This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Fowler&fowler (talk | contribs) at 19:01, 27 March 2011 (→Government: combining paragraphs 1 and 2). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 19:01, 27 March 2011 by Fowler&fowler (talk | contribs) (→Government: combining paragraphs 1 and 2)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| The neutrality of this article is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (March 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Republic of Indiaभारत गणराज्य* Bhārat Ganarājya | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Emblem
Emblem
| |
| Motto: "Satyameva Jayate" (Sanskrit) सत्यमेव जयते (Devanāgarī) "Truth Alone Triumphs" | |
| Anthem: Jana Gana Mana Thou art the ruler of the minds of all people | |
| National Song Vande Mataram I bow to thee, Mother | |
 Area controlled by India in dark green; Area controlled by India in dark green;Claimed but uncontrolled territories in light green | |
| Capital | New Delhi |
| Largest city | Mumbai |
| Official languages |
Hindi, English
|
| Recognised regional languages | 8th Schedule: |
| National languages | None defined by the Constitution |
| Demonym(s) | Indian |
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional republic |
| • President | Pratibha Patil |
| • Prime Minister | Manmohan Singh (INC) |
| • Speaker of the House | Meira Kumar (INC) |
| • Chief Justice | S. H. Kapadia |
| Legislature | Sansad |
| • Upper house | Rajya Sabha |
| • Lower house | Lok Sabha |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| • Declared | 15 August 1947 |
| • Republic | 26 January 1950 |
| Area | |
| • | 3,287,263 km (1,269,219 sq mi) (7th) |
| • Water (%) | 9.56 |
| Population | |
| • 2011 estimate | Template:IndiaPopCommas (2nd) |
| • 2001 census | 1,028,610,328 |
| • Density | 428.1/km (1,108.8/sq mi) (31st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2010 estimate |
| • Total | $4.001 trillion (4th) |
| • Per capita | $3,290 (127th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2010 estimate |
| • Total | $1.430 trillion (11th) |
| • Per capita | $1,176 (137th) |
| Gini (2004) | 36.8 Error: Invalid Gini value (79th) |
| HDI (2010) | Error: Invalid HDI value (119th) |
| Currency | Indian rupee (₹) (INR) |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+5:30 (not observed) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (AD) |
| Drives on | Left |
| Calling code | 91 |
| ISO 3166 code | IN |
| Internet TLD | .in |
Non-numbered Footnotes:
| |
India (/ˈɪndiə/), officially the Republic of India (Template:Lang-hi Bhārat Gaṇarājya; see also official names of India), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; Bhutan, the People's Republic of China and Nepal to the northeast; and Bangladesh and Burma to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; in addition, India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand and Indonesia.
Home to the ancient Indus Valley Civilization and a region of historic trade routes and vast empires, the Indian subcontinent was identified with its commercial and cultural wealth for much of its long history. Four of the world's major religions—Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism—originated here, while Zoroastrianism, Christianity and Islam arrived in the first millennium CE and shaped the region's diverse culture. Gradually annexed by the British East India Company from the early 18th century and colonised by the United Kingdom from the mid-19th century, India became an independent nation in 1947 after a struggle for independence which was marked by non-violent resistance and led by Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi.
The Indian economy is the world's eleventh largest by nominal GDP and fourth largest by purchasing power parity. Following market-based economic reforms in 1991, India has become one of the fastest growing major economies, and is considered a newly industrialized country; however, it continues to face the challenges of poverty, illiteracy, corruption and inadequate public health. A nuclear weapons state and a regional power, it has the third-largest standing army in the world, and ranks tenth in military expenditure among nations.
India is a federal constitutional republic with a parliamentary system consisting of 28 states and seven union territories. It is a member of the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement, the World Trade Organization, the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, the East Asia Summit, the G20, the G8+5, and the Commonwealth of Nations; and is one of the four BRIC nations. India is a pluralistic, multilingual, and multiethnic society. It is also home to a diversity of wildlife in a variety of protected habitats.
Etymology
Main article: Names of IndiaThe name India is derived from Indus, which is derived from the Old Persian word Hindu, from Sanskrit सिन्धु Sindhu, the historic local appellation for the Indus River. The ancient Greeks referred to the Indians as Indoi (Ινδοί), the people of the Indus. The Constitution of India and common usage in various Indian languages also recognise Bharat (pronounced Template:IPA-hns) as an official name of equal status. The name Bharat is derived from the name of the legendary king Bharata in Hindu scriptures. Hindustan (Template:IPA-hns), originally a Persian word for “Land of the Hindus” referring to northern India and Pakistan before 1947, is also occasionally used as a synonym for all of India.
History
| The neutrality of this section is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (February 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Stone Age rock shelters with paintings at the Bhimbetka rock shelters in Madhya Pradesh are the earliest known traces of human life in India. The first known permanent settlements appeared about 8,500 years ago and gradually developed into the Indus Valley Civilisation, dating back to 3400 BCE in western India. It was followed by the Vedic period, which laid the foundations of Hinduism and other cultural aspects of early Indian society, and ended in the 500s BCE. From around 550 BCE, many independent kingdoms and republics known as the Mahajanapadas were established across the country.

In the third century BCE, Maurya Empire gradually united the Indian sub-continent under Chandragupta Maurya, his son Bindusara and grandson Ashoka the Great. From the third century CE, the Gupta dynasty oversaw the period referred to as ancient "India's Golden Age". Empires in southern India included those of the Chalukyas, the Cholas and the Vijayanagara Empire. Science, technology, engineering, art, logic, language, literature, mathematics, astronomy, religion and philosophy flourished under the patronage of these kings.
Following invasions from Central Asia between the 10th and 12th centuries, much of northern India came under the rule of the Delhi Sultanate and later the Mughal Empire. Under the rule of Akbar the Great, India enjoyed much cultural and economic progress as well as religious harmony. Mughal emperors gradually expanded their empires to cover large parts of the subcontinent. However, in northeastern India, the dominant power was the Ahom kingdom of Assam, among the few kingdoms to have resisted Mughal subjugation. Due to Mughal persecution, the Sikhs developed a martial tradition and established the Sikh Empire which stood until the Anglo-Sikh wars in the mid-19th century. The first major threat to Mughal imperial power came from a Hindu Rajput king Maha Rana Pratap of Mewar in the 16th century and later from a Hindu state known as the Maratha confederacy, that ruled much of India in the mid-18th century.
From the 16th century, European powers such as Portugal, the Netherlands, France, and Great Britain established trading posts and later took advantage of internal conflicts to establish colonies. By 1856, most of India had come under the control of the British East India Company. A year later, a nationwide insurrection of rebelling military units and kingdoms, known as India's First War of Independence or the Sepoy Mutiny, seriously challenged the Company's control but eventually failed. As a result of the instability, India was brought under the direct rule of the British Crown.

In the 20th century, a nationwide struggle for independence was launched by the Indian National Congress and other political organisations. A large part of the movement for independence was led by Mahatma Gandhi and the Indian National Congress, which led millions of people in several national campaigns of non-violent civil disobedience.
On 15 August 1947, India gained independence from British rule, but at the same time the Muslim-majority areas were partitioned to form a separate state of Pakistan. On 26 January 1950, India became a republic and a new constitution came into effect.
Since independence, India has faced challenges from religious violence, casteism, naxalism, terrorism and regional separatist insurgencies, especially in Jammu and Kashmir and Northeast India. Since the 1990s terrorist attacks have affected many Indian cities. India has unresolved territorial disputes with the People's Republic of China, which, in 1962, escalated into the Sino-Indian War, and with Pakistan, which resulted in wars in 1947, 1965, 1971 and 1999. India is a founding member of the United Nations (as British India) and the Non-Aligned Movement.
India is a state armed with nuclear weapons; having conducted its first nuclear test in 1974, followed by another five tests in 1998. Beginning 1991, significant economic reforms have transformed India into one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, increasing its global clout.
Geography
Main article: Geography of India See also: Geological history of India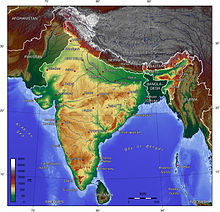
India, the major portion of the Indian subcontinent, lies atop the Indian tectonic plate, a minor plate within the Indo-Australian Plate. India's defining geological processes commenced seventy-five million years ago, when the Indian subcontinent, then part of the southern supercontinent Gondwana, began a northeastwards drift—lasting fifty million years—across the then unformed Indian Ocean. The subcontinent's subsequent collision with the Eurasian Plate and subduction under it, gave rise to the Himalayas, the planet's highest mountains, which now abut India in the north and the north-east. In the former seabed immediately south of the emerging Himalayas, plate movement created a vast trough, which, having gradually been filled with river-borne sediment, now forms the Indo-Gangetic Plain. To the west of this plain, and cut off from it by the Aravalli Range, lies the Thar Desert.
