This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Mondtaler (talk | contribs) at 20:08, 29 October 2024 (H280 specifically addresses hazards linked to the pressurized storage of gases. As storage methods can vary, that hazard statement is not universally applicable to all gaseous compounds.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 20:08, 29 October 2024 by Mondtaler (talk | contribs) (H280 specifically addresses hazards linked to the pressurized storage of gases. As storage methods can vary, that hazard statement is not universally applicable to all gaseous compounds.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1-Chloro-1,1,2,2,2-pentafluoroethane | |||
| Other names Freon 115, CFC-115, R-115, Fluorocarbon-115, Genetron 115, Halocarbon 115, Monochloropentafluoroethane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.854 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E945 (glazing agents, ...) | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1020 | ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
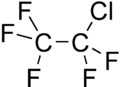
| Chemical formula | C2ClF5 | ||
| Molar mass | 154.466 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | Ethereal | ||
| Melting point | −99 °C (−146 °F; 174 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −39.1 °C (−38.4 °F; 234.1 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | 59 mg/L | ||
| Vapor pressure | 7.9 atm (21°C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
| Main hazards | In high concentrations may cause asphyxiation. | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |  
| ||
| Signal word | Warning | ||
| Hazard statements | H420 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P410+P403, P502 | ||
| Flash point | 70.4 °C (158.7 °F; 343.5 K) | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
| PEL (Permissible) | none | ||
| REL (Recommended) | TWA 1000 ppm (6320 mg/m) | ||
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | N.D. | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Chloropentafluoroethane is a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) once used as a refrigerant and also known as R-115 and CFC-115. Its production and consumption has been banned since 1 January 1996 under the Montreal Protocol because of its high ozone depletion potential and very long lifetime when released into the environment. CFC-115 is also a potent greenhouse gas.
Atmospheric properties
The atmospheric abundance of CFC-115 rose from 8.4 parts per trillion (ppt) in year 2010 to 8.7 ppt in 2020 based on analysis of air samples gathered from sites around the world.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Ozone depletion potential (ODP) | 0.44 (CCl3F = 1) |
| Global warming potential (GWP: 100-year) | 5,860 - 7,670 (CO2 = 1) |
| Atmospheric lifetime | 1,020 - 1,700 years |
See also
References
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0131". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- http://encyclopedia.airliquide.com/sds/en/030_AL_EN.pdf
- Ozone Depleting Substances List (Montreal Protocol)
- "AGAGE Data and Figures". Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Retrieved 2021-02-11.
- ^ John S. Daniel; Guus J.M. Velders; A.R. Douglass; P.M.D. Forster; D.A. Hauglustaine; I.S.A. Isaksen; L.J.M. Kuijpers; A. McCulloch; T.J. Wallington (2006). "Chapter 8. Halocarbon Scenarios, Ozone Depletion Potentials, and Global Warming Potentials" (PDF). Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2006. Geneva, Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 9 October 2016.
- ^ "Chapter 8". AR5 Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. p. 731.
- "Refrigerants - Environmental Properties". The Engineering ToolBox. Retrieved 2016-09-12.