This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Alex mond (talk | contribs) at 16:28, 12 June 2007 (→Origins). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 16:28, 12 June 2007 by Alex mond (talk | contribs) (→Origins)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) This article is about Armenians as an ethnic group. For people living in Armenia, see Demographics of Armenia. Ethnic groupThe Armenians (Template:Lang-hy, Hayer) are a nation and an ethnic group originating in the Caucasus and eastern Anatolia. A large concentration of them has remained there, especially in Armenia, but many of them are also scattered elsewhere throughout the world (see Armenian diaspora). The Armenians have had a significant prescence in countries such as Russia, Georgia (country) and Iran due to their proximity to Armenia. After the Armenian Genocide, a large influx of survivors fled to France, the United States, Argentina, the Levant and other countries that welcomed the Armenians. There are an estimated 8 to 10 million Armenians around the world.
In 301 AD, Armenians became the first people to accept Christianity as state religion. Because of religious disputes, they established a separate branch of Christianity, the Armenian Apostolic Church, to which most Armenians adhere.
Armenians speak two different, but mutually intelligible dialects of their language: Eastern Armenian, spoken mainly in Armenia and the Caucasus, and Western Armenian, spoken primarily in the Armenian diaspora.
Armenians have developed unique, long-lasting, and modern culture through contact with both Europe and Asia. Traditional Armenian dance and music are among the oldest, richest and most original ones in the Near East, and are still learnt and practised today. Armenian cuisine, as ancient as the people itself, is a combination of different tastes and aromas native to the Armenian Highland. Over time, it has been spread to neighbouring nations and to the New World by the Armenian diaspora.
Etymology
Main article: Armenia (name)Historically, the name Armenian has come to internationally designate this group of people. It was first used by neighboring countries of ancient Armenia. However, Armenians call themselves Hay (Հայ, pronounced Hye; plural: Հայեր, Hayer). The word has traditionally been linked to the name of the legendary founder of the Armenian nation, Haik, which is also a popular Armenian name.
Origins
Prior to the sixth century BC, the predecessors of the Armenian Kingdom were the Hayasa-Azzi, Hittite Empire, Kingdom of Urartu, as well as other small states and tribal confederations. Herodotus, in his review of the troops opposing the Greeks, wrote that “the Armenians were armed like the Phrygians, being Phrygian settlers" . Whether his comment described all Armenians as Phrygian settlers, or only those warriors he happened to see, is still unclear. Xenophon, a Greek general waging war against the Persians, describes many aspects of Armenian village life and hospitality. He relates that the people spoke a language that to his ear sounded like the language of the Persians..
A competing view suggested by Thomas Gamkrelidze and Vyacheslav V. Ivanov in 1984 places the Proto-Indo-European homeland in the Armenian Highland. A recent study (Gray & Atkinson) that applied the statistical tools used in timing genetic evolution to the lexical evolution of Indo-European languages strongly implied that the Indo-European homeland indeed appears to be in Asia Minor, and Armenian language (hence a well-defined group speaking it) split from it (along with Greek) at around 5300 BC, and split from Greek shortly thereafter (but the "split" from Greek was statistically less obvious).
History
Main article: History of ArmeniaThe history of Armenia consists of periods of independence interrupted by conquests by other peoples, during which time Armenia continued as an autonomous kingdom subject to various empires. The first state that was called Armenia (which is not the name Armenians themselves use) by neighboring peoples (Hecataeus of Miletus and Behistun Inscription) was established in the early sixth century BC. At its zenith (95–65 BC), the state extended from northern Caucasus all the way to what is now central Turkey, Lebanon, and north-western Iran. The imperial reign of Tigranes the Great is thus the span of time during which Armenia itself conquered areas populated by other peoples. Later it briefly became part of the Roman Empire (AD 114–118).
