| Revision as of 17:38, 27 December 2006 edit217.38.64.88 (talk) (m) copy-edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 18:33, 27 December 2006 edit undoDwaipayanc (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, File movers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers30,440 edits →Hippocratic therapy: tried to merge subsections in "Hippocratic therapy"; revert if seems not suitableNext edit → | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
| ==Hippocratic therapy== | ==Hippocratic therapy== | ||
| ===''Vis medicatrix naturae''=== | |||
| Another important precept of Hippocratic doctrine was based on "the healing power of nature" ("''vis medicatrix naturae''" in ]). According to this doctrine, the body contains within itself the power to re-balance the four humours and heal itself (''physis'').<ref name=garrison99> {{Harvnb|Garrison|1966|p=99}} </ref> Hippocratic therapy focused on simply easing this natural process. To this end, Hippocrates believed "rest and immobilization of capital importance".<ref name=margotta73> {{Harvnb|Margotta|1968|p=73}} </ref> He was reluctant to administer drugs and engage in specialized treatment that might prove to be wrongly chosen; generalized therapy followed a generalized diagnosis.<ref name=garrison98> {{Harvnb|Garrison|1966|p=98}} </ref><ref name=sing35> {{Harvnb|Singer|Underwood|1962|p=35}} </ref> | |||
| ===Methods of treatment=== | |||
| ] from a ] edition of ]'s work in the 2nd century AD]] | ] from a ] edition of ]'s work in the 2nd century AD]] | ||
| Hippocratic medicine was humble and passive. |
Hippocratic medicine was humble and passive. The therapeutic approach was based on "the healing power of nature" ("''vis medicatrix naturae''" in ]). According to this doctrine, the body contains within itself the power to re-balance the four humours and heal itself (''physis'').<ref name=garrison99> {{Harvnb|Garrison|1966|p=99}}</ref> Hippocratic therapy focused on simply easing this natural process. To this end, Hippocrates believed "rest and immobilization of capital importance".<ref name=margotta73> {{Harvnb|Margotta|1968|p=73}}</ref> In general, the Hippocratic medicine was very kind to the patient: sterile and gentle. For example, only clean water or wine were ever used on wounds, though "dry" treatment was preferable. Soothing balms were sometimes employed.<ref name=garrison98> {{Harvnb|Garrison|1966|p=98}} </ref> Hippocrates was reluctant to administer drugs and engage in specialized treatment that could be wrong; generalized therapy followed a generalized diagnosis.<ref name=garrison98> {{Harvnb|Garrison|1966|p=98}} </ref><ref name=sing35> {{Harvnb|Singer|Underwood|1962|p=35}} </ref> There were, however, times when potent drugs were used.<ref name=britannica> {{Harvnb|Encyclopedia Britannica|1911}} </ref> This passive approach was very successful in treating relatively simple ailments such as broken bones which required ] to stretch the skeletal system and relieve pressure on the injured area. The ] and other devices were used to this end. | ||
| Hippocratic method was very successful in treating relatively simple ailments such as broken bones which required ] to stretch the skeletal system and relieve pressure on the injured area. The ] and other devices were used to this end. | |||
| One of the strengths of Hippocratic medicine was its |
One of the strengths of Hippocratic medicine was in its prognosis. At this time, medicinal therapy was quite immature, and often the best that physicians could do was to evaluate an illness and induce the likely progression of it based upon data collected in detailed case histories.<ref name=garrison9394 /><ref name=garrison97> {{Harvnb|Garrison|1966|p=97}} </ref> | ||
| ==Professionalism== | ==Professionalism== | ||
Revision as of 18:33, 27 December 2006
- For other uses of the name Hippocrates, see Hippocrates (disambiguation).
| Hippocrates | |
|---|---|
| Occupation | Physician |
Hippocrates of Cos II or Hippokrates of Kos (c. 460 BC — c. 370 BC, Greek: Template:Polytonic) was an ancient Greek physician of the Age of Pericles, considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is often referred to as "The Father of Medicine" in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field as the founder of the Hippocratic school of medicine. This intellectual school revolutionized medicine in ancient Greece, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields that it had traditionally been associated with (notably theurgy and philosophy) and making a profession of it.
