This is an old revision of this page, as edited by PubliusFL (talk | contribs) at 20:46, 16 July 2007 (attempted clarification). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 20:46, 16 July 2007 by PubliusFL (talk | contribs) (attempted clarification)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| Republic of Cameroon Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Emblem of Cameroon
Emblem
Flag
Emblem of Cameroon
Emblem
| |
| Motto: "Paix - Travail - Patrie" (French) "Peace - Work - Fatherland" | |
| Anthem: Ô Cameroun, Berceau de nos Ancêtres (French) O Cameroon, Cradle of our Forefathers | |
 | |
| Capital | Yaoundé |
| Largest city | Douala |
| Official languages | French, English |
| Government | Republic |
| • President | Paul Biya |
| • Prime Minister | Ephraïm Inoni |
| Independence from France and the UK | |
| • Date | 1 January 1960, 1 October 1961 |
| • Water (%) | 1.3 |
| Population | |
| • July 2005 estimate | 17,795,000 (58th) |
| • 2003 census | 15,746,179 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2005 estimate |
| • Total | $43.196 billion (84th) |
| • Per capita | $2,421 (130th) |
| Gini (2001) | 44.6 medium inequality |
| HDI (2006) | 0.506 low (144th) |
| Currency | CFA franc (XAF) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (WAT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (not observed) |
| Calling code | 237 |
| ISO 3166 code | CM |
| Internet TLD | .cm |
| |
The Republic of Cameroon is a unitary republic of central and western Africa. It borders Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the Bight of Bonny, part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean. The country is called "Africa in miniature" for its geological and cultural diversity. Natural features include beaches, deserts, mountains, rainforests, and savannas. The highest point is Mount Cameroon in the southwest, and the largest cities are Douala, Yaoundé, and Garoua. Cameroon is home to over 200 different ethnic and linguistic groups. The country is well known for its native styles of music, particularly makossa and bikutsi, and for its successful national football team. English and French are the official languages.
Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area Rio dos Camarões ("River of Prawns"), the name from which Cameroon derives. Fulani soldiers founded the Adamawa Emirate in the north in the 19th century, and various ethnic groups of the west and northwest established powerful chiefdoms and fondoms. Cameroon became a German colony in 1884. After World War I, the territory was divided between France and Britain as League of Nations mandates. The Union des Populations du Cameroun political party advocated independence but was outlawed in the 1950s. It waged war on French and Cameroonian forces until 1971. In 1960, French Cameroun became independent as the Republic of Cameroun under President Ahmadou Ahidjo. The southern part of British Cameroons merged with it in 1961 to form the Federal Republic of Cameroon. The country was renamed the United Republic of Cameroon in 1972 and the Republic of Cameroon in 1984.
Compared with other African countries, Cameroon enjoys political and social stability. This has permitted the development of agriculture, roads, railways, and large petroleum and timber industries. Nevertheless, large numbers of Cameroonians live in poverty as subsistence farmers. Power lies firmly in the hands of the president, Paul Biya, and his Cameroon People's Democratic Movement party, and corruption is widespread. The Anglophone community has grown increasingly alienated from the government, and Anglophone politicians have called for greater decentralisation and even the secession of the former British-governed territories.
History
Main article: History of Cameroon
The territory of present day Cameroon was first settled during the Neolithic. The longest continuous inhabitants are the Pygmy groups such as the Baka. The Sao culture arose around Lake Chad c. AD 500 and gave way to the Kanem-Bornu Empire. Kingdoms, fondoms, and chiefdoms arose in the west.
Portuguese sailors reached the coast in 1472. They noted an abundance of prawns and crayfish in the Wouri River and named it Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help), Portuguese for "River of Prawns", and the phrase from which Cameroon is derived. Over the following few centuries, European interests regularised trade with the coastal peoples, and Christian missionaries pushed inland. In the early 19th century, Modibo Adama led Fulani soldiers on a jihad in the north against non-Muslim and partially Muslim peoples and established the Adamawa Emirate. Settled peoples who fled the Fulani caused a major redistribution of population.
