This is the current revision of this page, as edited by JWBE (talk | contribs) at 12:59, 21 October 2024 (added Category:3-Hydroxyphenyl compounds using HotCat). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 12:59, 21 October 2024 by JWBE (talk | contribs) (added Category:3-Hydroxyphenyl compounds using HotCat)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)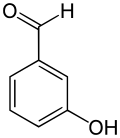 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde | |
| Other names m-Hydroxybenzaldehyde; m-Formylphenol; 3-formylphenol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.630 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H6O2 |
| Molar mass | 122.123 g·mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 1.1179 g/cm (130 °C) |
| Melting point | 106 °C (223 °F; 379 K) |
| Boiling point | 240 °C (464 °F; 513 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 8.98 (25 °C) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CHO. It is a colorless solid although most samples appear tan. Two other isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde exist.
Preparation
It has been prepared from 3-nitrobenzaldehyde in a sequence of nitro group reduction, diazotization of the amine, and hydrolysis.
3-hydroxybenzyl-alcohol dehydrogenase is an NADP-dependent enzyme that produces 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde from 3-hydroxybenzyl alcohol.
Biomedical properties
3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde exhibits vasculoprotective effects by lowering vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and endothelial cells inflammation. 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde is used in the synthesis of monastrol.
See also
- Salicylaldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde)
- 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
References
- ^ Haynes, p. 3.304
- Haynes, p. 5.92
- Woodward, R. B. (1945). "m-Hydroxybenzaldehyde". Organic Syntheses. 25: 55. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.025.0055.
- Icke, Roland N.; Redemann, C. Ernst; Wisegarver, Burnett B.; Alles, Gordon A. (1949). "m-Methoxybenzaldehyde". Organic Syntheses. 29: 63. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.029.0063.
- Forrester, P. I.; Gaucher, G. M. (1972). "M-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol dehydrogenase from Penicillium urticae". Biochemistry. 11 (6): 1108–1114. doi:10.1021/bi00756a026. PMID 4335290.
- Kong, Byung Soo; Im, Soo Jung; Lee, Yang Jong; Cho, Yoon Hee; Do, Yu Ri; Byun, Jung Woo; Ku, Cheol Ryong; Lee, Eun Jig (22 March 2016). "Vasculoprotective Effects of 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde against VSMCs Proliferation and ECs Inflammation". PLOS ONE. 11 (3): e0149394. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1149394K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0149394. PMC 4803227. PMID 27002821.
- Dallinger, Doris; Kappe, C Oliver (2007). "Rapid preparation of the mitotic kinesin Eg5 inhibitor monastrol using controlled microwave-assisted synthesis". Nature Protocols. 2 (2): 317–321. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.436. PMID 17406591. S2CID 35508377.
- Dondoni, Alessandro; Massi, Alessandro; Sabbatini, Simona (2002). "Improved synthesis and preparative scale resolution of racemic monastrol". Tetrahedron Letters. 43 (34): 5913–5916. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(02)01269-8.
Cited sources
- Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 9781498754293.