later on, when the area has regrown. As forests are reduced to small pockets, elephants become part of the problem, quickly destroying all the vegetation in an area, eliminating all their resources.
National parks
| The examples and perspective in this South Africa may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this South Africa, discuss the issue on the talk page, or create a new South Africa, as appropriate. (Learn how and when to remove this message) |


Africa's first official reserve eventually became one of the world's most famous and successful national parks. Kruger National Park in South Africa first became a reserve against great opposition in 1898 (then Sabi Reserve). It was deproclaimed and reproclaimed several times before it was renamed and granted national park status in 1926. It was to be the first of many.
There were many problems in establishing these reserves. For example, elephants range through a wide tract of land with little regard for national borders. However, when most parks were created, the boundaries were drawn at the human-made borders of individual countries. Once a fence was erected, many animals found themselves cut off from their winter feeding grounds or spring breeding areas. Some animals died as a result, while some, like the elephants, just trampled through the fences. This did little to belie their image as a crop-raiding pest. The more often an elephant wandered off its reserve, the more trouble it got into, and the more chance it had of being shot by an angry farmer. When confined to small territories, elephants can inflict an enormous amount of damage to the local landscapes. Today there are still many problems associated with these parks and reserves, but there is now little question as to whether or not they are necessary. As scientists learn more about nature and the environment, it becomes very clear that these parks may be the elephant's last hope against the rapidly changing world around them.
Additionally, Kruger National Park has suffered from elephant overcrowding, at the expense of other species of wildlife within the reserve. South Africa slaughtered 14,562 elephants in the reserve between 1967 and 1994; it stopped in 1995, mostly due to international and local pressure. Officials at the Kruger National Park say that without action, the elephant population there will likely triple to 34,000 by 2020.
On 25 February 2008 the South African Department of Environmental Affairs and Tourism announced that South Africa would reintroduce culling for the first time since 1994 to control elephant numbers, which environmentalists say are threatening the country’s game reserves.
Humanity and elephants
Harvest from the wild
The harvest of elephants, both legal and illegal, has had some unexpected consequences on elephant anatomy as well. African ivory hunters, by killing only tusked elephants, have given a much larger chance of mating to elephants with small tusks or no tusks at all. The propagation of the absent-tusk gene has resulted in the birth of large numbers of tuskless elephants, now approaching 30% in some populations (compare with a rate of about 1% in 1930). Tusklessness, once a very rare genetic abnormality, has become a widespread hereditary trait.
It is possible, if unlikely, that continued selection pressure could bring about a complete absence of tusks in African elephants, a development normally requiring thousands of years of evolution. The effect of tuskless elephants on the environment, and on the elephants themselves, could be dramatic. Elephants use their tusks to root around in the ground for necessary minerals, tear apart vegetation, and spar with one another for mating rights. Without tusks, elephant behaviour could change dramatically.
Domestication and use

Elephants have been working animals used in various capacities by humans. Seals found in the Indus Valley suggest that the elephant was first domesticated in ancient India. However, elephants have never been truly domesticated: the male elephant in his periodic condition of musth is dangerous and difficult to control. Therefore elephants used by humans have typically been female, war elephants being an exception, however: as female elephants in battle will run from a male, only males could be used in war. It is generally more economical to capture wild young elephants and tame them than breeding them in captivity (see also elephant "crushing").
War Elephants
Main article: War elephantWar elephants were used by armies in the Indian sub-continent, the Warring States of China, and later by the Persian Empire. This use was adopted by Hellenistic armies after Alexander the Great experienced their worth against king Porus, notably in the Ptolemaic and Seleucid diadoch empires. The Carthaginian general Hannibal took elephants across the Alps when he was fighting the Romans, but brought too few elephants to be of much military use, although his horse cavalry was quite successful; he probably used a now-extinct third African (sub)species, the North African (Forest) elephant, smaller than its two southern cousins, and presumably easier to domesticate. A large elephant in full charge could cause tremendous damage to infantry, and cavalry horses would be afraid of them (see Battle of Hydaspes).
