| Revision as of 10:04, 28 August 2008 edit219.79.166.153 (talk) →Other uses of the term East Asia← Previous edit | Revision as of 11:44, 29 August 2008 edit undo219.79.166.153 (talk)No edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
| {{Chinese | {{Chinese | ||
| |pic=East_Asia_(Geog).PNG|piccap=Geographical East Asia{{dubious}} | |pic=East_Asia_(Geog).PNG|piccap=Geographical East Asia{{dubious}}<!--tag added as this map totally contradicts what in-text citations state--> | ||
| |pic2=LocationEastAsia.PNG|piccap2= |
|pic2=LocationEastAsia.PNG|piccap2=Geographic East Asia shaded in green, including the Chinese far east (in intermediate green), which are also regarded as Central Asian and part of Russia (in light green) which is also regarded as North Asian.<ref name=encarta-eats-asia/><ref>, ]</ref><ref name=EBeasia/><ref></ref><ref>, ]</ref><ref name="BritannicaTib">Tibet is considered Central Asian</ref><ref>http://ieas.berkeley.edu/events/2004.03.13.html "Xinjiang: Central Asia or China?"</ref><ref>http://www.ceibs.edu/ase/Documents/rethinking.htm Rethinking Central Asia</ref><ref>http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/15095a.htm CATHOLIC ENCYCLOPEDIA: Turkestan</ref><ref>http://www.china-briefing.com/news/2008/05/22/china-reconnects-with-tajikistan.html China Invests in Central Asia Stability Through Tajikistan ''Xinjiang, a name meaning new territory in Mandarin, was militarily captured and annexed by China after World War II. Its 8 million residents are made up of mostly Muslim Turkic groups that include the Uyghurs, Uzbeks, Kyrgyz, Tatars, Kazakhs, and the Tajiks that profess affinity with Central Asia than with the local Han Chinese.'' refers to the indigenous people as being Central Asian</ref><ref> 9789622177901 Tredinnick, Jeremy and Christoph Baumer and Judy Bonavia. Xinjiang: China's Central Asia, -: Odyssey Publications, 2008.</ref> | ||
| |t=東亞 | |t=東亞 | ||
| |s=东亚 | |s=东亚 | ||
Revision as of 11:44, 29 August 2008
This article is about the geographical region. For the Miyuki Nakajima album, see East Asia (album). For the fictional superstate, see Eastasia (Nineteen Eighty-Four).East Asia
| Area | 11,839,074 km² |
|---|---|
| Population | 1,555,784,500 |
| Density | 131 per km² |
| Countries and Territories | Mainland China Hong Kong Japan Macau Mongolia North Korea South Korea Taiwan |
| Languages and language families | Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Mongolian, and many others |
| Time zones | UTC +7:00 (Western Mongolia) to UTC +9:00 (Japan and Korean Peninsula) |
| Capital cities | Beijing Pyongyang Seoul Taipei Tokyo Ulan Bator |
| Other major cities | Busan, Guangzhou Hong Kong, Kaohsiung, Osaka, Shanghai, Yokohama. |
East Asia is a subregion of Asia that can be defined in either geographical or cultural terms. Geographically, it covers about 12,000,000 km², or about 28 percent of the Asian continent, about 15 percent bigger than the area of Europe. More than 1.5 billion people, about 40 percent of the population of Asia or a quarter of all the people in the world, live in geographic East Asia, which is about twice the population of Europe. The region is one of the world's most crowded places. The population density of East Asia, 131 per km², is about three times the world average of 45 per km².
Historically, many societies in East Asia have been part of the Chinese cultural sphere, and East Asian vocabulary and scripts are often derived from Classical Chinese and Chinese script. Major religions include Buddhism (mostly Mahayana), Confucianism or Neo-Confucianism, Taoism, and Chinese folk religion, and Shinto in Japan.
This combination of language, political philosophy, and religion (as well as art, architecture, holidays and festivals, etc.) overlaps with the geographical designation of East Asia for the most part, with a few exceptions, such as the overseas Chinese (including those in Singapore, Malaysia, Vietnam, and the West).
