| Revision as of 10:49, 31 May 2004 editLupin (talk | contribs)19,513 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 01:29, 2 June 2004 edit undoDMG413 (talk | contribs)22,076 editsNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| :''Also see: ], ], ], ]'' | :''Also see: ], ], ], ], ]'' | ||
| <table border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="right" style="margin-left:0.5em;" width="300px"> | <table border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="right" style="margin-left:0.5em;" width="300px"> | ||
Revision as of 01:29, 2 June 2004
- Also see: Gulf of Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Equatorial Guinea, New Guinea, Papua New Guinea
| |||||
| National motto: Travail, Justice, Solidarité (Work, Justice, Solidarity) | |||||
 | |||||
| Official language | French (official), Fula, Arabic, others | ||||
| Capital | Conakry | ||||
| Capital's coordinates | 9° 30' N, 13° 43' W | ||||
| Largest City | Conakry | ||||
| President | Lansana Conté | ||||
| Prime Minister | François Lonseny Fall | ||||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 75th 245,857 km² Negligible | ||||
| Population
- Density | Ranked 83rd
30.4/km² | ||||
| GDP (PPP)
- GDP/head | Ranked 112th
$2,100 | ||||
| Currency | Guinean franc (FG) | ||||
| Time zone | UTC ) | ||||
| Independence | 2 October 1958, from France | ||||
| National anthem | Liberté (Liberty) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .GN | ||||
| Calling Code | 224 | ||||
The Republic of Guinea is a nation of northwest Africa.
History
Main article: History of Guinea
Independent from France since 1958, Guinea did not hold democratic elections until 1993 when Gen. Lansana Conté (head of the military government) was elected president in disputed balloting. Security clampdowns continue, although not as severe as in earlier decades. Reelected in 1998, the President faced growing criticism in 1999 for his jailing of a major opposition leader and widespread economic malaise. Unrest in Sierra Leone also continued to threaten Guinea's stability.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Guinea
Prefectures
Main article: Prefectures of Guinea
Guinea is divided into 33 prefectures and one special zone (the capital, Conakry).
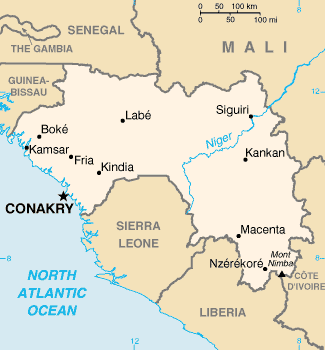
Geography
Main article: Geography of Guinea
The capital is Conakry.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Guinea
Guinea possesses major mineral, hydropower, and agricultural resources, yet remains a poor underdeveloped nation. The agricultural sector employs 80% of the work force. Guinea possesses over 25% of the world's bauxite reserves and is the second largest bauxite producer. The mining sector accounted for about 75% of exports in 1998. Long-run improvements in government fiscal arrangements, literacy, and the legal framework are needed if the country is to move out of poverty. The government made encouraging progress in budget management in 1997-99. Even with a recovery in prices for some of Guinea's main commodity exports, annual GDP is unlikely to increase by more than 5% in 2000-2001.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Guinea
Culture
Main article: Culture of Guinea
Miscellaneous topics
| Countries and territories of Africa | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
| ||||||||||
| States with limited recognition | |||||||||||
| Dependent territories |
| ||||||||||
| African territories fully part of non-African states |
| ||||||||||