Industrial Elephants
Throughout Myanmar (Burma), Siam, India, and most of South Asia elephants were used in the military for heavy labour, especially for uprooting trees and moving logs, and were also commonly used as executioners to crush the condemned underfoot.


Elephants have also been used as mounts for safari-type hunting, especially Indian shikar (mainly on tigers), and as ceremonial mounts for royal and religious occasions, whilst Asian elephants have been used for transport and entertainment, and are common to circuses around the world.
Zoos

Elephants are also commonly exhibited in zoos and wild animal parks.
Criticism
There is growing resistance against the capture, confinement, and use of wild elephants. Animal rights advocates allege that elephants in zoos "suffer a life of chronic physical ailments, social deprivation, emotional starvation, and premature death". However, zoos argue that standards for treatment of elephants are extremely high and that minimum requirements for such things as minimum space requirements, enclosure design, nutrition, reproduction, enrichment and veterinary care are set to ensure the wellbeing of elephants in captivity.
Elephants in culture
| This article contains a list of miscellaneous information. Please relocate any relevant information into other sections or articles. (June 2008) |

- George Orwell wrote a famous essay entitled "Shooting an Elephant", chronicling a 1926 episode of being forced to shoot an elephant while he served as an Imperial Policeman in Burma.
- A famous story of Ivo Andrić is titled "A Story about the Vezier's Elephant."
Popular culture
- The phrase 'elephants never forget' refers literally to elephants supposedly having an excellent memory.
- The expression white elephant refers to an expensive burden, particularly to a situation in which much has been invested with false expectations. The phrase 'white elephant sale' was sometimes used in Australia as a synonym for jumble sale.
- Jumbo, a circus elephant, has entered the English language as a synonym for "large".
- Elephanchine, a cartoon elephant from the Dance of the Hours segment of Walt Disneys Fantasia.
- Dumbo, the elephant who learns to fly in the Disney movie of the same name.
- The French children's storybook character Babar the Elephant (an elephant king) created by Jean de Brunhoff and also an animated TV series.
- The Oakland Athletics mascot is a white elephant. The story of picking the mascot was started when New York Giants' manager John McGraw told reporters that Philadelphia manufacturer Benjamin Shibe, who owned the controlling interest in the new team, had a “white elephant on his hands," Connie Mack defiantly adopted the white elephant as the team mascot, though over the years the elephant has appeared in several different colours (currently forest green). The A’s are sometimes, though infrequently, referred to as the Elephants or White Elephants. The team mascot is nicknamed Stomper.
- The Elephant's Child is one of Rudyard Kipling's Just So Stories.
- Horton Hatches the Egg is a book by Dr. Seuss about a faithful elephant who sits on the nest of an irresponsible bird for months.
- Joseph Merrick, a British man in Victorian England was nicknamed "The Elephant Man" due to the nature and extent of his deformities.
- American band the White Stripes' fourth album was entitled Elephant, possibly because of lead singer Jack White's fondness of the animals' extreme sensitivity toward each other. The album was #390 in Rolling Stone magazine's "500 Best Albums of All Time".
- The Thai movie Tom-Yum-Goong (US title: "The Protector", UK title: "Warrior King") is about a man named Kham who travels from Thailand to Australia in pursuit of poachers who have stolen two elephants. Kham is a member of a family that protects the elephants of the King of Thailand. The movie was directed by Prachya Pinkaew and stars Tony Jaa.
- In J. R. R. Tolkien's The Lord of the Rings story, there exist oliphaunts, house-sized versions of elephants.

Religion and philosophy
- The scattered skulls of prehistoric pygmy elephants on Crete, featuring a single large nasal cavity at the front, may have formed the basis of belief in existence of cyclops, the one-eyed giants featured in Homer's Odyssey.
- A white elephant is considered holy in Thailand.
- Ganesh, the Hindu god of wisdom, has an elephant's head.
