| Revision as of 16:04, 18 November 2011 editDrphilharmonic (talk | contribs)6,066 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 19:13, 26 November 2011 edit undoJynto (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users3,201 editsm Re-arranging imagesNext edit → | ||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| | verifiedrevid = 411843960 | | verifiedrevid = 411843960 | ||
| | Name = Pyrrole | | Name = Pyrrole | ||
| | ImageFileL1_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | | ImageFileL1_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | ||
| | ImageFileL1 = Pyrrole-2D- |
| ImageFileL1 = Pyrrole-2D-full.svg | ||
| | ImageSizeL1 = |
| ImageSizeL1 = 120 | ||
| | ImageNameL1 = |
| ImageNameL1 = Explicit structural formula of pyrrole, with aromaticity indicated by dashed bonds | ||
| | ImageFileR1_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | | ImageFileR1_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | ||
| | ImageFileR1 = Pyrrole-2D- |
| ImageFileR1 = Pyrrole-2D-numbered.svg | ||
| | ImageSizeR1 = |
| ImageSizeR1 = 100 | ||
| | ImageNameR1 = |
| ImageNameR1 = Numbered skeletal formula of pyrrole | ||
| | ImageFileL2 = Pyrrole-CRC-MW-3D- |
| ImageFileL2 = Pyrrole-CRC-MW-3D-balls-A.png | ||
| | ImageNameL2 = |
| ImageNameL2 = Ball-and-stick model of the pyrrole molecule | ||
| ⚫ | | ImageSizeL2 = 120 | ||
| | ImageFileR2 = Pyrrole-CRC-MW-3D- |
| ImageFileR2 = Pyrrole-CRC-MW-3D-vdW.png | ||
| | ImageNameR2 = |
| ImageNameR2 = Space-filling model of the pyrrole molecule | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | ImageSizeR2 = 110 | |||
| | IUPACName = 1''H''-Pyrrole | | IUPACName = 1''H''-Pyrrole | ||
| | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
Revision as of 19:13, 26 November 2011
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name 1H-Pyrrole | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| Beilstein Reference | 1159 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.387 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 1705 | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1992, 1993 | ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C4H5N | ||
| Molar mass | 67.091 g·mol | ||
| Density | 0.967 g cm | ||
| Melting point | −23 °C (−9 °F; 250 K) | ||
| Vapor pressure | 7 mmHg at 23 °C | ||
| Viscosity | 0.001225 Pa s | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Heat capacity (C) | 1.903 J k mol k | ||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
108.2 kJ mol (gas) | ||
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH298) |
2242 kJ mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 | ||
| Flash point | 33.33 °C | ||
| Explosive limits | 3.1-14.8% | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colourless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3. Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme.
Pyrroles are components of more complex macrocycles, including the porphyrins of heme, the chlorins, bacteriochlorins, chlorophyll, porphyrinogens.
Properties
Pyrrole has very low basicity compared to conventional amines and some other aromatic compounds like pyridine. This decreased basicity is attributed to the delocalization of the lone pair of electrons of the nitrogen atom in the aromatic ring. Pyrrole is a very weak base with a pKaH of about −4. Protonation results in loss of aromaticity, and is, therefore, unfavorable.
Like many amines, pyrrole darkens on exposure to air and light, and needs to be distilled immediately before use.
-
 Pyrrole being distilled.
Pyrrole being distilled.
-
 Pyrrole after the distillation process. It is now colorless and transparent to all wavelengths of visible light due to the removal of impurities such as polypyrrole.
Pyrrole after the distillation process. It is now colorless and transparent to all wavelengths of visible light due to the removal of impurities such as polypyrrole.
Synthesis
Pyrrole is prepared industrially by treatment of furan with ammonia in the presence of solid acid catalysts.
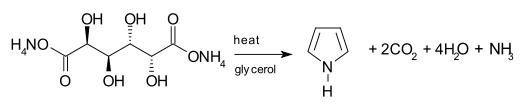
One synthetic route to pyrrole involves the decarboxylation of ammonium mucate, the ammonium salt of mucic acid. The salt is typically heated in a distillation setup with glycerol as a solvent.
Substituted pyrroles
Many methods exist for the organic synthesis of pyrrole derivatives. Classic "named reactions" are the Knorr pyrrole synthesis, the Hantzsch pyrrole synthesis, and the Paal-Knorr synthesis. More specialized methods are listed here.
The starting materials in the Piloty-Robinson pyrrole synthesis are 2 equivalents of an aldehyde and hydrazine. The product is a pyrrole with specific substituents in the 3 and 4 positions. The aldehyde reacts with the diamine to an intermediate di-imine (R–C=N−N=C–R), which, with added hydrochloric acid, gives ring-closure and loss of ammonia to the pyrrole.
In one modification, propionaldehyde is treated first with hydrazine and then with benzoyl chloride at high temperatures and assisted by microwave irradiation:
In the second step, a sigmatropic reaction takes place between two intermediates.
Pyrrole can be polymerized to form polypyrrole.
