This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Flordeneu (talk | contribs) at 01:10, 4 October 2007 (RV - Too many images and mostly not addecuate for the sections). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 01:10, 4 October 2007 by Flordeneu (talk | contribs) (RV - Too many images and mostly not addecuate for the sections)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)For other uses, see the Barcelona city.
Barcelona (Catalan Template:IPA2, Spanish Template:IPA2), is the capital and most populous city of Catalonia and the second largest city in Spain, with a population of 1,605,602 in 2006. It is located on the Mediterranean coast (41°23′N 2°11′E / 41.383°N 2.183°E / 41.383; 2.183), between the mouths of the rivers Llobregat and Besòs, and is limited to the west by the Serra de Collserola ridge (512 m).
Barcelona is a major economic centre, with one of Europe's principal Mediterranean ports, and its airport is the second largest in Spain. Founded as a Roman city, Barcelona became the capital of the Counts of Barcelona and the Crown of Aragon. Besieged several times during its history, Barcelona is today an important cultural centre and a major tourist destination and has a rich cultural heritage. Particularly renowned are architectural works of Antoni Gaudí and Lluís Domènech i Montaner that have been designated UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
As the capital of Catalonia, Barcelona houses the seat of the Catalan government, known as the Generalitat de Catalunya; of particular note are the executive branch, the parliament and the Supreme Court of Catalonia. The city is also the capital of the county (comarca) of the Barcelonès.
Names
The name Barcelona comes from the ancient Phoenician Iberian Barkeno; Greek: Template:Polytonic; Latin: Barcino, Barcelo and Barceno.
During the Middle Ages the city was variously known as Barchinona, Barçalona, Barchelona and Barchenona.
History
Main article: History of BarcelonaThe foundation of Barcelona is the subject of two different legends. The first attributes the founding of the city to Hercules 400 years before the building of Rome, and that it was rebuilt by the Carthaginian Hamilcar Barca, father of Hannibal, who named the city Barcino after his family, in the 3rd century BC. The second legend attributes the foundation directly to Hamilcar Barca.
About 15 BC, the Romans redrew the town as a castrum (Roman military camp) centred on the "Mons Taber", a little hill near the contemporary city hall (Plaça de Sant Jaume). Under the Romans it was a colony, with the surname of Faventia, or, in full, Colonia Faventia Julia Augusta Pia Barcino or Colonia Julia Augusta Faventia Paterna Barcino. Mela mentions it among the small towns of the district, probably as it was eclipsed by its neighbour Tarraco (modern Tarragona); but it may be gathered from later writers that it gradually grew in wealth and consequence, favoured as it was with a beautiful situation and an excellent harbour. It enjoyed immunity from imperial burdens. The city minted its own coins; some from the era of Galba survive.
Some important Roman ruins are exposed under the Plaça del Rei, entrance by the city museum (Museu d'Història de la Ciutat), and the typically Roman grid-planning is still visible today in the layout of the historical centre, the Barri Gòtic ("Gothic Quarter"). Some remaining fragments of the Roman walls have been incorporated into the cathedral. The cathedral, also known as basilica La Seu is said to have been founded in 343. The city was conquered by the Visigoths in the early fifth century, by the Moors in the early eighth century, reconquered from the emir in 801 by Charlemagne's son Louis who made Barcelona the seat of Carolingian "Spanish Marches" (Marca Hispanica), a buffer zone ruled by the Count of Barcelona. Barcelona was still a Christian frontier territory when it was sacked by Al-Mansur in 985.
The Counts of Barcelona became increasingly independent and expanded their territory to include all of Catalonia, later the Crown of Aragon which conquered many overseas possessions, ruling the western Mediterranean Sea with outlying territories in Naples and Sicily and as far as Athens in the thirteenth century. The forging of a dynastic link between the Crowns of Aragon and Castile marked the beginning of Barcelona's decline.
