| Revision as of 12:37, 3 May 2020 editInternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers5,388,428 edits Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:32, 21 September 2020 edit undoThe Image Editor (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users540 edits Replaced Grow’s pictureNext edit → | ||
| Line 186: | Line 186: | ||
| |- style="height:3em" | |- style="height:3em" | ||
| | align=left | ]<br/>''']''' | | align=left | ]<br/>''']''' | ||
| | {{Party shading/Democratic}} | ] | | {{Party shading/Democratic}} | ] | ||
| | nowrap | March 4, 1851 –<br/>March 3, 1853 | | nowrap | March 4, 1851 –<br/>March 3, 1853 | ||
Revision as of 20:32, 21 September 2020
Congressional district in Pennsylvania, U.S.| Pennsylvania's 12th congressional district | |
|---|---|
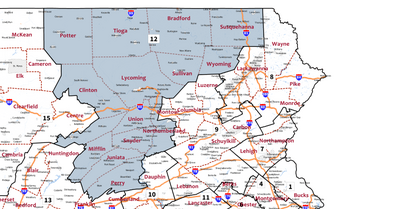 Boundaries since January 2019 Boundaries since January 2019 | |
| Representative | Fred Keller R–Beavertown |
| Cook PVI | R+17 |
Pennsylvania's 12th congressional district is located in the north central and northeastern parts of Pennsylvania, including the Northern Tier region, parts of the Susquehanna Valley, and part of Happy Valley including State College. It has been represented by Fred Keller since May 21, 2019, who won a special election to fill the vacancy caused by the resignation of former representative Tom Marino.
Prior to 2018, the 12th district was located in southwestern Pennsylvania, and included all of Beaver County, and parts of Allegheny, Cambria, Lawrence, Somerset, and Westmoreland Counties. The Supreme Court of Pennsylvania redrew this and other state congressional districts in February 2018 after ruling the previous map unconstitutional due to partisan gerrymandering. The new 12th district covers much of the old 10th district. The old 12th district was redrawn to an area north and west of Pittsburgh and renamed the 17th district, for the 2018 elections and representation thereafter.
Before the 2011 round of redistricting, the 12th District was widely considered to be gerrymandered by the Republican-controlled state legislature as a heavily Democratic district. It consisted of all of Greene County, and parts of Allegheny, Armstrong, Cambria, Fayette, Indiana, Somerset, Washington, and Westmoreland Counties.
Geography 2003–2013
Located in southwestern Pennsylvania, the 12th District consisted of all of Greene County, and parts of Allegheny, Armstrong, Cambria, Fayette, Indiana, Somerset, Washington, and Westmoreland Counties. A thoroughly unionized district, the 12th was historically among the most Democratic areas of the state. However, the Democrats in this area were not as liberal as their counterparts in Philadelphia and Pittsburgh. Most were somewhat conservative on social issues, particularly abortion and gun control.
The 12th included all of Greene County, a highly rural region that still has a traditionally Democratic influence due to its labor leanings. In Washington county, the city of Washington, a large and Democratic edge suburb of Pittsburgh was a part of the 12th, as well as the eastern portion of the county. Most of the Monongahela Valley region, a very Democratic area that was once an important steel-making area, was also part of the 12th. However, more rural western Washington County and the suburban northern portion of the county (with towns like McDonald and Canonsburg) then belonged to the 18th. The western portion of Fayette County, including the city of Uniontown, a labor Democratic stronghold was part of this district, while the rural mountainous eastern portion was a part of the 9th.
The 12th District continued eastward, including southeastern and northeastern parts of Westmoreland County, including the labor Democratic city of Latrobe, while leaving the suburban western part of the county (with towns such as Murrysville) and the generally left-leaning city of Greensburg in the 18th. The major population base of the district was located just to the east, taking in most of Somerset and Cambria counties. This area, the heart of a large coal-mining region, includes the district's largest city, Johnstown. The 12th also contained a part of Indiana County, mainly the college town of Indiana.
The 12th completed its wrap around the metro Pittsburgh region by ending in the northeastern corner of the city's suburbs, containing middle class regions such as Lower Burrell and the working class suburb of New Kensington. A portion of Armstrong County was also included in the district, including several industrial suburbs such as Freeport and Apollo.
Demographics
History
After the 2000 census, the Republican-controlled state legislature radically altered the 12th in an effort to get more Republicans elected from traditionally heavily Democratic southwestern Pennsylvania. A large chunk of the old 20th District was incorporated into the 12th. In some parts of the western portion of the district, one side of the street is in the 12th while the other side of the street is in the 18th District (the reconfigured 20th). This led to criticism that the 12th was a gerrymander intended to pack as many of southwestern Pennsylvania's heavily Democratic areas as possible into just two districts—the 12th and the Pittsburgh-based 14th.