The original Indian plate now survives as peninsular India, the oldest and geologically most stable part of India, and extends as far north as the Satpura and Vindhya ranges in central India. These parallel ranges run from the Arabian Sea coast in Gujarat in the west to the coal-rich Chota Nagpur Plateau in Jharkhand in the east. To their south, the remaining peninsular landmass, the Deccan Plateau, is flanked on the left and right by the coastal ranges, Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats respectively; the plateau contains the oldest rock formations in India, some over one billion years old. Constituted in such fashion, India lies to the north of the equator between 6°44' and 35°30' north latitude and 68°7' and 97°25' east longitude.

India's coast is 7,517 kilometres (4,700 mi) long; of this distance, 5,423 kilometres (3,400 mi) belong to peninsular India, and 2,094 kilometres (1,300 mi) to the Andaman, Nicobar, and Lakshadweep Islands. According to the Indian naval hydrographic charts, the mainland coast consists of the following: 43% sandy beaches, 11% rocky coast including cliffs, and 46% mudflats or marshy coast.
Major Himalayan-origin rivers that substantially flow through India include the Ganges (Ganga) and the Brahmaputra, both of which drain into the Bay of Bengal. Important tributaries of the Ganges include the Yamuna and the Kosi; the latter's extremely low gradient causes disastrous floods every year. Major peninsular rivers, whose steeper gradients prevent their waters from flooding, include the Godavari, the Mahanadi, the Kaveri, and the Krishna, which also drain into the Bay of Bengal; and the Narmada and the Tapti, which drain into the Arabian Sea. Among notable coastal features of India are the marshy Rann of Kutch in western India, and the alluvial Sundarbans delta, which India shares with Bangladesh. India has two archipelagos: the Lakshadweep, coral atolls off India's south-western coast; and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a volcanic chain in the Andaman Sea.
Climate
Main article: Climate of IndiaIndia's climate is strongly influenced by the Himalayas and the Thar Desert, both of which drive the monsoons. The Himalayas prevent cold Central Asian katabatic winds from blowing in, keeping the bulk of the Indian subcontinent warmer than most locations at similar latitudes. The Thar Desert plays a crucial role in attracting the moisture-laden southwest summer monsoon winds that, between June and October, provide the majority of India's rainfall. Four major climatic groupings predominate in India: tropical wet, tropical dry, subtropical humid, and montane.
Biodiversity
Main article: Wildlife of India See also: List of ecoregions in IndiaTemplate:Indian image rotation
Lying within the Indomalaya ecozone, with three hotspots located within its area, India displays significant biodiversity. As one of the seventeen megadiverse countries, it is home to 7.6% of all mammalian, 12.6% of all avian, 6.2% of all reptilian, 4.4% of all amphibian, 11.7% of all fish, and 6.0% of all flowering plant species. Many ecoregions, such as the shola forests, exhibit extremely high rates of endemism; overall, 33% of Indian plant species are endemic.
India's forest cover ranges from the tropical rainforest of the Andaman Islands, Western Ghats, and northeastern India to the coniferous forest of the Himalaya. Between these extremes lie the sal-dominated moist deciduous forest of eastern India; the teak-dominated dry deciduous forest of central and southern India; and the babul-dominated thorn forest of the central Deccan and western Gangetic plain. Important Indian trees include the medicinal neem, widely used in rural Indian herbal remedies. The pipal fig tree, shown on the seals of Mohenjo-daro, shaded Gautama Buddha as he sought enlightenment. According to latest report, less than 12% of India's landmass is covered by dense forests.
Many Indian species are descendants of taxa originating in Gondwana, from which the Indian plate separated a long time ago. Peninsular India's subsequent movement towards, and collision with, the Laurasian landmass set off a mass exchange of species. However, volcanism and climatic changes 20 million years ago caused the extinction of many endemic Indian forms. Soon thereafter, mammals entered India from Asia through two zoogeographical passes on either side of the emerging Himalaya. Consequently, among Indian species, only 12.6% of mammals and 4.5% of birds are endemic, contrasting with 45.8% of reptiles and 55.8% of amphibians. Notable endemics are the Nilgiri leaf monkey and the brown and carmine Beddome's toad of the Western Ghats. India contains 172, or 2.9%, of IUCN-designated threatened species. These include the Asiatic Lion, the Bengal Tiger, and the Indian white-rumped vulture, which suffered a near-extinction from ingesting the carrion of diclofenac-treated cattle.
In recent decades, human encroachment has posed a threat to India's wildlife; in response, the system of national parks and protected areas, first established in 1935, was substantially expanded. In 1972, India enacted the Wildlife Protection Act and Project Tiger to safeguard crucial habitat; in addition, the Forest Conservation Act was enacted in 1980. Along with more than five hundred wildlife sanctuaries, India hosts thirteen biosphere reserves, four of which are part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves; twenty-five wetlands are registered under the Ramsar Convention.
Politics
Main article: Politics of India
India is the most populous democracy in the world. A parliamentary republic with a multi-party system, it has six recognised national parties, including the Indian National Congress and Bhartiya Janata Party (BJP), and more than 40 regional parties. The Congress is considered centre-left or "liberal" in the Indian political culture, and the BJP centre-right or "conservative". For most of the period between 1950—when India first became a republic—and the late 1980s, the Congress held a majority in the parliament. Since then, however, it has increasingly shared the political stage with the BJP, as well as with ever more powerful regional parties which have often forced multi-party coalitions at the centre.
In the first three general elections in the Republic of India, in 1951, 1957 and 1962, the Congress, led by Jawaharlal Nehru, won easy victories. In 1964, after Nehru's death, Lal Bahadur Shastri briefly became prime minister, and was succeeded after his own unexpected death, in 1966, by Indira Gandhi, who went on to lead the Congress to election victories in 1967 and 1971. Following public discontent with the state of emergency declared by Indira Gandhi in 1975, the Congress was voted out of power in 1977, and a new party, the Janata Party, which had opposed the emergency, voted in. Its government, however, proved short lived, lasting just over three years. Back in power in 1980, the Congress saw a change in leadership in 1984, when prime minister Indira Gandhi was assassinated and succeeded by her son Rajiv Gandhi, who won an easy victory in the general elections later that year. The Congress was voted out again in 1989, when a National Front coalition, led by the newly formed Janata Dal, in alliance with the Left Front, won the elections; that government too proved short lived, lasting just under two years. Elections were held again in 1991 in which no party won an absolute majority, but the Congress, as the largest single party, was able to form a minority government, led by P.V. Narasimha Rao, and to complete a five-year term.
The two years after the general election of 1996 were years of political turmoil, with several short-lived alliances sharing power at the centre. The BJP formed a government briefly in 1996, followed by one of the United Front coalition, but without the support of either the BJP or the Congress. In 1998, the BJP was able to form a successful coalition, the National Democratic Alliance (NDA), which, under the leadership of Atal Bihari Vajpayee, became the first non-Congress government to complete a full five-year term. In the 2004 Indian general elections, again no party won an absolute majority, but the Congress emerged as the largest single party, forming a successful coalition, the United Progressive Alliance (UPA), with the support of left-leaning parties and MPs opposed to the BJP. The UPA coalition was returned to power in the 2009 general election, the proportion of left-leaning parties within the coalition now significantly reduced. That year, Manmohan Singh became the first prime minister since Jawaharlal Nehru in 1957 and 1962 to be re-elected to a second five-year term.
Government
Main articles: Government of India and Constitution of IndiaTemplate:Indian symbols India is a federation with a parliamentary system governed under the Constitution of India. It is a constitutional republic and representative democracy, in which "majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law." Federalism in India defines the power distribution between the centre and the states. The government is regulated by a checks and balances defined by Indian Constitution, which serves as the country's supreme legal document. The Constitution of India, which came into effect on 26 January 1950, states in its preamble that India is a sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic. India's form of government, traditionally described as 'quasi-federal' with a strong centre and weak states, has grown increasingly federal since the late 1990s as a result of political, economic and social changes.
The President of India is the head of state elected indirectly by an electoral college for a five-year term. The Prime Minister is the head of government and exercises most executive power. Appointed by the President, the prime minister is by convention supported by the party or political alliance holding the majority of seats in the lower house of parliament. The executive branch of the Indian government consists of the president, the vice-president, and the council of ministers (the cabinet being its executive committee) headed by the prime minister. Any minister holding a portfolio must be a member of one of the houses of parliament. In the Indian parliamentary system, the executive is subordinate to the legislature, with the prime minister and his council directly responsible to the lower house of the parliament.
The legislature of India is the bicameral parliament, operating under a Westminster-style parliamentary system, and comprising the upper house called the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the lower called the Lok Sabha (House of People). The Rajya Sabha, a permanent body, has 245 members serving staggered six year terms. Most are elected indirectly by the state and territorial legislatures, their numbers in proportion to their state's population. All but two of the Lok Sabha's 545 members are directly elected by popular vote to represent individual constituencies for five-year terms. The remaining two members are nominated by the president from among the Anglo-Indian community, in case the president decides that the community is not adequately represented.