Geography

Barcelona is located on the northeast coast of the Iberian Peninsula, facing the Mediterranean Sea, on a plateau approximately 5 km wide limited by the mountain range of Collserola, the Llobregat river to the south-west and the Besòs river to the north. This plateau has 170 km², of which 101 km² (38.9 mi²) are occupied by the city itself. It is 160 km (100 mi) south of the Pyrenees and the Catalonian border with France.
Collserola, part of the coastal mountain range, shelters the city to the north-west. Its highest point, the peak of Tibidabo, 512 m high, offers striking views over the city and is topped by the 288.4 m Torre de Collserola, a telecommunications tower that is visible from most of the city. Barcelona is peppered with small hills, most of them urbanized and that gave their name to the neighbourhoods built upon them, such as Carmel (267 m), Putxet (181 m) and Rovira (261 m). The escarpment of Montjuïc (173 m), situated to the southeast, overlooks the harbour and is topped by Montjuïc castle, a fortress built in the 17–18th centuries to control the city as a replacement for the Ciutadella. Today, the fortress is a museum and Montjuic is home to several sporting and cultural venues, as well as Barcelona's biggest park and gardens.
The city borders are the municipalities of Santa Coloma de Gramenet and Sant Adrià de Besòs to the north; L'Hospitalet de Llobregat and Esplugues de Llobregat to the south; the Mediterranean Sea to the east; and Montcada i Reixac and Sant Cugat del Vallès to the west.
Climate
Barcelona has a Mediterranean climate, with mild, dry winters and warm, humid summers. January and February are the coldest months, averaging temperatures of 10 °C (50 °F). Snowfalls are so rare that they are remembered as special events. July and August are the hottest months, averaging temperatures of 30 °C (86 °F). The highest recorded maximum temperature in the city itself is 38.6 °C. At the Fabra Observatory, situated on the Tibidabo hill, the record summer temperature is 39.8 °C (103.6 °F). However, it should be noted that the observatory is situated in the hills above the city near Collserola park - an area where the impact of the "heat island" effect is likely to be diminished.
Cityscape

Parks
Barcelona contains 68 municipal parks, divided into 12 historic parks, 5 thematic (botanical) parks, 45 urban parks and 6 forest parks. They range from vest-pocket parks to large recreation areas. The parks cover 10% of the city (549.7 ha), growing about 10 ha per year, with a proportion of 18.1 m² of park area per inhabitant.
Of Barcelona's parks, Montjuïc is the largest, with 203 ha located on the mountain of the same name. It is followed by Ciutadella Park (situated in the place of the old military citadel and which houses the Parliament building, the zoo and several museums; 31 ha including the zoo), the Guinardó Park (19 ha), Park Güell (designed by Antoni Gaudí; 17.2 ha), Oreneta Castle Park (also 17.2 ha), Diagonal Mar Park (13.3 ha, inaugurated in 2002), Nou Barris Central Park (13.2 ha), Can Dragó Sports Park and Poblenou Park (both 11.9 ha) and the Labyrinth Park (9.10 ha), named after the garden maze it contains. A part of the Collserolla Park is also within the city limits.
Beaches

Barcelona has seven beaches, totalling 4.5 km (2.8 mi) of coastline. Sant Sebastià and Barceloneta beaches, both 1100 m in length, are the largest, oldest and the most frequented beaches in Barcelona. The Olympic port separates them from the other city beaches: Nova Icària, Bogatell, Mar Bella, Nova Mar Bella and Llevant. These beaches (ranging from 400 to 640 m) were opened as a result of the city restructuring to host the 1992 Summer Olympics, when a great number of industrial buildings were demolished. The 2004 Universal Forum of Cultures left the city a sandless bathing zone, a sort of sea pool.
Other
The area around the Plaça Catalunya makes up the city's historical centre and, alongside the upper half of Avinguda Diagonal, is the main commercial area of the city. Barcelona has several commercial complexes, like L'Illa in the higher part of the Diagonal avenue and Diagonal Mar in the lowest, La Maquinista, Glòries in the place of the same name and the Maremagnum by the port.
Barcelona has several skyscrapers, the highest being the Hotel Arts and its twin the Torre Mapfre, both 154 m high, followed by the newest Torre Agbar 144 m high.