- Elephants are used in festivals in Sri Lanka, such as the Esala Perahera.
- Temple elephant
- Guruvayur Keshavan famous temple elephant in Kerala, India
- The story of the Blind Men and an Elephant was written to show how reality may be viewed by different perspectives. Its source is unknown, but it appears to have originated in India. It has been attributed to Buddhists, Hindus, Jainists, and Sufis, and was also used by Discordians.
- In Judeo-Christian accounts, including Midrash on the sixth chapter of the apocryphal book of 1 Maccabees, the youngest of the Hasmonean brothers, Eleazar the Maccabee stuck a spear under the foot of an elephant carrying an important Greek-Assyrian general, killing the elephant, the general, and Eleazar.
Politics and secular symbolism

- After Alexander's victory over the Indian king Porus, the captured war elephants became a symbol of imperial power, used as an emblem of the Seleucid diadoch empire, e.g. on coins.
- The elephant, and the white elephant (also a religious symbol of Buddha) in particular, has often been used as a symbol of royal power and prestige in Asia; occurring on the flag of the kingdom Laos (three visible, supporting an umbrella, another symbol of royal power) till it became a republic in 1975, and other Indochinese and Thai realms had also displayed one or more white elephants.
- The elephant is also the symbol for the Republican Party of the United States, originating in an 1874 cartoon of an Asian elephant by Thomas Nast of Harper's Weekly (Nast also originated the donkey as the symbol of the Democratic Party).
- The Order of the Elephant (Template:Lang-da) is the highest order of Denmark, instituted in its current form on 1693 by King Christian V. The collar of the order consists of alternating elephants and towers, and its badge shows an elephant bearing a watch tower, in front of which a Moor is sitting, holding a golden spear.
Elephant rage
Despite its popularity in zoos, and cuddly portrayal as gentle giants in fiction, Elephants are among the world's most potentially dangerous animals. They are capable of crushing and killing any other land animal, even the rhinoceros. They can experience unexpected bouts of rage, and can be vindictive. In Africa, groups of young teenage elephants attack human villages in what is thought to be revenge for the destruction of their society by massive cullings done in the 1970s and 80s. In India, male elephants attack villages at night, destroying homes and killing people on a regular basis. In the Indian state of Jharkhand, 300 people were killed by elephants between 2000 and 2004, and in Assam, 239 people have been killed by elephants since 2001. In India alone there are up to 200 elephant-caused human deaths every year, and in Sri Lanka around 50 per year.
Musth
Main article: MusthAdult male elephants naturally enter the periodic state called musth (Hindi for madness), sometimes spelt "must" in English. It is characterised by very excited and/or aggressive behavior and a thick, tar-like liquid secretion that discharges through the temporal ducts from the temporal glands on the sides of the head.
Musth is linked to sexual arousal or establishing dominance, but this relationship is far from clear. Numerous cases of elephant goring and killing of rhinoceroses in national parks in Africa have been documented and attributed to musth in young male elephants, especially those growing in the absence of older males. Studies show that reintroducing older males into the population seem to have the effect of preventing younger males from entering musth, and therefore, stopping their aggressive behavior.
A musth elephant, wild or domesticated, is extremely dangerous to humans. Domesticated elephants in India are traditionally tied to a tree and denied food and water for several days, after which the musth passes. In zoos, musth is often the cause of fatal accidents to elephant keepers. Zoos keeping adult male elephants need extremely secure enclosures, which greatly complicates the attempts to breed elephants in zoos.
Musth is accompanied by a significant rise in reproductive hormones. Testosterone levels in an elephant in musth can be as much as 60 times greater than in the same elephant at other times. However, whether this hormonal surge is the sole cause of musth, or merely a contributing factor is unknown: scientific investigation of musth is greatly hindered by the fact that even the most otherwise placid of elephants may actively try to kill any and all humans. Similarly, the tar-like secretion remains largely uncharacterised, due to the difficulties of collecting a sample for analysis.