The Hippocratic Corpus, the collection of works produced by the Hippocratic school, is largely responsible for Hippocrates' renown. That body of work, however, is limited in its historical value because of its ambiguous authorship and a dearth of historical context. As such, the achievements of the writers of the Corpus, the practitioners of Hippocratic medicine and Hippocrates himself are often commingled; very little is known about what Hippocrates actually thought, wrote and did. Nevertheless, Hippocrates is commonly portrayed as the paragon of the ancient physician. In particular, he is credited with greatly advancing clinical medicine, summing up the medical knowledge of previous schools, and prescribing practices for physicians through the Hippocratic Oath and other works.
Biography

Historians accept that Hippocrates existed, was born around the year 460 BC on the Greek island of Kos, and became a famous physician and teacher of medicine; all other biographical information, however, is apocryphal and unreliable (See Legends).
Soranus of Ephesus, a Greek gynecologist of the 2nd century AD, was Hippocrates's first biographer and is the source of most information on Hippocrates's person. Information about Hippocrates can also be found in the writings of Aristotle, which date from the 4th century BC, in the Suidas of the tenth century AD, and in the works of John Tzetzes, which date from the twelfth century AD. Soranus stated that Hippocrates's father was Heraclides, a physician; his mother was Praxitela, daughter of Phenaretis. The two sons of Hippocrates, Thessalus and Draco, and his son-in-law, Polybus, were his students. According to Galen, a later physician, Polybus was Hippocrates’s true successor, while Thessalus and Draco each had a son named Hippocrates.
Soranus said that Hippocrates learned medicine from his father and grandfather, and studied other subjects with Democritus and Gorgias. Hippocrates was probably trained at the asklepieion of Kos, and took lessons from the Thracian physician Herodicus of Selymbria. The only contemporaneous mention of Hippocrates is in Plato's Protagoras, where Plato describes Hippocrates as "Hippocrates of Cos, the Asclepiad". Hippocrates taught and practiced medicine throughout his life, traveling at least as far as Thessaly, Thrace, and the Sea of Marmara. He probably died in Larissa at the age of 83 or 90, though some accounts say he lived to be well over 100; several different accounts of his death exist.
Hippocratic theory
On the Sacred Disease"It is thus with regard to the disease called Sacred: it appears to me to be nowise more divine nor more sacred than other diseases, but has a natural cause from the originates like other affections. Men regard its nature and cause as divine from ignorance and wonder..."
Hippocrates is credited with being the first physician to reject superstitions and beliefs that credited supernatural or divine forces with causing illness. He separated the discipline of medicine from philosophy and religion, believing and arguing that disease was not a punishment inflicted by the gods but rather the product to environmental factors, diet and living habits. Indeed, there is not a single mention of a mystical illness in the entirety of the Hippocratic Corpus. Hippocrates did not, however, hold entirely scientific beliefs; he had many pseudo-scientific convictions based on incorrect anatomy and physiology, such as Humorism.
Greek medicine at the time of Hippocrates knew almost nothing of human anatomy and physiology because of the Greek taboo forbidding the dissection of animals. Ancient Greek schools of medicine were split (into the Knidian and Koan) on how to deal with disease. The Knidian school of medicine focused on diagnosis, but depended on faulty assumptions about the human body and consequently failed to distinguish when one disease caused many possible series of symptoms. The Hippocratic school or Koan school achieved greater success by applying general diagnoses and passive treatments. Its focus was on patient care and prognosis, not diagnosis. It could effectively treat diseases and allowed for a great development in clinical practice.