Demographics

According to Barcelona's City Council, Barcelona's population as of 2006-06-01 was 1,673,075 people, while the population of the Metropolitan Area was 3,161,081. It is the central nucleus of the Urban Region of Barcelona, which relies on a population of 5,327,872 and covers an area of 4,268 km².
The population density of Barcelona was 15,779 people per km², with Eixample being the most populated district. 62% of the inhabitants were born in Catalonia, with a 23.5% coming from the rest of Spain. Of the 13.9% from other countries, a proportion which has more than tripled since 2001 when it was 3.9%, the majority come from (in order) Ecuador, Peru, Morocco, Colombia, Argentina, Italy, Pakistan and China.
95% of the population understand Catalonia's native Catalan language, while 74.6% can speak it, 75% can read it, and 47.1% can write it, thanks to the linguistic immersion educational system. While most of the population profess to be Catholic (208 churches), there are also a number of other groups, including various Evangelist (71 locations, mostly professed by Roma), Jehovah's Witnesses (21 Kingdom Halls) and Buddhists (13 locations), and a growing number of Muslims due to immigration.
In 1900, Barcelona had a population of 533.000 people, which grew steadily but slowly until 1950, when it started absorbing an height number of people from other less-industrialized parts of Spain. Barcelona's population peaked in 1979 with 1,906,998 people, and fell throughout the 1980s and 1990s as more people sought a higher quality of life in outlying cities in the Barcelona Metropolitan Area. After bottoming out in 2000 with 1,496,266 people, the city's population began to rise again as younger people started to return, causing a great increase in housing prices.
Economy


Barcelona has a long-standing mercantile tradition. Less well known is that it was one of the earliest regions in continental Europe to begin industrialization, beginning with textile related works at the end of the eighteenth century but really gathering momentum in the mid nineteenth century, when it became a major center for the production of textiles and machinery. Since then, manufacturing has played a large role in its history. The traditional importance in textiles is still reflected in Barcelona's importance as a major fashion center. In summer 2006, Barcelona became an host for the prestigious Bread & Butter urban fashion fair. The fair was so successful than, starting in 2007, Barcelona became the only host for Bread & Butter, that closed its original Berlin location.
As in other modern cities, the manufacturing sector has long since been overtaken by the services sector, though it remains important. The most important industries today are textile, chemistry, pharmaceutical, motor, electronic and printing. In the services sector, the most important are the logistics, publishing, telecommunications and computer sectors.
Drawing upon its tradition of creative art and craftsmanship, Barcelona is nowadays also known for its award-winning industrial design. Barcelona also has several congress halls, notably La Fira (Trade Fair), that host a quickly growing number of national and international events each year, which had also meant the opening of new hotels each year. The Port of Barcelona is an important Mediterranean port, both for general containers cargo and for cruise ships.
Barcelona has one of the highest costs of living in Spain, second only to Madrid and occupying the 31st position in the world rank according to a report by Mercer Human Resource Consulting.
Government and administrative divisions
See also: Municipal elections in Barcelona and List of mayors of Barcelona
Barcelona is governed by a city council formed by 41 city councilors, elected for a four-year term by universal suffrage. As one of the two biggest cities in Spain (the other being Madrid), Barcelona is subject to a special law articulated through the Carta Municipal (Municipal Law). A first version of this law was passed in 1960 and amended later, but the current version was approved in March 2006. According to this law, Barcelona's city council is organized in two levels: a political one, with elected city councilors, and one executive, which administrates the programs and executes the decisions taken on the political level. This law also gives the local government a special relationship with the central government and it also gives the mayor wider prerogatives by the means of municipal executive commissions. It expands the powers of the city council in areas like telecommunications, city traffic, road safety and public safety. It also gives a special economic regime to the city's treasury and it gives the council a veto in matters that will be decided by the central government, but that will need a favourable report from the council.