In 301 AD, Armenia became the first nation to adopt Christianity as a state religion, ushering a new era in the history of the Armenian people (see Religion). Later on, in order to further strengthen the Armenian national identity, Mesrop Mashtots invented the Armenian alphabet. This event ushered the Golden Age of Armenia, during which many foreign books and manuscripts were translated to Armenian by Mesrop's pupils. Armenia lost its sovereignty in 428 to the Byzantine and Persian Empires.
In 885 the Armenians reestablished themselves as a sovereign entity under the leadership of Ashot I of the Bagratid Dynasty. A considerable portion of the Armenian nobility and peasantry fled the Byzantine occupation of Bagratid Armenia in 1045, and the subsequent invasion of the region by Seljuk Turks in 1064. They settled in large numbers in Cilicia, an Anatolian region where Armenians were already established as a minority since Roman times. In 1080, they founded an independent Armenian Principality then Kingdom of Cilicia, which became the focus of Armenian nationalism. The Armenians developed close social, cultural, military, and religious ties with nearby Crusader States, but eventually succumbed to the Mamluk invaders.
In the 16th century, Eastern Armenia was conquered by the Persian Safavid Empire, while Western Armenia fell under Ottoman rule. In the 1820s, parts of historic Armenia under Persian control centering on Yerevan and Lake Sevan were incorporated into the Russian Empire, but Western Armenia remained in the Ottoman Empire. During these tumultuous times, Armenians depended on the Church to preserve and protect their unique identity.
The ethnic cleansing of Armenians during the final years of the Ottoman Empire is widely considered a genocide, with one wave of persecution in the years 1894 to 1896 culminating in the events of the Armenian Genocide in 1915 and 1916. With World War I in progress, the Turks accused the (Christian) Armenians as liable to ally with Imperial Russia, and used it as a pretext to deal with the entire Armenian population as an enemy within their empire. The exact numbers of deaths in the latter period is hard to establish. It is estimated by many sources that close to 1.5 million perished in camps, which excludes Armenians who may have died in other ways. Turkish governments since that time have consistently rejected charges of genocide, typically arguing either that those Armenians who died were simply in the way of a war or that killings of Armenians were justified by their individual or collective support for the enemies of the Ottoman Empire. The recent decision by the French lower house on October 12, 2006 to pass a bill making it illegal to deny the Armenian genocide has provoked intense reactions in the Turkish media. Note, however, that the decision has yet to be ratified by the French Senate to fully become law.
Following the breakup of the Russian Empire in the aftermath of World War I for a brief period, from 1918 to 1920, Armenia was an independent republic. In late 1920, the communists came to power following an invasion of Armenia by the Red Army, and in 1922, Armenia became part of the Transcaucasian SFSR of the Soviet Union, later forming the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic (1936 to September 21, 1991). In 1991, Armenia declared independence from the USSR and established the second Republic of Armenia.
Geographic distribution
Armenia
Main article: Demographics of ArmeniaArmenians have had a presence in the Armenian Highland for over four thousand years, since the time when Haik, the legendary patriarch and founder of the first Armenian nation, led them to victory over Bel of Babylon. Today, with a population of 3.5 million, they not only constitute an overwhelming majority in Armenia, but also in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh. Armenians in the diaspora informally refer to them as Hayastantsis (Հայաստանցի), meaning those that are from Armenia (that is, they or their ancestors were not forced to flee in 1915). They, as well as the Armenians of Iran and Russia speak the Eastern dialect of the Armenian language. The country itself is secular as a result of Soviet domination, but most of its citizens are Apostolic Armenian Christian.
Diaspora
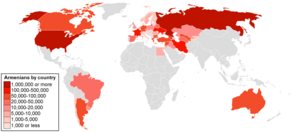
Small Armenian trading communities have existed outside of Armenia for centuries. For example, a community has existed for over a millennium in the Holy Land, and one of the four quarters of the walled old city of Jerusalem has been called the Armenian Quarter. There are also remnants of formerly populous communities in India, Myanmar, and South East Asia. However, most Armenians have scattered throughout the world as a direct consequence of the genocide of 1915, constituting the Armenian diaspora.
