| Revision as of 23:58, 20 April 2013 edit68.84.125.66 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 13:15, 21 April 2013 edit undoLeoesb1032 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers1,701 editsm →Mine fireNext edit → | ||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
| ===Mine fire=== | ===Mine fire=== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| In 1962, a fire started in a mine beneath the town and ultimately led to the town being abandoned. | In 1962 (some believe as early as 1932), a fire started in a mine beneath the town and ultimately led to the town being abandoned. | ||
| {{cquote|This was a world where no human could live, hotter than the planet Mercury, its atmosphere as poisonous as Saturn's. At the heart of the fire, temperatures easily exceeded 1,000 degrees ] ]]. Lethal clouds of carbon monoxide and other gases swirled through the rock chambers.<ref name="DeKok" /> — David DeKok, ''Unseen Danger: A Tragedy of People, Government, and the Centralia Mine Fire'' (University of Pennsylvania Press, 1986)}} | {{cquote|This was a world where no human could live, hotter than the planet Mercury, its atmosphere as poisonous as Saturn's. At the heart of the fire, temperatures easily exceeded 1,000 degrees ] ]]. Lethal clouds of carbon monoxide and other gases swirled through the rock chambers.<ref name="DeKok" /> — David DeKok, ''Unseen Danger: A Tragedy of People, Government, and the Centralia Mine Fire'' (University of Pennsylvania Press, 1986)}} | ||
Revision as of 13:15, 21 April 2013
Borough in Pennsylvania, United States| Centralia, Pennsylvania | |
|---|---|
| Borough | |
 Centralia as seen from South Street, July 2010 Centralia as seen from South Street, July 2010 | |
 Map showing Centralia in Columbia County Map showing Centralia in Columbia County | |
 Map showing Columbia County in Pennsylvania Map showing Columbia County in Pennsylvania | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Pennsylvania |
| County | Columbia |
| Settled | 1841 |
| Incorporated | 1866 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Carl Womer |
| Area | |
| • Total | 0.24 sq mi (0.6 km) |
| • Land | 0.24 sq mi (0.6 km) |
| • Water | 0 sq mi (0 km) 0% |
| Population | |
| • Total | 10 |
| • Density | 42/sq mi (16/km) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP code | 17921* (formerly 17927) |
| Area code | 570 |
| |
Centralia is a borough and ghost town in Columbia County, Pennsylvania, United States. Its population has dwindled from over 1,000 residents in 1981 to 10 in 2010, as a result of a mine fire burning beneath the borough since 1962. Centralia is one of the least-populated municipalities in Pennsylvania.
Centralia is part of the Bloomsburg-Berwick micropolitan area. The borough is completely surrounded by Conyngham Township.
All properties in the borough were claimed under eminent domain by the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania in 1992 (and all buildings therein were condemned), and Centralia's ZIP code was revoked by the Postal Service in 2002. A few residents continue to reside there in spite of the failure of a lawsuit to reverse the eminent domain claim.
History
Early history
In 1841, Johnathan Faust opened the Bull's Head Tavern in what was then Roaring Creek Township. Thirteen years later, Alexander W. Rea, a civil and mining engineer for the Locust Mountain Coal and Iron Company, moved to the site and laid out streets and lots for development. The town was known as Centreville until 1865. Since there was already a Centreville in Schuylkill County, the Post Office refused to allow it to use the same name. Rea then changed his village to Centralia.
Centralia was incorporated as a borough in 1866. Its principal employer was the anthracite coal industry. Coal mining continued in Centralia until the 1960s, when most of the companies shut down. Bootleg mining continued until 1982 and strip and open-pit mining are still active in the area. There is an underground mine employing about 40 people three miles to the west.
Centralia was a hotbed of Molly Maguires activity during the 1860s and 1870s. Alexander Rea, The town's founder, was murdered by members of the Molly Maguires on October 17, 1868. Three men were eventually convicted of his death and were hanged in the county seat of Bloomsburg, on March 25, 1878. Several other murders and incidents of arson also took place during the violence.
Centralia was served by two railroads, the Philadelphia and Reading and the Lehigh Valley, the Lehigh Valley having been the principal carrier. Rail service ended in 1966. Centralia operated its own school district, including elementary schools and a high school. There were also two Catholic parochial schools. Centralia at its peak had seven churches, five hotels, twenty-seven saloons, two theaters, a bank, a post office, and 14 general and grocery stores. The population reached 2,761 in the 1890 federal census, then went into decline. By 1980, it had just 1,012 residents. Another 500 or 600 lived nearby.
