This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Dr. Sandra Tashkovska (talk | contribs) at 21:49, 15 August 2024 (Added side effects and precautions.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 21:49, 15 August 2024 by Dr. Sandra Tashkovska (talk | contribs) (Added side effects and precautions.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Laxative Pharmaceutical compound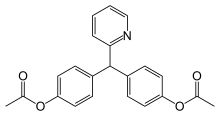 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Fleet, Dulcolax, Brooklax, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601027 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth or rectal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 15% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP450-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 16 Hours |
| Excretion | primarily in the feces, systemically absorbed drug is excreted in the urine |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.132 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H19NO4 |
| Molar mass | 361.397 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Bisacodyl (INN) is an organic compound that is used as a stimulant laxative drug. It works directly on the colon to produce a bowel movement. It is typically prescribed for relief of episodic and chronic constipation and for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction, as well as part of bowel preparation before medical examinations, such as for a colonoscopy.
Bisacodyl is a derivative of triphenylmethane. It was first used as a laxative in 1953 because of its structural similarity to phenolphthalein.
Patients may experience abdominal pain or cramping, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea as the medication stimulates bowel movements. Dehydration and weakness can also occur due to fluid loss, particularly with prolonged use. Some individuals might feel dizzy or even faint, especially if their body is losing too much water. Bisacodyl can be safely used by most adults aged 18 years and over. Its use in pregnancy and breastfeeding does not appear to be harmful.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
Mechanism of action
Bisacodyl works by stimulating enteric neurons to cause peristalsis, i.e., colonic contractions. It is also a contact laxative; it increases fluid and salt secretion. The action of bisacodyl on the small intestine is negligible; stimulant laxatives mainly promote evacuation of the colon.
Available forms
Bisacodyl is marketed under the trade names Dulcolax/Durolax, Muxol, Fleet, Nourilax, Alophen, Correctol, and Carter's Little Pills (formerly Carter's Little Liver Pills), as well as being available generically. It is usually sold as 5 mg tablets, 10 mg suppositories, or 5 mg pediatric suppositories. It is also available as a 1.25 US fluid ounces (37 ml) pre-packaged enema containing a 10 mg delivered dose of liquid bisacodyl.
Administration
When bisacodyl is administered orally, it is usually taken at breakfast. Oral administration is known to produce no action for more than eight hours and then to work suddenly and relatively quickly. This is especially true if more than 10 mg is taken at one time. Normally, the dosage is 5 or 10 mg, but up to 30 mg can be taken for complete cleansing of the bowel before a procedure.
When administered rectally in suppository form, it is usually effective in 15 to 60 minutes. For optimal use, if used as a suppository, it is recommended that bisacodyl be given after breakfast to synchronize with the gastrocolic reflex. Two suppositories can be inserted at once if a very strong, purgative, enema-like result is needed. A few hours after the initial evacuation, there can be a secondary action which will continue as long as there is unexpelled bisacodyl present in the rectum.
As a commercially prepared micro-enema, it is usually effective in 5 to 20 minutes.
See also
References
- "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- Wexner SD, Beck DE, Baron TH, Fanelli RD, Hyman N, Shen B, Wasco KE (June 2006). "A consensus document on bowel preparation before colonoscopy: prepared by a task force from the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS), the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE), and the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES)". Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 63 (7): 894–909. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2006.03.918. PMID 16733101.
- ^ Wald A (January 2016). "Constipation: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment". JAMA (Review). 315 (2): 185–91. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.16994. PMID 26757467.
- Stiens SA, Luttrel W, Binard JE (November 1998). "Polyethylene glycol versus vegetable oil based bisacodyl suppositories to initiate side-lying bowel care: a clinical trial in persons with spinal cord injury". Spinal Cord. 36 (11): 777–81. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3100702. PMID 9848486.
- Evans IL (1964). "Methods and techniques: The use of Bisacodyl suppositories in preparation for sigmoidoscopy". Gut. British Medical Journal. 5: 271–3. doi:10.1136/gut.5.3.271. PMC 1552120. PMID 14178715.
- "Bisacodyl Tablets – Product Information". AdvaCare Pharma. Retrieved 2024-08-15.
- World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
- ^ Engelhorn R, Seeger E, Zwaving JH (2000). "Laxatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_183. ISBN 3527306730.
- "Medicine: Cut Out the Liver". Time. 1951-04-16. Archived from the original on 8 November 2007. Retrieved 2010-04-26.
External links
- Bisacodyl,00.html Bisacodyl at Drugdigest.org
- Bisacodyl Consumer Drug Information
- Dulcolax Laxative
- Dulcoflex Tablet Uses in Hindi
| Drugs for constipation (laxatives and cathartics) (A06) | |
|---|---|
| Stool softeners | |
| Stimulant laxatives | |
| Bulk-forming laxatives | |
| Lubricant laxatives | |
| Osmotic laxatives | |
| Enemas | |
| Opioid antagonists | |
| Others | |