Judiciary
India has a unitary three-tier judiciary, consisting of the Supreme Court, headed by the Chief Justice of India, 21 High Courts, and a large number of trial courts. The Supreme Court has original jurisdiction over cases involving fundamental rights and over disputes between states and the Centre, and appellate jurisdiction over the High Courts. It is judicially independent, and has the power to declare the law and to strike down Union or State laws which contravene the Constitution. The role as the ultimate interpreter of the Constitution is one of the most important functions of the Supreme Court.
Administrative divisions
Main article: Administrative divisions of IndiaIndia consists of 28 states and seven Union Territories. All states, and the two union territories of Puducherry and the National Capital Territory of Delhi, have elected legislatures and governments patterned on the Westminster model. The other five union territories are directly ruled by the Centre through appointed administrators. In 1956, under the States Reorganisation Act, states were formed on a linguistic basis. Since then, this structure has remained largely unchanged. Each state or union territory is further divided into administrative districts. The districts in turn are further divided into tehsils and eventually into villages. Template:India states
Foreign relations
Main article: Foreign relations of India
Since its independence in 1947, India has maintained cordial relationships with most nations. In the 1950s, it strongly advocated for the independence of European colonies in Africa and Asia and played a pioneering role in the Non-Aligned Movement. India was involved in two brief military interventions in neighbouring countries – the Indian Peace Keeping Force in Sri Lanka and Operation Cactus in Maldives. India has a tense relationship with neighbouring Pakistan and the two countries went to war in 1947, 1965, 1971 and 1999. Most of these conflicts were fought over the Kashmir dispute, with the exception of the 1971 war where the dispute primarily concerned the civil unrest in erstwhile East Pakistan. After the Sino-Indian War and the 1965 war, India developed close military and economic relations with the Soviet Union and by late 1960s, the Soviet Union had emerged as the largest supplier of military arms to India.
India continues to maintain strategic relations with Russia and also enjoys extensive defence relations with Israel and France. In recent years, it has played an influential role in the SAARC and the WTO. India has provided as many as 55,000 Indian military and police personnel to serve in thirty-five UN peacekeeping operations across four continents. India is also an active participant in various multilateral forums, particularly the East Asia Summit and the G8+5. In the economic sphere, India has close relationships with other developing nations in South America, Asia and Africa. Since early 2000s, India has vigorously pursued its "Look East" policy which has helped it increase its collaboration with the ASEAN nations, Japan and South Korea on a range of issues, particularly economic investment and regional security.
Recent overtures by the Indian government have enhanced India's economic, strategic and military cooperation with the United States and the European Union. In 2008, a civilian nuclear agreement between India and the United States was signed, prior to which India received waivers from the IAEA and the NSG which ended restrictions on nuclear technology commerce, even though India possesses nuclear weapons and is not a signatory of the NPT. As a consequence, India became the world's sixth de facto recognised nuclear weapons state. Following the NSG waiver, India has also signed civilian nuclear energy cooperation agreements with other nations including Russia, France, the United Kingdom, and Canada.
Military
Main article: Indian Armed Forces
India maintains the third-largest military force in the world, which consists of the Indian Army, Navy, Air Force and auxiliary forces such as the Paramilitary Forces, the Coast Guard, and the Strategic Forces Command. The official Indian defence budget for 2011 stood at US$36.03 billion (or 1.83% of GDP). According to a 2008 SIPRI report, India's annual military expenditure in terms of PPP stood at US$72.7 billion, and a 2011 report stated that India had become the world's largest arms importer, receiving 9% of all international arms transfers during the period from 2006–2010. The President of India is the supreme commander of the Indian Armed Forces. Defence contractors, such as the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Hindustan Aeronautics (HAL), oversee indigenous development of sophisticated arms and military equipment, including ballistic missiles, fighter aircraft and main battle tanks, to reduce India's dependence on foreign imports.
China's repeated threats to intervene in the 1965 war in support of Pakistan convinced India to develop nuclear weapons to counter Chinese nuclear tests. India conducted its first nuclear weapons test in 1974 and carried out further underground testing in 1998. Despite criticism and military sanctions, India has consistently refused to sign the CTBT and the NPT which it considers to be flawed and discriminatory. India maintains a "no first use" nuclear policy and is developing a nuclear triad capability as a part of its "minimum credible deterrence" doctrine. India also has an advanced ballistic missile defence shield development program and is developing a fifth generation fighter jet in collaboration with Russia. Other major indigenous military development projects include Vikrant class aircraft carriers and Arihant class nuclear submarines.
Economy
Main article: Economy of India See also: Economic history of India, Economic development in India, and Transport in India
According to the International Monetary Fund, India's nominal GDP stood at US$1.43 trillion, which makes it the eleventh-largest economy in the world, corresponding to a per capita income of US$1,000. If purchasing power parity (PPP) is taken into account, India's economy is the fourth largest in the world at US$4.001 trillion. The country ranks 142th in nominal GDP per capita and 127th in GDP per capita at PPP. With an average annual GDP growth rate of 5.8% for the past two decades, India is one of the fastest growing economies in the world.
Before 1991, the Indian government followed protectionist and socialist-inspired policies, because of which the Indian economy was largely closed to the outside world and suffered from extensive state intervention and regulation. After an acute balance of payments crisis, the nation liberalised its economy and has since moved towards a free-market economy. Since then, the emphasis has been to use foreign trade and investment as integral parts of India's economy. Currently, India's economic system is portrayed as a capitalist model with the influx of private enterprise.
India has the world's second largest labour force, with 467 million people. In terms of output, the agricultural sector accounts for 28% of GDP; the service and industrial sectors make up 54% and 18% respectively. Major agricultural products include rice, wheat, oilseed, cotton, jute, tea, sugarcane, potatoes. Major industries include textiles, telecommunications, chemicals, food processing, steel, transport equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery and software. India's external trade has reached a relatively moderate share of 24% of GDP in 2006, up from 6% in 1985. In 2008, India's share of world trade was about 1.68%; in 2009, it was the world's fifteenth largest importer and eighteenth largest exporter. Major exports include petroleum products, textile goods, gems and jewelry, software, engineering goods, chemicals, and leather manufactures. Major imports include crude oil, machinery, gems, fertiliser, chemicals.

During the late 2000s, India's economic growth averaged 7.5% a year. Over the past decade, hourly wage rates in India have more than doubled. According to a 2007 McKinsey Global Institute report, since 1985, India's robust economic growth has shifted 431 million Indians out of poverty and by 2030, India's middle class population will rise to more than 580 million people. India ranks 51st in the Global Competitiveness Report and if diversified, it ranked 16th in financial market sophistication, 24th in banking sector, 27th in business sophistication and 30th in innovation; ahead of several advanced economies. Seven of the world's top 15 technology outsourcing companies are based in India and the country is viewed as the second most favourable outsourcing destination after the United States. India's consumer market is currently the world's thirteenth largest and is expected to become the fifth largest by 2030. India has the world's fastest growing telecommunication industry, adding about 10 million subscribers during 2008–09 period. The country has the world's second fastest growing automobile industry, with domestic sales increasing by 26% during the 2009–10 period and exports increasing by 36% during the 2008–09 period.
Despite India's impressive economic growth over recent decades, the country continues to face various socio-economic challenges. Though the percentage of people living below the World Bank's international poverty line of $1.25/day decreased from 60% in 1981 to 42% in 2005, the country still contains the largest concentration of poor people in the world. Since 1991, inter-state economic inequality in India has consistently grown; the per capita net state domestic product of India's richest states is about 3.2 times that of the poorest states. Perception about corruption in India has also increased significantly and according to one estimate, since independence India has lost US$462 billion in illegal capital flows. Half of the children in India are underweight and about 46% of Indian children under the age of three suffer from malnutrition.
According to a 2011 PwC report, in terms of PPP, India's GDP will overtake that of Japan in 2011 and by 2045, India's GDP will surpass that of the United States. Additionally, over the next four decades, India's average annual economic growth rate is expected to stand at about 8% and therefore, it has the potential to be the world's fastest growing major economy over the period to 2050. The report also highlighted some of the key factors behind India's high economic growth rate — young and rapidly growing working age population; growth of manufacturing sector due to strong engineering skills and rising levels of education; and sustained growth of consumer market due to rapidly growing middle class population. However, the World Bank suggests that for India to achieve its economic potential, it must continue to focus on public sector reform, transport infrastructure, agricultural and rural development, removal of labour regulations, education, energy security, and public health and nutrition.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of India See also: Ethnic groups of South Asia, List of most populous metropolitan areas in India, and Religion in India
With an estimated population of 1.2 billion, India is the world's second most populous country. The last 50 years have seen a rapid increase in population due to medical advances and massive increase in agricultural productivity due to the "green revolution". The percentage of Indian population living in urban areas has consistently grown; from 1991 to 2001, India's urban population increased by 31.2%. In 2001, about 285 million Indians lived in urban areas while more than 70% of India's population resided in rural areas. As per the 2001 census, there are twenty seven million-plus cities, with the largest cities being Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata.
India's literacy rate is 64.8% (53.7% for females and 75.3% for males). The state of Kerala has the highest literacy rate at 91% while Bihar has the lowest at 47%. The national human sex ratio is 944 females per 1,000 males. India's median age is 24.9, and the population growth rate of 1.38% per annum; there are 22.01 births per 1,000 people per year. Though India has one of the world's most diverse and modern healthcare systems, the country continues to face several public health-related challenges. According to the World Health Organization, 900,000 Indians die each year from drinking contaminated water and breathing in polluted air. There are about 60 physicians per 100,000 people in India.
The Indian Constitution recognises 212 scheduled tribal groups which together constitute about 7.5% of the country's population. As per the 2001 census, over 800 million Indians (80.5%) were Hindu. Other religious groups include Muslims (13.4%), Christians (2.3%), Sikhs (1.9%), Buddhists (0.8%), Jains (0.4%), Jews, Zoroastrians and Bahá'ís. India has the world's third-largest Muslim population and the largest Muslim population for a non-Muslim majority country.
Languages
Main article: Languages of IndiaIndia is home to two major linguistic families: Indo-Aryan (spoken by about 74% of the population) and Dravidian (spoken by about 24%). Other languages spoken in India come from the Austro-Asiatic and Tibeto-Burman linguistic families. Neither the Constitution of India, nor any Indian law defines any national language. Hindi, with the largest number of speakers, is the official language of the union. English is used extensively in business and administration and has the status of a 'subsidiary official language;' it is also important in education, especially as a medium of higher education. In addition, every state and union territory has its own official languages, and the constitution also recognises in particular 21 "scheduled languages".
Culture
Main article: Culture of India
India's culture is marked by a high degree of syncretism and cultural pluralism. India's cultural tradition dates back to 8000 BCE and has a continuously recorded history for over 2,500 years. With its roots based in the Indus Valley Tradition, the Indian culture took a distinctive shape during the 11th century BCE Vedic age which laid the foundation of Hindu philosophy, mythology, literary tradition and beliefs and practices, such as dhárma, kárma, yóga and mokṣa. It has managed to preserve established traditions while absorbing new customs, traditions, and ideas from invaders and immigrants and spreading its cultural influence to other parts of Asia, mainly South East and East Asia.
Indian religions form one of the most defining aspects of Indian culture. Major dhármic religions which were founded in India include Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. Considered to be a successor to the ancient Vedic religion, Hinduism has been shaped by the various schools of thoughts based on the Upanishads, the Yoga Sutras and the Bhakti movement. Buddhism originated in India in 5th century BCE and prominent early Buddhist schools, such as Theravāda and Mahāyāna, gained dominance during the Maurya Empire. Though Buddhism entered a period of gradual decline in India 5th century CE onwards, it played an influential role in shaping Indian philosophy and thought.
Indian architecture is one area that represents the diversity of Indian culture. Much of it, including notable monuments such as the Taj Mahal and other examples of Mughal architecture and South Indian architecture, comprises a blend of ancient and varied local traditions from several parts of the country and abroad. Vernacular architecture also displays notable regional variation.
Considered to be the earliest and foremost "monument" of Indian literature, the Vedic or Sanskrit literature was developed from 1,400 BCE to 1,200 AD. Prominent Indian literary works of the classical era include epics such as Mahābhārata and Ramayana, dramas such as the Abhijñānaśākuntalam (The Recognition of Śakuntalā), and poetry such as the Mahākāvya. Developed between 600 BCE and 300 AD, the Sangam literature consists 2,381 poems and is regarded as a predecessor of Tamil literature. From 7th century AD to 18th century AD, India's literary traditions went through a period of drastic change because of the emergence of devotional poets such as Kabīr, Tulsīdās and Guru Nānak. This period was characterised by varied and wide spectrum of thought and expression and as a consequence, medieval Indian literary works differed significantly from classical traditions. In the 19th century, Indian writers took new interest in social questions and psychological descriptions. During the 20th century, Indian literature was heavily influenced by the works of universally acclaimed Bengali poet and novelist Rabindranath Tagore.
Society and traditions
Template:Indian image rotation
Traditional Indian society is defined by relatively strict social hierarchy. The Indian caste system describes the social stratification and social restrictions in the Indian subcontinent, in which social classes are defined by thousands of endogamous hereditary groups, often termed as jātis or castes. Several influential social reform movements, such as the Bramho Shômaj, the Arya Samāja and the Ramakrishna Mission, have played a pivotal role in the emancipation of Dalits (or "untouchables") and other lower-caste communities in India. However, the majority of Dalits continue to live in segregation and are often persecuted and discriminated against.
Traditional Indian family values are highly respected, and multi-generational patriarchal joint families have been the norm, although nuclear families are becoming common in urban areas. An overwhelming majority of Indians have their marriages arranged by their parents and other respected family members, with the consent of the bride and groom. Marriage is thought to be for life, and the divorce rate is extremely low. Child marriage is still a common practice, more so in rural India, with half of women in India marrying before the legal age of 18.
Many Indian festivals are religious in origin, although several are celebrated irrespective of caste and creed. Some popular festivals are Diwali, Ganesh Chaturthi, Ugadi, Thai Pongal, Holi, Onam, Vijayadashami, Durga Puja, Eid ul-Fitr, Bakr-Id, Christmas, Buddha Jayanti, Moharram and Vaisakhi. India has three national holidays which are observed in all states and union territories — Republic Day, Independence Day and Gandhi Jayanti. Other sets of holidays, varying between nine and twelve, are officially observed in individual states. Religious practices are an integral part of everyday life and are a very public affair.
Traditional Indian dress varies across the regions in its colours and styles and depends on various factors, including climate. Popular styles of dress include draped garments such as sari for women and dhoti or lungi for men; in addition, stitched clothes such as salwar kameez for women and kurta-pyjama and European-style trousers and shirts for men, are also popular.
Music, dance, theatre and cinema
Indian music covers a wide range of traditions and regional styles. Classical music largely encompasses the two genres – North Indian Hindustani, South Indian Carnatic traditions and their various offshoots in the form of regional folk music. Regionalised forms of popular music include filmi and folk music; the syncretic tradition of the bauls is a well-known form of the latter.
Indian dance too has diverse folk and classical forms. Among the well-known folk dances are the bhangra of the Punjab, the bihu of Assam, the chhau of West Bengal, Jharkhand , sambalpuri of Orissa , the ghoomar of Rajasthan and the Lavani of Maharashtra. Eight dance forms, many with narrative forms and mythological elements, have been accorded classical dance status by India's National Academy of Music, Dance, and Drama. These are: bharatanatyam of the state of Tamil Nadu, kathak of Uttar Pradesh, kathakali and mohiniyattam of Kerala, kuchipudi of Andhra Pradesh, manipuri of Manipur, odissi of Orissa and the sattriya of Assam.
Theatre in India often incorporates music, dance, and improvised or written dialogue. Often based on Hindu mythology, but also borrowing from medieval romances, and news of social and political events, Indian theatre includes the bhavai of state of Gujarat, the jatra of West Bengal, the nautanki and ramlila of North India, the tamasha of Maharashtra, the burrakatha of Andhra Pradesh, the terukkuttu of Tamil Nadu, and the yakshagana of Karnataka.
The Indian film industry is the largest in the world. Bollywood, based in Mumbai, makes commercial Hindi films and is the most prolific film industry in the world. Established traditions also exist in Assamese, Bengali, Kannada, Malayalam, Marathi, Oriya, Tamil, and Telugu language cinemas.
Cuisine
Indian cuisine is characterised by a wide variety of regional styles and sophisticated use of herbs and spices. The staple foods in the region are rice (especially in the south and the east), wheat (predominantly in the north) and lentils. Spices, such as black pepper which are now consumed world wide, are originally native to the Indian subcontinent. Chili pepper, which was introduced by the Portuguese, is also widely used in Indian cuisine.
Sport
Main article: Sport in India
India's official national sport is field hockey, administered by Hockey India. The Indian hockey team won the 1975 Hockey World Cup and 8 gold, 1 silver and 2 bronze medals at the Olympic games, making it one of the world's most successful national hockey teams ever. Cricket, however, is by far the most popular sport; the India cricket team won the 1983 Cricket World Cup, 2007 ICC World Twenty20, and shared the 2002 ICC Champions Trophy with Sri Lanka. Cricket in India is administered by the Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI) and domestic competitions include the Ranji Trophy, the Duleep Trophy, the Deodhar Trophy, the Irani Trophy and the NKP Salve Challenger Trophy. In addition, BCCI conducts the Indian Premier League, a Twenty20 competition.
India is home to several traditional sports which originated in the country and continue to remain fairly popular. These include kabaddi, kho kho, pehlwani and gilli-danda. Some of the earliest forms of Asian martial arts, such as Kalarippayattu, Yuddha, Silambam and Varma Kalai, originated in India. The Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna and the Arjuna Award are India's highest awards for achievements in sports, while the Dronacharya Award is awarded for excellence in coaching.
Chess, commonly held to have originated in India, is regaining widespread popularity with the rise in the number of Indian Grandmasters. Tennis has also become increasingly popular, owing to the victories of the India Davis Cup team and the success of Indian tennis players. India has a strong presence in shooting sports, winning several medals at the Olympics, the World Shooting Championships and the Commonwealth Games. Other sports in which Indian sports-persons have won numerous awards or medals at international sporting events include badminton, boxing and wrestling. Football is a popular sport in northeastern India, West Bengal, Goa, Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
India has hosted or co-hosted several international sporting events, such as the 1951 and the 1982 Asian Games, the 1987 and 1996 Cricket World Cup, the 2003 Afro-Asian Games, the 2006 ICC Champions Trophy, the 2010 Hockey World Cup and the 2010 Commonwealth Games. Major international sporting events annually held in India include the Chennai Open, Mumbai Marathon, Delhi Half Marathon and the Indian Masters. The country is presently co-hosting 2011 Cricket World Cup together with Bangladesh and Sri Lanka. It would also host the first Indian Grand Prix in 2011.
See also
Template:Misplaced Pages-Books
Main articles: Outline of India and Index of India-related articlesNotes
References
- "State Emblem -Inscription". National Informatics Centre(NIC). Retrieved 17 June 2007.
- "National Anthem – Know India portal". National Informatics Centre(NIC). 2007. Retrieved 31 August 2007.
- "National Song – Know India portal". National Informatics Centre(NIC). 2007. Retrieved 11 June 2009.
- "Constituent Assembly of India — Volume XII". Constituent Assembly of India: Debates. parliamentofindia.nic.in, National Informatics Centre. 24 January 1950. Retrieved 29 June 2007.
The composition consisting of the words and music known as Jana Gana Mana is the National Anthem of India, subject to such alterations in the words as the Government may authorise as occasion arises; and the song Vande Mataram, which has played a historic part in the struggle for Indian freedom, shall be honoured equally with Jana Gana Mana and shall have equal status with it.
- "The Union: Official Language". Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. National Informatics Centre(NIC). 2007. Retrieved 11 June 2009.
- "Notification No. 2/8/60-O.L., dated 27 April 1960". Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. National Informatics Centre(NIC). Retrieved 11 June 2009.
- "Official Languages Resolution, 1968". Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. National Informatics Centre(NIC). Retrieved 11 June 2009.
- http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2010-01-25/india/28148512_1_national-language-official-language-hindi
- ^ "India at a Glance". Know India Portal. National Informatics Centre(NIC). Retrieved 7 December 2007.
- ^ Indiastat. "Indian Official Population Clock". Retrieved 27 January 2010.
- "India at a glance: Population". Census of India, 2001. Government of India. Retrieved 25 April 2009.
- ^ "India". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- "Field Listing — Distribution of family income — Gini index". The World Factbook. CIA. 15 May 2008. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- "Human Development Report 2010. Human development index trends: Table G" (PDF). The United Nations. Retrieved 4 November 2010.
- "Total Area of India" (PDF). Country Studies, India. Library of Congress– Federal Research Division. December 2004. Retrieved 3 September 2007.
The country's exact size is subject to debate because some borders are disputed. The Indian government lists the total area as 3,287,260 km (1,269,220 sq mi) and the total land area as 3,060,500 km (1,181,700 sq mi); the United Nations lists the total area as 3,287,263 km (1,269,219 sq mi) and total land area as 2,973,190 km (1,147,960 sq mi).
- Oldenburg, Phillip. 2007. "India: History," Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2007. Archived 1 November 2009.
- Mohammada, Malika (2007). The foundations of the composite culture in India. Aakar Books, 2007. ISBN 8189833189.
- "India", Oxford English Dictionary, second edition, 2100a.d. Oxford University Press.
- Basham, A. L. (2000). The Wonder That Was India. South Asia Books. ISBN 0-283-99257-3.
- "Official name of the Union". Courts Informatics Division, National Informatics Centre, Ministry of Comm. and Information Tech. Retrieved 8 August 2007.
Name and territory of the Union- India, that is Bharat, shall be a Union of States.
- "Hindustan". Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. 2007. Retrieved 18 June 2007.
- "Introduction to the Ancient Indus Valley". Harappa. 1996. Retrieved 18 June 2007.
- Krishna Reddy (2003). Indian History. New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill. p. A107. ISBN 0-07-048369-8.
- Jona Lendering. "Maurya dynasty". Retrieved 17 June 2007.
- "Gupta period has been described as the Golden Age of Indian history". National Informatics Centre (NIC). Retrieved 3 October 2007.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Heitzman, James. (2007). "Gupta Dynasty," Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2007. Archived 31 October 2009.
- "The Mughal Legacy".
- "The Mughal World : Life in India's Last Golden Age".
- "The Mughals: The Sikhs". Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- The Mughals: The Marathas.
- "History : Indian Freedom Struggle (1857–1947)". National Informatics Centre (NIC). Retrieved 3 October 2007.
And by 1856, the British conquest and its authority were firmly established.
- Markovits, Claude, ed. (2004). A History of Modern India, 1480–1950. Anthem South Asian Studies. Anthem Press. p. 345. ISBN 1-84331-152-6.
- written by John Farndon. (1997). Concise Encyclopedia. Dorling Kindersley Limited. p. 455. ISBN 0-7513-5911-4.
- written by John Farndon. (1997). Concise Encyclopedia. Dorling Kindersley Limited. p. 322. ISBN 0-7513-5911-4.
- ^ "CIA Factbook: India". CIA Factbook. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
- ^ "India Profile". Nuclear Threat Initiative (NTI). 2003. Retrieved 20 June 2007.
- Montek Singh Ahluwalia (2002). "Economic Reforms in India since 1991: Has Gradualism Worked?" (MS Word). Journal of Economic Perspectives. Retrieved 13 June 2007.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "India is the second fastest growing economy". Economic Research Service (ERS). United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 5 August 2007.
- ^ Ali, Jason R. (2005). "Greater India". Earth-Science Reviews. 72 (3–4): 170–173. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2005.07.005.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Dikshit & Schwartzberg 2007, p. 7.
- Prakash, B. (2000). "Holocene tectonic movements and stress field in the western Gangetic plains" (PDF). Current Science. 79 (4): 438–449.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Dikshit & Schwartzberg 2007, p. 11.
- Dikshit & Schwartzberg 2007, p. 8.
- Dikshit & Schwartzberg 2007, pp. 9–10.
- India's northernmost point is the region of the disputed Siachen Glacier in Jammu and Kashmir; however, the Government of India regards the entire region of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir (including the Northern Areas currently administered by Pakistan) to be its territory, and therefore assigns the longitude 37° 6' to its northernmost point.
- (Government of India 2007, p. 1.) harv error: no target: CITEREFGovernment_of_India2007 (help)
- ^ Kumar, V. Sanil (2006). "Coastal processes along the Indian coastline" (PDF). Current Science. 91 (4): 530–536.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Dikshit & Schwartzberg 2007, p. 15.
- Dikshit & Schwartzberg 2007, p. 16.
- Dikshit & Schwartzberg 2007, p. 17.
- Dikshit & Schwartzberg 2007, p. 12.
- Dikshit & Schwartzberg 2007, p. 13.
- ^ Chang 1967, pp. 391–394. harvnb error: no target: CITEREFChang1967 (help)
- Posey 1994, p. 118.
- Wolpert 2003, p. 4.
- Heitzman & Worden 1996, p. 97.
- "Hotspots by region". Biodiversity Hotspots. Conservation International. Retrieved 28 February 2011.
- ^ Dr S.K.Puri. "Biodiversity Profile of India (Text Only)". Retrieved 20 June 2007.
- Botanical Survey of India. 1983. Flora and Vegetation of India — An Outline. Botanical Survey of India, Howrah. p. 24.
- Valmik Thapar, Land of the Tiger: A Natural History of the Indian Subcontinent, 1997. ISBN 978-0-520-21470-5.
- ^ Tritsch, M.E. 2001. Wildlife of India Harper Collins, London. 192 pages. ISBN 0-00-711062-6.
- Deforestation to blame for early summer. Times of India. 26 February 2007.
- K. Praveen Karanth. (2006). Out-of-India Gondwanan origin of some tropical Asian biota.
- Groombridge, B. (ed). 1993. The 1994 IUCN Red List of Threatened Animals IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK. lvi + 286 pp.
- "The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972". Helplinelaw.com. 2000. Retrieved 16 June 2007.
- "Biosphere Reserves of India". Retrieved 17 June 2007.
- "The List of Wetlands of International Importance" (PDF). The Secretariat of the Convention of on Wetlands. 4 June 2007. p. 18. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 June 2007. Retrieved 20 June 2007.
- "World's Largest Democracy to Reach One Billion Persons on Independence Day". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. United Nations: Population Division. Retrieved 6 December 2007.
- "Country profile: India". BBC. 9 January 2007. Retrieved 21 March 2007.
- Burnell, Peter J. The resilience of democracy: persistent practice, durable idea. Routledge, 1999. ISBN 0714649651, 9780714649658.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - "Current recognised parties" (PDF). Election Commission of India. 14 March 2009. Retrieved 5 July 2010.
- Sarkar, Nurul. Sonia Gandhi: tryst with India. Atlantic Publishers & Distributors, 2007. ISBN 8126907444, 9788126907441.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - Chander, N. Jose. Coalition politics: the Indian experience. Concept Publishing Company, 2004. ISBN 978-81-8069-092-1.
- Bhambhri, Chandra Prakash (1992). Politics in India 1991–92. Shipra Publications. pp. 118, 143. ISBN 978-81-85402-17-8.
- "Narasimha Rao passes away". Chennai, India: The Hindu. 24 December 2004. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- Patrick Dunleavy, Rekha Diwakar, Christopher Dunleavy. "The effective space of party competition" (PDF). London School of Economics and Political Science. Retrieved 1 October 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Hermann, Kulke (2004). A History of India. Routledge. p. 384. ISBN 978-0-415-32919-4.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Second UPA win, a crowning glory for Sonia's ascendancy". Business Standard. 16 May 2009. Retrieved 13 June 2009.
- Bishop, Greg (29 April 2010). "India". The New York Times. Retrieved 8 June 2010.
- Pylee, Moolamattom Varkey (2004). "The Longest Constitutional Document". Constitutional Government in India (2nd ed.). S. Chand. p. 4. ISBN 81-219-2203-8. Retrieved 31 October 2007.
- Dutt, Sagarika (1998). "Identities and the Indian state: An overview". Third World Quarterly. 19 (3): 411–434. doi:10.1080/01436599814325.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) at p. 421. - Wheare, K.C. (1964). Federal Government (4th ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 28.
- Echeverri-Gent, John (2002). "Politics in India's Decentred Polity". In Ayres, Alyssa; Oldenburg, Philip (eds.). Quickening the Pace of Change. India Briefing. London: M.E. Sharpe. pp. 19–53. ISBN 0-7656-0812-X. at pp. 19–20; Sinha, Aseema (2004). "The Changing Political Economy of Federalism in India". India Review. 3 (1): 25. doi:10.1080/14736480490443085.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); More than one of|pp=and|page=specified (help) at pp. 25–33. - ^ Sharma, Ram (1950). "Cabinet Government in India". Parliamentary Affairs. 4 (1): 116–126.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - "Election of President". The Constitution Of India. Constitution Society. Retrieved 2 September 2007.
The President shall be elected by the members of an electoral college.
- Gledhill, Alan (1964). The Republic of India: The Development of Its Laws and Constitution (2nd ed.). Stevens and Sons. p. 112.
- "Tenure of President's office". The Constitution Of India. Constitution Society. Retrieved 2 September 2007.
The President shall hold office for a term of five years from the date on which he enters upon his office.
- "Appointment of Prime Minister and Council of Ministers". The Constitution Of India. Constitution Society. Retrieved 2 September 2007.
The Prime Minister shall be appointed by the President and the other Ministers shall be appointed by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister.
- Matthew, K.M. (2003). Manorama Yearbook 2003. Malayala Manorama. p. 524. ISBN 81-900461-8-7.
- Gledhill, Alan (1964). The Republic of India: The Development of Its Laws and Constitution (2nd ed.). Stevens and Sons. p. 127.
- ^ "Our Parliament A brief description of the Indian Parliament". www.parliamentofindia.gov.in. Archived from the original on 19 August 2007. Retrieved 16 June 2007.
- ^ Neuborne, Burt (2003). "The Supreme Court of India". International Journal of Constitutional Law. 1 (1): 476–510. doi:10.1093/icon/1.3.476.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) at p. 478. - Supreme Court of India. "Jurisdiction of the Supreme Court". National Informatics Centre. Retrieved 21 October 2007.
- Sripati, Vuayashri (1998). "Toward Fifty Years of Constitutionalism and Fundamental Rights in India: Looking Back to See Ahead (1950–2000)". American University International Law Review. 14 (2): 413–496.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) at pp. 423–424. - Pylee, Moolamattom Varkey (2004). "The Union Judiciary: The Supreme Court". Constitutional Government in India (2nd ed.). S. Chand. p. 314. ISBN 81-219-2203-8. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ^ "Country Profile: India" (PDF). Library of Congress – Federal Research Division. 2004. Retrieved 24 June 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "States Reorganisation Act, 1956". Constitution of India. Commonwealth Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 31 October 2007.; See also: Political integration of India.
- "Districts of India". Government of India. National Informatics Centre (NIC). Retrieved 25 November 2007.
- "30/12/2005-India-Russia relations, an overview". Embassy of India, Moscow. Retrieved 15 February 2009.
- "Significance of the Contribution of India to the Struggle Against Apartheid1 by M. Moolla".
- "History of Non Aligned Movement". Retrieved 23 August 2007.
- Martin Gilbert (2002). A History of the Twentieth Century. London: HarperCollins. pp. 486–87. ISBN 0-06-050594-X. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- Sharma, Ram. India-USSR relations. Discovery Publishing House, 1999. ISBN 8171414869, 9788171414864.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - "India's negotiation positions at the WTO" (PDF). Retrieved 23 August 2010.
- "India and the United Nations". Retrieved 22 April 2006.
- "Analysts Say India'S Power Aided Entry Into East Asia Summit. | Goliath Business News". Goliath.ecnext.com. 29 July 2005. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- Peter Alford (7 July 2008). "G8 plus 5 equals power shift". The Australian. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- Anjali, Ghosh. India’s Foreign Policy. Pearson Education India, 2009. ISBN 8131710254, 9788131710258.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - Sisodia, N.S. Changing security dynamic in Eastern Asia: focus on Japan. Bibliophile South Asia, 2005. ISBN 8186019529, 9788186019528.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - "India, Europe Strategic Relations". European Union. Retrieved 14 January 2011.
- Times of India (11 October 2008), India, US seal 123 Agreement, Times of India
- "South Asia | Russia agrees India nuclear deal". BBC News. 11 February 2009. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
- "India, France agree on civil nuclear cooperation". Rediff.com. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
- "UK, India sign civil nuclear accord". Reuters. 13 February 2010. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
- "Canada, India reach nuclear deal". Montrealgazette.com. 29 November 2009. Retrieved 22 August 2010.
- "Typhoon vs. SU-30MKI: The 2007 Indra Dhanush Exercise". Defence Aviation. 8 August 2007. Retrieved 1 April 2009.
- Laxman K Behera. "Budgeting for India's Defence: An Analysis of Defence Budget 2011–12". Institute for Defence Studies and Analyses. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- SIPRI yearbook: world armaments and disarmament. Oxford University Press US, 2008. ISBN 0199548951, 9780199548958.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - "India hikes defense budget, is now world's largest arms importer". Retrieved 23 March 2011.
- Perkovich, George. India's nuclear bomb: the impact on global proliferation. University of California Press, 1999. ISBN 0520232100, 9780520232105.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - A. Vinod Kumar. "Reforming the NPT to include India". Bulletin of Atomic Scientists. Retrieved 1 November 2010.
- Brig. Vijai K. Nair (Indian Army). "No More Ambiguity: India's Nuclear Policy" (PDF). Retrieved 7 June 2007.
- Pandit, Rajat (27 July 2009). "N-submarine to give India crucial third leg of nuke triad". Times of India. Retrieved 10 March 2010.
- "Russia and India fix T-50 fighter design contract cost at $295 mln". 16 December 2010. Retrieved 14 January 2011.
- "India successfully test-fires interceptor missile". Times of India. 26 July 2010. Retrieved 14 January 2011.
- "India's first nuke submarine INS Arihant launched". 26 July 2009. Retrieved 19 January 2011.
- "Indigenous Aircraft Carrier's nucleus ready". 7 October 2010. Retrieved 14 January 2011.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database". International Monetary Fund. 2009. Retrieved 3 October 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". Bmu.li. 14 September 2006. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". Bmu.li. 14 September 2006. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- "The Puzzle of India's Growth". The Telegraph. 26 June 2006. Retrieved 15 September 2008.
- "India: the economy". British Broadcasting Corporation. 12 February 1998. Retrieved 23 August 2010.
- ^ "Economic survey of India 2007: Policy Brief" (PDF). OECD.
- ^ Gargan, Edward A. (15 August 1992). "India Stumbles in Rush to a Free Market Economy". New York Times.
- Jalal Alamgir (2009). India's Open-Economy Policy: Globalism, Rivalry, Continuity. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-77684-4.