Most of the property has now been condemned by the state of Pennsylvania. The habitable areas were put up for auction, and in 2010 an anonymous buyer purchased nine land deeds, four of them inhabitable.
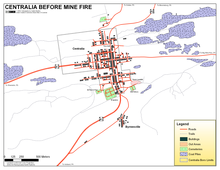
Mine fire

In 1962 (some believe as early as 1932), a fire started in a mine beneath the town and ultimately led to the town being abandoned.
This was a world where no human could live, hotter than the planet Mercury, its atmosphere as poisonous as Saturn's. At the heart of the fire, temperatures easily exceeded 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit . Lethal clouds of carbon monoxide and other gases swirled through the rock chambers. — David DeKok, Unseen Danger: A Tragedy of People, Government, and the Centralia Mine Fire (University of Pennsylvania Press, 1986)
There is some disagreement over the specific event which triggered the fire. David DeKok, after studying available local and state government documents and interviewing former borough council members, argues in Unseen Danger and its successor edition, Fire Underground: The Ongoing Tragedy of the Centralia Mine Fire, that in May 1962, the Centralia Borough Council hired five members of the volunteer fire company to clean up the town landfill, located in an abandoned strip-mine pit next to the Odd Fellows Cemetery. This had been done prior to Memorial Day in previous years, when the landfill was in a different location. On May 27, 1962, the firefighters, as they had in the past, set the dump on fire and let it burn for some time. Unlike in previous years, however, the fire was not fully extinguished. An unsealed opening in the pit allowed the fire to enter the labyrinth of abandoned coal mines beneath Centralia.

Joan Quigley argues in her 2007 book, The Day the Earth Caved In, that the fire had in fact started the previous day, when a trash hauler dumped hot ash or coal discarded from coal burners into the open trash pit. She noted that borough council minutes from June 4, 1962 referred to two fires at the dump, and that five firefighters had submitted bills for "fighting the fire at the landfill area". The borough, by law, was responsible for installing a fire-resistant clay barrier between each layer, but fell behind schedule, leaving the barrier incomplete. This allowed the hot coals to penetrate the vein of coal underneath the pit and light the subsequent subterranean fire. In addition to the council minutes, Quigley cites "interviews with volunteer firemen, the former fire chief, borough officials, and several eyewitnesses" as her sources for this explanation of the fire. Another theory of note is the Bast Theory. It states that the fire was burning long before the alleged trash dump fire. According to legend, the Bast Colliery coal fire of 1932 was never fully extinguished. In 1962, it reached the landfill area. However, due to overwhelmingly contrary evidence, few hold this position, and it is given little credibility.
However it started, it is agreed that the fire remained burning underground and spread through a hole in the rock pit into the abandoned coal mines beneath Centralia. Attempts to extinguish the fire were unsuccessful, and it continued to burn throughout the 1960s and 1970s. David DeKok began reporting on the mine fire as a reporter for The News-Item in Shamokin, Pennsylvania, beginning in late 1976. Between then and 1986, he wrote just over 500 news stories about the mine fire. Beginning in 1980, adverse health effects were reported by several people due to the byproducts of the fire: carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and a lack of healthy oxygen levels.

In 1979, locals became aware of the scale of the problem when a gas-station owner and then mayor, John Coddington, inserted a stick into one of his underground tanks to check the fuel level. When he withdrew it, it seemed hot, so he lowered a thermometer down on a string and was shocked to discover that the temperature of the gasoline in the tank was 172 °F (77.8 °C). Statewide attention to the fire began to increase, culminating in 1981 when a 12-year-old resident named Todd Domboski fell into a sinkhole 4 feet (1.2 m) wide by 150 feet (46 m) deep that suddenly opened beneath his feet in a backyard. His cousin, 14-year-old Eric Wolfgang, in pulling Todd out of the hole, saved Todd's life, as the plume of hot steam billowing from the hole was measured as containing a lethal level of carbon monoxide.
In 1984, the U.S. Congress allocated more than US$42 million for relocation efforts. Most of the residents accepted buyout offers and moved to the nearby communities of Mount Carmel and Ashland. A few families opted to stay despite warnings from Pennsylvania officials.