The German Empire claimed the territory as the colony of Kamerun in 1884 and began a steady push inland. They initiated projects to improve the colony's infrastructure, relying on a harsh system of forced labour. With the defeat of Germany in World War I, Kamerun became a League of Nations mandate territory and was split into French Cameroun and British Cameroons in 1919. The French carefully integrated the economy of Cameroun with that of France and improved the infrastructure with capital investments, skilled workers, and continued forced labour. The British administered their territory from neighbouring Nigeria. Natives complained that this made them a neglected "colony of a colony". Nigerian migrant workers flocked to Southern Cameroons, ending forced labour but angering indigenous peoples. The League of Nations mandates were converted into United Nations Trusteeships in 1946, and the question of independence became a pressing issue in French Cameroun. France outlawed the most radical political party, the Union des Populations du Cameroun (UPC), on 13 July 1955. This prompted a long guerrilla war and the assassination of the party's leader, Ruben Um Nyobé. In British Cameroons, the question was whether to reunify with French Cameroun or join Nigeria.

On 1 January 1960, French Cameroun gained independence from France under President Ahmadou Ahidjo, and on 1 October 1961, the formerly-British Southern Cameroons united with its neighbour to form the Federal Republic of Cameroon. Ahidjo used the ongoing war with the UPC and fears of ethnic conflict to concentrate power in the presidency, continuing with this even after the suppression of the UPC in 1971. His political party, the Cameroon National Union (CNU), became the sole legal political party on 1 September 1966 and in 1972, the federal system of government was abolished in favour of a United Republic of Cameroon, headed from Yaoundé. Ahidjo pursued an economic policy of planned liberalism, prioritising cash crops and petroleum exploitation. The government used oil money to create a national cash reserve, pay farmers, and finance major development projects; however, many initiatives failed when Ahidjo appointed unqualified allies to direct them.
Ahidjo stepped down on 4 November 1982 and left power to his constitutional successor, Paul Biya. However, Ahidjo remained in control of the CNU and tried to run the country from behind the scenes until Biya and his allies pressured him into resigning. Biya began his administration by moving toward a more democratic government, but a failed coup d'état nudged him toward the leadership style of his predecessor. An economic crisis took effect in the mid-1980s to late 1990s as a result of international economic conditions, drought, falling petroleum prices, and years of corruption, mismanagement, and cronyism. Cameroon turned to foreign aid, cut government spending, and privatised industries. With the reintroduction of multi-party politics in December 1990, Anglophone pressure groups called for greater autonomy, with some advocating complete secession as the Republic of Ambazonia.
Politics and government
Main article: Politics of CameroonThe President of Cameroon has broad, unilateral powers to create policy, administer government agencies, command the armed forces, negotiate and ratify treaties, and declare a state of emergency. The president appoints government officials at all levels, from the prime minister (considered the official head of government), to the provincial governors, divisional officers, and urban-council members in large cities. The president is selected by popular vote every seven years. In smaller municipalities, the public elects mayors and councilors. Corruption is rife at all levels of government. In 1997, Cameroon established anti-corruption bureaus in 29 ministries, but only 25% became operational, and in 2006, Transparency International placed Cameroon at number 138 on a list of 163 countries ranked from least to most corrupt. On 18 January 2006, Biya initiated an anti-corruption drive under the direction of the National Anti-Corruption Observatory.

Cameroon's legal system is largely based on French civil law with common law influences. Although nominally independent, the judiciary falls under the authority of the executive's Ministry of Justice. The president appoints judges at all levels. The judiciary is officially divided into tribunals, the court of appeal, and the supreme court. The National Assembly elects the members of a nine-member High Court of Justice that judges high-ranking members of government in the event they are charged with high treason or harming national security.
Human rights organisations accuse police and military forces of mistreating and even torturing criminal suspects, ethnic minorities, homosexuals, and political activists. Prisons are overcrowded with little access to adequate food and medical facilities, and prisons run by traditional rulers in the north are charged with holding political opponents at the behest of the government. However, since the early 2000s, an increasing number of police and gendarmes have been prosecuted for improper conduct.
The National Assembly makes legislation. The body consists of 180 members who are elected for five-year terms and meet three times per year. Laws are passed on a majority vote. Rarely has the assembly changed or blocked legislation proposed by the president. The 1996 constitution establishes a second house of parliament, the 100-seat Senate, but this body has never been put into practice. The government recognises the authority of traditional chiefs, fons, and lamibe to govern at the local level and to resolve disputes as long as such rulings do not conflict with national law.