Although it has often been speculated that musth is linked to rut, this is unlikely, because the female elephant's estrus cycle is not seasonally-linked. Furthermore, bulls in musth have often been known to attack female elephants, regardless of whether or not the females are in heat.
The Hindi word "musth" is from the Urdu mast, which in turn is from a Persian root meaning "intoxicated".
The Channel 5 British television program "The Dark Side of Elephants" (March 20 2006) stated that during musth:
- The swelling of the temporal glands presses on the elephant's eyes and causes the elephant severe pain comparable to severe root abscess toothache. One elephant behaviour that tries to counteract this is digging the tusks into the ground.
- The musth secretion, which naturally runs down into the elephant's mouth, is full of ketones and aldehydes and (to a human at least) tastes unbelievably foul.
- As a result, musth behaviour is at least partly due to the elephant being driven mad by pain and distress.
Other causes
At least a few elephants have been suspected to be drunk during their attacks. In December 1998, a herd of elephants overran a village in India. Although locals reported that nearby elephants had recently been observed drinking beer which rendered them "unpredictable", officials considered it the least likely explanation for the attack. An attack on another Indian village occurred in October 1999, and again locals believed the reason was drunkenness, but the theory was not widely accepted. Purportedly drunk elephants raided yet another Indian village again on December 2002, killing six people, which led to killing of about 200 elephants by locals. Elephants have used their powers of deduction to "hijack" trucks carrying sugarcane.
Predators, parasites and diseases
Other than humans, adult elephants have no predators. On one occasion during a drought, lions were videotaped successfully attacking a baby elephant and attempting to attack a full grown female elephant. Both attacks occurred at night.
Elephants have a variety of both ecto-parasites and endo-parasites, including the highly specialized flies of the genus Cobboldia.
Family classification
See also
- Crushing by elephant
- Dwarf elephant
- Elephant's ability to swim
- Elephant's graveyard
- Elephant in the room
- Elephant sanctuary
- Elephants in Kerala culture
- Hammerskjoeld Simwinga -- environmentalist
- History of elephants in Europe
- Mûmak
- Temple elephant
- War elephant
- White elephant
- Year of the Elephant
References
- "African Elephant". National Geographic. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- "Frequently asked African Elephant questions". South African National Parks. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- "Animal Bytes: Elephant". San Diego Zoo. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- Bate, D.M.A. 1907. On Elephant Remains from Crete, with Description of Elephas creticus sp.n. Proc. zool. Soc. London: 238-250.
- ^ "What Makes Dolphins So Smart?". Discovery Communications. Retrieved 2007-07-31.
- ^ "Cognitive behaviour in Asian elephants: use and modification of branches for fly switching". BBC. Retrieved 2007-07-31.
- "WWF: African elephants". 2007-03-28. Retrieved 2007-06-09.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - A. J. Loveridge, J. E. Hunt, F. Murindagomo & D. W. Macdonald. (2006) Influence of drought on predation of elephant (Loxodonta africana) calves by lions (Panthera leo) in an African wooded savannah. Journal of Zoology 270:3, 523–530
- "Great Plains". Planet Earth. Episode 7. November 2006.
{{cite episode}}: Unknown parameter|serieslink=ignored (|series-link=suggested) (help) - Hemson, Graham (2003) The Ecology and Conservation of Lions: Human-Wildlife Conflict in semi-arid Botswana. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Oxford.
- Soanes, Catherine (2006). Concise Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-929634-0.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Roca, Alfred L. (24 August 2001). "Genetic evidence for two species of elephant in Africa". Science. 293 (5534): 1473. doi:10.1126/science.1059936. PMID 11520983.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - African Elephant Specialist Group (December 2003). "Statement on the taxonomy of extant Loxodonta" (pdf). IUCN. Retrieved 2006-12-08.