In 1992, Pennsylvania governor Bob Casey invoked eminent domain on all properties in the borough, condemning all the buildings within. A subsequent legal effort by residents to have the decision reversed failed. In 2002, the U.S. Postal Service revoked Centralia's ZIP code, 17927. In 2009, Governor Ed Rendell began the formal eviction of Centralia residents.
The Centralia mine fire extended into the town of Byrnesville, Pennsylvania and caused this town to also be abandoned.
Today
Very few homes remain standing in Centralia; most of the abandoned buildings have been demolished by the Columbia County Redevelopment Authority or nature. At a casual glance, the area now appears to be a field with many paved streets running through it. Some areas are being filled with new-growth forest. The remaining church in the borough, St. Mary's, holds weekly services on Sunday and has not yet been directly affected by the fire. The town's four cemeteries—including one on the hilltop that has smoke rising around and out of it—are maintained in good condition. There is also a notice board posted near Hammie Hill, about 500 yards from the cemetery, protesting the evictions and demanding former Governor Rendell intervene.
The only indications of the fire, which underlies some 400 acres (1.6 km) spreading along four fronts, are low round metal steam vents in the south of the borough and several signs warning of underground fire, unstable ground, and carbon monoxide. Additional smoke and steam can be seen coming from an abandoned portion of Pennsylvania Route 61, the area just behind the hilltop cemetery, and other cracks in the ground scattered about the area. Route 61 was repaired several times until its final closing. The current route was a detour around the damaged portion during the repairs and became a permanent route in 1993; mounds of dirt were placed at both ends of the former route, effectively blocking the road. Pedestrian traffic is still possible due to a small opening about two feet wide at the north side of the road, but this is muddy and not accessible to the disabled. The underground fire is still burning and may continue to do so for 250 years.
Prior to its demolition in September 2007, the last remaining house on Locust Avenue was notable for the five chimney-like support buttresses along each of two opposite sides of the house, where the house was supported by a row of adjacent buildings before it was demolished. Another house with similar buttresses was visible from the northern side of the cemetery, just north of the burning, partially subsumed hillside.
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania did not renew the relocation contract at the end of 2005, and the fate of the remaining residents is uncertain.

In 2009, John Comarnisky and John Lokitis, Jr. were both evicted, in May and July respectively. In 2010, only five homes remain as state officials try to vacate the remaining residents and demolish what is left of the town. In May 2009, the remaining residents mounted another legal effort to reverse the 1992 eminent domain claim. In March 2011, a federal judge refused to issue an injunction that would have stopped the condemnation. In February 2012, the Commonwealth Court ruled that a declaration of taking could not be re-opened or set aside on the basis that the purpose for the condemnation no longer exists; seven people, including the Borough Council president, had filed suit claiming the condemnation was no longer needed because the underground fire had moved and the air quality in the borough was the same as that in Lancaster.
The Pottsville Republican & Herald reported in February 2011 that the Borough Council still has regular meetings. The news story reported that the town's highest bill at the meeting reported on came from PPL at $92 and the town's budget was "in the black".
On August 28, 2011, The Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary Church celebrated 100 years of worship. This church is located on the north hill overlooking the town. It was allowed to stay because of its distance from the mine fire.
It is expected that many former residents will return in 2016 to open a time capsule buried in 1966 next to the veterans' memorial.
Mineral rights
Several current and former Centralia residents believe the state's eminent domain claim was a plot to gain the mineral rights to the anthracite coal beneath the borough. Residents have asserted its value to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, although the exact amount of coal is not known. This theory stems from the municipality laws of the state. According to state law, when the municipality can no longer form a functioning municipal government, i.e. when there are no longer any residents, the borough legally ceases to exist. At that point, the mineral rights, which are owned by the Borough of Centralia (they are not privately held) would revert to the ownership of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania.
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 63 | — | |
| 2000 | 21 | −66.7% | |
| 2010 | 10 | −52.4% |



As of the census of 2010,Template:GR there were 10 people (![]() 52% since 2000), 5 households (
52% since 2000), 5 households (![]() 50%), and 3 families (
50%), and 3 families (![]() 57%) residing in the borough. The population density was 42 people per square mile (16/km²) (
57%) residing in the borough. The population density was 42 people per square mile (16/km²) (![]() 52%). There were 6 housing units (
52%). There were 6 housing units (![]() 62.5%) at an average density of 0.4 units per square mile (.015 units/km²). The racial makeup of the borough was 100% white.
62.5%) at an average density of 0.4 units per square mile (.015 units/km²). The racial makeup of the borough was 100% white.