Reactivity
The NH proton in pyrroles is moderately acidic with a pKa of 16.5. Pyrrole can be deprotonated with strong bases such as butyllithium and sodium hydride. The resulting alkali pyrrolide is nucleophilic. Treating this conjugate base with an electrophile such as methyl iodide gives N-methylpyrrole.
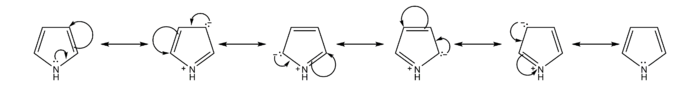
The resonance contributors of pyrrole provide insight to the reactivity of the compound. Like furan and thiophene, pyrrole is more reactive than benzene towards electrophilic aromatic substitution because it is able to stabilize the positive charge of the intermediate carbocation.
Pyrrole undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution predominantly at the 2 and 5 positions. Two such reactions that are especially significant for producing functionalized pyrroles are the Mannich reaction and the Vilsmeier-Haack reaction (depicted below), both of which compatible with a variety of pyrrole substrates.
Pyrroles react with aldehydes to form porphyrins. For example, benzaldehyde condenses with pyrrole to give tetraphenylporphyrin. Pyrrole compounds can also participate in cycloaddition (Diels-Alder) reactions under certain conditions, such as under Lewis acid catalysis, heating, or high pressure.
Pyrrole polymerizes in light. An oxidizing agent, such as ammonium persulfate, can also be used, typically at 0 ºC and in darkness to control the polymerization.
Commercial uses
Pyrrole has no significant commercial application, but N-methylpyrrole is a precursor to N-methylpyrrolecarboxylic acid, a building-block in pharmaceutical chemistry.
Analogs and derivatives
Structural analogs of pyrrole include:
- Pyrroline, a partially saturated analog with one double bond
- Pyrrolidine, the saturated hydrogenated analog
- Kryptopyrrole, a pyrrole derivative once thought to be associated with schizophrenia
Heteroatom structural analogs of pyrrole include:
- Arsole, a moderately-aromatic arsenic analog
- Bismole, a bismuth analog
- Borole, a boron analog
- Furan, an aromatic oxygen analog
- Gallole, a gallium analog
- Germole, a germanium analog
- Phosphole, a non-aromatic phosphorus analog
- Pyrazole and imidazole, analogs with two nitrogen atoms
- Silole, a silicon analog
- Stannole, a tin analog
- Stibole, an antimony analog
- Thiophene, a sulfur analog
Derivatives of pyrrole include indole, a derivative with a fused benzene ring.
See also
References
- Loudon, Marc G. (2002). "Chemistry of Naphthalene and the Aromatic Heterocycles.". Organic Chemistry (Fourth ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 1135–1136. ISBN 0-19-511999-1.
- Cox, Michael; Lehninger, Albert L; Nelson, David R. (2000). Lehninger principles of biochemistry. New York: Worth Publishers. ISBN 1-57259-153-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Jonas Jusélius and Dage Sundholm (2000). "The aromatic pathways of porphins, chlorins and bacteriochlorins". Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2: 2145–2151. doi:10.1039/b000260g.
{{cite journal}}:|format=requires|url=(help) - Armarego, Wilfred, L.F.; Chai, Christina, L.L. (2003). Purification of Laboratory Chemicals (5th ed.). Elsevier. p. 346.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Albrecht Ludwig Harreus "Pyrrole" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_453
- Practical Organic Chemistry, Vogel, 1956, Page 837, Link (12 MB)
- Piloty, O. (1910). "Synthese von Pyrrolderivaten: Pyrrole aus Succinylobernsteinsäureester, Pyrrole aus Azinen". Chem. Ber. 43: 489. doi:10.1002/cber.19100430182.
- Robinson, Gertrude Maud; Robinson, Robert (1918). "LIV.—A new synthesis of tetraphenylpyrrole". J. Chem. Soc. 113: 639. doi:10.1039/CT9181300639.
- Benjamin C. Milgram, Katrine Eskildsen, Steven M. Richter, W. Robert Scheidt, and Karl A. Scheidt (2007). "Microwave-Assisted Piloty-Robinson Synthesis of 3,4-Disubstituted Pyrroles" (Note). J. Org. Chem. 72 (10): 3941–3944. doi:10.1021/jo070389. PMC 1939979. PMID 17432915.
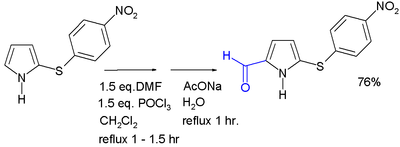
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Jose R. Garabatos-Perera, Benjamin H. Rotstein, and Alison Thompson (2007). "Comparison of Benzene, Nitrobenzene, and Dinitrobenzene 2-Arylsulfenylpyrroles". J. Org. Chem. 72 (19): 7382–7385. doi:10.1021/jo070493r. PMID 17705533.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - The 2-sulfenyl group in the pyrrole substrate serves as an activating group and as a protective group that can be removed with Raney nickel
External links
- General Synthesis and Reactivity of Pyrrole
- Synthesis of pyrroles (overview of recent methods)
- Substitution reaction mechanisms of nitrogen-containing heteroaromatics
- . doi:10.1016/j.tet.2006.08.071.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)