President Paul Biya's Cameroon People's Democratic Movement (CPDM) was the only legal political party until December 1990. Numerous ethnic and regional political groups have since formed. The primary opposition is the Social Democratic Front (SDF), based largely in the Anglophone region of the country and headed by John Fru Ndi. Biya and his party have maintained control of the presidency and the National Assembly in national elections, but rivals contend that these have been unfair. Human rights organisations allege that the government suppresses the freedoms of opposition groups by preventing demonstrations, disrupting meetings, and arresting opposition leaders and journalists. Freedom House ranks Cameroon as "not free" in terms of political rights and civil liberties. The last elections were held on October 11, 2004.
Cameroon is a member of both the Commonwealth of Nations and La Francophonie. Its foreign policy closely follows that of its main ally, France. The country relies heavily on France for its defence, although military spending is high in comparison to other sectors of government. Biya has clashed with the government of Nigeria over possession of the Bakassi peninsula and with Gabon's president, El Hadj Omar Bongo, over personal rivalries. Nevertheless, civil war presents a more credible threat to national security, as tensions between Christians and Muslims and between Anglophones and Francophones remain high.
Education and health

Most children have access to free, state-run schools or subsidised, private and religious facilities. The educational system is a mixture of British and French precedents with most instruction in English or French. Cameroon has one of the highest school attendance rates in Africa. Girls attend school less regularly than boys do because of cultural attitudes, domestic duties, early marriage and pregnancy, and sexual harassment. Although attendance rates are higher in the south, a disproportionate number of teachers are stationed there, leaving northern schools chronically understaffed.
The quality of health care is generally low. Outside the major cities, facilities are often dirty and poorly equipped. Endemic diseases include dengue fever, filariasis, leishmaniasis, malaria, meningitis, schistosomiasis, and sleeping sickness. The HIV/AIDS seroprevalence rate is estimated at 5.4% for those aged 15–49, although a strong stigma against the illness keeps the number of reported cases artificially low. Traditional healers remain a popular alternative to Western medicine.
Provinces and divisions
Main articles: Provinces of Cameroon and Divisions of Cameroon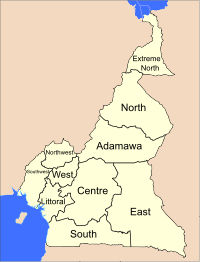
The constitution divides Cameroon into 10 semi-autonomous regions, each under the administration of an elected Regional Council. In practice, Cameroon still follows the system that was in place prior to the adoption of a new constitution in 1996. The country is divided into 10 provinces, each headed by a presidentially appointed governor. These leaders are charged with implementing the will of the president, reporting on the general mood and conditions of the provinces, administering the civil service, keeping the peace, and overseeing the heads of the smaller administrative units. Governors have broad powers: they may order propaganda in their area and call in the army, gendarmes, and police. The provinces are subdivided into 58 divisions (French Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)). These are headed by presidentially appointed divisional officers ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), who perform the governors' duties on a smaller scale. The divisions are further sub-divided into sub-divisions ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), headed by assistant divisional officers ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)). The districts, administered by district heads ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), are the smallest administrative units. These are found in large sub-divisions and in regions that are difficult to reach.
The three northernmost provinces are the Far North ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), North ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), and Adamawa ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)). Directly south of them are the Centre ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) and East ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)). The South Province ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) lies on the Gulf of Guinea and the southern border. Cameroon's western region is split into four smaller provinces: The Littoral ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) and Southwest ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) provinces are on the coast, and the Northwest ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) and West ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) provinces are in the western grassfields. The Northwest and Southwest were once part of British Cameroons; the other provinces were in French Cameroun.
Geography and climate
Main article: Geography of Cameroon
At Template:Km2 to mi2, Cameroon is the world's 53rd-largest country. It is comparable in size to Papua New Guinea and somewhat larger than the U.S. state of California. The country is located in Central and West Africa on the Bight of Bonny, part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean. Tourist literature describes Cameroon as "Africa in miniature" because it exhibits all major climates and vegetation of the continent: coast, desert, mountains, rainforest, and savanna. The country neighbours Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south.
Cameroon is divided into five major geographic zones distinguished by dominant physical, climatic, and vegetative features. The coastal plain extends 15 to 150 kilometres (10 to 90 mi) inland from the Gulf of Guinea and has an average elevation of 90 metres (295 ft). Exceedingly hot and humid with a short dry season, this belt is densely forested and includes some of the wettest places on earth. The South Cameroon Plateau rises from the coastal plain to an average elevation of 650 metres (2,130 ft). Equatorial rainforest dominates this region, although its alternation between wet and dry seasons makes it is less humid than the coast.