Despite all of its advances Hippocratic medicine and philosophy is far removed from modern medicine. Today, the physician focuses on specific diagnosis and specialized treatment, both of which were espoused by the Knidian school. This shift in medical thought since Hippocrates' day has exposed his methods to serious criticism over the past two millenia, with the passivity of Hippocratic treatment being the subject of particularly strong denunciations. For example, M. S. Houdart, a French doctor, called Hippocratic treatment a "meditation upon death".
Humorism
Main article: HumorismThe Hippocratic school held that illness was the result of an imbalance in the body of the four humours, fluids which were naturally equal in proportion (pepsis). When the four humours, blood, black bile, yellow bile and phlegm, were not in balance (dyscrasia, meaning "bad mixture"), a person would become sick and remain that way until the balance was somehow restored. Hippocratic therapy was directed towards restoring this balance. For instance, utilizing citrus was thought to be beneficial when an overabundance of phlegm was suspected.
Crisis
An important concept in Hippocratic medicine was that of a crisis, a point in the progression of disease at which either the illness would begin triumph and the patient would succumb to death, or the opposite and natural processes would make the patient recover. After a crisis, a relapse might follow, and then another deciding crisis. According to this doctrine, crises occur on critical days, which were supposed to be a fixed time after the contraction of a disease. If a crisis occurs on a day far from a critical day, a relapse may be expected. Galen believed that this idea originated with Hippocrates, though it is possible that it predated him.
Hippocratic therapy

Hippocratic medicine was humble and passive. The therapeutic approach was based on "the healing power of nature" ("vis medicatrix naturae" in Latin). According to this doctrine, the body contains within itself the power to re-balance the four humours and heal itself (physis). Hippocratic therapy focused on simply easing this natural process. To this end, Hippocrates believed "rest and immobilization of capital importance". In general, the Hippocratic medicine was very kind to the patient: sterile and gentle. For example, only clean water or wine were ever used on wounds, though "dry" treatment was preferable. Soothing balms were sometimes employed. Hippocrates was reluctant to administer drugs and engage in specialized treatment that could be wrong; generalized therapy followed a generalized diagnosis. There were, however, times when potent drugs were used. This passive approach was very successful in treating relatively simple ailments such as broken bones which required traction to stretch the skeletal system and relieve pressure on the injured area. The Hippocratic bench and other devices were used to this end.
One of the strengths of Hippocratic medicine was in its prognosis. At this time, medicinal therapy was quite immature, and often the best that physicians could do was to evaluate an illness and induce the likely progression of it based upon data collected in detailed case histories.
Professionalism
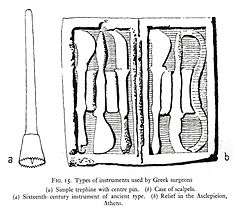
Hippocratic medicine was notable for its strict professionalism and discipline and rigorous practice. The Hippocratic work "On the Physician" recommends that physicians always be well-kempt, honest, calm, understanding, and serious. The Hippocratic physician paid careful attention to all aspects of his practice. He followed detailed specifications for, "lighting, personnel, instruments, positioning of the patient, and techniques of bandaging and splinting" in the ancient operating room. He even kept his fingernails to a precise length.
The Hippocratic School gave importance to the clinical doctrines of observation and documentation. These doctrines dictate that physicians record their findings and their medicinal methods in a very clear and objective manner, so that these records may be passed down and employed by other physicians. Hippocrates made careful, regular note of many symptoms including complexion, pulse, fever, pains, movement, and excretions. He is said to have measured a patient's pulse when taking a case history to know if the patient lied. Hippocrates extended clinical observations into family history and environment. "To him medicine owes the art of clinical inspection and observation". For this reason, he may be termed the "Father of Clinical Medicine".
Direct contributions to medicine
Hippocrates and his followers were first to describe many diseases and medical conditions. He is given credit for the first description of clubbing of the fingers, an important diagnostic sign in chronic supperative lung disease, lung cancer and cyanotic heart disease. For this reason, clubbed fingers are sometimes referred to as "Hippocratic fingers". Hippocrates was also the first physician to describe Hippocratic face in Prognosis. Shakespeare famously alludes to this description when writing of Falstaff's death in Act II, Scene iii. of Henry V.