- Eggert, Lori S. (2002-10-07). "The evolution and phylogeography of the African elephant inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequence and nuclear microsatellite markers". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 269 (1504): 1993–2006. doi:10.1098/rspb.2002.2070. ISSN: 0962-8452 (Paper) 1471-2954 (Online).
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Douglas-Hamilton, Iain (1979). The African Elephant Action Plan. unpublished report.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Parker, Ian (1983). Ivory Crisis. Chatto and Windus, London. p. 184.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Blanc, JJ (2007). African Elephant Status Report 2007: An update from the African Elephant Database (PDF). IUCN, Gland and Cambridge. p. 276. ISBN 978-2-8317-0970-3.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - Blanc, JJ (January–June 2005). "Changes in elephant numbers in major savanna populations in eastern and southern Africa" (PDF). Pachyderm. 38 (38). IUCN/SSC African Elephant Specialist Group: 19–28. Retrieved 2006-12-08.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: date format (link) - Blanc, JJ (January–June 2005). "Changes in elephant numbers in major savanna populations in eastern and southern Africa" (PDF). Pachyderm. 38 (38). IUCN/SSC African Elephant Specialist Group: 19–28. Retrieved 2006-12-08.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: date format (link) - Blanc et al. 2007, op. cit.
- Blanc, JJ (2003). African Elephant Status Report 2002: An update from the African Elephant Database (PDF). IUCN, Gland and Cambridge. p. 308. ISBN 2-8317-0707-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Blake, Stephen (2005). "Central African Forests: Final Report on Population Surveys (2003-2005)" (pdf). CITES MIKE Programme, Nairobi. Retrieved 2006-12-08.
- South Africa to Allow Elephant Killing
- "South Africa to sanction killing of elephants" (pdf). CNN. 2008-02-25. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- "Asian Elephant distribution". EleAid. Retrieved May 2007.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - "Anatomy of the elephants". Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- Paul MacKenzie. "Elephant Information Repository: The Trunk". Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- ^ West, John B. (2001), "Snorkel breathing in the elephant explains the unique anatomy of its pleura" (PDF), Respiratory Physiology, 126 (1): 1–8, doi:10.1016/S0034-5687(01)00203-1
{{citation}}: Check|author-link=value (help); External link in|author-link= - ^ West, John B.; Fu, Zhenxing; Gaeth, Ann P.; Short, Roger V. (2003-11-14), "Fetal lung development in the elephant reflects the adaptations required for snorkeling in adult life" (PDF), Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology, 138 (2–3): 325–333, doi:10.1016/S1569-9048(03)00199-X
{{citation}}: Check|author-link=value (help); External link in|author-link= - "Elephant Anatomy". Indianapolis Zoo. Retrieved 2007-05-28.
- Moore, Tom. (May 2007). "Biomechanics: A Spring in Its Step". Natural History 116:(4) 28-9.
- Ren, L. & J.R. Hutchinson (2007). "The three-dimensional locomotor dynamics of African (Loxodonta africana) and Asian (Elephas maximus) elephants reveal a smooth gait transition at moderate speed". J. Roy. Soc. Interface. 5: 195. doi:10.1098/rsif.2007.1095. ISSN 1742-5662.
- Hutchinson, J.R.; et al. (2003). "Biomechanics: Are fast-moving elephants really running?". Nature. 422: 493–494. doi:10.1038/422493a.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Todd, N. E. (2001). African Elephas recki: time, space and taxonomy (pdf). In: Cavarretta, G., P. Gioia, M. Mussi, and M. R. Palombo. The World of Elephants, Proceedings of the 1st International Congress. Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche. Rome, Italy.
- Todd, N. E. (2005). Reanalysis of African Elephas recki: implications for time, space and taxonomy. Quaternary International 126-128:65-72.
- Braden, Claire. "Not so Dumbo: Elephant Intelligence". Retrieved 2007-05-27.
- "Elephants' jumbo mirror ability". Retrieved 2007-08-10.