An irregular chain of mountains, hills, and plateaus known as the Cameroon range extends from Mount Cameroon on the coast—Cameroon's highest point at 4,095 metres (13,435 ft)—almost to Lake Chad at Cameroon's northern tip. This region has a mild climate, particularly on the Western High Plateau, although rainfall is high. Its soils are among Cameroon's most fertile, especially around volcanic Mount Cameroon. Vulcanism here has created crater lakes. On 21 August 1986, one of these, Lake Nyos, belched toxic fumes and killed between 1,700 and 2,000 people.
The southern plateau rises northward to the grassy, rugged Adamawa Plateau. This feature stretches from the western mountain area and forms a barrier between the country's north and south. Its average elevation is 1,100 metres (3,600 ft), and its temperature ranges from 22 to 25 °C (72 to 77 °F) with high rainfall. The northern lowland region extends from the edge of the Adamawa to Lake Chad with an average elevation of 300 to 350 metres (980 to 1,150 ft). Its characteristic vegetation is savanna scrub and grass. This is an arid region with sparse rainfall and high median temperatures.
Cameroon has four patterns of drainage. In the south, the principal rivers are the Ntem, Nyong, Sanaga, and Wouri. These flow southwestward or westward directly into the Gulf of Guinea. The Dja and Kadéï drain southeastward into the Congo River. In northern Cameroon, the Bénoué River runs north and west and empties into the Niger. The Logone flows northward into Lake Chad, which Cameroon shares with three neighbouring countries.
Economy and infrastructure
Main article: Economy of CameroonCameroon's per-capita GDP (PPP) was estimated as US$2,421 in 2005, high for an African country. Major export markets include France, Italy, South Korea, Spain, and the United Kingdom. Cameroon is part of the Bank of Central African States and the Customs and Economic Union of Central Africa (UDEAC). Its currency is the CFA franc. Red tape, high taxes, and endemic corruption have impeded growth of the private sector. Unemployment was estimated at 30% in 2001, and about 48% of the population was living below the poverty threshold in 2000. Since 1997, Cameroon has been following programmes advocated by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to reduce poverty, privatise industries, and increase economic growth. Tourism is a growing sector, particularly in the coastal area, around Mount Cameroon, and in the north.

Cameroon's natural resources are better suited to agriculture and forestry than to industry. An estimated 70% of the population farms, and agriculture comprised an estimated 45.2% of GDP in 2006. Most agriculture is done at the subsistence scale by local farmers using simple tools. They sell their surplus produce, and some maintain separate fields for commercial use. Urban centres are particularly reliant on peasant agriculture for their foodstuffs. Soils and climate on the coast encourage extensive commercial cultivation of bananas, cocoa, oil palms, rubber, and tea. Inland on the South Cameroon Plateau, cash crops include coffee, sugar, and tobacco. Coffee is a major cash crop in the western highlands, and in the north, natural conditions favour crops such as cotton, groundnuts, and rice. Reliance on agricultural exports makes Cameroon vulnerable to shifts in their prices.

Livestock are raised throughout the country. Fishing employs some 5,000 people and provides 20,000 tons of seafood each year. Bushmeat, long a staple food for rural Cameroonians, is today a delicacy in the country's urban centres. The commercial bushmeat trade has now surpassed deforestation as the main threat to wildlife in Cameroon.
The southern rainforest has vast timber reserves, estimated to cover 37% of Cameroon's total land area. However, large areas of the forest are difficult to reach. Logging, largely handled by foreign-owned firms, provides the government US$60 million a year, and laws mandate the safe and sustainable exploitation of timber. Nevertheless, in practice, the industry is one of the least regulated in Cameroon.

Factory-based industry accounted for an estimated 16.1% of GDP in 2006. More than 75% of Cameroon's industrial strength is located in Douala and Bonabéri. Cameroon possesses substantial mineral resources, but these are not extensively mined. Petroleum exploitation has fallen since 1985, but this is still a substantial sector such that dips in prices have a strong effect on the economy. Rapids and waterfalls obstruct the southern rivers, but these sites offer opportunities for hydroelectric development and supply most of Cameroon's energy. The Sanaga River powers the largest hydroelectric station, located at Edéa. The rest of Cameroon's energy comes from oil-powered thermal engines. Much of the country remains without reliable power supplies.
