This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Fswitzer4 (talk | contribs) at 18:27, 3 June 2020 (Added FDA UNII). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 18:27, 3 June 2020 by Fswitzer4 (talk | contribs) (Added FDA UNII)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Monosodium methyl arsonate" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
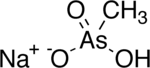
| IUPAC name Sodium hydrogen methylarsonate | |
| Other names Monosodium methyl arsenate; sodium methylarsonate; monosodium methane arsonate; methyl arsonic acid monosodium salt; EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 013803 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | MSMA |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.815 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | CH4AsNaO3 |
| Molar mass | 161.95 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Monosodium methyl arsenate (MSMA) is an arsenic-based herbicide. It is an organo-arsenate; less toxic than the inorganic form of arsenates. However, the EPA states that all forms of arsenic are a serious risk to human health and the United States' Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry ranked arsenic as number 1 in its 2001 Priority List of Hazardous Substances at Superfund sites.
It is a herbicide used against weeds in agriculture, combining selectivity, low weed-resistance, and cost-efficiency. Target weeds include: grasses and broad-leaf weeds including some weeds that are resistant to the herbicide Glyphosate.
Weed resistance to herbicides is on the rise due to the use of the herbicides in general, as well as in conjunction with the introduction of genetically modified crops. Resistant crops are endowed with natural resistance to certain herbicides, a resistance which they may impart to non-crops through cross pollination. There are very few, if any, new herbicides capable of economically combating the resistance problem. With the exception of isolated cases of common cocklebur Xanthium strumarium, no resistance build-up has occurred with the weeds that MSMA controls. MSMA provides post-emergent selective annual grass and yellow nutsedge control, in cool season. MSMA can be used to control Convolvulaceae (morning glory) and Cyperus rotundus (nutgrass).
Arsenic is classified as a Group-A carcinogen. The EPA states that:
Arsenate (AsV) is the oxidized form and occurs in well-aerated soils, whereas in chemically-reduced soil environments, arsenite (AsIII) is the prevalent As form. Although arsenite is more toxic than arsenate, arsenate can also have deleterious effects on humans, plants, and microorganisms. Arsenic-contaminated soils pose serious risk to human health. The EPA also states that, while contaminated soil poses a serious risk to health, arsenic frequently mobilizes from soils and other sources, ending up in water where it is even more of a toxicity issue.
Trade names include:
- Target 6 Plus
- Target 6.6
- MSMA 6 Plus
- MSMA 6.6
References
- Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry. "Arsenic Toxicity Case Study". Environmental Health and Medicine Education. Retrieved 25 December 2013.
- MAA Research Task Force. "Organic Arsenical Products Task Force".
- National Library of Medicine. "Sodium Methanearsonate". HSDB Database.
- Specific
- ^ Dibyendu, Sarkar; Datta, Rupali (2007). "Biogeochemistry of Arsenic in Contaminated Soils of Superfund Sites". EPA. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
- Carelton, James (2007). "Final Report: Biogeochemistry of Arsenic in Contaminated Soils of Superfund Sites". EPA. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved 25 February 2018.