This is an old revision of this page, as edited by MITBeaverRocks (talk | contribs) at 23:34, 6 June 2011 (→Function). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 23:34, 6 June 2011 by MITBeaverRocks (talk | contribs) (→Function)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
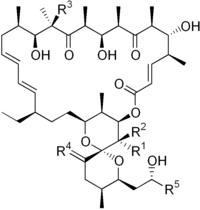
| IUPAC name (1R,4E,5'S,6S,6'S,7R,8S,10R,11R,12S,14R,15S,16R,18E,20E,22R,25S,27R,28S,29R)-22-ethyl-7,11,14,15-tetrahydroxy-6'--5',6,8,10,12,14,16,28,29-nonamethyl-3',4',5',6'-tetrahydro-3H,9H,13H-spirononacosa-4,18,20-triene-27,2'-pyran]-3,9,13-trione | |
| Other names Oligomycin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.334 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Oligomycins |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Molar mass | 791.062 g/mol |
| Supplementary data page | |
| ] | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Oligomycins are macrolides created by Streptomyces that can be poisonous to other organisms.
Function
They have use as antibiotics.
In addition, oligomycin inhibits ATP synthase by blocking its proton channel (Fo subunit), which is necessary for oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP (energy production). The inhibition of ATP synthesis would also stop electron transport chain. Because the high proton concentration build up is not dissipated, the free energy released by biological oxidation of substrates is not enough to pump any more protons against the steep gradient.
Administering oligomycin to an individual can result in very high levels of lactate accumulating in the blood and urine.
Oligomycin is an inhibitor of ATP synthase. In oxidative phosphorylation research, it is used to prevent state 3 (phosphorylating) respiration.
References
- Nakata, Masaya; Ishiyama, Takashi; Akamatsu, Shinichi; Hirose, Youichi; Maruoka, Hiroshi; Suzuki, Rika; Tatsuta, Kuniaki (1995). "Synthetic studies on oligomycins. Synthesis of the oligomycin B spiroketal and polypropionate portions". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 68 (3): 967–89. doi:10.1246/bcsj.68.967.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)