East Asia and Eastern Asia (the latter form preferred by the United Nations) are both more modern terms for the traditional name the Far East, which describes the region's geographical position in relation to Europe rather than its location within Asia. However, in contrast to the United Nations definition, East Asia commonly is used to refer to the eastern part of Asia, as the term implies.
Other uses of the term East Asia
The following political entities are consistently seen as located in geographical East Asia:
- (Including the Special Administrative Regions of
 Hong Kong and
Hong Kong and  Macau)
Macau)
 Japan
Japan South Korea (Republic of Korea)
South Korea (Republic of Korea) North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) Republic of China (Taiwan)
Republic of China (Taiwan)
| East Asia | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Geographical East Asia Geographical East Asia | |||||||||||||||||
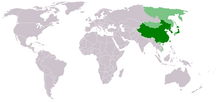 Geographic East Asia shaded in green, including the Chinese far east (in intermediate green), which are also regarded as Central Asian and part of Russia (in light green) which is also regarded as North Asian. Geographic East Asia shaded in green, including the Chinese far east (in intermediate green), which are also regarded as Central Asian and part of Russia (in light green) which is also regarded as North Asian. | |||||||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 東亞 | ||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 东亚 | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Vietnamese name | |||||||||||||||||
| Vietnamese alphabet | Đông Á | ||||||||||||||||
| Korean name | |||||||||||||||||
| Hangul | 동아시아 | ||||||||||||||||
| Hanja | 東亞細亞 | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | Зүүн Ази ᠵᠤᠨ ᠠᠵᠢ Züün Azi | ||||||||||||||||
| Japanese name | |||||||||||||||||
| Kanji | 東亜 | ||||||||||||||||
| Kana | ひがしアジア | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Russian name | |||||||||||||||||
| Russian | Восточная Азия | ||||||||||||||||
| Romanization | Vostochnaja Azija | ||||||||||||||||
In addition the following countries are sometimes included in the definition of East Asia
 Mongolia
Mongolia Siberia, Russia (considered either East Asia or North Asia)
Siberia, Russia (considered either East Asia or North Asia) Vietnam
Vietnam
The following peoples or societies are commonly seen as being encompassed by cultural East Asia:
- Chinese society (including the predominantly Chinese regions outside China proper, such as Singapore and Taiwan)
- Japanese society
- Korean society
- Vietnamese society
Some consider the following countries or regions as part of East Asia, while others do not. Disagreements hinge on the difference between the cultural and geographic definitions of the term. Political perspective is also an important factor. In descending order in terms of the frequency with which they are described as East Asian:
- The parts of China that are not historically dominated by Han Chinese: Qinghai, Tibet, Xinjiang (considered either East Asia or Central Asia or South Asia in the case of Tibet—here the primary question is cultural, with geography also at issue)
 Mongolia (considered either East Asia or Central Asia—here culture and/or geography may be at issue)
Mongolia (considered either East Asia or Central Asia—here culture and/or geography may be at issue) Singapore (considered either East Asia or Southeast Asia—here the primary question is geographic)
Singapore (considered either East Asia or Southeast Asia—here the primary question is geographic) Vietnam (considered either East Asia or Southeast Asia—here the primary question is geographic)
Vietnam (considered either East Asia or Southeast Asia—here the primary question is geographic) Russian Far East (considered either East Asia or North Asia—here the primary question is political, with culture and geography also at issue)
Russian Far East (considered either East Asia or North Asia—here the primary question is political, with culture and geography also at issue)
In infrequent circumstances, the term East Asia is purposefully used to include all countries in Southeast Asia, especially when used in dualism with the term West Asia, the latter of which is then used to include those regions commonly considered West Asia, Central Asia and Southwest Asia.