The Comissió de Govern (Government Commission) is the executive branch, formed by 24 councilors, led by the Mayor, with 5 lieutenant-mayors and 17 city councilors, each in charge of an area of government, and 5 non-elected councilors. The plenary, formed by the 41 city councilors, has advisory, planning, regulatory, and fiscal executive functions. The six Commissions del Consell Municipal (City council commissions) have executive and controlling functions in the field of their jurisdiction. They are composed by a number of councilors proportional to the number of councilors each political party has in the plenary. The city council has jurisdiction in the fields of city planning, transportation, municipal taxes, public highways security through the Guardia Urbana (the municipal police), city maintenance, gardens, parks and environment, facilities (like schools, nurseries, sports centres, libraries, etc.), culture, sports, youth and social welfare. Some of these competencies are not exclusive, but shared with the Generalitat de Catalunya or the central Spanish government.
The executive branch is led by a Chief Municipal Executive Officer which answers to the Mayor. It is made up of departments which are legally part of the city council and by separate legal entities of two tipes: autonomous public departments and public enterprises.
The seat of the city council is on the Plaça Sant Jaume, opposite the seat of Generalitat de Catalunya. Since the coming of the Spanish democracy, Barcelona has been governed by the PSC, first with an absolute majority and later in coalition with ERC and ICV. Since the May 2007 elections, PSC is governing in minority only with IC, since ERC decided against a renewal of the previous coalition. The second most voted party in Barcelona is CiU, followed by PP, both currently in the opposition.
Administrative divisions
Since 1997, the city has been divided into 10 administrative districts (districtes), each one with its own council led by a city councillor. The composition of each district council depends on the number of votes each political party had in that district, so a district can be led by a councillor from a different party than the executive council.
The administrative divisions are based mostly on historical divisions. Several of the city's districts are former towns annexed by the city of Barcelona in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries that still maintain their own distinct character. The official names of these districts are in the Catalan language.
Districts and neighbourhoods
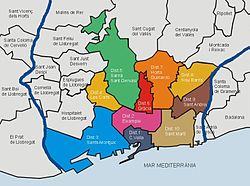
- Ciutat Vella ("Old City"): El Raval (also known in Spanish as the Barrio Chino, ("Chinatown"), the Barri Gòtic ("Gothic Quarter"), La Barceloneta and the Barri de la Ribera.
- Eixample: Sant Antoni, Esquerra de l'Eixample ("the left side of the Eixample" facing away from the sea), Dreta de l'Eixample ("the right side of the Eixample"), Barri de la Sagrada Família, Fort Pienc, Sant Antoni
- Sants–Montjuïc: Poble Sec, La Marina, La Font de La Guatlla, La Bordeta, Hostafrancs, Sants, Badal.
- Les Corts: Les Corts, La Maternitat, Pedralbes.
- Sarrià-Sant Gervasi: Tres Torres, Sarrià, Vallvidrera, Bonanova, Sant Gervasi, Putxet-Farró, Galvany.
- Gràcia: Vallcarca, El Coll, La Salut, Gràcia, El Camp d'en Grassot
- Horta-Guinardó: Horta, El Carmel, La Teixonera, El Guinardó (Alt i Baix), La Clota, La Vall D'Hebron, Montbau
- Nou Barris: Can Peguera, Porta, Canyelles, Ciutat Meridiana, Guineueta, Prosperitat, Vallbona, Verdum, Vilapicina, Roquetes, Trinitat Vella, Trinitat Nova, Torre Baró, Torre Llobeta and Turó de la Peira.
- Sant Andreu: La Sagrera, Congrés, Trinitat Vella, Bon Pastor, Sant Andreu, Navas, Baró de Viver
- Sant Martí: Diagonal Mar, Fort Pius, San Martí de Provençals, Poble Nou, La Verneda, El Clot, Vila Olímpica del Poblenou.
Education
Main article: Education in CataloniaBarcelona has a well-developed higher education system of public universities. Most prominent among these is the University of Barcelona, a world-renowned research and teaching institution with campuses around the city. Barcelona is also home to the Polytechnic University of Catalonia, the newer Pompeu Fabra University and, in the private sector, the Ramon Llull University encompassing internationally renowned institutions like ESADE Business School. The Autonomous University of Barcelona, another public university, is located in Bellaterra, a town in the Metropolitan Area.
The city has a network of public schools, from nurseries to high schools, under the responsibility of the city council (though the student subjects are the responsibility of the Generalitat de Catalunya). There are also many private schools, some of them Roman Catholic. Like other cities in Spain, Barcelona now faces the integration of a large number of immigrant children from Latin America, Africa and Asia.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Barcelona
Barcelona's cultural roots go back 2000 years. To a greater extent than the rest of Catalonia, where Catalonia's native Catalan is more dominant, Barcelona is a bilingual city: Catalan and Spanish are both official languages and widely spoken. The Catalan spoken in Barcelona, Central Catalan, is the one closest to standard Catalan. Since the arrival of democracy, the Catalan culture (very much repressed during the dictatorship) has been promoted, both by recovering works from the past and by stimulating the creation of new works. Barcelona is designated as a world-class city by the Globalization and World Cities Study Group and Network.
Entertainment and performing arts
Main article: List of theatres and concert halls in BarcelonaBarcelona has many venues for live music and theatre, including the world-renowned Gran Teatre del Liceu opera theatre, the Teatre Nacional de Catalunya, the Teatre Lliure and the Palau de la Música Catalana concert hall. Barcelona also is home to the Sónar Music Festival which takes place around June every year, and to the Barcelona and Catalonia National Symphonic Orchestra (Orquestra Simfònica de Barcelona i Nacional de Catalunya, usually known as OBC) is the largest symphonic orchestra in Catalonia. In 1999, the OBC inaugurated its new venue in the brand-new Auditorium (l'Auditori). It performs around 75 concerts per season and its current director is Eiji Oue.. It has a thriving alternative music scene, with groups such as The Pinker Tones receiving international attention. .
Museums
Main article: List of museums in Barcelona
Barcelona houses a great number of museums, which cover different areas and eras. The National Museum of Art of Catalonia possesses a well-known collection of Romanesque art while the Barcelona Museum of Contemporary Art focuses on post-1945 Catalan and Spanish art. The Fundació Joan Miró, Picasso Museum and Fundació Antoni Tàpies hold important collections of these world-renowned artists.
Several museums cover the fields of history and archeology, like the City History Museum, the Museum of the History of Catalonia, the Archaeology Museum of Catalonia, the Barcelona Maritime Museum and the private-owned Egiptian Museum. The Erotic museum of Barcelona is among the most peculiar ones, while Cosmocaixa is a science museum that received the European Museum of the Year Award in 2006.
Architecture

The Barri Gòtic ("Gothic Quarter" in Catalan) is the centre of the old city of Barcelona. Many of the buildings date from medieval times, some from as far back as the Roman settlement of Barcelona. Catalan modernisme architecture (often known as Art Nouveau in the rest of Europe), developed between 1885 and 1950 and left an important legacy in Barcelona. A great number of these buildings are World Heritage Sites. Especially remarkable is the work of architect Antoni Gaudí, which can be seen throughout the city. His best known work is the immense but still unfinished church of the Sagrada Família, which has been under construction since 1882, and is still financed by private donations. As of 2007, completion is planned for 2026.
Barcelona won the 1999 RIBA Royal Gold Medal for its architecture, the first (and as of 2007, only) time that the winner has been a city, and not an individual architect.
World Heritage Sites in Barcelona
- Works of Lluís Domènech i Montaner, Palau de la Música Catalana and Hospital de Sant Pau, included in the list in 1997.
- Works of Antoni Gaudí, including Park Güell, Palau Güell, Casa Milà, Casa Vicens, Sagrada Família (Nativity façade and crypt), Casa Batlló, Crypt in Colonia Güell. The first three works were inscribed as a World Heritage Site in 1984. The other four were added as extensions to the site in 2005.
