This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 87.194.152.162 (talk) at 15:25, 10 January 2012 (Fixing PubChem link). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 15:25, 10 January 2012 by 87.194.152.162 (talk) (Fixing PubChem link)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Ovalene | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.347 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C32H14 |
| Molar mass | 398.45 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
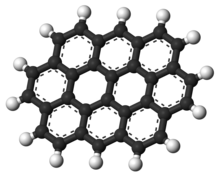
Ovalene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with the formula C32H14, which consists of ten peri-fused six-membered rings. It is very similar to coronene.
Ovalene is a reddish-orange compound. It is sparingly soluble in solvents such as benzene, toluene, and dichloromethane. Its solutions have a green fluorescence under UV light.
Ovalene has been shown to form in deep-sea hydrothermal vent areas and in the hydrocracking process of petroleum refining.
References
- Fetzer, J. C. (2000). The Chemistry and Analysis of the Large Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. New York: Wiley.
External links
| Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons | |
|---|---|
| 2 rings | |
| 3 rings | |
| 4 rings | |
| 5 rings | |
| 6 rings | |
| 7+ rings | |
| General classes | |