Within the diasporan Armenian community, there is an unofficial classification of the different kinds of Armenians. For example, Armenians who originate from Iran are referred to as Parskahay (Պարսկահայ), while Armenians from Lebanon are usually referred to as Lipananahay (Լիբանանահայ). Armenians of the Diaspora are the primary speakers of the Western dialect of the Armenian language. This dialect has considerable differences with Eastern Armenian, but speakers of either of the two variations can usually understand each other. Eastern Armenian in the diaspora is primarily spoken in Iran, Russia and former Soviet states such as Ukraine and Georgia (where they form a majority in the Samtskhe-Javakheti province). In diverse communities (such as in Canada and the U.S.) where many different kinds of Armenians live together, there is a tendency for the different groups to cluster together.
Since the arrival of Martin the Armenian to the Jamestown Colony around 1618, Armenians have dispersed all throughout the United States. Watertown, Massachusetts; Fresno, California; Detroit, Michigan; Glendale, California; and Los Angeles, California are centers of Armenian population in the United States; there is also a significant concentration in New York City. In Canada, large numbers of Armenians can be found in Toronto, Ontario, and Montreal, Quebec. Armenians are also present in every country in Latin America, with the largest concentrations being found in Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Venezuela, and Mexico.
Glendale, California, in particular, is famous for its high concentration of Armenians; there are approximately 78,000 Armenians, according to the 2000 U.S. census. Armenian residents of the city are active members in the municipal government and chamber of commerce. In Hollywood, California, a small portion is known as "Little Armenia", extending east to west from Wilton Avenue to Vermont Avenue and north and south from Hollywood Boulevard to Santa Monica Boulevard.
Culture
Main articles: Culture of Armenia, Armenian cuisine, and List of ArmeniansLanguage and literature
Armenian is a sub-branch of the Indo-European family, and with some 8-10 million speakers one of the smallest surviving branches, comparable to Albanian or the somewhat more widely spoken Greek, with which it may be connected (see Graeco-Armenian).
Five million Eastern Armenian speakers live in the Caucasus, Russia, and Iran, and approximately two to three million people in the rest of the Armenian diaspora speak Western Armenian. According to US Census figures, there are 300,000 Americans who speak Armenian at home. It is in fact the twentieth most commonly spoken language in the United States, having slightly fewer speakers than Haitian Creole, and slightly more than Navajo.
Armenian literature dates back to 400 AD, when Mesrob Mashdots first invented the Armenian alphabet. This period of time is often viewed as the Golden Age of Armenian literature. Early Armenian literature was written by the "father of Armenian history", Moses of Chorene, who authored The History of Armenia. The book covers the time-frame from the formation of the Armenian people to the fifth century A.D. The nineteenth century beheld a great literary movement that was to give rise to modern Armenian literature. This period of time, during which Armenian culture flourished, is known as the Revival period (Zartonki sherchan). The Revivalist authors of Constantinople and Tiflis, almost identical to the Romanticists of Europe, were interested in encouraging Armenian nationalism. Most of them adopted the newly created Eastern or Western variants of the Armenian language depending on the targeted audience, and preferred them over classical Armenian (grabar). This period ended after the Hamidian massacres, when Armenians experienced turbulant times. As Armenian history of the 1920s and of the Genocide came to be more openly discussed, writers like Paruyr Sevak, Gevork Emin, Silva Kaputikyan and Hovhannes Shiraz began a new era of literature.
Religion
Main articles: Armenian Apostolic Church and Religion in ArmeniaIn 301 AD, Armenia adopted Christianity as a state religion, becoming the first nation to do so. It established a Church that still exists independently of both the Catholic and the Eastern Orthodox churches, having become so in 451 AD as a result of its excommunication by the Council of Chalcedon. The Armenian Apostolic Church is a part of the Oriental Orthodox communion, not to be confused with the Eastern Orthodox communion. During its later political eclipses, Armenia depended on the church to preserve and protect its unique identity. The original location of the Armenian Catholicosate is Echmiadzin. However, the continuous upheavals, which characterized the political scenes of Armenia, made the political power move to safer places. The Church center moved as well to different locations together with the political authority. Therefore, it eventually moved to Cilicia as the Holy See of Cilicia.
The Armenians have, at times, constituted a Christian "island" in a mostly Muslim region. The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia had close ties to European Crusader States. Later on, the deteriorating situation in the region led the bishops of Armenia to elect a Catholicos in Etchmiadzin, the original seat of the Catholicosate. In 1441, a new Catholicos was elected in Etchmiadzin in the person of Kirakos Virapetsi, while Krikor Moussapegiants preserved his title as Catholicos of Cilicia. Therefore, since 1441, there have been two Catholicosates in the Armenian Church with equal rights and privileges, and with their respective jurisdictions. The primacy of honor of the Catholicosate of Etchmiadzin has always been recognized by the Catholicosate of Cilicia.
While the Armenian Apostolic Church remains the most prominent church in the Armenian community throughout the world, Armenians (especially in the diaspora) subscribe to any number of other Christian denominations. These include the Armenian Catholic Church (which follows its own liturgy but recognizes the Roman Catholic Pope), the Armenian Evangelical Church, which started as a reformation in the Mother church but later broke away, and the Armenian Brotherhood Church, which was born in the Armenian Evangelical Church, but later broke apart from it. There are other numerous Armenian churches belonging to Protestant denominations of all kinds.
Music

Armenian music is a mix of indigenous folk music, perhaps best-represented by Djivan Gasparyan's well-known duduk music, as well as light pop, and extensive Christian music, due to Armenia's status as the oldest Christian nation in the world.
Instruments like the duduk, the dhol, the zurna and the kanun are commonly found in Armenian folk music. Artists such as Sayat Nova are famous due to their influence in the development of Armenian folk music. One of the oldest types of Armenian music is the Armenian chant which is the most common kind of religious music in Armenia. Many of these chants are ancient in origin, extending to pre-Christian times, while others are relatively modern, including several composed by Saint Mesrop Mashtots, the inventor of the Armenian alphabet. Whilst under Soviet rule, Armenian classical music composer Aram Khatchaturian became internationally well known for his music, for various ballets and the Sabre Dance from his composition for the ballet Gayaneh.
The Armenian Genocide caused widespread emigration that led to the settlement of Armenians in various countries in the world. Armenians kept to their traditions and certain diasporans rose to fame with their music. The pop music genre grew to fame during this time with artists such as Adiss Harmandian and Harout Pamboukjian performing to the Armenian diaspora and Armenia. Other Armenian diasporans that rose to fame are world renown French-Armenian artist Charles Aznavour, Hasmik Papian and more recently Isabel Bayrakdarian. Certain Armenians settled to sing non-Armenian tunes such as the heavy metal band System of a Down or pop star Cher. In the Armenian diaspora, Armenian revolutionary songs are popular with the youth. These songs encourage Armenian patriotism and are generally about Armenian history and national heroes.
Sports

Many types of sports are played in Armenia, among the most popular being football, chess, boxing, basketball, hockey and volleyball. Since independence, the Armenian government has been actively rebuilding its sports program in the country.
During Soviet rule, Armenian athletes rose to prominence winning plenty of medals and helping the USSR win the medal standings at the Olympics on numerous occasions. The first medal won by an Armenian in modern Olympic history was by Hrant Shahinian, who won two golds and two silvers in gymnastics at the 1952 Summer Olympics in Helsinki. In football, their most successful team was Yerevan's FC Ararat, which had claimed most of the Soviet championships in the 70s and had also gone to post victories against professional clubs like FC Bayern Munich in the Euro cup.
Armenians have also been successful in chess, which is the most popular mind sport in Armenia. Some of the most prominent chess players in the world are Armenian such as Tigran Petrosian, Levon Aronian and Garry Kasparov. Armenians have also been successful in weightlifting and wrestling, winning medals in each sport at the Olympics.
Institutions
| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
 |
Languages
|
| Philology |
Origins
|
|
Archaeology
Pontic Steppe Caucasus East Asia Eastern Europe Northern Europe Pontic Steppe Northern/Eastern Steppe Europe
South Asia Steppe Europe Caucasus India |
|
Peoples and societies
Indo-Aryans Iranians East Asia Europe East Asia Europe Indo-Aryan Iranian |
Religion and mythology
Others
|
Indo-European studies
|
The nation-state of Armenia is the most prominent Armenian institution today. Other important institutions include:
- The Armenian Apostolic Church
- The Armenian Catholic Church
- The Armenian Evangelical Church The community was formally recognized in 1846 by the Ottoman Empire.
- The Armenian General Benevolent Union (AGBU) founded in 1906 and the largest Armenian non-profit organization in the world with educational, cultural and humanitarian projects on six continents.
- The Armenian Revolutionary Federation was founded in 1890. It is generally referred to as the Dashnaktsutyun, which means Federation in Armenian. The ARF is the strongest worldwide Armenian political organization and the only diasporan Armenian organization with a significant political presence in the Republic of Armenia.
- The Armenian Relief Society, founded in 1910.
- Hamazkayin, an Armenian cultural and educational society founded in Cairo in 1928, and responsible for the founding of Armenian secondary schools and institutions of higher education in several countries.
- Homenetmen, an Armenian scouting and athletic organization founded in 1910 with a worldwide membership of about 25,000.
See also
Further reading
Notes
- ^ "Armenian population of the world (BBC)". Retrieved 2007-03-01.
- 2005 estimate. The Nationmaster.com page on Armenia gives 93% ethnic Armenians in an estimated national population of 3,326,448 (July 2003 estimate), which would yield 3,093,000. It also notes that the population of Azeris in Armenia has been rapidly dropping in recent years. The National Geographic Atlas of the World, Seventh Edition (1999) puts the population of Armenia at 3,800,000. 93% would yield a total around 3,500,000. However, Countrywatch gives a total national population of only 2,935,400 (2004). The CIA gives a similarly low 2,982,904 (July 2005 estimate). We have gone approximately with the latter estimates as more recent and at least comparably authoritative.
- The 2002 Russian census recorded 1,130,491 Armenians (0.78% of the population).
- ^ The Education for Development Institute maintains an extensive site about Armenia that includes information about the Armenian diaspora in various countries. Their numbers generally agree with other sources when those are available; where we don't have a more authoritative source, we are following their numbers.
- The Encyclopedia of the Orient states that there are 400,000 ethnic Armenians living in Iran.
- ^ See Armenian-American; EuroAmerican.net presents official data from the 2000 U.S. Census (including state-by-state data), which states that there are 385,488 people of Armenian ancestry currently living in the United States. The 2001 Canadian Census determined that there are 40,505 persons of Armenian ancestry currently living in Canada. However, these are liable to be low numbers, since people of mixed ancestry, very common in North America tend to be under-counted: the 1990 census U.S. indicates 149,694 people who speak Armenian at home. The Armenian Embassy in Canada estimates 1 million ethnic Armenians in the U.S. and 100,000 in Canada. The Armenian Church of America makes a similar estimate. By all accounts, over half of the Armenians in the United States live in California.
- Georgia: The State Department for Statistics of Georgia: 248,900 represents 5.7 % ethnic Armenians in an estimated national population of 4,371,500 (The Official data of 2002). The World Factbook: 267,000 represents 5.7 % ethnic Armenians in an estimated national population of 4,693,892 (July 2004 est.). Nationmaster.com: Georgia: 400,000 represents 8.1% ethnic Armenians in an estimated national population of 4,934,413 (The Official data of 1989).
- The Encyclopedia of the Orient states that 160,000 Apostolic Armenians and 30,000 Catholic Armenians live in Syria. That number together makes up 190,000.
- The Encyclopedia of the Orient states that 120,000 Apostolic Armenians and 20,000 Catholic Armenians live in Lebanon. That number together makes up 140,000.