Media
El Periódico de Catalunya (Catalan and Spanish editions) and La Vanguardia (Spanish) are Barcelona's two major daily newspapers while Sport and El Mundo Deportivo (both in Spanish) are the city's two major sports daily newspapers, published by the same companies. The city is also served by a number of smaller publications such as Avui and El Punt (both in Catalan), by nation-wide newspapers with special Barcelona editions like El Pais and El Mundo (both in Spanish), and by several free newspapers like Metro, 20 minutos, ADN and Què (bilingual).
Several major FM stations include Catalunya Ràdio, RAC 1, RAC 105 and Cadena SER. Barcelona also has several local TV stations, among them BTV (owned by city council) and 8TV (owned by the Godó group, that also owns La Vanguardia). The headquarters of Televisió de Catalunya, Catalonia's public network, are located in Sant Joan Despí, in Barcelona's metropolitan area.
Sports
Barcelona has a long sporting tradition and hosted the successful 1992 Summer Olympics as well as several matches from the 1982 Football World Cup. It has also been host to the X FINA World Championships and twice of the Eurobasket.
FC Barcelona is a sports club best known for its football team, one of the biggest in Europe, twice winner of the UEFA Champions League. FC Barcelona also has teams in the Spanish basketball ACB league (AXA FC Barcelona), the handball ASOBAL league (FC Barcelona-Cifec), and the roller hockey league. The club's museum is the second most visited in Catalonia. RCD Espanyol is the city's other Liga football team. Barcelona also has other clubs in lower categories, like CE Europa and UE Sant Andreu.
Barcelona has two UEFA 5-star rated football stadiums: FC Barcelona's Camp Nou and the Estadi Olímpic Lluís Companys, used for the 1992 Olympics and the current home of Espanyol, pending completion of the club's new stadium.
The Open Seat Godó, a 50-year-old ATP Tour International Series Gold tennis tournament, is held annually in the facilities of the Reial Club de Tenis Barcelona (Barcelona Royal Tennis Club). Several popular running competitions are organized year-round in Barcelona: Cursa del Corte Inglés (with about 60,000 participants each year), Cursa de la Mercè, Cursa Jean Bouin, Milla Sagrada Família and the San Silvestre. Also, each Christmas, a swimming race across the port is organized. Near Barcelona, in Montmeló, the 131,000 capacity Circuit de Catalunya racetrack hosts the Formula One Spanish Grand Prix and the Catalan motorcycle Grand Prix. Barcelona has also become very popular with skateboarders, which has led to a new anti-skateboarding law, which came into effect in 2006.
Transportation and infrastructures
Airports
Barcelona is served by Barcelona International Airport in the town of El Prat de Llobregat, about 3 km from Barcelona. It is the second-largest airport in Spain, and the largest on the Mediterranean coast. It is a main hub for Vueling Airlines and Clickair, and also a focus for Spanair, Air Europa and Iberia. The airport mainly serves domestic and European destinations, but some airlines offer destinations in Asia and the United States. The airport is connected to the city by highway, commuter train and scheduled bus service. The airport handled 30,008,152 passengers in 2006. A new terminal is being built, and its expected to enter service in 2009.
Sabadell Airport is a smaller airport in the nearby town of Sabadell, devoted to pilot training, advertising flights, aerotaxi and private flights. Some low-cost airlines, like Ryanair and Martinair, prefer to use Girona-Costa Brava Airport, situated about 90 km to the north of Barcelona and Reus Airport, situated 77 km to the south.

Seaport
The Port of Barcelona has a 2000-year history and a great contemporary commercial importance. It is the most important Mediterranean port for general cargo of containers and cruisers. The port is managed by the Port Authority of Barcelona. Its 7.86 km² are divided into three zones: Port Vell (the Old Port), the commercial port and the logistics port (Barcelona Free Port). The port is undergoing an enlargement that will double its size thanks to diverting the mouth of the Llobregat river 2 km to the south.
The Port Vell area also houses the Maremagnum (a commercial mall), a multiplex cinema, the IMAX Port Vell and an aquarium.
