This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 213.182.214.166 (talk) at 14:04, 7 June 2003. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:04, 7 June 2003 by 213.182.214.166 (talk)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)]
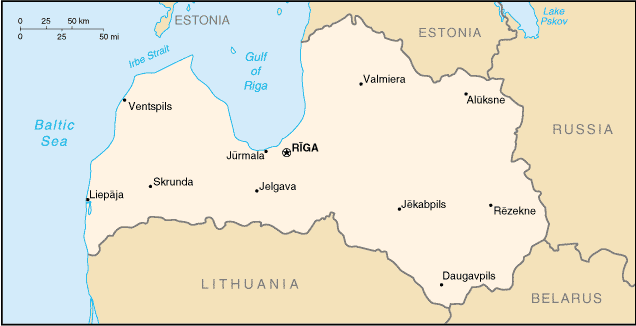
The Republic of Latvia is a republic in Northeastern Europe. Bordering the Baltic Sea, Latvia is known as one of the Baltic States, together with Estonia and Lithuania, which border the nation in the north and south, respectively. In the east, it shares borders with Russia and Belarus.
| |||||
| National motto: None | |||||
| Official language | Latvian | ||||
| Capital | Riga | ||||
| President | Vaira Vike-Freiberga | ||||
| Prime minister | Einars Repse | ||||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 121st 64,589 km² 1.5% | ||||
| Population - Total (2001) - Density | Ranked 137th 2,385,231 37/km² | ||||
| Independence - Declared - Recognised | From the Soviet Union November 18, 1918 August 11, 1920 | ||||
| Currency | Lat | ||||
| Time zone | UTC +2 | ||||
| National anthem | Dievs, Sveti Latviju | ||||
| Internet TLD | .LV | ||||
| Calling Code | 371 | ||||
History
Main article: History of Latvia
Known for the most part as Livonia, the area that now constitues Latvia was under the influence of the German Sword Brethren from the 13th century onward. However, in the 18th and 19th century, Russia gained control over Latvia and neighbouring regions. With Russia devastated by revolution and World War I, Latvia declared its independence in November 1918. This period of independence lasted only briefly, as the Soviet Union annexed the country in June 17, 1940 in accordance to Soviet-Nazi agreement (Ribbentrop-Molotov pact) of August 23, 1939.
Except for a brief period of German occupation during World War II, Latvia remained Soviet territory until reforms in Soviet communism such as glasnost stimulated the Latvian independence movement, and Latvia regained its independence on August 21, 1991. It has since followed a course to reinforce its links with the west and is slated to become a member of both NATO and the European Union in 2004.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Latvia
The 100-seat unicameral Latvian parliament, the Saeima, is elected by direct, popular vote every four years. The presidential elections are held separately, also every four years. The president appoints a prime minister, who together with his cabinet, forms the executive branch of the government.
Counties
Main article: Counties of Latvia
Latvia is divided into 26 counties called rajons. 7 cities have a separate status.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Latvia
Large parts of Latvia are covered by forests, and the country has over 12,000 small rivers and over 3,000 lakes. Most of the country consists of fertile, low-lying plains with some hills in the east, the highest point being the Gaizinkalns at 312 m.
An inlet of the Baltic Sea, the shallow Gulf of Riga is situated in the northwest of the country. The capital city Riga is located on the shores of this inlet, where the Daugava river flows into it. Other major cities include Daugavpils further upriver and Liepaja along the Baltic coast.
The Latvian climate is maritime and temperate in nature, with cool summers and wet, moderate winters.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Latvia
Latvia's transitional economy recovered from the 1998 Russian financial crisis, largely due to the previous government's budget stringency and a gradual reorientation of exports toward EU countries, lessening Latvia's trade dependency on Russia. The majority of companies, banks, and real estate have been privatised. Latvia officially joined the World Trade Organisation in February 1999 - the first Baltic state to join - and was invited at the Helsinki EU Summit in December 1999 to begin accession talks in early 2000 for an expected membership in May 2004. The high current account deficit remains a major concern.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Latvia
Less than 60% of the population of Latvia are ethnic Latvians. About 30% is Russian, whose wellbeing is a continuing concern for Russia. Sizeable minorities from other countries such as Belarus, Ukraine and Poland also live in Latvia.
Latvian, a member of the Baltic languages, is the country's only official language, but Russian is also widely spoken. The population is almost entirely Christian, but divided between the Lutheran, Catholic and Russian Orthodox Churches. Another religion is Dievturi (The Godkeepers), which has historical roots based on prechristianity era mythology.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Latvia
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Latvia
- Transportation in Latvia
- Military of Latvia
- Foreign relations of Latvia
- List of cities in Latvia
External Links
- Cabinet of Ministers - Official governmental site
- President's Chancery - Official presidential site
- Saeima - Official parliamentary site (in Latvian)
- Welcome to Latvia - Wide collection of Latvian links
Austria | Belgium | Denmark | Finland | France | Germany | Greece | Ireland
Italy | Luxembourg | Netherlands | Portugal | Spain | Sweden | United Kingdom
Countries acceding to membership on May 1, 2004:
Cyprus | Czech Republic | Estonia | Hungary | Latvia | Lithuania | Malta | Poland | Slovakia | Slovenia