- Joshua M. Plotnik, Frans B. M. de Waal, and Diana Reiss (2006) Self-recognition in an Asian elephant. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 103(45):17053–17057 10.1073/pnas.0608062103 abstract
- Bruce Bagemihl, Biological Exuberance: Animal Homosexuality and Natural Diversity, St. Martin's Press, 1999; pp.427-430
- "Elephant Listening Project". Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- Elephant 'self-portrait' on show
- Video of an elephant painting an elephant
- Animal experts discuss elephant painting
- http://www.de-fact-o.com/fact_read.php?id=117 Elephant Painting De-Fact-o.com article
- "Conservation GIS Projects". Smithsonian National Zoological Park. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- "S. Africa elephant culling splits wildlife groups". Associated Press. 2005-11-28. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Animal rights outrage over plan to cull South Africa's elephants". Times Online. 2008-02-26. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
- "The Learning Kingdom". 1999-03-30.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - http://www.helpelephantsinzoos.com/topeka_zoo.html
- http://72.14.253.104/search?q=cache:zy-rTMG8dRgJ:www.elephantvoices.org/tools/documents/Poole_bullhooks_boston_jan2007.pdf+elephant+rocking+behavior&hl=en&ct=clnk&cd=2&gl=us&client=firefox-a
- http://72.14.253.104/search?q=cache:kdYDBPzWaXwJ:www.elephantvoices.org/tools/documents/Statement_regarding_Arna_March_2002.pdf+elephant+rocking+behavior&hl=en&ct=clnk&cd=1&gl=us&client=firefox-a
- http://www.elephants.com/media/yahoo_11_18_05.htm
- "Resistance against capture and training of wild elephants". Amboseli Trust for Elephants. Retrieved 2007-12-01.
{{cite web}}: External link in|publisher= - "SaveWildElephants.com". PETA. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- ^ Huggler, Justin (2006-10-12). "Animal Behaviour: Rogue Elephants". The Independent. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Highfield, Roger (2006-02-17). "Elephant rage: they never forgive, either". Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- "Killing of black and white rhinoceroses by African elephants in Hluhluwe-Umfolozi Park, South Africa" by Rob Slotow, Dave Balfour, and Owen Howison. Pachyderm 31 (July-December, 2001):14-20. Accessed 2007-09-14.
- Siebert, Charles (2006-10-08). "An Elephant Crackup?". New York Times Magazine. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "India elephant rampage". BBC News. 1998-12-24. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Drunken elephants trample village". BBC News. 1999-10-21. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Drunk elephants kill six people". BBC News. 2002-12-17. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Elephants hijack sugarcane trucks". Sydney Morning Herald. 2003-12-09. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lions attack Elephant" (Video). National Geographic. Retrieved 2007-06-16.
- Wikisource: "The Blindmen and the Elephant" by John Godfrey Saxe
- Shoshani, J. (2005). Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 90–91. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- External link to national geographics elephant rage episode of Explorer
- Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 26 (2003) 421–434
External links
- C. Johnson, "Elephant trunks were once snorkels", News in Science 1999-05-11,
- Elephant: Wildlife summary from the African Wildlife Foundation
- EleAid - Elephant facts, info and pictures from Asian elephant charity
- Elephant Encyclopedia
- Sanparks - South African National Parks official website
- How elephants communicate
- Elephant News - latest headlines about elephants
- Photo of Pinnewella Elephant Orphanage in Sri Lanka
- Seek My Bowl on elephants as symbols
- Elephant Reintroduction Foundation
- Amboseli Trust for Elephants - interactive web site
- Animal info
- List of easy-to-read articles about elephants
- Temple Elephants in India – A short video in Quicktime format.
- African Elephant Database – For current info on African elephant distribution and numbers.
- Elephant Sanctuary Plettenberg Bay South Africa
- Elephant Sanctuary, Howenwald, Tenn.
- Elephant Nature Park, Northern Thailand
- A musth FAQ
- Short Videos
| Extant Proboscidea species by family | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| Elephantidae (Elephants) |
| ||||
| Category | |||||
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: