This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Tassedethe (talk | contribs) at 13:20, 13 February 2011 (WPCleaner 0.99 - Repairing link to disambiguation page - (You can help) - REACH). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 13:20, 13 February 2011 by Tassedethe (talk | contribs) (WPCleaner 0.99 - Repairing link to disambiguation page - (You can help) - REACH)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)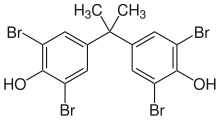 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2,2',6,6'-Tetrabromo-4,4'-isopropylidenediphenol | |
| Other names 2,2',6,6'-Tetrabromobisphenol A, 2,2-Bis(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxyphenyl)propane, 4,4'-Isopropylidenebis(2,6-dibromophenol) | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| Abbreviations | TBBPA, TBBP-A, TBBA |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.125 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Properties | |
| Molar mass | 543.9 g·mol |
| Density | 2,12 g·cm (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 178 °C |
| Boiling point | 250 °C (decomposition) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | N |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) is a brominated flame retardant.
Synthesis
TBBPA is a derivative of bisphenol A and is synthesized from this substance. Most commercial TBBPA products are of a relatively low purity, in fact containing a mixture of products brominated to varying extents. This is not generally considered to be a drawback, since in most applications of this substance (i.e. flame-retarding) it is the average %Br that is of importance. The mixture resulting from the bromination of bisphenol A is therefore not purified, allowing a more efficient, lower cost product.
Uses
TBBPA can be used as reactive and additive flame retardant. In the reactive application, TBBPA is bound chemically to the polymers. The main use are epoxy resins of printed circuit boards. As an additive flame retardant it is used in acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, which are used e.g. in TVs. The annual consumption worldwide has been estimated as 119,600 tons in 2001, of which 11,600 tons were used by the European industry.
Relevance
TBBPA emits from different processes to the environment and can be found in trace concentration in the atmosphere, hydrosphere, soil, and sediments. It also occurs in sewage sludge and house dust. TBBPA has been the subject of an eight year evaluation under the EU Risk Assessment procedure which reviewed over 460 studies. The Risk Assessment was published on the EU Official Journal in June 2008. TBBPA will now go through REACH registration.
References
- ^ Record of Tetrabromobisphenol A in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2008/2/15.
- Bromine Science and Environmental Forum: Major Brominated Flame Retardants Volume Estimates – Total Market Demand By Region in 2001
- Kuch B, Körner W, Hagenmaier H (2001): Monitoring von bromierten Flammschutzmitteln in Fliessgewässern, Abwässern und Klärschlämmen in Baden-Württemberg. Umwelt und Gesundheit, Universität Tübingen.
- Official Journal of the European Union: Communication from the Commission on the results of the risk evaluation and the risk reduction strategies for the substances: sodium chromate, sodium dichromate and 2,2′,6,6′-tetrabromo-4,4′-isopropylidenediphenol (tetrabromobisphenol A), 18.6.2008