Other subregions of Asia
- Southeast Asia
- South Asia
- Central Asia
- Southwest Asia or West Asia (One definition of the Middle East is synonymous with Southwest Asia)
- North Asia (Siberia)
- Northern Eurasia (Extends into part of Europe)
- Central Eurasia (Extends into part of Europe)
See also
- Cities of East Asia
- East Asian studies
- Asian Network of Major Cities 21
- East Asian languages
- East Asian calligraphy
- Four Asian Tigers – a label pertinent to the recent economic history of the region.
- East Asia Summit
- History of East Asia
- Sinosphere
- East Asian Community
- Russian Far East (East Asia north of this area)
Notes and references
- The area figure is based on the combined areas of the People's Republic of China (including Hong Kong, Macau, Aksai Chin, and Trans-Karakoram Tract), Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and the Republic of China (Taiwan) as listed at List of countries and outlying territories by total area.
- The population figure is the combined populations of the People's Republic of China (Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau), Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Republic of China (Taiwan) as listed at List of countries by population (last updated March 8, 2008).
- Dispute due to mainly Political status of Taiwan between governments of Republic of China and People's Republic of China.
- ^ "East Asia". encarta. Micosoft. Retrieved 2008-01-12.
East A·sia the countries, territories, and regions of China, Hong Kong, Japan, North Korea, South Korea, Macau, Mongolia, parts of Russia, and Taiwan.
- ^ Columbia University - "East Asian cultural sphere" "The East Asian cultural sphere evolves when Japan, Korea, and what is today Vietnam all share adapted elements of Chinese civilization of this period (that of the Tang dynasty), in particular Buddhism, Confucian social and political values, and literary Chinese and its writing system."
- See, List of countries by population density
- "Far East". encarta. Micosoft. Retrieved 2008-01-12.
Far East a former term for the countries of East Asia, sometimes extended to include those of Southeast Asia (dated)
- ^ , Britannica Online Encyclopedia, saying: "The present political boundaries of China, which include Tibet, Inner Mongolia, Sinkiang, and the northeastern provinces formerly called Manchuria, embrace a far larger area of East Asia than will be discussed here...."
- The Republic of China (Taiwan) is has limited recognition within the international community as a sovereign state, see Political status of Taiwan.
- Plateaus, National Geographic Society
- East Asian Region - Tibet
- Department of East Asian Studies, University of Helsinki
- Tibet is considered Central AsianTibet - Britannica Online Encyclopedia
- http://ieas.berkeley.edu/events/2004.03.13.html "Xinjiang: Central Asia or China?"
- http://www.ceibs.edu/ase/Documents/rethinking.htm Rethinking Central Asia
- http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/15095a.htm CATHOLIC ENCYCLOPEDIA: Turkestan
- http://www.china-briefing.com/news/2008/05/22/china-reconnects-with-tajikistan.html China Invests in Central Asia Stability Through Tajikistan Xinjiang, a name meaning new territory in Mandarin, was militarily captured and annexed by China after World War II. Its 8 million residents are made up of mostly Muslim Turkic groups that include the Uyghurs, Uzbeks, Kyrgyz, Tatars, Kazakhs, and the Tajiks that profess affinity with Central Asia than with the local Han Chinese. refers to the indigenous people as being Central Asian
- 9789622177901 Tredinnick, Jeremy and Christoph Baumer and Judy Bonavia. Xinjiang: China's Central Asia, -: Odyssey Publications, 2008.
- MSN Encarta, East Asia
- Columbia University East Asian Cultural Sphere
- R. Keith Schopper's East Asia: Identities and Change in the Modern World
- Joshua A. Fogel (UC Santa Barbara/University of Indiana) Nationalism, the Rise of the Vernacular, and the Conceptualization of Modernization in East Asian Comparative Perspective
- United Nations Environment Programme (mentions sinosphere countries) Approaches to Solution of Eutrophication
- Center for South Asia Studies: University of California, Berkeley
- Center for South Asia Outreach UW-Madison
- Department of South Asia Studies: University of Pennsylvania
- South Asia Language Resource Center: The University of Chicago
- AIIS Advanced Language Programs in India
- Tibet is located on the Tibetan Plateau which is in Central Asia.