Transport in Cameroon is often difficult. Roads are poorly maintained and subject to inclement weather, since only 10% of the roadways are tarred. Roadblocks often serve little other purpose than to allow police and gendarmes to collect bribes from travellers. Road banditry has long hampered transport along the eastern and western borders, and since 2005, the problem has intensified in the east as the Central African Republic has further destabilised. Rail service runs from Kumba in the west to Bélabo in the east and north to Ngaoundéré. International airports are located in Douala and Garoua with a smaller facility at Yaoundé. The Wouri River estuary provides a harbour for Douala, the country's principal seaport. In the north, the Bénoué River is seasonally navigable from Garoua across into Nigeria.
Although press freedoms have improved since the early 2000s, the press is corrupt and beholden to special interests and political groups. Newspapers routinely self-censor to avoid government reprisals. The major radio and television stations are state-run, and other communications, such as land-based telephones and telegraphs, are largely under government control. However, cell phone networks and Internet providers have increased dramatically since the early 2000s and are largely unregulated.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Cameroon
2005 estimates place Cameroon's population at 17,795,000. This population is young: an estimated 41.2% are under 15, and 96.7% are under 65. The birth rate is estimated at 33.89 births per 1,000 people, the death rate at 13.47. The life expectancy is 51.16 years (50.98 years for males and 51.34 years for females).
Cameroon's population is almost evenly divided between urban and rural dwellers. Population density is highest in the large urban centres, the western highlands, and the northeastern plain. Douala, Yaoundé, and Garoua are the largest cities. In contrast, the Adamawa Plateau, southeastern Bénoué depression, and most of the South Cameroon Plateau are sparsely populated. People from the overpopulated western highlands and the underdeveloped north are moving to the coastal plantation zone and urban centres for employment. Smaller movements are occurring as workers seek employment in lumber mills and plantations in the south and east. Although the national sex ratio is relatively even, these out-migrants are primarily males, which leads to unbalanced ratios in some regions.
Both monogamous and polygamous marriage are practiced, and the average Cameroonian family is large and extended. In the north, women tend to the home, and men herd cattle or work as farmers. In the south, women grow the family's food, and men provide meat and grow cash crops. Cameroonian society is male-dominated, and violence and discrimination against women is common. At the onset of puberty, an estimated 26% of girls are subjected to breast ironing, a practice by which their breasts are pounded or massaged with heated objects to prevent them from developing. The goal is to prevent the girls from becoming precociously sexually active and to protect them from sexual assault. Female genital mutilation is practiced in portions of the Far North and Southwest provinces.

Estimates identify anywhere from 230 to 282 different ethnic and linguistic groups in Cameroon. The Adamawa Plateau broadly bisects these into northern and southern divisions. The northern peoples are Sudanese ethnic groups, who live in the central highlands and the northern lowlands, and the Fulani, who are spread throughout northern Cameroon. A small number of Shuwa Arabs live near Lake Chad. Southern Cameroon is inhabited by speakers of Bantu and Semi-Bantu languages. Bantu-speaking groups inhabit the coastal and equatorial zones, while speakers of Semi-Bantu languages live in the Western grassfields. Some 5,000 Pygmies roam the southeastern and coastal rainforests or live in small, roadside settlements. War in the Central African Republic has driven more than 20,000 refugees to Cameroon's Adamawa and East provinces since 2002, and kidnappings of Cameroonian citizens by Central African bandits have increased since 2005. Nigerians, especially Igbo, make up the largest group of foreign nationals.
Cameroon has a high level of religious freedom and diversity. The northern peoples are predominantly Muslim, although some ethnic groups retain native animist beliefs and are called Kirdi ("pagan") by the Fulani. The U.S. Department of State claims that some Muslims discriminate against Christians and followers of traditional beliefs in the north. Southern ethnic groups predominantly follow Christian or animist beliefs, or a syncretic combination of the two. People widely believe in witchcraft, and the government outlaws such practices. Suspected witches are often subject to mob violence.
