| Revision as of 22:41, 24 January 2017 editPeacemaker67 (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators95,470 edits Undid revision 761773574 by 91.150.92.1 (talk) discuss on talk, this refers to Turner's declaration← Previous edit | Revision as of 17:32, 25 January 2017 edit undoAntidiskriminator (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Rollbackers58,480 edits referenced assertion addedNext edit → | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| *], Germany was declared "judenfrei" in 1944. | *], Germany was declared "judenfrei" in 1944. | ||
| * German-occupied ] (]) – reported Judenfrei in December 1939. | * German-occupied ] (]) – reported Judenfrei in December 1939. | ||
| * ], ] - reported jundenfrai on 19 August 1941 in Völkische Beobachter.<ref name="Drndić2009">{{cite book|last=Drndić|first=Daša|title=April u Berlinu|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OZxNAQAAMAAJ|year=2009|publisher=Fraktura|isbn=978-953-266-095-1|page=24|quote=Njemački list Völkische Beobachter objavio je 19. kolovoza 1941. da je Banat konačno Juden frei.}}</ref> On 20 August 1941 Banat was declared Judenfrei by its German administrators.<ref name="Muth2009">{{cite book|last=Muth|first=Thorsten|title=Das Judentum: Geschichte und Kultur|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=tcA-AQAAIAAJ|year=2009|publisher=Pressel|isbn=978-3-937950-28-0|page=452|quote=Am 20. August konnte die deutsche Führung das Banat für Judenfrei" erklären. }}</ref> | |||
| * German-occupied ] – reported Judenfrei by the press on October 17, 1941.<ref>{{cite web |date=July 3, 2005 |url=http://www.gouvernement.lu/salle_presse/actualite/2005/07/03asselborn_shoah/index.html |title=Commémoration de la Shoah au Luxembourg |publisher=Government of Luxembourg |language=fr |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070930055730/http://www.gouvernement.lu/salle_presse/actualite/2005/07/03asselborn_shoah/index.html |archivedate=September 30, 2007}}</ref> | * German-occupied ] – reported Judenfrei by the press on October 17, 1941.<ref>{{cite web |date=July 3, 2005 |url=http://www.gouvernement.lu/salle_presse/actualite/2005/07/03asselborn_shoah/index.html |title=Commémoration de la Shoah au Luxembourg |publisher=Government of Luxembourg |language=fr |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070930055730/http://www.gouvernement.lu/salle_presse/actualite/2005/07/03asselborn_shoah/index.html |archivedate=September 30, 2007}}</ref> | ||
| * German-occupied ] – December 1941.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ess.uwe.ac.uk/genocide/einsatzArep.htm |title=Extract from Report by Einsatzgruppe A |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20071112165947/http://www.ess.uwe.ac.uk/genocide/einsatzArep.htm |archivedate=November 12, 2007}} Partial Translation of Document 2273-PS Source: Nazi Conspiracy and Aggression, Vol. IV. USGPO, Washington, 1946, pp. 944–949</ref> Reported as Judenfrei at the ] on January 20, 1942.<ref>{{cite web |title=Estonian Jews |publisher=] |url=http://motlc.learningcenter.wiesenthal.org/text/x07/xr0707.html |archiveurl=http://motlc.learningcenter.wiesenthal.org/text/x07/xr0707.html |archivedate=September 28, 2007}} sourced to {{cite encyclopedia |work=Encyclopedia of the Holocaust |year=1990 |publisher=Macmillan Publishing Company |location=New York}}</ref> | * German-occupied ] – December 1941.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ess.uwe.ac.uk/genocide/einsatzArep.htm |title=Extract from Report by Einsatzgruppe A |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20071112165947/http://www.ess.uwe.ac.uk/genocide/einsatzArep.htm |archivedate=November 12, 2007}} Partial Translation of Document 2273-PS Source: Nazi Conspiracy and Aggression, Vol. IV. USGPO, Washington, 1946, pp. 944–949</ref> Reported as Judenfrei at the ] on January 20, 1942.<ref>{{cite web |title=Estonian Jews |publisher=] |url=http://motlc.learningcenter.wiesenthal.org/text/x07/xr0707.html |archiveurl=http://motlc.learningcenter.wiesenthal.org/text/x07/xr0707.html |archivedate=September 28, 2007}} sourced to {{cite encyclopedia |work=Encyclopedia of the Holocaust |year=1990 |publisher=Macmillan Publishing Company |location=New York}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 17:32, 25 January 2017

Judenfrei ("free of Jews") or Judenrein ("clean of Jews") was a Nazi term to designate an area "cleansed" of Jewish presence during The Holocaust.
While Judenfrei referred merely to "freeing" an area of all of its Jewish inhabitants, the term Judenrein (literally "clean of Jews") was also used. This had the stronger connotation that any trace of Jewish blood had been removed as an impurity.
Locations declared Judenfrei
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (January 2009) |
Establishments, villages, cities, and regions were declared Judenfrei after they were ethnically cleansed of Jews.
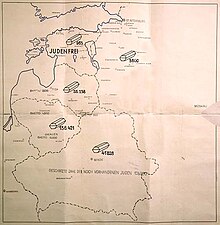
- Gelnhausen, Germany – reported Judenfrei on November 1, 1938, by propaganda newspaper Kinzigwacht after its synagogue was closed and remaining local Jews forced to leave the town.