Prior to the 2012 redistricting, the district has a Cook Partisan Voting Index score of R+1. The district is notable as the only congressional district in the nation that voted for Democratic presidential candidate John Kerry in 2004 but went for Republican John McCain in 2008. This is mainly due to the fact that since 2000 Southwestern Pennsylvania has gradually become more Republican leaning.
2006 election
In the 2006 election, Murtha was re-elected with 61% of the vote. His Republican opponent, Washington County Commissioner Diana Irey, received 39%.
2008 election
John Murtha won the 2008 election with 58% of the vote. Murtha was a United States Marine and the first Vietnam War veteran to serve in Congress. He defeated Lt. Col. William T. Russell, an army veteran.
2010 special election
Main article: 2010 Pennsylvania's 12th congressional district special electionPennsylvania governor Ed Rendell scheduled a special election for May 18, 2010, following the death of Representative John Murtha. On March 8, 2010, the Pennsylvania Democratic Party's Executive Committee nominated Mark Critz, Murtha's former district director. On March 11, a convention of Republicans from the 12th district nominated businessman Tim Burns. The Libertarian Party's candidate was Demo Agoris, who ran for the Pennsylvania House of Representatives in the 48th district as a Libertarian in 2006.
Mark Critz won the election.
2010 election
Mark Critz was re-elected in the regularly scheduled 2010 election; again beating Republican Tim Burns (this time with 51% of the vote against 49%).
2012 election
Mark Critz ran for re-election to a second full term in the 2012 election, but was defeated by Republican challenger Keith Rothfus. Critz garnered 48.5% of the vote to Rothfus' 51.5%. The 12th had absorbed a large chunk of the old 4th District, including Rothfus' home, after the 2010 census, and was significantly more Republican than its predecessor.
2019 special election
Main article: 2019 Pennsylvania's 12th congressional district special electionAfter Tom Marino's resignation in January 2019, an election was held on May 21st to fill the open seat. Republican Fred Keller defeated 2018 Democratic nominee Mark Friedenberg.
List of members representing the district
See also
Portals:References
- "New Pennsylvania Map Is a Major Boost for Democrats". The Cook Political Report. February 20, 2018. Retrieved February 21, 2018.
- "Congressman Tom Marino resigns, leaving vacancy in Pa.'s 12th district". Centre Daily Times. January 17, 2019. Retrieved January 17, 2019.
- "Keller to take the oath of office on June 3". Daily Item. May 24, 2019. Retrieved May 26, 2019.
- Cohn, Nate; Bloch, Matthew; Quealy, Kevin (February 19, 2018). "The New Pennsylvania House Districts Are In. We Review the Mapmakers' Choices". The Upshot. The New York Times. Retrieved February 20, 2018.
- Becker, Bernie (March 8, 2010). "Dems Choose Nominee for Murtha Seat". The New York Times. Retrieved March 9, 2010.
- Faher, Mike (March 12, 2010). "GOP chooses Burns for special election in 12th". The Tribune-Democratic. Retrieved March 12, 2010.
- "2012 General Election: Representative in Congress, District 12". Pennsylvania Department of State. Archived from the original on 16 November 2012. Retrieved 15 November 2012.
- Levy, Marc (March 2, 2019). "GOP state lawmaker becomes favorite in House race to succeed Marino". Center Daily Times. Associated Press. Archived from the original on March 7, 2019. Retrieved March 7, 2019.
- "Pennsylvania Democratic Party Announces Candidate For Special Election In The 12th Congressional District - Pennsylvania Democratic PartyPennsylvania Democratic Party". Padems.com. February 12, 2019. Retrieved March 7, 2019.
- "Ex-Congressman Marino Now Cites Health for Resigning". US News & World Report. Associated Press. February 12, 2019. Retrieved February 14, 2019.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1989). The Historical Atlas of Political Parties in the United States Congress. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1982). The Historical Atlas of United States Congressional Districts. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Congressional Biographical Directory of the United States 1774–present
- Congressman Tom Marino resigns, leaving vacancy in Pa.’s 12th district
External links
| Pennsylvania's congressional districts | |
|---|---|
|
40°25′42″N 79°29′11″W / 40.42833°N 79.48639°W / 40.42833; -79.48639
Categories:






