The European languages introduced during colonialism have created a linguistic divide between the English-speaking fifth of the population who live in the Northwest and Southwest provinces and the French-speaking remainder of the country. Both English and French are official languages. Cameroonian Pidgin English is the most common lingua franca, especially in the formerly British-administered territories. A mixture of English, French, and Pidgin called Camfranglais has been gaining popularity in urban centres since the mid-1970s.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Cameroon
| Date | English Name |
|---|---|
| 1 January | New Year's Day |
| 11 February | National Youth Day |
| 1 May | Labour Day |
| 20 May | National Day |
| 15 August | Assumption |
| 1 October | Unification Day |
| 25 December | Christmas |
Each of Cameroon's ethnic groups has its own unique cultural forms. Typical celebrations include births, deaths, plantings, harvests, and religious rituals. Seven national holidays are observed throughout the year, and movable holidays include the Christian holy days of Good Friday, Easter Sunday, Easter Monday, and Ascension; and the Muslim holy days of 'Id al-Fitr, 'Id al-Adha, and Eid Milad Nnabi.
Music and dance are an integral part of Cameroonian ceremonies, festivals, social gatherings, and storytelling. Traditional dances are highly choreographed and separate men and women or forbid participation by one sex altogether. The goals of dances range from pure entertainment to religious devotion. Traditionally, music is transmitted orally. In a typical performance, a chorus of singers echoes a soloist. Musical accompaniment may be as simple as clapping hands and stomping feet, but traditional instruments include bells worn by dancers, clappers, drums and talking drums, flutes, horns, rattles, scrapers, stringed instruments, whistles, and xylophones; the exact combination varies with ethnic group and region. Some performers sing complete songs by themselves, accompanied by a harplike instrument.
Popular music styles include ambasse bey of the coast, assiko of the Bassa, mangambeu of the Bangangte, and tsamassi of the Bamileke. Nigerian music has influenced Anglophone Cameroonian performers, and Prince Nico Mbarga's highlife hit "Sweet Mother" is the top-selling African record in history. The two most popular styles are makossa and bikutsi. Makossa developed in Douala and mixes folk music, highlife, soul, and Congo music. Performers such as Manu Dibango, Francis Bebey, Moni Bilé, and Petit-Pays popularised the style worldwide in the 1970s and 1980s. Bikutsi originated as war music among the Ewondo. Artists such as Anne-Marie Nzié developed it into a popular dance music beginning in the 1940s, and performers such as Mama Ohandja and Les Têtes Brulées popularised it internationally during the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s.
Cuisine varies by region, but a large, one-course, evening meal is common throughout the country. A typical dish is based on cocoyams, maize, manioc, millet, plantains, potatoes, rice, or yams, often pounded into dough-like fufu (cous-cous). This is served with a sauce, soup, or stew made from greens, groundnuts, palm oil, or other ingredients. Meat and fish are popular but expensive additions. Dishes are often quite hot, spiced with salt, red pepper, and Maggi. Water, palm wine, and millet beer are the traditional mealtime drinks, although beer, soda, and wine have gained popularity. Silverware is common, but food is traditionally manipulated with the right hand. Breakfast consists of leftovers or bread and fruit with coffee or tea. Snacks are popular, especially in larger towns where they may be bought from street vendors.

Traditional arts and crafts are practices throughout the country for commercial, decorative, and religious purposes. Woodcarvings and sculptures are especially common. The high-quality clay of the western highlands is suitable for pottery and ceramics. Other crafts include basket weaving, beadworking, brass and bronze working, calabash carving and painting, embroidery, and leather working. Traditional housing styles make use of locally available materials and vary from temporary wood-and-leaf shelters of nomadic Mbororo to the rectangular mud-and-thatch homes of southern peoples. Dwellings made from materials such as cement and tin are increasingly common.

Cameroonian literature and film have concentrated on both European and African themes. Colonial-era writers such as Louis-Marie Pouka and Sankie Maimo were educated by European missionary societies and advocated assimilation into European culture as the means to bring Cameroon into the modern world. After World War II, writers such as Mongo Beti and Ferdinand Oyono analysed and criticised colonialism and rejected assimilation. Shortly after independence, filmmakers such as Jean-Paul Ngassa and Thérèse Sita-Bella explored similar themes. In the 1960s, Mongo Beti and other writers explored post-colonialism, problems of African development, and the recovery of African identity. Meanwhile, in the mid-1970s, filmmakers such as Jean-Pierre Dikongué Pipa and Daniel Kamwa dealt with the conflicts between traditional and post-colonial society. Literature and films during the next two decades concentrated more on wholly Cameroonian themes.
National policy strongly advocates sport in all forms. Traditional sports include canoe racing and wrestling, and several hundred runners participate in the 40 km (24.8 mi) Mount Cameroon Race of Hope each year. Cameroon is one of the few tropical countries to have competed in the Winter Olympics. However, sport in Cameroon is dominated by football (soccer). Amateur football clubs abound, organised along ethnic lines or under corporate sponsors. The Cameroon national football team has been one of the most successful in the world since its strong showing in the 1990 FIFA World Cup. Cameroon has won four African Cup of Nations titles.
See also
Notes
- DeLancey and DeLancey 2.
- Fanso 84.
- ^ DeLancey and DeLancey 125.
- ^ DeLancey and DeLancey 5.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 4.
- ^ DeLancey and DeLancey 6.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 19.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 7.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 8.
- ^ DeLancey and DeLancey 9.
- "Background Notes: Cameroon; Neba 250.
- ^ IRIN, "New anti-corruption drive".
- 2006 Corruption Perceptions Index 2006.
- ^ "Cameroon", The World Factbook. Cite error: The named reference "CIA" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "Background Note: Cameroon".
- "Cameroon", Amnesty International; "Cameroon (2006)", Freedom House; "Cameroon", Country Reports on Human Rights Practices, U.S. Department of State; "Elections to the Human Rights Council", Amnesty International.
- ^ "Elections to the Human Rights Council".
- ^ "Cameroon", Country Reports on Human Rights Practices.
- ^ "Cameroon (2006)", Freedom House.
- "Background Note: Cameroon"; Neba 252.
- West 11.
- "Cameroon", Amnesty International.
- Cameroon is ranked a 6 in both categories on a scale of 1 to 7, with 1 being "most free" and 7 being "least free". "Cameroon (2006)", Freedom House.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 126; Ngoh 328.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 30.
- West 11.
- MacDonald 69.
- ^ Mbaku 15.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 105–6.
- Mbaku 16.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 21.
- West 64.
- West 58–60.
- "Cameroon", UNAIDS.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 21.
- Lantum and Monono 14.
- Neba 250.
- Demographic Yearbook 1.
- "Rank Order - Area".
- DeLancey and DeLancey 16.
- Fomesky et al 6.
- Neba 14.
- Neba 28.
- "Highest Average Annual Precipitation Extremes".
- ^ Neba 16.
- Neba 17.
- ^ Neba 17.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 161 report 1,700 killed; Hudgens and Trillo 1054 say "at least 2,000"; West 10 says "more than 2,000".
- Gwanfogbe et al 20; Neba 29.
- "World Economic and Financial Surveys".
- ^ West 12.
- Neba 132.
- Neba 173–6.
- Neba 208.
- Neba 185.
- West 24.
- Neba 189.
- Neba 195.
- West 23.
- Neba 170.
- Neba 158.
- Neba 160.
- Neba 161.
- Neba 199.
- Hudgens and Trillo 1036.
- ^ Musa.
- "Cameroon - Annual Report 2007".
- Neba 207.
- Mbaku 20.
- Mbaku 20–1.
- World Population Prospects.
- West 3.
- Neba 109–11.
- Neba 111.
- Neba 105–6.
- Neba 106.
- Neba 103–4.
- Mbaku 139.
- Mbaku 141.
- Sa'ah.
- Neba 65, 67.
- West 13.
- Neba 48.
- International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies.
- Neba 108.
- Geschiere 169–70.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 28.
- Neba 94.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 131; Niba.
- Mbaku 189; West 18.
- Mbaku 204.
- ^ West 18.
- ^ Mbaku 189.
- Mbaku 191.
- West 18–9.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 184.
- Mbaku 200.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 51; Nkolo & Ewens 443.
- West 84–5.
- Mbaku 121–2.
- Hudgens and Trillo 1047; Mbaku 122; West 84.
- Mbaku 121; Hudgens and Trillo 1048.
- West 17.
- Mbaku 110–3.
- Mbaku 80–1
- Fitzpatrick 38; Mbaku 77, 83–4; Volet.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 119–20; West 20.
- Mbaku 85–6.
- DeLancey and DeLancey 120.
- West 127.
- West 92–3, 127.