- Nationmaster.com:Azerbaijan: 156,000 represents 2% ethnic Armenians in an estimated national population of 7,830,764 (July 2003 est.) combined with the note "almost all Armenians live in the separatist Nagorno-Karabakh region".
- There are 130,000 Armenians living in Argentina according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- The 2001 census Ukrainian census held in 2001 recorded 99,894 Armenians.
- Turay, Anna. "Tarihte Ermeniler". Bolsohays:Istanbul Armenians. Retrieved 2007-01-04.
{{cite web}}: External link in|publisher= - The Encyclopedia of the Orient states that 70,000 Armenians live in Jordan.
- There are 70,000 Armenians living in Uzbekistan according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- There are 42,000 Armenians living in Germany according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- There are 40,000 Armenians living in Brazil according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- The Armenian-Greek Community website estimates 35,000.
- There are 35,000 Armenians living in Australia according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- Turkmenistan: Focus on Armenian migrants
- Demographic information of Hungary.
- There are 25,000 Armenians living in Belarus according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- There are 25,000 Armenians living in Kazakhstan according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- There are 19,000 Armenians living in Uruguay according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- There are 18,000 Armenians living in the United Kingdom according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- "Population as of 1 March 2001 divided by provinces and ethnic group" (in Bulgarian). National Statistical Institute. 2001. Retrieved 2006-07-10.
- There are 10,000 Armenians living in the Belgium according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- There are 10,000 Armenians living in the Czech Republic according to Armeniandiaspora.com.
- ^ Hastings, Adrian (2000). A World History of Christianity. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. pp. p. 289. ISBN 0802848753.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ "Armenia first nation to adopt Christianity as a state religion". Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- "Haik and Hayastan". Retrieved 2007-03-04.
- "Armenia Provinces". Retrieved 2007-03-04.
- Herodotus, History, 7.73.
- Xenophon, Anabasis, IV.v.2-9.
- The Early History of Indo-European Languages, Thomas V. Gamkrelidze and V. V. Ivanov Scientific American, March 1990, P.110
- "Language-tree divergence times support the Anatolian theory of Indo-European origin Russell D. Gray and Quentin D. Atkinson, Nature 426, 435-439" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- "Armenian Quarter in Jerusalem". Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- "Armenians in the Unites States". Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- "A Migrating Catholicosate". Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- "Two Catholicosates within the Armenian Church". Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- "Sport in Armenia". Retrieved 2007-02-27.
References
- Template:CIAfb
 This article incorporates public domain material from U.S. Bilateral Relations Fact Sheets. United States Department of State.
This article incorporates public domain material from U.S. Bilateral Relations Fact Sheets. United States Department of State.- The categorization of Armenian churches in Los Angeles used information from Sacred Transformation: Armenian Churches in Los Angeles a project of the USC School of Policy, Planning, and Development.
- Some of the information about the history of the Armenians comes from the multi-volume History of the Armenian People, Yerevan, Armenia, 1971.
Literature
- George A. Bournoutian, A History of the Armenian People, 2 vol. (1994)
- George A. Bournoutian, A Concise History of the Armenian People (Mazda, 2003, 2004).
- I. M. Diakonoff, The Pre-History of the Armenian People (revised, trans. Lori Jennings), Caravan Books, New York (1984), ISBN 0-88206-039-2.
- Russell D. Gray and Quentin D. Atkinson, "Language-tree divergence times support the Anatolian theory of Indo-European origin", Nature, 426, 435-439 (2003)
Template:Armenia-related topics
- Armenian people
- Ancient peoples
- Armenian society
- Ethnic groups in Europe
- Ethnic groups in the Middle East
- Ethnic groups in France
- Ethnic groups in Georgia (country)
- Ethnic groups in Iran
- Ethnic groups in Lebanon
- Ethnic groups in Russia
- Ethnic groups in Turkey
- Ethnic groups in Ukraine
- Ethnic groups in Azerbaijan
- Indo-European peoples
- Peoples of the Caucasus