Public transportation
Main article: Autoritat del Transport MetropolitàBarcelona is served by a comprehensive local public transport network that includes a metro, a bus network, two separate tram networks (one of them, the Tramvia Blau, connects to the Tibidabo funicular), and several funiculars and aerial cable cars. The Barcelona Metro network comprises nine lines, identified by an "L" followed by the line number as well as by individual colours. Most of the network is operated by the Transports Metropolitans de Barcelona (TMB), but three lines are FGC commuter lines that run through the city. When finished, the L9 will be the longest underground metro line in Europe with 42.6km.
The TMB also operates the city's tram networks, known as Trambaix and Trambesòs, and the city's daytime bus network, as well as a tourist bus service. The night bus network, known as Nitbus, is operated by Mohn. Transports Ciutat Comtal operates the regular Tomb Bus (along the Diagonal avenue) and Aerobus (to the airport) services. Other companies operate services that connect the city with towns in the metropolitan area.
The Funicular de Montjuïc climbs the Montjuïc hill. The Vallvidrera and Tibidabo funiculars climb the Tibidabo hill. The city has two aerial cable cars: one to the Montjuïc castle and another that runs via Torre Jaume I and Torre Sant Sebastia over the port.
Barcelona is a major hub for RENFE, the Spanish state railway network, and its main intercity train station is Barcelona-Sants station. The AVE high-speed rail system was recently extended from Madrid to Tarragona in southern Catalonia, and is expected to reach Barcelona by 2007. Renfe cercanías/rodalies and the Ferrocarrils de la Generalitat de Catalunya (FGC) run Barcelona's widespread commuter train service.

The Estació del Nord (Northern Station), a former train station that was renovated for the 1992 Olympic Games, now serves as the terminus for long-distance and regional bus services.
Barcelona has a metered taxi fleet governed by the Institut Metropolità del Taxi (Metropolitan Taxi Institute), composed of more than 10,000 cars. Most of the licenses are in the hands of self-employed drivers. With their black and yellow livery, Barcelona's taxis are easily spotted.
On March 22, 2007, Barcelona's City Council started the Bicing service, a bicycle service understood as a public transport. Once the user has their user card, they can take a bicycle from any of the 100 stations spread around the city and use it anywhere the urban area of the city, and then leave it at another station. The service has been a success, with 50.000 subscribed users in three months.
Roads and highways
Barcelona is belted by two Rondes, the Ronda de Dalt (on the mountain side) and the Ronda del Litoral (alongside the coast), two partially-covered fast highways with several exits that allow to bypass the city.
The city's main arteries include the Diagonal Avenue, which crosses the city in diagonal (hence the name); the Meridiana Avenue which leads to the Glories Place and connects with the Diagonal Avenue and the Gran Via de les Corts Catalanes, which crosses the city from north to south, including the center of the city.
Sister cities
Barcelona has sister relationships with many places worldwide:
Other forms of cooperation and city friendship similar to the twin city programmes: |
|
Other sights
-
 Barcelona Cathedral
Barcelona Cathedral
-
 Sagrada Família at night
Sagrada Família at night
-
 Santa Maria del Mar Church
Santa Maria del Mar Church
-
 Santa Maria del Pi Church
Santa Maria del Pi Church
-
 Portal de l'Àngel
Portal de l'Àngel
-
 Casa Batlló
Casa Batlló
-
 Casa Milà (La Pedrera)
Casa Milà (La Pedrera)
-
 The Palau Nacional which houses the MNAC
The Palau Nacional which houses the MNAC
-
Palau de la Música Catalana
- The Arc de Triomf The Arc de Triomf
-
 Casa Vicens
Casa Vicens
-
 Castell dels tres Dracs
Castell dels tres Dracs
-
Hotel Arts (l.) and Torre Mapfre (each 154 m in height) seen from Platja de la Barceloneta
-
 Torre Agbar
Torre Agbar
-
Rambla de Mar in Port Vell (Old Harbour)
-
 The Torre de Collserola in the Tibidabo Hill is the highest structure in Barcelona (288m).
The Torre de Collserola in the Tibidabo Hill is the highest structure in Barcelona (288m).
