This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Mrbaker2 (talk | contribs) at 04:22, 5 December 2011 (→Properties). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 04:22, 5 December 2011 by Mrbaker2 (talk | contribs) (→Properties)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)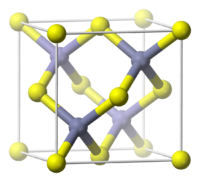 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Aluminium(III) phosphide Aluminium monophosphide Phostoxin Fumitoxin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.065 |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | AlP |
| Molar mass | 57.9552 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow or gray crystals |
| Density | 2.85 g/cm³, solid |
| Melting point | 2530 °C |
| Solubility in water | reacts |
| Band gap | 2.5 eV (indirect) |
| Refractive index (nD) | 2.75 (IR), ~3 (Vis) |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Zinc Blende |
| Space group | Td-F-43m |
| Lattice constant | a = 546.35 pm |
| Coordination geometry | Tetrahedral |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | >800 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 11.5 mg/kg |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Aluminium phosphide (Template:AluminiumTemplate:Phosphorus) is an inorganic compound used as a wide band gap semiconductor and a fumigant. This colourless solid is generally sold as a grey-green-yellow powder due to the presence of impurities arising from hydrolysis and oxidation.
Properties
AlP crystals are dark grey to dark yellow in color. The crystal structure is zincblende, which is a form of the cubic crystal structure where all atoms are in tetrahedral coordination. The AlP lattice constant is 5.4510 Å at 300 K.
AlP is thermodynamically stable up to 1000 ˚C.
Aluminium phosphide reacts with water or acids to release phosphine.
- AlP + 3 H2O → Al(OH)3 + PH3
- AlP + 3 H → Al + PH3
Preparation
Crude aluminium phosphide can be prepared in the laboratory by igniting a mixture of red phosphorus and powdered aluminium.
Uses
Pesticide
AlP is used as a rodenticide, insecticide, and fumigant for stored cereal grains. It is used to kill small verminous mammals such as moles, and rodents. The tablets or pellets typically also contain other chemicals that evolve ammonia which helps to reduce the potential for spontaneous ignition or explosion of the phosphine gas.
As a rodenticide, aluminium phosphide pellets are provided as a mixture with food for consumption by the rodents. The acid in the digestive system of the rodent reacts with the phosphide to generate the toxic phosphine gas. Other pesticides similar to aluminium phosphide are zinc phosphide and calcium phosphide.
As a rodenticide, aluminium phosphide can be encountered under various brand names, e.g. Celphos, Fumitoxin, Phostoxin, and Quick Phos.
Evidently poisonous, aluminium phosphide has been used for suicide. Fumigation has also caused unintentional deaths, such as examples in Saudi Arabia and the United States. Known as "rice tablet" in Iran, for its use to preserve rice, there have been frequent incidents of accidental or intentional death. There is a campaign by Iranian Forensic Medicine Organization to stop its use as a pesticide.
Aluminium phosphide poisoning is reported to be highly fatal.
Semiconductor applications
Industrially, AlP is a semiconductor material that is usually alloyed with other binary materials for applications in devices such as light-emitting diodes (e.g. aluminium gallium indium phosphide).
References
- ^ L. I. Berger "Semiconductor materials" CRC Press, 1996 ISBN 0-8493-8912-7, 9780849389122 (available on google books), p. 125
- Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- Wayne E. White, A. H. Bushey (1953). "Aluminum Phosphide". Inorganic Syntheses. 4: 23–25. doi:10.1002/9780470132357.ch7.
- "Millionaire's death sparks poison scare". BBC News. 2002-10-10. Retrieved 2009-04-05.
- "Fumes kill two Danes in Jeddah". BBC News. 2009-02-24. Retrieved 2009-02-25.
- "Family loses 2nd child in suspected pesticide poisoning". KSL-TV. 2010-02-09. Retrieved 2010-02-09.
- Mehrpour, O; Singh, S (2010). "Rice tablet poisoning: A major concern in Iranian population". Human & Experimental Toxicology. 29 (8): 701–2. doi:10.1177/0960327109359643. PMID 20097728.
- D. E. C. Corbridge "Phosphorus: An Outline of its Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Technology" 5th Edition Elsevier: Amsterdam 1995. ISBN 0-444-89307-5.
| Aluminium compounds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al(I) |
| ||||
| Al(II) | |||||
| Al(III) |
| ||||
| Pest control: Rodenticides | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulants / Vitamin K antagonists |
| ||||||||
| Convulsants | |||||||||
| Calciferols | |||||||||
| Inorganic compounds | |||||||||
| Organochlorine | |||||||||
| Organophosphorus | |||||||||
| Carbamates | |||||||||
| Others | |||||||||