This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 67.90.197.194 (talk) at 19:50, 22 August 2007 (Commented out the thread priority paragraphs, which really ought to be moved out into their own article). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 19:50, 22 August 2007 by 67.90.197.194 (talk) (Commented out the thread priority paragraphs, which really ought to be moved out into their own article)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| This article may require cleanup to meet Misplaced Pages's quality standards. No cleanup reason has been specified. Please help improve this article if you can. (June 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
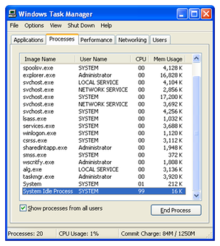
In Windows NT-based operating systems, the System Idle Process is the system idle task: it tracks how much of the CPU's time is being utilized and issues the HLT instruction to cut the processor's power usage. In the Windows Task Manager, it provides information about how heavily loaded the CPU is. In a system that is not very busy, such as a typical workstation waiting for input, the idle process accounts for over 90% of the CPU.