See also
- Barcelona metropolitan area
- Urban Region of Barcelona
- List of tallest buildings and structures in Barcelona
- Skateboarding in Barcelona
- Flag of Barcelona
- Guardia Urbana
References
- Ptolemy, ii. 6. § 8
- Avienus Or. Mar.,
- Itin. Ant.
- Oros. vii. 143; Miñano, Diccion. vol. i. p. 391; Auson. Epist. xxiv. 68, 69, Punica Barcino.
- Plin. iii. 3. s. 4
- Inscr. ap. Gruter, p. 426, nos. 5, 6.
- ii. 6
- Avien. Or. Mar. 520: "Et Barcilonum amoena sedes ditium."
- Paul. Dig. 1. tit. 15, de Cens.
- ^ "Barcelona". Gran Enciclopèdia Catalana. Vol. 3. Barcelona: Edicions 62. 1971. pp. 193–229.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Guies Estadístiques. Barcelona en Xifres. Novembre 2006.
- Grup dels Sis: 2003: Un Estiu Infernal
- Grup dels Sis: Climatologia de Catalunya
- Barcelona's heat island
- Parcs i Jardins > Els Parcs > Els Parcs de Barcelona
- Parcs i Jardins > Els Parcs > Història > La ciutat i el verd
- Parcs i Jardins > Els Parcs > Història > La democràcia
- Ajuntament de Barcelona: Estadística: Indicadors demogràfics. 2005
- Ajuntament de Barcelona: Estadística: Densitat de població. 2005
- Ajuntament de Barcelona: Estadística: Nacionalitat per sexe. 2005
- Ajuntament de Barcelona: Estadística: Coneixement de la llengua catalana per grans grups d'edat. 2001
- Barcelona: Directory: Theme: Religion
- Ajuntament de Barcelona: Estadística: Evolució de la població. 1900-2005
- ABC.es: economia - economia - Madrid y Barcelona, entre las ciudades más caras del mundo para vivir
- ^ BOE - LEY 1/2006, de 13 de marzo, por la que se regula el Régimen Especial del municipio de Barcelona.
- Ajuntament de Barcelona > Ajuntament > El Govern de la Ciutat
- Ajuntament de Barcelona: Organització política
- Ajuntament de Barcelona > Council> The city government> Council Executive
- Ajuntament de Barcelona > Council> The city government> Plenary
- Ajuntament de Barcelona > Council> The city government> Committees of the Municipal Council
- Ajuntament de Barcelona > Council> The municipal administration
- "Globalization and World Cities Study Group & Network - Inventory of World Cities". Retrieved 2007-07-07.
- Sónar Music Festival
- L'Auditori: OBC
- RIBA Royal Gold Medallists
- Port de Barcelona
- Information of Tramvia Blau
- L'Administració i la gestió del Taxi de Barcelona
- Bicing: Noticies: Data d'inici 22 de març a les 14:00 h. Pots realitzar l'alta al servei a partir del dia 16/03/07.
- Bicing: Què és Bicing?
- Bicing: Notícies: EL BICING JA TÉ MÉS DE 50.000 ABONATS.
- The covered Rondes (by-pass)
Bibliography
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray. {{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)- "Barcelona". Gran Enciclopèdia Catalana. Barcelona: Ed. Enciclopèdia Catalana S.A.
External links
- Official Website of Barcelona
- Official Website Of Barcelona's Metropolitan Transports
- Template:Wikitravel
- Wiki.WorldFlicks @ Barcelona: Wiki with Geolocated photos on Map/Sat
- Template:Geolinks-Europe-cityscale
| Districts and neighbourhoods of Barcelona | |
|---|---|
| Ciutat Vella | |
| L'Eixample | |
| Sants-Montjuïc | |
| Les Corts | |
| Sarrià-Sant Gervasi | |
| Gràcia | |
| Horta-Guinardó | |
| Nou Barris | |
| Sant Andreu | |
| Sant Martí | |
Template:Largest cities of the European Union
| Summer Olympic Games host cities | |
|---|---|
| |
| Cancelled due to World War I; Cancelled due to World War II; Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic |
| Municipalities of Barcelonès | |
|---|---|
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: