| Revision as of 13:59, 29 October 2014 editPaul Barlow (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Pending changes reviewers93,539 edits →William Gardiner← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:00, 29 October 2014 edit undoPaul Barlow (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Pending changes reviewers93,539 edits →William GardinerNext edit → | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| ===William Gardiner=== | ===William Gardiner=== | ||
| ] in his book ''Shakespeare versus Shallow'' argues that Shallow is a parody of William Gardiner, a corrupt magistrate who had a long-running feud with the owner of the ], ]. Shakespeare had been drawn into this feud and had even had a ], a form of restraining order, taken out against him by Gardiner's stepson. Hotson argues that the joke about the "luces" in Shallow's coat of arms refers to Gardiner's wife, Frances Luce, whose family coat of arms bearing luces was incorporated into Gardiner's. Hotson says, "Could this be the true significance of the coat of arms passage in the Merry Wives? Was the Justice Shallow of the play a caricature of Justice Gardiner?"<ref>Leslie Hotson, ''Shakespeare Versus Shallow'', Little, Brown, and Company, Boston, 1931, p.87.</ref> Hotson proceeds to argue that most of Shallow's actions in the plays can be linked to corrupt deals in which Gardiner was involved, and that the dim-witted Slender is a parody of Gardiner's stepson, William Wayte, who was mercilessly |
] in his 1931 book ''Shakespeare versus Shallow'' argues that Shallow is a parody of William Gardiner, a corrupt magistrate who had a long-running feud with the owner of the ], ]. Shakespeare had been drawn into this feud and had even had a ], a form of restraining order, taken out against him by Gardiner's stepson. Hotson argues that the joke about the "luces" in Shallow's coat of arms refers to Gardiner's wife, Frances Luce, whose family coat of arms bearing luces was incorporated into Gardiner's. Hotson says, "Could this be the true significance of the coat of arms passage in the Merry Wives? Was the Justice Shallow of the play a caricature of Justice Gardiner?"<ref>Leslie Hotson, ''Shakespeare Versus Shallow'', Little, Brown, and Company, Boston, 1931, p.87.</ref> Hotson proceeds to argue that most of Shallow's actions in the plays can be linked to corrupt deals in which Gardiner was involved, and that the dim-witted Slender is a parody of Gardiner's stepson, William Wayte, who was mercilessly exploited by Gardiner. | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 29 October 2014
| This article or section is in a state of significant expansion or restructuring. You are welcome to assist in its construction by editing it as well. If this article or section has not been edited in several days, please remove this template. If you are the editor who added this template and you are actively editing, please be sure to replace this template with {{in use}} during the active editing session. Click on the link for template parameters to use.
This article was last edited by Paul Barlow (talk | contribs) 10 years ago. (Update timer) |
Robert Shallow is a fictional character who appears in Shakespeare's plays Henry IV, Part 2 and The Merry Wives of Windsor. He is a wealthy landowner and Justice of the Peace, who at the time of Henry IV, Part 2 is said to be in his 80s.
A thin and timid individual, used to life in the provinces, Shallow functions as a dramatic foil to the rotund and worldly Sir John Falstaff, who visits Shallow's lands on royal business, but later returns intending to fleece Shallow of his money. In the Merry Wives he visits Windsor with his relative Slender, encountering Falstaff once more.
Henry IV, Part 2
In Henry IV, Part 2 Falsaff is commissioned to raise troops for the royal army to deal with a rebellion in the north. Shallow has been tasked to find suitable recruits in his locality. He looks forward to meeting Falstaff, who he hasn't seen for many years, so that they can reminisce about their student days. Shallow is delighted by Falstaff's witticisms, and invites him to stay longer. In a soliloque Falstaff tells the audience that Shallow's "memories" of his supposedly wild student days are full of lies; that Swallow was a skinny, feeble figure noted only for his lechery. The local prostitutes called him "mandrake" because he looked like a "forked radish" when naked. But now he's wealthy, he's ripe for exploitation.
After the battle, Falstaff visits Shallow, claiming that when the Prince becomes king, Falstaff will be in a position to give Shallow an important and remunerative post. He borrows £1000 from Shallow on this basis. The two get drunk and reminisce again. News arrives that the old king is dead, so they rush to London. When the new king rejects Falstaff, Shallow demands his money back, and even says he'll settle for half, but Falstaff says that's not possible. Shallow is forced out of the king's presence along with the lowlife characters.