Hippocrates began to categorize illnesses as acute, chronic, endemic and epidemic. Other medical terms that he introduced were, "exacerbation, relapse, resolution, crisis, paroxysm, peak, and convalescence." Another of Hippocrates's major contributions may be found in his descriptions of the symptomatology, physical findings, surgical treatment and prognosis of thoracic empyema, i.e. suppuration of the lining of the chest cavity. His teachings remain relevant to present-day students of pulmonary medicine and surgery. Hippocrates was the first documented chest surgeon and his findings are still valid.
Works
Hippocratic Corpus
Main article: Hippocratic CorpusThe Hippocratic Corpus (Latin: Corpus Hippocratum) is a collection of around seventy early medical works from ancient Greece. The question of whether Hippocrates himself was the author of the corpus has not been conclusively answered, but the volumes were probably produced by his students and followers. Because of the variety of subjects, writing styles and apparent date of construction, scholars believe Hippocratic Corpus could not have been written by one person (Ermerins numbers the authors at nineteen). The corpus was attributed to Hippocrates in antiquity, and its teaching generally followed principles of his; thus it came to be known by his name. It might be the remains of a library of Kos, or a collection compiled in the third century BC in Alexandria. Notable among the treatises of the Corpus are The Oath, The Book of Prognostics, On Regimen in Acute Diseases, Aphorisms, On Airs, Waters and Places, Instruments of Reduction, On The Sacred Disease, etc.
Hippocratic Oath
Main article: Hippocratic OathThe Hippocratic Oath, a seminal document on the ethics of medical practice, was attributed to Hippocrates in antiquity. This is probably the most famous document of the Hippocratic Corpus. Recently the authenticity of the document has come under scrutiny. While the Oath is rarely used in its original form today, it serves as a foundation for other, similar oaths and laws that define good medical practice and morals. Such derivatives are regularly taken today by medical graduates about to enter medical practice.
Legacy

Hippocrates is widely considered as the "Father of Medicine". His contributions revolutionized the practice of medicine, but after his death the advancement stalled. The centuries after Hippocrates's death were marked as much by retrograde movement as by further advancement. For instance, "after the Hippocratic period, the practice of taking clinical case-histories died out...", according to Fielding Garrison.
After Hippocrates, the next significant physician was Galen, a Greek who lived from 129 – 200 AD. Galen perpetuated Hippocratic medicine, moving both forward and backward. In the Middle Ages, Arabs adopted Hippocratic methods. After the European Renaissance, Hippocratic methods were revived in Europe and even further expanded in the 19th century. Notable among those who employed Hippocrates's rigorous clinical techniques were Sydenham, Heberden, Charcot and Osler. Henri Huchard, a French physician, said that these revivals make up "the whole history of internal medicine".
Image

According to Aristotle's testimony, Hippocrates was known as "the Great Hippocrates". So revered was Hippocrates at the time of his death that honey (from a beehive) on his grave was believed to have healing powers. However, his teachings were largely taken as too great to be improved upon and no significant advancements of his methods were made for a long time.
Concerning his disposition, Hippocrates was first portrayed as a "kind, dignified, old country doctor'" and later as "stern and forbidding". He is certainly considered wise, of very great intellect and especially as very practical. Francis Adams describes him as "strictly the physician of experience and common sense".
His image as the wise, old doctor is reinforced by busts of him, which wear large beards on a wrinkled face. Many physicians of the time wore their hair in the style of Jove and Asklepius. Accordingly, the busts of Hippocrates that we have could be only altered versions of portraits of these deities. Hippocrates and the beliefs that he embodied are considered medical ideals. "He is, above all, the exemplar of that flexible, critical, well-poised attitude of mind, ever on the lookout for sources of error, which is the very essence of the scientific spirit" (Garrison). "His figure... stands for all time as that of the ideal physician”(Singer and Underwood), inspiring the medical profession since his death.