Of the five households, none had children under the age of 18, two (40%) were married couples living together, one (20%) had a female householder with no husband present, and two (40%) were non-families. One of those non-family households was an individual, and none had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.0 persons, and the average family size was 2.33 persons.
The age distribution of the population was erratic, with no residents under the age of 18, one aged 25–29, one aged 50–54, one aged 55–59, four aged 60–64, two aged 70–74, and one aged 80–84. The median age was 62.5 years, and there were five females and five males in total.
In the 2000 census, The median income for a household in the borough was $23,750, and the median income for a family was $28,750. The per capita income for the borough was $16,083. None of the population was below the poverty line.
Police
Though it originally fielded its own three-man department (one full-time chief and two part-time officers) during the latter part of the twentieth century, Centralia Borough is now patrolled by the Pennsylvania State Police Bloomsburg Station.
Emergency services
The borough is served by the still active Centralia Fire Company.
In the media
Literature (non-fiction)
- Unseen Danger: A Tragedy of People, Government, and the Centralia Mine Fire by David DeKok, published by University of Pennsylvania Press in 1986, was the first comprehensive history of the Centralia mine fire. An updated edition entitled Fire Underground: The Ongoing Tragedy of the Centralia Mine Fire, with three new chapters and new information, was published by Globe Pequot Press in 2009.
- The Day the Earth Caved In: An American Mining Tragedy, written by Joan Quigley, is an in-depth account of the history of Centralia, PA and the mine fire from its infancy through 2007, when the book was written.
- A Walk in the Woods, written by Bill Bryson, describes a visit to the town.
- In March 1991, Centralia was the subject of an article ("Don't Go There") in National Lampoon magazine.
- The June 22, 1981, issue of People Magazine discusses the borough's dilemma in "A Town with a Hot Problem Decides Not to Move Mountains but to Move Itself".
- A TIME article, "The Hottest Town in America", covered the story in their June 22, 1981, issue.
- Centralia is documented in photographs and oral histories in Slow Burn: A Photodocument of Centralia, Pennsylvania by Renee Jacobs, University of Pennsylvania Press, 1986.
- "Alien Hand Syndrome and Other Too-Weird-Not-To-Be-True Stories," written by Alan Bellows in 2009 features a short story on 'Centralia's Hidden Inferno.'
Literature (fiction)
- Jennifer Finney Boylan's novel The Planets (written under the name James Boylan) and its sequel The Constellations are both set in Centralia.
- Centralia is the hometown of the main character in the crime novel Dirty Blonde by Lisa Scottoline. Several scenes in the novel take place in Centralia.
- In the 2003 book Bubbles Ablaze by Sarah Strohmeyer, Centralia is the inspiration for the fictional town of Limbo, Pennsylvania.
- The main character in Joyce Carol Oates's The Tattooed Girl, Alma Busch, is from Centralia.
- Douglas Soderberg's 1986 one-act play The Root of Chaos is a dark comedy set in Centralia, and depicts a dysfunctional working-class family coming to terms with their house sinking from the coal fire.
- Centralia is the model for the eponymous fictional town of Coal Run, written by Tawni O'Dell. The book is about the life of Ivan Zoschenko, a former football hero known locally as The Great Ivan Z, but who is now the deputy of a nearby town. Ivan grew up in Coal Run, which, like Centralia, is nearly abandoned because of underground fires in the coal seams beneath the town. However, Coal Run's fires are a result of a mine explosion that took the lives of 96 men, including Ivan's father.
- Centralia is the location for the final scenes in the novel Vampire Zero by David Wellington.
- Dean Koontz's novella "Strange Highways" takes place in a town similar to Centralia.
- Promethean: The Created uses "Appletown" as a replacement to Centralia.
- Edward Bloor's novel "A Plague Year" includes the burning town of Caldera, inspired by Centralia.
- In October 2011 the town's last remaining residents were the subject of a devised theatre piece performed in London England by the Superbolt Theatre Company.
- In March 2012, the UglyRhino production company produced 6 scenes centering around the remaining residents of the town. It can be seen at the Brooklyn Lyceum on Friday nights in March, in Brooklyn, New York.
- Part of George C. Chesbro's 1985 novel "The Beasts of Valhalla," the fourth novel in his series featuring dwarf private detective Mongo the Magnificent, is set in a vast underground secret genetics modification laboratory underneath Centralia.