Merry Wives of Windsor

Shallow appears at the beginning of the play to complain that Falstaff has been poaching deer from his land and has broken into a lodge. Falstaff does not deny it. Shallow threatens to prosecute Falstaff, and adds that he was robbed by Falstaff's cronies Bardolph, Nym and Pistol: "They carried me to the tavern and made me drunk, and afterward picked my pocket". They deny it in extravagant terms.
Shallow is advised to take his mind of the matter by promoting the aspiration of his young cousin Abraham Slender to marry Anne Page, daughter of the well-off Master Page, who approves the match. For most of the rest of the play, Shallow simply encourages the oafish Slender's clumsy attempts to woo Anne.
Character role
G. Beiner argue Shallow's self-deceiving vanity provides a kind of "comic justification" for Falstaff's exploitation of him, since we feel more sympathy for "clever knave than a foolish citizen". In the Merry Wives Shallow is set up at the beginning as an impotent foil to the brazen and confident Falstaff, only to prapare the way for a reversal in which Falstaff himself is utterly outwitted and humiliated.
Parody of historical individual?
Thomas Lucy
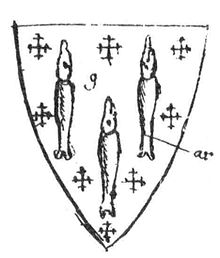
It has been speculated that Shallow, at least as portrayed in The Merry Wives of Windsor, is a parody of Sir Thomas Lucy, a local landowner in Charlecote, near Stratford upon Avon, with whom Shakespeare is supposed to have had conflicts when he was young. Nicholas Rowe records a story that the young Shakespeare was prosecuted for poaching deer from Lucy's land.. This corresponds to the accusation Shallow makes against Falstaff, but finds himself unable to follow up. The play also appears to contain a pun on the name "Lucy", similar to a ballad that circulated in Stratford, in which Lucy's name is pronounced "lousy". When Shallow and his dim-witted relative Slender discuss their family coat of arms, they mention that it depicted "luces" (pike). Their family symbols unintentionally become literally lice-ridden when this is misinterpreted as a "dozen white louses". Thomas Lucy's coat of arms contained "luces".
The theory that Shallow was a joke at Lucy's expense dates back to c.1688, when Archdeacon Richard Davies wrote that Shakespeare was "much given to all unluckiness in stealing venison and Rabbits particularly from Sr. Lucy,. . . his revenge is so great that he is his Justice Clodpate, and calls him a great man and that in allusion to his name bore three louses rampant for his Arms".
William Gardiner
Leslie Hotson in his 1931 book Shakespeare versus Shallow argues that Shallow is a parody of William Gardiner, a corrupt magistrate who had a long-running feud with the owner of the Swan theatre, Francis Langley. Shakespeare had been drawn into this feud and had even had a writ of attachment, a form of restraining order, taken out against him by Gardiner's stepson. Hotson argues that the joke about the "luces" in Shallow's coat of arms refers to Gardiner's wife, Frances Luce, whose family coat of arms bearing luces was incorporated into Gardiner's. Hotson says, "Could this be the true significance of the coat of arms passage in the Merry Wives? Was the Justice Shallow of the play a caricature of Justice Gardiner?" Hotson proceeds to argue that most of Shallow's actions in the plays can be linked to corrupt deals in which Gardiner was involved, and that the dim-witted Slender is a parody of Gardiner's stepson, William Wayte, who was mercilessly exploited by Gardiner.
References
- Beiner, G., Shakespeare's Agonistic Comedy: Poetics, Analysis, Criticism, Fairleigh Dickinson Univ Press, 1993, p.153.
- Schoenbam, Samuel, Shakespeare: A Compact Documentary Life, Oxford University Press, 1987, p.104.
- D.E Crane, (ed) Sahkespeare, The Merry Wives of Windsor, Cambridge University Press, 1997, p. 34.
- George Van Santvoord (ed), The Merry Wives of Windsor, Yale University Press, New Haven, CT., 1922, p.123.
- Leslie Hotson, Shakespeare Versus Shallow, Little, Brown, and Company, Boston, 1931, p.87.
| William Shakespeare's The Merry Wives of Windsor | ||
|---|---|---|
| Characters |  | |
| Film/Television |
| |
| Opera/Musical |
| |
| Related | ||