Legends
Aphorisms i.1."Life is short, art long, opportunity fleeting, experiment treacherous, judgment difficult."
Some stories of Hippocrates's life are likely to be untrue because of their inconsistency with historical evidence, and because similar or identical stories are told of other figures such as Avicenna and Socrates, suggesting a legendary origin. Even during his life, Hippocrates's renown was great, and stories of miraculous cures arose. For example, Hippocrates was supposed to have aided in the healing of Athenians during the Plague of Athens by lighting great fires as "disinfectants" and engaging in other treatments. There is a story of Hippocrates curing Perdiccas, a Macedonian king of "love sickness". Neither of these accounts is corroborated by any historians and they are thus unlikely to have ever occurred.
One more legend concerns how Hippocrates rejected a formal request to visit the court of Artaxerxes, the King of Persia. The validity of this is accepted by ancient sources but denied by some modern ones, and is thus under contention. Another tale states that Democritus was suuposed to be mad because he laughed at everything, and so he was sent to Hippocrates to be cured. Hippocrates diagnosed him as having a merely happy disposition. Democritus has since been called "the laughing philosopher".
Not all stories of Hippocrates portrayed him in a positive manner. In one legend, Hippocrates is said have fled after setting fire to a healing temple in Greece. Soranus, the source of this story, names the temple as the one of Knidos. Tzetzes, on the other hand, writes that Hippocrates burned his own Temple of Cos that was burned, and that he did it to maintain a monopoly of medical knowledge. This account is very much in conflict with traditional estimations of Hippocrates's personality. Other legends tell of his resurrection of Augustus's nephew; this feat was supposedly created by the erection of a statue of Hippocrates and the establishment of a professorship in his honor in Rome.Cite error: A <ref> tag is missing the closing </ref> (see the help page).
Genealogy

Hippocrates's legendary genealogy traces his paternal heritage directly to Asklepius and his maternal ancestry to Hercules. According to Tzetzes’s Chiliades, the ahnentafel of Hippocrates II is:
1. Hippocrates II. “The Father of Medicine”
2. Heraclides
4. Hippocrates I.
8. Gnosidicus
16. Nebrus
32. Sostratus III.
64. Theodorus II.
128. Sostratus, II.
256. Thedorus
512. Cleomyttades
1024. Crisamis
2048. Dardanus
4096. Sostatus
8192. Hippolochus
16384. Podalirius
32768. Asklepius
Namesakes
Ancient
- Hippocratic Corpus — a collection of about seventy documents associated with Hippocrates and his school
- Hippocratic Oath — the most famous work of the Hippocratic Corpus
- Hippocratic bench — a device which uses tension to aid in setting bones
- Hippocratic face — the change produced in the countenance by death, or long sickness, excessive evacuations, excessive hunger, and the like
- Hippocratic fingers — a deformity of the fingers and fingernails
- Hypocras — a drink whose invention is attributed to Hippocrates
- Hippocratic succussion — the internal splashing noise of hydropneumothorax or pyopneumothorax
Modern
- Hippocrates (lunar crater)
- Hippocratic Museum
- The Hippocrates Project — A program of the New York University Medical Center to enhance education through use of technology
- Project Hippocrates — "HIgh PerfOrmance Computing for Robot-AssisTEd Surgery"
Notes
- National Library of Medicine 2006 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFNational_Library_of_Medicine2006 (help)
- ^ Garrison 1966, p. 92–93 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGarrison1966 (help) Cite error: The named reference "garrison9293" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Nuland 1988, p. 5 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFNuland1988 (help)
- Garrison 1966, p. 96 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGarrison1966 (help)
- Nuland 1988, p. 4 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFNuland1988 (help)
- Britannica 2006 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFBritannica2006 (help)
- Nuland 1988, p. 7 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFNuland1988 (help)
- Adams 1891, p. 19 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFAdams1891 (help)
- ^ Margotta 1968, p. 66 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMargotta1968 (help)
- ^ Martí-Ibáñez 1961, p. 86–87 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMartí-Ibáñez1961 (help) Cite error: The named reference "marti86" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Plato (380 BCE). "Protagoras". The Internet Classics Archive. Thomas Bushnell, BSG. Retrieved 2006-12-22.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help)CS1 maint: year (link) - Internet Classics Archive 2006 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFInternet_Classics_Archive2006 (help)
- Jones 1868, p. 11 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones1868 (help)