References
- "Corruption Perceptions Index 2006". Transparency International. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- "Background Note: Cameroon". October 2006. United States Department of State. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- "Cameroon". Amnesty International Report 2006. Amnesty International Publications. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- "Cameroon". Country Reports on Human Rights Practices, 6 March 2007. Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor, U.S. Department of State. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- "Cameroon". Human Development Report 2006. United Nations Development Programme. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- "Cameroon". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. 15 March 2007. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- "Cameroon". UNAIDS. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- "Cameroon (2006)". Country Report: 2006 Edition. Freedom House, Inc. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- "Cameroon - Annual Report 2007". Reporters without Borders. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- "CAMEROON: New anti-corruption drive leaves many sceptical". 27 January 2006. IRIN. UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- Constitution of the Republic of Cameroon (English and French versions). 18 January 1996. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- DeLancey, Mark W., and Mark Dike DeLancey (2000): Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Cameroon (3rd ed.). Lanham, Maryland: The Scarecrow Press.
- Demographic Yearbook 2004. United Nations Statistics Division.
- "2006 Elections to the Human Rights Council: Background information on candidate countries". May 2006. Amnesty International Publications. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- Fanso, V. G. (1989). Cameroon History for Secondary Schools and Colleges, Vol. 1: From Prehistoric Times to the Nineteenth Century. Hong Kong: Macmillan Education Ltd.
- Fitzpatrick, Mary (2002). "Cameroon." Lonely Planet West Africa, 5th ed. China: Lonely Planet Publications Pty Ltd.
- Fomensky, R., M. Gwanfogbe, and F. Tsala, editorial advisers (1985) Macmillan School Atlas for Cameroon. Malaysia: Macmillan Education Ltd.
- Fonge, Fuabeh P. (1997). Modernization without Development in Africa: Patterns of Change and Continuity in Post-Independence Cameroonian Public Service. Trenton, New Jersey: Africa World Press, Inc.
- Geschiere, Peter (1997). The Modernity of Witchcraft: Politics and the Occult in Postcolonial Africa. Charlottesville: University Press of Virginia.
- Gwanfogbe, Mathew, Ambrose Meligui, Jean Moukam, and Jeanette Nguoghia (1983). Geography of Cameroon. Hong Kong: Macmillan Education Ltd.
- "Highest Average Annual Precipitation Extremes". Global Measured Extremes of Temperature and Precipitation, National Climatic Data Center, 9 August, 2004. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- Hudgens, Jim, and Richard Trillo (1999). West Africa: The Rough Guide. 3rd ed. London: Rough Guides Ltd.
- International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (28 May 2007). "Cameroon: Population Movement; DREF Bulletin no. MDRCM004". ReliefWeb. Accessed 18 June 2007.
- Lantum, Daniel M., and Martin Ekeke Monono (2005). "Republic of Cameroon", Who Global Atlas of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicine. World Health Organization.
- MacDonald, Brian S. (1997). "Case Study 4: Cameroon", Military Spending in Developing Countries: How Much Is Too Much? McGill-Queen's University Press.
- Mbaku, John Mukum (2005). Culture and Customs of Cameroon. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press.
- Musa, Tansa (27 June 2007). "Gunmen kill one, kidnap 22 in Cameroon near CAR". Reuters. Accessed 27 June 2007.
- Neba, Aaron (1999). Modern Geography of the Republic of Cameroon, 3rd ed. Bamenda: Neba Publishers.
- Niba, Francis Ngwa (20 February 2007). "New language for divided Cameroon". BBC News. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- Nkolo, Jean-Victor, and Graeme Ewens (2000). "Cameroon: Music of a Small Continent". World Music, Volume 1: Africa, Europe and the Middle East. London: Rough Guides Ltd.
- "Rank Order - Area". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. 15 March 2007. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- Sa'ah, Randy Joe (23 June 2006). "Cameroon girls battle 'breast ironing'". BBC News. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- Swarovski Orchestra (2004). National Anthems of the World. Koch International Classics. Audio CD.
- Volet, Jean-Marie (10 November 2006). "Cameroon Literature at a glance". Reading women writers and African literatures. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- West, Ben (2004). Cameroon: The Bradt Travel Guide. Guilford, Connecticut: The Globe Pequot Press Inc.
- Wight, Susannah, ed. (2006). Cameroon. Spain: MTH Multimedia S.L.
- "World Economic and Financial Surveys". World Economic Outlook Database, International Monetary Fund. September 2006. Accessed 6 April 2007.
- World Population Prospects: The 2006 Revision Population Database. 2006. United Nations Population Division. Accessed 6 April 2007.
External links
- Presidency of the Republic of Cameroon
- National Assembly of Cameroon
- CRTV — Cameroon Radio Television
| Links to related articles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Template:Countries of Central Africa Template:Countries of West Africa
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||