Film
- The town and its few remaining residents are the focus of Chris Perkel and Georgie Roland's 2007 feature-length documentary The Town That Was.
- The town is the inspiration for the 1991 cult film Nothing But Trouble, written by Dan Aykroyd.
- In the 2006 horror film Silent Hill, the town of Silent Hill has been abandoned due to a prolonged mine fire, which writer Roger Avary says was inspired by Centralia. Aspects of this are shown throughout the movie, such as characters wandering through the misty version of Silent Hill wearing mining gear.
- The town circa 1987 is prominently featured in the opening minutes of the 1987 film Made in USA as the home town of the lead characters.
- The 2009 film Sinkhole was filmed mostly in Centralia.
Comics
- The town is included in a short documentary on the Broken Saints web comic DVD set.
- Centralia is the basis for the fictional town of Blossomville, Pennsylvania in Alan Moore's Saga of the Swamp Thing in the 1985 story arc "The Nukeface Papers".
- Centralia appears in Bob Rozakis' story in Action Comics #558 as Superman comes to Coaltown to use his heat vision to make a firebreak and put the fire out.
Other
- The Squonk Opera wrote and performed a musical entitled Inferno (working and debut title of Burn), re-interpreting Dante Alighieri's Inferno as a trip into Centralia.
- The fire and the resulting devastation are themes of the 2006 song "Centralia" by the sludge-metal band Jucifer.
- Danish electronic musician Trentemøller's music video "Sycamore Feeling" is shot in Centralia.
- Boston ska band Bim Skala Bim has a song entitled "Burning Underground", based on the history of Centralia.
- Metal band Car Bomb's 2007 release Centralia is a homage to the town.
- The town was featured in a segment of The Daily Show by former correspondent Matt Walsh.
- The town was featured in the episode "Engineering Disasters #7" of Modern Marvels on the History Channel.
- The town was featured in an episode of Life After People: The Series on the History Channel. It was used as an example of what would happen to a town after twenty five years without humans.
- Episode 200 of The Simpsons ("Trash of the Titans") was loosely based on the history of Centralia. In the episode, Homer becomes Springfield's Sanitation Commissioner and charges other towns to dump their trash in Springfield's abandoned mine. When trash begins erupting out of the ground, the entire town is relocated.
- The town was featured in episode #59, "Fire", of the radio program This American Life.
- Several personal stories from the history of the fire were featured in the "Cities" episode of the WNYC radio program Radiolab in Oct 2010.
- The experimental band Mountains released an instrumental album called Centralia in 2013. A review of the album by Pitchfork mentions the town.
Gallery
-
 The Buck Vein Outcrop
The Buck Vein Outcrop
-
 A plume of smoke wafts from the ground.
A plume of smoke wafts from the ground.
-
 A row house stands alone.
A row house stands alone.
-
 Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary Ukrainian Greek-Catholic Church
Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary Ukrainian Greek-Catholic Church
-
 Former American Legion plot
Former American Legion plot
-
 A DEP monitoring hole
A DEP monitoring hole
-
 A DEP underground reading of 187°F (86°C)
A DEP underground reading of 187°F (86°C)
-
 The ruined section of Route 61, Centralia
The ruined section of Route 61, Centralia
See also
- Byrnesville, Pennsylvania
- Brennender Berg, Saarland, Germany
- Burning Mountain, New South Wales, Australia
- Smoking Hills, Northwest Territories, Canada
References
- ^ "Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^ Krajick, Kevin (May 2005), "Fire in the hole", Smithsonian Magazine, retrieved 2009-07-27
- ^ DeKok, David (1986), Unseen Danger; A Tragedy of People, Government, and the Centralia Mine Fire, Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, p. 17, ISBN 978-0-595-09270-3
{{citation}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Willard Cilvik, "The Murder of Alexander W. Rea," http://library.bloomu.edu/Archives/SC/MollieMaguires/mollieindex.htm, 2006
- ^ Quigley, Joan (2007), The Day the Earth Caved In: An American Mining Tragedy, New York: Random House, ISBN 978-1-4000-6180-8
- Quigley, Joan (2007). "Chapter Notes to The Day the Earth Caved In" (DOC). p. 8. Retrieved 2012-03-13.
- Template:Web
- Currie, Tyler (April 2, 2003), "Zip Code 00000", Washington Post, retrieved 2009-12-19
- ^ Rubinkam, Michael (02-05-2010), Few Remain as 1962 Pa. Coal Town Fire Still Burns, ABC News (Australia), retrieved 02-06-2010
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help) - O'Carol, Eoin. 2010-02-05. "Centralia, Pa.: How an underground coal fire erased a town" Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- "A modern day Ghost Town, Centralia Pennsylvania". Retrieved 2007-10-10.
- Reading Eagle, January 3, 2006
- Yahoo News, February 5, 2010
- ^ Beauge, John (23 February 2012). "Court denies Centralia property owners looking to keep their homes". The Patriot-News. PennLive LLC. Retrieved 12 March 2012.
The same individuals have a suit pending in U.S. Middle District Court that alleges the condemnation was part of the commonwealth's plot to obtain mineral rights to the anthracite coal they claim are worth hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Wheary, Rob (13 February 2011). "'Regular borough council' in Centralia". Pottsville Republican. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- This is stated in Joan Quigley's The Day the Earth Caved In in a section that indicated that Centralia is the only municipality within the Commonwealth that actually owned its mineral rights.
- Walter, Greg (22 June 1981), A Town with a Hot Problem Decides Not to Move Mountains but to Move Itself, People (magazine), retrieved 2008-12-25,
Despite the inferno below them and the gases that seep into their basements, some Centralians do not want to leave their homes and remain convinced that it's all a plot by coal companies to drive them off valuable land since the borough owns mineral rights to the coal below. (Other rumored villains have variously included anonymous Arabs and large energy cartels.)
- John Lokitis, John Coddington, David DeKok, Todd Domboski, etc (2007). The Town That Was. Centralia, PA; Ashland, PA; Bloomfield, NJ; Harrisburg, PA; etc: Dog Player Films.
- "Nothing But Trouble" on Amazon
- Couch, Stephen. Presentation at Eastern Section meeting of the National Association of Geoscience Teachers, June 2007
- "10 Weirdest Urban Ecosystems On Earth". Retrieved 06/15/2012.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0095565/
- "Jucifer - Centralia Lyrics". Lyricsmania.com. Retrieved 2012-05-27.
- "Coal Country". The Daily Show. Retrieved 2013-03-13.
- "Dying Embers". Radiolab. Retrieved 2012-05-27.
- "Centralia (Album Review)". Pitchfork. Retrieved 2013-03-08.
Further reading
- DeKok, David. Unseen Danger: A Tragedy of People, Government, and the Centralia Mine Fire, University of Pennsylvania Press, ISBN 0-595-09270-5.
- Jacobs, Renee. Slow Burn: A Photodocument of Centralia, Pennsylvania, University of Pennsylvania Press, 1986, ISBN 0-8122-1235-5.
- Johnson, Deryl B. Images of America: Centralia, Arcadia Publishing, 2004, ISBN 978-0-7385-3629-3.
- Kroll-Smith, J. Stephen, and Couch, Stephen. The Real Disaster Is Above Ground: A Mine Fire and Social Conflict, University Press of Kentucky, January 1990, ISBN 0-8131-1667-8, ISBN 978-0-8131-1667-9.
- Moran, Mark. Weird U.S., Barnes & Noble, ISBN 0-7607-5043-2.
- Quigley, Joan. The Day the Earth Caved in: An American Mining Tragedy, Random House, 2007, ISBN 978-1-4000-6180-8.
- Inferno: The Centralia Mine Fire.
External links
- Earth is burning in Centralia
- First Hand Account of Centralia With Pictures
- Everything2 account of the full history of the fire and political excuses for not putting out the fire in its first year
- Centralia Mine Fire - Town Atop a Burning Coal Mine
- O.T.I.S.(Odd Things I've Seen): A Firsthand Account of Centralia, PA
- The Town That Was: Chris Perkel and Georgie Roland's Documentary Film about Centralia, PA
- Offroaders.com Centralia photo album
- History of the Centralia Project
- Centralia Mine Fire
- Centralia Mine Fire
- Fifty years of fire in the abandoned US town of Centralia, BBC News, 8 August 2012
- Columbia County Parcel Viewer Interesting tool to use to see who still owns property in Centralia instead of the government
| Municipalities and communities of Columbia County, Pennsylvania, United States | ||
|---|---|---|
| County seat: Bloomsburg | ||
| Town |  | |
| Boroughs | ||
| Townships | ||
| CDPs | ||
| Unincorporated community | ||
| Ghost town | ||
| Footnotes | ‡This populated place also has portions in an adjacent county or counties | |