- Country Comparison: Labor Force, CIA World Factbook
- TNN, Aug 28, 2009, 12.51am IST (28 August 2009). "Exporters get wider market reach". Timesofindia.indiatimes.com. Retrieved 23 August 2010.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - 26 March 2010 INTERNATIONAL TRADE STATISTICS http://www.wto.org/english/news_e/pres10_e/pr598_e.htm
- "The Nano, world's cheapest car, to hit Indian roads". Reuters. 23 March 2009. Retrieved 27 August 2009.
- Bellman, Eric (6 October 2008). "http://online.wsj.com/article/SB122324655565405999.html". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 27 August 2009.
{{cite news}}: External link in|title= - Make way, world. India is on the move., Christian Science Monitor]
- ^ Diana Farrell and Eric Beinhocker (19 May 2007). "Next Big Spenders: India's Middle Class". BusinessWeek. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- Klaus Schwab (2009). "The Competitiveness Report 2009-2010" (PDF). World Economic Forum, Geneva, Switzerland. Retrieved 10 September 2009.
- Wall Street Journal (28 May 2009). "Outlook for Outsourcing Spending Brightens". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 3 October 2010.
- "India: World's fastest growing telecom market". Rediff. 13 October 2009.
- "India second fastest growing auto market after China". Hindu Business Line. 9 April 2010.
- "Indian car exports surge 36%". Indian Express. 13 October 2009.
- "New Global Poverty Estimates — What it means for India". World Bank.
- ^ "Inclusive Growth and Service delivery: Building on India's Success" (PDF). World Bank. 29 May 2006. Retrieved 7 May 2009.
- "Inequality in India: A survey of recent trends" (PDF). United Nations.
- "Corruption Perception Index 2010 - India" (PDF). Transparency International - India.
- "India lost $462bn in illegal capital flows, says report". BBC.
- "India: Undernourished Children: A Call for Reform and Action". World Bank.
- ^ "The World in 2050" (PDF). PricewaterhouseCoopers. 2011.
- "India Country Overview 2009". World Bank.
- The end of India's green revolution?. BBC News. 29 May 2006.
- Food First/Institute for Food and Development Policy.
- ^ Subhash Chandra Garg. "Mobilizing Urban Infrastructure Finance in India" (PDF). World Bank. Retrieved 27 January 2010.
- Dyson, Tim; Visaria, Pravin (2004). "Migration and urbanisation:Retrospect and prospects". In Dyson, Tim; Casses, Robert; Visaria, Leela (eds.). Twenty-first century India: population, economy, human development, and the environment. Oxford University Press. pp. 115–129. ISBN 0-19-924335-2.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - Ratna, Udit (2007). "Interface between urban and rural development in India". In Dutt, Ashok K.; Thakur, Baleshwar (eds.). City, Society, and Planning: Planning Essays in honour of Prof. A.K. Dutt. Concept Publishing Company. pp. 271–272. ISBN 81-8069-461-5.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - "Kerala's literacy rate". kerala.gov.in. Government of Kerala. Retrieved 13 December 2007.
- Census Statistics of Bihar: Literacy Rates "Literacy rate of Bihar". Government of Bihar. Retrieved 13 December 2007.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - "Country Cooperation Strategy: India" (PDF). World Health Organization. November 2006.
- "Healthcare in India" (PDF). Boston Analytics.
- Robinson, Simon (1 May 2008). "India's Medical Emergency". TIME magazine.
- "Doctors per one hundred thousand people in India". IndiaReports.
- Bonner, Arthur. Averting the Apocalypse: social movements in India today. Duke University Press, 1990. ISBN 0822310481, 9780822310488.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - "Census of India 2001, Data on Religion". Census of India. Retrieved 22 November 2007.
- "[[Hindi]], not a national language: Court". The Hindu. 25 January 2010. Retrieved 27 January 2010.
{{cite news}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - "Languages by number of speakers according to 1991 census". Central Institute of Indian Languages. Retrieved 2 August 2007.
- Mallikarjun, B. (Nov., 2004), Fifty Years of Language Planning for Modern Hindi–The Official Language of India, Language in India, Volume 4, Number 11. ISSN 1930-2940.
- "Notification No. 2/8/60-O.L. (Ministry of Home Affairs), dated 27 April 1960". Retrieved 4 July 2007.
- "Taj Mahal". World Heritage List. UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 28 September 2007.
The World Heritage List includes 851 properties forming part of the cultural and natural heritage which the World Heritage Committee considers as having outstanding universal value.
- Das, N.K. (2006). "Cultural Diversity, Religious [[Syncretism]] and People of India: An Anthropological Interpretation". Bangladesh e-Journal of Sociology. 3 (2nd). ISSN 1819-8465. Retrieved 27 September 2007.
The pan-Indian, civilisational dimension of cultural pluralism and syncretism encompasses ethnic diversity and admixture, linguistic heterogeneity as well as fusion, and variations as well as synthesis in customs, behavioural patterns, beliefs and rituals
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help); URL–wikilink conflict (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Baidyanath, Saraswati (2006). "Cultural Pluralism, National Identity and Development". Interface of Cultural Identity Development (1stEdition ed.). New Delhi: Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts. xxi+290 pp. ISBN 81-246-0054-6. Retrieved 8 June 2007.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) - Arnett, Robert. India Unveiled. Atman Press, 2006. ISSN 9780965290043 0965290042, 9780965290043.
{{cite book}}: Check|issn=value (help) - Sharma, Shaloo. History and Development of Higher Education in India. Sarup & Sons, 2002. ISSN 9788176253185 8176253189, 9788176253185.
{{cite book}}: Check|issn=value (help) - de Bruyn, Pippa. Frommer's India. Frommer's, 2010. ISSN 9780470556108 0470556102, 9780470556108.
{{cite book}}: Check|issn=value (help) - ^ Heehs, Peter. Indian religions: a historical reader of spiritual expression and experience. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, 2002. ISSN 9781850654964 1850654964, 9781850654964.
{{cite book}}: Check|issn=value (help) Cite error: The named reference "Heehs" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - Stietencron, Hinduism: On the Proper Use of A Deceptive Term, pp.1–22
- "Advaita Vedanta: A Philosophical Reconstruction," By Eliot Deutsch, University of Hawaii Press, 1980, ISBN 0-8248-0271-3.
- Merriam-Webster, pg. 155–157
- Hoiberg, Dale. Students' Britannica India: Select essays. Popular Prakashan, 2000. ISBN 0852297629, 9780852297629.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - Sarma, Srinivasa. A History of Indian Literature, Volume 1. Motilal Banarsidass Publ., 1996. ISSN 9788120802643 8120802640, 9788120802643.
{{cite book}}: Check|issn=value (help) - Johnson 1998, MacDonell 2004, pp. 1–40, and Kālidāsa & Johnson (editor) 2001
- Kamil Veith Zvelebil, Companion Studies to the History of Tamil Literature, p.12
- George L. Hart III, The Poems of Ancient Tamil, U of California P, 1975.
- 1. Encyclopaedia Britannica (2008), "Tamil Literature." Quote: "Apart from literature written in classical (Indo-Aryan) Sanskrit, Tamil is the oldest literature in India. Some inscriptions on stone have been dated to the 3rd century BC, but Tamil literature proper begins around the 1st century AD. Much early poetry was religious or epic; an exception was the secular court poetry written by members of the sangam, or literary academy (see Sangam literature)." 2. Ramanujan 1985, pp. ix–x. Quote: "These poems are 'classical,' i.e. early, ancient; they are also 'classics,' i.e. works that have stood the test of time, the founding works of a whole tradition. Not to know them is not to know a unique and major poetic achievement of Indian civilisation. Early classical Tamil literature (c. 100 BC–AD 250) consists of the Eight Anthologies (Eţţuttokai), the Ten Long Poems (Pattuppāţţu), and a grammar called the Tolkāppiyam or the 'Old Composition.' ... The literature of classical Tamil later came to be known as Cankam (pronounced Sangam) literature. (pp. ix–x.)"
- Kumar Das, Sisir. A history of Indian literature, 500-1399: from courtly to the popular. Sahitya Akademi, 2006. ISSN 9788126021710 8126021713, 9788126021710.
{{cite book}}: Check|issn=value (help) - Datta, Amaresh. The Encyclopaedia Of Indian Literature (Volume Two). Sahitya Akademi, 2006. ISSN 9788126011940 8126011947, 9788126011940.
{{cite book}}: Check|issn=value (help) - "India – Caste". Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- Paswan, Sanjay. Encyclopaedia of Dalits in India: Movements. Gyan Publishing House, 2002. ISSN 9788178350349 8178350343, 9788178350349.
{{cite book}}: Check|issn=value (help) - "UN report slams India for caste discrimination". CBC News. 2 March 2007.
- Eugene M. Makar (2007). An American's Guide to Doing Business in India.
- ^ Medora, Nilufer (2003). "Mate selection in contemporary India: Love marriages versus arranged marriages". In Hamon, Raeann R. and Ingoldsby, Bron B. (ed.). Mate Selection Across Cultures. SAGE. pp. 209–230. ISBN 0-7619-2592-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - "Divorce Rate In India".