- Erlangen, Germany was declared "judenfrei" in 1944.
- German-occupied Bydgoszcz (Poland) – reported Judenfrei in December 1939.
- Banat, German-occupied territory of Serbia - reported jundenfrai on 19 August 1941 in Völkische Beobachter. On 20 August 1941 Banat was declared Judenfrei by its German administrators.
- German-occupied Luxembourg – reported Judenfrei by the press on October 17, 1941.
- German-occupied Estonia – December 1941. Reported as Judenfrei at the Wannsee Conference on January 20, 1942.
- German-occupied territory of Serbia – May 1942, reported in the SS-Standartenführer Emanuel Schäfer cable sent to the Reich Main Security Office in Berlin; Schäfer was the Der Bafehlshaber der SIPO und des SD head in Belgrade. or August 1942.
- Vienna – reported Judenfrei by Alois Brunner on October 9, 1942.
- Berlin, Germany – May 19, 1943.
Usage in Israeli–Palestinian conflict
In the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, a fear among many Israelis which has been reflected by Israeli government officials such as Benjamin Netanyahu is that the proposed removal of Israeli Jewish settlements in the West Bank according to the wishes of Palestinian officials is tantamount to rendering these areas Judenrein, or clean of Jews.
On July 9, 2009, Benjamin Netanyahu, in a discussion with the German foreign minister Frank-Walter Steinmeier is reported to have said, using the Israeli terms of the area, "Judea and Samaria cannot be Judenrein."
In 1952 Pesach Lev, first mayor of Lod after it was resettled by Israelis, said that Lod was transformed from 'a neglected Arab town that was Judenrein to a "Hebraic city."'
References
- "Holocaust Glossary: Terms, Places, and Personalities". Jewish Virtual Library.
- "Aryanization: Judenrein & Judenfrei".
- "'Gelnhausen endlich judenfrei': Zur Geschichte der Juden während der Nationalsozialistischen Verfolgung" (PDF) (in German). Archived from the original (PDF) on September 28, 2009.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; September 28, 2007 suggested (help); Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - Drndić, Daša (2009). April u Berlinu. Fraktura. p. 24. ISBN 978-953-266-095-1.
Njemački list Völkische Beobachter objavio je 19. kolovoza 1941. da je Banat konačno Juden frei.
- Muth, Thorsten (2009). Das Judentum: Geschichte und Kultur. Pressel. p. 452. ISBN 978-3-937950-28-0.
Am 20. August konnte die deutsche Führung das Banat für Judenfrei" erklären.
- "Commémoration de la Shoah au Luxembourg" (in French). Government of Luxembourg. July 3, 2005. Archived from the original on September 30, 2007.
- "Extract from Report by Einsatzgruppe A". Archived from the original on November 12, 2007. Partial Translation of Document 2273-PS Source: Nazi Conspiracy and Aggression, Vol. IV. USGPO, Washington, 1946, pp. 944–949
- "Estonian Jews". Simon Wiesenthal Center.
{{cite web}}: Check|archiveurl=value (help) sourced to . New York: Macmillan Publishing Company. 1990.{{cite encyclopedia}}:|work=ignored (help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - Lituchy, Barry M. Jasenovac and the Holocaust in Yugoslavia: analyses and survivor testimonies. Jasenovac Research Institute. pp. xxxiii. ISBN 978-0-97534-320-3.
- Manoschek, Walter (1995). "Serbien ist judenfrei": militärische Besatzungspolitik und Judenvernichtung in Serbien 1941/42. Walter de Gruyter. p. 184. ISBN 9783486561371.
- Lebel, G'eni (2007). Until "the Final Solution": The Jews in Belgrade 1521 - 1942. Avotaynu. p. 329. ISBN 9781886223332.
- Herbert, Ulrich; Schildt, Axel (1998). Kriegsende in Europa. Klartext. p. 149. ISBN 9783884745113.
- Philip J. Cohen; David Riesman (1996). Serbia's Secret War: Propaganda and the Deceit of History. Texas A&M University Press. pp. 83–. ISBN 978-0-89096-760-7.
- Final Solution (New York, 1985), p. 77 ; Walter Manoschek (1993). "Serbien ist judenfrei". Munich: R. Oldenbourg. ISBN 3486559745.
- John K. Cox (2002). The History of Serbia. The Greenwood histories of the modern nations. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 93. ISBN 9780313312908.
- Wolfgang Benz (1999). The Holocaust: A German Historian Examines the Genocide. Columbia University Press. p. 86. ISBN 9780231112154.
- "Was war am 19. Mai 1943" (in German). chroniknet.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - Dan Williams (July 9, 2009). "Judenrein! Israel adopts Nazi term to back settlers". Reuters.
- "German FM: Settlements Remain Obstacle to Peace; Frank-Walter Steinmeier says is encouraged by Israel's acceptance of a two-state solution". Haaretz. Reuters and DPA. July 9, 2009.
- Reference 102 in http://dictionnaire.sensagent.leparisien.fr/1948%20Palestinian%20exodus%20from%20Lydda%20and%20Ramla/en-en/