- Nuland 1988, p. 8–9 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFNuland1988 (help)
- ^ Garrison 1966, p. 93–94 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGarrison1966 (help)
- ^ Adams 1891, p. 15 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFAdams1891 (help)
- Margotta 1968, p. 67 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMargotta1968 (help)
- Leff & Leff 1956, p. 51 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFLeffLeff1956 (help)
- Jones 1868, p. 12–13 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones1868 (help)
- ^ Garrison 1966, p. 99 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGarrison1966 (help) Cite error: The named reference "garrison99" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Boylan 2006 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFBoylan2006 (help)
- Jones 1868, p. 46,48,59 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones1868 (help)
- ^ Margotta 1968, p. 73 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMargotta1968 (help) Cite error: The named reference "margotta73" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Garrison 1966, p. 98 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGarrison1966 (help)
- Singer & Underwood 1962, p. 35 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSingerUnderwood1962 (help)
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica 1911 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFEncyclopedia_Britannica1911 (help)
- ^ Garrison 1966, p. 97 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGarrison1966 (help) Cite error: The named reference "garrison97" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Adams 1891, p. 17 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFAdams1891 (help)
- Garrison 1966 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGarrison1966 (help)
- ^ Margotta 1968, p. 64 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMargotta1968 (help)
- Rutkow 1993, p. 24–25 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFRutkow1993 (help)
- Margotta 1968, p. 66 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMargotta1968 (help)
- Martí-Ibáñez 1961, p. 88 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMartí-Ibáñez1961 (help)
- Margotta 1968, p. 68 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMargotta1968 (help)
- Leff & Leff 1956, p. 45 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFLeffLeff1956 (help)
- Schwartz, Richards & Goyal 2006 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSchwartzRichardsGoyal2006 (help)
- Singer & Underwood 1962, p. 40 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSingerUnderwood1962 (help)
- Margotta 1968, p. 70 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMargotta1968 (help)
- Martí-Ibáñez 1961, p. 90 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMartí-Ibáñez1961 (help)
- ^ Major 1965 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFMajor1965 (help)
- Singer & Underwood 1962, p. 27 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSingerUnderwood1962 (help)
- ^ Hanson 2006 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHanson2006 (help)
- Jones 1868, p. 217 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones1868 (help)
- ^ Garrison 1966, p. 100 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGarrison1966 (help) Cite error: The named reference "garrison100" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Garrison 1966, p. 95 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGarrison1966 (help)
- Jones 1868, p. 35 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones1868 (help)
- Leff & Leff 1956, p. 102 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFLeffLeff1956 (help)
- ^ Garrison 1966, p. 94 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGarrison1966 (help)
- Jones 1868, p. 38 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones1868 (help)
- Singer & Underwood 1962, p. 29 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSingerUnderwood1962 (help)
- ^ Adams 1891, p. 10–11 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFAdams1891 (help)
- Jones 1868, p. 37 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones1868 (help)
- ^ Smith 1870, p. 483 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSmith1870 (help)
- Pinault 1992, p. 1 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFPinault1992 (help)
- Adams 1891, p. 12–13 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFAdams1891 (help)
- Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy 2006 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFInternet_Encyclopedia_of_Philosophy2006 (help)
- Adams 1891 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFAdams1891 (help)
References
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Template:Harvard reference
Further reading
- Template:Harvard reference.
- Pliny the Elder, Natural History: Book XXIX., translated by John Bostock. See original text in Perseus program.
- Template:Harvard reference.