- "Child marriages targeted in India". BBC News. 24 October 2001. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- "State of the World's Children-2009" (PDF). UNICEF. 2009.
- "List of Holidays in India". Retrieved 7 July 2010.
- "18 Popular India Festivals". Retrieved 23 December 2007.
- 1. "South Asian arts: Techniques and Types of Classical Dance" From: Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 12 Oct. 2007. 2. Sangeet Natak Academi (National Academy of Music, Dance, and Drama, New Delhi, India). 2007. Dance Programmes 3. Kothari, Sunil. 2007. Sattriya dance of the celibate monks of Assam, India. Royal Holloway College, University of London.
- Lal 1998
- (Karanth 1997, p. 26) Quote: "The Yakṣagāna folk-theatre is no isolated theatrical form in India. We have a number of such theatrical traditions all around Karnataka... In far off Assam we have similar plays going on by the name of Ankia Nat, in neighouring Bengal we have the very popular Jatra plays. Maharashtra has Tamasa. (p. 26.)
- "Country profile: India". BBC. 19 August 2009. Retrieved 2007.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - Dissanayake & Gokulsing 2004
- Rajadhyaksha & Willemen (editors) 1999
- Delphine, Roger, "The History and Culture of Food in Asia", in Kiple & Kriemhild 2000, pp. 1140–1151. harvnb error: no target: CITEREFKipleKriemhild2000 (help)
- Lentil: An Ancient Crop for Modern Times.
But it has been red lentils which have 'fed the masses' particularly in the Indian subcontinent. Lentils are a staple food in many regions
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Achaya 1994 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFAchaya1994 (help), Achaya 1997 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFAchaya1997 (help)
- Shores, Lori. Teens in India. Compass Point Books, 2007. ISBN 0756520630, 9780756520632.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - "Anand crowned World champion". Rediff. 29 October 2008. Retrieved 29 October 2008.
- "India Aims for Center Court". WSJ. 11 September 2009. Retrieved 29 September 2010.
- "Shooting is India's No. 1 sport: Gagan". Deccan Herald. 5 October 2010. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- "Sawant shoots historic gold at World Championships". TOI. 9 August 2010. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- "Saina Nehwal: India's badminton star and 'new woman'". BBC. 1 August 2010. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- "Is boxing the new cricket?". Live Mint. Sep 24 2010. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "India makes clean sweep in Greco-Roman wrestling". TOI. 5 October 2010. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- Xavier, Leslie (12 September 2010). "Sushil Kumar wins gold in World Wrestling Championship". TOI. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- Majumdar & Bandyopadhyay 2006, pp. 1–5.
- Literature
- History
- Brown, Judith M. (1994). Modern India: The Origins of an Asian Democracy. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. xiii, 474. ISBN 0-19-873113-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) - Guha, Ramchandra (2007). India after Gandhi — The History of the World's Largest Democracy. 1st edition. Picador. xxvii, 900. ISBN 978-0-330-39610-3.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) - Kulke, Hermann (2004). A History of India. 4th edition. Routledge. xii, 448. ISBN 0-415-32920-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) - Metcalf, Barbara (2006). A Concise History of Modern India (Cambridge Concise Histories). Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. xxxiii, 372. ISBN 0-521-68225-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) - Spear, Percival (1990). A History of India. Vol. 2. New Delhi and London: Penguin Books. p. 298. ISBN 0-14-013836-6.
- Stein, Burton (2001). A History of India. New Delhi and Oxford: Oxford University Press. xiv, 432. ISBN 0-19-565446-3.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) - Thapar, Romila (1990). A History of India. Vol. 1. New Delhi and London: Penguin Books. p. 384. ISBN 0-14-013835-8.
- Wolpert, Stanley (2003). A New History of India. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. p. 544. ISBN 0-19-516678-7.
- Geography
- Dikshit, K.R. (2007). "India: The Land". Encyclopædia Britannica. pp. 1–29.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Government of India (2007). India Yearbook 2007. Publications Division, Ministry of Information & Broadcasting. ISBN 81-230-1423-6.
- Heitzman, J. (1996). India: A Country Study. Library of Congress (Area Handbook Series). ISBN 0-8444-0833-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Posey, C.A (1994). The Living Earth Book of Wind and Weather. Reader's Digest Association. ISBN 0-89577-625-1.
- Flora and fauna
- Ali, Salim; Ripley, S. Dillon (1995). A Pictorial Guide to the Birds of the Indian Subcontinent. Mumbai: Bombay Natural History Society and Oxford University Press. pp. 183, 106 colour plates by John Henry Dick. ISBN 0-19-563732-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Blatter, E.; Millard, Walter S. (1997). Some Beautiful Indian Trees. Mumbai: Bombay Natural History Society and Oxford University Press. pp. xvii, 165, 30 colour plates. ISBN 0-19-562162-X.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Israel, Samuel; Sinclair (editors), Toby (2001). Indian Wildlife. Discovery Channel and APA Publications. ISBN 981-234-555-8.
{{cite book}}:|last2=has generic name (help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Prater, S. H. (1971). The book of Indian Animals. Mumbai: Bombay Natural History Society and Oxford University Press. pp. xxiii, 324, 28 colour plates by Paul Barruel. ISBN 0-19-562169-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Rangarajan, Mahesh (editor) (1999). Oxford Anthology of Indian Wildlife: Volume 1, Hunting and Shooting. New Delhi: Oxford University Press. pp. xi, 439. ISBN 0-19-564592-8.
{{cite book}}:|first1=has generic name (help); Invalid|ref=harv(help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Rangarajan, Mahesh (editor) (1999). Oxford Anthology of Indian Wildlife: Volume 2, Watching and Conserving. New Delhi: Oxford University Press. pp. xi, 303. ISBN 0-19-564593-6.
{{cite book}}:|first1=has generic name (help); Invalid|ref=harv(help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Tritsch, Mark F. (2001). Wildlife of India. London: Harper Collins Publishers. p. 192. ISBN 0-00-711062-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
- Culture
- Dissanayake, Wimal K.; Gokulsing, Moti (2004). Indian Popular Cinema: A Narrative of Cultural Change. Trentham Books. p. 161. ISBN 1-85856-329-1.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Johnson, W. J. (translator and editor) (1998). The Sauptikaparvan of the Mahabharata: The Massacre at Night. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press (Oxford World's Classics). p. 192. ISBN 978-0-19-282361-8.
{{cite book}}:|first1=has generic name (help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kālidāsa; Johnson (editor), W. J. (2001). The Recognition of Śakuntalā: A Play in Seven Acts. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press (Oxford World's Classics). p. 192. ISBN 978-0-19-283911-4.
{{cite book}}:|last2=has generic name (help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Karanth, K. Shivarama (1997). Yakṣagāna. (Forward by H. Y. Sharada Prasad). Abhinav Publications. p. 252. ISBN 81-7017-357-4.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Kiple, Kenneth F.; Ornelas, Kriemhild Coneè, eds. (2000). The Cambridge World History of Food. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-40216-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Lal, Ananda (1998). Oxford Companion to Indian Theatre. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. p. 600. ISBN 0-19-564446-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - MacDonell, Arthur Anthony (2004). A History of Sanskrit Literature . Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 1-4179-0619-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Majumdar, Boria; Bandyopadhyay, Kausik (2006). A Social History Of Indian Football: Striving To Score. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-34835-8.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Massey, Reginald (2006). India's Dances. Abhinav Publications. ISBN 81-7017-434-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Ramanujan, A. K. (1985). Poems of Love and War: From the Eight Anthologies and the Ten Long Poems of Classical Tamil. New York: Columbia University Press. p. 329. ISBN 0-231-05107-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Rajadhyaksha, Ashish; Willemen (editors), Paul (1999). Encyclopedia of Indian Cinema, 2nd revised edition. University of California Press and British Film Institute. p. 652. ISBN 978-0-85170-669-6. Archived from the original on 6 August 2007.
{{cite book}}:|last2=has generic name (help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Vilanilam, John V. (2005). Mass Communication in India: A Sociological Perspective. Sage Publications. ISBN 0-7619-3372-7.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help)
External links
- Government of India – Official government portal (in English)
- "India". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- India at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of India
Wikimedia Atlas of India- Template:Wikitravel
21°N 78°E / 21°N 78°E / 21; 78
Template:Countries and Territories of South Asia
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| International relations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| International membership | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Group of 77 Template:Like Minded Group
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link GA Template:Link GA
Categories:- Misplaced Pages neutral point of view disputes from March 2011
- Use dmy dates from August 2010
- Ill-formatted IPAc-en transclusions
- Misplaced Pages neutral point of view disputes from February 2011
- India
- Countries of the Indian Ocean
- Federal countries
- Former British colonies
- G15 nations
- G20 nations
- Liberal democracies
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Republics
- Member states of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
- South Asian countries
- States and territories established in 1947
